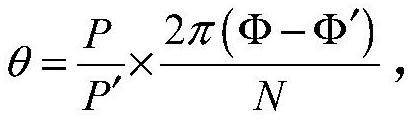Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
12 results about "Pulse-width modulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulse width modulation (PWM), or pulse-duration modulation (PDM), is a method of reducing the average power delivered by an electrical signal, by effectively chopping it up into discrete parts. The average value of voltage (and current) fed to the load is controlled by turning the switch between supply and load on and off at a fast rate. The longer the switch is on compared to the off periods, the higher the total power supplied to the load. Along with MPPT maximum power point tracking, it is one of the primary methods of reducing the output of solar panels to that which can be utilized by a battery. PWM is particularly suited for running inertial loads such as motors, which are not as easily affected by this discrete switching, because they have inertia to react slow. The PWM switching frequency has to be high enough not to affect the load, which is to say that the resultant waveform perceived by the load must be as smooth as possible.
Modifying Duty Cycles of PWM Drive Signals to Compensate for LED Driver Mismatches in a Multi-Channel LED System
ActiveUS20150076999A1Quality improvementImprove viewabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesVIT signalsError signal
An LED (Light Emitting Diode) controller comprises a first LED driver to generate a first PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) drive signal to turn on or turn off, respectively, a first current through a first LED string. Additionally, the LED controller comprises a compensation circuit to generate the first PWM drive signal responsive to a first duty set signals. The first duty set signal is indicative of a first duty cycle set for the first PWM drive signal. The compensation circuit receives a first feedback signal indicative of the first current, generates a first error signal indicative of a difference between a first predetermined target value and the first feedback signal, and generates the first PWM drive signal to have the first duty cycle corresponding to the first duty set signal and further adjusted by the first error signal.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
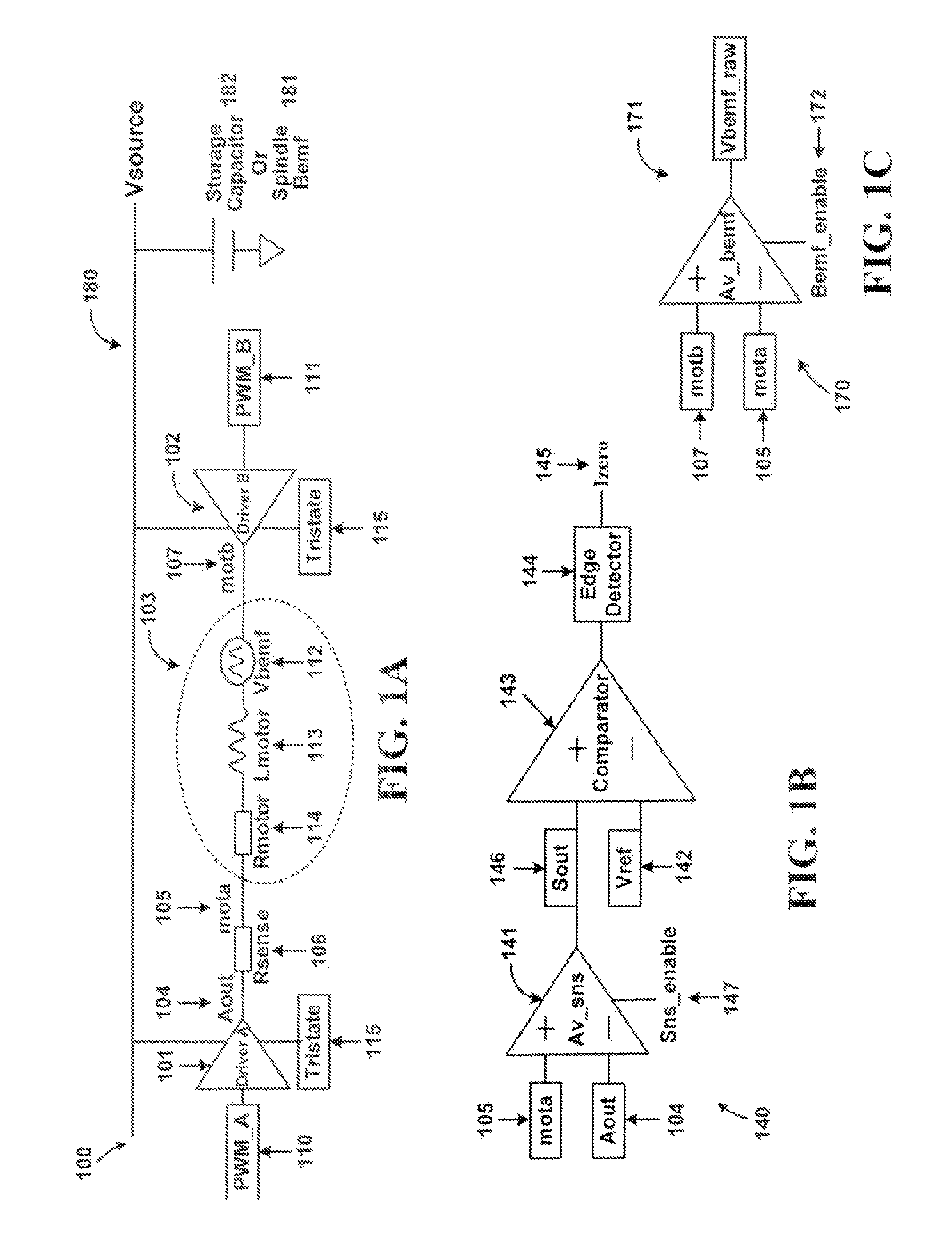
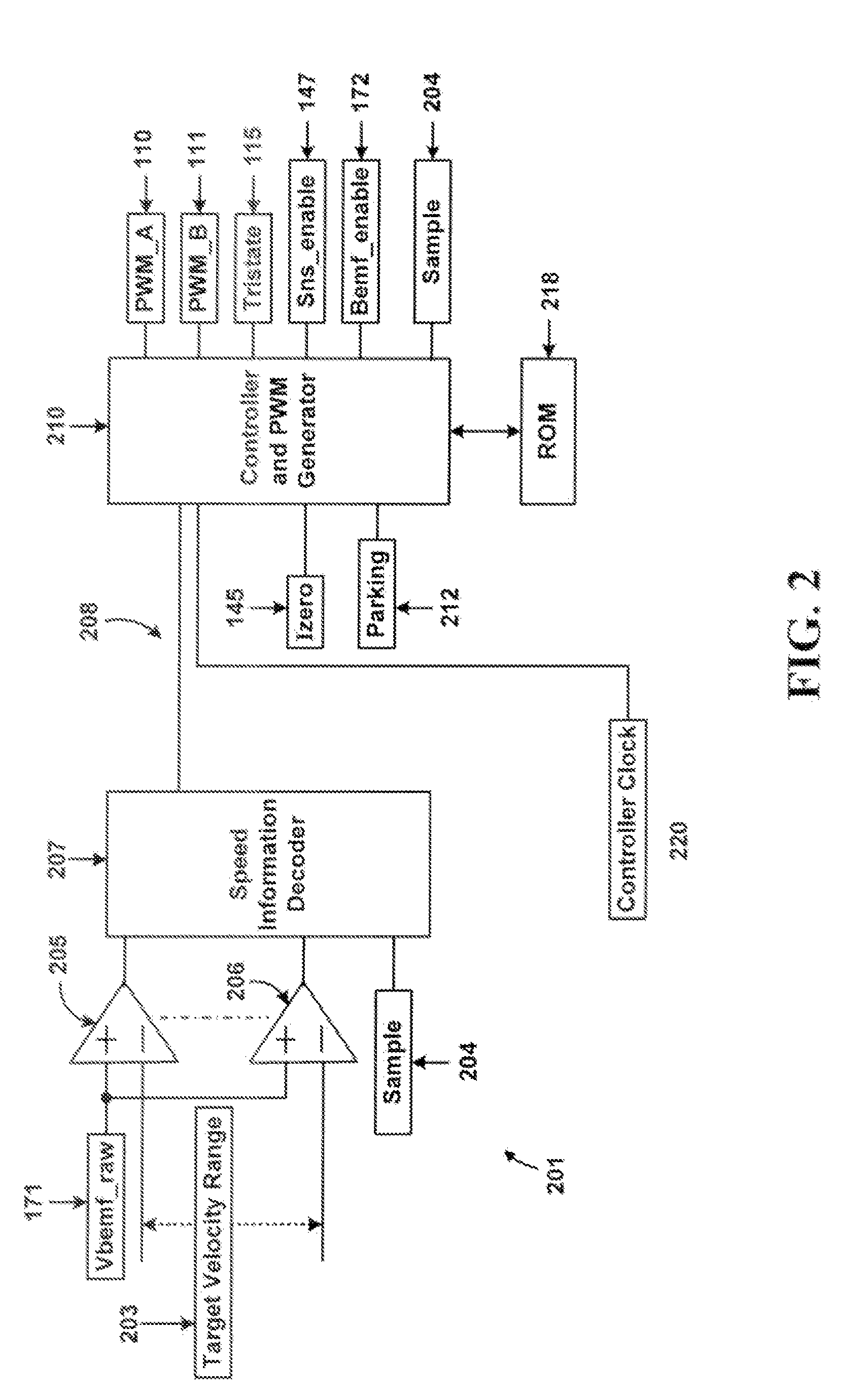
Fan motor speed control circuit
ActiveUS20050019168A1Reduce the degree of vibrationReduce noise problemsAC motor controlSingle motor speed/torque controlElectricityPulse-width modulation
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Voice-coil motor control with zero-current sensing
InactiveUS7622880B1Synchronous motors startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringPulse-width modulation
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Semiconductor lighting driving circuit, semiconductor lighting device, and dimming method for semiconductor lighting device
ActiveCN102510618AGuaranteed uptimeReduce electromagnetic interferenceAc-dc conversion without reversalElectric light circuit arrangementPower factorControl signal
Owner:惠州雷士光电科技有限公司
Improved EMPT algorithm applicable to average model of PWM current transformer
The invention discloses an improved EMPT (electromagnetic pulse technology) algorithm applicable to the average model of a PWM (Pulse-Width Modulation) current transformer. According to the algorithm provided by the invention, a complex switch processing submodule in a traditional EMPT algorithm is omitted, and meanwhile 2 submodules are added for respectively predicting parameters of a subsection average model and rectifying simulation errors caused by inaccurate parameter. According to the invention, simulation is performed by flexibly using segmental average of the PWM current transformer; and while greater integration step simulation is adopted, the correctness of simulation results can also be ensured, so that the improved EMPT algorithm is more convenient to be applied to an actual power system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Wafer spot heating with beam width modulation
ActiveUS20190371631A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLight beamHeat treated
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide a thermal process chamber that includes a substrate support, a first plurality of heating elements disposed over or below the substrate support, and a spot heating module disposed over the substrate support. The spot heating module is utilized to provide local heating of regions on a substrate disposed on the substrate support during processing. Localized heating of the substrate alters temperature profile. The shape of the beam spot produced by the spot heating module can be modified without making changes to the optics of the spot heating module.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
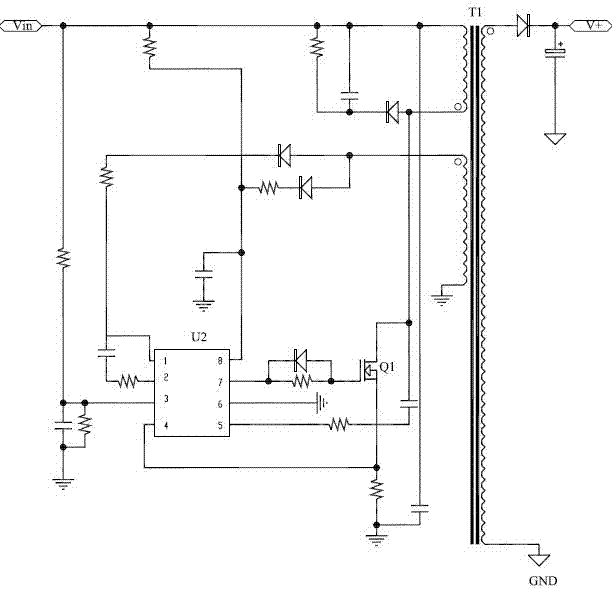
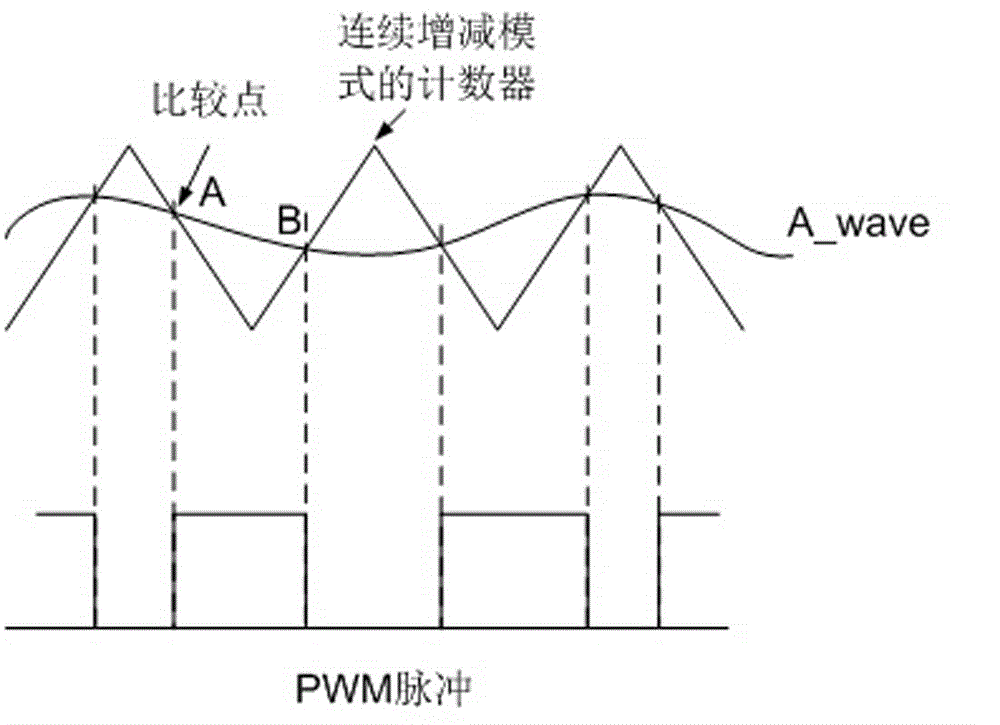
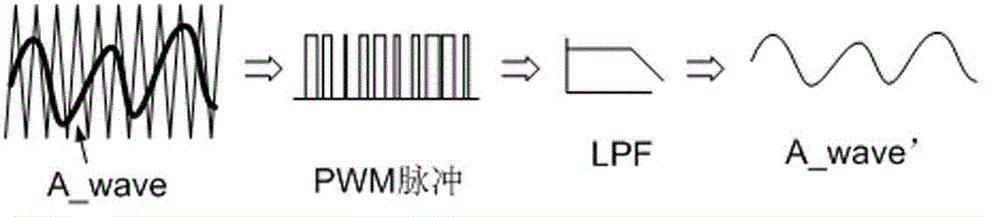
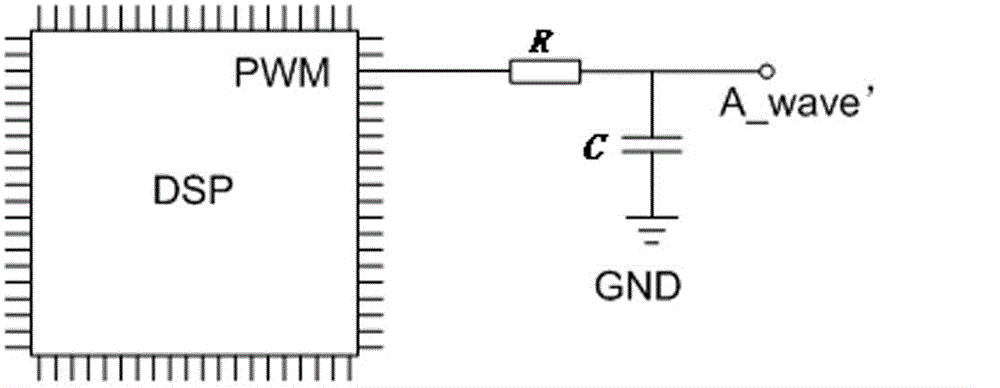
Digital-to-analogue conversion method based on PWM (pulse width modulation) pin of DSP (digital signal processor)
Owner:XIAN LONTEN RENEWABLE ENERGY TECH
Method for identifying grass conditions based on motor load by mowing robot
InactiveCN109997493AImprove work efficiencyFast operationMowersProportion integration differentiationElectric machine
Disclosed is a method for identifying grass conditions based on the motor load by a mowing robot. A processor for central control is arranged on the mowing robot, and is connected with a motor controller. The motor controller is connected with a mowing motor, the mowing motor is connected with a mowing mechanism, and the grass condition identification method is set in the processor. The method includes the following steps: starting a PID (proportion integration differentiation) controller to set the speed of the mowing motor to be V; measuring the PWM (pulse-width modulation) output as D undera no-load condition; if the PWM value output by the PID controller exceeds a set value, determining that grass flourishes at the current position; allowing the mowing robot to reciprocate in situ until the PWM value output by the PID controller returns to normal. The method has the advantages that the grass conditions at the current position can be directly determined, the working mode of the mowing robot can be guided, and accordingly, the working efficiency is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU JINGYI INTELLIGENT SCI & TECH
Photoelectric pod and photoelectric pod control method
ActiveCN113241974ALighten processing tasksEasy wiringAircraft componentsMultiple motor speed/torque controlComputer hardwareElectric machine
The embodiment of the invention discloses a photoelectric pod and a photoelectric pod control method. The photoelectric pod comprises a core processor, an angle analysis processor and a plurality of motor encoders, wherein the core processor is connected with the angle analysis processor, and the angle analysis processor is connected with the plurality of motor encoders; each motor encoder is used for acquiring rotation angle information of the corresponding motor and sending the rotation angle information to the angle analysis processor; the angle analysis processor is used for receiving the rotation angle information sent by each motor encoder, preprocessing the rotation angle information and sending the preprocessed rotation angle information to the core processor; and the core processor is used for generating a pulse width modulation signal for at least one target motor according to the preprocessed rotation angle information when the preprocessed rotation angle information is received. By implementing the photoelectric pod, the wiring in the photoelectric pod can be simplified, and the wiring complexity is reduced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KEII ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
Aviation permanent magnet motor rotor position angle redundancy control system and method based on AD2S1210
PendingCN114865976AImplement redundant controlGuaranteed uptimeElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlAviationLoop control
Owner:SHAANXI AVIATION ELECTRICAL
Electric motor and air-conditioning device equipped with same
PendingCN113169697AInhibition lossReduce power lossElectric motor controlAC motor controlRotational axisCarrier signal
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap