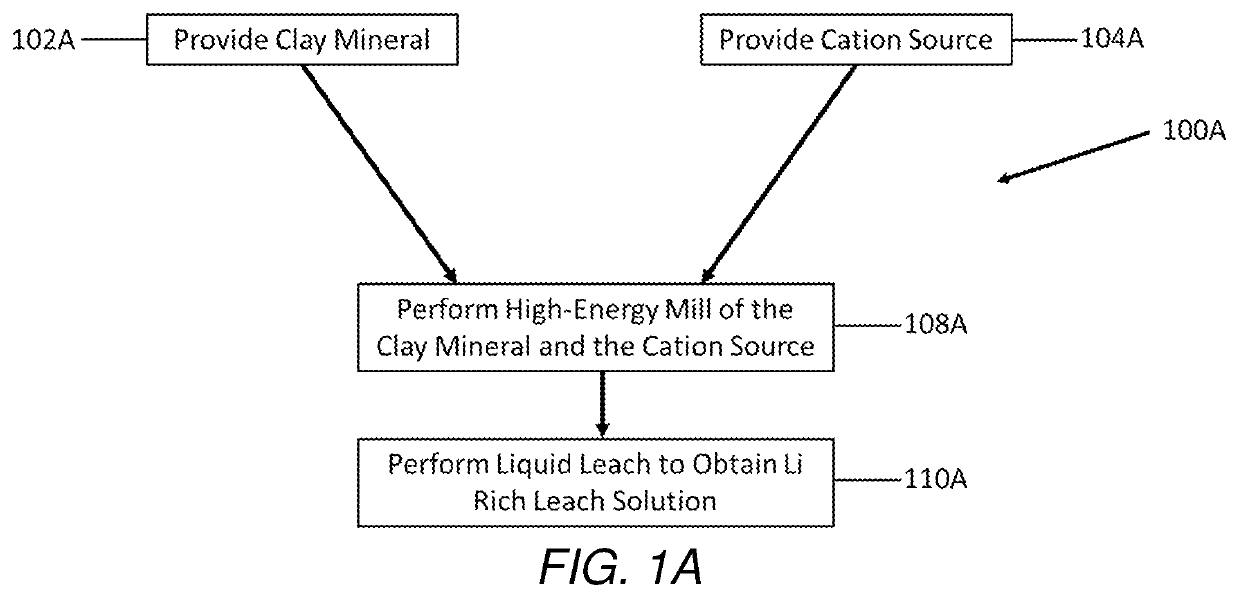
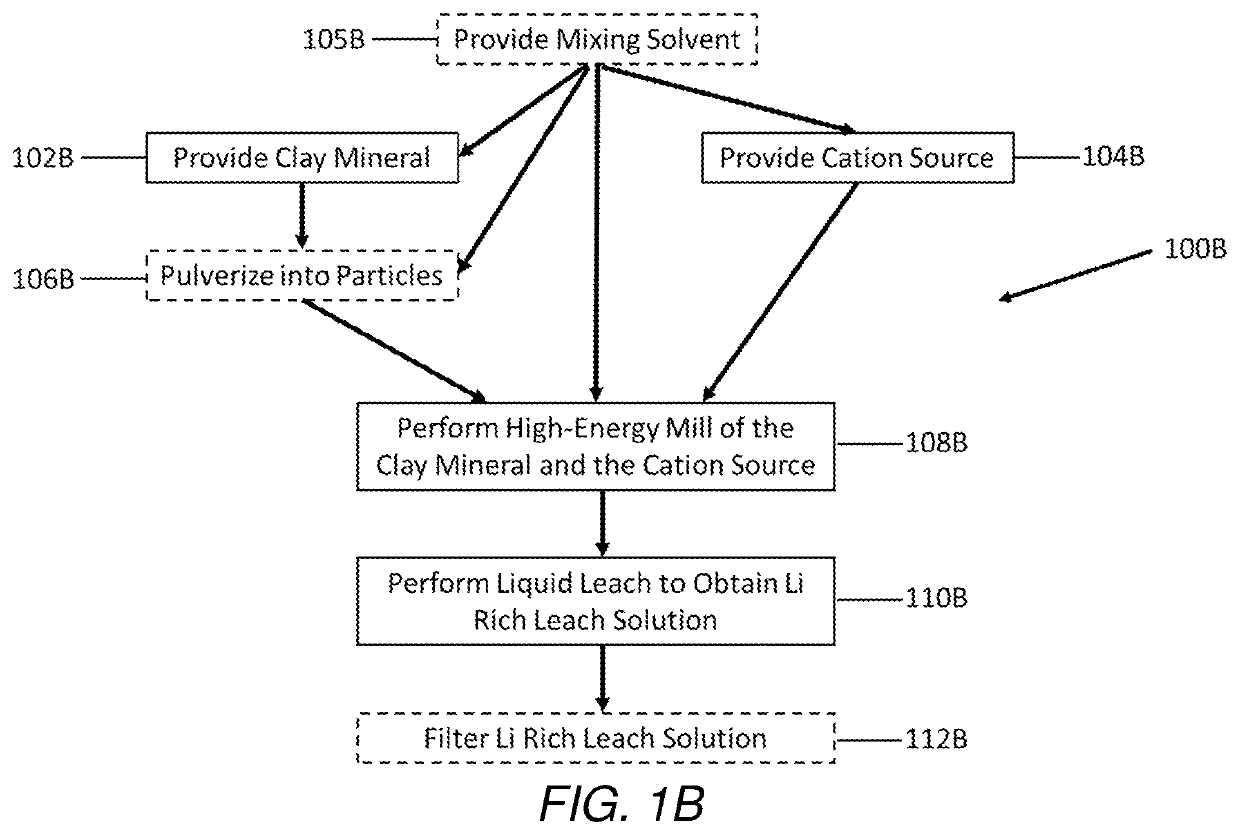
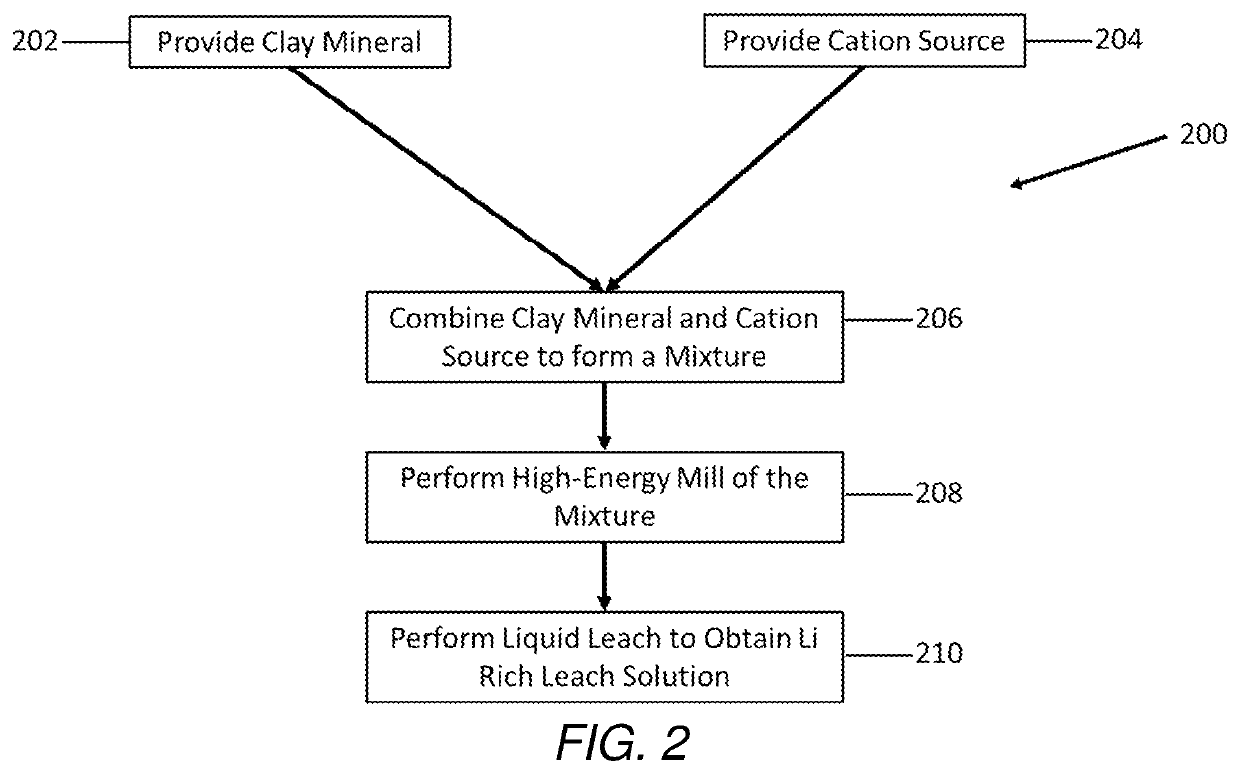
Selective extraction of lithium from clay minerals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0055]FIG. 4 is a chart showing the results of an experiment wherein lithium was extracted from clay materials by a “Non-Selective H2SO4 Leach” process, a “Selective Extraction” process, and a “Selective Leach” process. In the “Non-Selective H2SO4 Leach” process, 37.5 g of clay material was mixed with 112.5 g of H2SO4 (conc. 196 g / L) to form a 150 g slurry. The slurry was leached at 65° C. for 2 hours to form a leaching solution by a non-selective leach. The “Non-Selective H2SO4 Leach” uses conditions typical for H2SO4 leach including acid concentration, temperature, and leach duration. In the “Selective Extraction” process, 40 g of clay material and 4 g NaCl were added into a PM100 planetary ball mill and milled for 2 hours at 500 rpm to form the selective extraction product. In the “Selective Leach” process, 33 g of the milled mixture from the “Selective Extraction” process (i.e. 30 g clay material and 3 g NaCl) was added into 117 g of water to form a slurry, and leached at 65° C....
example 2
tions
[0057]The effect of adding NaCl to the milling step of the process was measured. NaCl powders and fine clay mineral particles in weight ratios of 3:97 (i.e. NaCl to total mixture (i.e. NaCl+Clay)=3%; and corresponding to a Na:Li molar ratio of about 2.7:1) were weighed and placed into a PM100 planetary ball mill and continuously milled for up to 3 hours at 500 rpm rotation. The ball-milled NaCl / clay mixture was then collected and transferred into a glass reactor for water leaching. 31 gram of the NaCl / clay mixture was loaded into the reactor with water added to create 150 gram slurries with salt / clay mixture to water weight ratios of 1:4 (i.e. a 20 wt. % salt / clay mixture loading in water). Once the slurry is created, water leaching is performed at 90° C. under 1000 RPM agitation for up to 20 minutes. A condenser is used to minimize the water loss during leaching. Following a subsequent filtration using 5 um filter paper, the leach solution was collected for further chemical co...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap