Gene GmRmd1 for resisting powdery mildew of soybean as well as encoded protein and application of gene GmRmd1
A powdery mildew resistance and protein technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of uncloned soybean powdery mildew resistance genes, less functional analysis of disease resistance genes, less soybean powdery mildew, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0055] Example 1: Cloning of soybean powdery mildew resistance gene GmRmd1
[0056] The inventors of the present invention isolated and cloned a soybean powdery mildew resistance gene related gene GmRmd1 from soybean, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence listing, and named the encoded protein as GmRmd1 protein, as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence listing. The specific cloning method is as follows:
[0057] The total RNA of soybean material B13 leaves was extracted with a plant total RNA extraction kit (TR02, GeneMark), and its integrity was detected by 1% agarose electrophoresis; cDNA synthesis was performed according to PrimeScript TM RT reagent Kit with gDNA Eraser kit instructions. Using the above cDNA as a template, sequence 3 and sequence 4 (sequence 3: 5'-ATGGCTGCAACAACACGTTC-3'; sequence 4: 5'-TTAGGCTAGATTGCCATACT-3') were used as primers for PCR amplification. Prepare PCR reaction solution (50μl system) according to the following components: 2×Phanta Max Buffer
Embodiment 2
[0059] Example 2: Obtainment of soybean powdery mildew resistance gene GmRmd1 transgenic soybean and gene editing mutants
[0060] 1. Construction of the vector
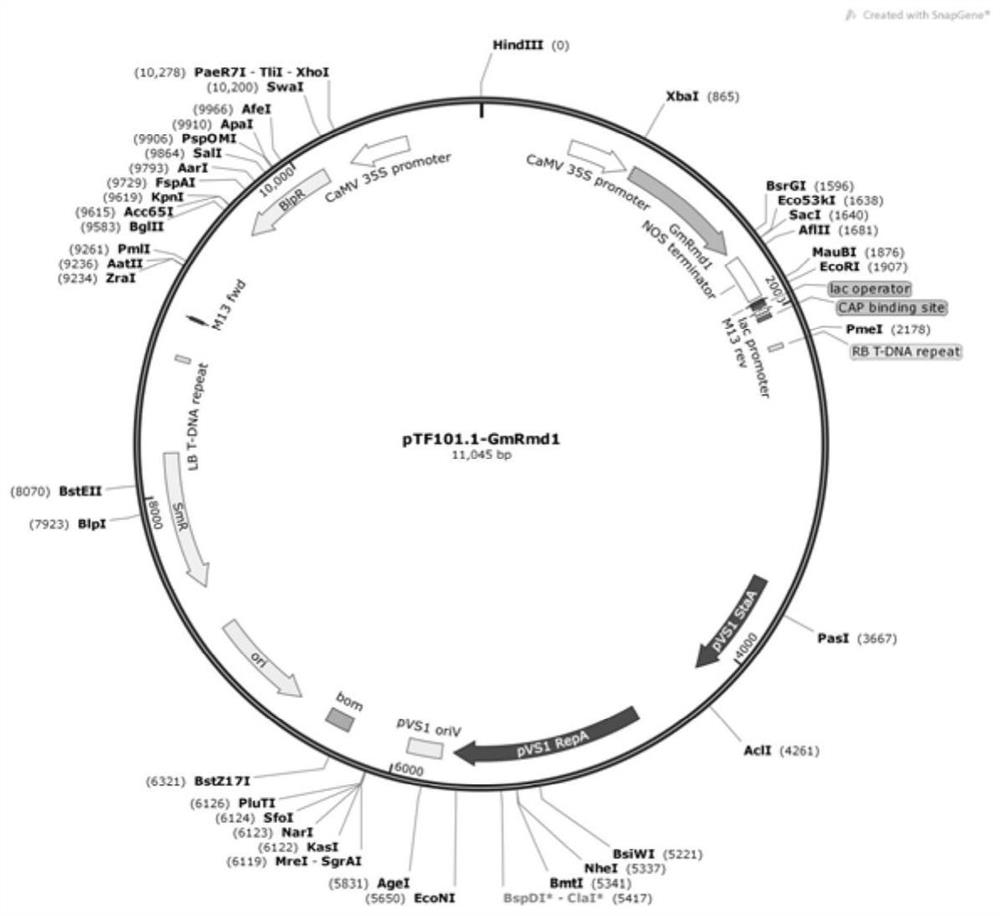
[0061] Construction of plant expression vector: The sequence between the XbaI site and the SacI site of the vector pTF101 (BioVector NTCC Type Culture Collection) was replaced with the sequence of Sequence 1 and other sequences were kept unchanged to obtain a recombinant vector pTF101-GmRmd1, which structure as figure 1 shown.
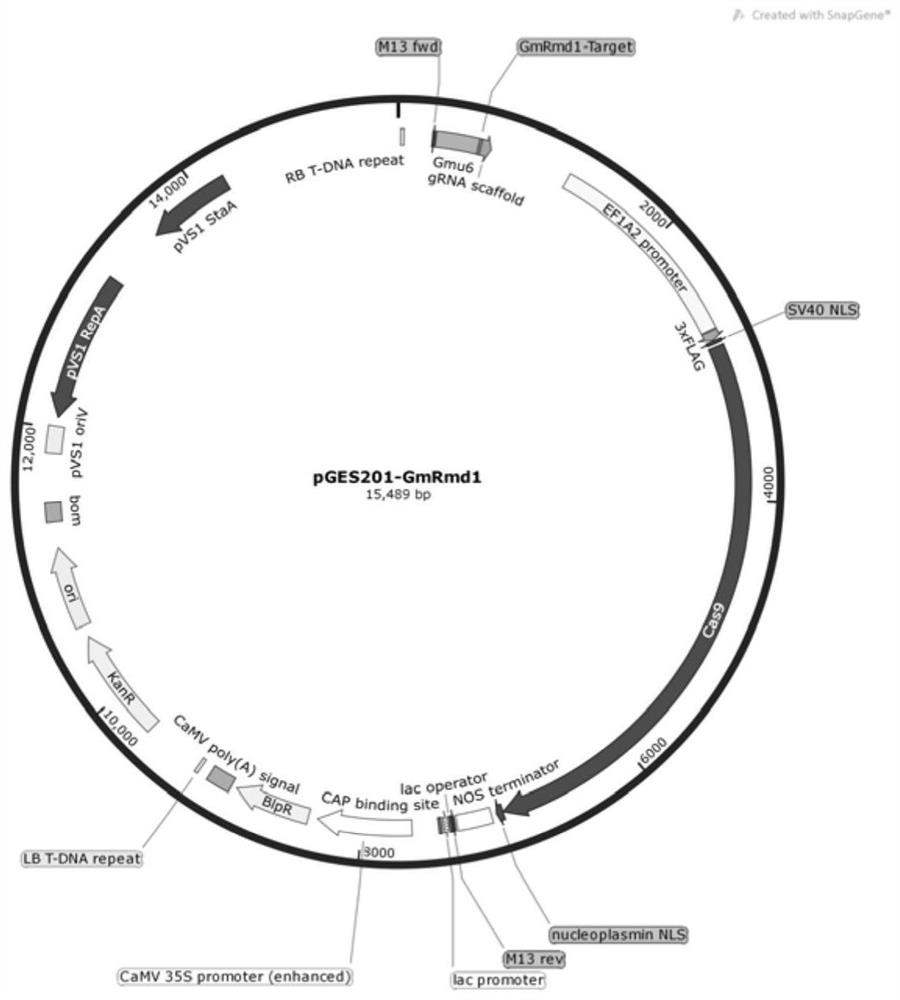
[0062] Construction of gene editing vector: The gene target (sequence 5) of GmRmd1 of the present invention was replaced with the vector pGES201 (Bai M, Yuan J, Kuang H, et al. Generation of a multiplex mutagenesis population via pooled CRISPR-Cas9 in soya bean. Plant Biotechnol J. 2020; 18(3): 721-731. doi: 10.1111 / pbi.13239) to obtain the recombinant vector pGES201-GmRmd1, whose structure is as follows figure 2 shown.
[0063] 2. The recombinant vectors pTF101-GmRmd1 and pGES201-GmRmd1
Embodiment 3
[0065] Example 3: Functional verification of soybean powdery mildew resistance gene GmRmd1
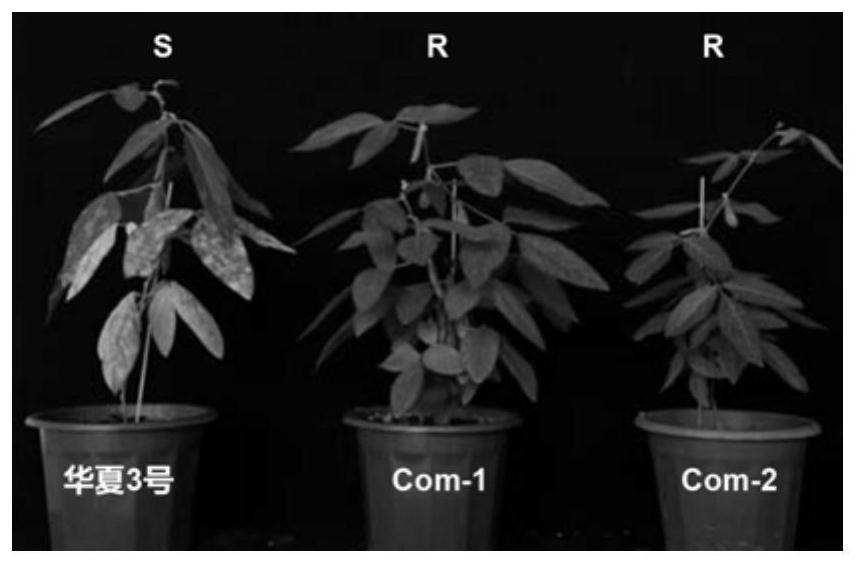
[0066] 2 independent transgenic lines and 4 gene editing mutants prepared in Example 2, and susceptible control varieties Guizao 1 and Huaxia 3 (Zhong Caixia, Zhong Kaizhen, Zhao Yunyun, Chen Lin, Nian Hai, Ma Qibin, etc.) , Yang Cunyi. Evaluation of Phosphorus Efficiency of Brazilian Soybean Resources and Its Derivatives in South China[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crops, 2013, 35(02): 162-170.) and the resistant control material Young were inoculated with powdery mildew and artificially inoculated After 15 days, the phenotype observation was started. The plants with powdery mildew on the leaf surface of the plants were susceptible plants, and the plants without powdery mildew on the leaves were resistant plants. Among them, the inoculation method is: collecting diseased leaves covered with powdery mildew in an incubator, then using a brush to pick up the spores on the diseased leaves, plac
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap