Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
24 results about "Forging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it is performed: cold forging (a type of cold working), warm forging, or hot forging (a type of hot working). For the latter two, the metal is heated, usually in a forge. Forged parts can range in weight from less than a kilogram to hundreds of metric tons. Forging has been done by smiths for millennia; the traditional products were kitchenware, hardware, hand tools, edged weapons, cymbals, and jewellery. Since the Industrial Revolution, forged parts are widely used in mechanisms and machines wherever a component requires high strength; such forgings usually require further processing (such as machining) to achieve a finished part. Today, forging is a major worldwide industry.
Manufacturing method of pure copper plates, and pure copper plate
ActiveCN102652182AFine uniform grainsEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIngotCopper
Owner:MITSUBISHI SHINDOH CO LTD +1
Forging method of driving shaft for gearbox
ActiveCN102989982AExtend your lifeReduce contaminationMetallic material coating processesEngine componentsChemical compositionDrive shaft
Owner:CHANGLI FORGING
Forging method of nickel base alloy containing copper and nickel base alloy containing copper
ActiveCN104741494AImprove plasticityAvoid defects such as cracking and scrappingMetal-working apparatusIngotHeating furnace
The invention provides a forging method of nickel base alloy containing copper and the nickel base alloy containing copper and belongs to the technical field of forging technologies. The forging method overcomes the defects that because copper is added to the nickel base alloy, the hot working character is poor, and forge cracking is caused, and the yield can be effectively improved. The forging method comprises the steps of conducting billet forging, wherein preprocessed nickel base alloy ingots containing copper are placed in a heating furnace, the nickel base alloy ingots containing copper are heated to the temperature T1, the temperature T1 is kept, forging is conducted according to the forging ratio y1, so that forging stocks are obtained, the temperature T1 is 1120+ / -10 DEG C, and y1 is smaller than or equal to 1.4; conducting initial forming, wherein the forging stocks are arranged in the heating furnace to be heated, the temperature is kept, and forged pieces which are initially formed are obtained through forging; conducting final forging, wherein the initially formed forged pieces are arranged in the heating furnace to be heated to the temperature T3, the temperature T3 is kept, forging is conducted according to the forging ratio y3, so that finished forged pieces are obtained, the temperature T3 is higher than 1000 DEG C and lower than 1080+ / -10 DEG C, and y3 is larger than 1.5 and smaller than 2. The forging method can be used for forging of the nickel base alloy containing copper.
Owner:ENN ENVIROTECH CO LTD
Fine grain surface layer steel part and method of production of same
InactiveUS20090095383A1Strength differenceMetal-working apparatusSurface layerUltimate tensile strength
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Preparation method of aluminum alloy rod materials
Owner:NORTHEAST LIGHT ALLOY CO LTD
Dual-purpose steel for hot forging, warm extruding and cold stamping tools and dies
ActiveCN106191694AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh strengthManufacturing technologyUltimate tensile strength
Owner:沈阳市嘉泰模具材料开发有限公司
Welding wire made of Cr28 Ni48 W5 nickel base alloy
ActiveCN103949800AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove liquidityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagForging
The invention relates to a welding wire made of nickel base alloy. The welding wire comprises the following components by mass percent: 0.4-0.45% of C, 1.0-1.5% of Mn, 0.15-1.2% of Si, less than or equal to 0.025% of P, less than or equal to 0.02% of S, 28-30% of Cr, 49-51% of Ni, less than or equal to 0.1% of Co, less than or equal to 0.1% of Mo, less than or equal to 0.1% of Ti, less than or equal to 0.1% of Al, 4.0-5.0% of W and the balance of Fe. A method for preparing the welding wire comprises the steps of smelting the alloy, remelting electro-slag, carrying out hot forging and cogging down, carrying out hot rolling and annealing, carrying out acid pickling, polishing, carrying out cold drawing and removing hydrogen, wherein a CaF2, Al2O3 or CaO slag system is adopted in the step of remelting the electro-slag. The thinner welding wire can be prepared by the method for preparing the welding wire made of the nickel base alloy, the performances of the welding wire meet the requirements, and the welding wire is high in yield.
Owner:JIANGSU TOLAND ALLOY
Semiconductor radiator and processing method thereof
ActiveCN109531083AImprove processing strengthImprove surface roughnessBearing componentsSemiconductorMaterials science
Owner:同共(湖北)精密成形有限公司
Water meter shell body forging and pressing die
Owner:宁波宁水仪表有限公司
5CrNiMo tempering process
InactiveCN105755240ALow experience requirementEasy to operateFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesRoom temperatureHardness
Owner:CHONGQING HUANDE TECH CO LTD
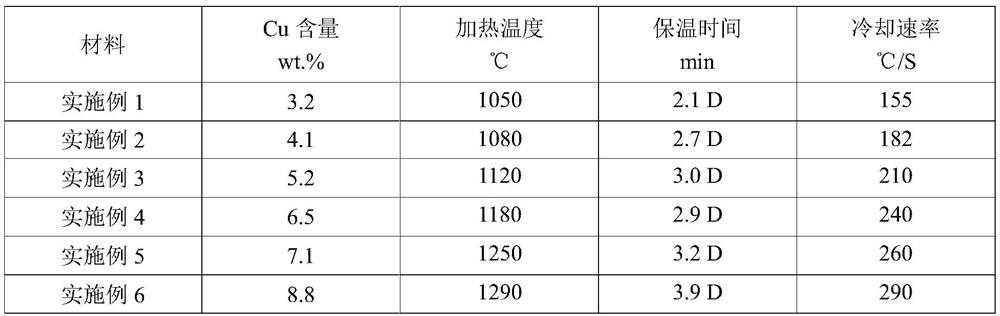
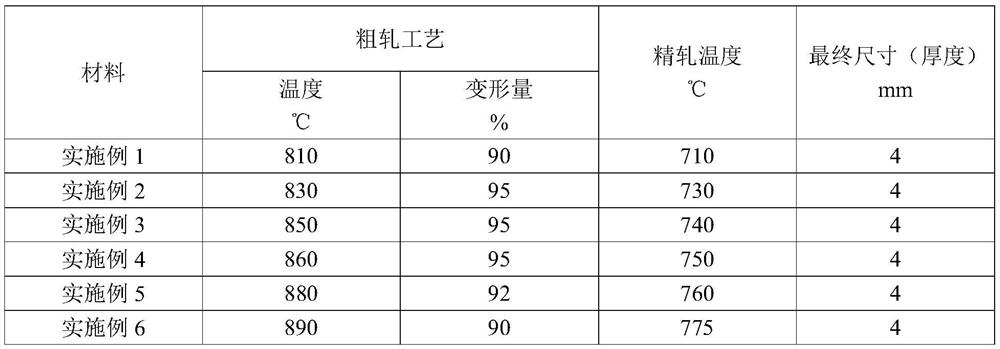
Processing method of zirconium oxygen-free copper forging rod
InactiveCN111408632ABreak through the problem that ultrasonic flaw detection cannot be performedNon-destructive monitoring of internal qualityMetal-working apparatusFurnace typesSolution treatmentEngineering
The invention discloses a processing method of a zirconium oxygen-free copper forging rod. A rod material adopts zirconium oxygen-free copper casting billets. After forging and blanking, the casting billets are produced by hot forging, upsetting and stretching, solid solution treatment, cold forging, machining, aging and machining again. The specification can reach Phi (100-300)*(500-1500) mm. Theimportant thing to note that after the rod material is subjected to cold forging and machining, ultrasonic flaw detection is needed for nondestructive testing of internal quality. The processing method can successfully realize the feasibility of nondestructive flaw detection and avoid the problem that no echo exists or echo is weak in the ultrasonic flaw detection process of the rod material, sothat the detection requirement cannot be met. The product is applied to inner wall shrinkage parts of a power chamber groove of a rocket engine, the tensile strength and yield strength are still above150MPa at 500 DEG C, and the elongation rate is also above 15%.
Owner:SHENYANG TONGXING IND
Forging method for drive axle lifting oil cylinder
InactiveCN105057560AImprove corrosion resistanceHigh strengthEngine componentsAlloyUltimate tensile strength
Owner:ANHUI ZHENYE MACHINERY
Plug type oval shell structure of LED (Light Emitting Diode) lamp
InactiveCN104566239AImprove cooling efficiencyEasy to usePoint-like light sourceElectric circuit arrangementsLED lampLight-emitting diode
Owner:SUZHOU KUNK & SAM LIGHTING TECH CO LTD
High-strength antibacterial titanium alloy plate and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112251633AHigh elongationHigh tissue thermal stabilityProcess efficiency improvementIngotTitanium alloy
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Steel for high-quality bucket teeth for forging and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112159936AReduce hardnessSolve the difficulty of blanking (the saw can't moveProcess efficiency improvementCooling bedsHardnessMaterials science
Owner:ZENITH STEEL GROUP CORP +1
Automotive transmission gear forging method
InactiveCN105018685AImprove mechanical propertiesExtended service lifeFurnace typesSolid state diffusion coatingEnvironmental resistanceMechanical property
Owner:苏州优金金属成型科技有限公司
Assembling and welding method for truss layer corner column
PendingCN114515917AImprove securityReduce the amount of weldingFurnace typesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesStructural engineeringWeld seam
Owner:中冶(上海)钢结构科技有限公司
Method for manufacturing bottom shrunk type steel ingot mold
Owner:SHANGHAI BAOSTEEL CASTING
Transmission shaft forging process
Owner:JIANGSU JINYUAN FORGE
Forging technology of high-precision forklift bearing ring
Owner:CHANGSHU CHANGZHOU BEARING
Die forging process method of main starting connector of airplane
InactiveCN109590420AHigh dimensional accuracyUniform deformed tissueHeating/cooling devicesIngotHigh dimensional
Owner:SOUTHWEST ALUMINUM GRP
Repairing method for eliminating clutters generated during ultrasonic flaw detection of high-temperature alloy
PendingCN111207977AAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringForging
Owner:WUXI PAIKE HEAVY CASTING & FORGING
Surface-strengthened inner step shaft inner hole precision forming process
ActiveCN113118353AGuaranteed coaxialityImprove the coaxiality of the inner holeMetal-working apparatusEngineeringSwaging
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV +1
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap