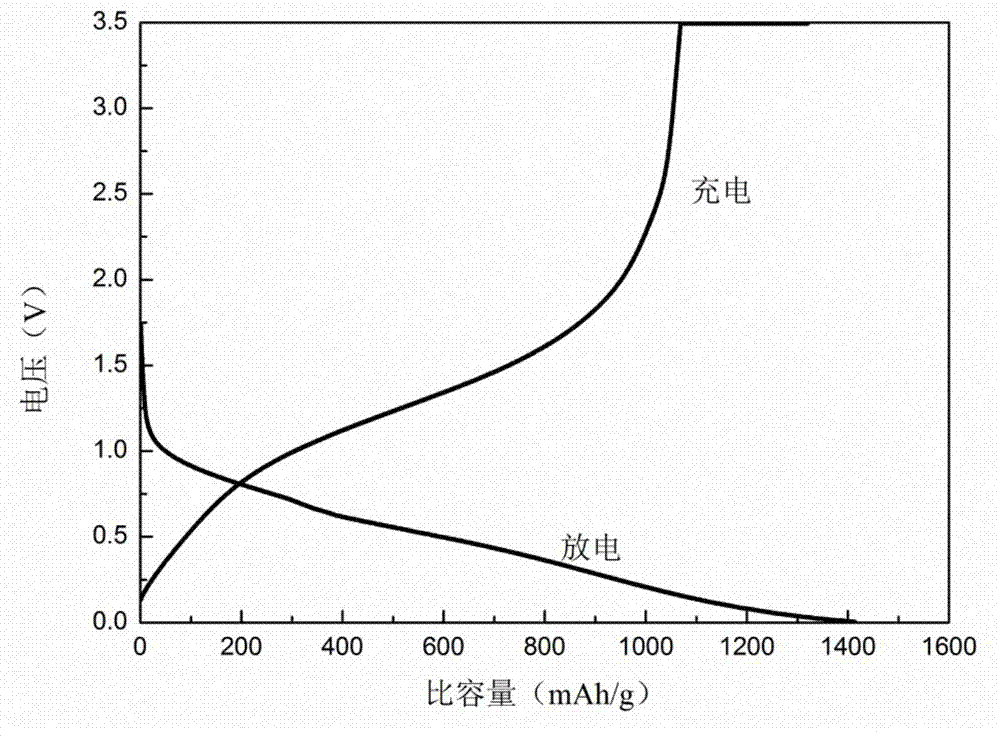
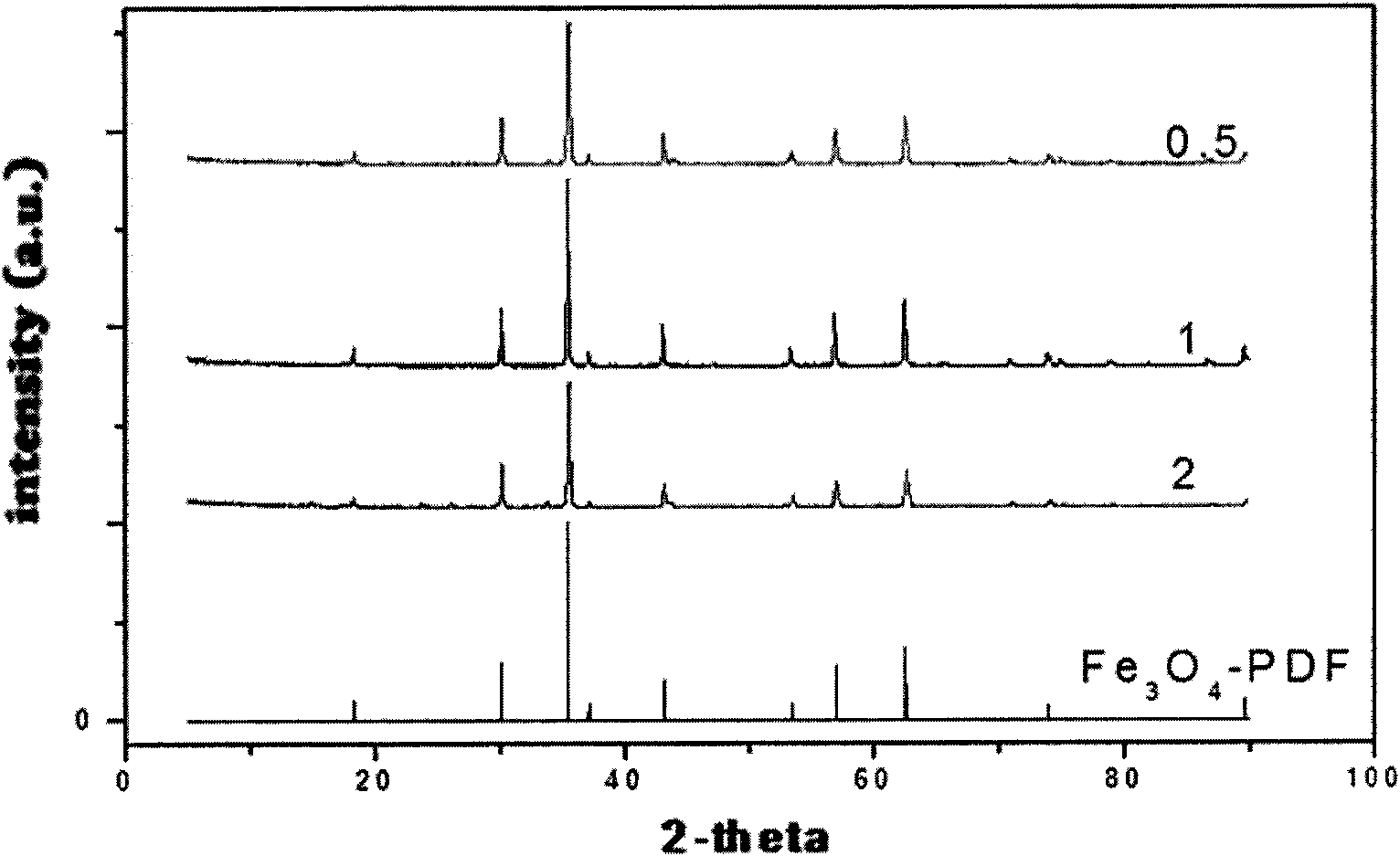
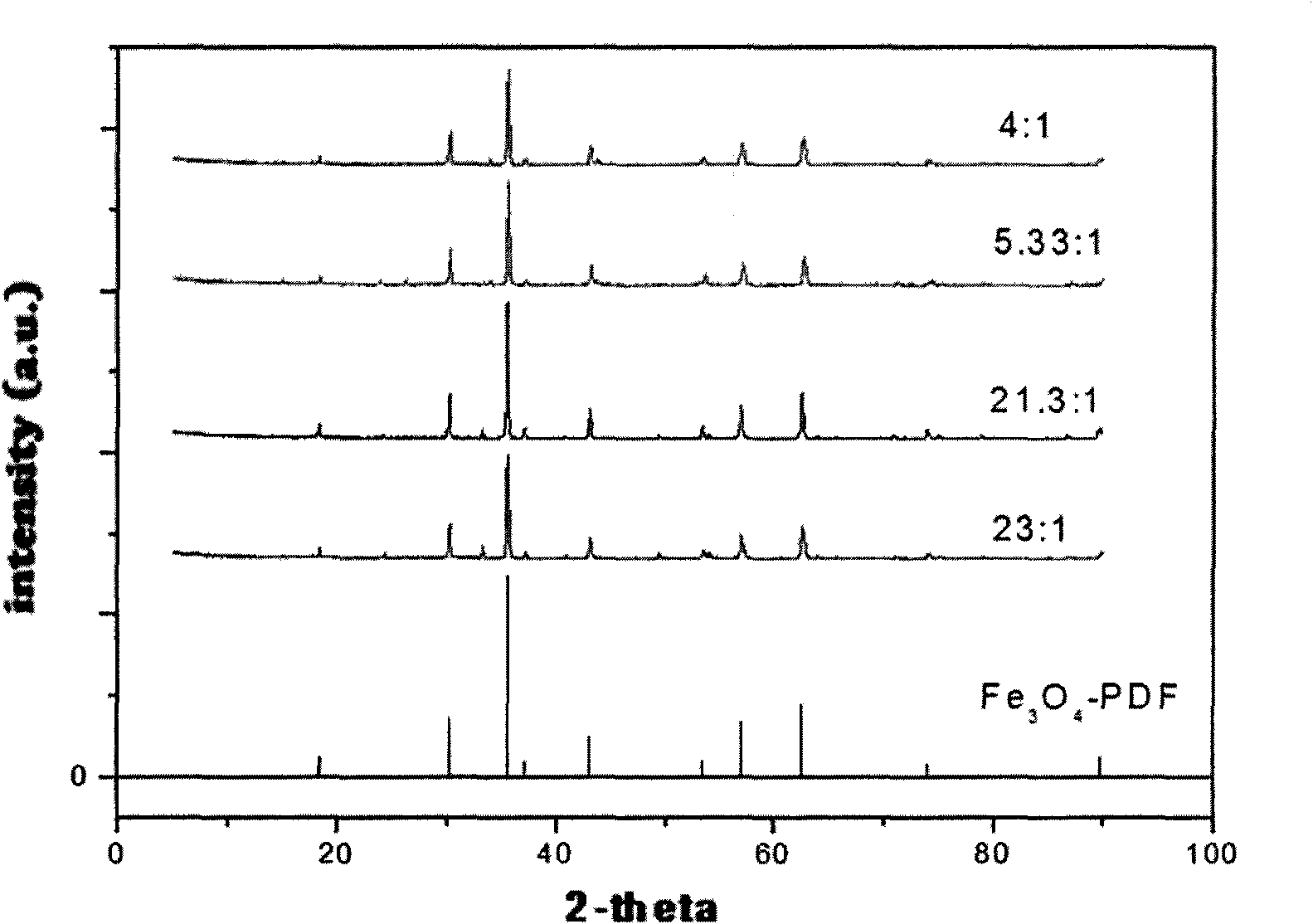
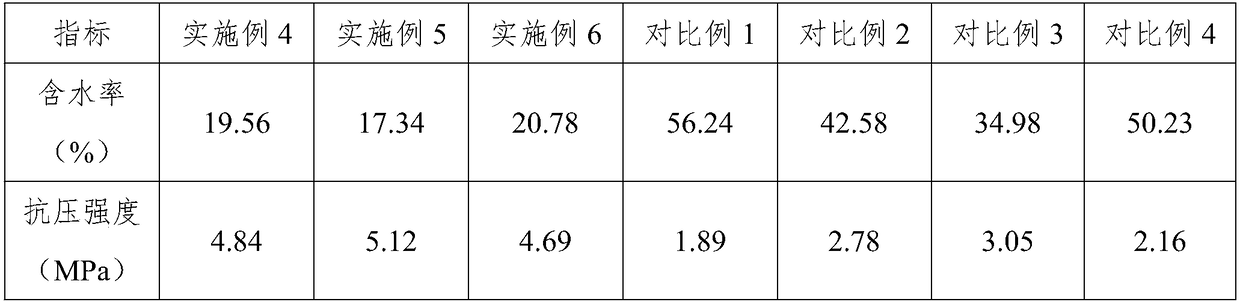
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
56 results about "Ferric" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, iron(III) refers to the element iron in its +3 oxidation state. In ionic compounds (salts), such an atom may occur as a separate cation (positive ion) denoted by Fe³⁺. The adjective ferric or the prefix ferri- is often used to specify such compounds — as in "ferric chloride" for iron(III) chloride, FeCl3. The adjective "ferrous" is used instead for iron(II) salts, containing the cation or Fe²⁺. The word ferric is derived from the Latin word ferrum for iron.
Preoxidized-composite electrolyzing method for removing arsenic in groundwater
InactiveCN101139150ALow toxicityImprove adsorption capacityMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationElectrolysisFenton reagent
A method to remove arsenic in underwater by preoxidation-combined electrolyzing relates to a method to remove arsenic from underwater, belonging to the technical field of water treatment. The present invention has solved the defect that more expensive pure nulvalent iron and slower corrosion speed of the pure nulvalent iron have limited the absorption of arsenic on the nulvalent iron. The present invention includes the following steps: the underwater containing arsenic is pre-oxidized by ozone, potassium ferrate, potassium permanganate, H2O2, photocatalysis oxidation reagent or Fenton reagent, thereby transferring As(III) to As(V). The water pre-oxidized passes through a filtering bed containing cast-iron scrap and carbon granules. The oxidizer left in the preoxidation section promotes the reaction of the step.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
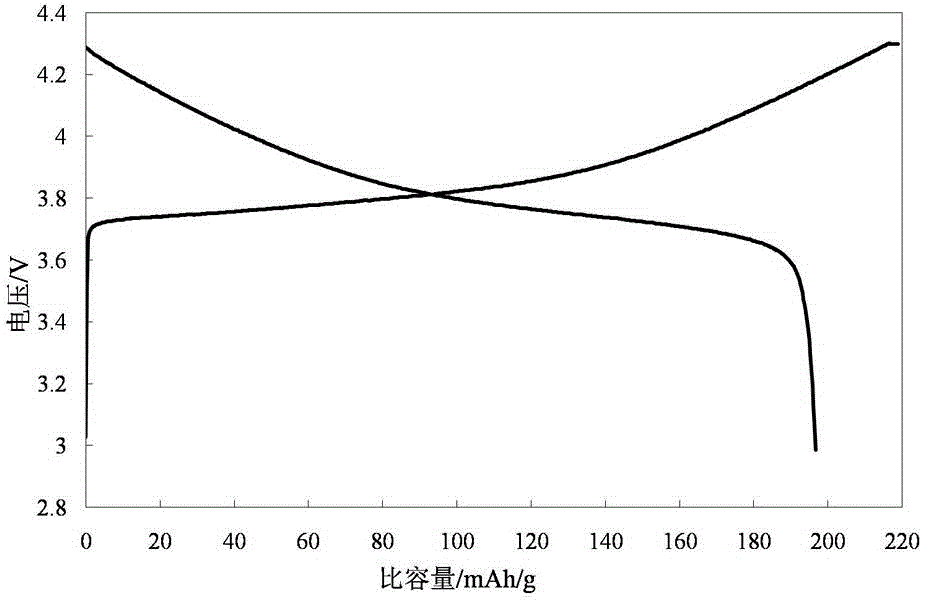
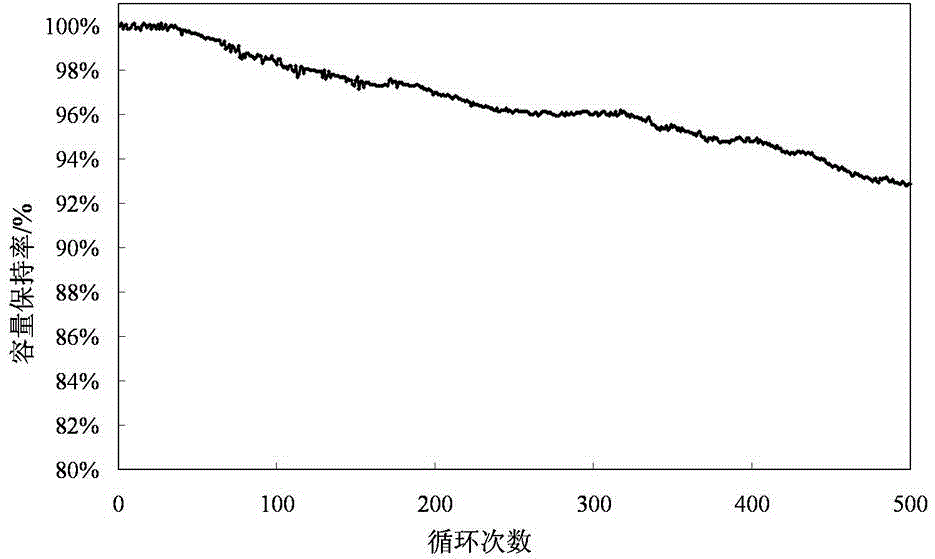
Surface coating modified lithium ion battery cathode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104577093AImprove securityNo significant reduction in specific capacityCell electrodesLithium iron phosphatePhysical chemistry
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIDARUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
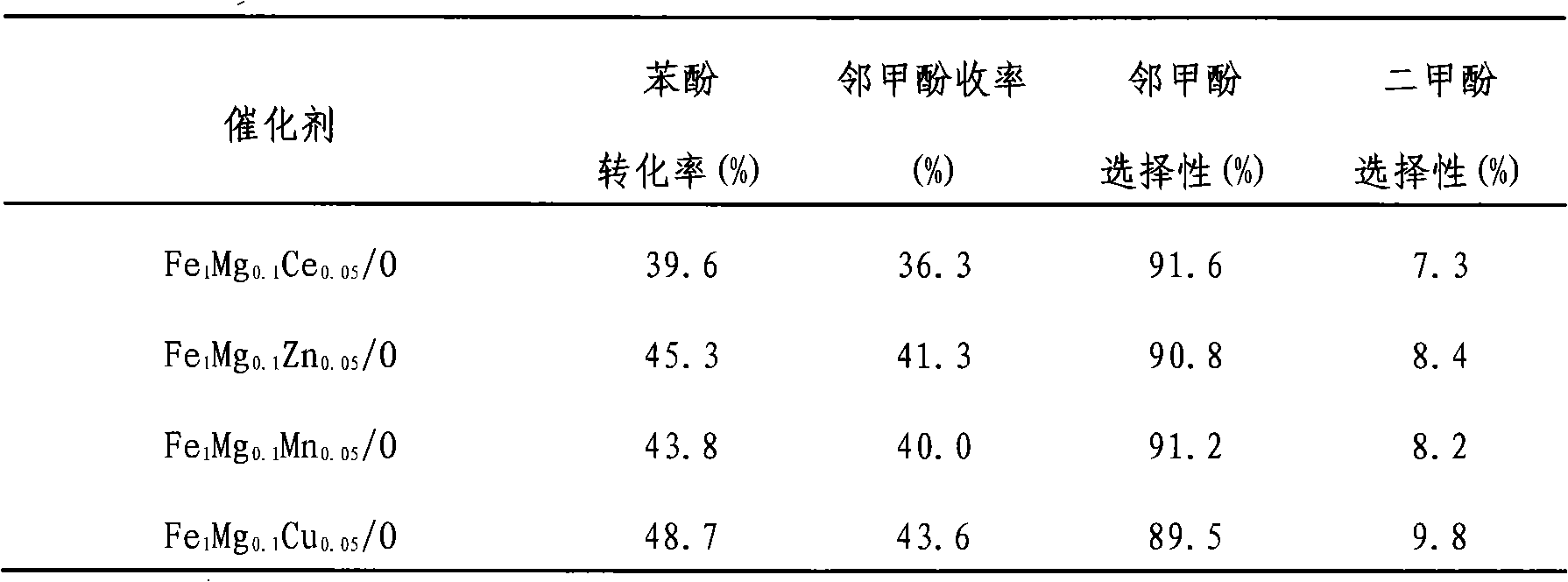
Phenol ortho-methylation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101513614AEasy to makeLow reaction temperatureOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationMagnesium saltOrtho position
Owner:HUNAN XINLING CHEM CO LTD
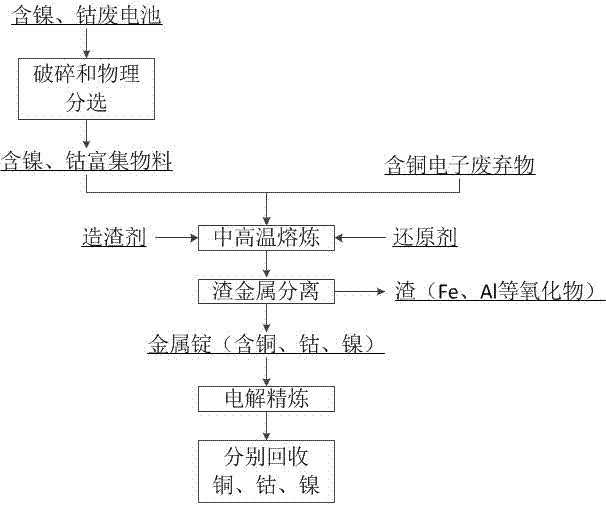
Synergetic metal recycling method for nickel and cobalt containing waste batteries and copper containing electronic waste
InactiveCN107012332AHigh purityAvoid efficiencyPhotography auxillary processesWaste accumulators reclaimingElectrolysisElectrical battery
Owner:SINO SCI PROCESS BEIJING SCI&TECH CO LTD
Control method of inclusions in thick steel plate used for high heat input welding
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Micro-electrolytic filler containing catalyst
Owner:ZHEJIANG BOHUA ENVIRONMENTAL TECH & ENG
Methods for purifying and stabilizing hydrofluoroolefins and hydrochlorofluoroolefins
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Titanium-carbide-based steel-bonded cemented carbide material and preparation method thereof
Owner:WUXI XINQUN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Technology for extracting zinc, lead and silver step by step by processing zinc-leached residues by full wet process
ActiveCN102719668AHigh extraction rateAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementHigh concentrationSlurry
Owner:JIANGXI LONGTIANYONG NONFERROUS METAL CO LTD
Copper and iron compound honeycomb coating type denitrification catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109499607AImprove thermal stabilityImprove anti-sulfur poisoning performanceMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationIon exchangeVacuum coating
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
Composite reinforced multinutrition rice and process thereof
ActiveCN102067969AMeeting nutritional needsShorten soakFood preparationCALCIUM LACTOBIONATEGluconates
Owner:天津知味米有限公司
High-temperature iron-based zeolite molecular sieve honeycomb type denitration catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107519926AEvenly dispersedSimple preparation processMolecular sieve catalystsDispersed particle separationFerrous saltsStearic acid
Owner:VALIANT CO LTD
Magnetic granule and attapulgite nanometer composite material, and hydrolytic method for preparing its ferrous salts
InactiveCN1830884AWith characteristicsResolve separabilityWater/sewage treatment by sorptionClaywaresFerrous saltsMagnetite Nanoparticles
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Flux for removing iron from Mg alloy and its preparing process
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A microwave-absorbing corrosion-resistant powder material and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108889939AReduce self-healing abilityMaintain electromagnetic propertiesOther chemical processesTransportation and packagingMesoporous silicaMetal particle
The invention discloses a corrosion-resistant powder material capable of absorbing microwave and a preparation method thereof, wherein the powder material is a core-shell structure, the core-shell structure comprises a shell and a core, the shell is a mesoporous silicon dioxide layer, the core is magnetic metal particles, a corrosion inhibitor is filled between the shell and the core, and the particle size of the magnetic metal particles is 0.6 1 micron, is iron carbonyl and nickel carbonyl, or a composite of iron carbonyl and cobalt carbonyl, the weight ratio of iron carbonyl to nickel or cobalt is 8: 1 4: 1. The invention can effectively solve the problems of insufficient microwave absorption and deterioration of corrosion resistance of conventional coatings.
Owner:SHANDONG GEWU NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
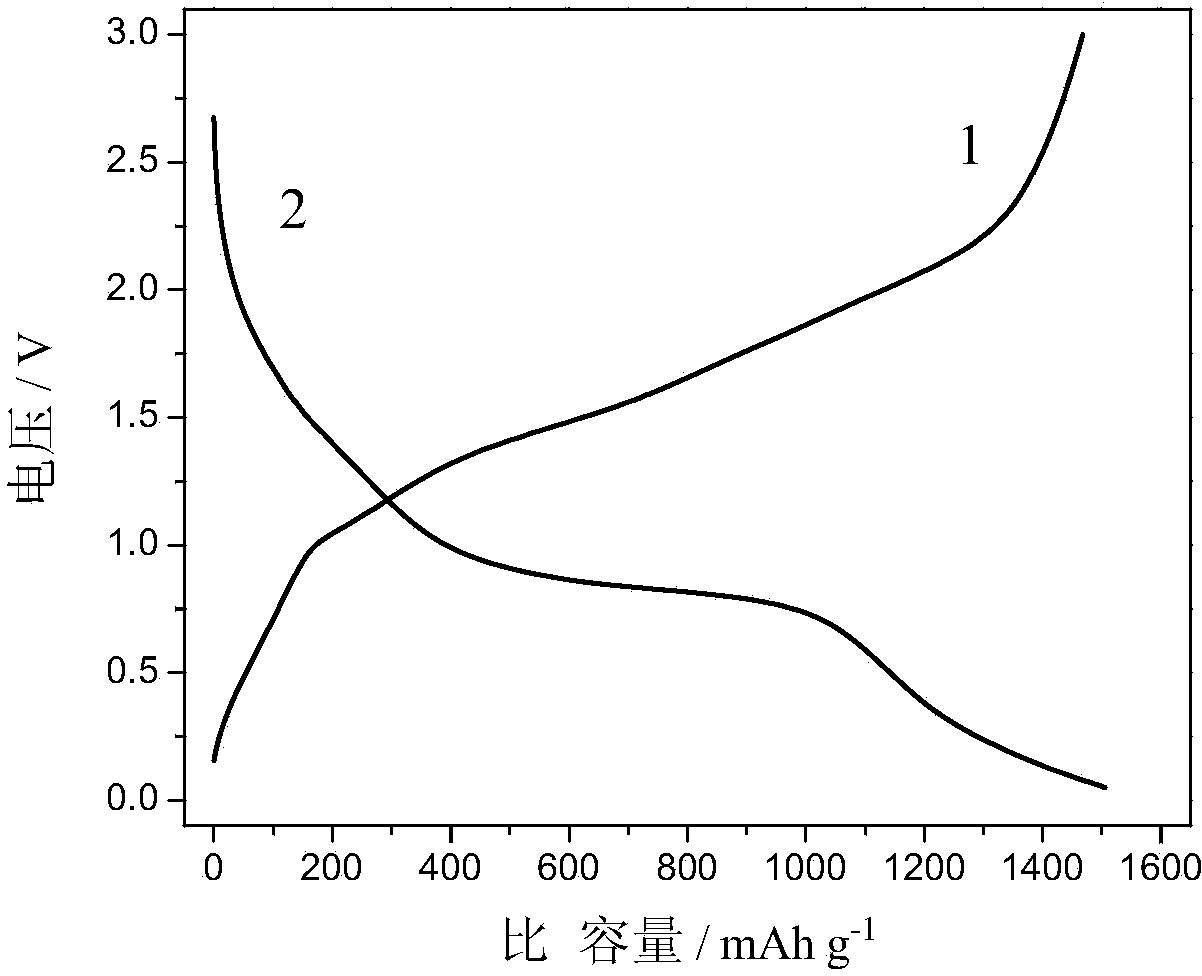
Method for preparing ferric vanadate-graphene negative electrode composite material
ActiveCN104766975AUniform textureGood dispersionNegative electrodesSecondary cellsDispersityReaction rate
Owner:SHENZHEN PANGU ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Method for processing red mud by utilizing iron pyrites
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Low-temperature photo-irradiation preparation method for rare earth doped bismuth titanate ferro-electricity membrane
InactiveCN101269957APromoting solidification and densificationImprove ferroelectric propertiesElectricityPhoto irradiation
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
NiCuSiFe alloy
Owner:WUFAN ALLOY ALUMINUM WUJIN
Glass ceramics made from high silicon iron tailings and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of solid waste resource utilization, in particular to glass ceramics made from high silicon iron tailings, which is characterized by comprising the raw materials in parts by weight: 30-70 parts of the iron tailings, 15-40 parts of quartz, 5-20 parts of calcium carbonate, 3.5-6.5 parts of aluminum oxide, 8.5-9.5 parts of sodium carbonate, 4-5 parts of zinc oxide, 3-6 parts of barium carbonate and 1-3 parts of borax. The manufacturing method of the glass ceramics comprises the following steps: putting the glass ceramics blended materials in a kiln for melting into molten glass; allowing the molten glass to directly flow into water for water quenching to form glass particles; and paving the glass particles in a refractory die, crystallizing the paved particles in a tunnel kiln, a shuttle kiln or a chamber electric furnace, and grinding and cutting the crystallized glass ceramics to finally obtain the finished product of the glass ceramics. The invention can reduce stockpile of the tailings, alleviate environmental pollution, realize comprehensive resource utilization, improve product performances and lower production cost, thus having good social benefit and good economic benefit.
Owner:ANSTEEL GRP MINING CO LTD
Sludge solidifier and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108314280AImprove water qualityReduce pollutionFixation/solidifcation sludge treatmentSulfateSludge
Owner:GUANGZHOU WATER CONSERVANCY & HYDROPOWER STATION CONSTR ENG
Ductile cast iron material, composition containing same and production method of bearing saddle and ductile cast iron
Owner:CRRC QIQIHAR ROLLING CO LTD
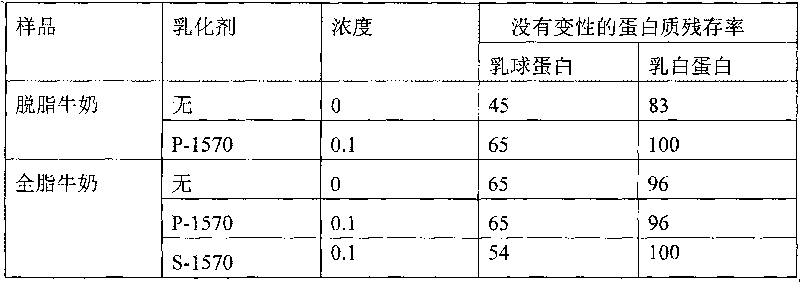
Milk oligopeptide added liquid milk and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101731346AImprove absorption rateAdd high absorption rate to high temperature liquid milkMilk preparationSucroseLiquid milk
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA YILI INDUSTRIAL GROUP CO LTD
Ferrous carbonate/graphene composite material and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103840132AHigh specific capacityImprove cycle performanceNegative electrodesSecondary cellsMass ratioConcentration ratio
Owner:HUNAN YACHENG NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Hexavalent chromium reducing agent and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a hexavalent chromium reducing agent and a preparation method thereof. The reducing agent contains the following components in parts by weight: 50-90 parts of an iron-based reducing agent, 0.57-3.6 parts of nanometer zero-valent iron and 0.9-7.1 parts of a dispersing agent. According to the hexavalent chromium reducing agent provided by the invention, an iron-based reducingagent is uniformly packaged by a dispersing agent solution containing nanometer zero-valent iron particles, and very high reaction activity is achieved by mixing nanometer zero-valent iron with the iron-based reducing agent, so that hexavalent chromium in the reducing agent solution can be rapidly reduced; dispersing agent molecules are capable of stabilizing nanometer zero-valent iron and packaging the iron-based reducing agent, so that the oxidation of the iron-based reducing agent by oxygen in the air is prevented, the hexavalent chromium reducing agent has a moisture preserving function, and the situations that because the partial water-entraining iron-based reducing agent is dehydrated under a high temperature condition, the solubleness is reduced, and the iron-based reducing agent isunlikely to participate in the reducing reaction of hexavalent chromium are prevented.
Owner:DONGYUAN HONGCHAO TECH
Boron-phosphorus alloy cast iron used in air compressor cylinder block and its manufacturing process
InactiveCN102268587AImprove wear resistanceImprove tensile propertiesProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceAlloyCylinder block
Owner:ZHUJI HUAJIA AIR COMPRESSOR
Method for melting purification of magnesia by using waste magnesium product
InactiveCN101837996ADoes not affect normal useQuality is not affectedChemical industryMagnesiaCompression moldingTunnel kiln
Owner:DASHIQIAO WEIMING FURNACE MATERIAL
Method for preparing lithium manganate by wet-doping method
InactiveCN103337619AIncrease the average oxidation stateSuppress purityCell electrodesManganates/permanganatesOxidation stateManganate
Owner:HUNAN DAHUA NEW ENERGY
High-temperature-resistant high-performance rare earth permanent magnet material
InactiveCN105374488AHigh temperature resistance and high performanceImprove stabilityInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementTemperature resistance
Owner:南通长江电器实业有限公司
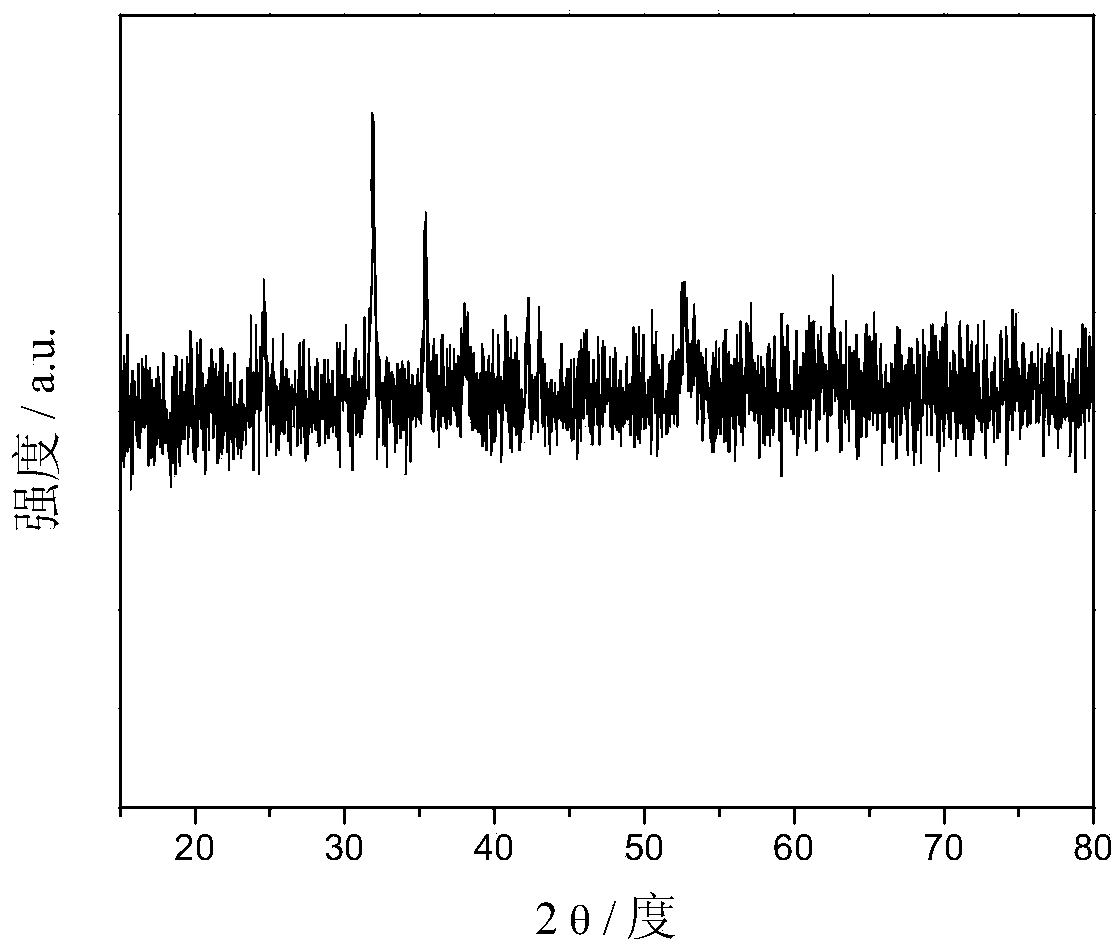
Dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres and preparation method thereof through electrochemical anode oxidation
InactiveCN103556169ASynthesis temperature is lowEasy to embedElectrolysis componentsMicrosphereElectrochemical anodization
The invention discloses dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres and a preparation method thereof through electrochemical anode oxidation, relating to dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres and a method for preparing the dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres through electrochemical anode oxidation, and aiming to solve the problems that iron phosphate micro nanoparticles prepared by the prior art are long in synthesis time, high in synthesis temperature and complex in operation step. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of preparing a mixed solution of phosphoric acid and ammonium fluoride of a certain molar concentration to serve as electrolyte for anode oxidation, and generating the dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres on the surface of an iron foil under conditions of certain current by taking a high-purity iron foil as an anode and a platinum sheet as a cathode. The iron phosphate obtained by the invention is used as a precursor when being used for preparing lithium iron phosphate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap