Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3 results about "Tool steel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tool steel refers to a variety of carbon and alloy steels that are particularly well-suited to be made into tools. Their suitability comes from their distinctive hardness, resistance to abrasion and deformation, and their ability to hold a cutting edge at elevated temperatures. As a result, tool steels are suited for use in the shaping of other materials. With a carbon content between 0.5% and 1.5%, tool steels are manufactured under carefully controlled conditions to produce the required quality. The presence of carbides in their matrix plays the dominant role in the qualities of tool steel. The four major alloying elements that form carbides in tool steel are: tungsten, chromium, vanadium and molybdenum. The rate of dissolution of the different carbides into the austenite form of the iron determines the high-temperature performance of steel (slower is better, making for a heat-resistant steel). Proper heat treatment of these steels is important for adequate performance. The manganese content is often kept low to minimize the possibility of cracking during water quenching.
Manufacturing process of high-carbon tool steel SK85 cold-rolled wide steel strip
The invention discloses a manufacturing process of a high-carbon tool steel SK85 cold-rolled wide steel strip. The process is characterized in that steel is subjected to converter smelting, LF furnacerefining and slab continuous casting to obtain continuous casting slabs with the thickness ranging from 210 mm to 230 mm, the continuous casting slabs are heated and subjected to hot continuous rolling and laminar cooling to reach the coiling temperature, a hot-rolled wide steel strip with the thickness ranging from 2.5 mm to 6.0 mm is obtained, the coiled hot-rolled wide steel strip is put in storage and slowly cooled to the room temperature, and the obtained metallographic structure is thin-sheet-shaped pearlite; the total reduction of first cold rolling is controlled to be 20%-50% after acid pickling of the hot-rolled wide steel strip, then spheroidizing annealing is conducted, the Vickers hardness HV5 is 180 or below, and the spheroidizing rate is 92% or above; after the steel strip is subjected to primary spheroidizing annealing, secondary cold rolling is conducted, the total reduction of cold rolling is controlled to be 30%-85%, and a cold-rolled wide steel strip with the finished product specification being 0.70-3.00 mm thick is obtained; the steel strip subjected to secondary cold rolling is further spheroidized and annealed, the Vickers hardness HV5 is 175 or below, and the spheroidizing rate is 94% or above; and then third cold rolling is conducted, the total reduction of cold rolling is controlled to be 50%-85%, and the cold-rolled wide steel strip with the finishedproduct specification being 0.10-0.70 mm thick is obtained.
Owner:新余钢铁股份有限公司
Titanium-carbide-based steel-bonded cemented carbide material and preparation method thereof
Owner:WUXI XINQUN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
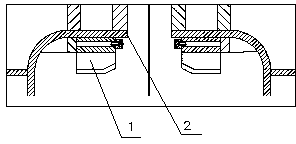
Fixed blade of residue anode pressure-disengaging machine
The invention relates to a fixed blade of a residue anode pressure-disengaging machine. The fixed blade is inverted-V-shaped and installed on the body of the residue anode pressure-disengaging machine in a dovetail splicing manner, the blade is made from CrWuMn high alloy tool steel, the quenching hardness of the cutter body is HRC45-50, and the surface nitrogenation treatment hardness of the cutting edge is as high as HRC63-65. The fixed blade is simple in structure, convenient to install, high in strength, low in production cost and long in service life.
Owner:扬州八方机电设备有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap