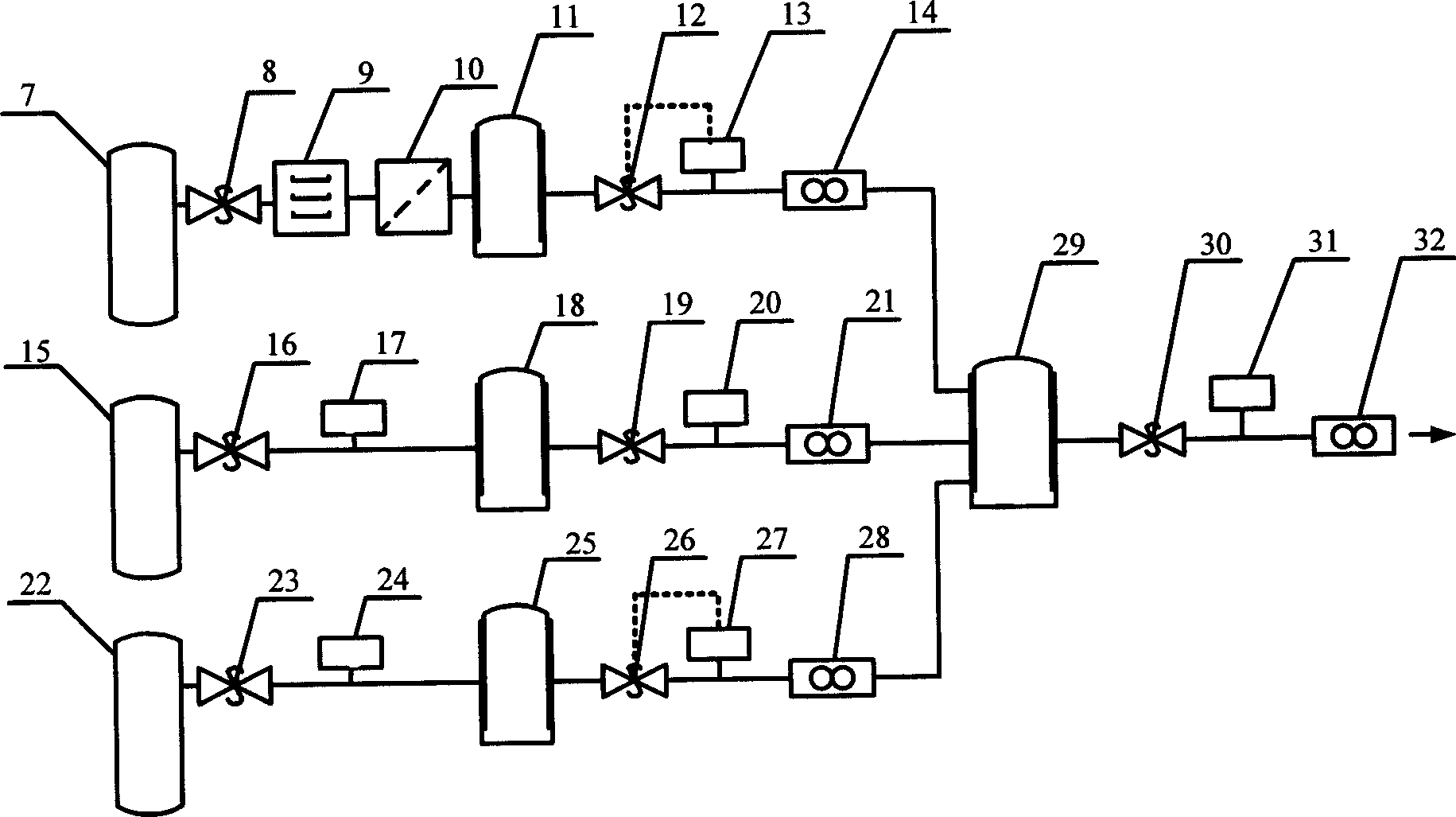
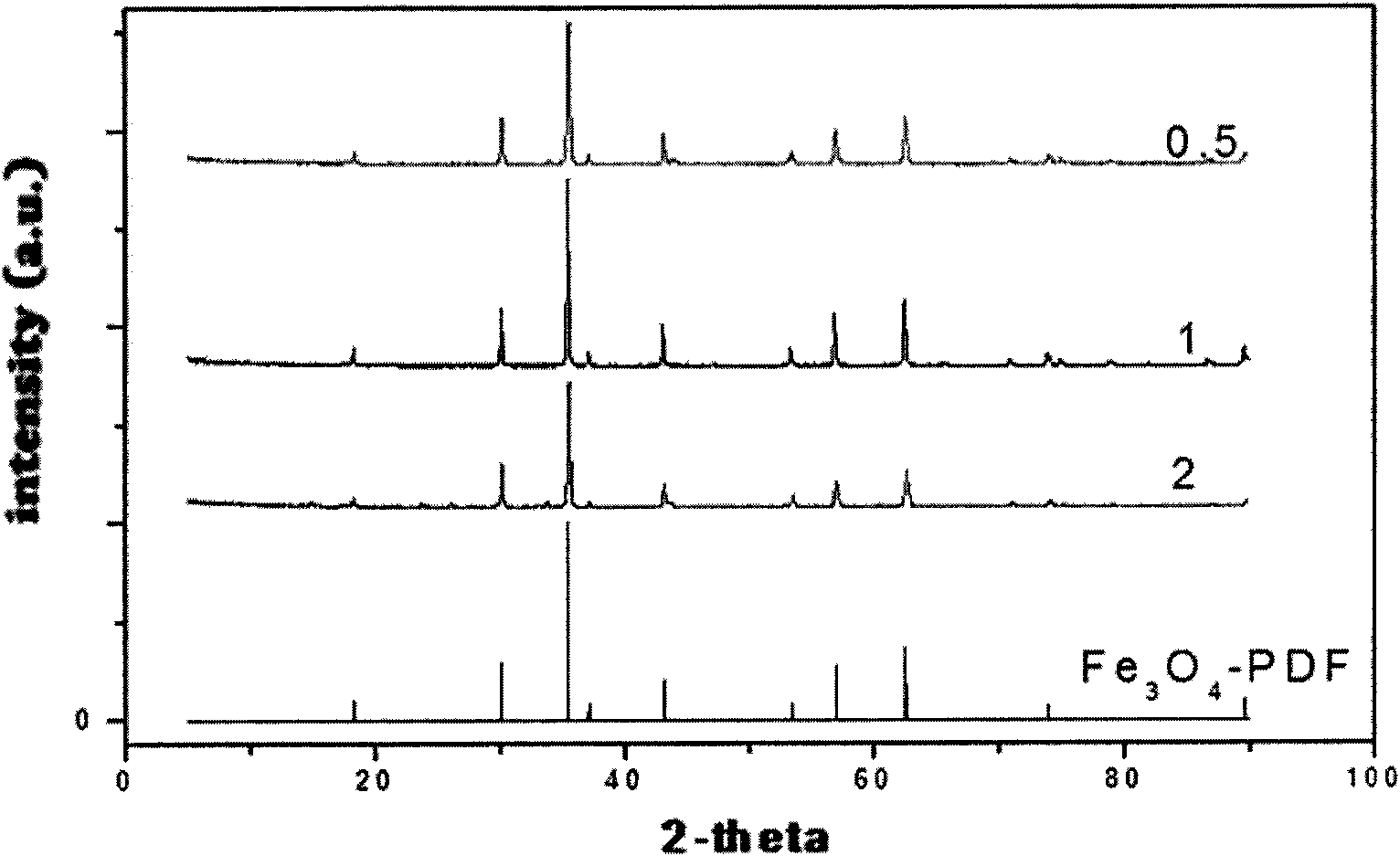
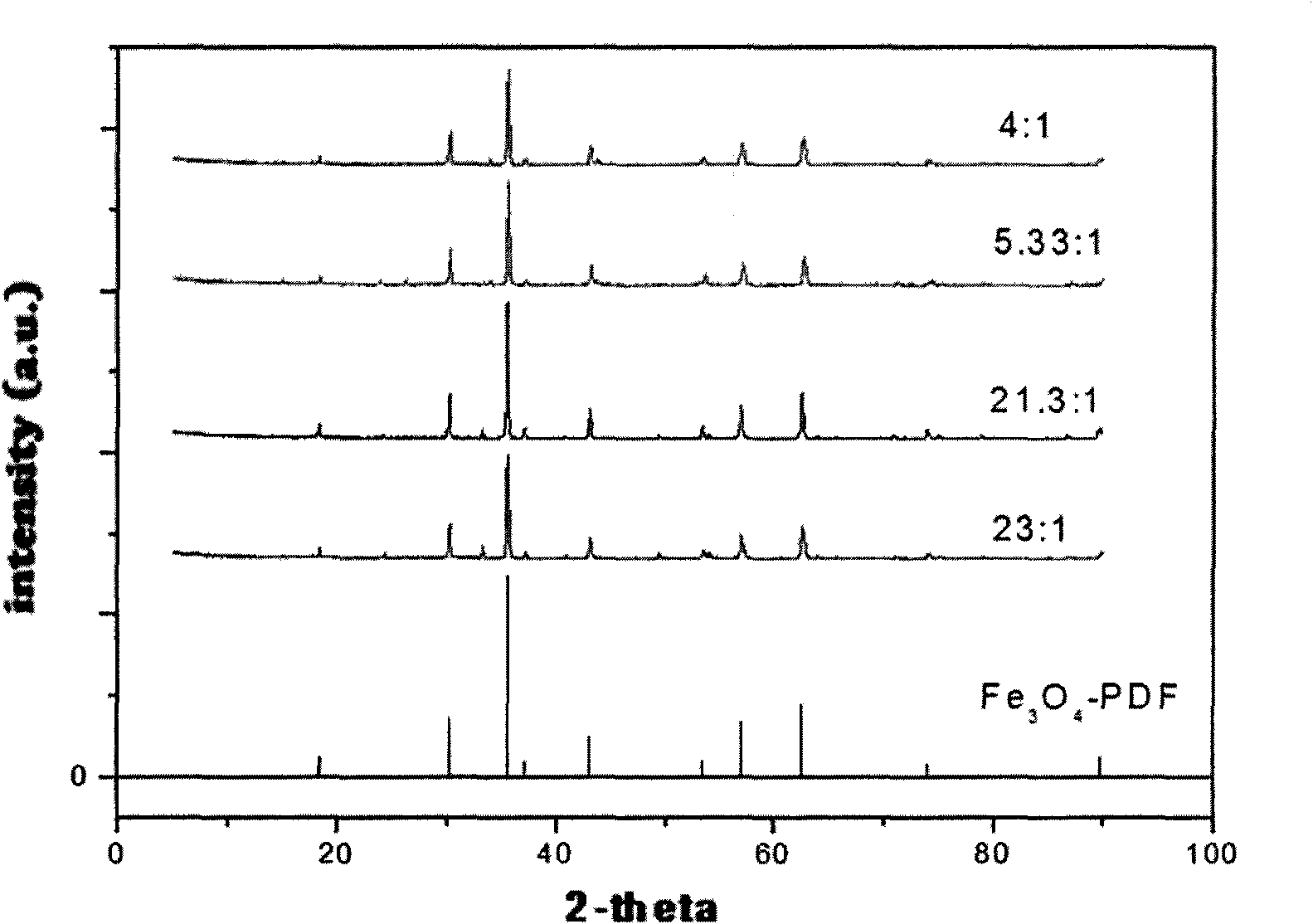
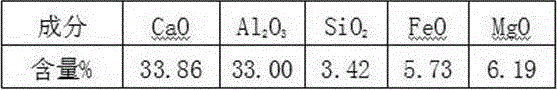
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Smelting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Smelting is a process of applying heat to ore in order to extract a base metal. It is a form of extractive metallurgy. It is used to extract many metals from their ores, including silver, iron, copper, and other base metals. Smelting uses heat and a chemical reducing agent to decompose the ore, driving off other elements as gases or slag and leaving the metal base behind. The reducing agent is commonly a source of carbon, such as coke—or, in earlier times, charcoal.
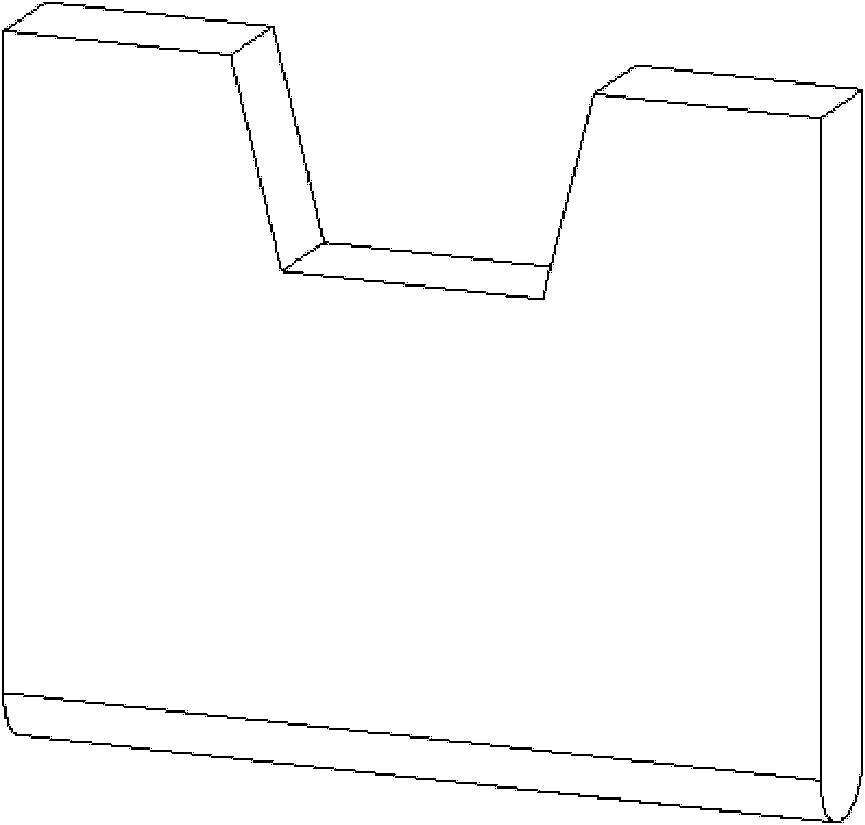
Manufacture method of slip sheet of air conditioner compressor
InactiveCN102251166AImprove the lubrication effectImprove wear resistanceFoundry mouldsSolid state diffusion coatingCarbideSlip sheet
Owner:乐金电子(秦皇岛)有限公司 +1
Casting-rolling process and equipment for magnesium alloy slab
InactiveCN1850378AOmit flaw detectionSave on sawingMetal rolling stand detailsRollsShielding gasIngot
Owner:CHINA NON-FERROUS METALS PROCESSING TECH CO LTD
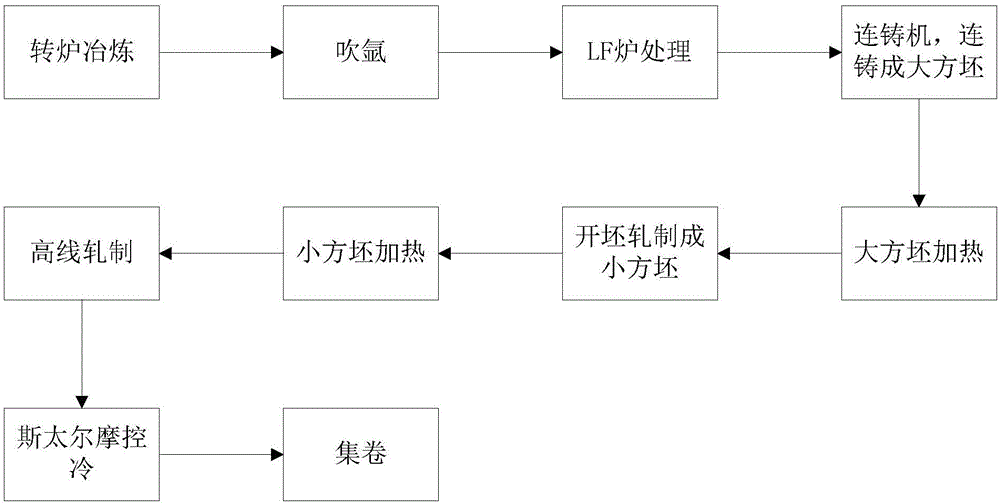
Manufacturing process of high-carbon tool steel SK85 cold-rolled wide steel strip
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a high-carbon tool steel SK85 cold-rolled wide steel strip. The process is characterized in that steel is subjected to converter smelting, LF furnacerefining and slab continuous casting to obtain continuous casting slabs with the thickness ranging from 210 mm to 230 mm, the continuous casting slabs are heated and subjected to hot continuous rolling and laminar cooling to reach the coiling temperature, a hot-rolled wide steel strip with the thickness ranging from 2.5 mm to 6.0 mm is obtained, the coiled hot-rolled wide steel strip is put in storage and slowly cooled to the room temperature, and the obtained metallographic structure is thin-sheet-shaped pearlite; the total reduction of first cold rolling is controlled to be 20%-50% after acid pickling of the hot-rolled wide steel strip, then spheroidizing annealing is conducted, the Vickers hardness HV5 is 180 or below, and the spheroidizing rate is 92% or above; after the steel strip is subjected to primary spheroidizing annealing, secondary cold rolling is conducted, the total reduction of cold rolling is controlled to be 30%-85%, and a cold-rolled wide steel strip with the finished product specification being 0.70-3.00 mm thick is obtained; the steel strip subjected to secondary cold rolling is further spheroidized and annealed, the Vickers hardness HV5 is 175 or below, and the spheroidizing rate is 94% or above; and then third cold rolling is conducted, the total reduction of cold rolling is controlled to be 50%-85%, and the cold-rolled wide steel strip with the finishedproduct specification being 0.10-0.70 mm thick is obtained.
Owner:新余钢铁股份有限公司
Aluminum-based composite material for composite pan bottom of stainless steel pan and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an aluminum-based composite material for the composite pan bottom of a stainless steel pan and a preparation method thereof. The aluminum-based composite material consists of an aluminum-based body and reinforced particles, wherein the aluminum-based body is pure aluminum or an aluminum alloy; the reinforced particles are any one of SiC, Al2O3, B4C or SiO2 particles; the particle diameter is between 30 and 100 mu m; the volume fraction is between 5 and 30 percent; and the reinforced particles are uniformly distributed in the aluminum-based body and has good combination with the interface of the aluminum-based body. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: smelting aluminum in a resistance furnace, adding proper active elements into the resistance furnace after refining, adding a certain amount of treated particles into the resistance furnace under the protection of atmosphere, stirring, pouring and molding. A product has high specific stiffness, good composite matching with stainless steel (thermal expansion coefficient is close to that of stainless steel) and high heat conductivity; and the prepared composite pan bottom has the characteristics of light weight, difficult deformation, uniform heat transfer and the like.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Transparent anti-static polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103102623AImprove antistatic performanceExcellent piezoelectric propertiesCarbon nanotubePolyvinylidene difluoride
The invention relates to a transparent anti-static polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material and a preparation method thereof. The filler is very difficult to uniformly disperse by adding carbon nano-tubes, graphene or zinc oxide to PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride) material in the prior art; and the material is directly transmitted to be conductive from insulating, and is not attractive. The polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material is a mixture of polyvinylidene fluoride and ionic liquid. The preparation method of the transparent anti-static polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material comprises the following steps of: drying the polyvinylidene fluoride and the ionic liquid for 24 hours to 48 hours at 80 DEG C to 110 DEG C in a vacuum environment; adding the dried polyvinylidene fluoride and ionic liquid in a mass ratio of 100:(0.5-40) to a fusion smelting device for melting-blending at 180 DEG C to 200 DEG C to obtain a mixture; and discharging the mixture from the melting-blending device, cooling the mixture to normal temperature and crystallizing the cooled mixture to obtain the polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material. The polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material disclosed by the invention has good antistatic property, good piezoelectricity and excellent transparency. According to the preparation method of the polyvinylidene fluoride piezoelectric material disclosed by the invention, the normal melting-blending device is only needed to be used, and the industrial preparation is simple.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Copper/cerium-containing antimicrobial stainless steel and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a copper / cerium-containing antimicrobial stainless steel and a preparation method thereof. The copper / cerium-containing antimicrobial stainless steel comprises the following chemical components in percentage by weight: at most 0.08% of C, at most 1% of Si, at most 2.00% of Mn, less than 0.045% of P, less than 0.030% of S, 17.5-20.0% of Cr, 8-11% of Ni, 0.5-2.8% of Cu, 0.01-0.45% of Ce, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The stainless steel is molten in an induction furnace after smelting, and is subjected to aging high-temperature diffusion heat treatment composed of 20-minute 1180 DEG C solid solution and 1-hour 685 DEG C thermal insulation so as to precipitate the antimicrobial phase epsilon-Cu and Ce, thereby endowing the stainless steel with antimicrobial property. The steel grade has stainless steel performance and broad-spectrum antibacterial property; the corrosion resistance, wear resistance, strength, toughness, oxidation resistance and other comprehensive properties of the stainless steel are improved; and the production technique is simple, has great utilization value in industry, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Ultra-low carbon martensitic stainless steel seamless tube and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN108277438AHigh tensile strengthHigh yield strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMartensitic stainless steelHigh pressure
The invention discloses an ultra-low carbon martensitic stainless steel seamless tube. The ultra-low carbon martensitic stainless steel seamless tube is prepared from ultra-low carbon martensitic stainless steel. The ultra-low carbon martensitic stainless steel is prepared from the following components in percentage by mass: less than or equal to 0.03% of C, 0.1-0.5% of Si, 0.2-0.5% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.015% of P, less than or equal to 0.002% of S, 12.2-13.2% of Cr, 5.2-5.7% of Ni, 1.9-2.1% of Mo, 0.1-1.6% of Cu and the balance of Fe and other impurities. The seamless tube can be suitable for oil and gas fields. The invention also provides a manufacturing method of the seamless tube. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: smelting; tube blank thermal processing;steel tube thermal processing; and thermal treatment, wherein the heating temperature of tube blank thermal processing is 1200-1280 DEG C, the heating temperature of tube manufacturing by means of anextruding method is 1150-1250 DEG C, the heating temperature of tube manufacturing by means of a perforating cold rolling method is 1200-1280 DEG C, and the temperatures for thermal treatment are as follows: quenching at 900-1050 DEG C and tempering at 550-680 DEG C. The seamless tube provided by the invention has excellent strength and corrosion resistance in a CO2 and Cl<-> coexisting corrosionenvironment and in high-temperature and high pressure conditions.
Owner:TAIYUAN IRON & STEEL (GRP) CO LTD
Glass ceramics prepared from tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting and preparation method thereof
The invention provides glass ceramics prepared from tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting and a preparation method thereof. The glass ceramics use the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting as main raw materials and silica or quartz sand (SiO2), limestone or calcite (CaCO3), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), alumina (Al2O3), potassium carbonate (K2CO3), magnesium oxide (MgO) and calcium fluoride (CaF2) as auxiliary raw materials. The preparation method comprises the steps of grinding the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting and the auxiliary raw materials, sieving the powder with a 20-mesh sieve, and mixing the powder uniformly in a mixer to obtain a base batch; melting the base batch at the temperature of 1450-1550 DEG C, homogenizing and clarifying the melt to obtain qualified molten glass, and then forming a base glass plate or granules through moulding by casting or water quenching of the molten glass; finally filling the base glass plate or the granules into a mould, and then carrying out crystallization thermal treatment, thus obtaining the glass ceramics prepared from the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting. The preparation process is simple in operation course and has the effects of not only expanding the way of resource comprehensive utilization of the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting but also reducing the environmental pollution of the tailings.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Factory formula for aging-resistant rubber strip
Owner:JIANGSU DAHAI PLASTIC
Method for processing red mud by utilizing iron pyrites
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Production method of ultra-low silicon peritectic steel
Owner:TANGSHAN IRON & STEEL GROUP +1
NiCuSiFe alloy
Owner:WUFAN ALLOY ALUMINUM WUJIN
Chromium-containing alloy bar material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109112398AImproved particle sizeAchieve fine grain strengthening effectChemical compositionEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a chromium-containing alloy bar material and a preparation method thereof. Al and N are added in a process of smelting steel with the trade mark of 40Cr to obtain the chromium-containing alloy bar material containing 0.020 to 0.030 weight percent of the Al and 0.007 to 0.010 weight percent of the N. Under the condition that existing equipment and technology are not changed, the problem that the grain size of the alloy bar material is large in a 40Cr steel low-rolling-ratio processing process is solved through adjusting chemical components; the grain size of a steel product is obviously changed under the matching effect of the Al and the N and a fine crystal reinforcing effect is realized. Under the same rolling condition, the grain size can be improved by 1.5 to 2.0 grades when being compared with that of existing 40Cr steel, and the problem that the capability of existing equipment is not enough so that the grain size is relatively high solved; the equipment investment is reduced and the chromium-containing alloy bar material has good economic benefits and application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDE JIANLONG SPECIAL STEEL
Production method of welding rod steel H08A
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
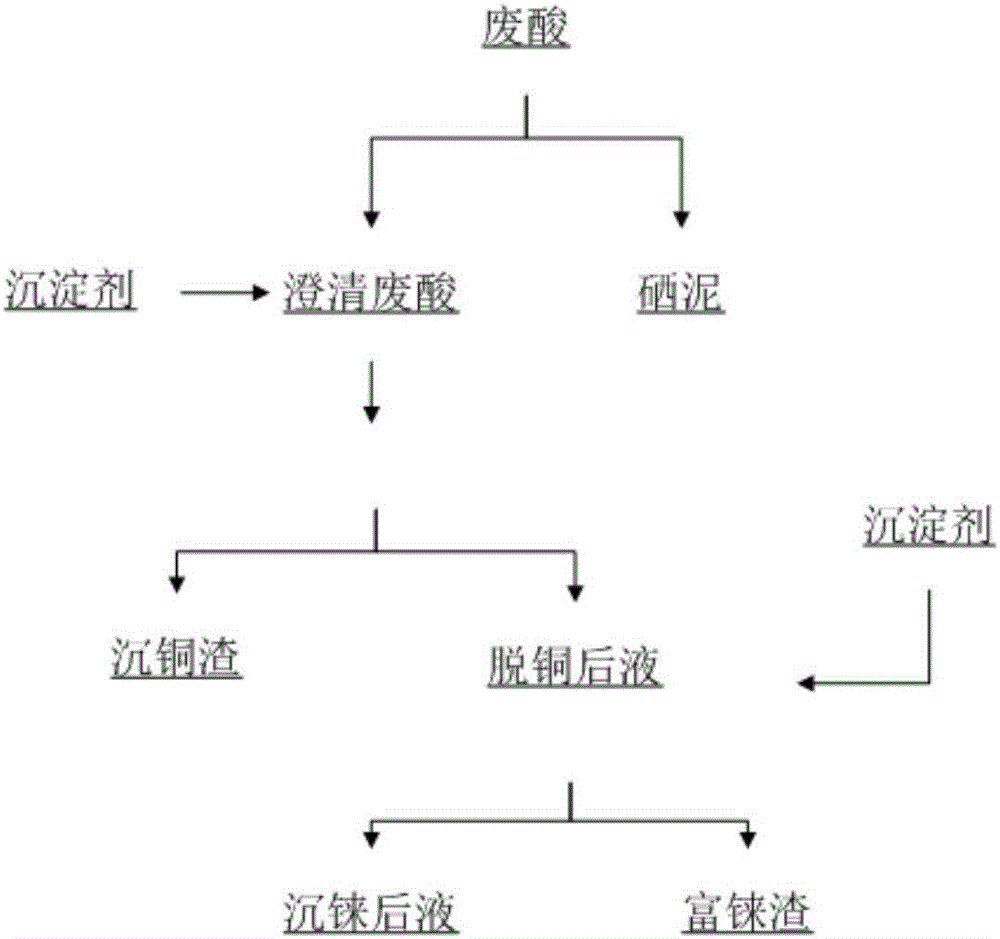
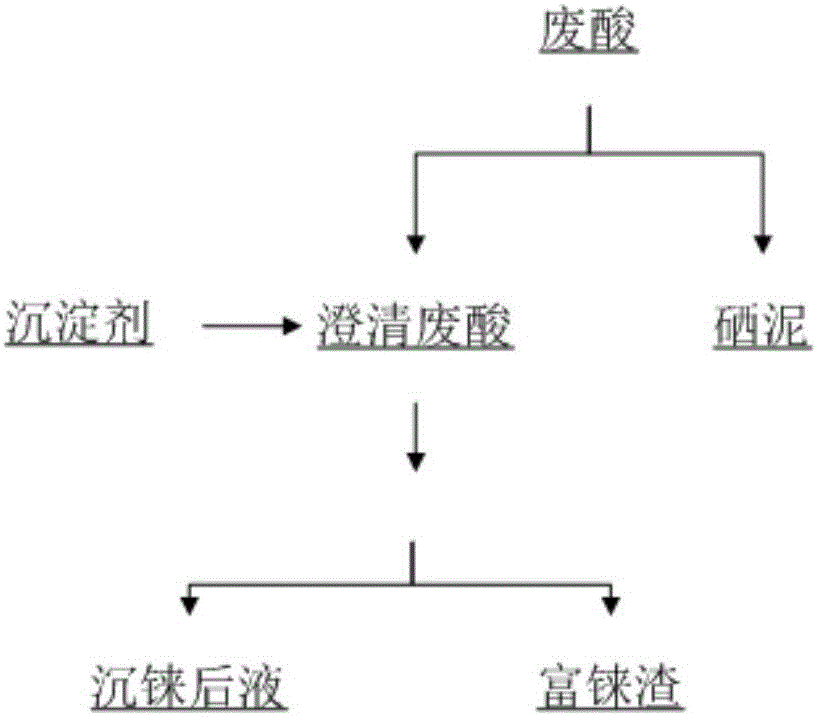
Method for recycling rhenium from copper smelting smoke washing waste acid
Owner:YANGGU XIANGGUANG COPPER
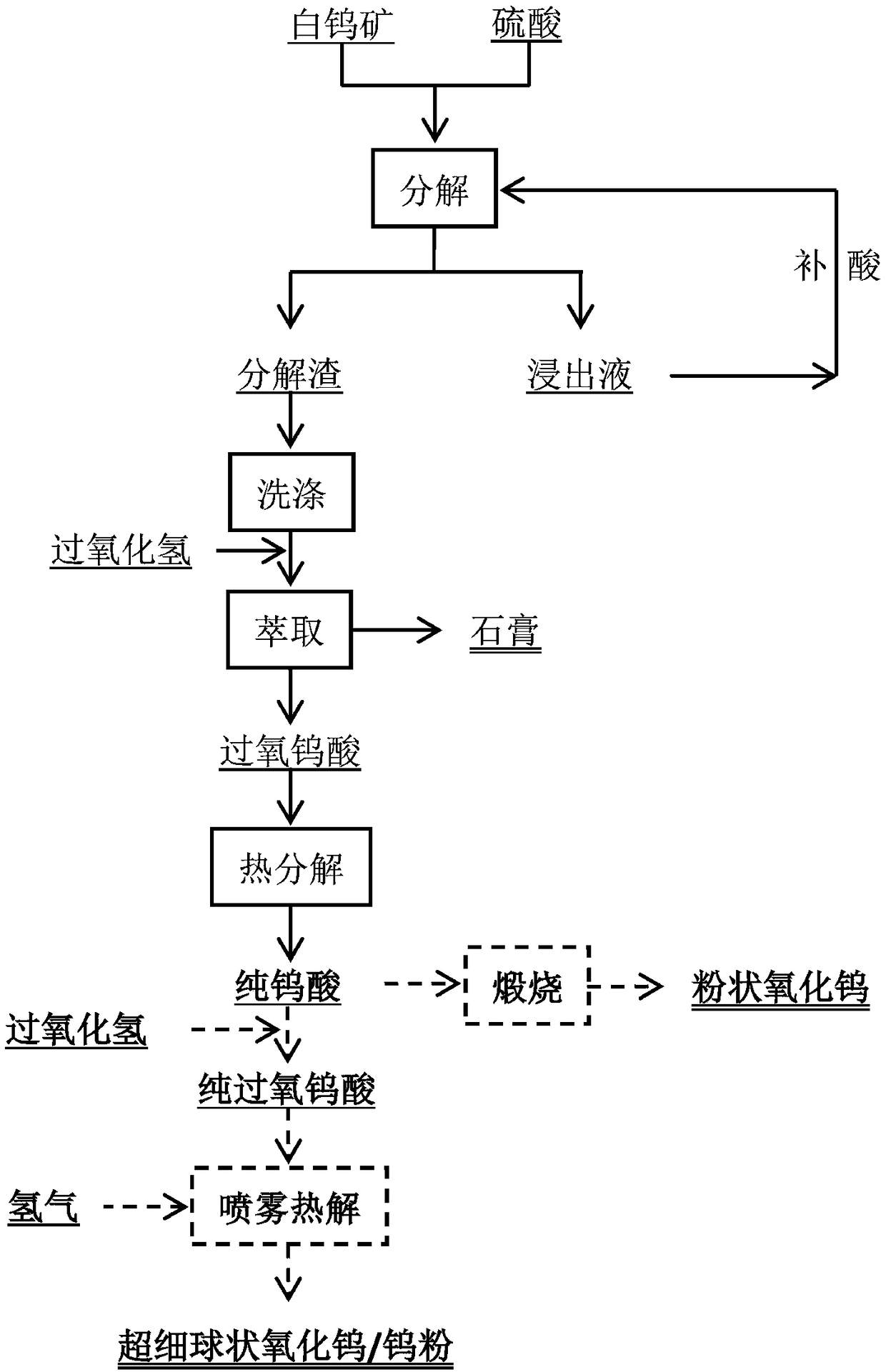
Method for preparing tungsten oxide and tungsten powder from scheelite
ActiveCN108640156AReduce break down costReduce manufacturing costTungsten oxides/hydroxidesProcess efficiency improvementDecompositionCalcination
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Small-dimension British standard deformed steel bar B500B and manufacturing technology thereof
The invention discloses a small-dimension British standard deformed steel bar B500B and a manufacturing technology thereof. The chemical component requirements of the small-dimension British standard deformed steel bar B500B are: C: 0.19-0.22 wt%, Si: 0.20-0.60 wt%, Mn: 0.70-0.90 wt%, Cr: 0.5-0.8%, P, S: less than or equal to 0.035 wt%, Ni, Cu: less than or equal to 0.25 wt%, Mo, Al: less than or equal to 0.10 wt%, and N: less than or equal to 0.011 wt%; the balance is Fe; carbon equivalent Ceq is less than or equal to 0.50%. The technology comprises converter or electric furnace smelting, LF refining or argon blowing refining, CCM bloom or billet continuous casting, bar controlled rolling, and controlled cooling. The component design takes chromium to replace expensive vanadium for alloying, is matched with reasonable-design controlled rolling temperature and air cooling temperature, realizes production of the small-dimension British standard deformed steel bar B500B with qualified performance in low cost, and acquires favorable economical and social benefits.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
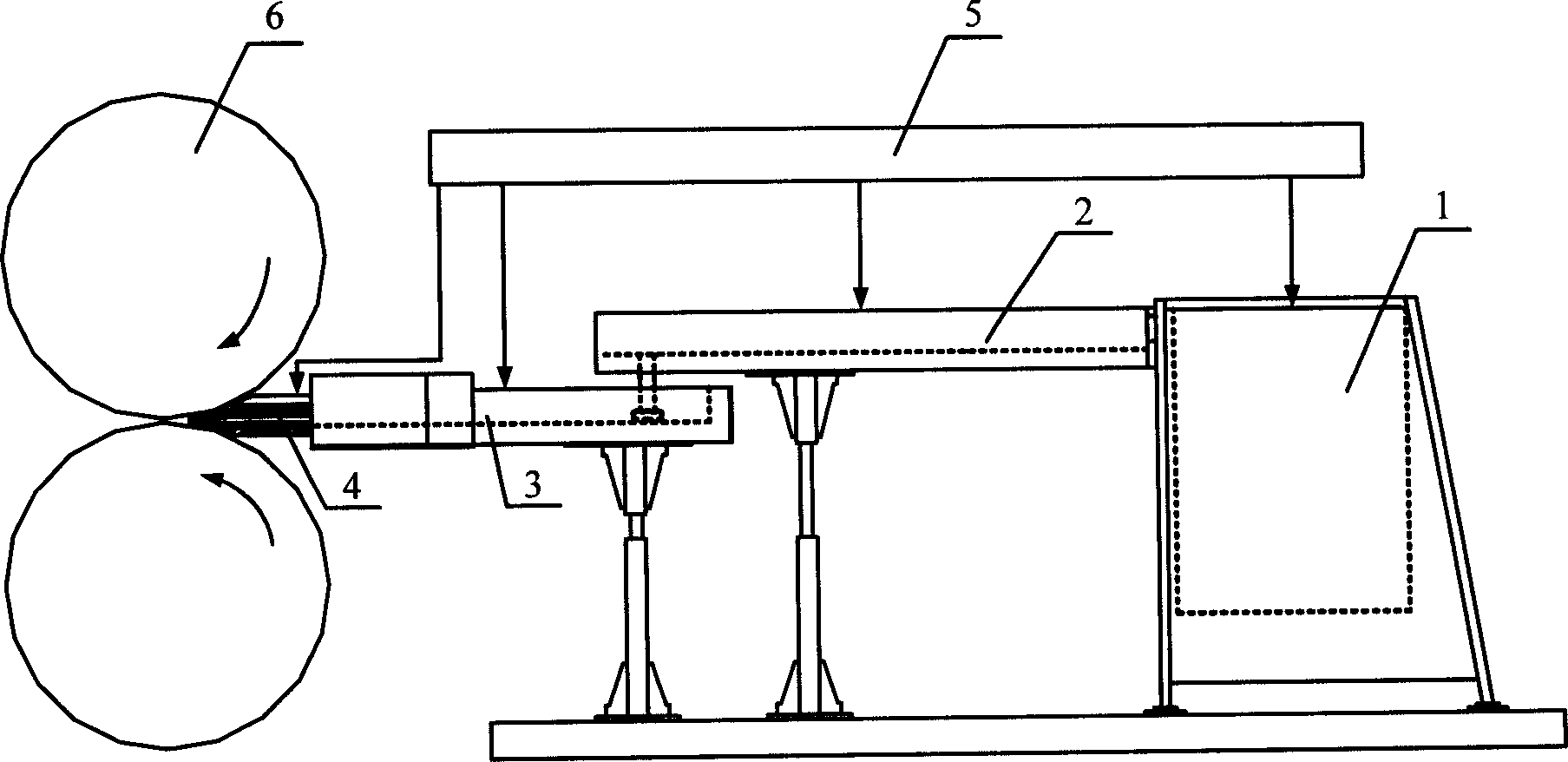
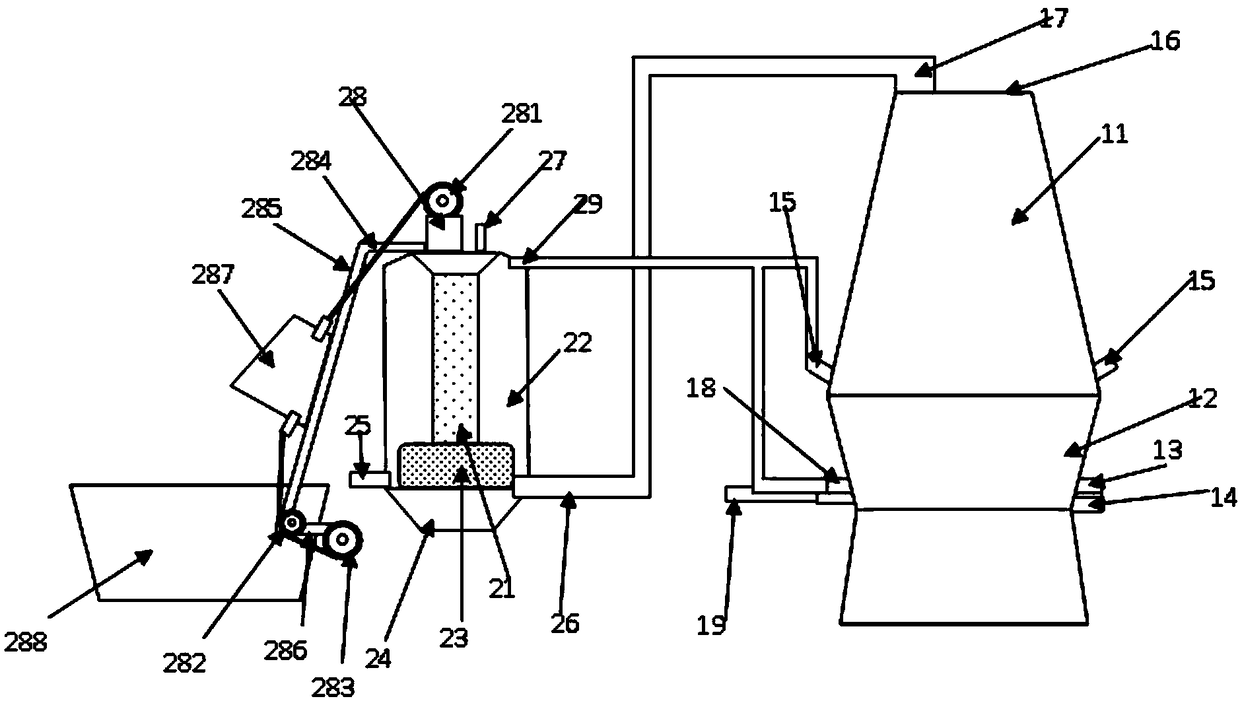
Vertical metal smelting device for alloy steel forging and casting
The invention discloses a vertical metal smelting device for alloy steel forging and casting. The vertical metal smelting device for alloy steel forging and casting comprises a high-temperature-resistant shell, wherein a first connector and a second connector are arranged in the middle of a connecting pipe; clamping slots are symmetrically formed in the outer sides of the first connector and the second connector; a filter screen is jointly arranged in the first connector and the second connector; an outer seal ring is jointly arranged on the outer sides of the first connector and the second connector; clamping blocks corresponding to the clamping slots are arranged on the inner side of the outer seal ring; and an inner seal ring corresponding to the filter screen is arranged on the inner side of the outer seal ring. According to the vertical metal smelting device for alloy steel forging and casting provided by the invention, through arranging the filter screen, metal particles in smokedust can be prevented from being discharged to cause the resource waste; and in addition, through taking off the outer seal ring and the inner seal ring on the outer sides of the first connector andthe second connector, the filter screen can be conveniently taken out so as to be conveniently cleaned and prevented from being blocked.
Owner:NANTONG JUXING CASTING & FORGING CO LTD
Rolling-cut type bilateral scissors and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104233101AMeet normal cutting needsFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesThick plateIngot casting
Owner:TAIER HEAVY IND
Hydrogen-rich oxygen blast furnace ironmaking method
InactiveCN108220514AAchieving no residueReduce inaccuracyBlast furnace detailsHydrogenHeating furnace
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
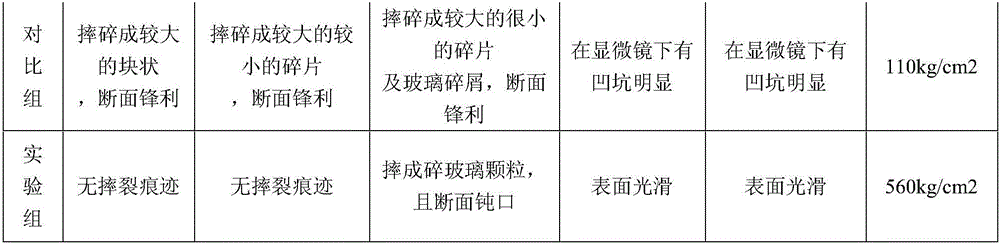
Anti-smashing glass bottle and production method thereof
InactiveCN106587605AGood chemical stabilityIncrease surface tensionGlass blowing apparatusGlass tempering apparatusManufacturing technologyBreak the glass
Owner:柳州市昌泉贸易有限公司
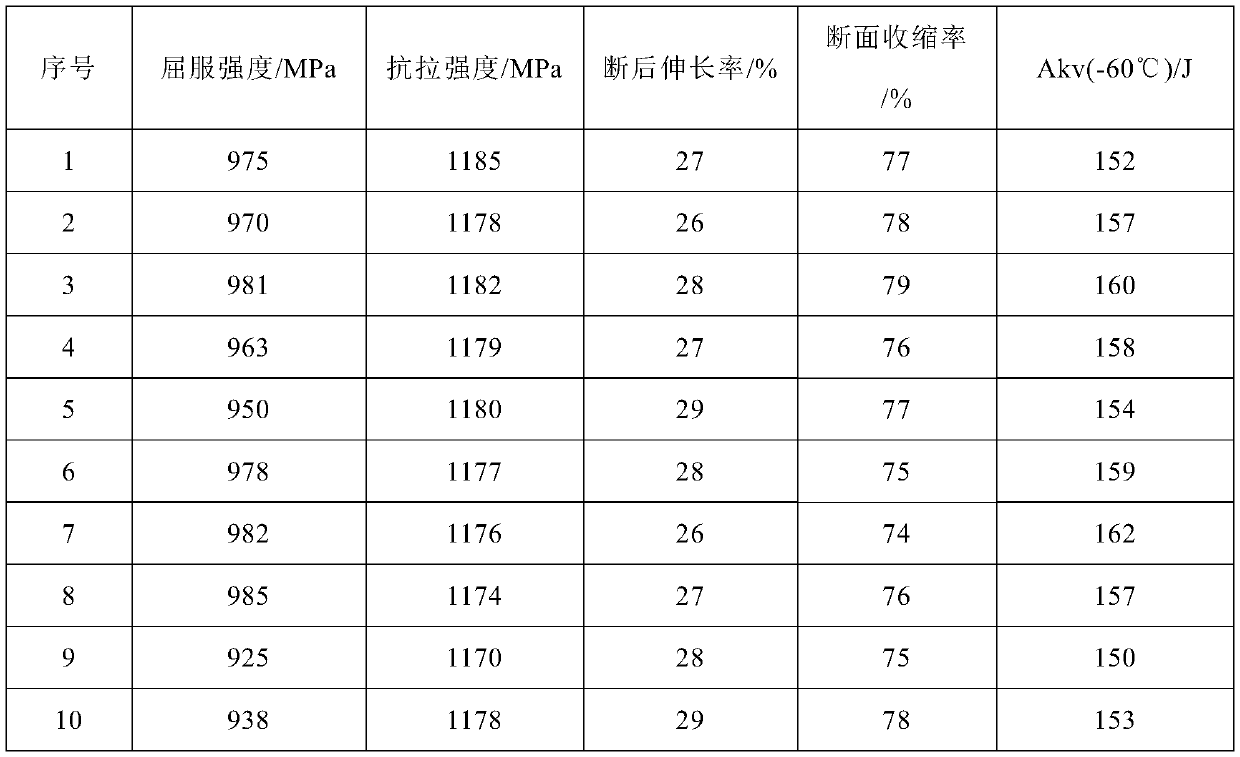
370MPa-yield-strength bridge steel without plate thickness effect and production method thereof
ActiveCN102936683ASimple rolling processEasy to controlTemperature control deviceUltimate tensile strengthSteel plates
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL GRP ECHENG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for relieving pattern segregation of spring steel
ActiveCN106399654ASolve the problem of resentmentReduce manufacturing costTemperature differenceSpring steel
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
High-strength 23Mn2CrNiMnVERA steel for railway train connection and preparation method thereof
Owner:SHANDONG XIWANG SPECIAL STEEL
Whole set smelting device for ferrotitanium series product
ActiveCN101054648AControl the intake air volumeHeating up fastFurnace componentsCrucible furnacesCombustion chamberHeating time
Owner:攀枝花市银江金勇工贸有限责任公司
Anti-corrosion and anti-wear high manganese steel and preparation method thereof
Owner:江苏久华环保科技股份有限公司
High-purity titanium ingot purification method
InactiveCN109266863AFully meltedLow elemental contentProcess efficiency improvementPurification methodsTitanium
Owner:宝鸡市华烨钛镍金属有限公司
Novel Fe-Co-based wave absorbing micro powder and preparing method thereof
The invention provides novel Fe-Co-based wave absorbing micro powder and a preparing method thereof. According to the method, Fe, Co, Al and Er are used as raw materials and are proportioned according to the atomic ratio of Fe10Co7AlxEr2-x (0.5<=x<=1), then smelting is conducted in a vacuum arc furnace, smelted alloy is placed in a vacuum glass tube for homogenizing annealing, then quenching and preliminary smashing are conducted, and finally, ball milling is conducted with a planetary ball mill under the protection of gasoline so that the wave absorbing micro powder can be obtained after the milled product is taken out and dried in the air.
Owner:孙炜炜
Spray method for preparing oxidation-resisting phosphorous copper alloy powder
InactiveCN106048298AGood sphericityUniform compositionTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusSurface oxidationIntermediate frequency
Owner:安徽旭晶粉体新材料科技有限公司
Sintering machine distributing device and distributing method using sintering machine distributing device
ActiveCN106959012ASimple structurePromote sinteringCharge treatment typeFurnace typesMixing tankParticle segregation
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap