Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4 results about "Exosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Exosomes are extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are produced in the endosomal compartment of most eukaryotic cells. The multivesicular body (MVB) is an endosome defined by intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that bud inward into the endosomal lumen. If the MVB fuses with the cell surface (the plasma membrane), these ILVs are released as exosomes. In multicellular organisms, exosomes and other EVs are present in tissues and can also be found in biological fluids including blood, urine, and cerebrospinal fluid. They are also released in vitro by cultured cells into their growth medium. Since the size of exosomes is limited by that of the parent MVB, exosomes are generally thought to be smaller than most other EVs, from about 30 to several hundred nanometres (nm) in diameter: around the same size as many lipoproteins but much smaller than cells. Compared with EVs in general, it is unclear whether exosomes have unique characteristics or functions or can be separated or distinguished effectively from other EVs. EVs including exosomes carry markers of cells of origin and have specialized functions in physiological processes, from coagulation and intercellular signalling to waste management. Consequently, there is a growing interest in clinical applications of EVs as biomarkers and therapies alike, prompting establishment of an International Society for Extracellular Vesicles (ISEV) and a scientific journal devoted to EVs, the Journal of Extracellular Vesicles.
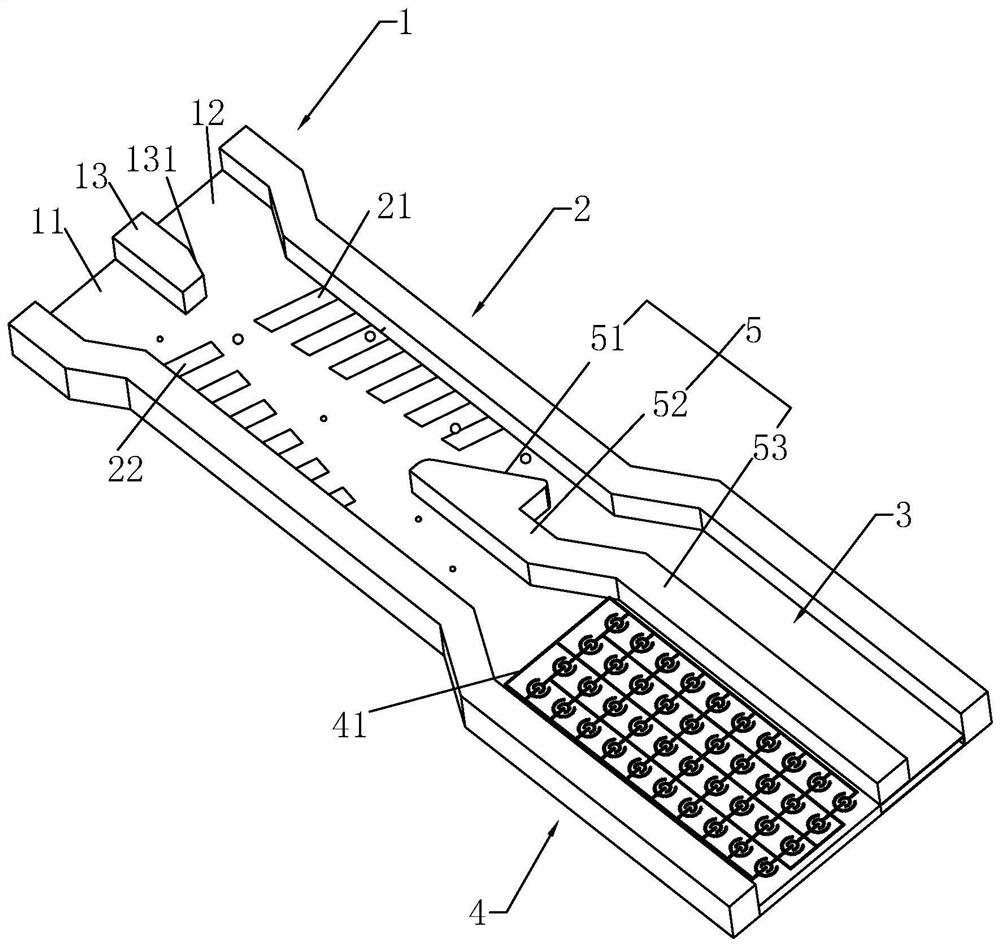
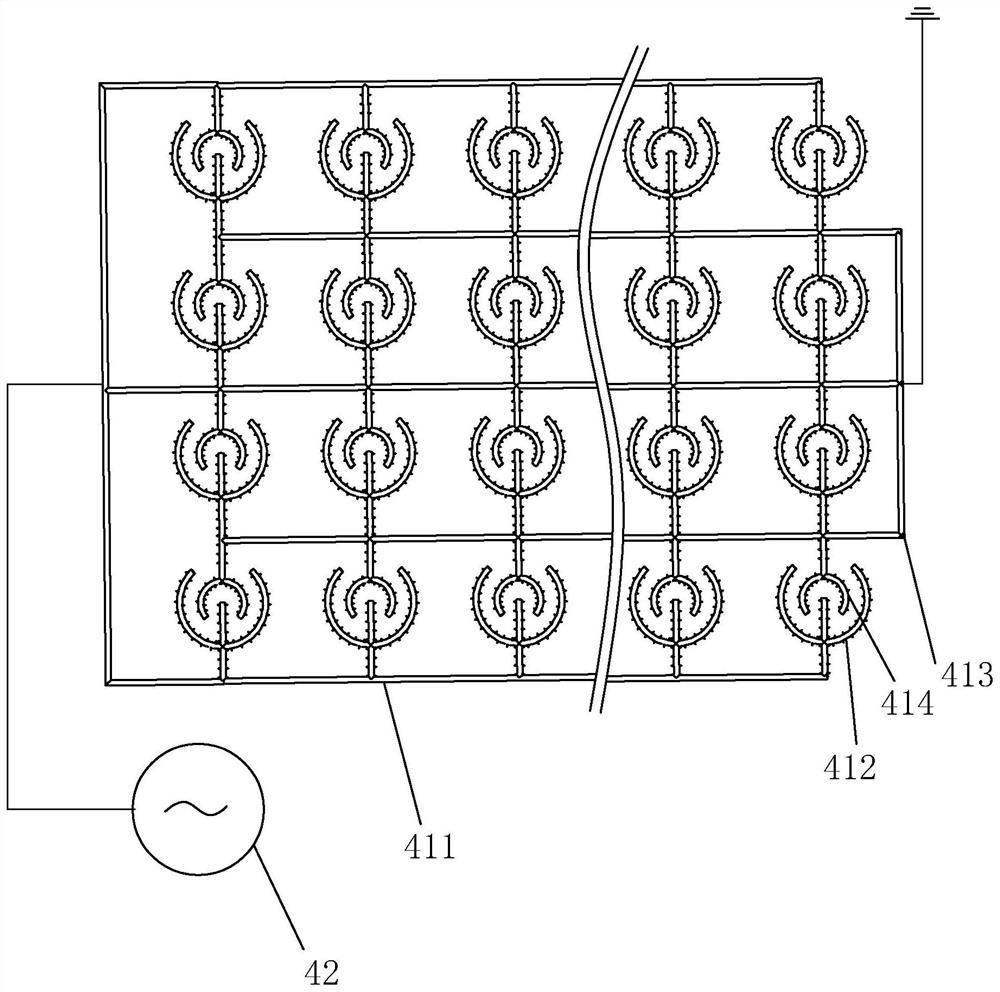
Method for separating exosomes in body fluid by electric field capture mechanism, and micro-fluidic chip
InactiveCN112048502AEasy to detectEasy to handleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical physicsEngineering
Owner:承启医学(深圳)科技有限公司
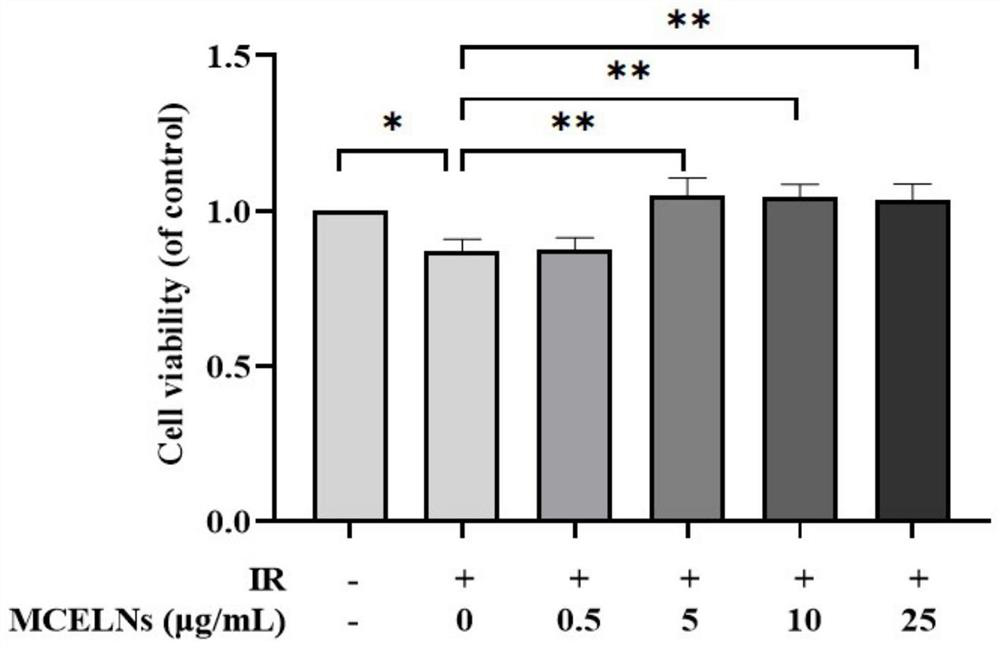
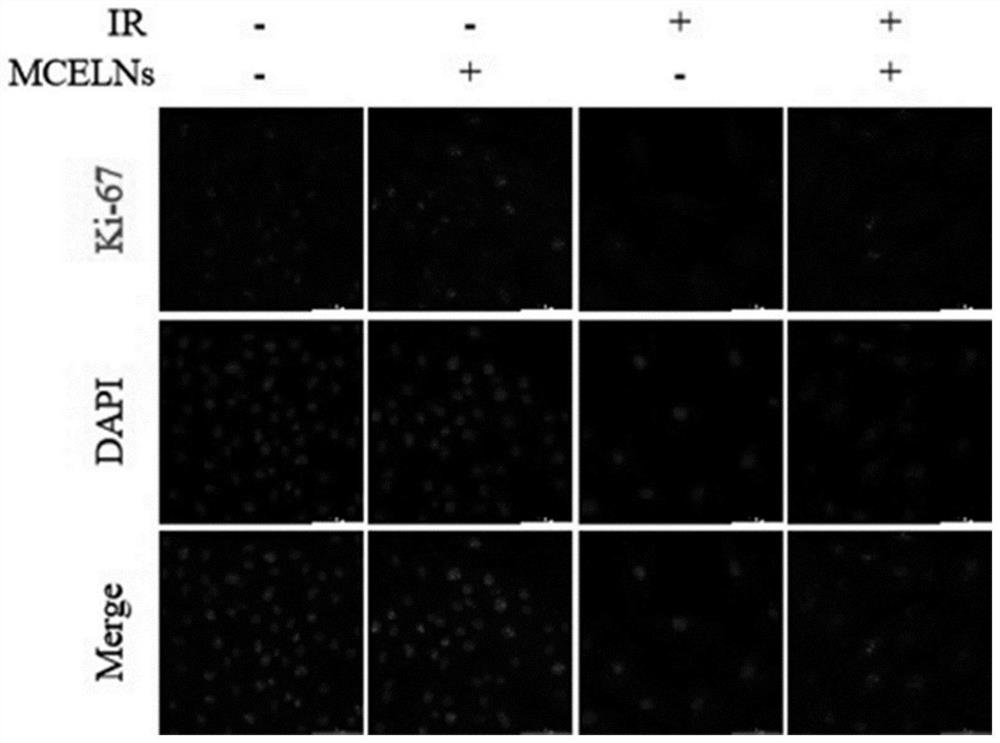
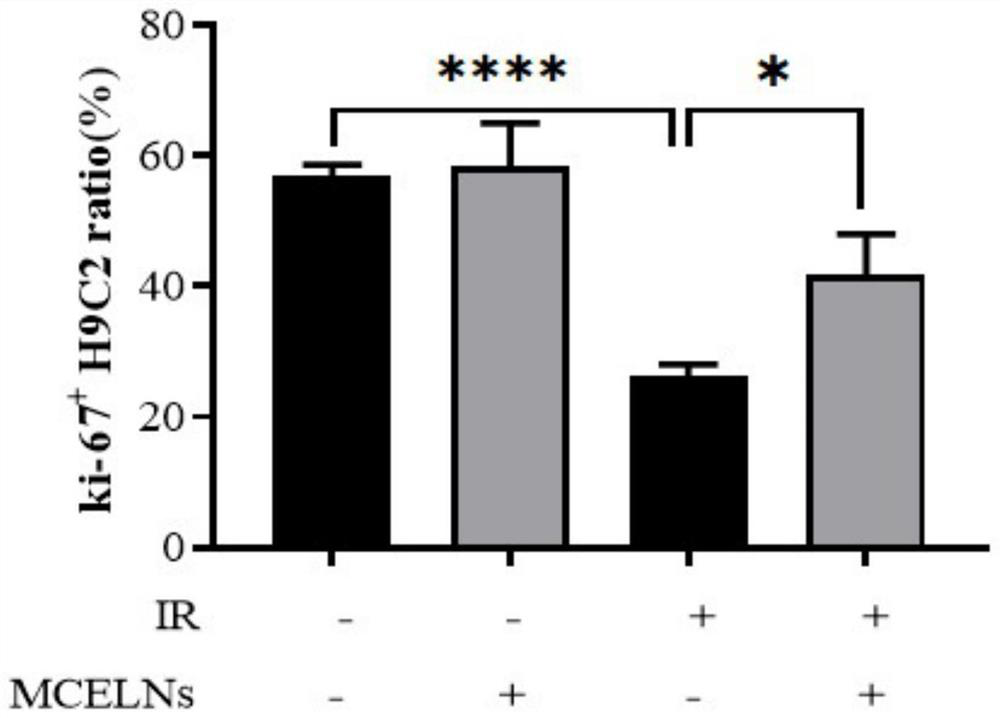
Application of bitter gourd exosome in radiation heart injury protection
ActiveCN114259511APromote proliferationInhibit apoptosisSkeletal/connective tissue cellsPlant cellsImmunofluorescence stainingBitter gourd
Owner:XUZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of human adipose mesenchymal stem cell exosome for treating myocardial infarction
PendingCN111944749AExosome effect is stableDamage reliefCell dissociation methodsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCardiac functioningCytokine
The invention provides a preparation method of human adipose mesenchymal stem cell exosome for treating myocardial infarction, and relates to the technical field of biology. The preparation method ofthe human mesenchymal stem cell exosome for treating myocardial infarction provided by the invention comprises the following steps: culturing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells, and collecting a cell culture solution; and carrying out differential centrifugation on the cell culture solution, collecting the supernatant, carrying out ultracentrifugation on the supernatant to obtain target microspheres, and then filtering, purifying and sterilizing the target microspheres to obtain the human adipose mesenchymal stem cell exosome for treating myocardial infarction. According to the present invention, the advantage is that the human adipose mesenchymal stem cell exosome is prepared by culturing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells, and the human adipose mesenchymal stem cell exosome containsvarious RNAs and cytokines, so that infarcted myocardial cells are effectively repaired, the cardiac function is enhanced, compensatory myocardial load is reduced, and heart failure is relieved; and atreatment medicine or a treatment strategy is provided for myocardial infarction.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV UNION HOSPITAL
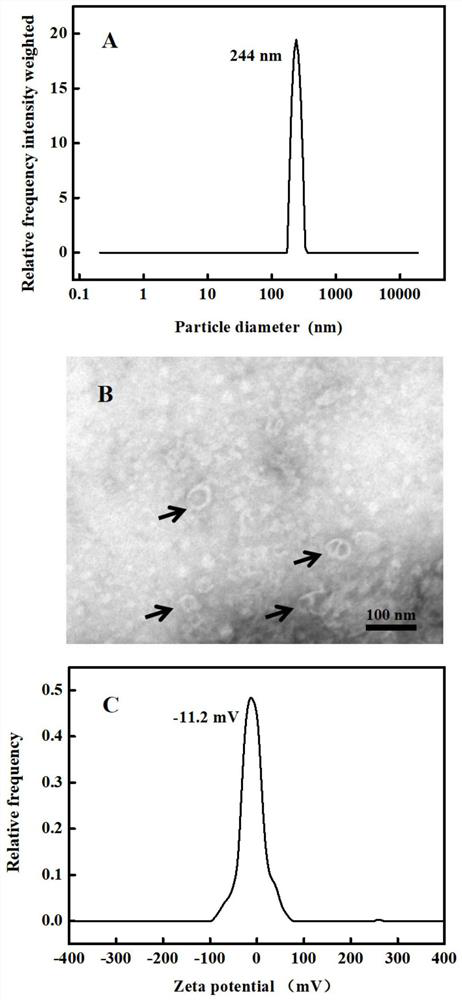
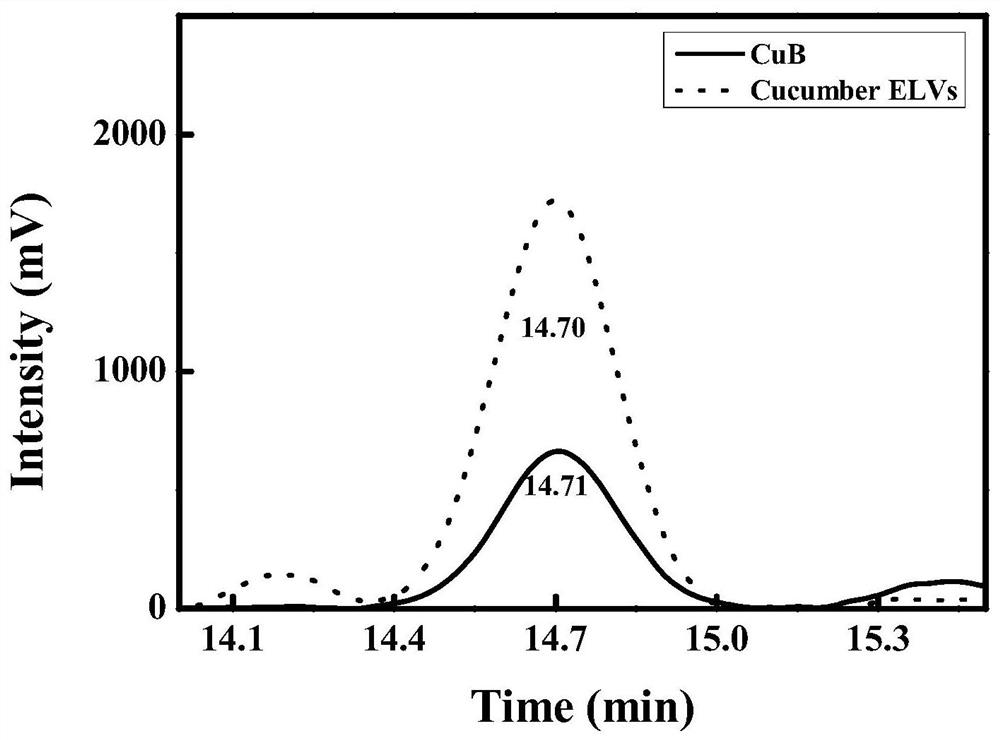
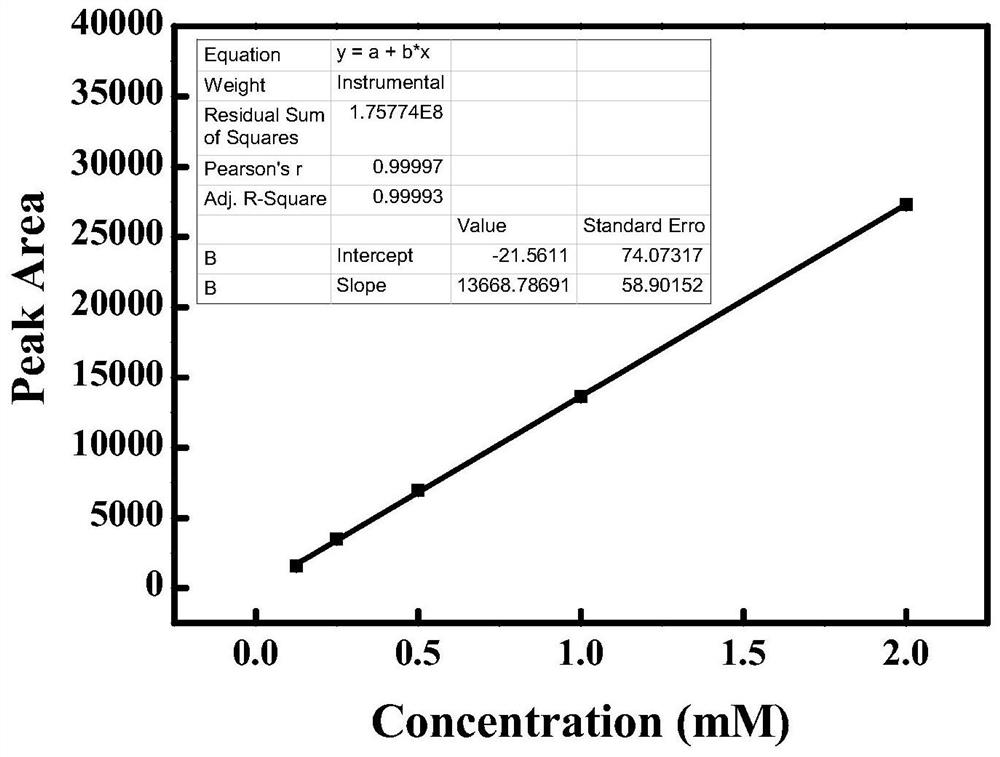
Cucumber exosome-like vesicles containing cucurbitacin B and capable of being used as anti-cancer drugs
ActiveCN112472731AGuaranteed stabilityInhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellTumor therapy
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap