Genetically engineered bacteria synthesizing styrene taking biomass hydrolysate as raw material and construction method and application thereof
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and hydrolyzate, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of limited yield and high toxicity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
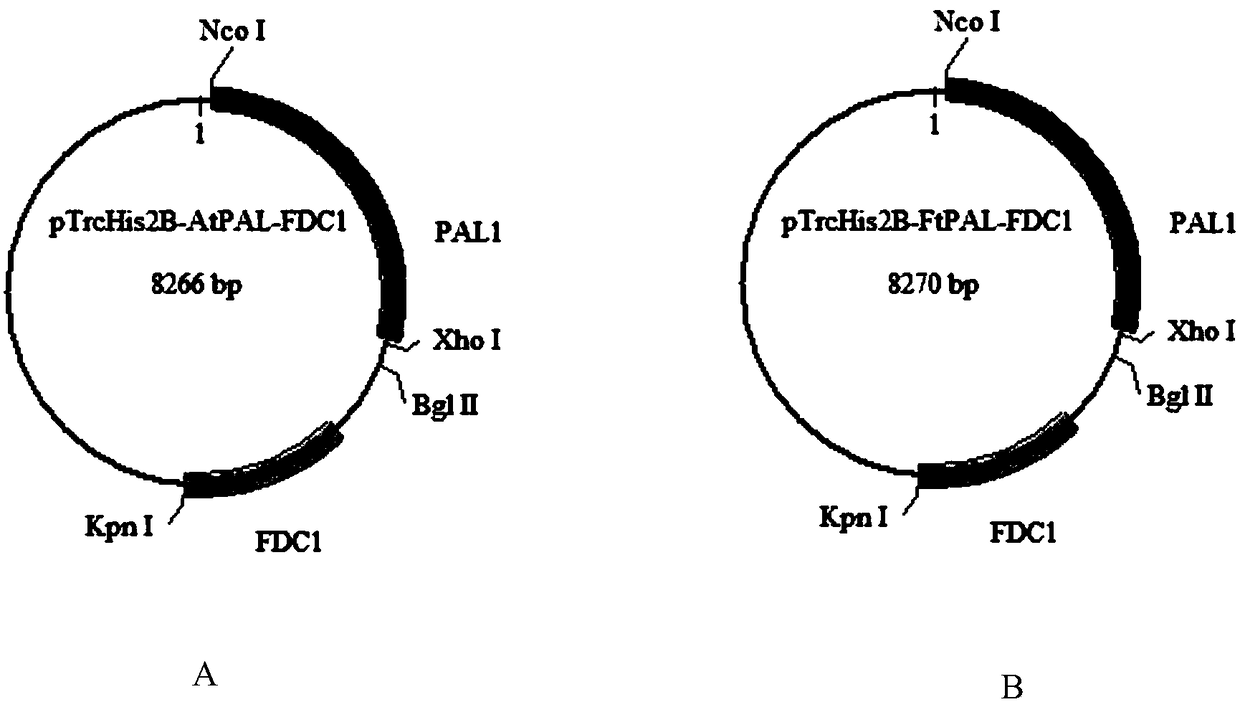
[0049] (1) Construction of phenylalanine ammonialase-related gene and cinnamic acid decarboxylase-related gene vector plasmid (pTrcHis plasmid) ( image 3 )
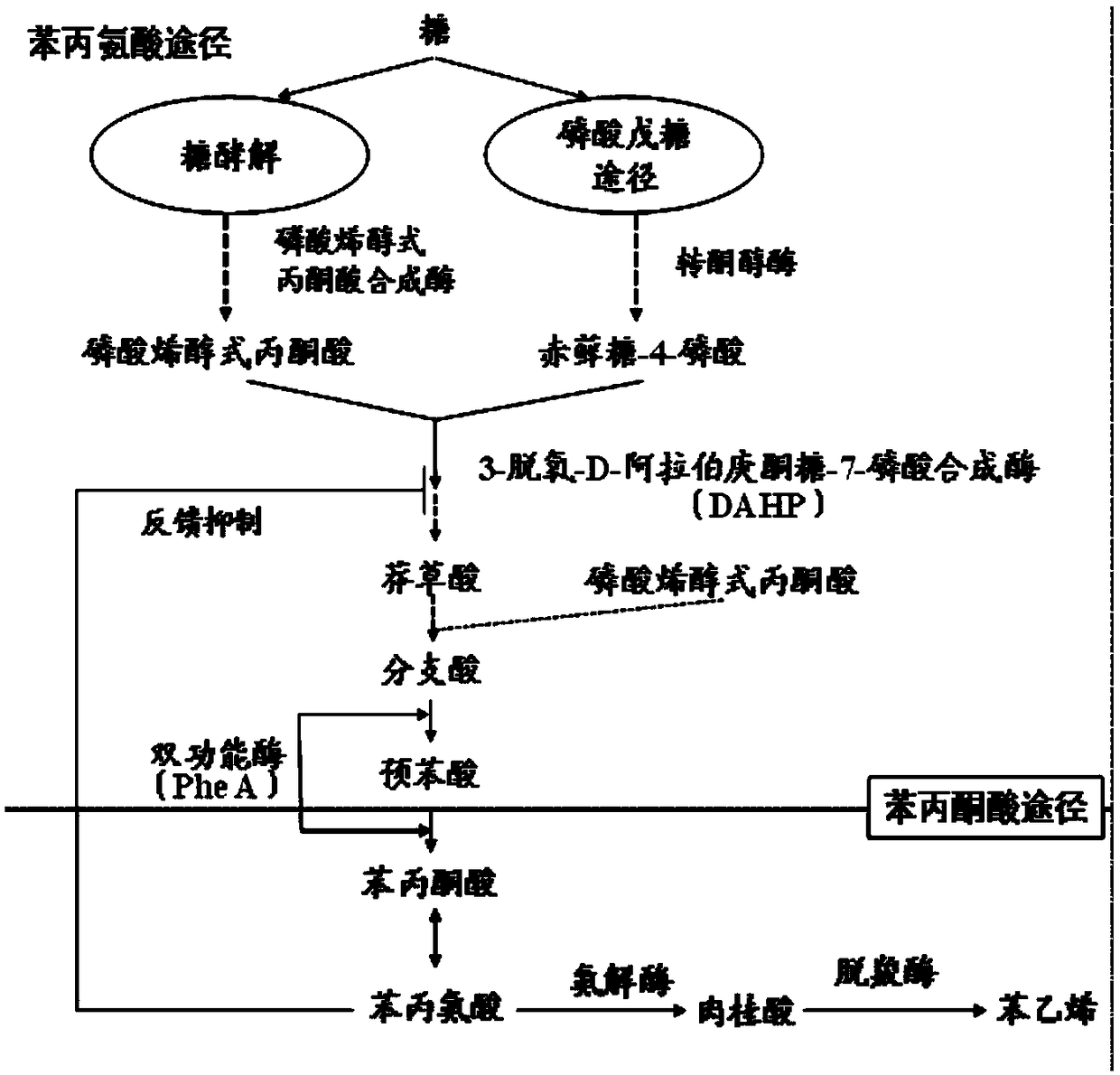
[0050] By co-expressing the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene AtPAL (AtPAL, ID: 824493) and the cinnamic acid decarboxylase gene (FDC1, GI: 330443520) from Arabidopsis thaliana in Escherichia coli (E.coli) Obtain the first set of plasmids.
[0051] By co-expressing the phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene (FtPAL, (EC: 4.3.1.24)) derived from wrinkled leaf parsley (Petroselinum crispum) in Escherichia coli (E.coli), the cinnamate decarboxylase gene (FDC1, GI: 330443520) to obtain a second set of plasmids.
[0052] The above genes are all known genes, and the acquisition method uses the genome as a template for PCR, or direct gene chemical synthesis. The above methods belong to mature molecular biology methods, and there is no particularity. The genes required for this experiment were codon-optimized and sent to BGI to synthesi
Embodiment 2
[0079] Example 2 Fermentation and Synthesis of Styrene Using Biomass Hydrolyzate as Raw Material
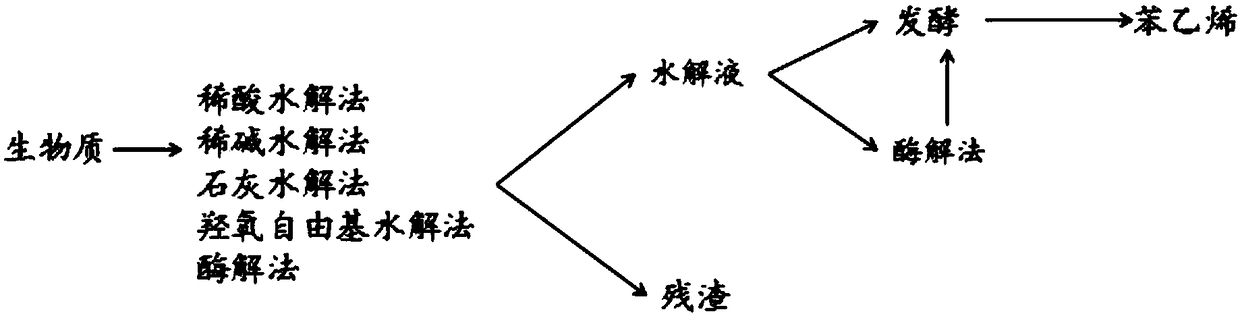
[0080] (1) Preparation of biomass hydrolyzate ( figure 1 )
[0081] Dilute acid hydrolysis method: take 20g of biomass pulverization (it can be one of straw, wood, duckweed, seaweed or corn, or a mixture of two or more of these substances, the mass ratio is 1; 1), and use 1% The sulfuric acid was hydrolyzed at 75-95°C for 5 hours, the residue was removed by filtration, and the residue was removed by centrifugation. After adjusting the pH value to 7.0±0.1 with NaOH, add 1g / L laccase or horseradish peroxidase or pass through soybean shell For oxidase, warm bath at 37°C for 1 hour, centrifuge and then use 1g / L laccase or horseradish peroxidase or bean hull peroxidase to warm bath at 37°C for 1 hour, and centrifuge the obtained hydrolyzate as carbon source for fermentation.
[0082] Dilute alkali hydrolysis method: Take 20g of crushed biomass, use 1% NaOH to hydrolyze at 75-95°C f
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap