Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
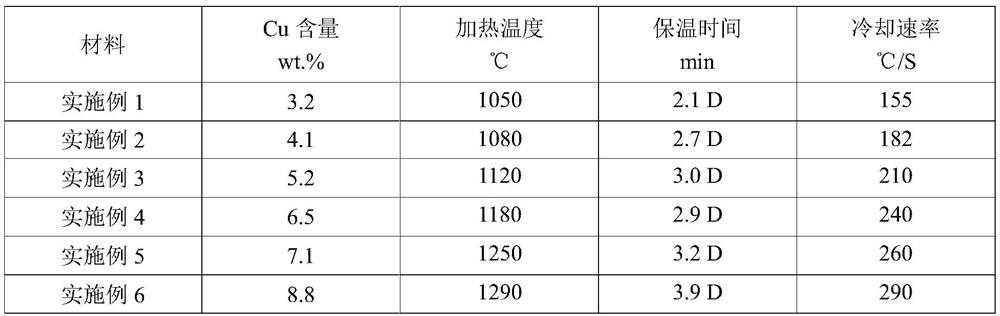
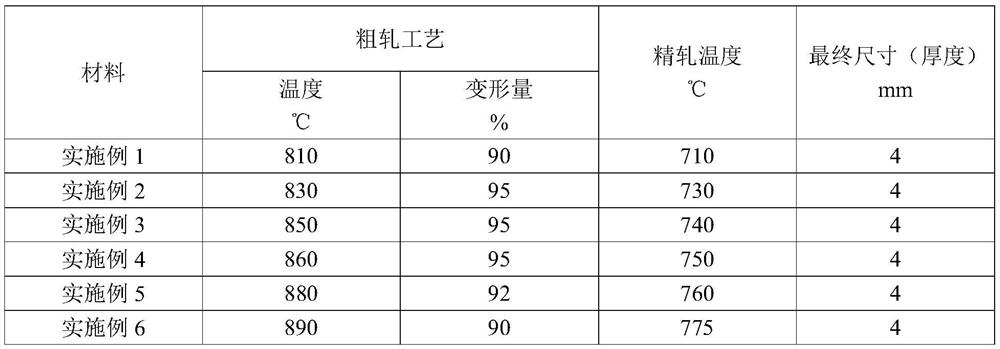
43 results about "Ingot" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ingot is a piece of relatively pure material, usually metal, that is cast into a shape suitable for further processing. In steelmaking, it is the first step among semi-finished casting products. Ingots usually require a second procedure of shaping, such as cold/hot working, cutting, or milling to produce a useful final product. Non-metallic and semiconductor materials prepared in bulk form may also be referred to as ingots, particularly when cast by mold based methods. Precious metal ingots can be used as currency (with or without being processed into other shapes), or as a currency reserve, as with gold bars.
Boron-containing semi-high speed steel cold roller and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101407891AReduce manufacturing costReduce the amount addedProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceIngotMolten steel
The invention relates to a boron-containing semi high-speed steel cold roller and a manufacturing method thereof and belongs to the field of steel rolling technology. The existing cold rollers have the problems of poor wear-resistance, high production cost and the like. The invention obtains the boron-containing semi high-speed steel cold roller by pouring the molten steel with the compositions of the following weight percentages of 0.30 to 0.45 of C, 3.8 to 4.2 of Cr, 0.2 to 0.6 of Si, 0.2 to 0.6 of Mn, 0.5 to 0.8 of Mo, 0.2 to 0.4 of Ni, 0.3 to 0.6 of Cu, 0.6 to 1.0 of B, 0.3 to 0.7 of V, 0.6 to 0.8 of Ti, 0.1 to 0.3 of Nb, 0.03 to 0.10 of N, 0.25 to 0.45 of Al, less than 0.03 of S, less than 0.04 of P and the residual quantity of Fe into an outer layer of the cold roller and adopting ductile cast iron as a core part or directly pouring the molten steel into ingots. The roller has the advantages of high hardness and intensity, good toughness and wear-resistance, simple production process, low cost, etc.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Deformed Al-Mn series alloy and preparing process thereof
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Casting-rolling process and equipment for magnesium alloy slab
InactiveCN1850378AOmit flaw detectionSave on sawingMetal rolling stand detailsRollsShielding gasIngot
Owner:CHINA NON-FERROUS METALS PROCESSING TECH CO LTD
Control method of inclusions in thick steel plate used for high heat input welding
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Au-Sn alloy sputtering target material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105132873ALow germanium contentVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIngotHeating furnace
The invention relates to an Au-Sn alloy sputtering target material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1, Au and Sn are taken as raw materials, vacuum induction melting and vacuum casting are used for casting so as to obtain an eutectic or hypo eutectic Au-Sn alloy ingot, wherein the content of Ge in the alloy ingot accounts for 2 to 12.5 wt percent, and the content of Au serves as the balance; 2, a heating furnace is used for carrying out homogenization heat treatment on the alloy ingot obtained in the step 1; the temperature of the homogenization heat treatment is 270 to 340 DEG C, and the time is 50 to 65 minutes; 3, plastic working equipment is used for carrying out hot plastic processing to the ingot in the thickness direction; 4, the blank is placed inside the heating furnace for temper heat treatment after each 1 to 2 times of processing, the temperature is 270 to 340 DEG C, and the time is 10 to 30 minutes; and 5, the step 3 and the step 4 are repeated until the required target blank dimension is obtained. The Au-Sn alloy sputtering target material obtained through the method is even in components, and has a microscopic structure mainly composed of an Au solid solution and bulks of Ge distributed in a diffused manner.
Owner:GRIKIN ADVANCED MATERIALS
Cold burden laying method and casting starting technology of sizing nozzle open type continuous casting billets
Owner:玉溪新兴钢铁有限公司
Processing method of seed crystal with big drift angle
Owner:新乡市神舟晶体科技发展有限公司
Preparation method for Nb-Zr alloy/Cu multi-core composite wire
ActiveCN105855316AOrganizational structure is stableHigh strengthCable/conductor manufactureOxidation resistantHigh intensity
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
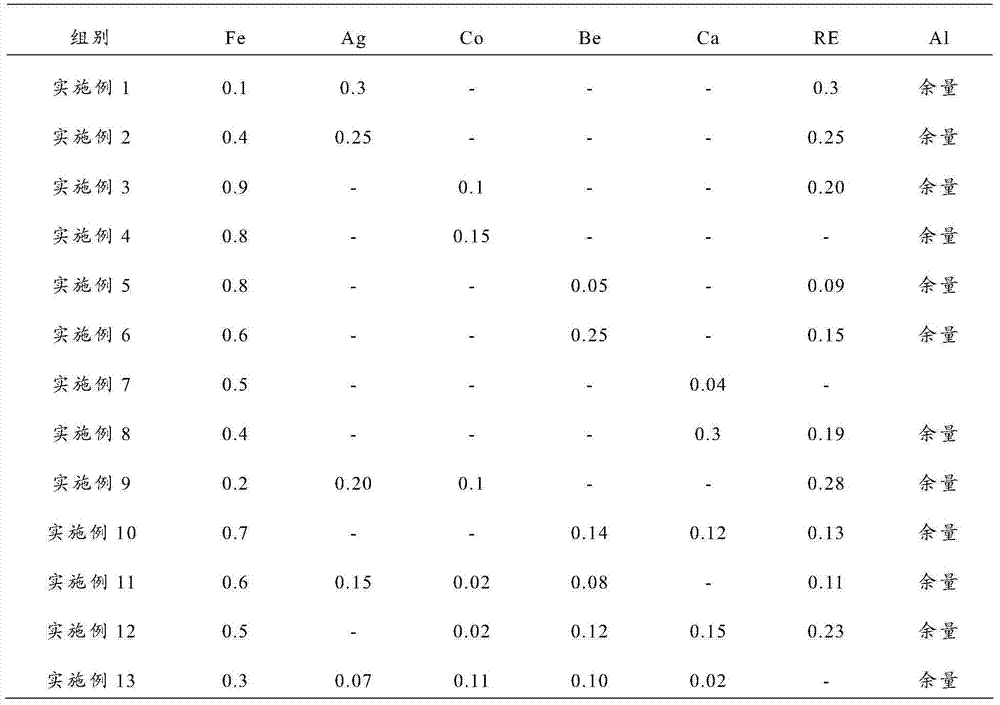
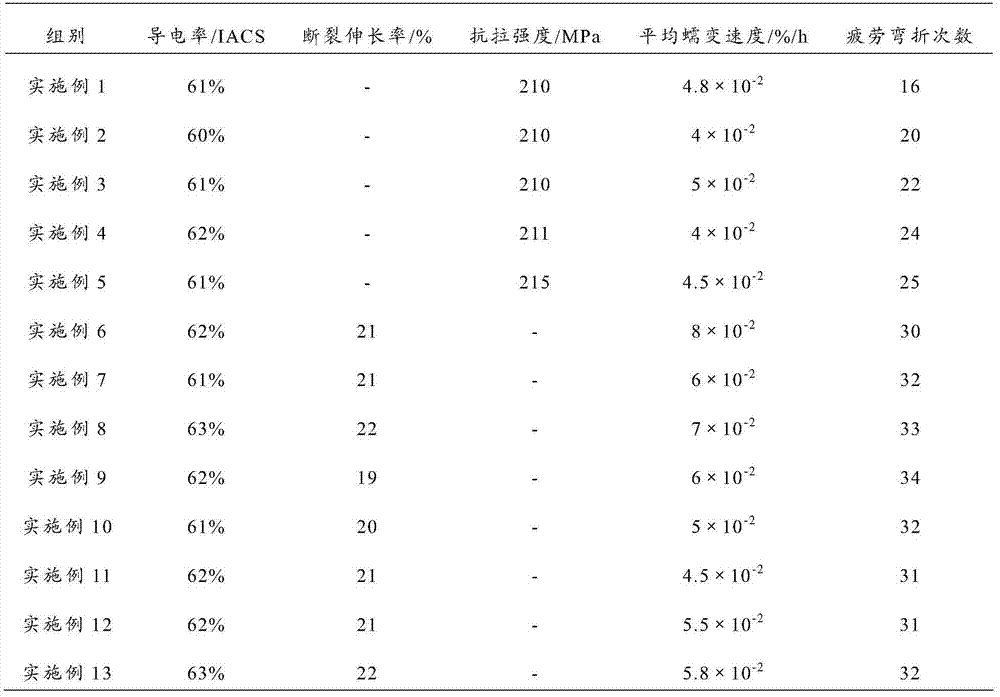
Al-Fe-Ag aluminum alloy, preparation method thereof and aluminum alloy cable
PendingCN103667806AHigh mechanical strengthImprove tensile propertiesMetal/alloy conductorsIngotSolid solution
Owner:ANHUI JOY SENSE CABLE
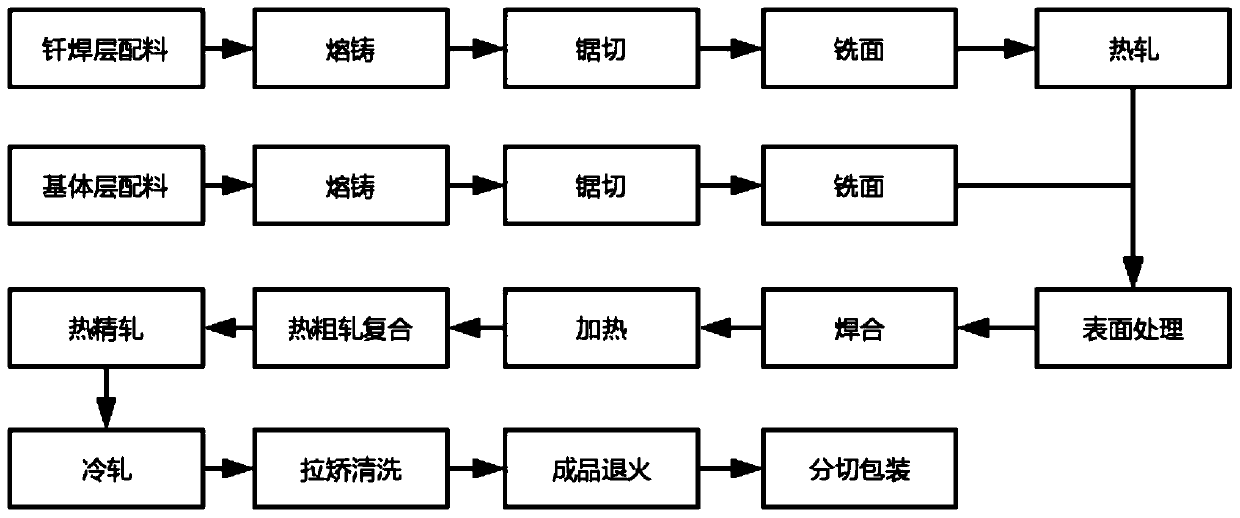
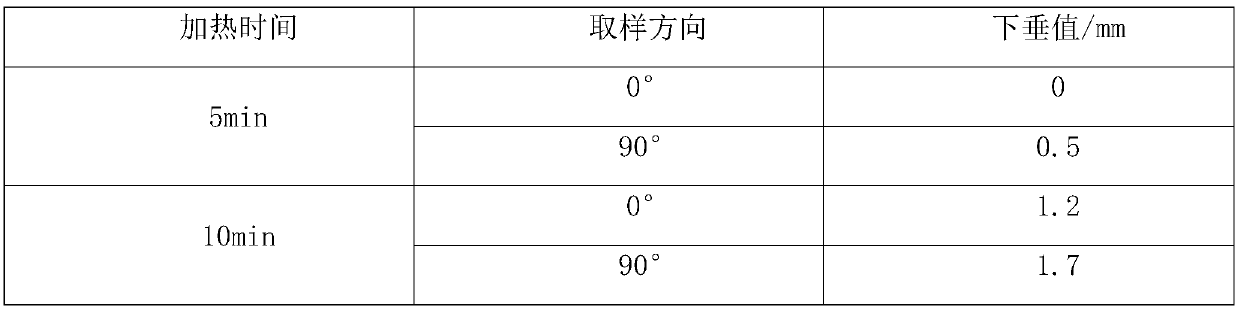
Manufacturing method of aluminum alloy three-layer composite material for brazing
Owner:TIANJIN ZHONGWANG ALUMINUM IND CO LTD
Nanostructuring process for ingot surface, wafer manufacturing method, and wafer using the same
InactiveUS20120193764A1Improve surface strengthReduce generationMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthWaferingMetallurgy
The instant disclosure relates to a nanostructuring process for an ingot surface prior to the slicing operation. A surface treatment step is performed for at least one surface of the ingot in forming a nanostructure layer thereon. The nanostructure layer is capable of enhancing the mechanical strength of the ingot surface to reduce the chipping ratio of the wafer during slicing.
Owner:SINO AMERICAN SILICON PROD
Manufacturing method of pure copper plates, and pure copper plate
ActiveCN102652182AFine uniform grainsEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIngotCopper
Owner:MITSUBISHI SHINDOH CO LTD +1
Superconducting niobium pipe and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103219459ALow residual resistivity dropSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentHydrogenIngot
The invention relates to the technical field of metal materials and provides a superconducting niobium pipe and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the specific steps of: forging superconducting niobium ingots, wherein the temperature during a forging process is lower than or equal to 60 DEG C; carrying out first thermal treatment on the forged superconducting niobium ingots; coating a lubricating agent on the surfaces of the superconducting niobium ingots after the first thermal treatment, and carrying out reverse extrusion; and carrying out secondary thermal treatment on the superconducting niobium ingots after the reverse extrusion, so as to obtain the superconducting niobium pipe. According to the superconducting niobium pipe and the preparation method thereof, the forging temperature is controlled in a forging process, and the lubricating agent is coated on the surfaces of the niobium ingots in an extrusion process, so that the carbon absorption, the hydrogen absorption and the oxygen absorption of the niobium ingots in a machining process are effectively avoided, and the decreasing amplitude of the residual resistivity of the prepared superconducting niobium pipe is relatively small.
Owner:NINGXIA ORIENT TANTALUM IND
Forging method of nickel base alloy containing copper and nickel base alloy containing copper
ActiveCN104741494AImprove plasticityAvoid defects such as cracking and scrappingMetal-working apparatusIngotHeating furnace
The invention provides a forging method of nickel base alloy containing copper and the nickel base alloy containing copper and belongs to the technical field of forging technologies. The forging method overcomes the defects that because copper is added to the nickel base alloy, the hot working character is poor, and forge cracking is caused, and the yield can be effectively improved. The forging method comprises the steps of conducting billet forging, wherein preprocessed nickel base alloy ingots containing copper are placed in a heating furnace, the nickel base alloy ingots containing copper are heated to the temperature T1, the temperature T1 is kept, forging is conducted according to the forging ratio y1, so that forging stocks are obtained, the temperature T1 is 1120+ / -10 DEG C, and y1 is smaller than or equal to 1.4; conducting initial forming, wherein the forging stocks are arranged in the heating furnace to be heated, the temperature is kept, and forged pieces which are initially formed are obtained through forging; conducting final forging, wherein the initially formed forged pieces are arranged in the heating furnace to be heated to the temperature T3, the temperature T3 is kept, forging is conducted according to the forging ratio y3, so that finished forged pieces are obtained, the temperature T3 is higher than 1000 DEG C and lower than 1080+ / -10 DEG C, and y3 is larger than 1.5 and smaller than 2. The forging method can be used for forging of the nickel base alloy containing copper.
Owner:ENN ENVIROTECH CO LTD
Rare-earth alloy permanent magnet material preparation device and technique
InactiveCN104308160ASolve segregationImprove coercive forceMagnetic materialsMaterials preparationRare earth
A rare-earth alloy permanent magnet material preparation device comprises a raw material treatment portion, a precipitation tank, an electrolytic furnace, a grinding mechanism, a stamping mechanism and a vacuum sintering furnace. The raw material treatment portion comprises a rare-earth metal treatment tank and a blending tank, a delivery pipe connected with the blending tank is arranged on the rear-earth metal treatment tank, the blending tank is connected with the precipitation tank through a complexing solution delivery pipe, the precipitation tank is connected with the electrolytic furnace, a feed inlet is arranged on one side of the electrolytic furnace, a casting chamber is arranged at the tail end of the electrolytic furnace and connected with a cooling chamber, the cooling chamber is connected with the grinding mechanism through a discharge pipe, and the grinding mechanism is connected with the stamping mechanism which is connected with the vacuum sintering furnace. The problem of segregation of alloy ingots is solved effectively, high temperature strength, structural stability, welding performance and corrosion resistance of the alloy ingots are improved beneficially due to addition of Sc, and the common electrolytic furnace can be used for smelting the alloy ingots by adopting mixture after Nd, Pr, Dy and Sc complexing.
Owner:NANJING SABER IND DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD
Doubling machine for metallic threads
The present invention discloses a tinsel yarn assembler. It contains payoff frame, annealing furnace and yarn-rewinding mechanism. The top portion and bottom portion of said payoff frame are respectively equipped with disk shaft and ceramic ring. The described yarn-rewinding mechanism contains supporting frame, the upper portion and lower portion of each of two sides of said supporting frame are respectively equipped with yarn-guiding wheel and yarn-rewinding disk, and the upper portion and lower portion of said annealing furnace are respectively with yarn tension controller and spindle. Said invention also provides the working principle of said tinsel yarn assembler and its operation method.
Owner:陈惠良
High-purity titanium ingot purification method
InactiveCN109266863AFully meltedLow elemental contentProcess efficiency improvementPurification methodsTitanium
Owner:宝鸡市华烨钛镍金属有限公司
Preparation method of aluminum alloy rod materials
Owner:NORTHEAST LIGHT ALLOY CO LTD
Hot dip galvanizing Al Bi rare earth alloy for steel and iron member hot dip galvanizing and its ingot type and method
PendingCN101086048AAvoid uneven compositionAvoid burnsHot-dipping/immersion processesSymmetrical earsRare earth
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
Titanium alloy for 3D printing ship and preparation method
ActiveCN111411260AGood mechanical propertiesHigh strengthAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyIngotTitanium alloy
Owner:XINXIANG UNIV
Draft tube of crystal growing furnace and the crystal growing furnace
InactiveUS20200255970A1Well formedPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltEngineeringIngot
Owner:ZING SEMICON CORP
Workpiece holder and workpiece cutting method
ActiveCN107848092ACut offSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWorking accessoriesAdhesiveIngot
The present invention provides a workpiece holder that is used when cutting a workpiece using a wire saw. The workpiece holder is provided with: a workpiece plate that is adhered and fixed to a workpiece with a back plate interposed therebetween; and a holder body that supports the workpiece plate. In a case where, among radial directions of the workpiece, the direction parallel to the workpiece adhesion surface of the workpiece plate is the x-axis direction and a direction perpendicular the workpiece adhesive surface is the y-axis direction, the workpiece plate corrects misalignment of a crystallographic orientation axis of the workpiece in the x-axis direction and is adhered and fixed to the workpiece. The workpiece holder adjusts a y-axis direction inclination of the workpiece held by the workpiece plate by inclining the workpiece plate in the y-axis direction and is able to fix the workpiece plate and the workpiece to the holder body at the adjusted inclination. Due to this configuration, there are provided a workpiece holder and a method of cutting a workpiece using the workpiece holder that can realize cutting of an ingot having strict directional standards for an external setup system.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Short-process preparation method of Ti-Al-V-Fe alloy seamless tube
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing coarse granularity chromium carbide powder
ActiveCN108046259AMeet wear resistanceCorrosiveCarbon compoundsChemical industryAdhesiveWear resistant
Owner:锦州市金属材料研究所
Zr-Fe alloy for tritium storage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108149070ALow costFast rate of hydrogen absorption and desorption (tritium)Electric arc furnaceDesorption
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
High-strength antibacterial titanium alloy plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112251633AHigh elongationHigh tissue thermal stabilityProcess efficiency improvementIngotTitanium alloy
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Feed device for feeding molten metal in to a crystallizer
InactiveUS20060162894A1Simple and compact shapeReduce kinetic energyMolten metal pouring equipmentsMolten metal supplying equipmentsMetallurgyIngot
Owner:DANIELI & C OFF MEC SPA
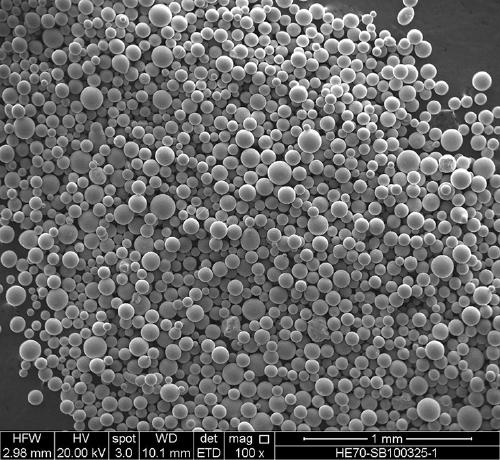
Method for preparing aluminum particles through rotary cup centrifugal granulation
The invention relates to a method for preparing aluminum particles through rotary cup centrifugal granulation. The aluminum particles are prepared through a granulation device. The device mainly comprises a rotating granulation system used for granulating molten aluminum, an air cooling system used for cooling aluminum drops splashing out during granulation, a metal particle collection structure used for collecting the falling aluminum particles, and an air collection system used for collecting hot air used for cooling the aluminum drops. The method comprises the steps that firstly, heating aluminum ingots, so as to obtain molten aluminum; then, adjusting a driving motor till a rotary cup has the target rotation speed; and pouring molten aluminum into the rotary cup, and starting to carry out granulation to obtain the aluminum particles. According to the method, the porous rotary cup and proper rotation speed are selected, so that the particle size of most of the obtained aluminum particles is guaranteed to be 4 mm to 8 mm as much as possible.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation method of niobium-zirconium 10 alloy tube
InactiveCN104561575ANo segregationImprove tissue uniformityNiobiumDehydrogenation
Owner:BAOJI TIANBO METAL MATERIAL
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap