Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
16 results about "Baseband" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Baseband is a signal that has a near-zero frequency range, i.e. a spectral magnitude that is nonzero only for frequencies in the vicinity of the origin (termed f = 0) and negligible elsewhere. In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband signals are transmitted without modulation, that is, without any shift in the range of frequencies of the signal. Baseband has a low-frequency—contained within the bandwidth frequency close to 0 hertz up to a higher cut-off frequency. Baseband can be synonymous with lowpass or non-modulated, and is differentiated from passband, bandpass, carrier-modulated, intermediate frequency, or radio frequency (RF).
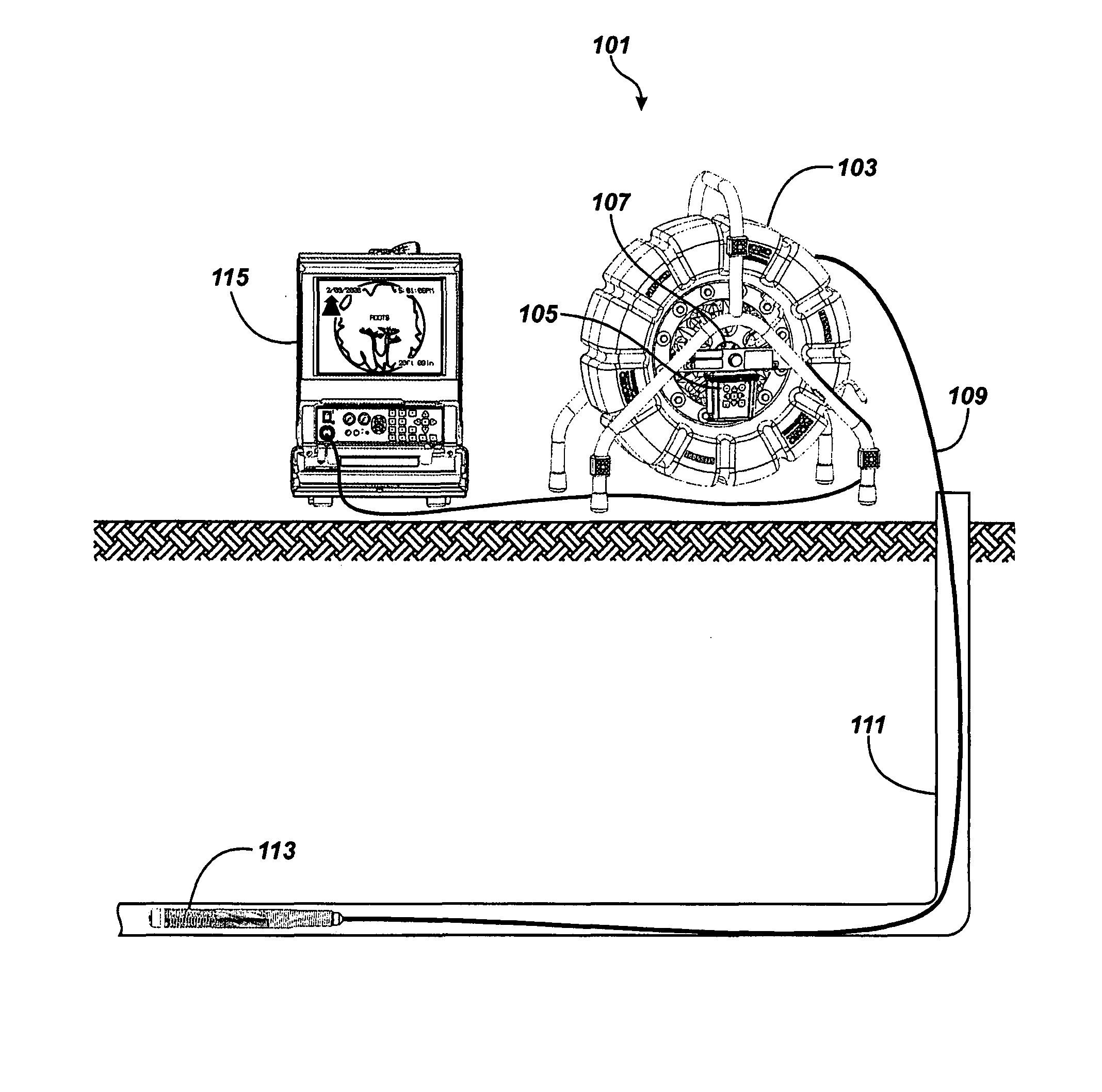
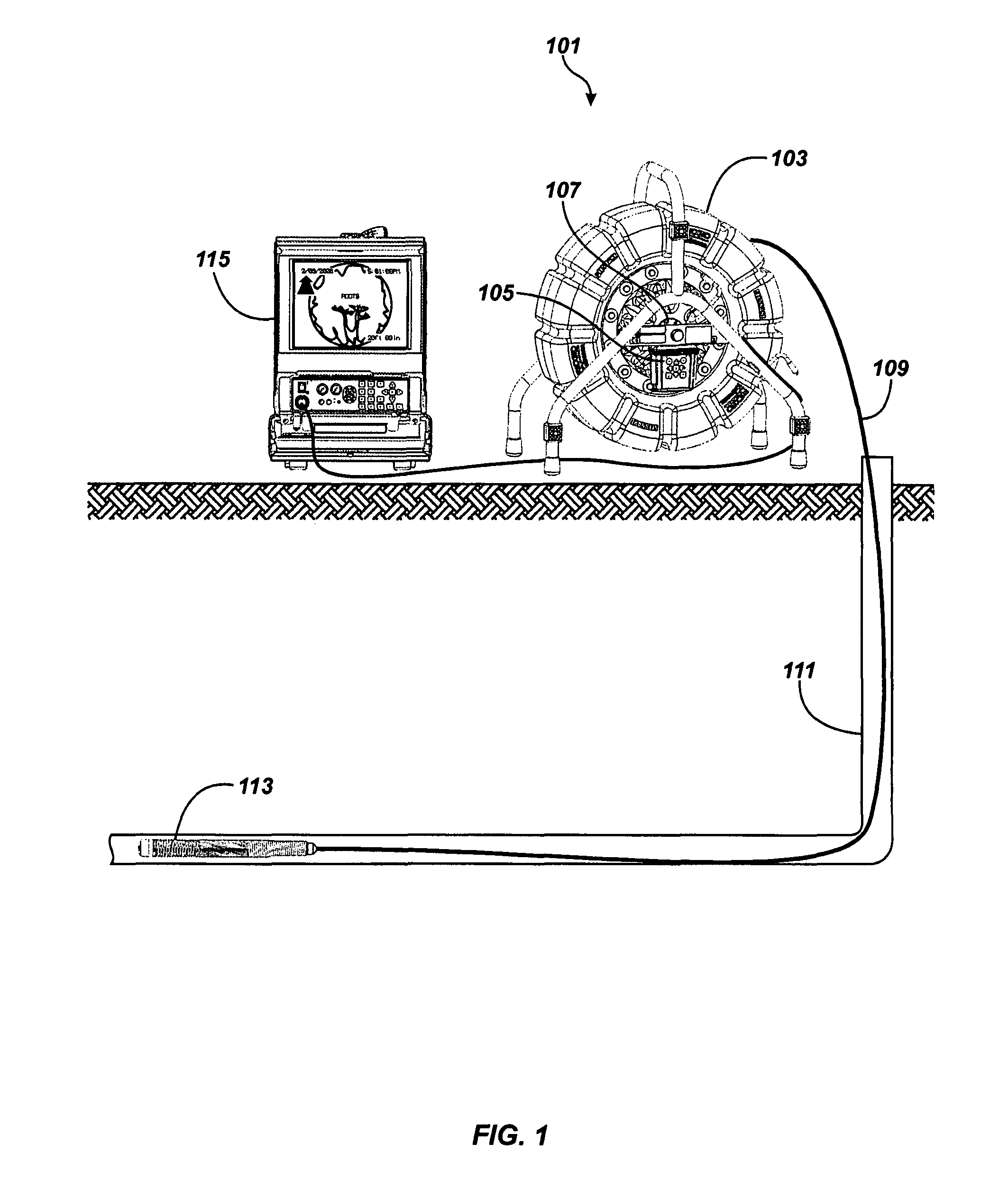
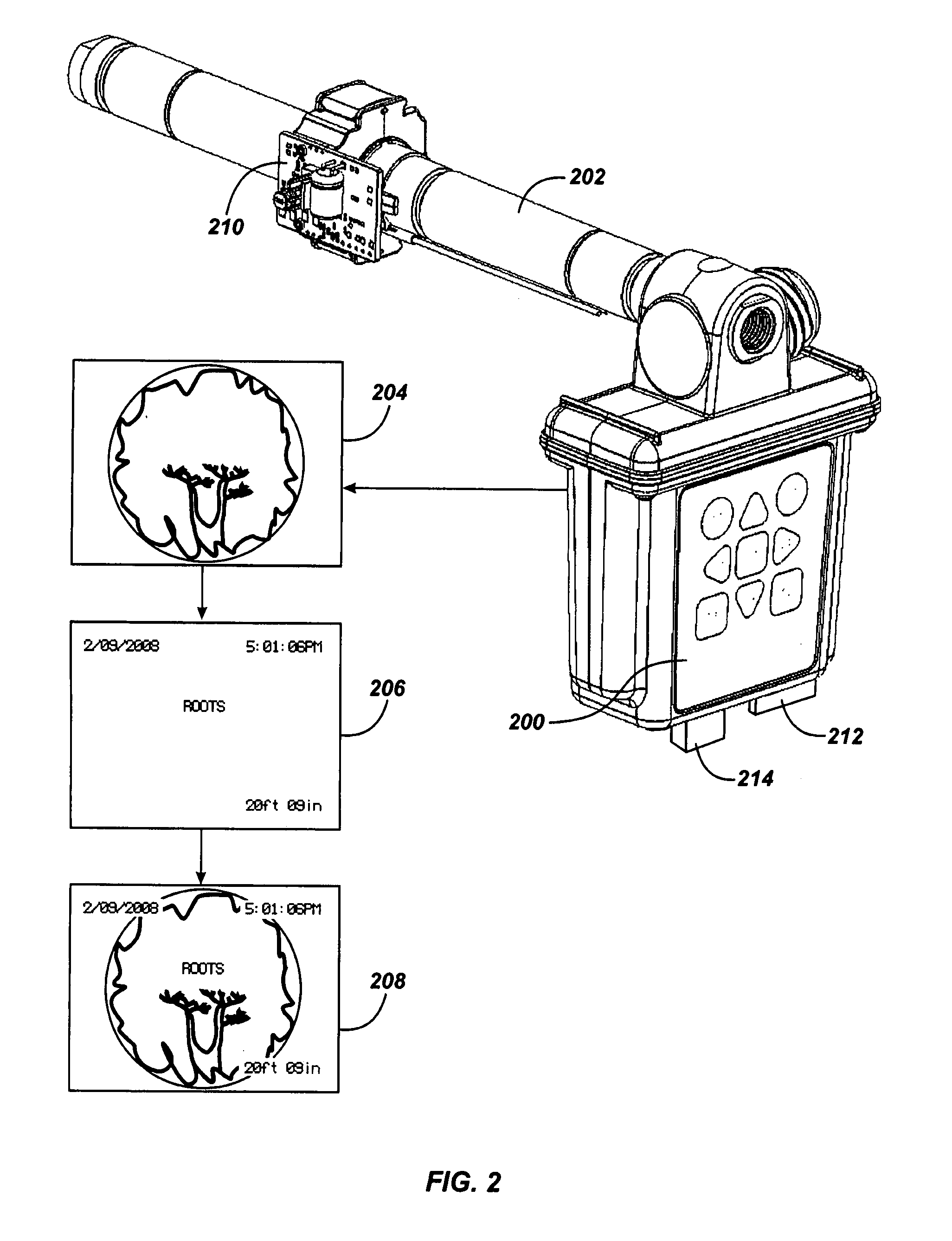
Pipe inspection system with selective image capture
ActiveUS8395661B1Additional imaging capabilityFacilitate communicationImage analysisMaterial analysis by optical meansVideo transmissionData transmission circuit
Owner:SEEKTECH
Double-layer multi-carrier ultra-wideband wireless communication method
ActiveUS20120269234A1Reduce frequencyLow costTransmission path divisionEqualisersUltra-widebandFrequency spectrum
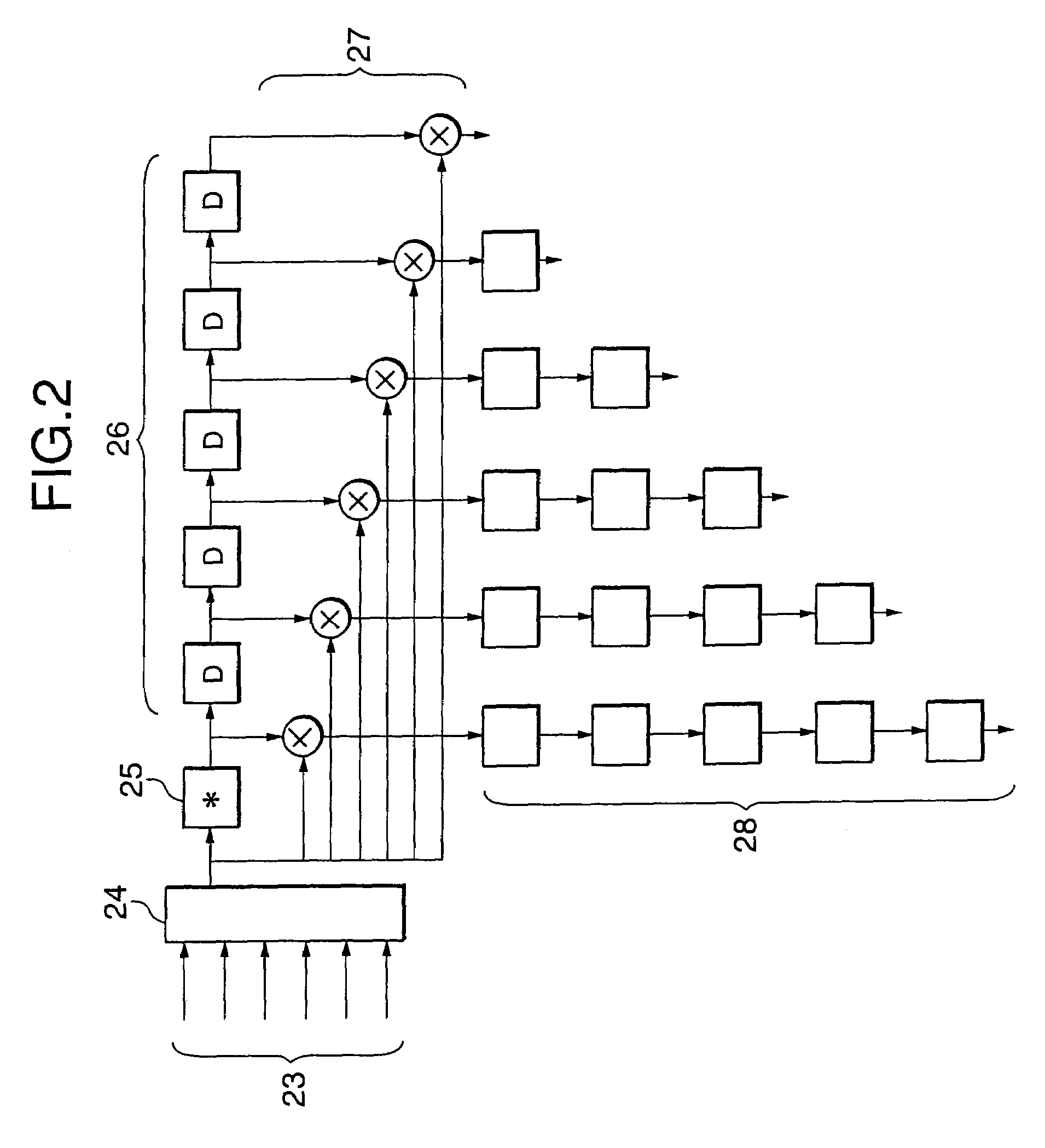
The present invention is a double-layer multi-carrier ultra-wideband wireless communication method, wherein the frequency band for ultra-wideband communication is divided into a plurality of sub-bands, then one or more sub-bands are used for data transmission, and the Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplex (OFDM) multi-carrier transmission technology is used in each sub-band. In the transmitting party, the data symbols to be transmitted are allocated on M branches corresponding to the M sub-bands, and the OFDM modulation is implemented on the data symbols on each branch to obtain M branches of parallel data, then digital baseband multi-carrier modulation is implemented on the M branches of parallel data. Thereby, the spectrum of data on each branch is moved onto the digital sub-band corresponding to the radio sub-band one to one, so the digital baseband signal of the radio signal to be transmitted is obtained. Then, the digital signal is converted to an analog signal with a D / A conversion and an up-conversion, and the signal spectrum is moved to the radio frequency band in use, then the analog signal is amplified, filtered and transmitted via an antenna, thus the task of modulating M branches of parallel data onto M sub-bands is completed.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and equipment for data transmission
ActiveCN102833000AReduce the number of bitsReduce the number of sampling pointsElectromagnetic transmissionData transmissionComputer science
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
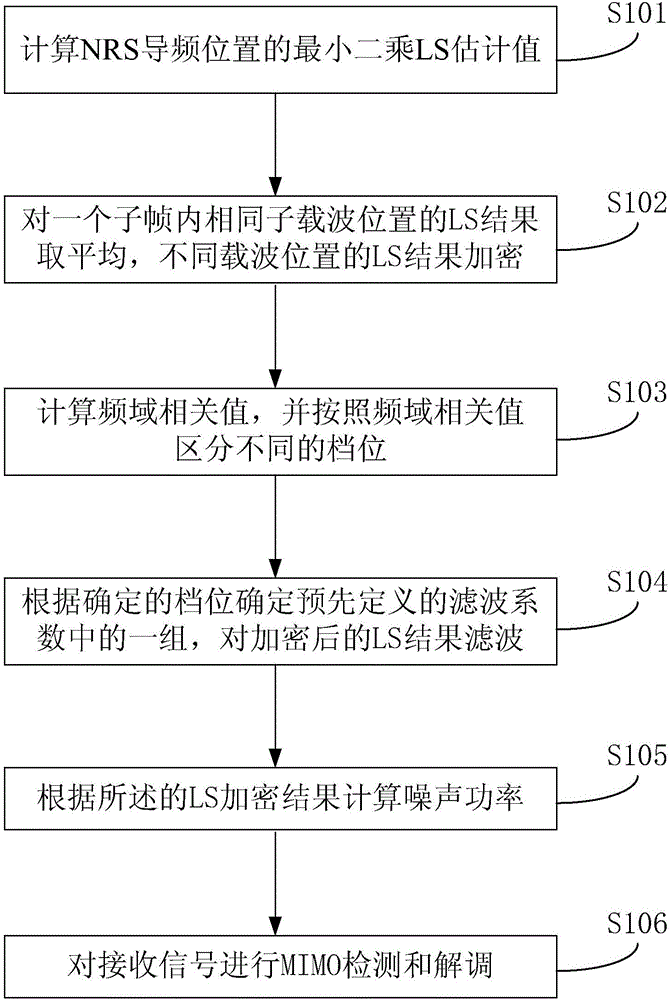
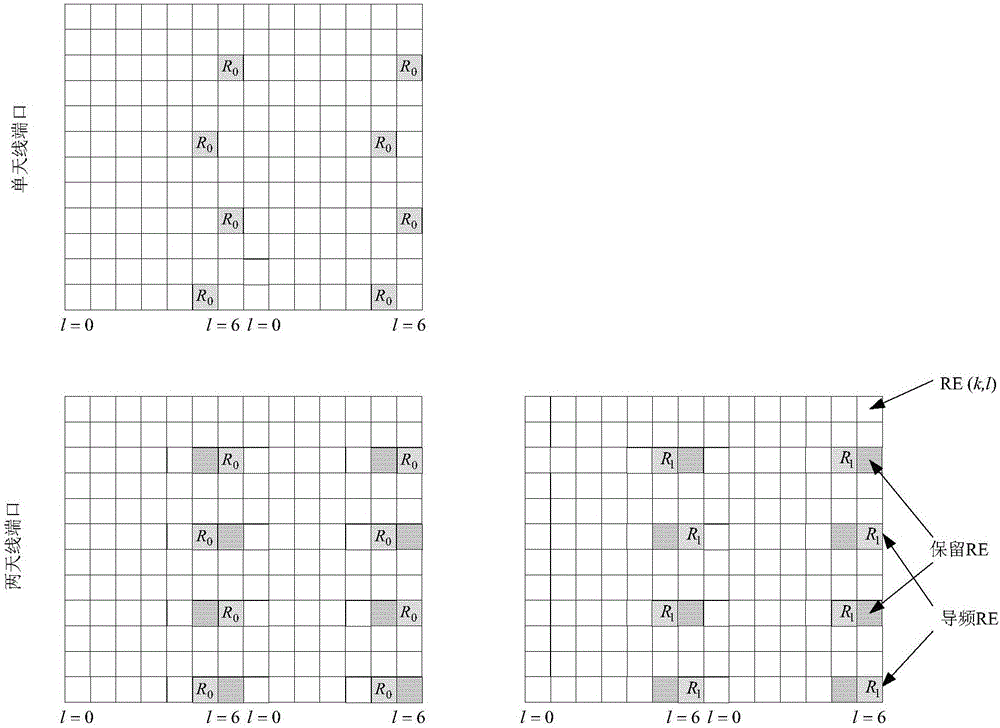
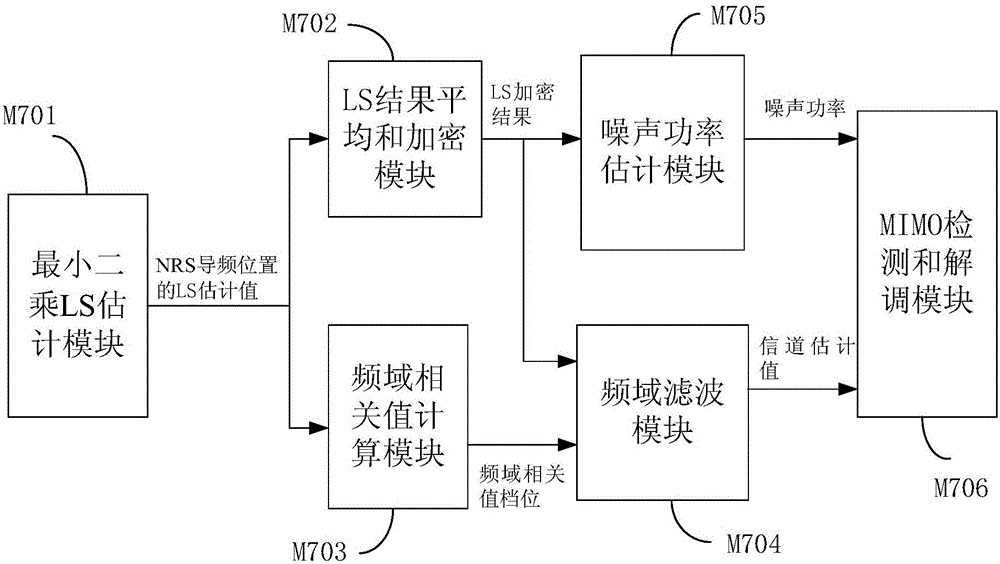
Baseband receiving method and device for narrow-band wireless receiver
ActiveCN106685865AReduce computationGood noise suppression effectChannel estimationPilot signal allocationSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioMultiple input
Owner:BEIJING WANRUI TIANRONG INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
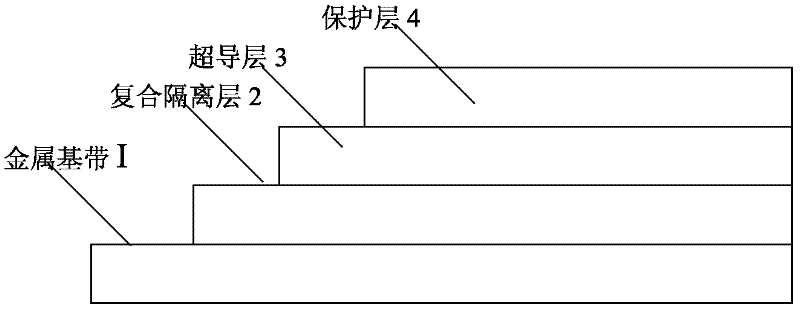
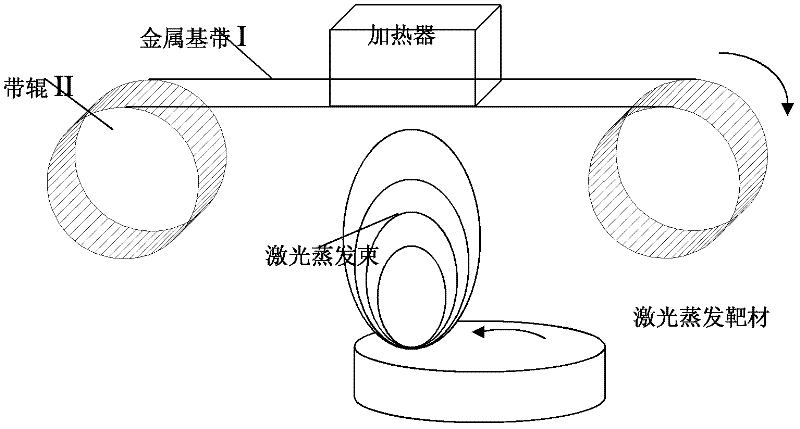
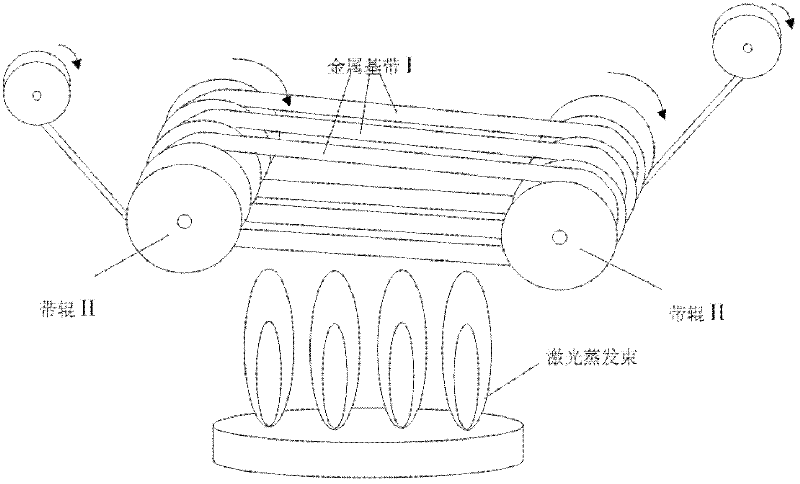
Method suitable for continuously preparing high-temperature superconductive belt material
ActiveCN102306702AFast manufacturingImprove laser utilizationSuperconductor device manufacture/treatmentSuperimposed coating processLaser coatingHigh-temperature superconductivity
Owner:SHANGHAI SUPERCONDUCTOR TECH CO LTD
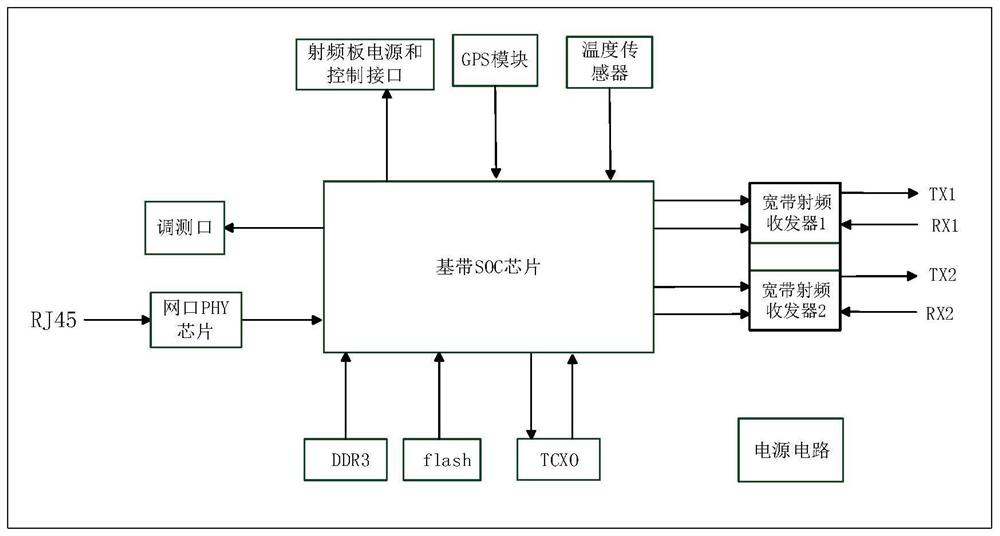
Digital interface radio frequency chip and implementation method thereof
ActiveCN103209070ALow costReduce power consumptionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksSynchronising arrangementMultiplexingDigital down converter
The invention discloses a digital interface radio frequency chip and an implementation method thereof. The digital interface radio frequency chip comprises a receiving antenna, a radio frequency analog front-end subsystem and an analog baseband subsystem, wherein the analog baseband subsystem comprises an oversampling analog-to-digital converter, an internal clock generating module, a digital signal processor and a multiplexing parallel module, an output end of the receiving antenna is connected with an input end of the multiplexing parallel module through the radio frequency analog front-end subsystem, the oversampling analog-to-digital converter and the digital signal processor sequentially, and an output end of the internal clock generating module is connected with a clock input end of the oversampling analog-to-digital converter and a clock input end of the multiplexing parallel module respectively. According to the digital interface radio frequency chip, clocks generated inside the radio frequency chip serve as reference clocks, so that the correctness of the baseband chip data collection can be guaranteed; and no complex first-in first-out (FIFO) structure is required, the structure is simple, the integration is easy, and the cost and the power consumption are reduced. The digital interface radio frequency chip and the implementation method thereof are widely applied in the technical field of communications.
Owner:TOLL MICROELECTRONIC CO LTD
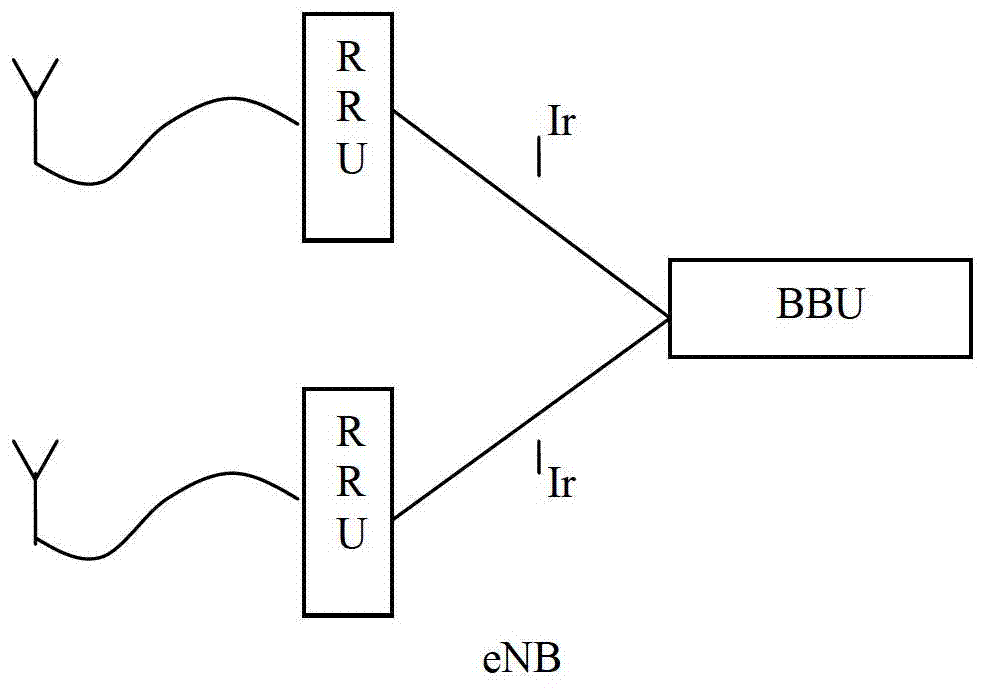
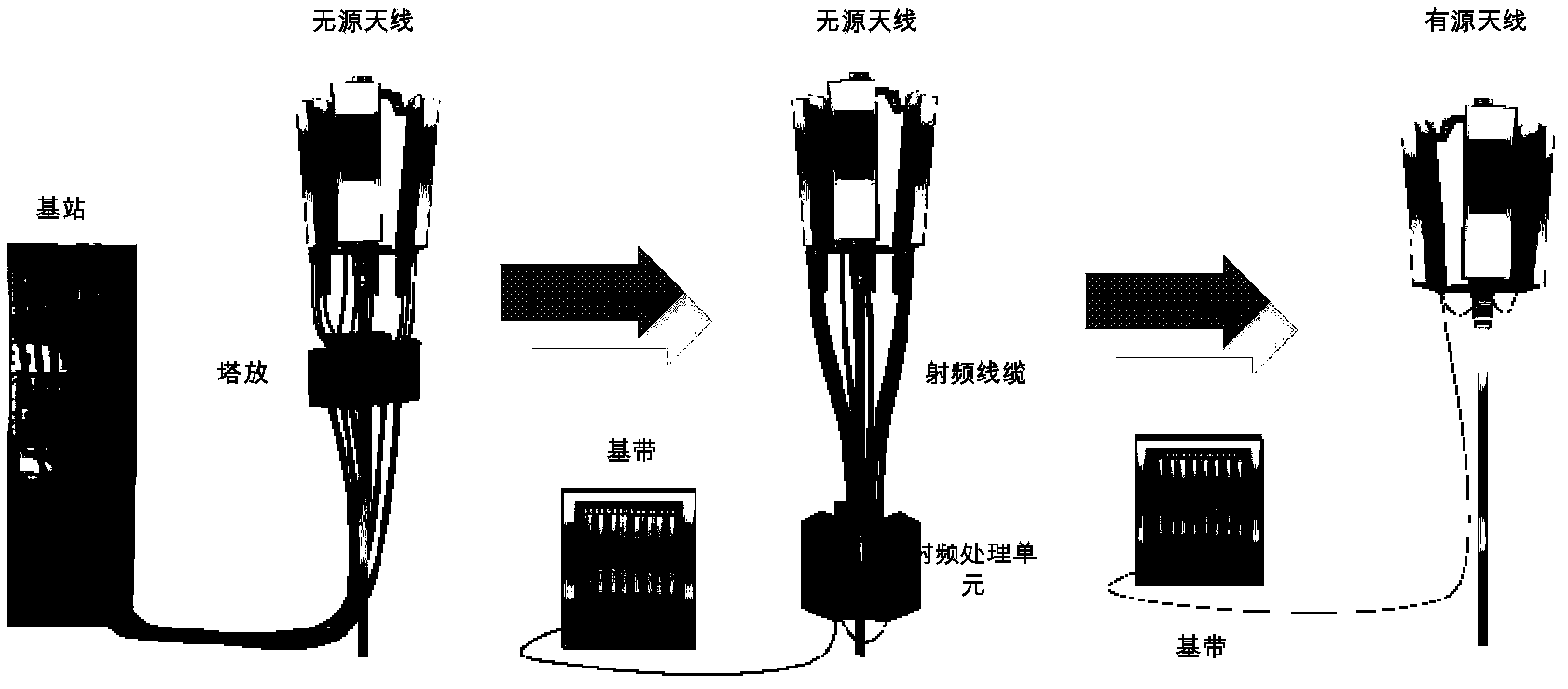
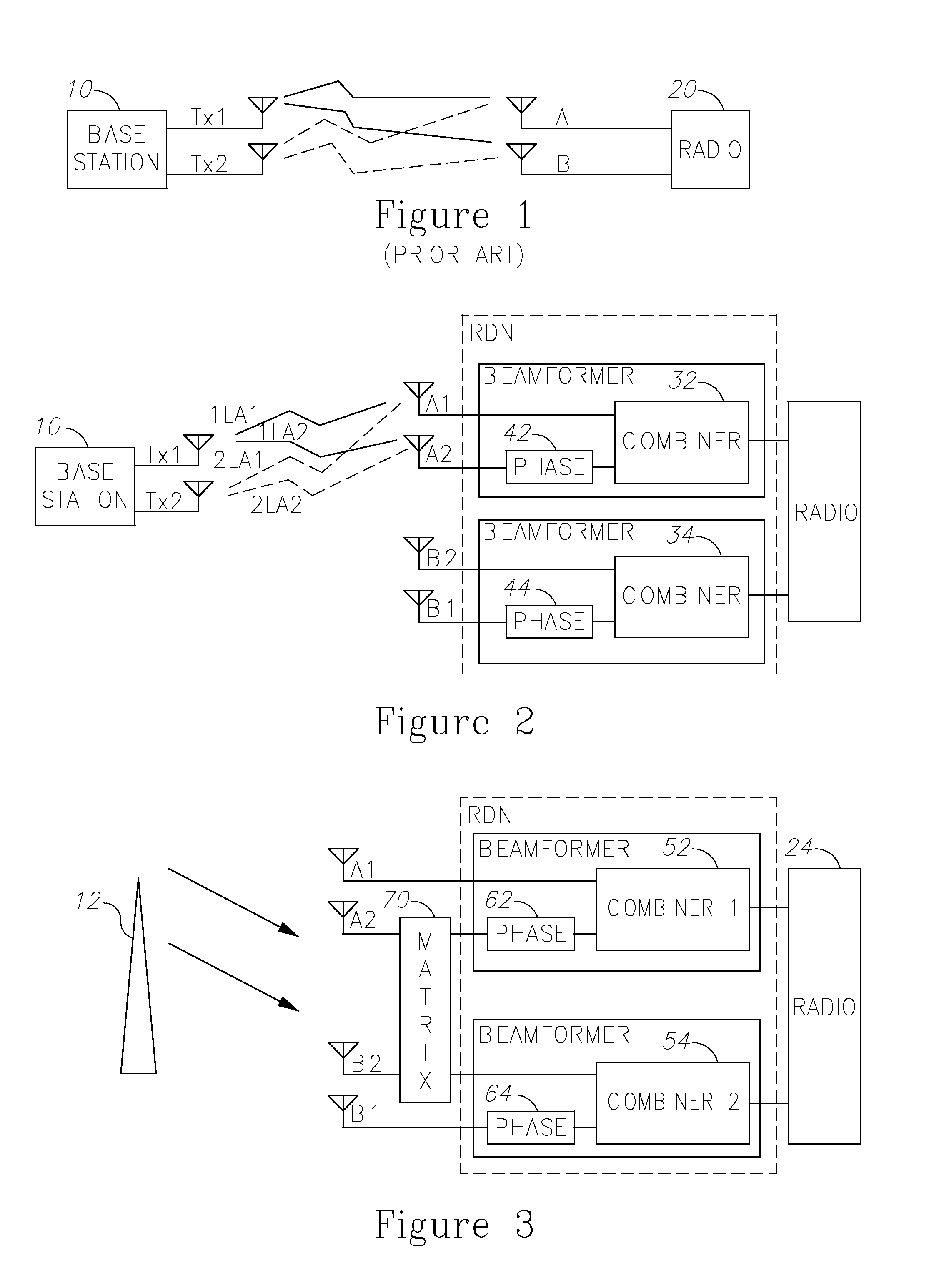
Antenna unit and radio base station therewith
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Apparatus and circuit for amplifying baseband signal
ActiveUS20130154741A1Reduce power consumptionCharge amplifiersPulse automatic controlSignal qualityAudio power amplifier
An operational amplifier circuit is provided. The operational amplifier circuit includes a differential amplifier of a cascade structure and a switched-capacitor type Common-Mode FeedBack (CMFB) circuit. The differential amplifier amplifies a difference between two input signals to output an anode output voltage and a negative output voltage. The switched-capacitor type CMFB circuit averages the anode output voltage and the negative output voltage of the differential amplifier, compares the average voltage with a reference voltage to generate a feedback signal based on a result of the comparison, and provides the feedback signal to the differential amplifier. Therefore, power consumption is reduced and a battery use time of a wireless terminal can be extended. Also, since an operational amplifier gain of each analog filter terminal is not negatively affected, a Direct Current (DC) offset is reduced, thereby improving signal quality.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
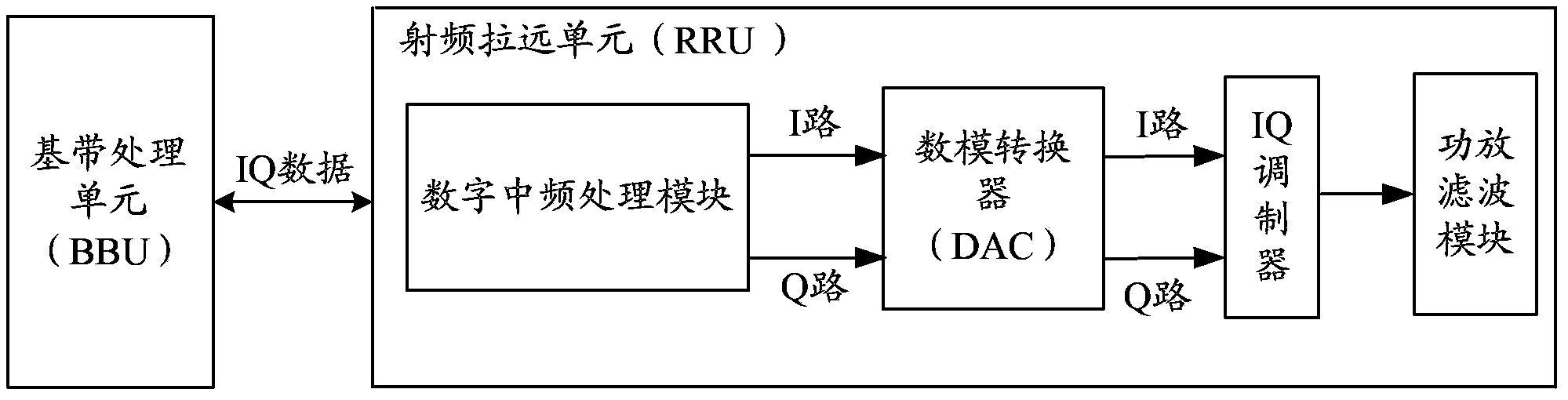
Method and system for processing IQ data of radio-frequency remote unit and radio remote unit
ActiveCN104219020AAvoid weakening or even offsetting problemsImprove abilitiesError prevention/detection by diversity receptionData processing systemCarrier signal
Owner:ZTE CORP
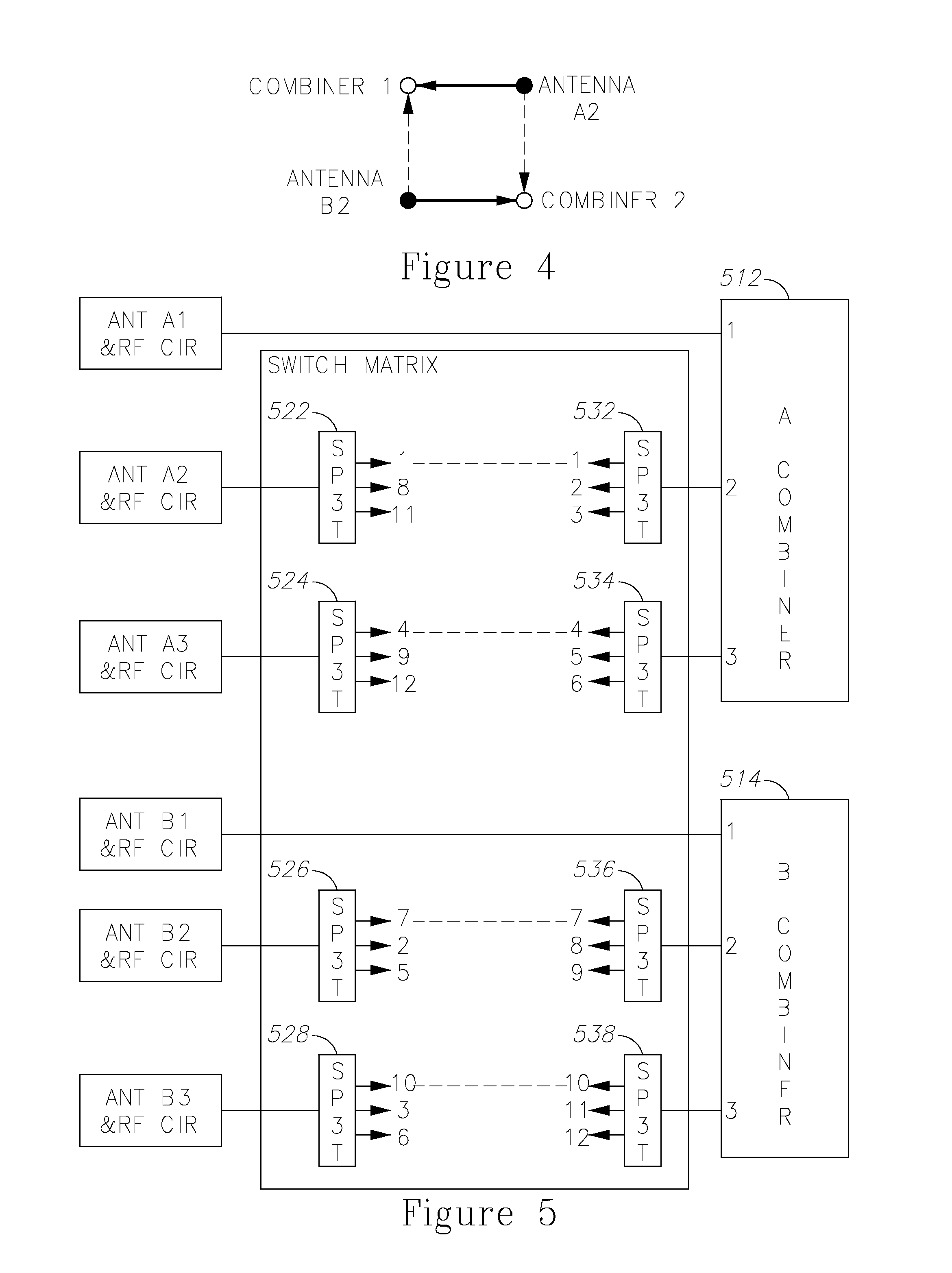
Multi-antenna system interference rejection device and method
InactiveCN103888228AGood interference suppression effectSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksTime domainEuclidean vector
The invention discloses a multi-antenna system interference rejection device and method. The method includes the following steps that S1, a baseband signal vector ym is received according to a time domain, an intrinsic domain transformation matrix U is estimated, the received baseband signal is transformed to obtain an interferential intrinsic domain representation rm of the received baseband signal, and rm is equal to Uym; S2, as for each sampling moment, weighting merging is carried out on transformed values Uy1[n], Uy2[n],..., UyM[n] of M antennas to obtain an intrinsic domain estimated value; S3, inverse transformation is carried out on the intrinsic domain estimated value to obtain a desired signal estimated value. Compared with a traditional interference rejection combining algorithm, the device and method have the advantages that nonuniformity of narrow-band interference energy is made full use of in an intrinsic domain, interference and rejection are combined, and a better interference rejection effect is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
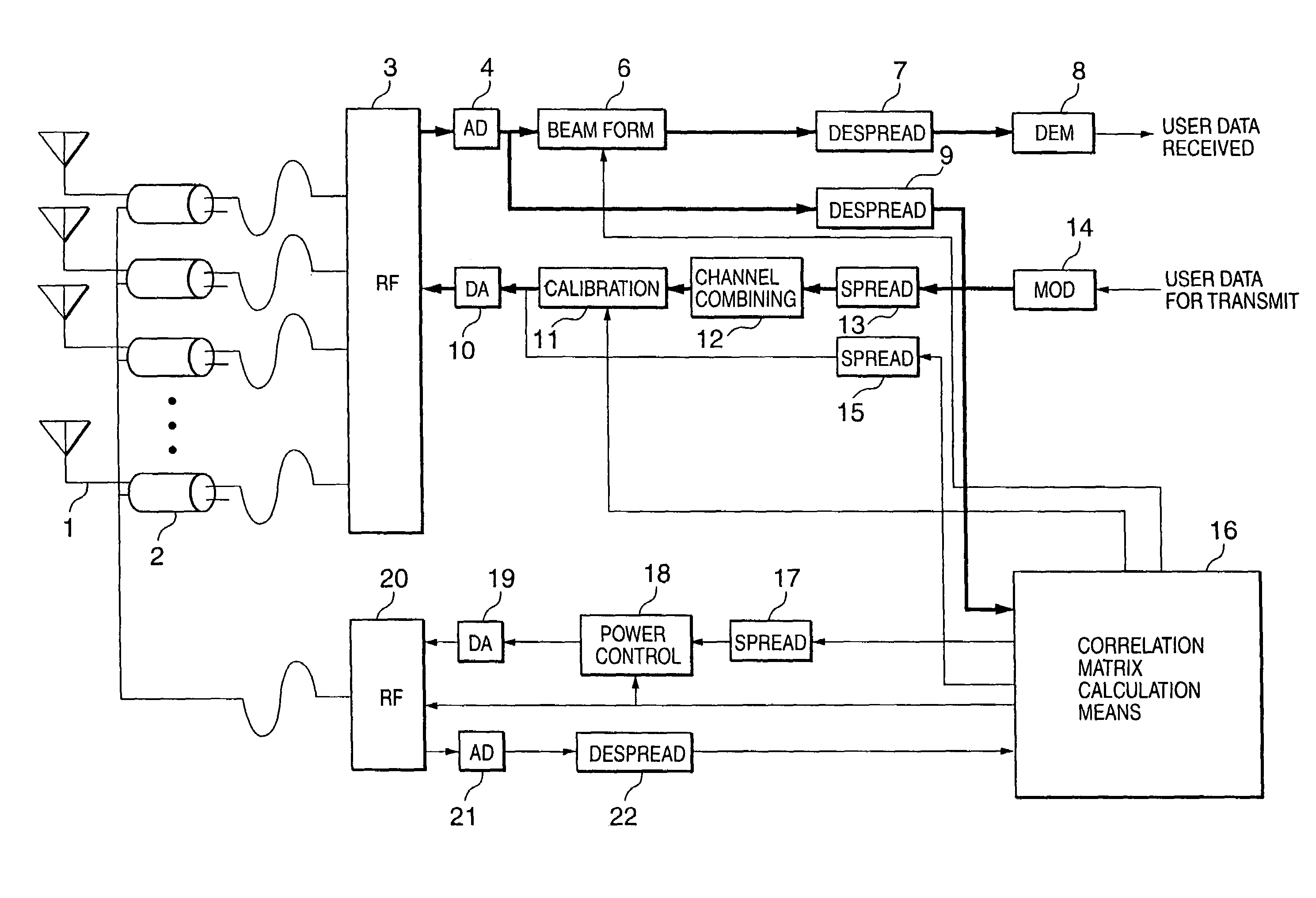
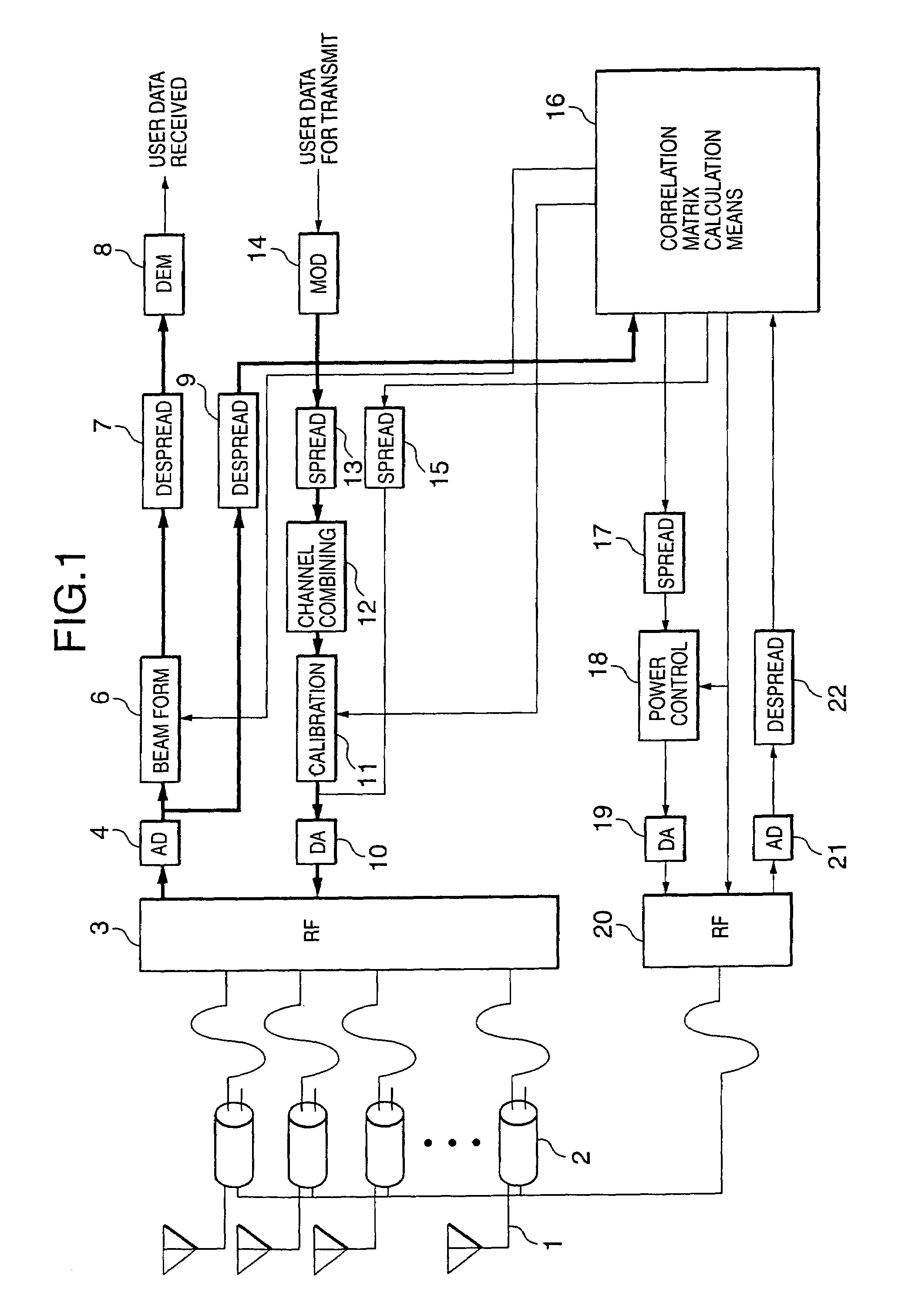
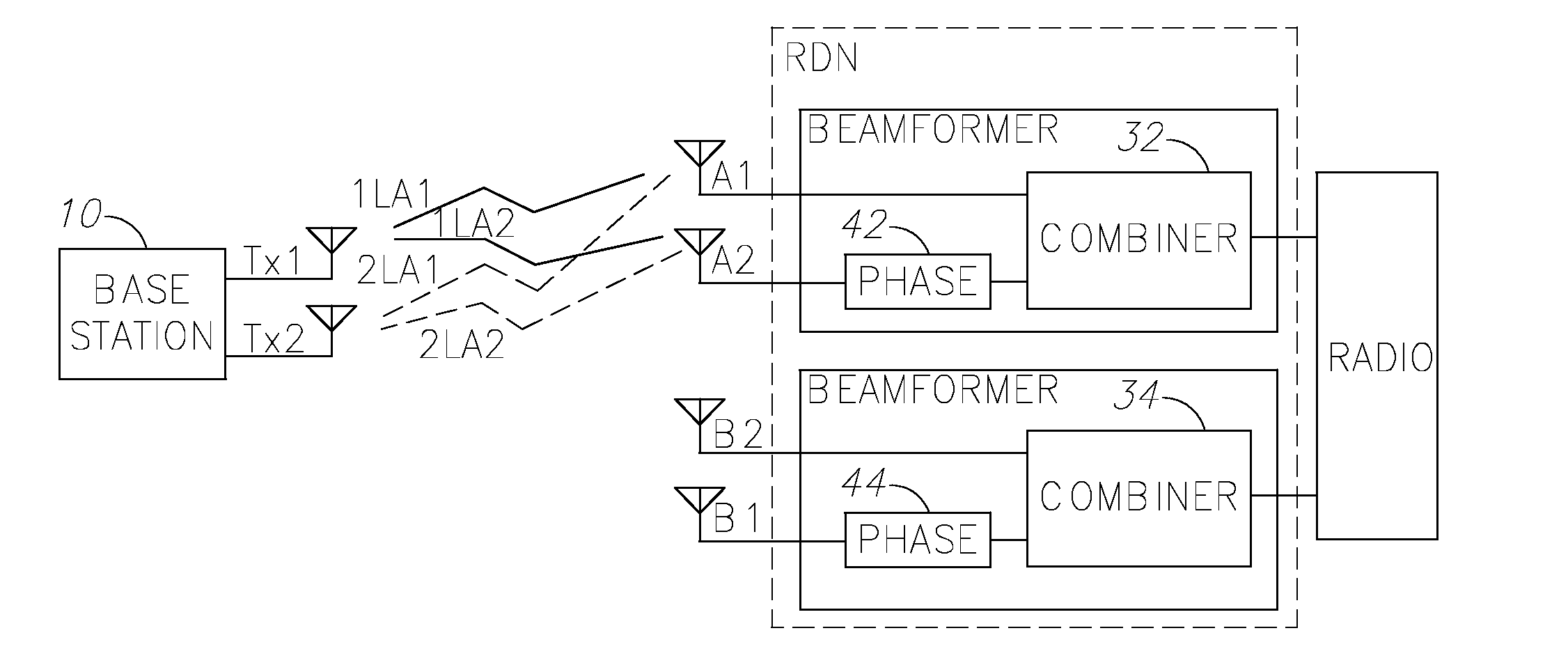
Using antenna pooling to enhance a MIMO receiver augmented by RF beamforming
InactiveUS20130322573A1Degraded performance and loss of performanceAdd settingsSpatial transmit diversityAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsEngineeringMulti stream
Owner:MAGNOLIA BROADLAND INC
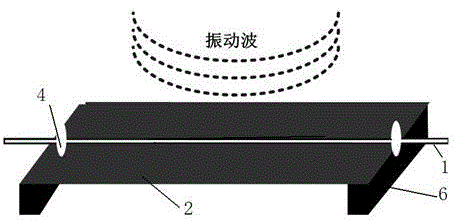
High-sensitivity metal baseband armored vibration sensing optical cable
PendingCN106405771AExtended service lifeEasy to processSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFibre mechanical structuresAdhesiveAcoustic wave
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
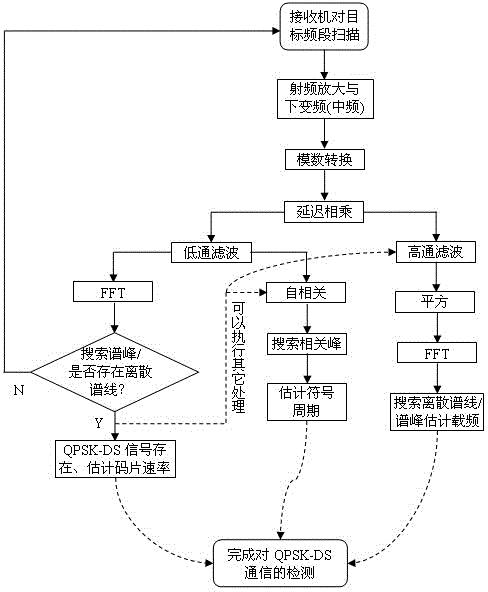
QPSK-DS communication detecting method based on delay multiplication
InactiveCN103957029AEasy to handleLower requirementModulated-carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency spectrumIntermediate frequency
Owner:XUCHANG UNIV
Half-blind channel estimation method for joint cooperative clustering of cloud wireless access network
ActiveCN107517169AImprove data transfer efficiencyReduce overheadSite diversitySpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationAccess network
The invention discloses a half-blind channel estimation method for joint cooperative clustering of a cloud wireless access network and belongs to the field of the cloud wireless access network. The method comprises the specific steps that all users send pilot and data information to remote radio units; after the pilot and data information is amplified by the remote radio units, own pilot information of the remote radio units is superposed with the amplified information; the information is forwarded to a centralized baseband processing unit pool; the centralized baseband processing unit pool processes the information to obtain channel state information; cooperative clusters are divided for the remote radio units; combination-split operation is carried out; utility functions corresponding to different clustering modes are evaluated, thereby obtaining the optimum clustering mode; corresponding processing is carried out on the received information of various clusters in the centralized baseband processing unit pool through utilization of the half-blind channel estimation method, thereby obtaining independent channel state information of access links and forward links; and data information is demodulated. According to the method, the pilot cost required by channel estimation is effectively reduced, and the data transmission efficiency of the cloud wireless access network is clearly improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Multi-mode signal micro-distribution system
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
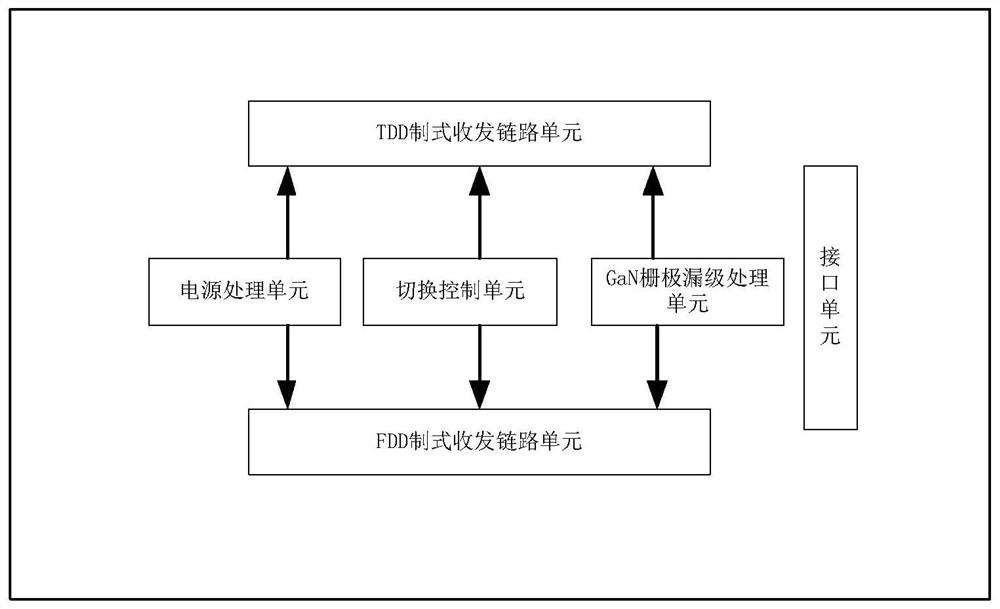
Uplink and downlink common-frequency spaceflight ground measurement and control station
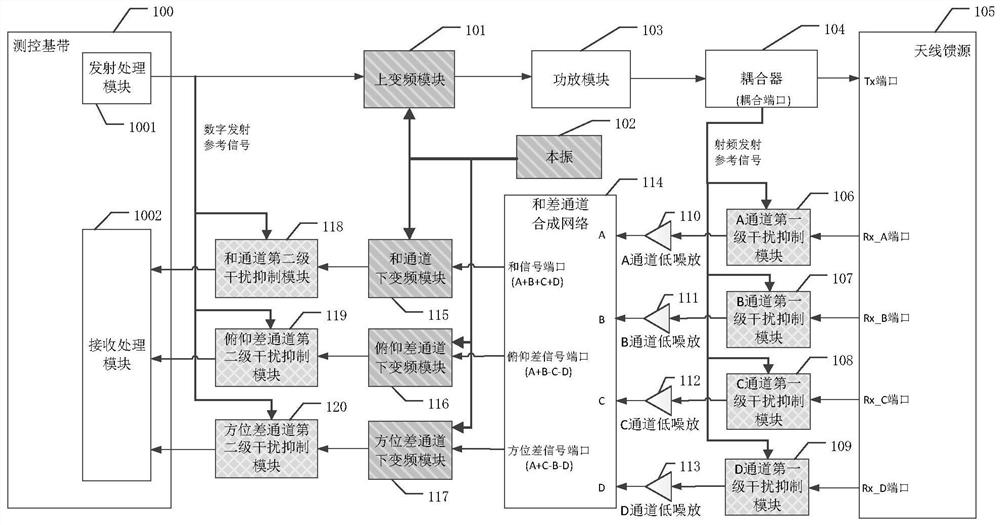
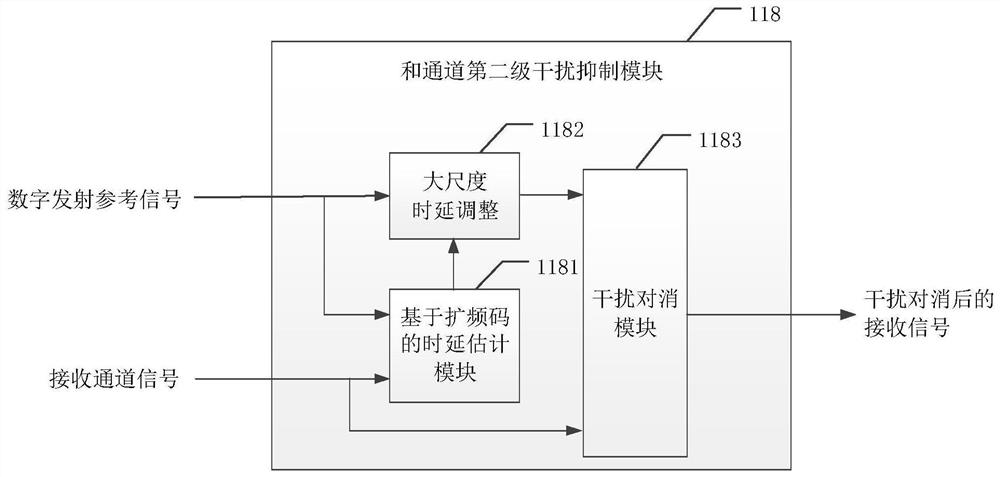
ActiveCN113630148AGuaranteed Phase ConsistencySame phase noise distributionWireless architecture usageTransmissionLocal oscillator signalPhase noise
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap