High-connectivity polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber membrane and preparation method thereof
A technology of polyvinylidene fluoride and fiber membrane, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, semipermeable membrane separation, etc., can solve problems such as unfavorable solvent recycling, membrane shrinkage due to temperature increase, unfavorable industrialization, etc. Flux, optimized membrane performance, easy to control the effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
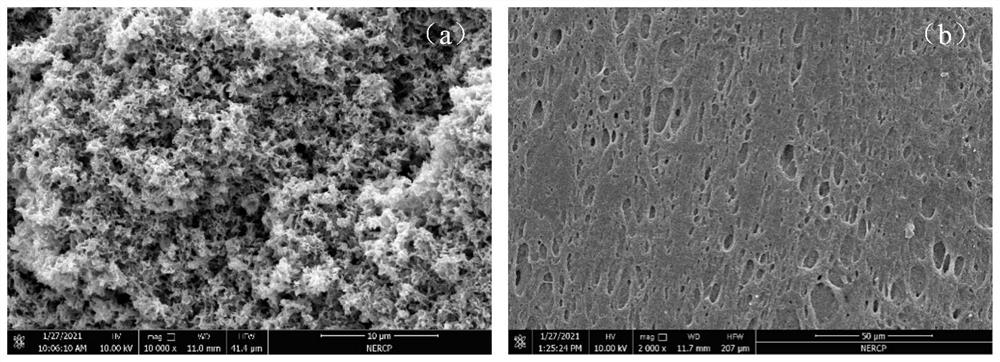
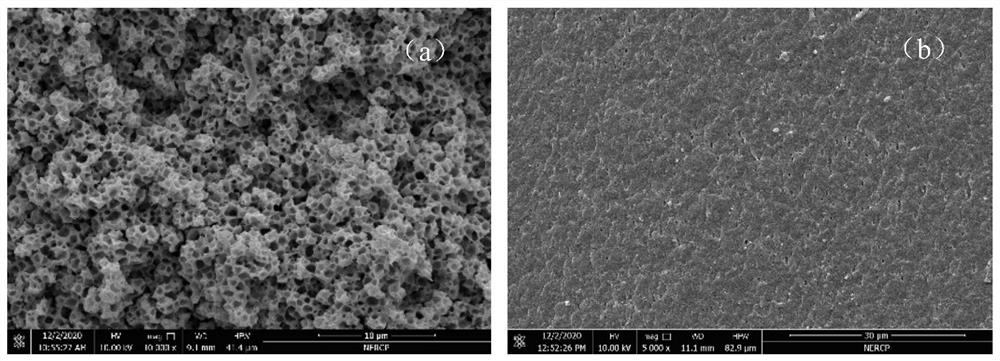
[0035] In view of the problems of poor porosity, dense cortex and low flux in the conventional solid-liquid phase separation in the prior art, the present invention provides a method for preparing a high-penetration polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber membrane to solve the problems existing in existing products. technical problems.
[0036] Specifically, the present invention uses a single diluent to prepare hollow fiber membranes below the melting point of polyvinylidene fluoride, and uses a water-soluble non-diluent heated to a certain temperature as the core liquid to fully exert its The efficiency of mass transfer, by adjusting the length of the air gap and the temperature of the coagulation bath, mass transfer occurs effectively, so that the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane and the cross-section are opened. The preparation method can be referred to as follows:
[0037] Fully heat and mix polyvinylidene fluoride and a single diluent to obtain a casting solution;
[
Embodiment 1
[0050] (1) Preparation of casting solution: In terms of parts by mass, mix 28 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride and 72 parts of acetyl tributyl citrate into the reaction kettle, heat to 130°C and keep stirring for 3 hours to fully dissolve into a uniform The solution of vacuum static degassing after 3h to obtain casting solution;
[0051] (2) Preparation of hollow fiber membrane: the casting solution after degassing enters the spinneret after passing through the filter screen and the metering pump under the nitrogen pressure of 0.3MPa, and is extruded from the casting solution channel of the spinneret, and the temperature Polyethylene glycol (molecular weight: 2000) at 80°C flows out from the core liquid channel in the spinneret at 30ml / min through a metering pump, and enters pure water at 50°C through an air gap of 200mm to solidify and shape. Under the condition of 10m / min, it is wound onto the winding wheel to form primary film filament;
[0052] (3) The prepared nascent m
Embodiment 2
[0059] (1) Preparation of casting solution: in parts by mass, mix 30 parts of polyvinylidene fluoride and 70 parts of tributyrin into the reaction kettle, heat to 130°C and keep stirring for 3 hours to fully dissolve into a uniform solution, after standing in vacuum for degassing for 3h, the casting solution was obtained;
[0060] (2) Preparation of hollow fiber membrane: the casting solution after degassing enters the spinneret after passing through the filter screen and the metering pump under the nitrogen pressure of 0.3MPa, and is extruded from the casting solution channel of the spinneret, and the temperature Polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 6000) at 100°C flows out from the core liquid channel in the spinneret at 30ml / min through a metering pump, and enters pure water at 60°C through an air gap of 280mm to solidify and shape. Under the condition of 10m / min, it is wound onto the winding wheel to form primary film filament;
[0061] (3) Soak the prepared membrane fi
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pure water flux | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Breaking strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap