Heat-resistant polyester plastic degrading enzyme and application thereof
A technology of polyester plastics and degrading enzymes, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem of PET degrading enzymes being less and resistant to high temperatures, and achieve the effect of strong heat resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Example 1 Synthesis of heat-resistant polyester plastic degrading enzyme encoding genes and construction of PM-T plasmid
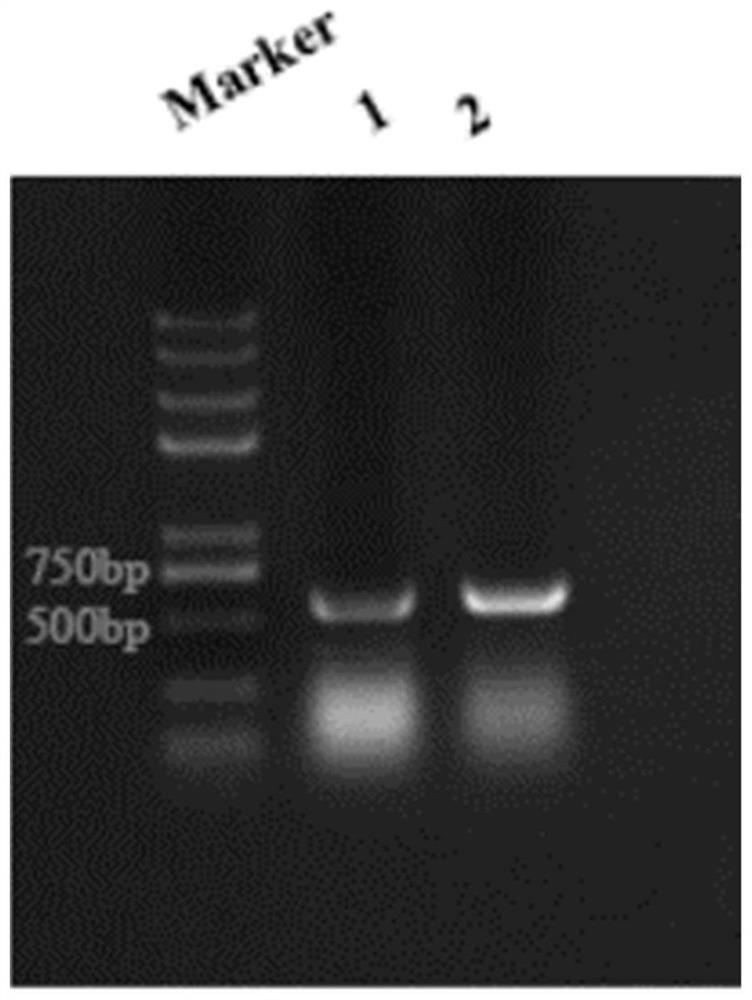
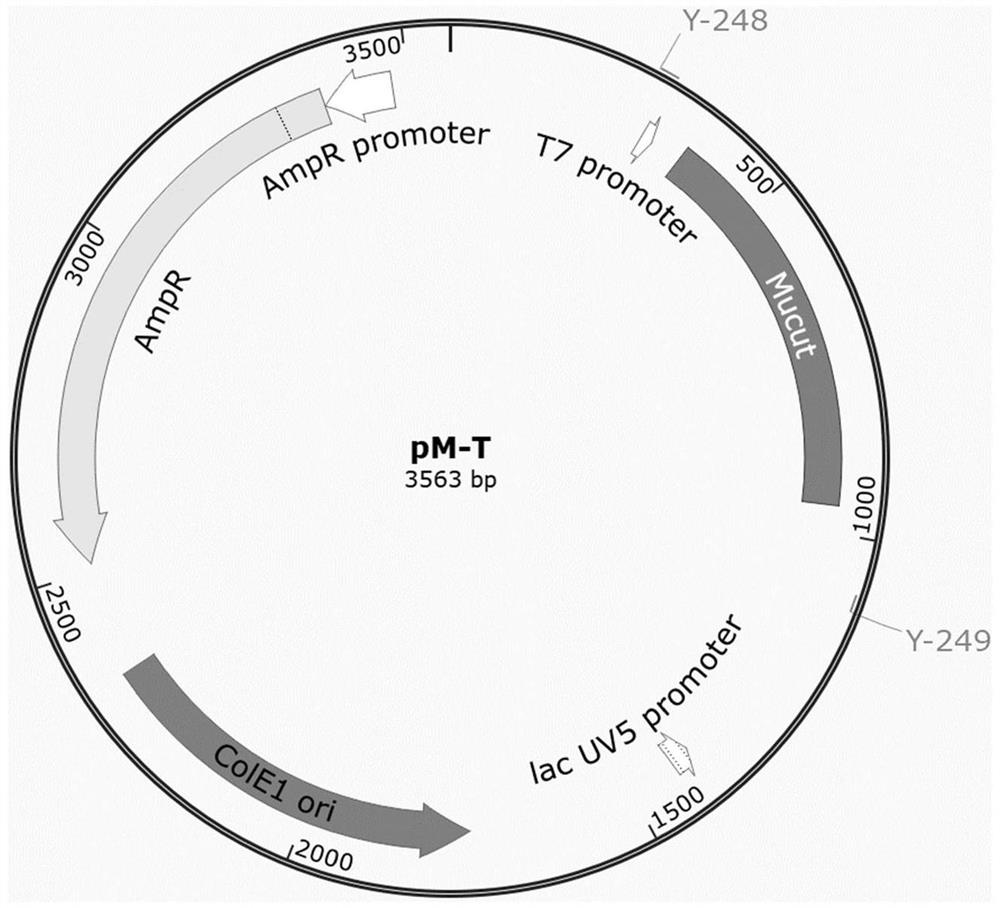
[0043] Based on the gene sequence (GenBank: KY568910.1) published on the US National Biological Information Technology Center (NCBI), the sequence is optimized, replacing a codon with a Pichia gauze to obtain a heat-resistant polyester plastic degradation. Enzyme encoding gene sequence SEQ ID NO.2, manually synthesized this gene (see figure 1 ), The gene cloned into the PJET1.2 / BLUNT vector to obtain plasmid PM-T by the method of flat end-end-digestive connection. figure 2 )
Embodiment 2
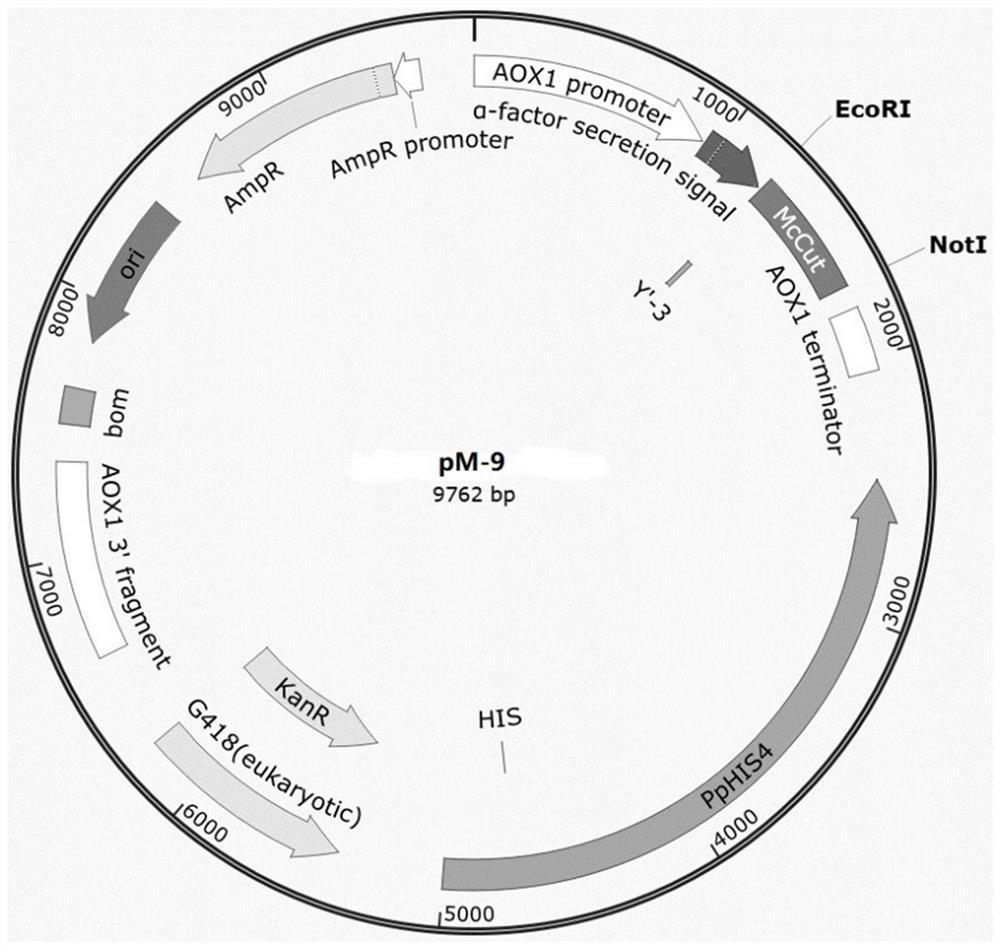
[0044] Example 2 Construction of recombinant plasmid PM-9 containing heat-resistant polyester plastic degrading enzyme gene
[0045] (1) Design amplification primers based on heat-resistant polyester plastic degrading enzymes:
[0046] Upstream primer F1 5'-TGCGA Gaattc TccccagttgcagTGGAGA-3 ', containing ECOR I-enzyme-sized (following line marking) and protecting base;
[0047] Downstream primer R1 5'-TGCGA GCGCCGC Ttacgagtctatcctcaagcc-3 ', containing NOT I enzyme dug points (under linear marks) and protecting bases.
[0048] (2) PCR amplification is performed by the plasmid PM-T in Example 1, and the PCR amplification is performed by F1 and R1 primers, and the PCR amplification procedure is: 95 ° C predetermined 2 min; 95 ° C denaturation 20S, 60 ° C annealing 20s, 72 ° C Extension 1 min, a total of 25 cycles; 72 ° C extends for 5 min.
[0049] (3) PCR product and plasmid PPIC9K were used to extract the compound, and then the enzyme digestion was purified by ECOR I and NOT I, and
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Construction of heat-resistant polyester plastic degrading enzyme production strain Pichia Pastoris GS115 / PM-9
[0052] Using the electroporation method of Example linearized pM-9 2 (using enzyme Sal I digested) plasmids were transformed Pichia Pastoris GS115, first in the MD plates (1.34% YNB, 4 × 10-5% biotin, 2% Glucose and 20 g of agar, dissolved in 1L water), followed by screening, then 0.5% methanol and 20g agar, dissolved in 1L water in mm plate (13.4% ynb, 4 × 10-5% biotin) and 0.5 mg / ml-3 mg G418 / ml of (geneticin) resistance YPD plates (1% YeastExtract, 2% Peptone, 2% Dextrose agar and 20g, was dissolved in 1L of water) were screened. Finally, the engineered strain with high copy was finally sequenced, and the correct sequencing was verified, the correct positive strain Pichia Pastorisgs115 / PM-9 was verified. The primers are 5'aox1 and 3'aox1, respectively, and the sequence is as follows:
[0053] 5'aox1 5'-gactggttccaattgacaagc;
[0054] 3'A
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap