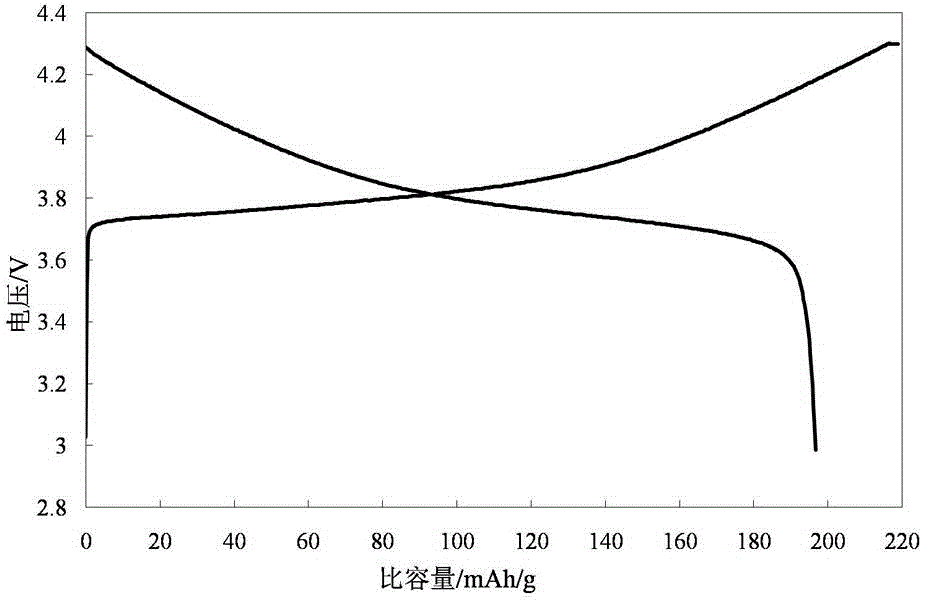
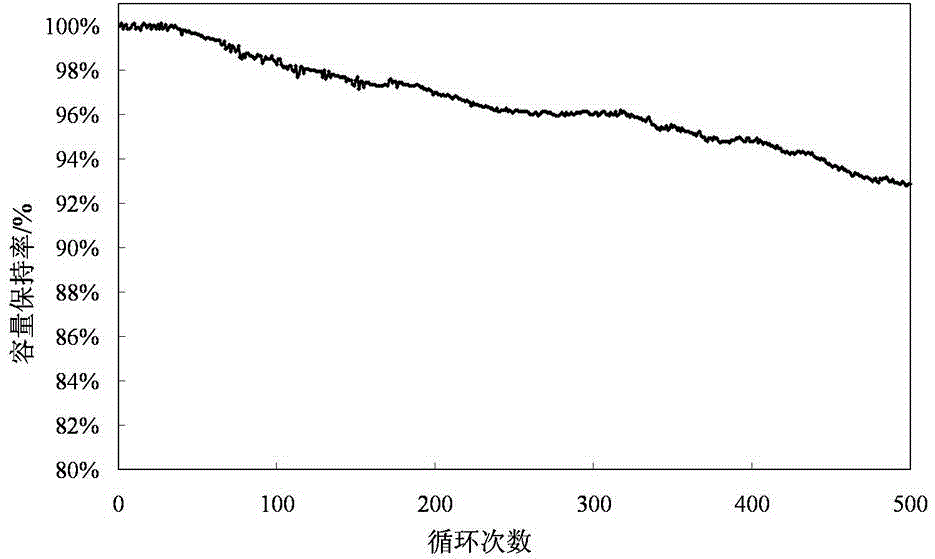
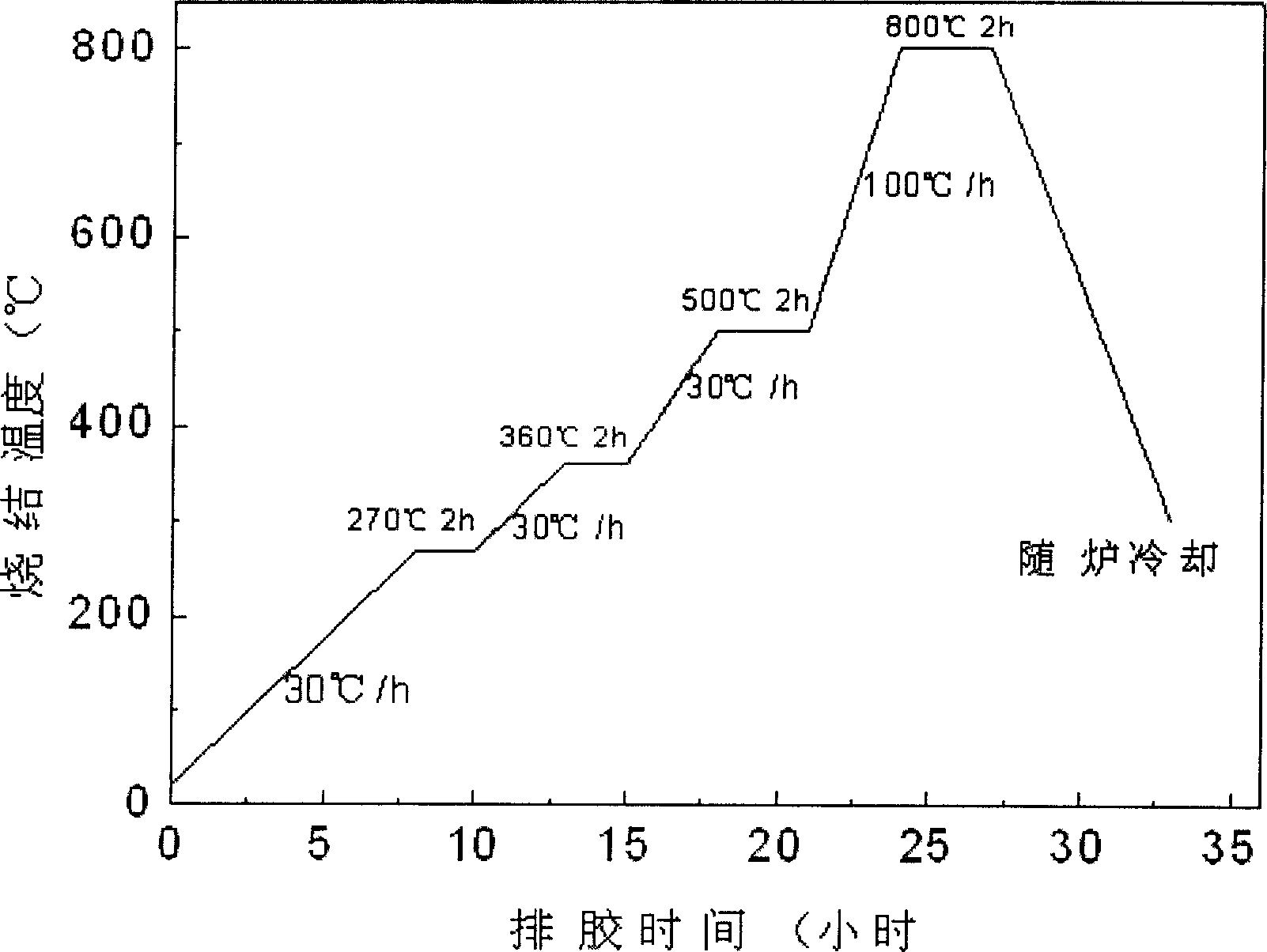
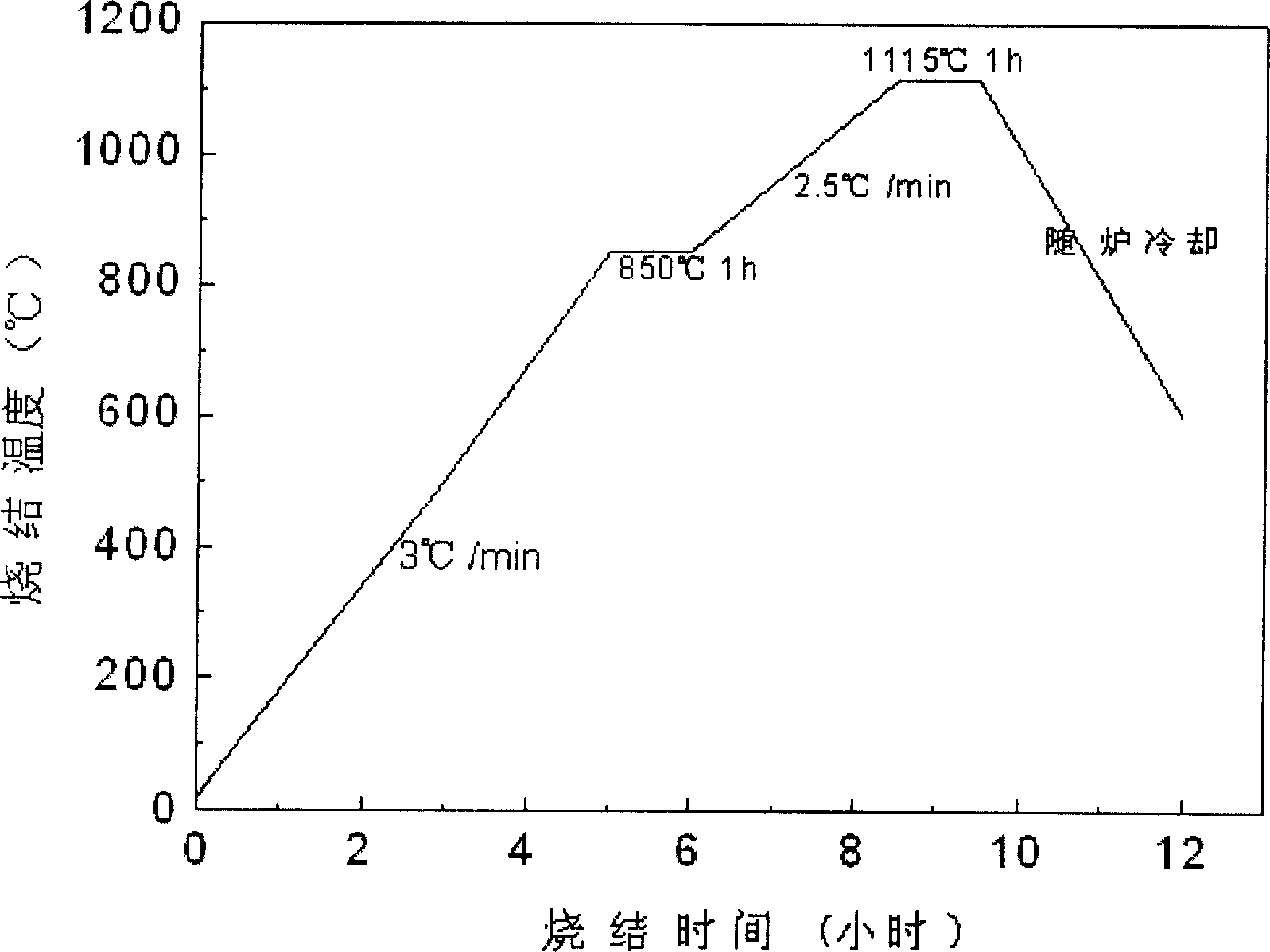
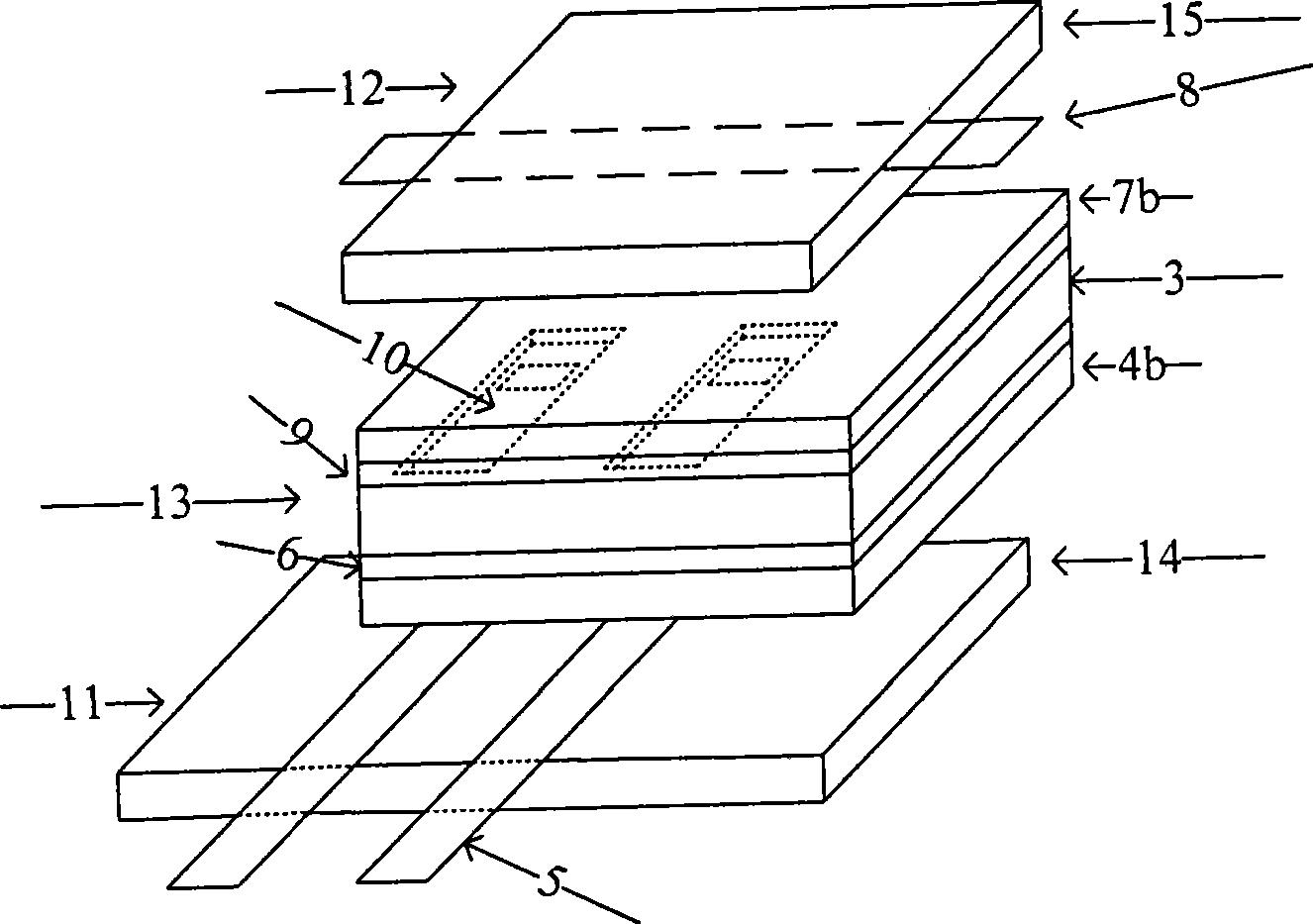
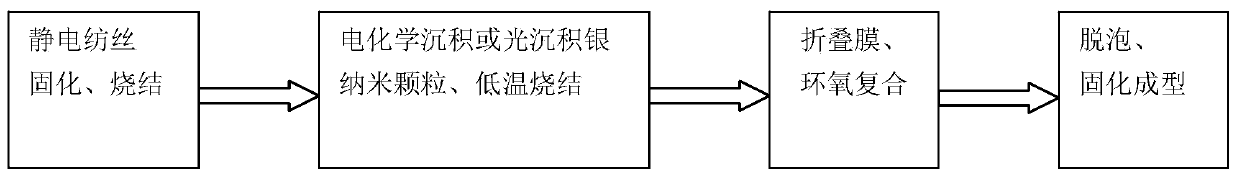
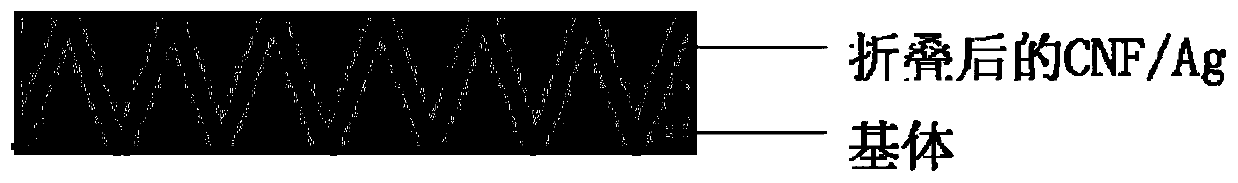
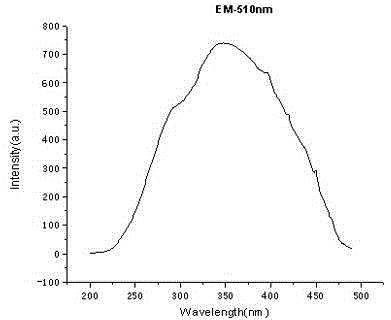
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
25 results about "Sintering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
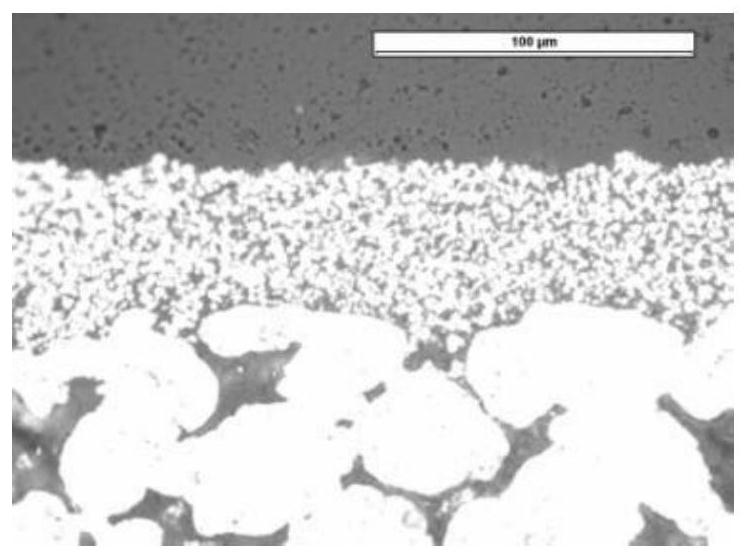
Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens naturally in mineral deposits or as a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms in the materials diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creating one solid piece. Because the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other, which is driven by the temperature difference between the water and the ice. Examples of pressure-driven sintering are the compacting of snowfall to a glacier, or the forming of a hard snowball by pressing loose snow together.
Surface coating modified lithium ion battery cathode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104577093AImprove securityNo significant reduction in specific capacityCell electrodesLithium iron phosphatePhysical chemistry
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIDARUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing silicon carbide ceramic material with low residual silicon by adopting multi-step reaction sintering method
ActiveCN106478105ASolve the mechanical propertiesSolving Elasticity ProblemsHeat conductingYoung's modulus
Owner:咸阳瞪羚谷新材料科技有限公司
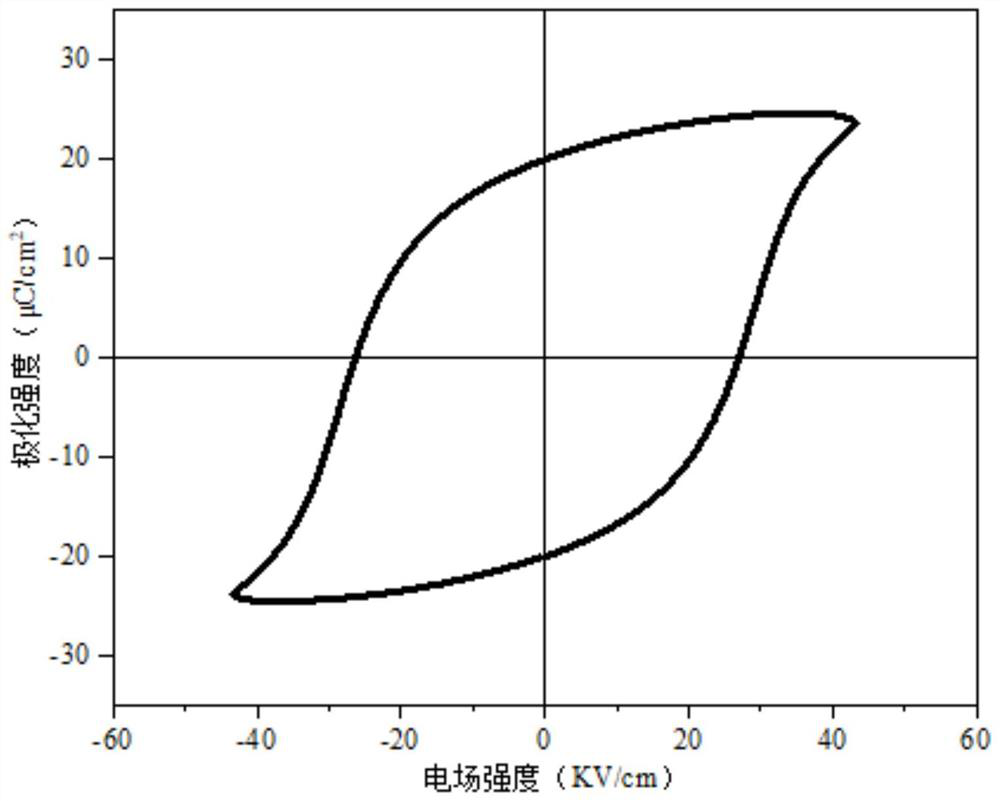
Bismuth sodium titanate-barium titanate base piezoelectric ceramic and its prepn process
InactiveCN1673178ALower coercive fieldLow resistivityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesBarium titanateAdhesive
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Saw-type sintering metal base diamond saw blade for cutting QFN (Quad Flat Non-leaded) package substrate
ActiveCN101870008AMetal sawing toolsInorganic fillerSintering
Owner:XIAN DIASH SUPERHARD MATERIALS DEV
Unleaded piezoelectric ceramic consisting of B-site composite Bi-based compound and preparation method thereof
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Composite high magnesia flux for sintering
InactiveCN101469365AAvoid negative effectsEliminate unfavorable situationsMaterials scienceWhite Spots
Owner:ANYANG IRON & STEEL GRP
Composite desulfurizer of iron and steel and its preparing process
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Lithium-rich anode material and preparation method thereof
Owner:MCNAIR TECH +1
Method for repairing ternary positive electrode material with deteriorated performance and acquired ternary positive electrode material
ActiveCN110534721ASolve dropSimple processSecondary cellsPositive electrodesOrganic solventUltrasonic dispersion
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Wear-resistant composite microcrystalline sheet material
Owner:HENAN JINGXIANG ABRASION PROOF MATERIAL
Ultrathin shadow mask type plasma display screen
InactiveCN101373693AReduce weightSimple manufacturing processSolid cathode detailsCold-cathode tubesEngineeringThin glass
Owner:NANJING HUAXIAN HIGH TECH CO LTD
Composite heat-conductive material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110452494AGood general applicabilityThe experimental operation method is simpleCarbon fibresElectrospinningWave shape
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing finished product rate of sintered ore
The invention relates to the field of iron and steel metallurgy, and discloses a method for increasing the finished product rate of sintered ore. The method for increasing the finished product rate ofthe sintered ore includes the steps that firstly, clear water is added in a sintered material and selectable return fines, first-time mixing is conducted, the amount of the return fines which are used is smaller than or equal to 30% of the weight of the sintered material, and the returned fines are vanadium-titanium sintered ore with the grain size being 5 mm or lower; secondly, second-time mixing is conducted on the mixed material obtained in the first step and mixed material reinforcement liquid; and thirdly, the mixed material obtained in the second step is subjected to material distribution, ignition and sintering, wherein the mixed material reinforcement liquid is prepared from corn starch and warm water according to the proportion being (0.05-1) : 99, and the temperature of the warmwater is 40 DEG C to 80 DEG C. By means of the method, the size composition of the mixed material can be improved, and therefore the finished product rate of the sintered ore is increased.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Ultrawhite stoneware and production process
Owner:SHENYANG SHUNXIN CERAMIC
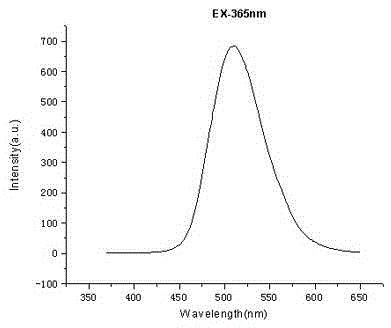
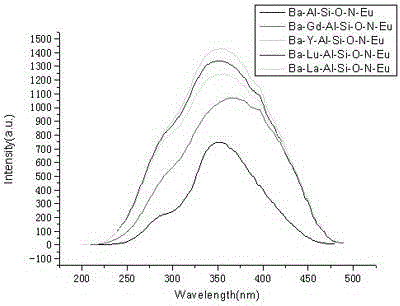
Rare-earth-doped nitrogen oxide green fluorescent powder and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104610967AImprove luminosityWide effective excitation rangeLuminescent compositionsNitrogen oxidesRare earth ions
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electrode cylinder
PendingCN110337153AImprove sintering qualityHigh strengthOhmic-resistance electrodesElectric heating for furnacesCooking & bakingEngineering
Owner:阳江翌川金属科技有限公司
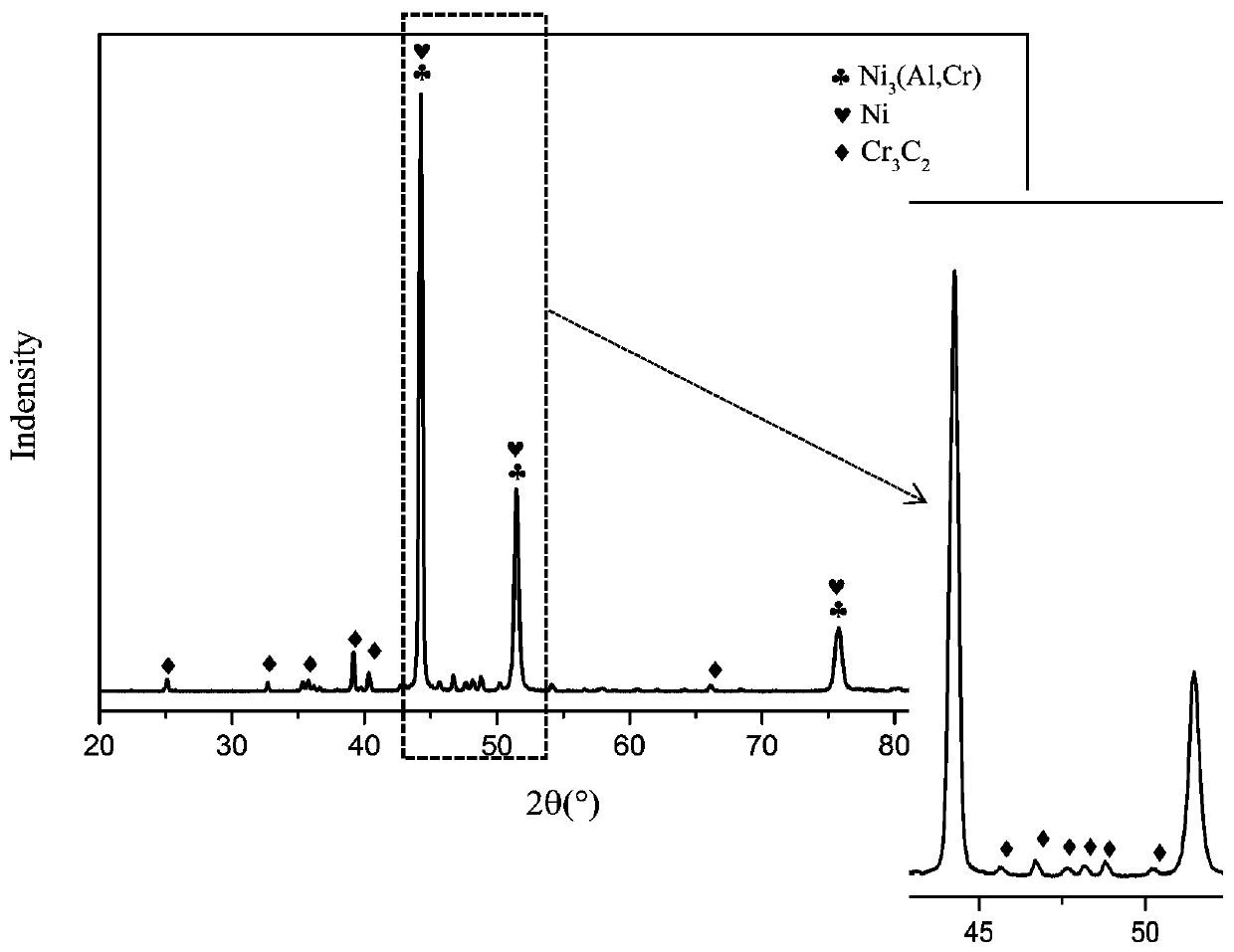
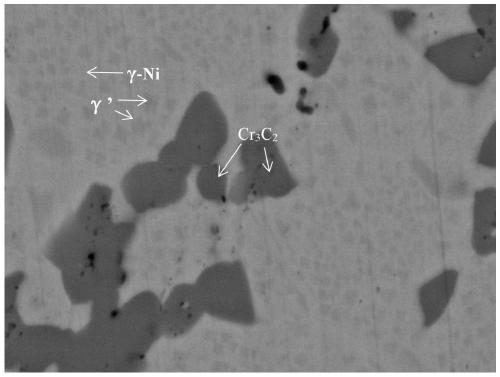
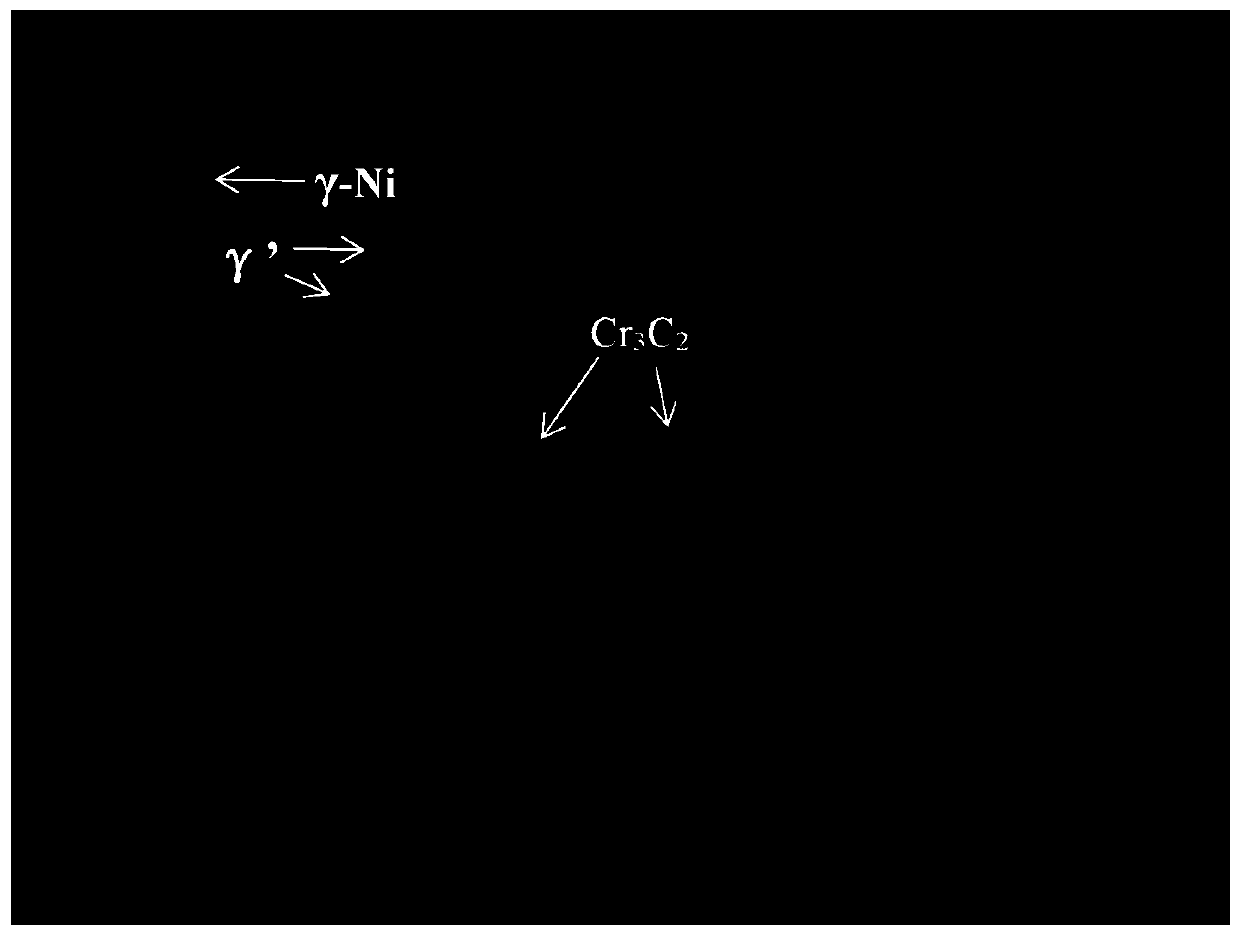
In-situ synthesized Cr3C2 reinforced Ni-based composite material and hot-press preparation method thereof
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
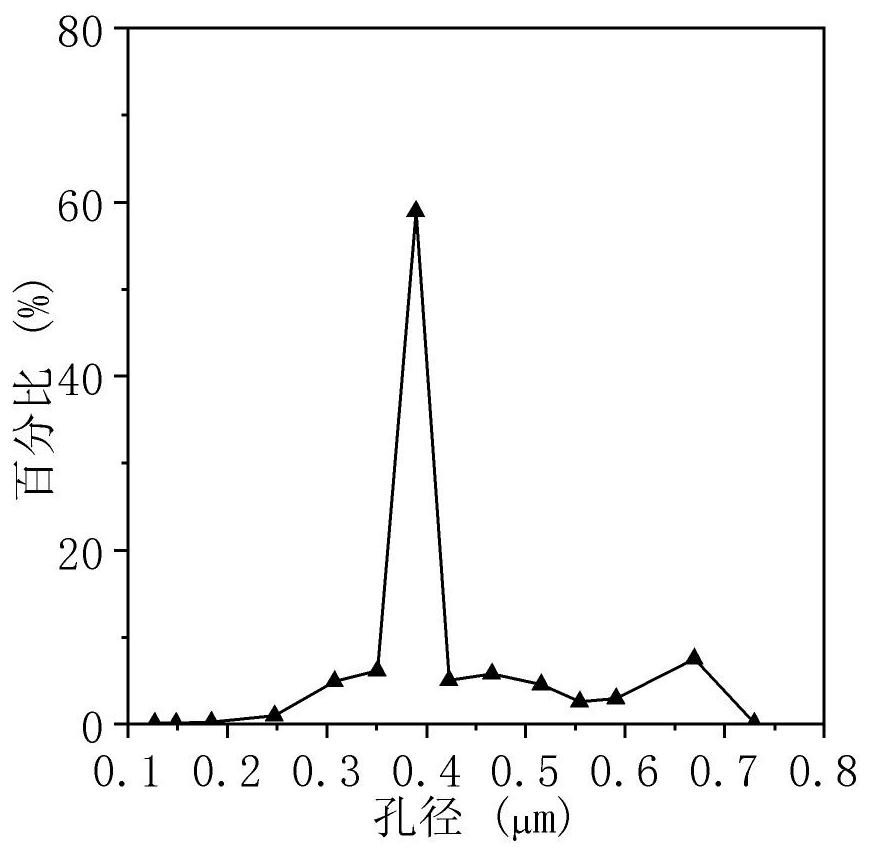
Preparation method of metal film of gradient aperture structure
ActiveCN112828280AReduce defectsReduce thicknessGeneral water supply conservationTransportation and packagingSlurryMetal powder
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Precision filter
InactiveCN101455917AImprove filtering effectEasy to useStationary filtering element filtersBiochemical engineeringFilter effect
Owner:薛文伟
High-temperature-resisting knuckle bearing for actuator
InactiveCN106321626AGuaranteed StrengthReduce structural weightShaftsRotary machine partsStress strengthHafnium
Owner:BEIJING POWER MACHINERY INST
Polyimide based insulation friction material and preparation method thereof
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Novel anti-electrostatic ceramic glaze as well as preparation method and application thereof
Owner:ZHONGSHAN ADVANCED ENG & TECH RES INST WUHAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Preparation method of doped bismuth ferrite-barium titanate-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramic material
PendingCN114180952ASmall grain sizeHigh densityFixed capacitor dielectricAcceleration measurementBarium titanatePolyvinyl alcohol
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A novel electrode material for a supercapacitor and a supercapacitor
InactiveCN109192534AHigh specific capacityFacilitated DiffusionHybrid capacitor electrodesMultiple hybrid/EDL capacitorsPolypyrroleFast charging
Owner:广东粤迪厚创科技发展有限公司 +1
Material guiding device for material sintering and material sintering furnace comprising material guiding device
InactiveCN113294999AUnique structureIncrease profitCharge manipulationFurnace typesContinuous productionSintering
The invention relates to a material guiding device for material sintering and a material sintering furnace comprising the material guiding device. The material guiding device for material sintering comprises a shell with a hollow structure, wherein the top of the shell enables materials to be dispersed and fall down along the periphery of the shell, the top of the shell is of a conical tip structure, or the top of the shell is of a curved surface structure, and the shell is provided with a first through hole for hot air to penetrate through. The material sintering furnace comprising the material guiding device comprises a cylindrical furnace body which is vertically arranged, wherein the material guiding device which can enable the materials to fall off in a scattered mode is arranged in a hearth, a material guiding hopper is further arranged above the material guiding device, the small-diameter end of the material guiding hopper is close to the material guiding device, and an auxiliary ignition area is formed by a gap between the material guiding hopper and a furnace wall; a calcining table is further arranged below the material guiding device and is of an umbrella-shaped structure, and a main ignition area is formed below the calcining table. The material sintering furnace comprising the material guiding device is unique in structure, a stirring device is not needed, the materials can be fully sintered, and the heat utilization rate is high; the sintering furnace is vertically arranged, the materials naturally move downwards under the action of gravity, sintering is completed, and continuous production can be achieved.
Owner:LUOYANG BLACK BOX INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap