Composite substrate material and process for producing the same
a substrate material and composite technology, applied in the field of composite substrate materials, can solve the problems of high cost, low long-term reliability of adhered areas, and optical scattering and reflection loss, and achieve high bond strength, good environmental temperature resistance characteristics, and long-term reliability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025]The present invention will hereinbelow be described in further detail with reference to the accompanying drawings.
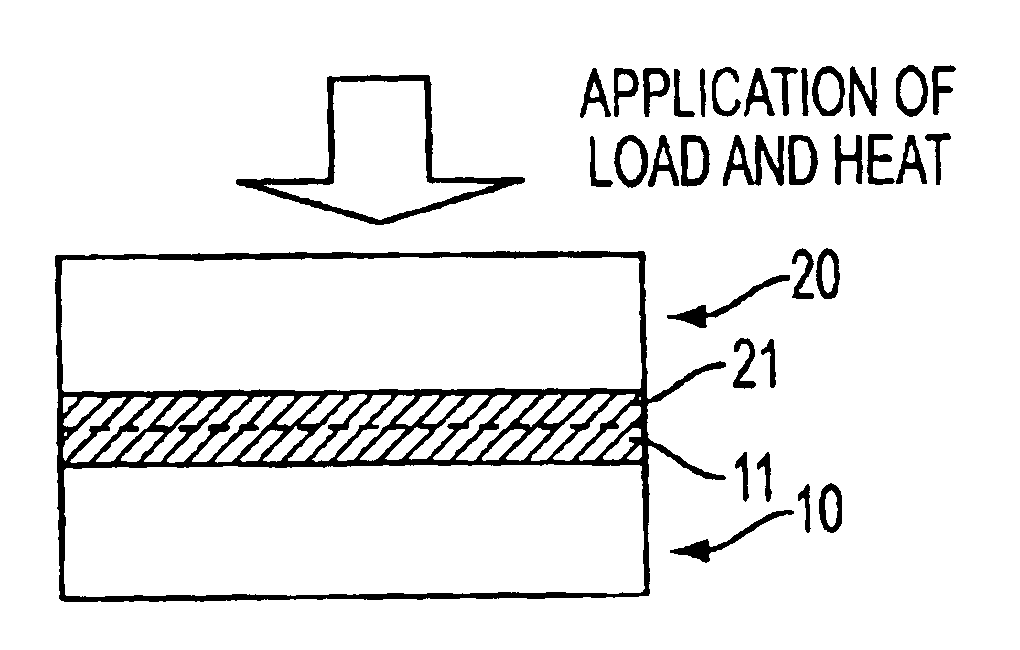
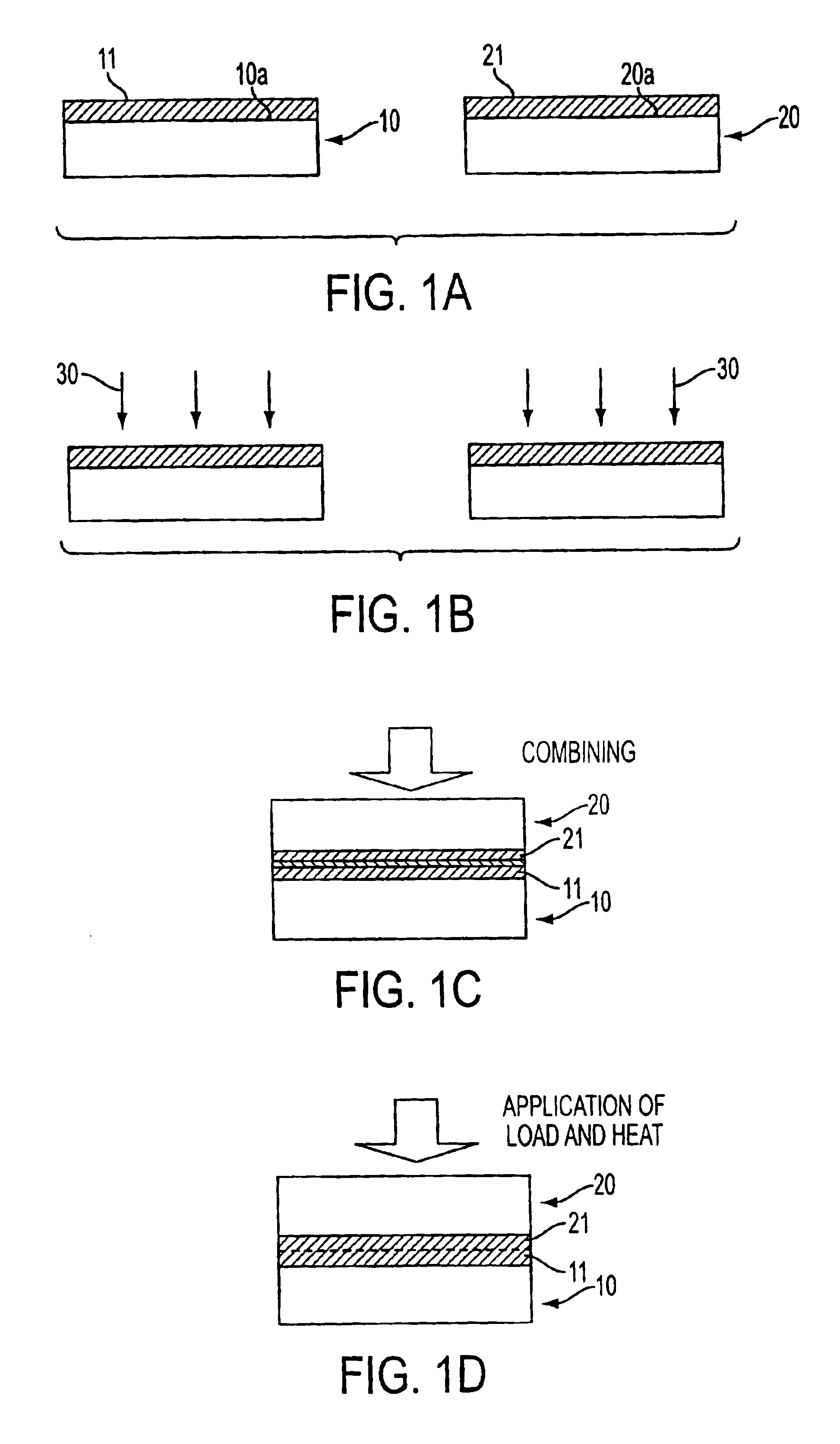
[0026]FIGS. 1A, 1B, 1C, and 1D show steps in a first embodiment of the process for producing a composite substrate material in accordance with the present invention.
[0027]Firstly, as illustrated in FIG. 1A, two Si wafers 10 and 20, which act as substrate materials, are prepared. The Si wafers 10 and 20 respectively have surfaces 10a and 20a, which have been subjected to mirror finish. Thereafter, TiO2 thin films 11 and 21, which act as functional films having photo-catalytic effects, are respectively formed on the surfaces 10a and 20a. In this embodiment, each of the Si wafers 10 and 20 has a thickness of 300 μm. Also, the TiO2 thin films 11 and 21 can be formed with, for example, a sputtering technique or a sol-gel technique.
[0028]Thereafter, as illustrated in FIG. 1B, the surface of each of the TiO2 thin films 11 and 21 is exposed to ultraviolet light 30 having a wa
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Catalyst | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap