Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
12 results about "Transfer function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of an electronic or control system component is a mathematical function which theoretically models the device's output for each possible input. In its simplest form, this function is a two-dimensional graph of an independent scalar input versus the dependent scalar output, called a transfer curve or characteristic curve. Transfer functions for components are used to design and analyze systems assembled from components, particularly using the block diagram technique, in electronics and control theory.
Method and apparatus for measuring temporal response characteristics of digital mirror devices
InactiveUS7095494B2Accurate measurementAngle measurementPhase-affecting property measurementsDamping factorPhotodetector
A method and system for measuring the temporal response of a micromirror array to a variety of driving signals. A micromirror array is illuminated with a coherent light source so that a diffraction pattern is reflected from the micromirror array. One or more photodetectors are aligned with spots of light in the diffraction pattern that correspond to orders of the diffraction pattern. Diffraction pattern theory predicts that the intensity of these spots of light will vary as the tilt angle of the micromirrors is changed. Thus, by measuring the relative intensity of the spots of light as the micromirror array is provided with a variety of driving signals, many performance characteristics of the micromirror array can be measured. Some of these characteristics include the impulse response, the forced resonant frequency (i.e. the natural frequency), the damped resonant frequency, the quality factor of the micromirror response, the damping factor of the micromirror response, and the frequency transfer function. According to another aspect of the invention, the electromechanical compliance of the micromirrors in the micromirror array can also be measured. It is further contemplated that all of these measurements can be localized to specific regions on the surface of the micromirror array so that the variance of different characteristics across its surface can be analyzed. Another aspect of the disclosed invention is the measurement of the tilt angle of the micromirror array at a non-biased state.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Apparatus and method to calibrate servo sensors in a noisy environment
InactiveUS6865052B2Alignment for track following on tapesRecord information storageEngineeringCalibration curve
A method and apparatus to calibrate a servo sensor disposed on a tape head located adjacent a moving magnetic tape is disclosed where that magnetic tape includes at least one servo edge comprising an interface between a first recorded signal and a second recorded signal, and where the servo sensor provides a servo signal, and where an independent position sensor provides an IPS signal. The method first samples the servo signal and the IPS signal, calculates a transfer function, and forms a first calibration curve. The method then forms an average residual error value. If that average residual error exceeds the maximum allowable residual error, then the method applies an offset to the first calibration curve to form a second calibration curve. That second calibration curve is saved for subsequent use during, for example, read / write / erase operations.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
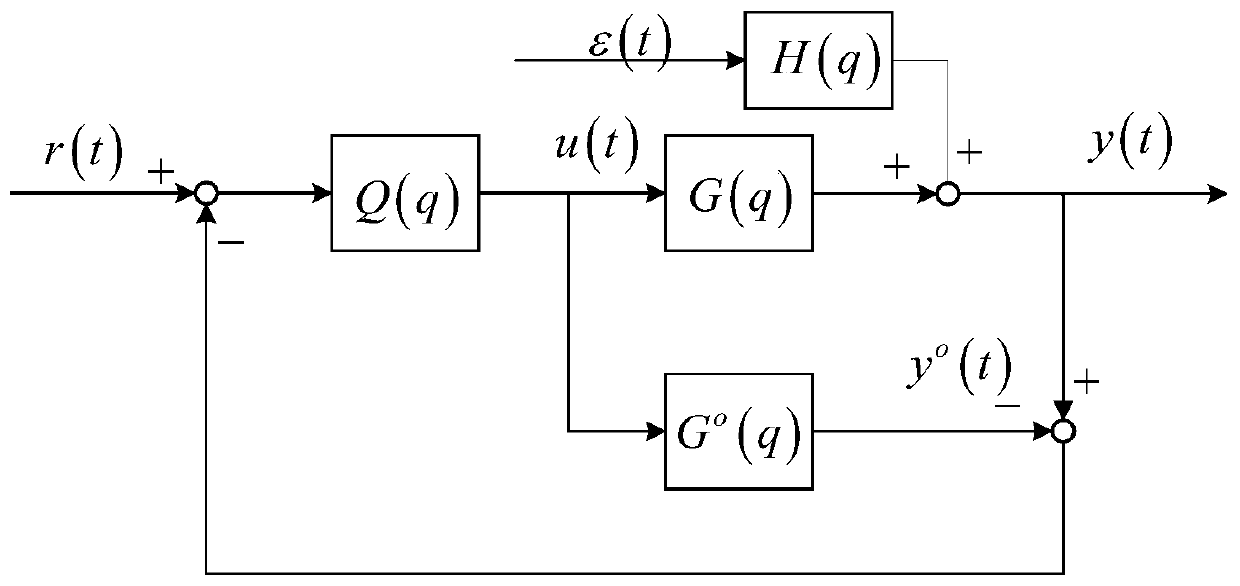
Closed-loop system identification method based on slope response and known time delay
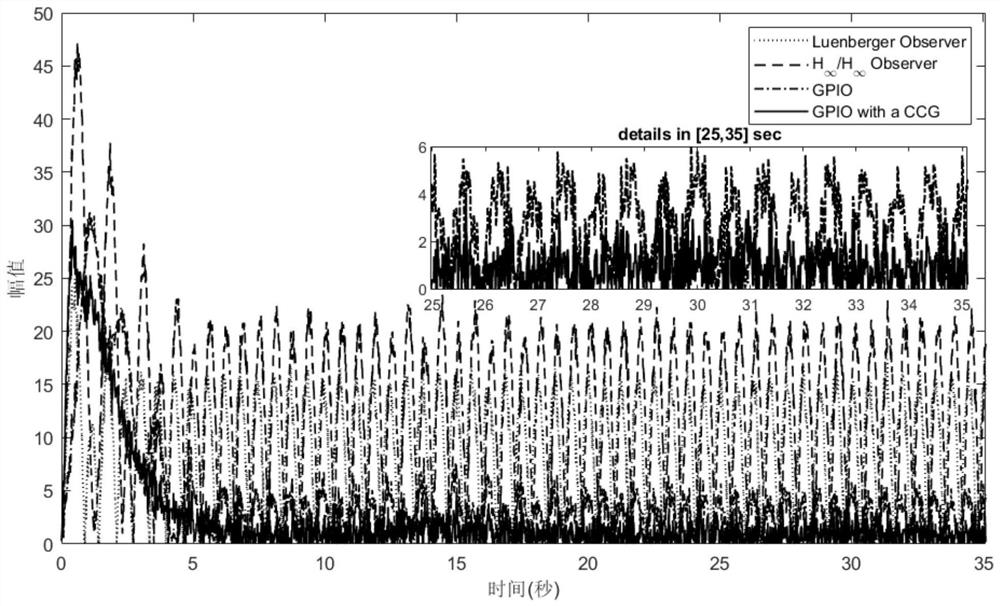
The invention provides a closed-loop system identification method based on slope response and known time delay, and belongs to the technical field of automatic control. The method comprises step: describing a controlled object by adopting a second-order inertia and pure delay transfer function; calculating the input data set and the output data set collected in the slope response process to obtainan available input data set and an available output data set; obtaining a processing input data set and a processing output data set through algebraic operation based on the available input data setand the available output data set; based on the feedback controller coefficient, processing the input data set and the output data set, calculating to obtain a final data set, and obtaining a final big data set through algebraic transformation; and obtaining a to-be-identified coefficient of the controlled object through matrix calculation based on the obtained last big data set and the availableoutput data set. According to the method, the controlled object can be identified as a continuous system, a basis is provided for dynamic characteristic analysis and controller design optimization ofthe controlled object, and the method has good industrial application potential.
Owner:HUADIAN WEIFANG POWER GENERATION CO LTD
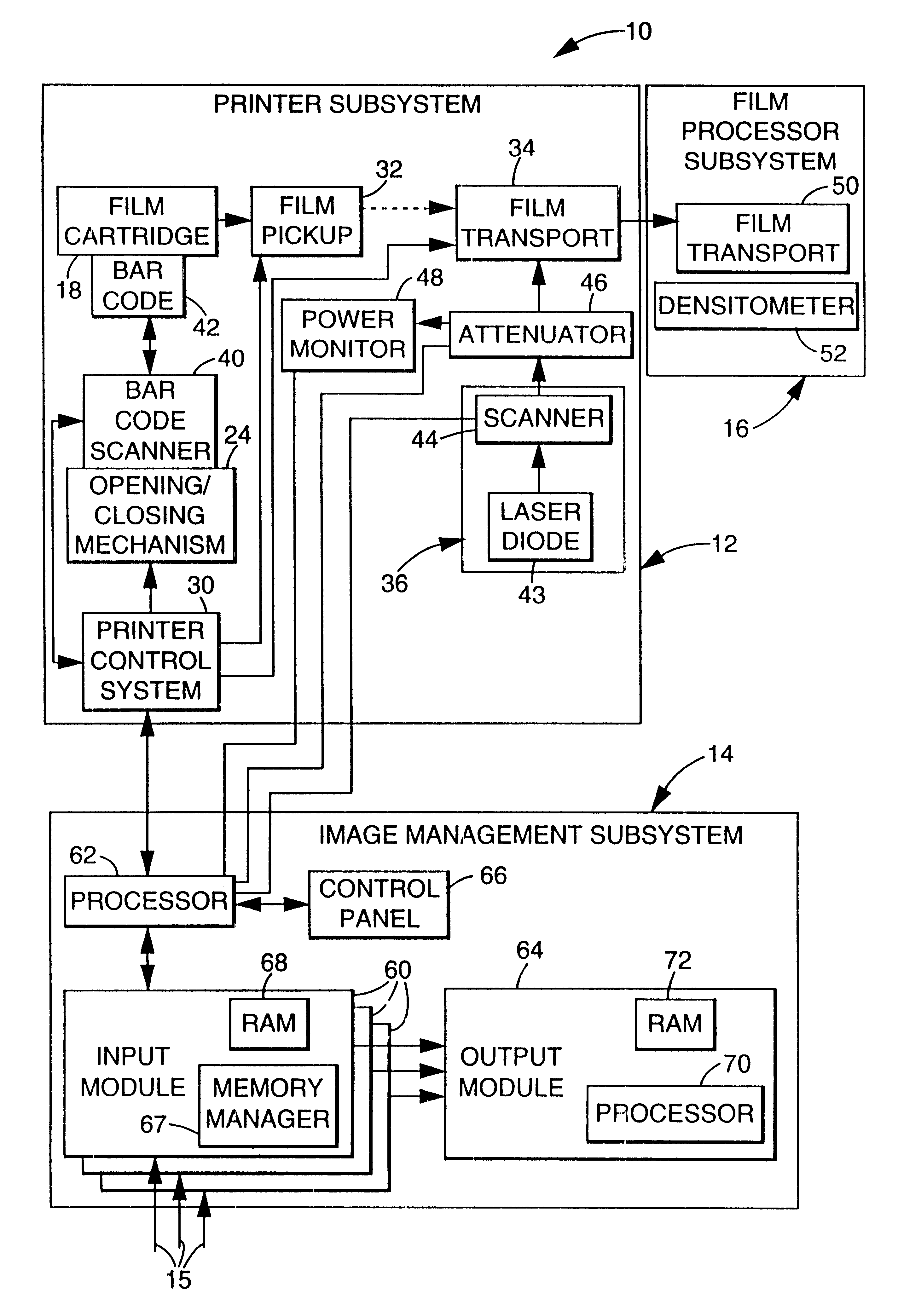
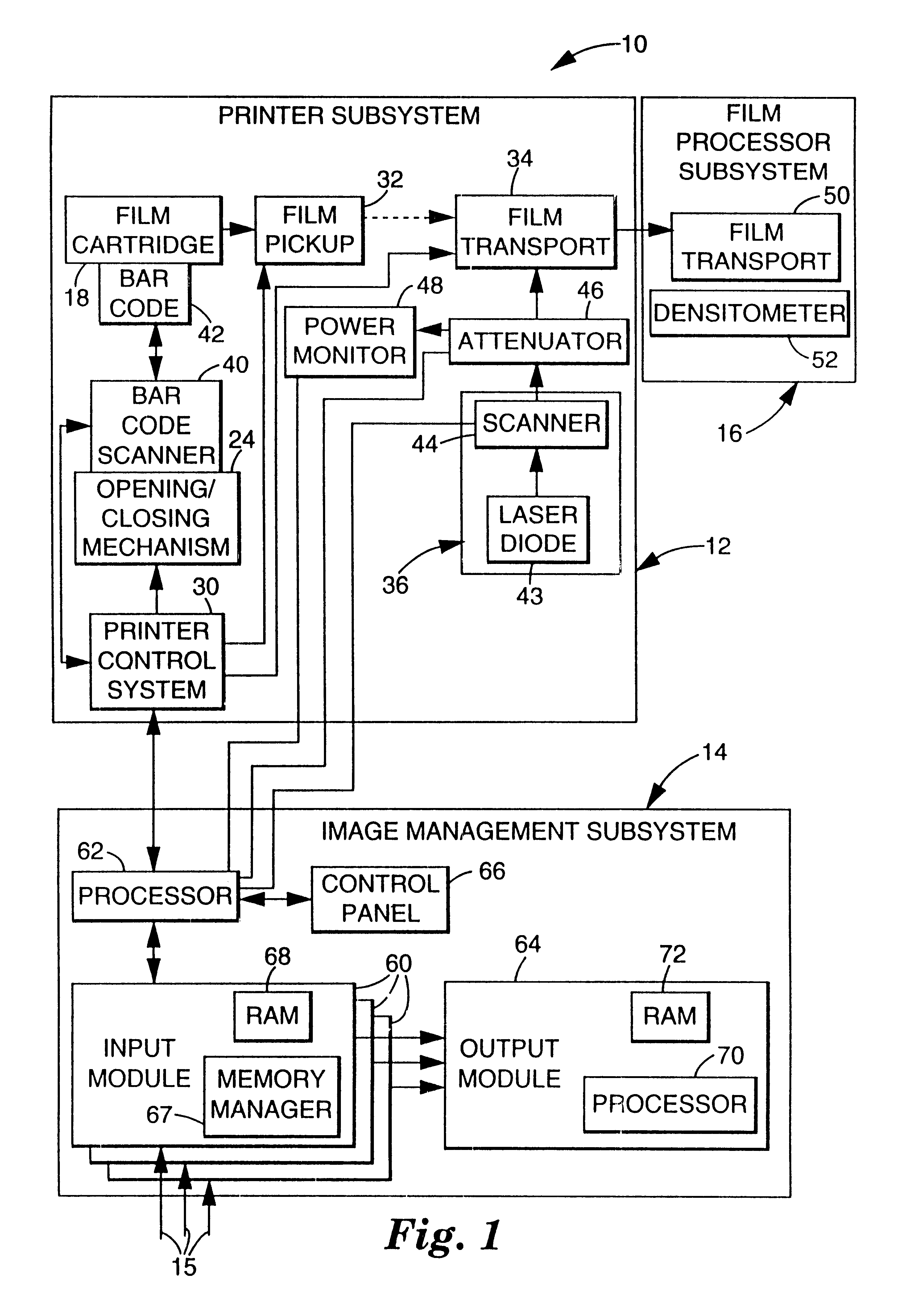
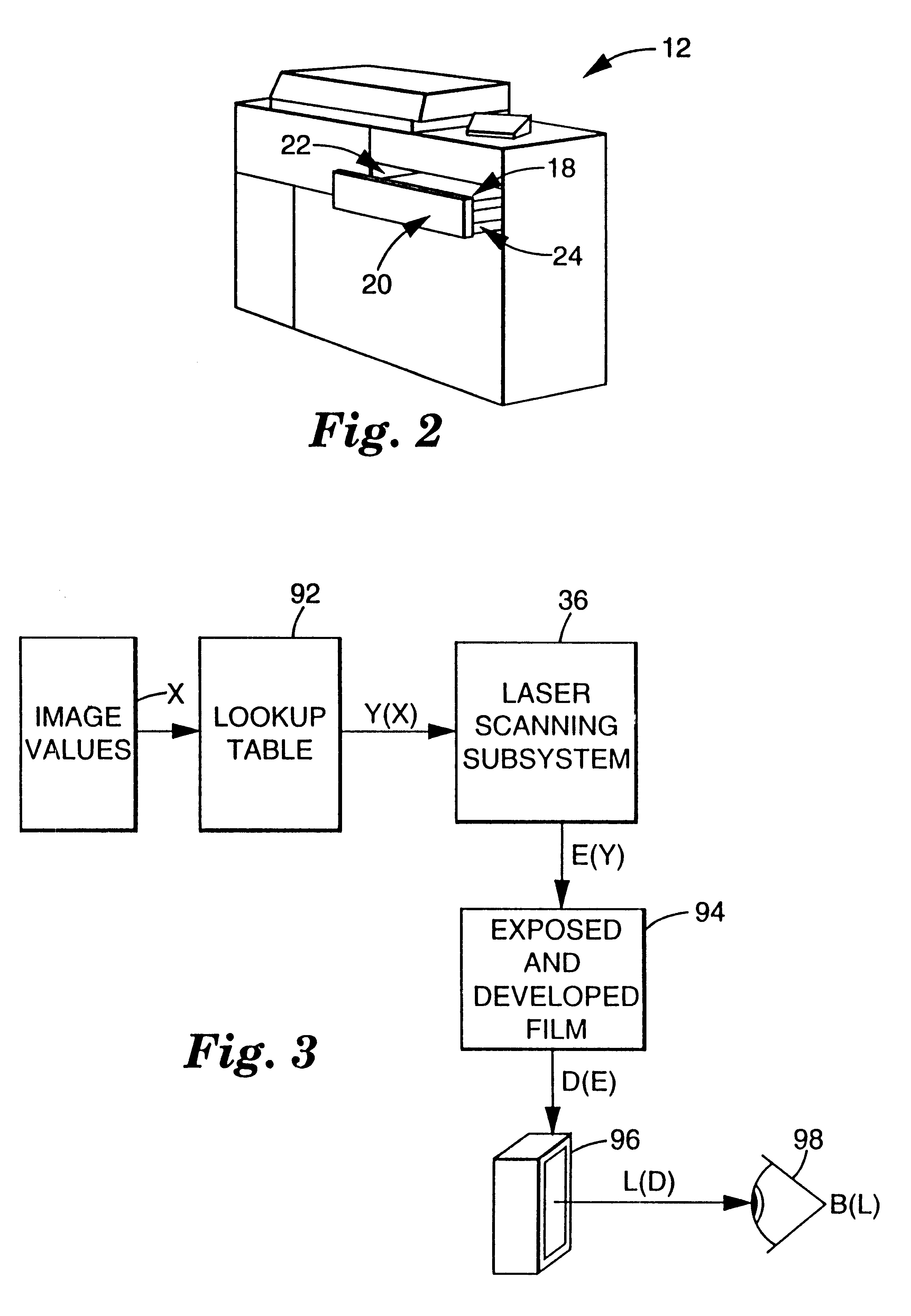
Multi-user digital laser imaging system
InactiveUSRE38005E1Minimize the differenceAddressing slow performanceCathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsLaser imagingBarcode
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Equalization of an Audio Signal
ActiveUS20130195286A1MicrophonesLoudspeakersPhase shiftedEqualization
A method of processing an input audio signal, the method comprising forming a plurality of output audio signals from the input audio signal, wherein each output audio signal is formed by performing respective processing on the input audio signal, wherein for a first output audio signal there is a target audio equalization operation comprising a target filter twice, wherein for the first output 10 audio signal, the respective processing comprises a first audio equalization operation, the first audio equalization operation being the target audio equalization operation modified to compensate for phase shifts that correspond to zeros of the transfer function of the target audio equalization operation, wherein for each output audio signal other than the first output audio signal, the respective 15 processing comprises a compensation filter that compensates for phase shifts that correspond to poles of the transfer function of the target audio equalization operation. 20
Owner:OXFORD DIGITAL
Thin shell movable powder pellet solid engine modal parameter test method
The invention provides a thin shell movable powder pellet solid engine modal parameter test method. The method comprises a step of using engine end part axial excitation, a step of uniformly distributing measuring points at an engine axial direction along a quadrant direction, a step of testing all transfer functions in one time, a step of using a least square frequency domain method to fit a modal parameter, and a step of judging a modal test correctness in the whole with the combination of vibration characteristics. According to the test method, the technical problems of difficult modal parameter rank determination, poor modal frequency repeatability and easy change of a vibration type in the modal parameter test of the thin shell movable powder pellet tactical solid motor are solved.
Owner:TIANJIN AEROSPACE RELIA TECH +2
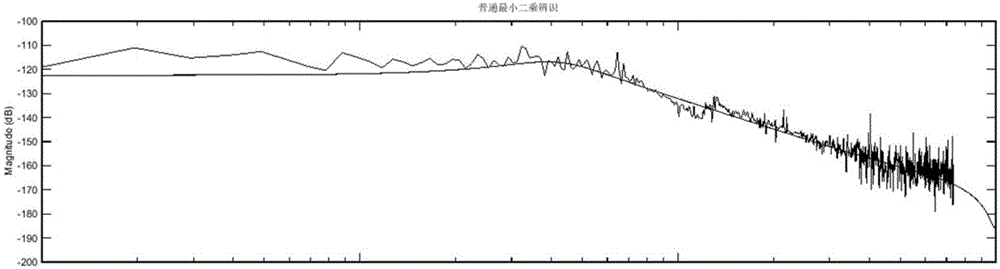
Spectral noise reduction method based on digital filtering
ActiveCN111289106ANo Runge phenomenonThe results are preciseRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationAlgorithmAmplitude response
Owner:上海如海仪器设备有限公司
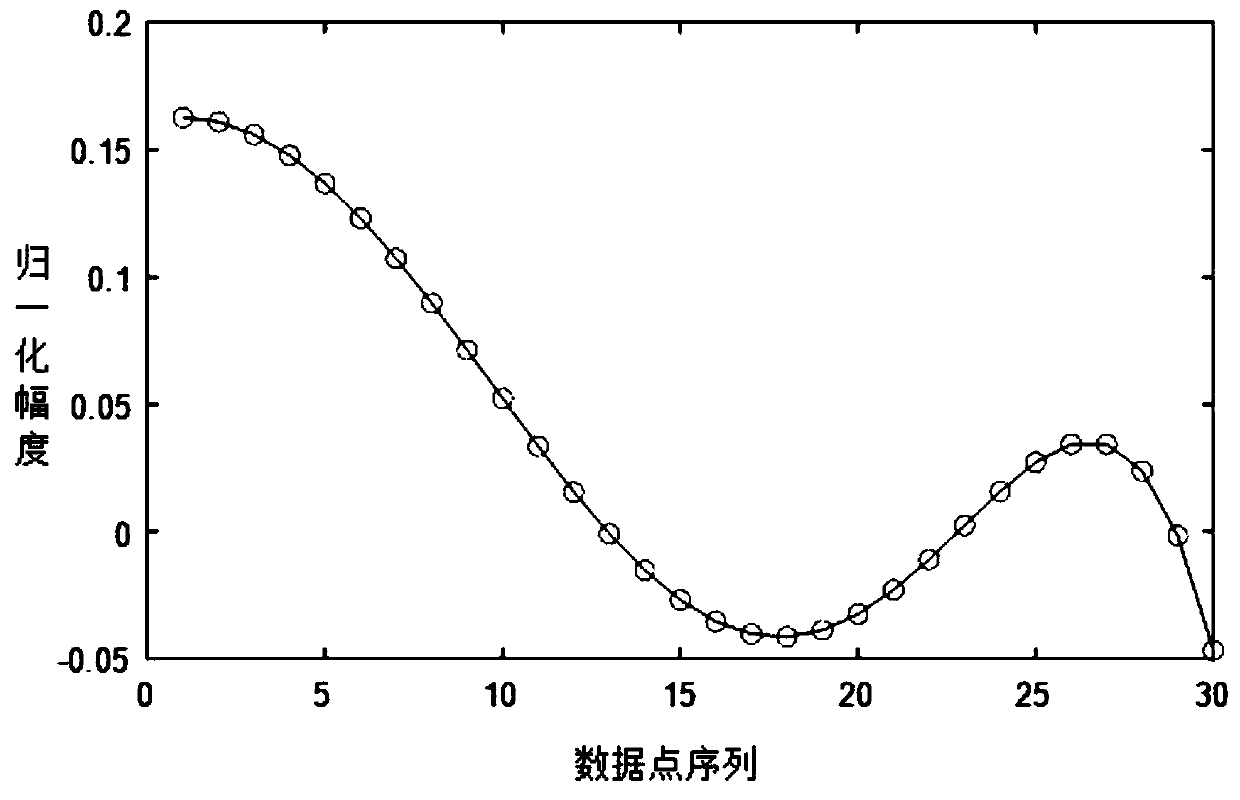
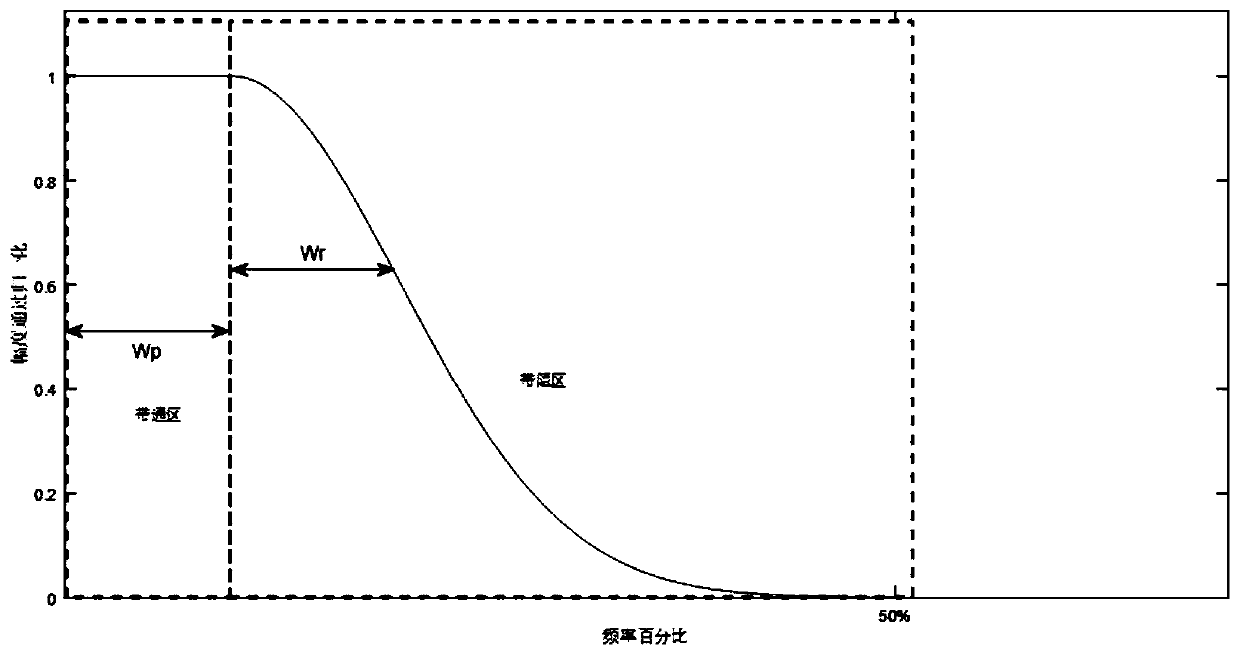
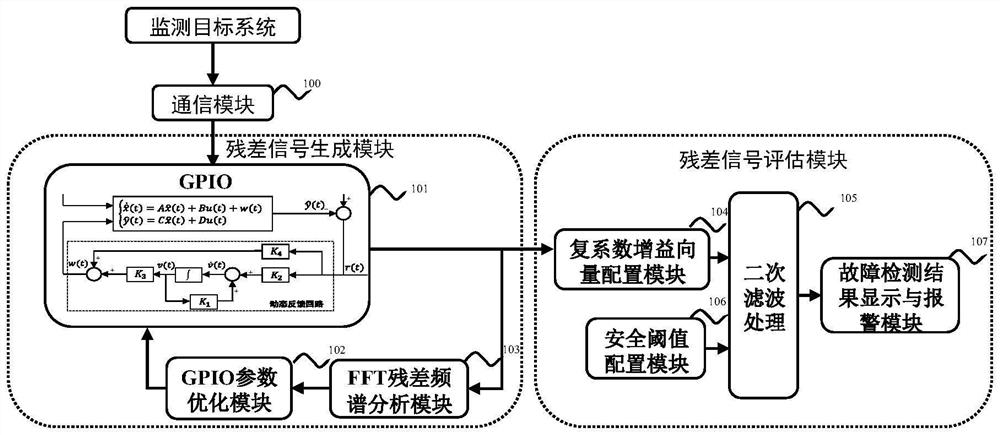
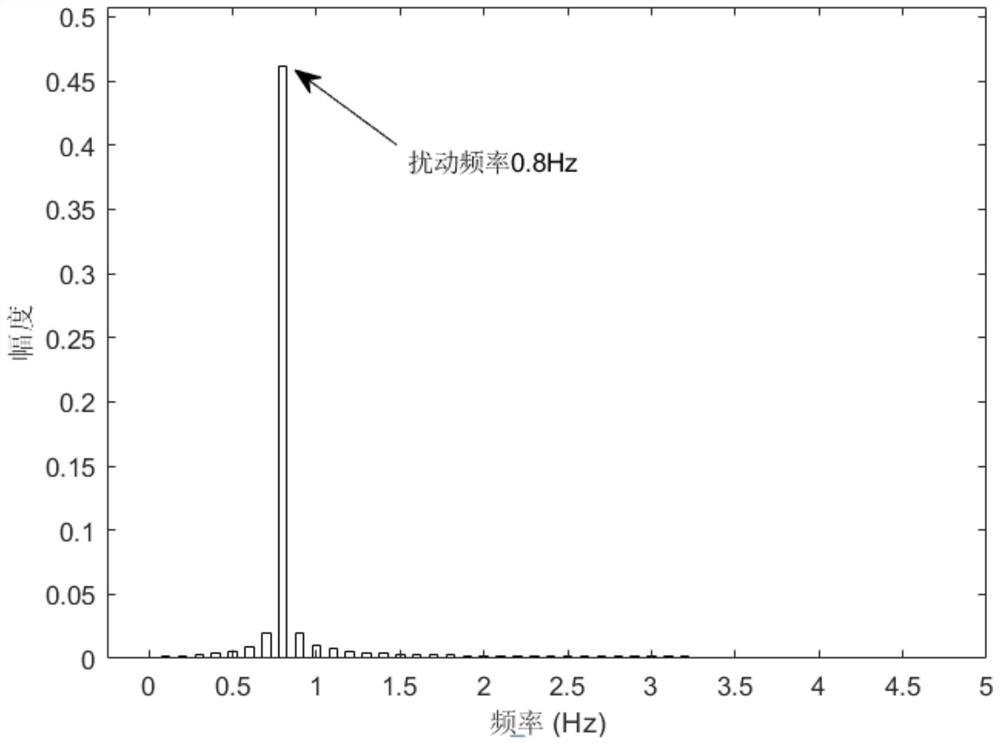
Fault detection system and method for eliminating periodic disturbance based on complex coefficient gain
PendingCN114237038AAchieve basic filteringRaise the weight of failureAdaptive controlFrequency spectrumReliability engineering
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Generation of a sound signal
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Audio equalization method and device, intelligent terminal and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN114697804AImprove soundImprove experienceStereophonic systemsTransducer circuitsEqualization (audio)Software engineering
The invention discloses an audio equalization method and device, an intelligent terminal and a computer readable storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a standard equalizer curve and a standard transfer function of target equipment; obtaining a to-be-calibrated transfer function of the target equipment; calibrating the to-be-calibrated transfer function based on the standard equalizer curve and the standard transfer function to obtain a target transfer function; and carrying out audio equalization on the target equipment based on the target transfer function. According to the audio equalization method provided by the scheme of the invention, in the process of measuring the transfer function of the room, the uncertainty caused by different measuring devices can be offset through calibration, and accurate adjustment of the equalizer is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN TCL DIGITAL TECH CO LTD
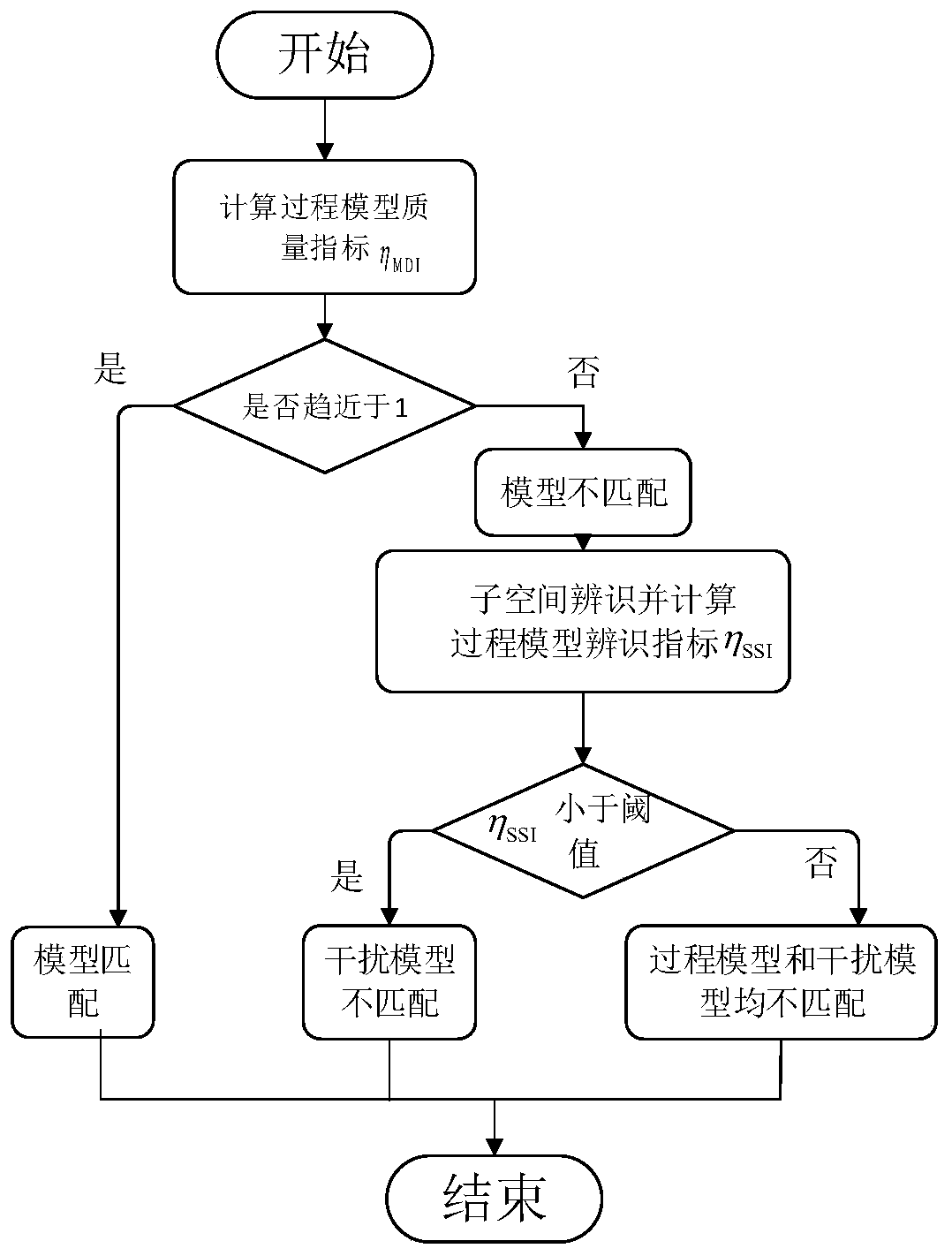
Process model mismatch detection method of closed-loop model predictive control system
InactiveCN111176155AEasy to operateDoes not affect the actual industrial processProgramme controlComputer controlSingular value decompositionAlgorithm
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
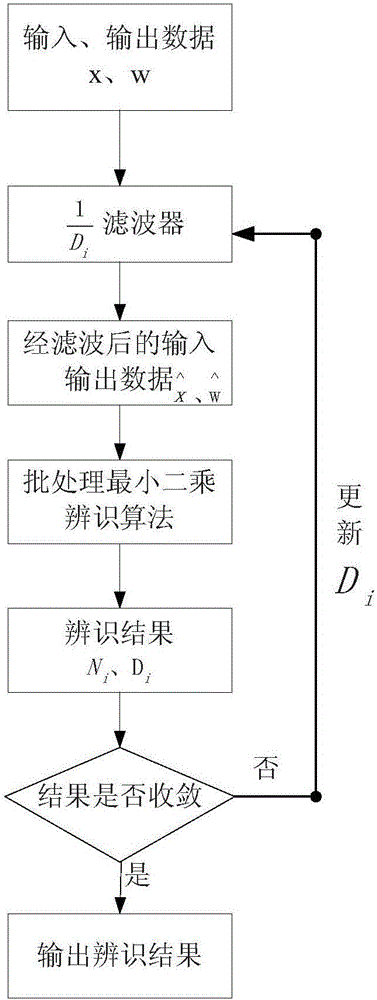
Iterative filtering identification method of linear motor transfer function
ActiveCN106650598ASimple designAccurate dataAC motor controlCharacter and pattern recognitionAnti jammingBatch processing
Owner:江苏希太芯科技有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap