Method and apparatus for the formation of solar cells with selective emitters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
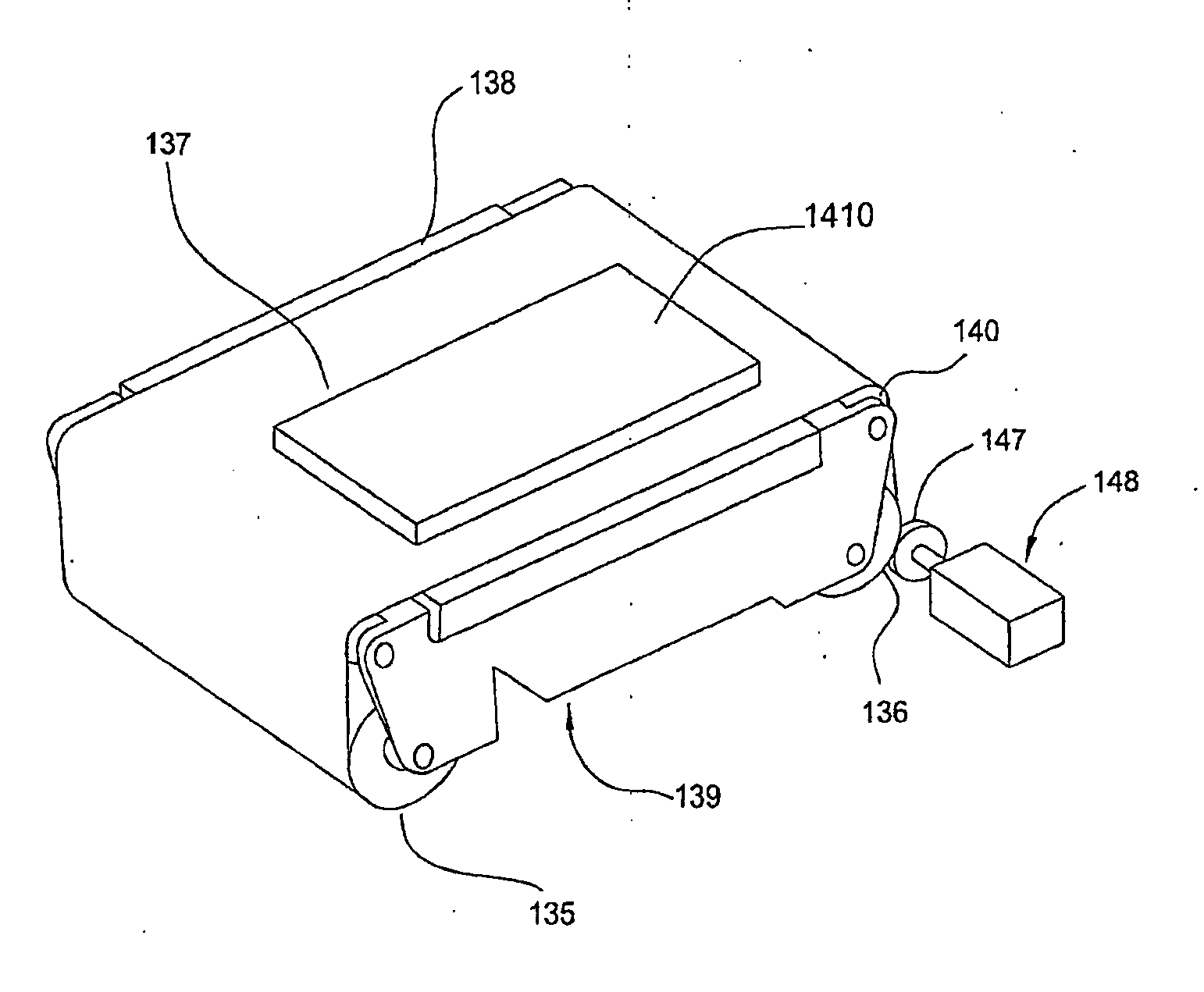
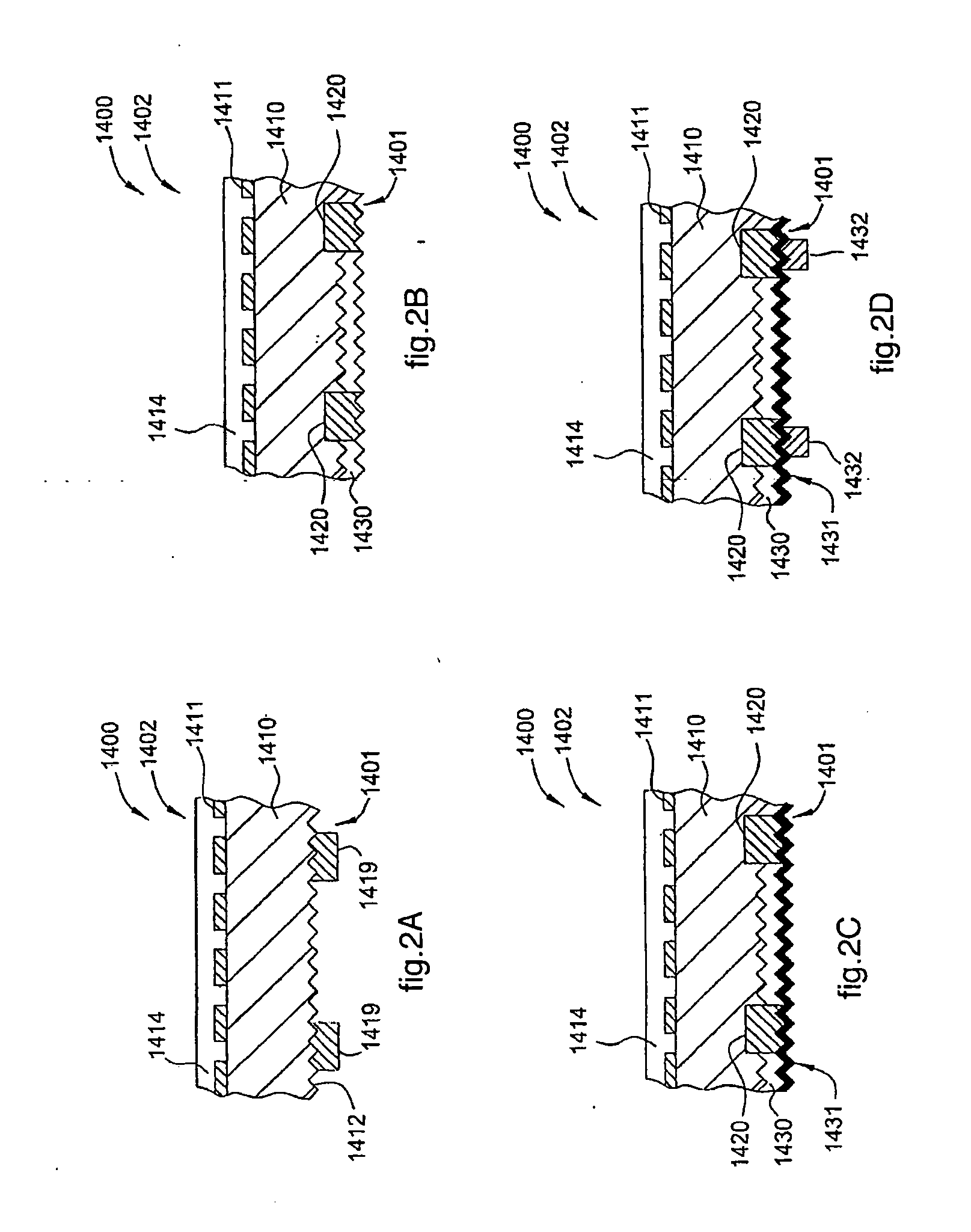
[0131]In a first embodiment, the acquisition of the pattern of the first heavily doped regions 1420 at step 704 provides operation in the field of visible light, adopting an optical filter, and using the optical inspection system 400 and a technique of processing the images acquired by the system 400, based on Fourier transform, while using the control system 101.
[0132]The first embodiment uses the optical inspection system 400, in which the electromagnetic radiation emitted by the radiation source 403 and received by the detector assembly 401, for example by the camera 401A (FIG. 4B), is in the visible wavelength of between about 400 nm and about 900 nm. It has been found that this first embodiment works well in the case of strong contrasts between the SE lines defined by the first heavily doped regions 1420 and the substrate, particularly in the second doped emitter region 1430, due to differences in the texture or steps of different heights. However, if there is a weak natural contr
second embodiment
[0139]The second embodiment according to the invention can be actuated in two variants.
[0140]A first variant of the second embodiment provides controlling the substrate 1410 optically with the detector assembly 401 while it is at a temperature above ambient temperature, even by only a few degrees Celsius (° C.) (FIG. 10). In one embodiment, the range of wavelengths is longer than, or equal to, about 8 μm. In another embodiment the range is between about 8 μm and 14 μm. In the above described ranges, it is possible, unlike in the detection in the visible or short waves of infrared, to use the contrast mechanism represented by the difference in heat emissivity between the SE lines defined by the first heavily doped regions 1420 and the substrate, in particular the second doped emitter region 1430, since at a given temperature the two regions emit different quantities of infrared light. The first variant has the advantage that it does not require any illumination by means of the radiation
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap