A method for reducing quantification errors caused by an optical artefact in digital polymerase chain reaction
A technology of chain reaction and quantification error, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, material analysis by optical means, measurement device, etc., can solve the problem of not considering quantification error, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
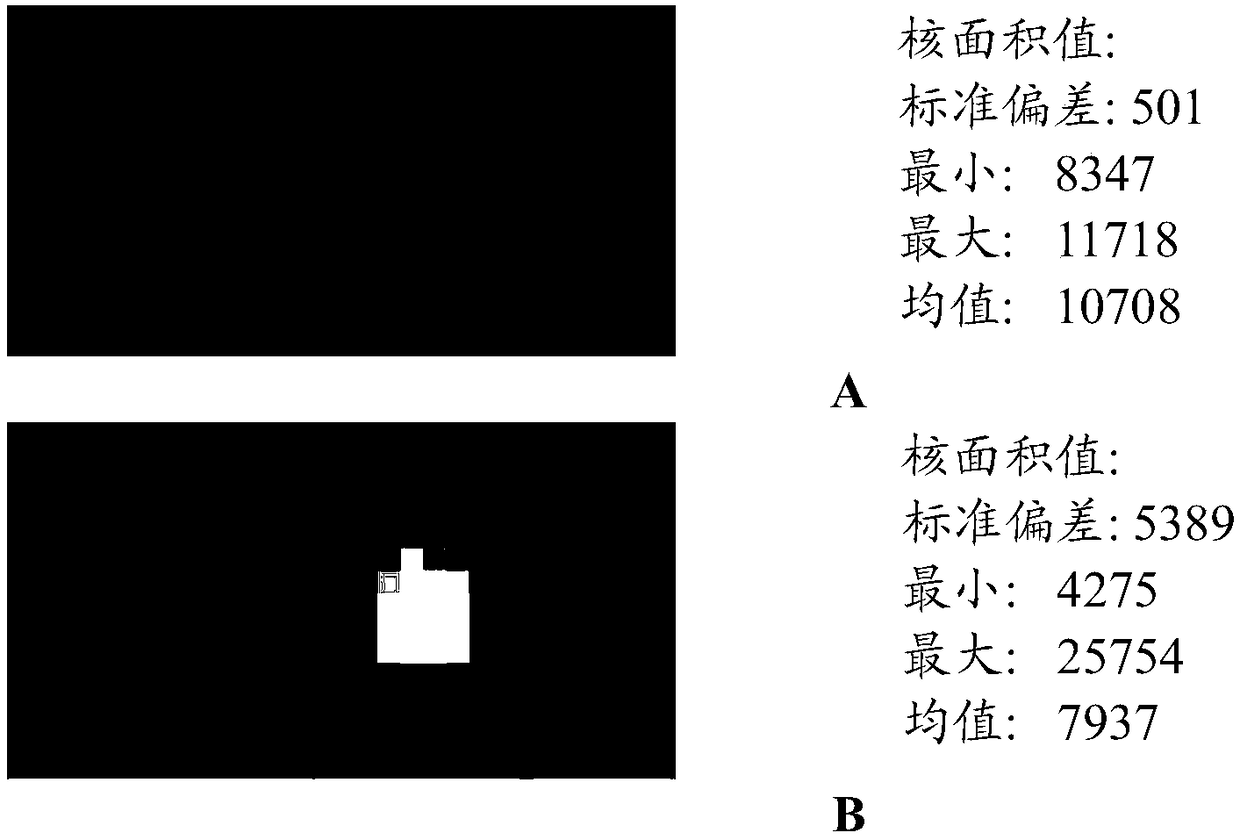
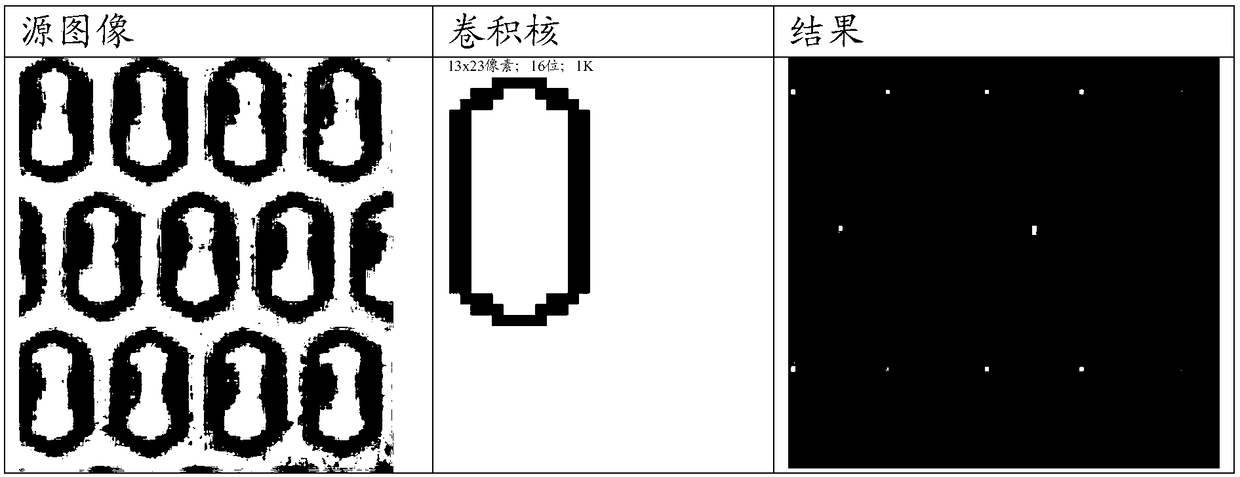
[0008] In a first aspect, the present invention relates to a method for reducing quantification errors caused by optical artifacts in a digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR), wherein the amount or concentration of a nucleic acid of interest is quantified in an array of reaction regions , the method consists of
[0009] a) providing an array of reaction regions used in dPCR;
[0010] b) determining the distribution of the optical signal in each reaction zone;
[0011] c) if the optical signal in the reaction region determined in step b) is not uniformly distributed in the reaction region
[0012] If not, identify the reaction zone as invalid; and
[0013] d) Eliminating reaction regions identified as invalid from the calculation of the amount or concentration of the nucleic acid of interest.
[0014] As detailed above, methods for the reliable determination of the amount or concentration of nucleic acids are of particular importance in several industrial applications, for...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap