Transmitting layer depositing organic luminous display device
A technology of light-emitting display and emission layer, which is applied in lighting devices, electroluminescent light sources, light sources, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing production volume
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
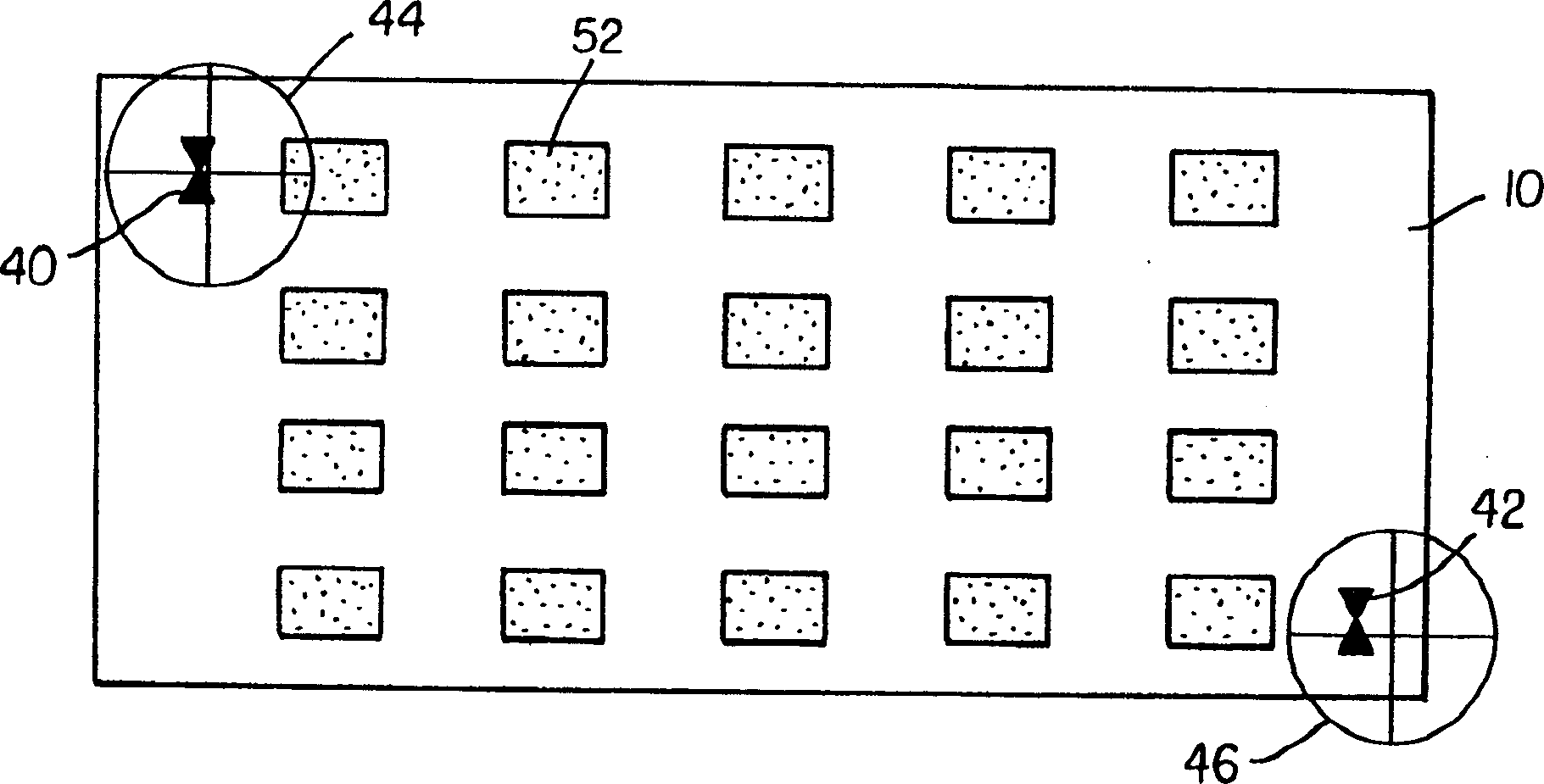
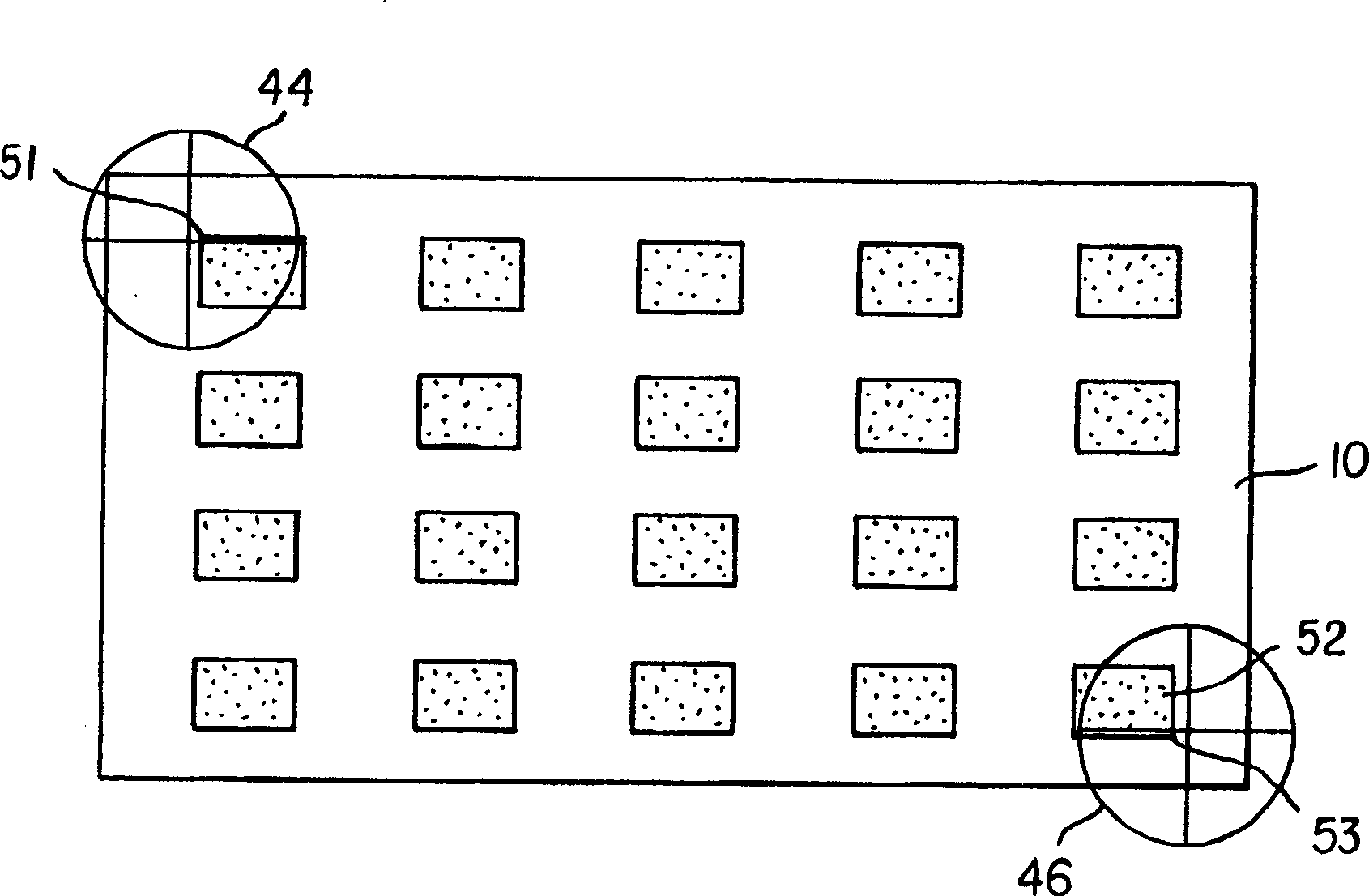
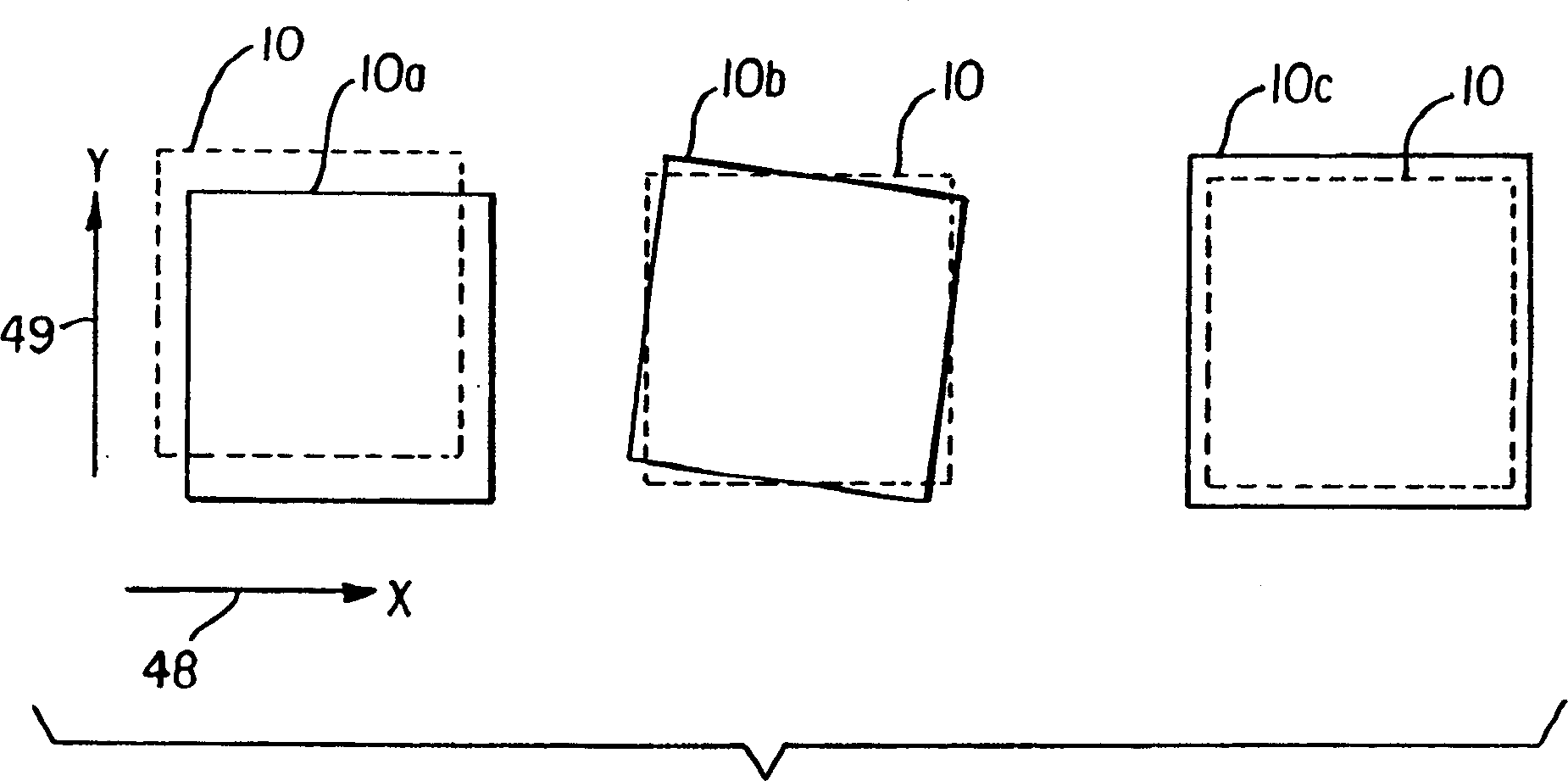
[0034]The term "display" or "display panel" is used to refer to a screen capable of electronically displaying video images or text. The term "pixel" is used in its field-recognized usage to indicate an area of the display panel that can be excited to emit light independently of other areas. The term "OLED device" is used in the meaning of a display device including organic light-emitting diodes as pixels recognized in the field. The color OLED device emits light of at least two colors. The term "multicolor" is used to describe a display panel capable of emitting light of different tones in different areas. In particular, it is used to describe a display panel capable of displaying color images. These areas do not have to be continuous. The term "full color" is used to describe a multi-color display panel capable of emitting in the red, green, and blue regions of the visible spectrum and displaying images in a wide range of tones or combinations of tones. The red, green, and blue co
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap