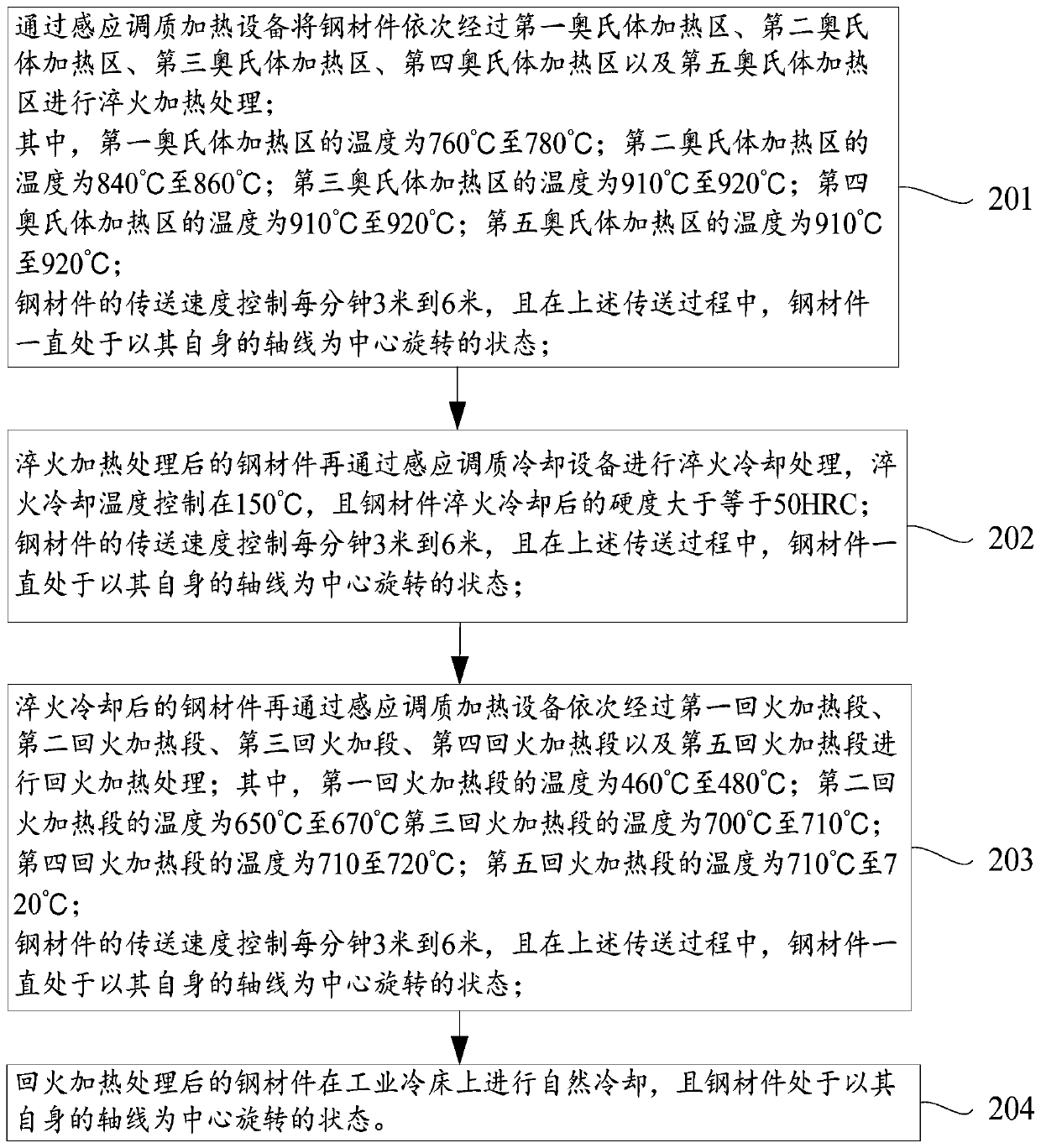
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5 results about "Austenite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Austenite, also known as gamma-phase iron (γ-Fe), is a metallic, non-magnetic allotrope of iron or a solid solution of iron, with an alloying element. In plain-carbon steel, austenite exists above the critical eutectoid temperature of 1000 K (727 °C); other alloys of steel have different eutectoid temperatures. The austenite allotrope is named after Sir William Chandler Roberts-Austen (1843–1902); it exists at room temperature in stainless steel.
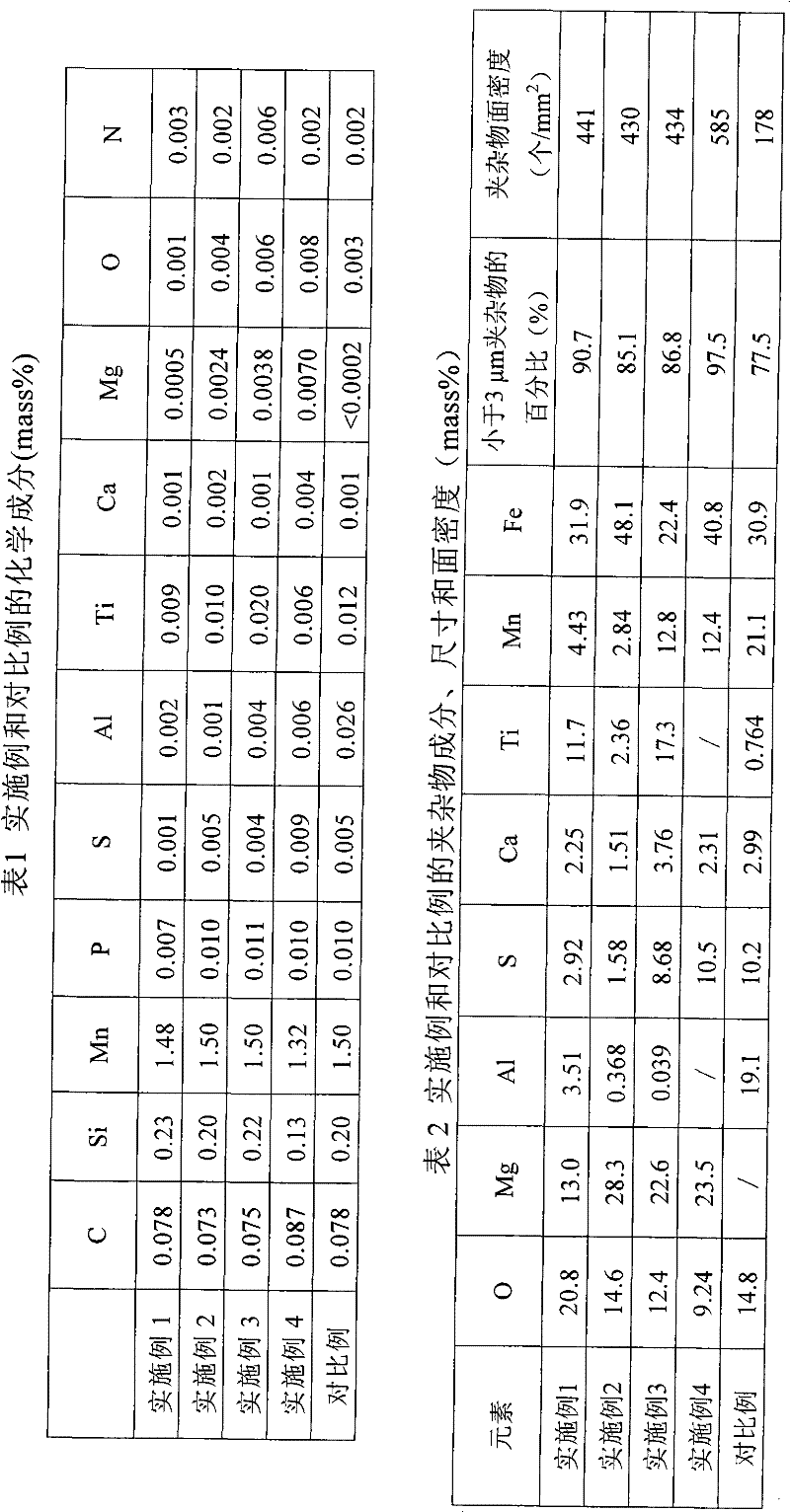
Control method of inclusions in thick steel plate used for high heat input welding
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Welding wire material for austenitic stainless steel
InactiveCN102303196AReduce sensitivityHigh deposition rateWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare-earth elementAustenite
Owner:JIANGSU XINGHAI SPECIAL STEEL
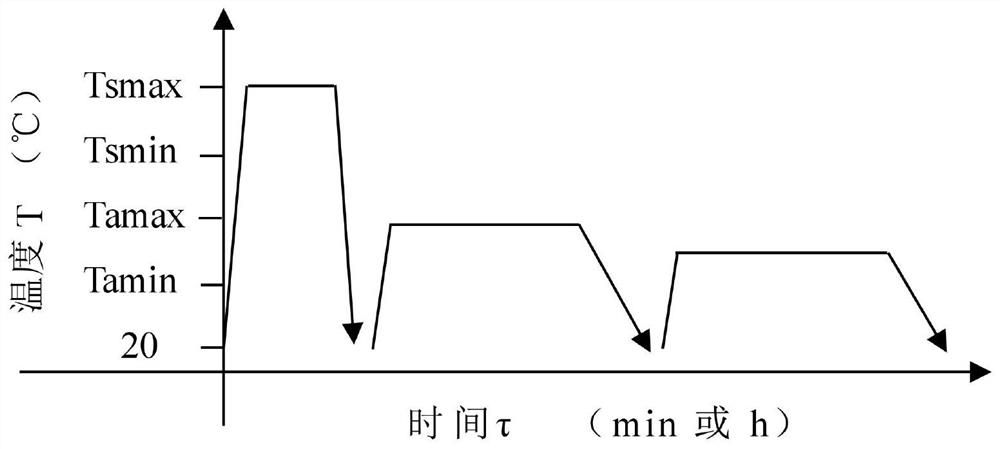
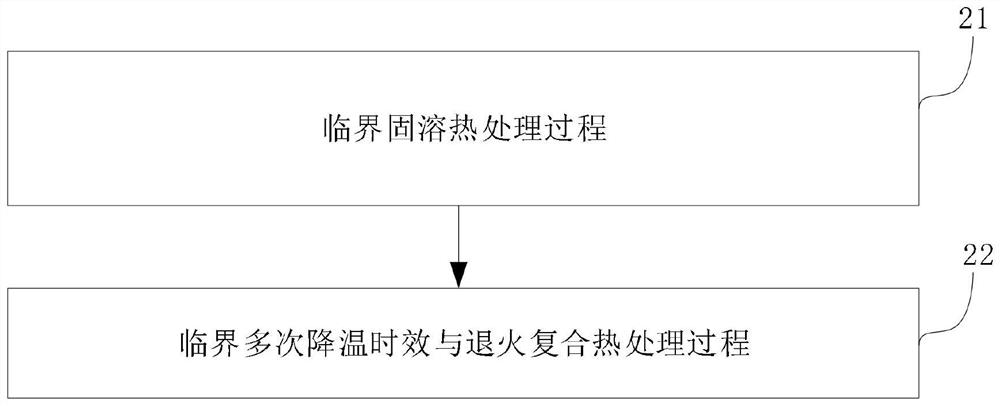
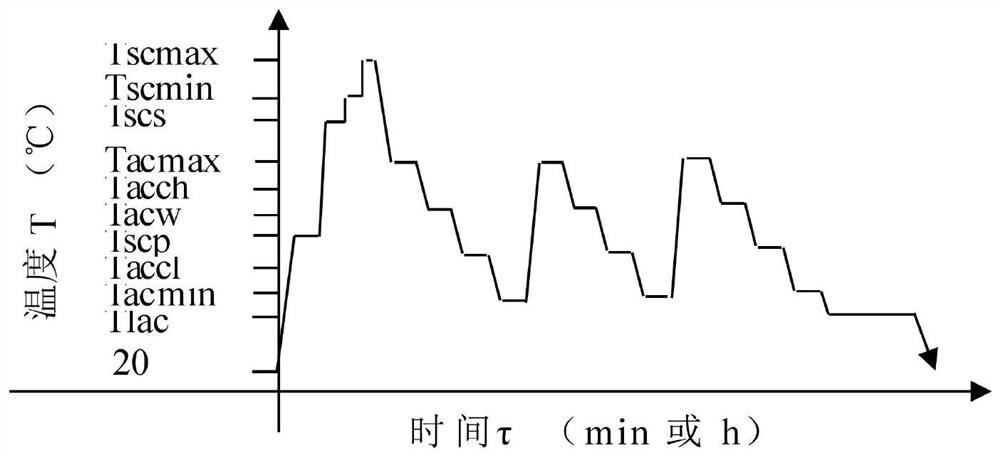
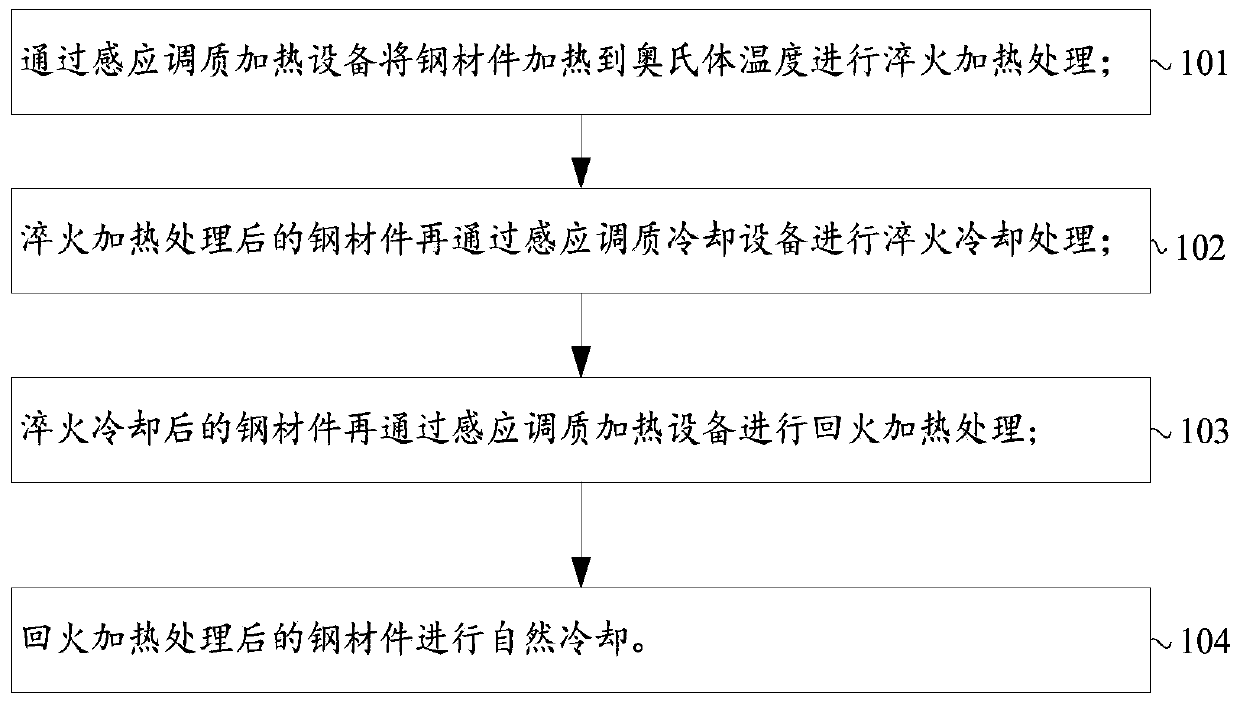
Critical solid solution and critical multiple cooling aging and annealing composite heat treatment method
PendingCN114395675ATechnically feasibleProcess adaptabilityHeat treatment process controlHeating timeSS - Stainless steel
Owner:山西柴油机工业有限责任公司
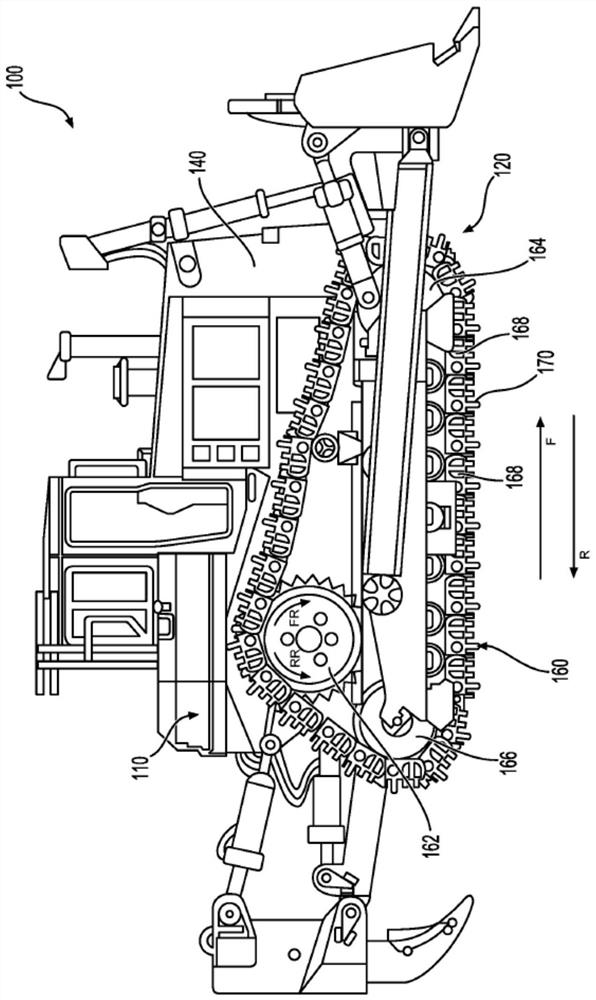
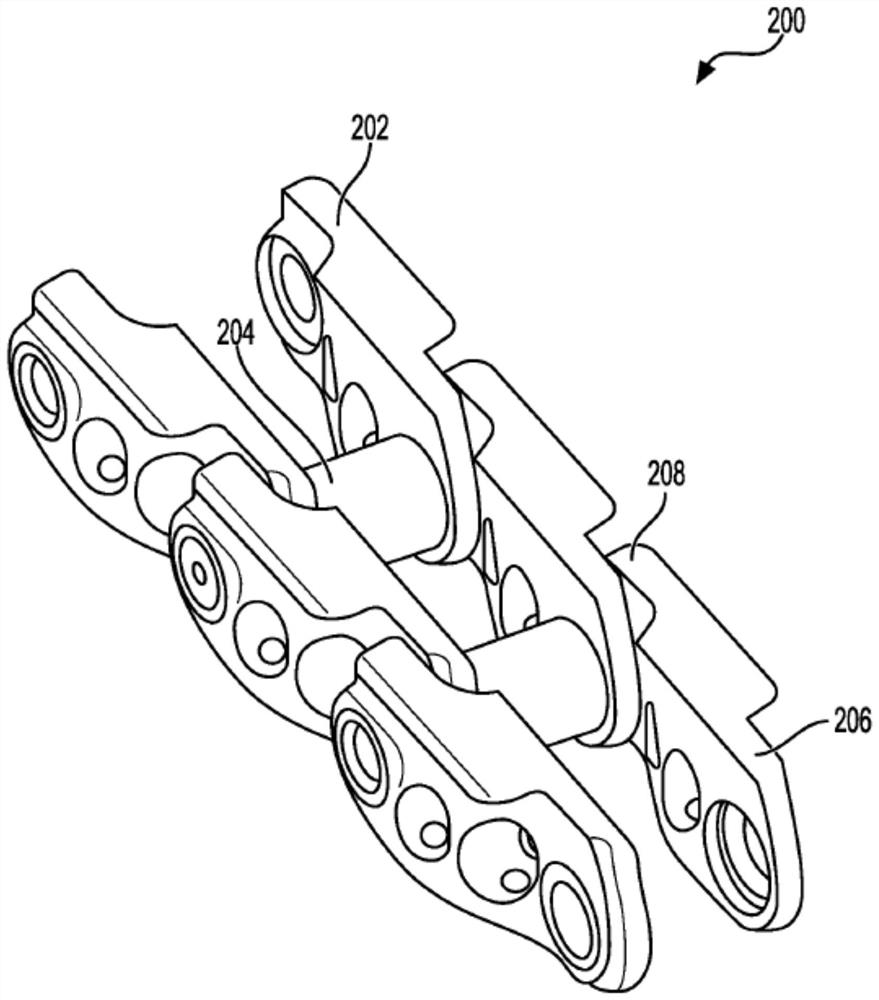
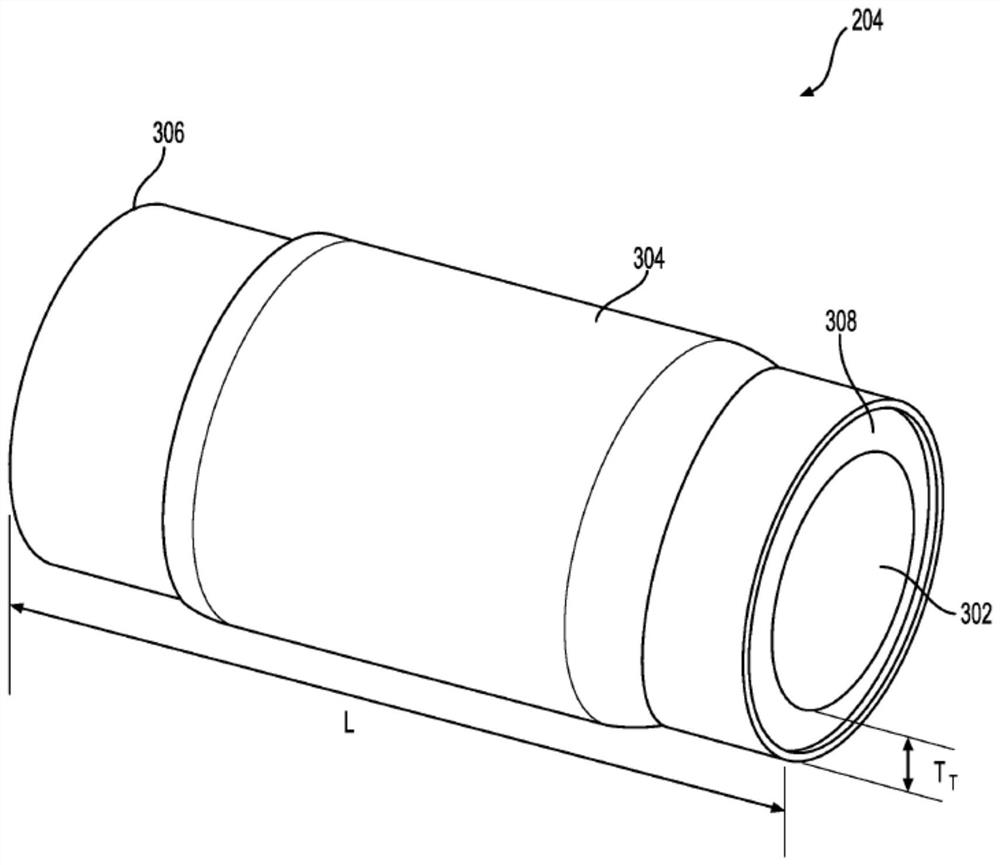
Track chain component with hardfacing wire covering layer
A steel track chain component (162, 164, 166, 168, 202, 204), such as a track bush (204), may be formed with a carburized portion (404), a hardfacing wire portion (412), and a core portion (410). The core portion 410 may be softer than the carburized portion 404, which may in turn be softer than the hardfacing wire portion 412. This configuration of various portions of the component (162, 164, 166, 168, 202, 204) may allow for relatively high wear resistance and toughness of the component (162, 164, 166, 168, 202, 204). The core portion 410 may be predominantly of a ferritic crystal structure, while the carburized portion 412 and the hardfacing wire portion 412 may include a martensite and / or austenite crystal structure. The carburized portion (412) may be formed by carburizing the track chain component (162, 164, 166, 168, 202, 204) in a heated and carbon-rich environment. The hardfacing wire portion (412) may be formed by welding a hardfacing wire alloy on at least a portion of the carburized portion (404).
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
GCr15 heat treatment process
InactiveCN111118260AHardness dispersion is smallReduce distortionIncreasing energy efficiencyHeat treatment process controlTemperature controlTempering
Owner:江苏南钢通恒特材科技有限公司
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap