Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7 results about "Acyl group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An acyl group is a moiety derived by the removal of one or more hydroxyl groups from an oxoacid, including inorganic acids. It contains a double-bonded oxygen atom and an alkyl group (R-C=O). In organic chemistry, the acyl group (IUPAC name: alkanoyl) is usually derived from a carboxylic acid. Therefore, it has the formula RCO–, where R represents an alkyl group that is linked to the carbon atom of the group by a single bond. Although the term is almost always applied to organic compounds, acyl groups can in principle be derived from other types of acids such as sulfonic acids, phosphonic acids. In the most common arrangement, acyl groups are attached to a larger molecular fragment, in which case the carbon and oxygen atoms are linked by a double bond.
Carbapenem derivatives
InactiveUS6908913B2High antibacterial activityHighly stable to DHPBiocideAntibacterial agentsMorpholineAcyl group
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Photosensitive resin composition and applications thereof
InactiveUS20140087308A1Good cross-sectional shapeLow linear thermal expansion coefficientPhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusHydrogenSilanes
Owner:CHI MEI CORP
Preparation method of pyroxsulam intermediate
ActiveCN113292487AAvoid Polymerization Side ReactionsGuaranteed purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcyl groupDouble bond
The invention discloses a preparation method of a pyroxsulam intermediate, which comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out condensation reaction on 4-alkoxy-1,1,1-trifluoro-3-buten-2-one and phosphonoacetic acid trialkyl ester in an alcohol solvent in the presence of sodium alcoholate to generate an intermediate 3-trifluoromethyl-5,5-dialkoxy pentenoic acid alkyl ester and an isomer of the intermediate 3-trifluoromethyl-5,5-dialkoxy pentenoic acid alkyl ester; and (2) carrying out cyclization reaction on the intermediate generated in the step (1) and ammonium acetate in the presence of a polymerization inhibition catalyst to generate 2-hydroxy-4-trifluoromethylpyridine. According to the method disclosed by the invention, hydroquinone and other polymerization inhibition catalysts are added in the cyclization process, so that polymerization side reaction of a condensation intermediate containing double bonds can be avoided, and the reaction yield and the product purity of the cyclization reaction are ensured. Meanwhile, the 4-butoxy-1,1,1-trifluoro-3-buten-2-one and the phosphonoacetic acid trimethyl ester are adopted as the condensation reaction raw materials, so that not only can higher condensation reaction yield be obtained, but also the cost is lower, and the safety is higher.
Owner:JIANGSU AGROCHEM LAB CO LTD
Method for synthesizing naphthopyran-2-ketone compound
ActiveCN111205261AReduce dosageSimple and mild reaction conditionsOrganic chemistryMeth-Ptru catalyst
Owner:HARBIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SHENZHEN (INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY INNOVATION HARBIN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY SHENZHEN)
Synthesis method of 2-chloro-1-(2, 2-dimethyl-4H-benzo [1, 3] dioxin-6-yl) ethanone
Owner:安徽有吉医药科技有限公司
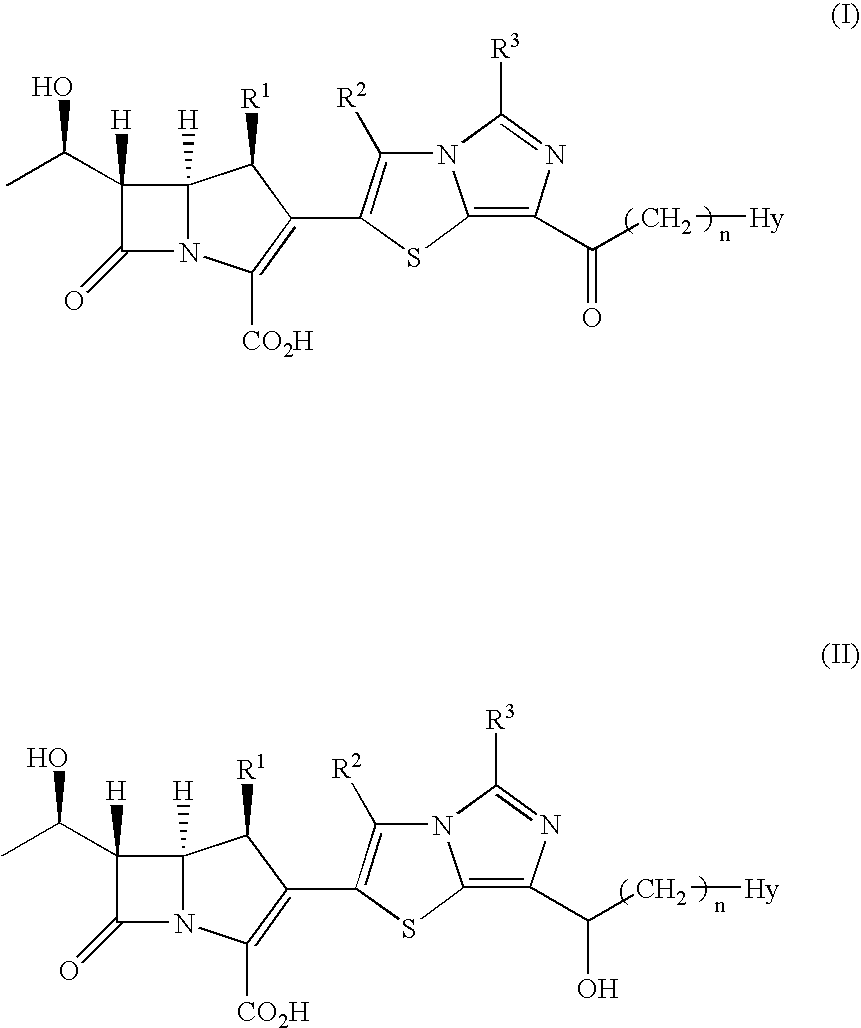
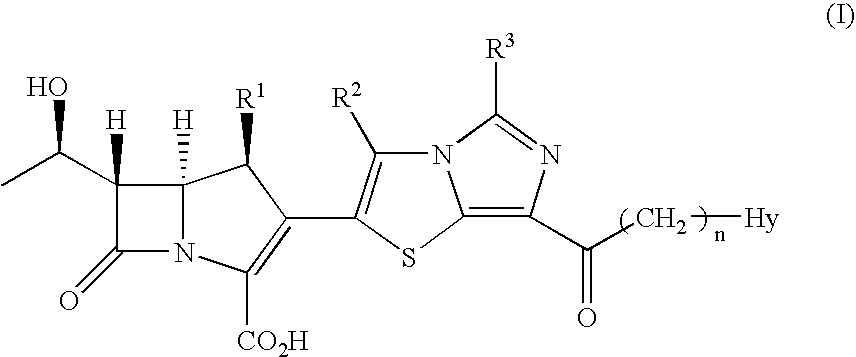
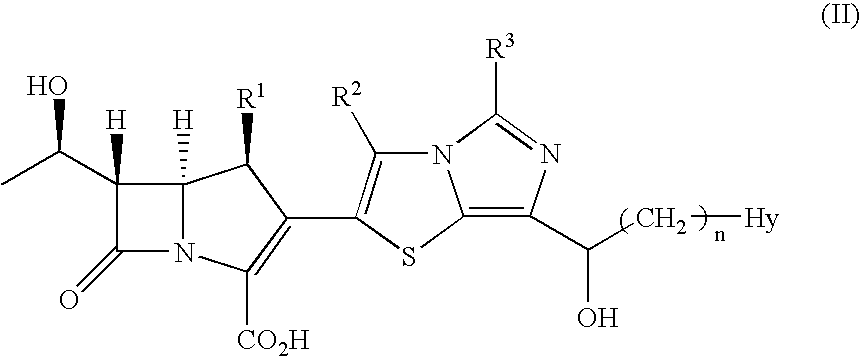
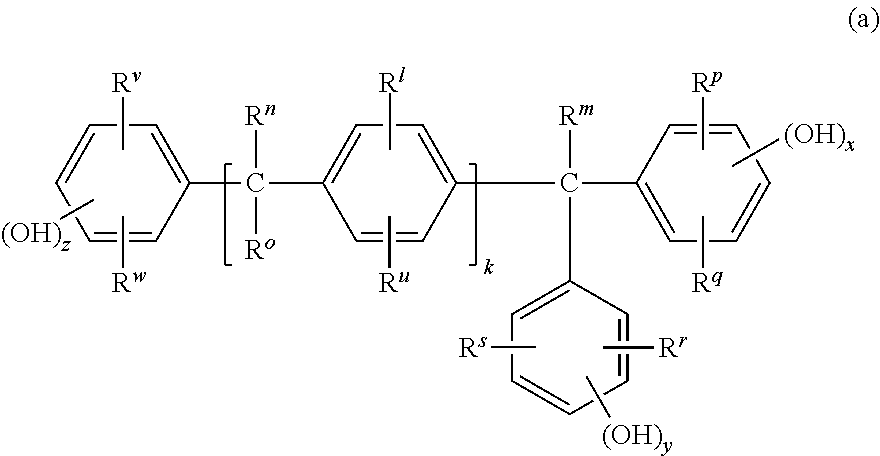
Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
Method for the synthesis of n-(phosphonomethyl)glycine
The present invention is related to a new method for the synthesis of N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine or one of its derivatives selected from the group consisting of its salts, its phosphonate esters and its phosphonate ester salts, comprising the steps of: a) forming a reaction mixture comprising an acid catalyst, N,N′-bis(carboxymethyl)-2,5-diketopiperazine and a compound comprising one or more P—O—P anhydride moieties, wherein said moieties comprise one P atom at the oxidation state (+111) and the other P atom at the oxidation state (+111) or (+V), to form N,N′-bis(phosphonomethyl)-2,5-diketopiperazine, its dehydrated forms or their phosphonate esters; b) hydrolyzing the reaction mixture to form N-(phosphonomethyl)glycine or one of its derivatives selected from the group consisting of its salts, its phosphonate esters and its phosphonate ester salts.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap
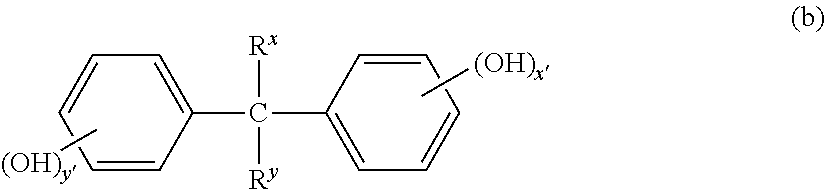

![Synthesis method of 2-chloro-1-(2, 2-dimethyl-4H-benzo [1, 3] dioxin-6-yl) ethanone Synthesis method of 2-chloro-1-(2, 2-dimethyl-4H-benzo [1, 3] dioxin-6-yl) ethanone](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/960fd456-d114-4c0f-98c4-62339868eec0/HDA0003274737570000011.png)
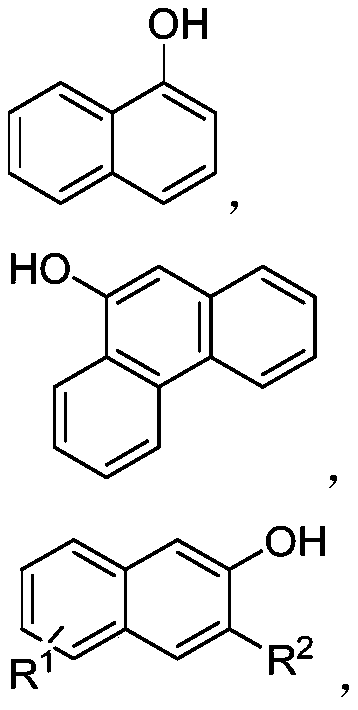
![Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/a21c000d-e2b7-46a7-a5b3-1d549c512639/US08039641-20111018-C00001.png)
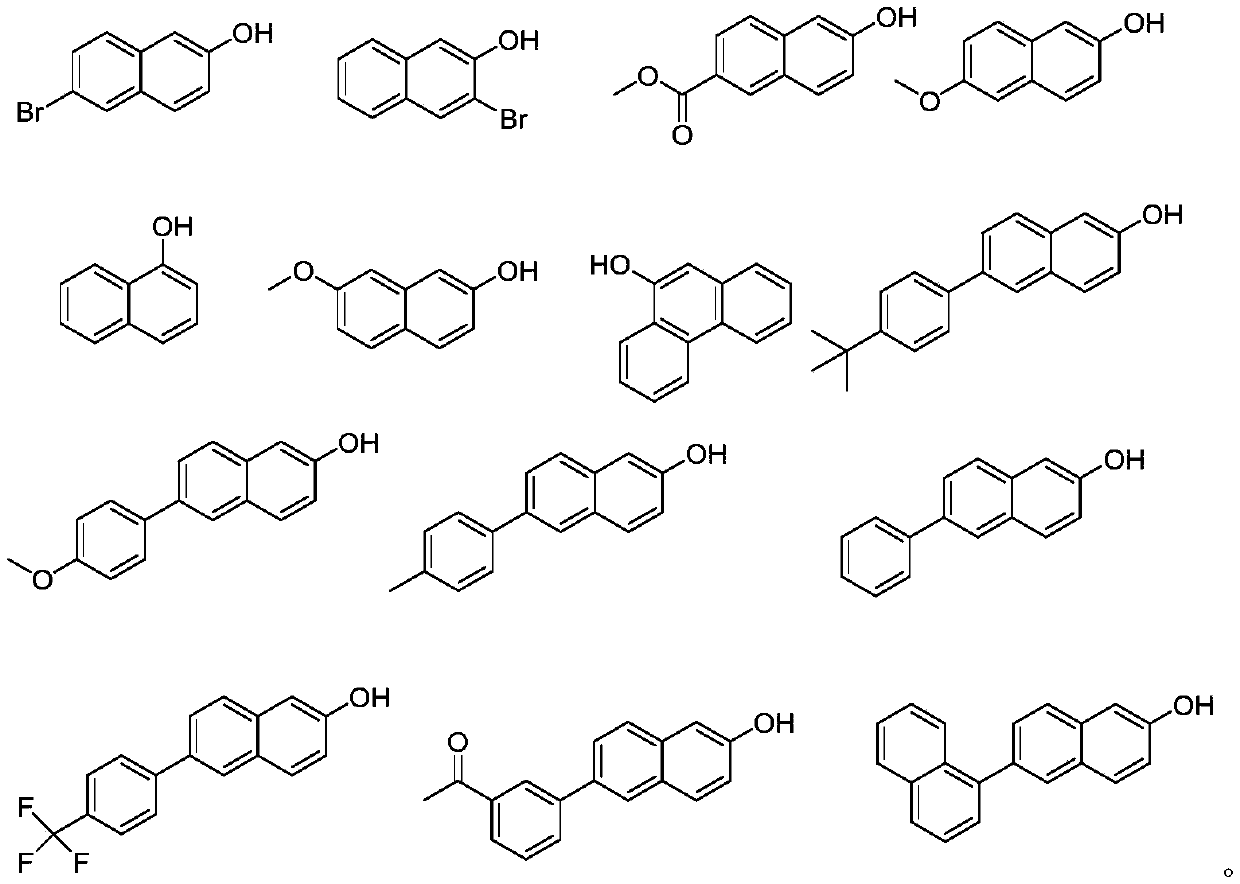
![Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/a21c000d-e2b7-46a7-a5b3-1d549c512639/US08039641-20111018-C00002.png)
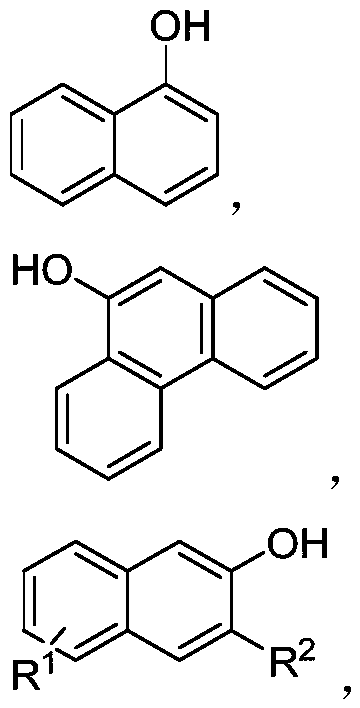
![Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates Tetrahydrofuro[3,2-b] pyrrol-3-one intermediates](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img_release/a21c000d-e2b7-46a7-a5b3-1d549c512639/US08039641-20111018-C00003.png)