High-yield production method of lovastatin
A technology of lovastatin and a production method, applied in the production method and the field of Monascus used in the production method, can solve the problems of staying, not forming an industrialized scale, etc., and achieve the effects of high production capacity and improved quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
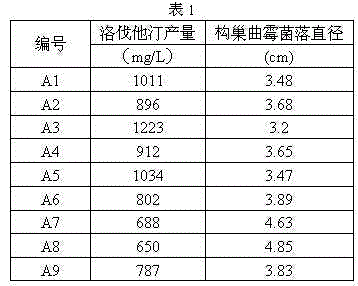
[0042] Mutation and preliminary screening of Monascus strain with high lovastatin production
[0043] Wash the spores from the growth slant of the initial strain Monascus purpureus with normal saline to obtain a spore suspension, inoculate the seed medium, and cultivate for about 36 hours. Take the bacterial suspension, filter it with sterile gauze, and shake it with glass beads Disperse to a single spore suspension and collect the single spore suspension for later use.
[0044] Add an equal volume of monospore suspension and 1% lithium chloride solution into a sterile test tube, mix well, let stand for 3 hours, and finally dilute 100 times with sterile phosphate buffer to terminate the reaction.
[0045] Draw 1 mL of the spore dilution treated with lithium chloride and inject it into a sterile small dish, and place it under laser irradiation. The irradiation time is 10 min. Laser wavelength: 632.8 nm, and the irradiation power density is 17.6 mw / cm2.
[0046] After the muta
Embodiment 2
[0048] Production of Lovastatin by Liquid Fermentation of Monascus
[0049] Fermentation strain: Monascus purpureus
[0050] Seed medium:
[0051] Rice flour 3 g, glucose 2 g, NaNO 3 0.2 g, peptone 1.5 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.15 g, add water to 100 mL.
[0052] Fermentation medium:
[0053] Rice flour 7 g, glycerin 5 mL, NaNO 3 0.2 g, peptone 1.5 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.15 g, add water to 100 mL.
[0054] Training conditions:
[0055] Monascus spores were scraped from the plate and transferred to a Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of seed medium, and cultured at 30°C for 3 days. According to the inoculation amount of 15%, the grown seed culture medium was transferred to 150 mL fermentation medium, and cultured on a shaker at 150 r / m at 30°C for 3 days, then cultured on a shaker at 150 r / m at 24°C for 20 days.
[0056] Sample processing and testing:
[0057] After the fermentation broth was centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 min,
Embodiment 3
[0060] Production of lovastatin by liquid state fermentation of monascus after mutagenesis of the present invention
[0061] Fermentation strain: Monascus purple
[0062] Seed Medium:
[0063] Rice flour 3 g, glucose 2 g, NaNO 3 0.2 g, peptone 1.5 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.15 g, add water to 100 mL.
[0064] Fermentation medium:
[0065] Rice flour 7 g, glycerin 5 mL, NaNO 3 0.2 g, peptone 1.5 g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.05 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.15 g, add water to 100 mL.
[0066] Training conditions:
[0067] The spores of Monascus MPB3 were scraped from the plate and transferred to a Erlenmeyer flask containing 50 mL of seed medium, and cultured at 30°C for 3 days. According to the inoculation amount of 15%, the grown seed culture medium was transferred to 150 mL fermentation medium, and cultured on a shaker at 150 r / m at 30°C for 3 days, and then cultured on a shaker at 150 r / m at 24°C for 20 days.
[0068] Sample processing and testing:
[0069] After t
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap