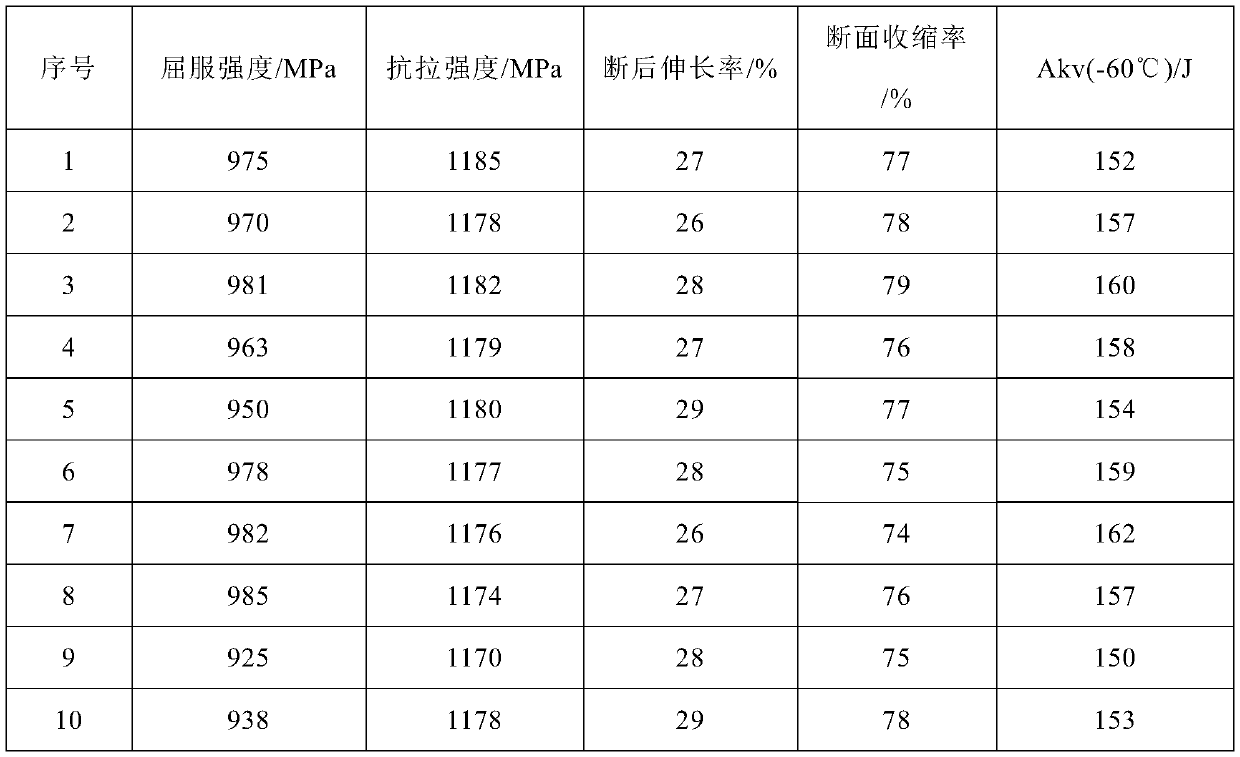
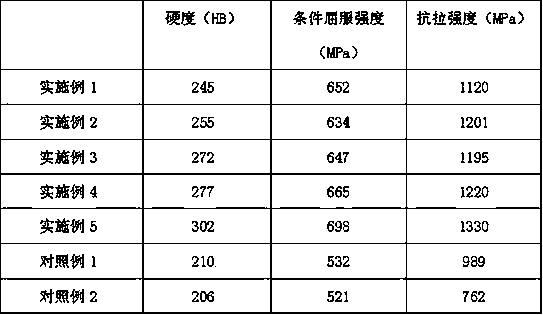
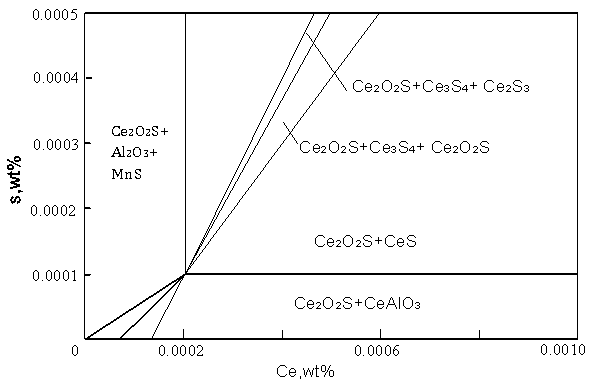
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
23 results about "Molybdenum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Molybdenum is a chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek Μόλυβδος molybdos, meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals have been known throughout history, but the element was discovered (in the sense of differentiating it as a new entity from the mineral salts of other metals) in 1778 by Carl Wilhelm Scheele. The metal was first isolated in 1781 by Peter Jacob Hjelm.
Micro-electrolytic filler containing catalyst
Owner:ZHEJIANG BOHUA ENVIRONMENTAL TECH & ENG
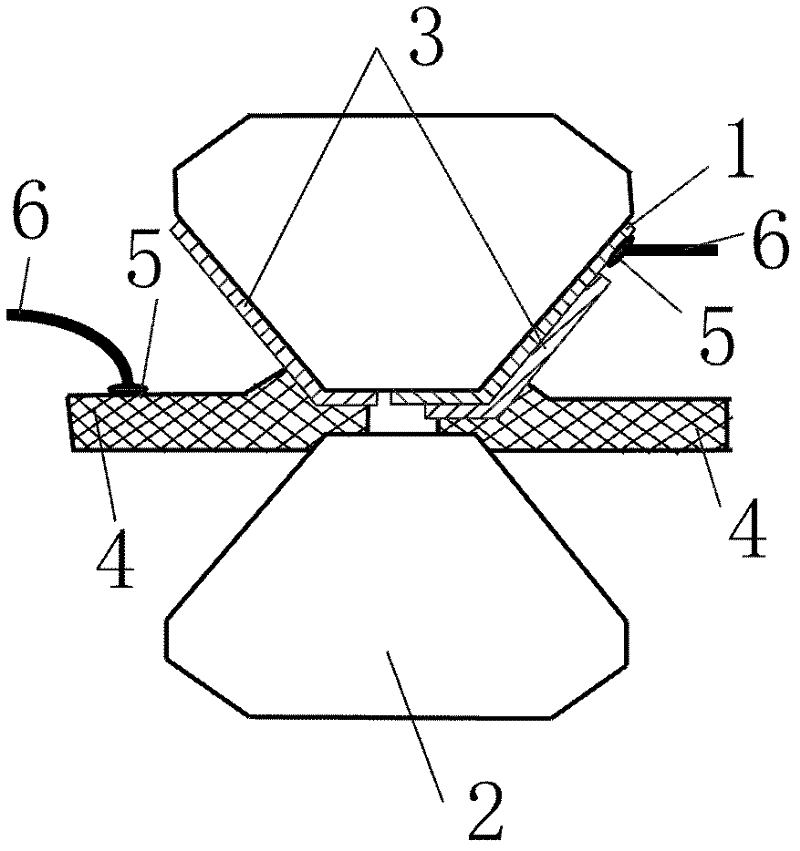
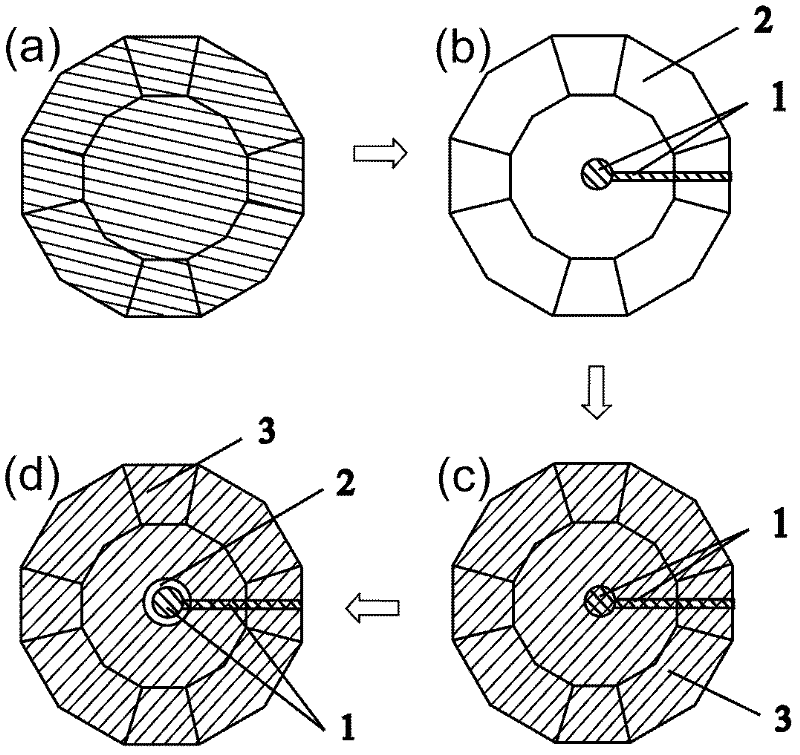
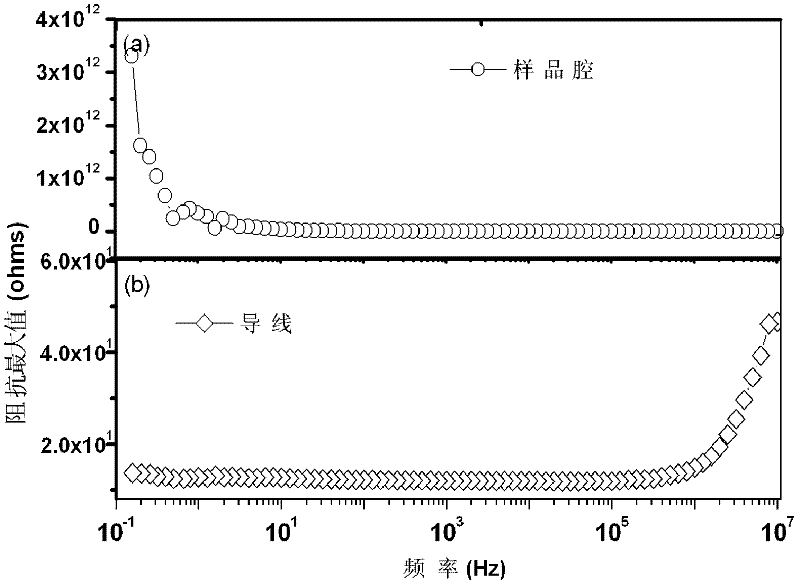
Electrode for high-voltage in-situ impedance spectroscopy measurement and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102288824AFix fixitySolve insulation problemsResistance/reactance/impedenceEtchingInsulation Problem
Owner:JILIN UNIV
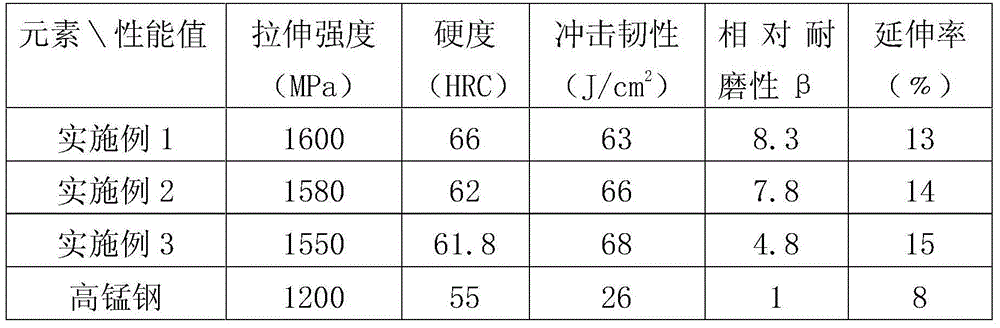
Titanium-carbide-based steel-bonded cemented carbide material and preparation method thereof
Owner:WUXI XINQUN NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
SPS connection method for tungsten and molybdenum dissimilar refractory metals
ActiveCN108262483AEfficient connectionFacilitated DiffusionRoom temperatureUltimate tensile strength
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Molybdenum fibre reinforced resin concrete material
InactiveCN101759397AGood physical and mechanical propertiesHigh compressive strengthKinetosomesResin-Based Composite
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Glass ceramics prepared from tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting and preparation method thereof
The invention provides glass ceramics prepared from tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting and a preparation method thereof. The glass ceramics use the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting as main raw materials and silica or quartz sand (SiO2), limestone or calcite (CaCO3), sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), alumina (Al2O3), potassium carbonate (K2CO3), magnesium oxide (MgO) and calcium fluoride (CaF2) as auxiliary raw materials. The preparation method comprises the steps of grinding the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting and the auxiliary raw materials, sieving the powder with a 20-mesh sieve, and mixing the powder uniformly in a mixer to obtain a base batch; melting the base batch at the temperature of 1450-1550 DEG C, homogenizing and clarifying the melt to obtain qualified molten glass, and then forming a base glass plate or granules through moulding by casting or water quenching of the molten glass; finally filling the base glass plate or the granules into a mould, and then carrying out crystallization thermal treatment, thus obtaining the glass ceramics prepared from the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting. The preparation process is simple in operation course and has the effects of not only expanding the way of resource comprehensive utilization of the tailings obtained by nickel-molybdenum ore dressing and smelting but also reducing the environmental pollution of the tailings.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Boron-bearing chromium molybdenum nickel wear-resistant alloy and preparation method thereof
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
High-strength 23Mn2CrNiMnVERA steel for railway train connection and preparation method thereof
Owner:SHANDONG XIWANG SPECIAL STEEL
High-temperature-resistant high-performance rare earth permanent magnet material
InactiveCN105374488AHigh temperature resistance and high performanceImprove stabilityInorganic material magnetismRare-earth elementTemperature resistance
Owner:南通长江电器实业有限公司
Fertilizer special for pasture
InactiveCN103553748ANutritional diversitySafe useFertilizer mixturesPhosphoric acidAdditional values
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & ECONOMY
Novel powder metallurgical gear
InactiveCN106041095AUniform densityLarge elongationTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusCarbon fibersALUMINUM STEARATES
Owner:黄宇
Novel thermoforming reinforcer and processing method thereof
Owner:JINGJIANG XINCHENG VEHICLE PARTS
Al2O3-TiC/Al2O3-TiC-CaF2 self-lubricating laminated ceramic drawing die and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a drawing die and particularly relates to an Al2O3-TiC / Al2O3-TiC-CaF2 self-lubricating laminated ceramic drawing die and also relates to a preparation method of the laminated ceramic drawing die. The technical scheme is as follows: the Al2O3-TiC / Al2O3-TiC-CaF2 self-lubricating laminated ceramic drawing die mainly comprises an Al2O3-TiC layer ceramic material and an Al2O3-TiC-CaF2 layer ceramic material, wherein the Al2O3-TiC layer ceramic material comprises the following components according to the volume ratio: 45% of aluminum oxide, 50% of titanium carbide, 0.5% of molybdenum, 4.5% of nickel and trace magnesium oxide and yttrium oxide; the Al2O3-TiC-CaF2 layer ceramic material comprises the following components according to the volume ratio: 30% of aluminum oxide, 60% of titanium carbide and 10% of calcium fluoride. The Al2O3-TiC layer ceramic material and the Al2O3-TiC-CaF2 layer ceramic material are laminated according to the design requirements of different wire processing sizes for the ceramic drawing die, and the ceramic die obtained after sintering retains higher hardness and strength, meanwhile, the toughness of the die is improved, and in addition, the whole die has a self-lubricating characteristic in the drawing process, so that the wear reducing and resisting effects are remarkable.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Smelting method for rare-earth microalloyed steel
Owner:内蒙古中天宏远稀土新材料股份公司
Molybdenum/steel connector and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108907492ARelief of residual thermal stressImprove performanceWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaMetal foilGlycerol
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Tungsten/molybdenum crucible for high-temperature heating furnace and manufacturing method of tungsten/molybdenum crucible
ActiveCN104534878AImprove structural strengthImprove heating effectCrucible furnacesRounded RectangleCrucible
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
Barium-tungsten cathode with high current density and preparation method of cathode
ActiveCN102637566AStable current densityMeet the needs of the cathodeTransit-tube cathodesCold cathode manufactureHigh current densityRhenium
Owner:HUADONG PHOTOELECTRIC TECHN INST OF ANHUI PROVINCE
Color ring chip inductor with high stability and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106158247AImprove plasticityLow coercivityTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsMagnetic materialsEpoxyPermalloy
Owner:宁波华众和创工业设计有限公司
Corrosion-resistant alloy
InactiveCN103265751ACorrosion resistant alloyLithium
The invention relates to a corrosion-resistant alloy, consisting of main components and auxiliary components, wherein the main components consist of the following components in percentage by mass: 32-38% of magnesium, 2-6% of molybdenum, 15-18% of lithium, 2-5% of cobalt, 18-23% of nickel and 2-5% of vanadium; and the auxiliary components consist of the following components in percentage by mass: 15-25% of ethylene-tetrafluoroethylene copolymer, and 1-2% of a lubricant. The corrosion-resistant alloy has good corrosion resistance.
Owner:CHUZHOU HAOYU SLIDING BEARING CO LTD
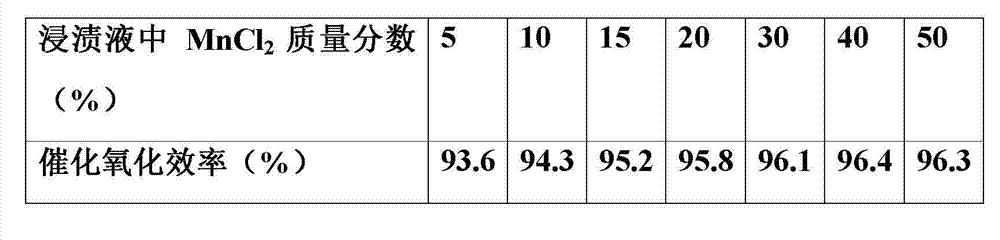
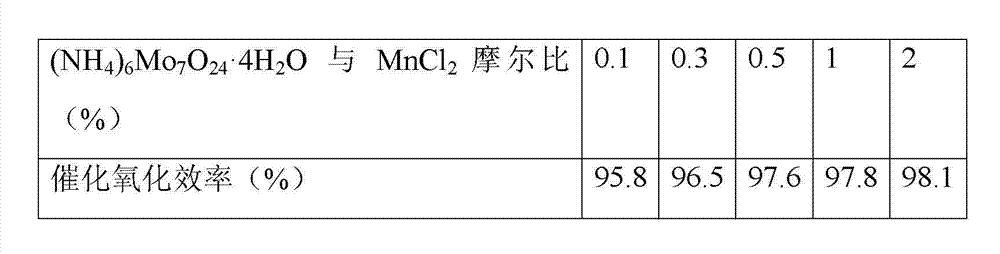
Modified catalyst for gaseous-state elemental mercury oxidation and preparation method of modified catalyst
ActiveCN102962083AAchieve sustainable developmentImprove catalytic oxidation efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsDispersed particle separationSulfurCatalytic oxidation
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
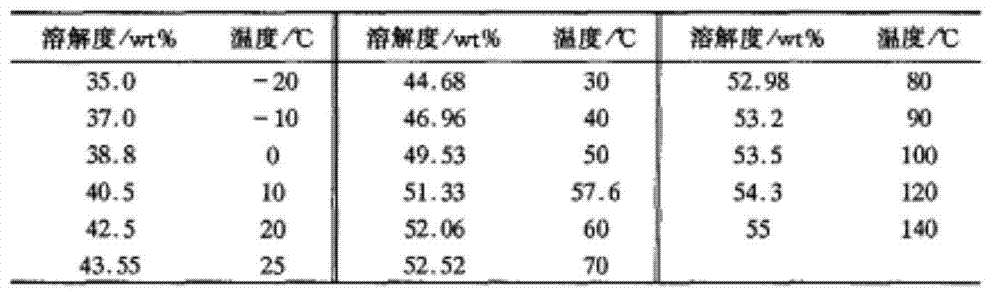
On-line detector for molybdenum concentration in water solution
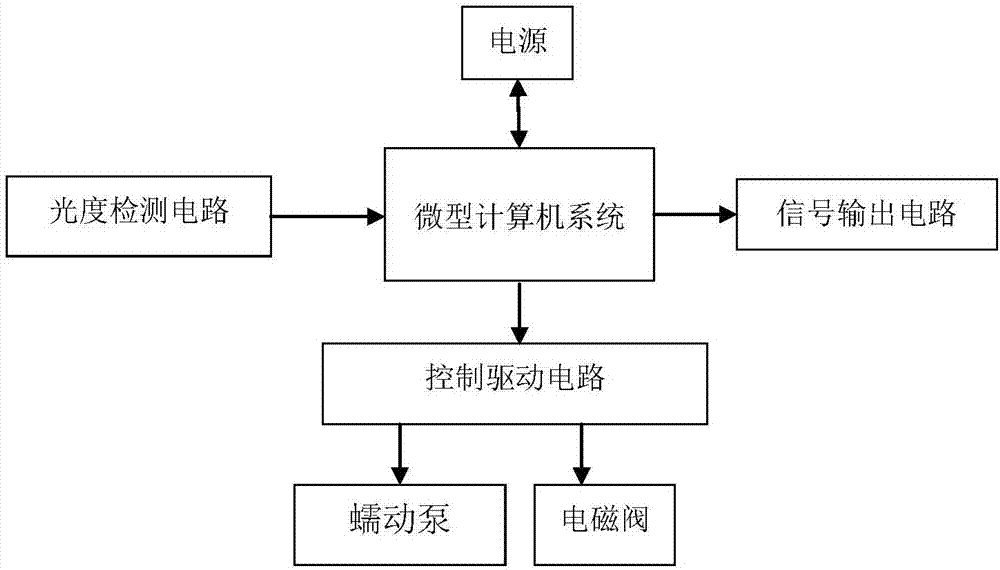
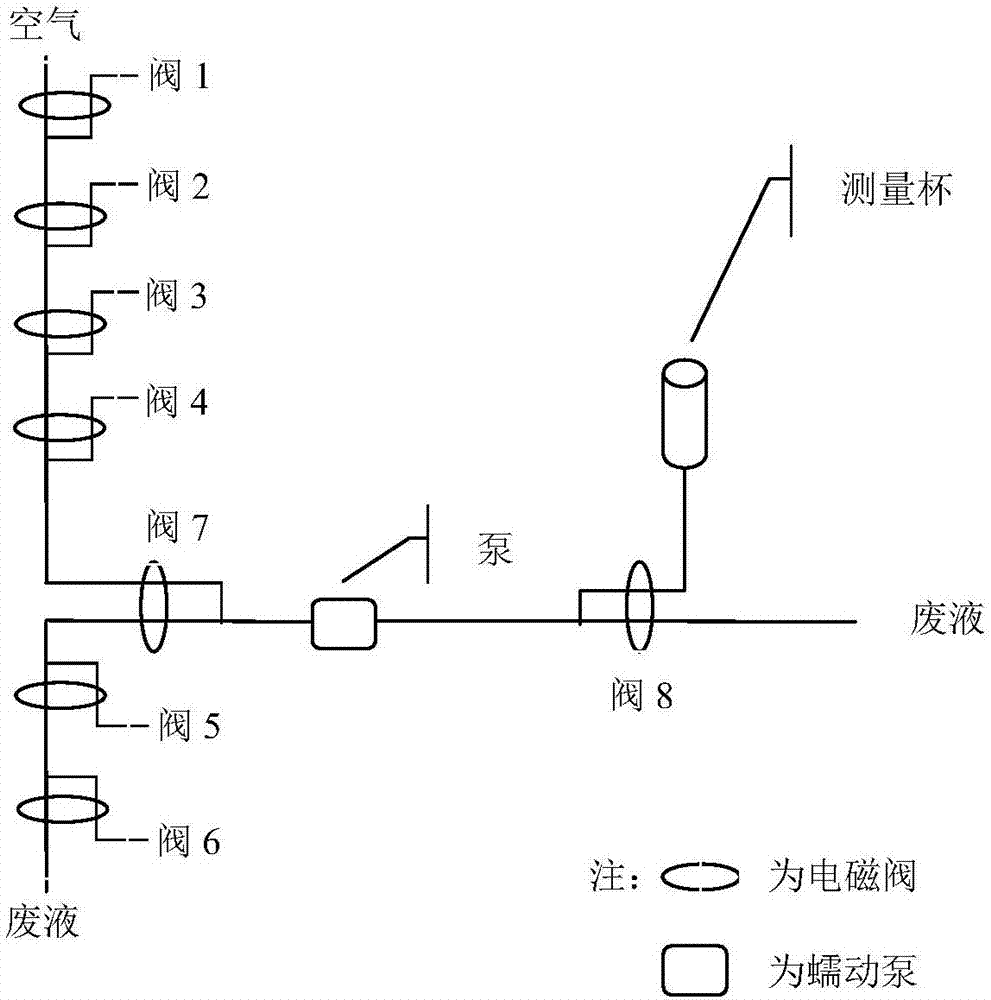
InactiveCN106950184AImplement automatic detectionReduce labor costsPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsPeristaltic pumpMicrocomputer system
Owner:BEIJING RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERING AND METALLURGY
Novel rack
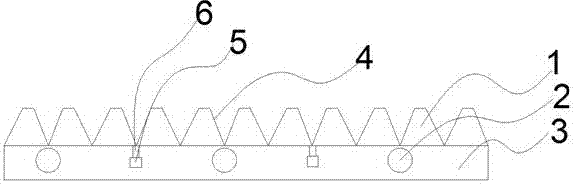
InactiveCN107542897AImprove heat resistanceImprove cooling effectPortable liftingGear lubrication/coolingManufacturing cost reductionHeat resistance
Owner:JIANGYIN SHENGYUAN COPPER MATERIAL
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap