Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5 results about "Food consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Reinforced feed for promoting pig feed intake and its preparation method
InactiveCN1802989AIncrease contact areaImprove bioavailabilityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsOrganic acidVitamin C
Owner:河南广安生物科技股份有限公司
Crayfish feed
The invention relates to the technical field of aquaculture, and in particular relates to a crayfish feed which is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20-25 parts of corn flour, 12-15 parts of soybean cake, 5-6 parts of wheat middling, 8-10 parts of wheat bran, 3-4 fish intestine powder, 2-3 parts of clam worm powder, 3-4 parts of freshwater shrimp powder, 5-6 parts of fresh soybean milk, 4-5 parts of pondweed, 2-3 parts of bone meal, 3-4 parts of fermented duck blood powder, 5-6 parts of alternanthera philoxeroide stem and leaf, 4-5 parts of bread crumb, 2-3 parts of sleeve-fish powder, a proper amount of salt and 4-5 parts of phagostimulant. The feed provided by the invention is completely accordant with the omnivorous characteristics of crayfish and contains multiple high-quality protein raw materials, the palatability of the feed can be improved because of the fishy smell of the raw materials such as the fish intestine powder, the clam worm powder and the sleeve-fish powder, the food consumption of the crayfish is increased, the fed crayfish can grow and develop rapidly, the weight can be remarkably increased, and moreover, as the raw materials are all pure natural green raw materials, the problem of medicine residue is prevented, and the quality of crayfish is ensured.
Owner:ANHUI ZHIHUI ELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing jerusalem artichoke straw micro-storage feed
InactiveCN103315197AHigh in nutrientsImprove digestibilityAnimal fodder preservationEngineeringFood consumption
The invention relates to a method for preparing a jerusalem artichoke straw micro-storage feed. The method comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving white sugar into clean water, adding straw fermented live bacillus, and placing the obtained object for 1-2h at room temperature so as to obtain resurrected straw fermented live bacillus; (2) pouring the resurrected straw fermented live bacillus into salt water, and uniformly stirring the obtained object so as to obtain a bacterium agent; (3) cutting jerusalem artichoke straws into small sections with a length of 3-8cm, paving the small sections at the bottom of a pit, wherein the thickness of each layer of straws is 20-30cm; uniformly spraying the bacterium agent on each layer of straws, compacting the straws until the thickness of the straws is 40cm higher than the mouth of the pit; and at this moment, fully compacting the straws, uniformly sprinkling salt powder on the upmost layer of straws, and after compacting the straws, covering a plastic film on the straws; and finally, scattering straws with the thickness of 20-30cm on the plastic film, and covering soil with the thickness of 15-20cm, and sealing the pit; and (4) 21-30 days later, when the moisture content of jerusalem artichoke straws is 60-70%, obtaining the jerusalem artichoke straw micro-storage feed. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the process is simple, the cost is low; obtained products are high in nutritional ingredients, high in digestibility, good in palatability, and high in food consumption.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SCI NORTHWEST HIGHLAND BIOLOGY INST
Method for improving silking amount of silkworms
Owner:宿州青果知识产权服务有限公司
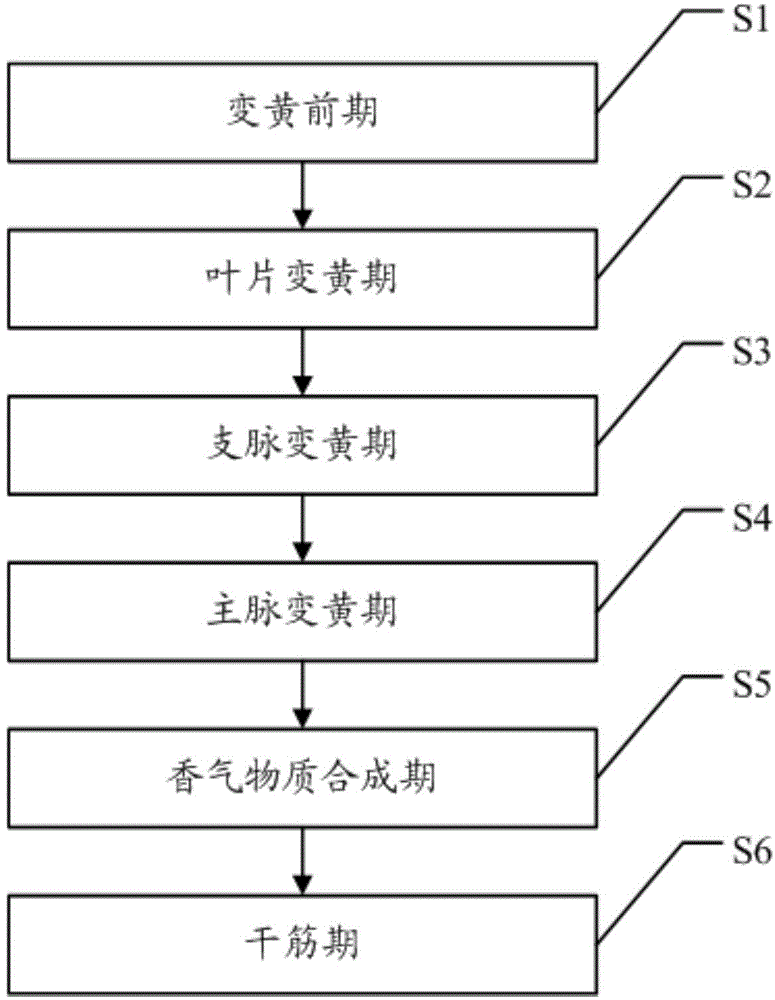
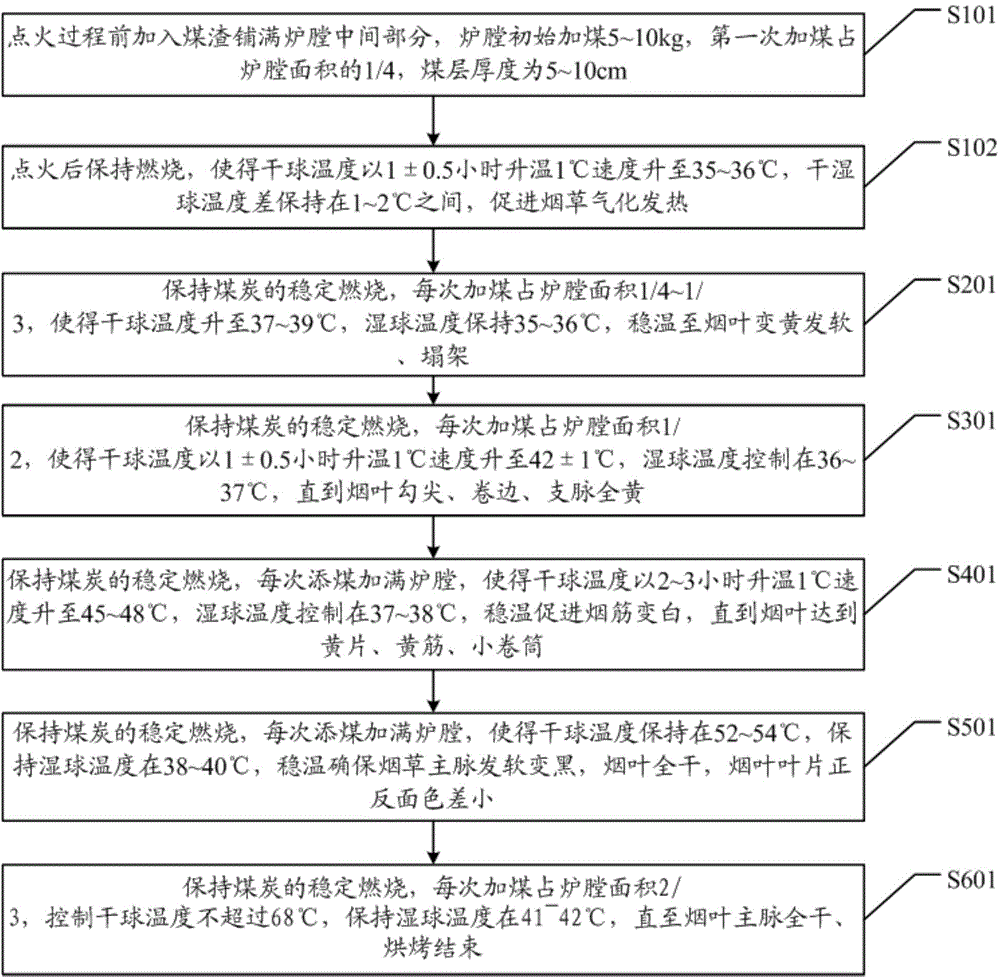
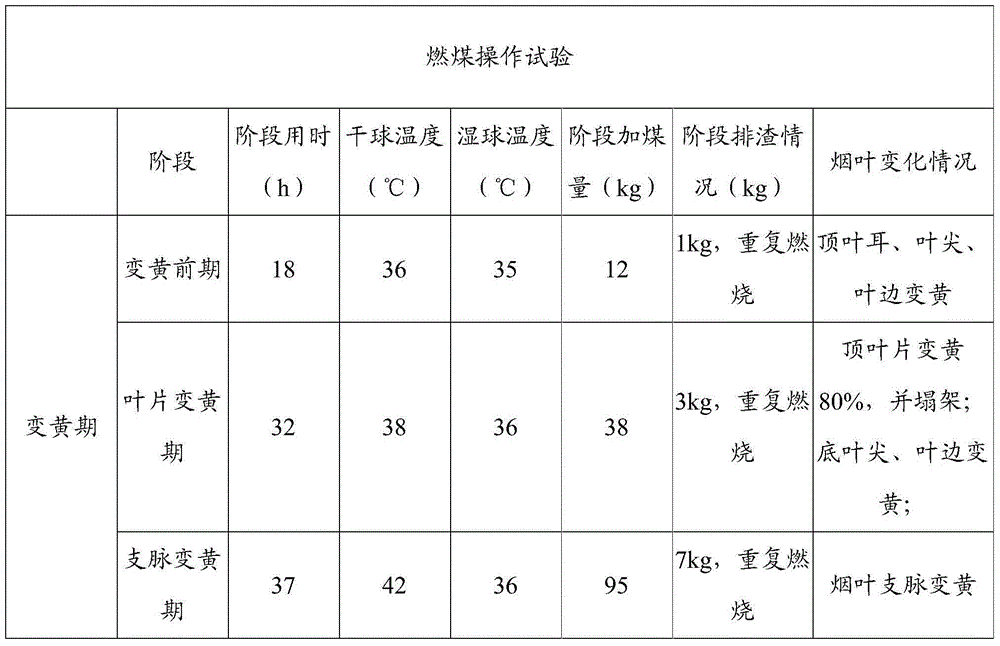
Tobacco leaf baking method
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO GUANGDONG IND
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap