Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7 results about "Butane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Butane (/ˈbjuːteɪn/) is an organic compound with the formula C₄H₁₀ that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. Butane is a gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. The term may refer to either of two structural isomers, n-butane or isobutane (also called "methylpropane"), or to a mixture of these isomers. In the IUPAC nomenclature, however, "butane" refers only to the n-butane isomer (which is the isomer with the unbranched structure). Butanes are highly flammable, colorless, easily liquefied gases that quickly vaporize at room temperature. The name butane comes from the roots but- (from butyric acid, named after the Greek word for butter) and -ane. It was discovered by the chemist Edward Frankland in 1849. It was found dissolved in crude petroleum in 1864 by Edmund Ronalds, who was the first to describe its properties.
Method for preparing temperature sensitive intelligent anti-dip facing material and product thereof
InactiveCN101302718ATemperature-sensitive intelligenceReduce voidsTextiles and paperCarboxylic acidTert butyl
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Trace heavy hydrocarbon gas isotope sampling system and method
InactiveCN107478488AEfficient enrichmentEfficient removalPreparing sample for investigationPhysical chemistryMethane gas
The invention provides a trace heavy hydrocarbon gas isotope sampling system and method. The system includes a heavy hydrocarbon gas separating and enriching apparatus, an original sample reaction apparatus, and a finished product sample extraction apparatus, wherein the heavy hydrocarbon gas separating and enriching apparatus receives a sample, separates heavy hydrocarbon gas from methane gas in the sample, and efficiently enriches and separates the heavy hydrocarbon gas; ethane, propane and butane obtained from heavy hydrocarbon gas separation undergo an oxidation reaction in sequence in the original sample reaction apparatus to obtain CO2; and the finished product sample extraction apparatus purifies CO2 gas obtained from the oxidation reaction, removes H2O impurity gas generated at the same time, and allows purified CO2 to be obtained at multiple sample ports from ethane, propane and butane reactions. The trace heavy hydrocarbon gas isotope sampling system and method allow low-concentration trace heavy hydrocarbon gas and methane to be effectively separated and enriched, and the isotopic value of ethane, propane and butane are accurately determined.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
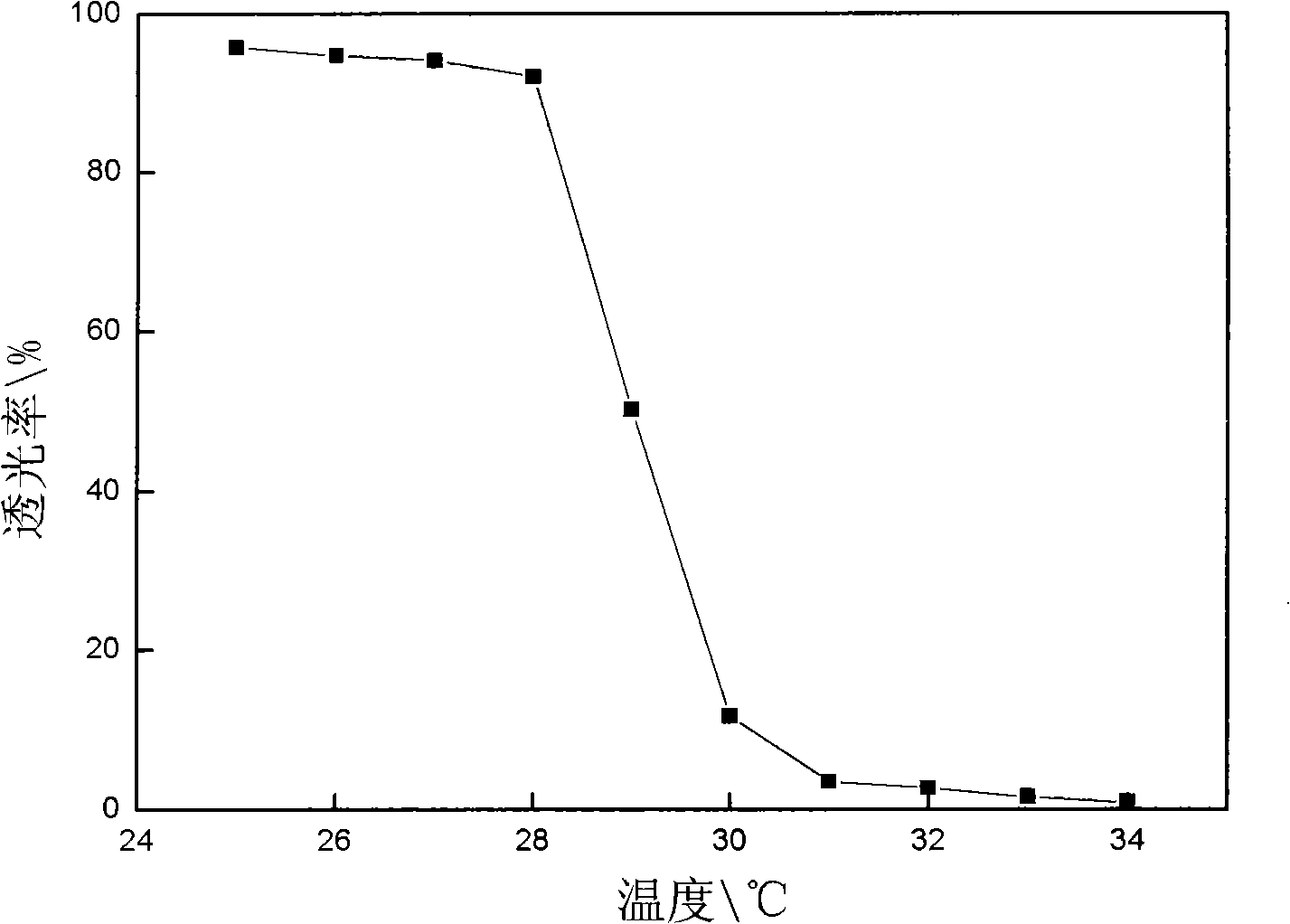
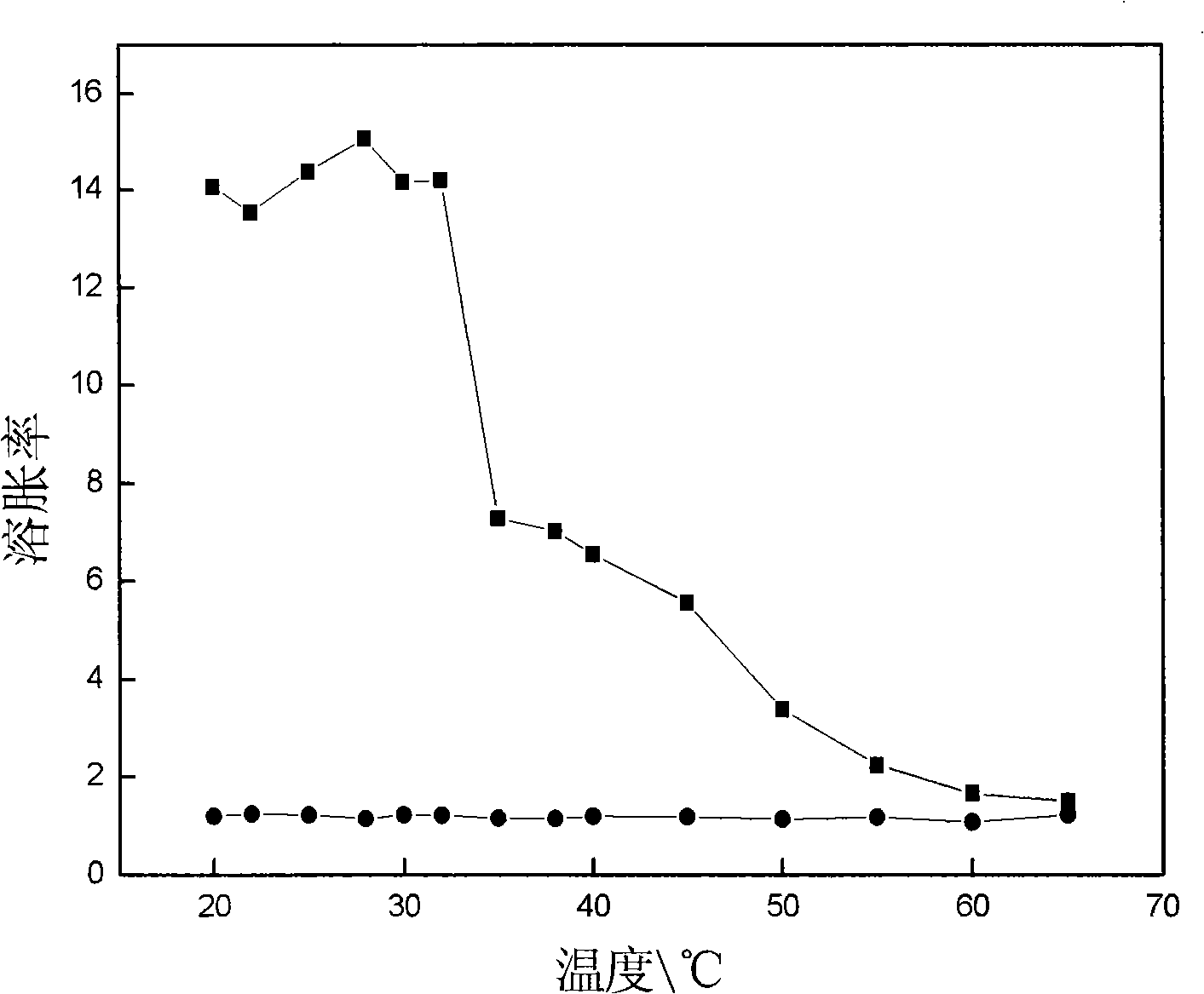
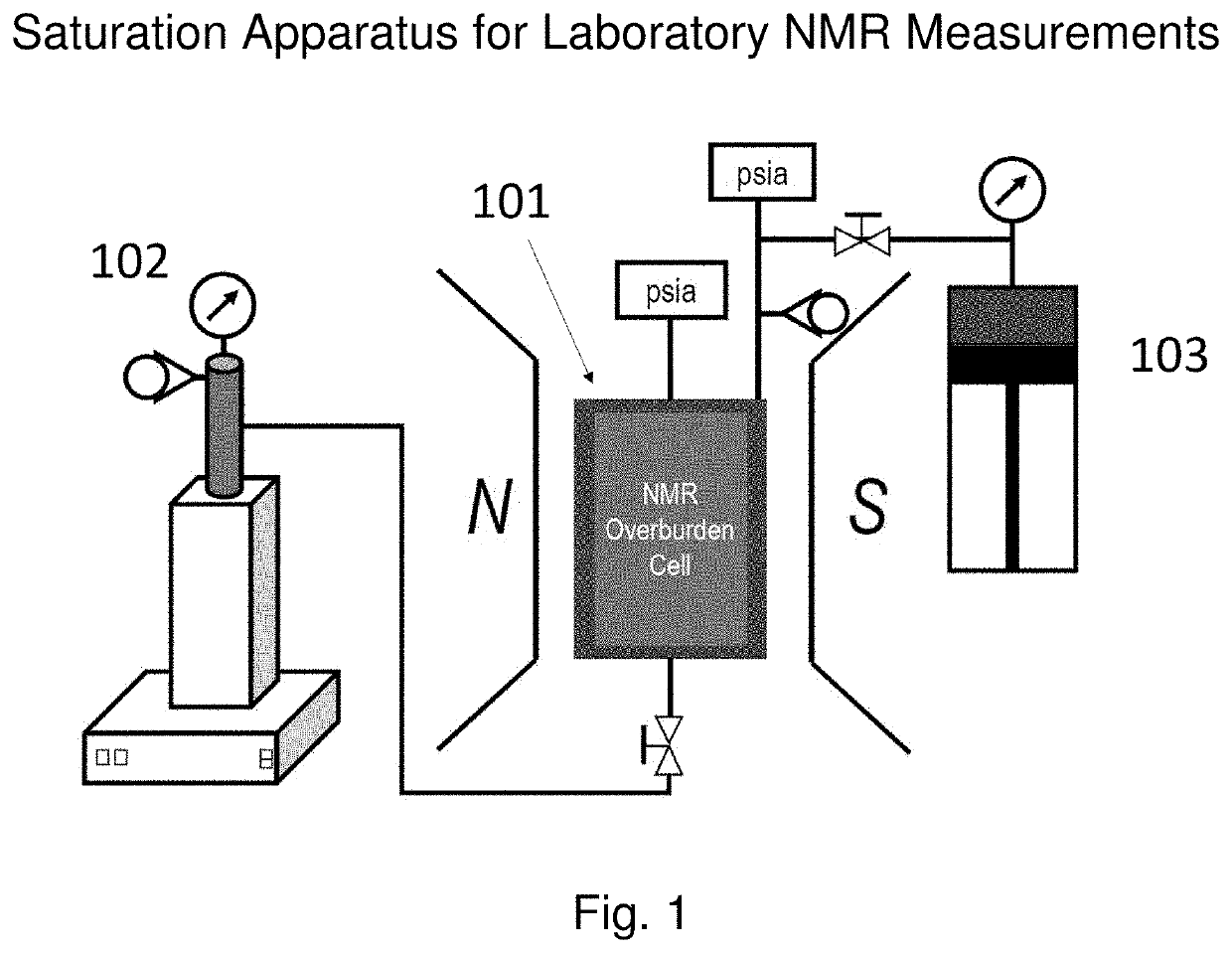
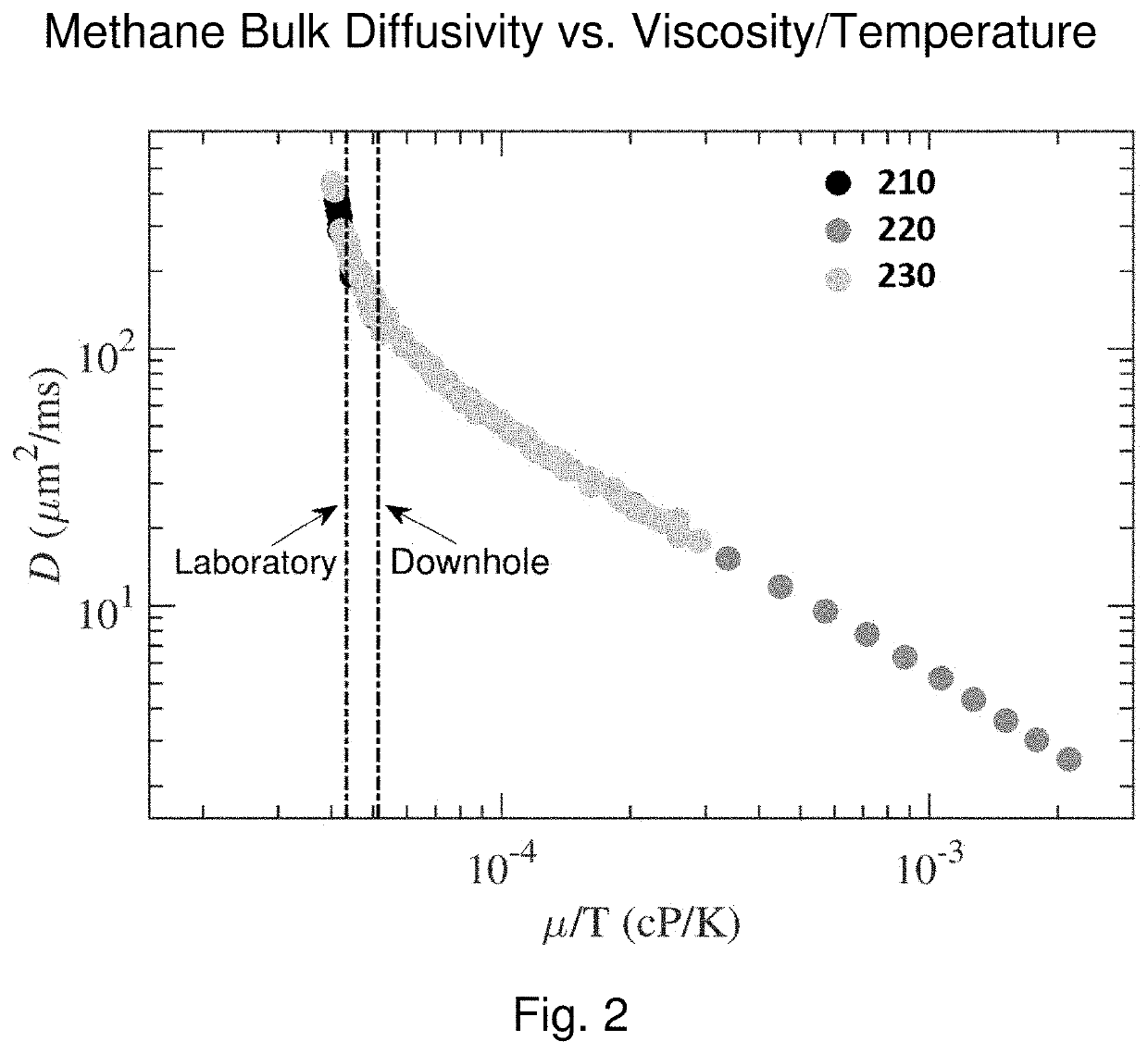
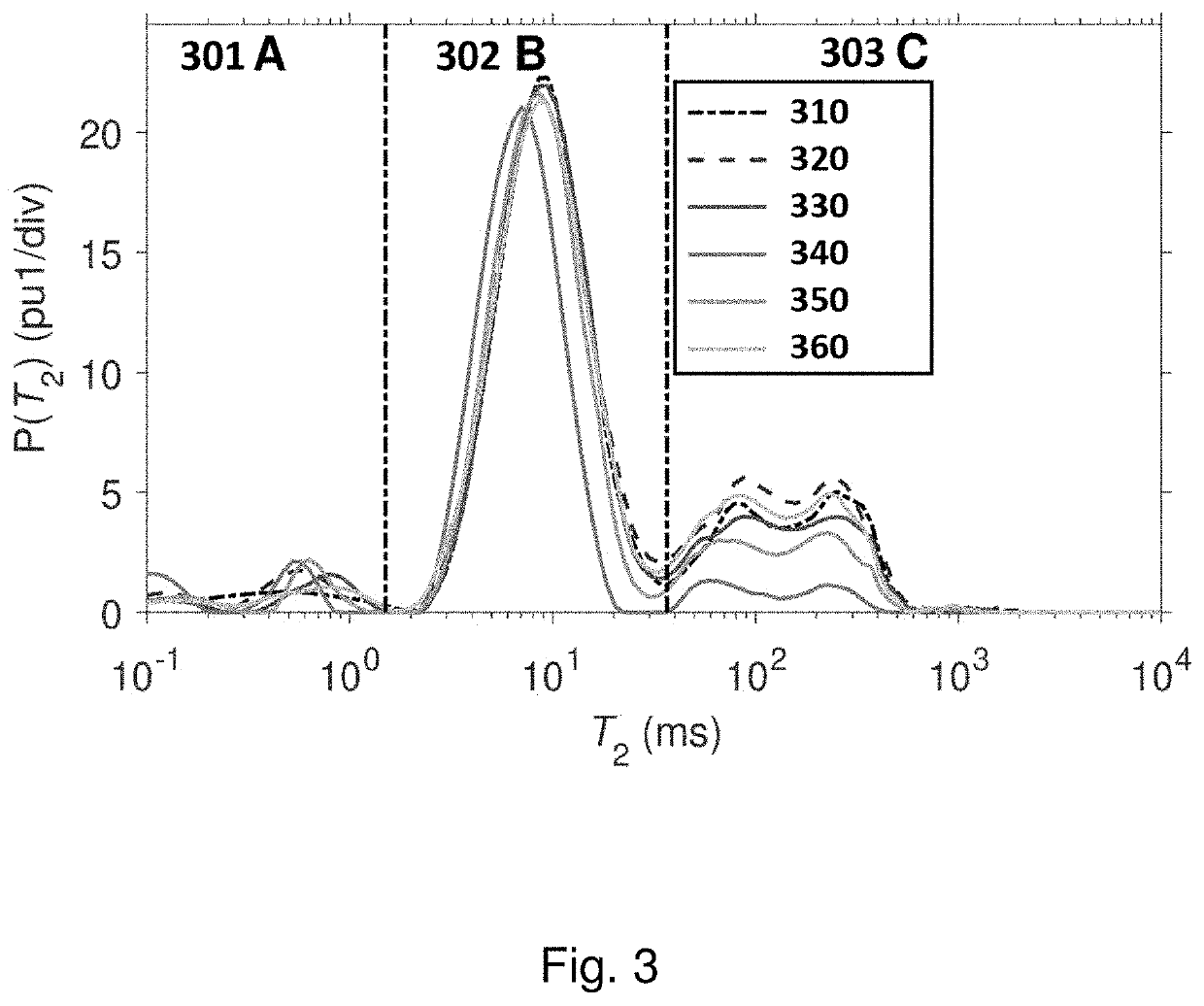
Method for determining the composition of natural gas liquids, mean pore-size and tortuosity in a subsurface formation using NMR
ActiveUS11099292B1Big contrastError minimizationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonancePhysical chemistry
Owner:VINEGAR TECH LLC +1
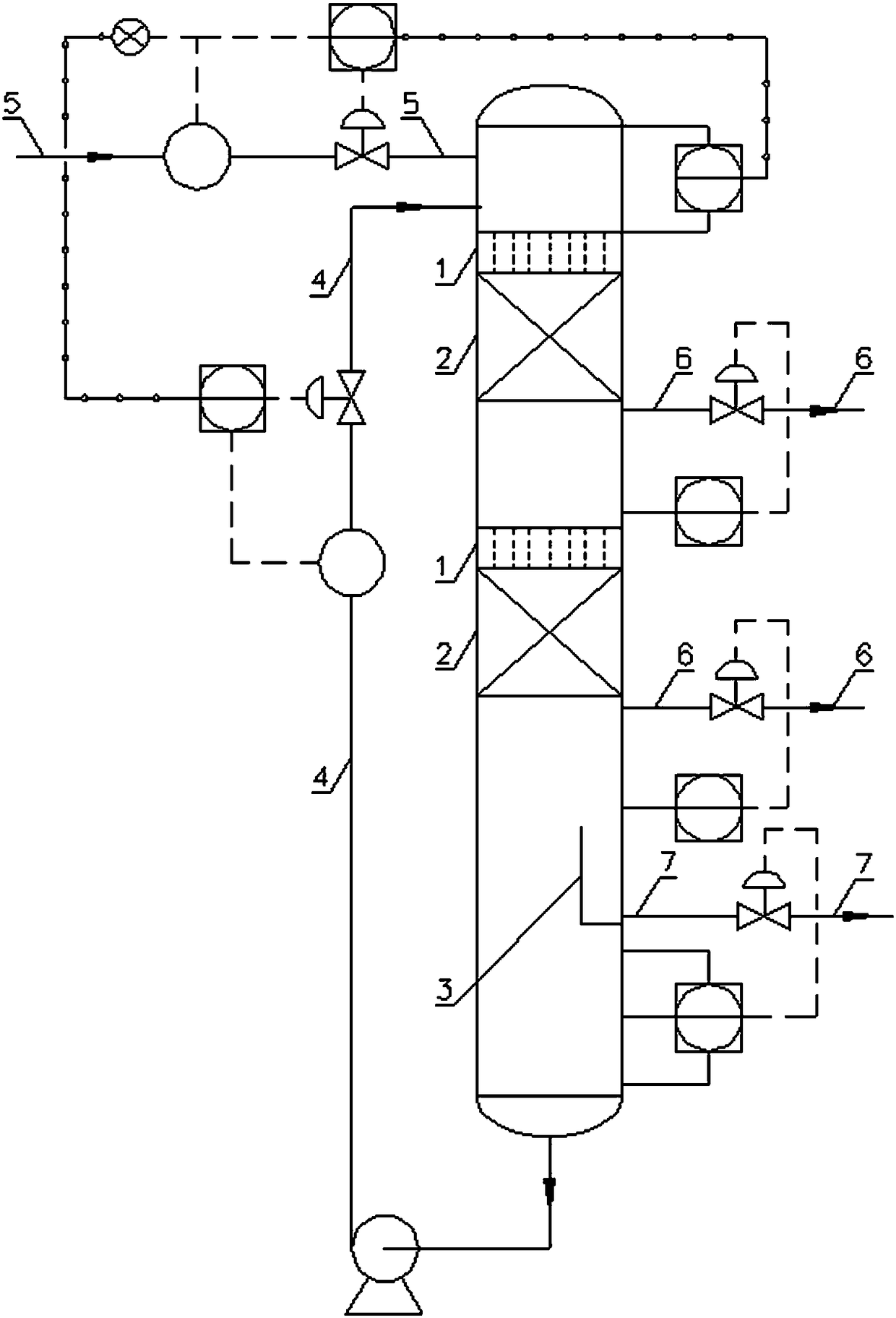
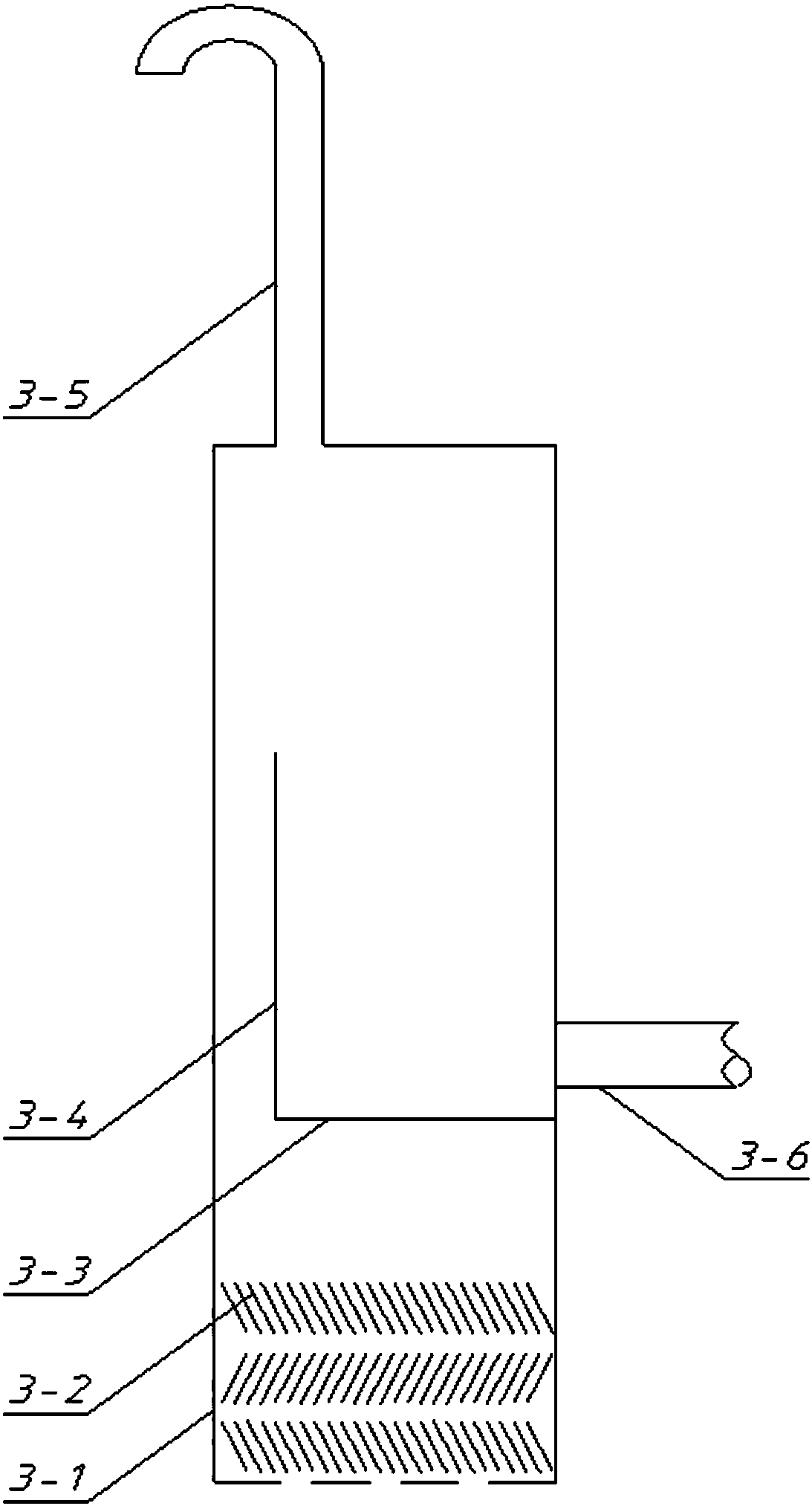
Silicon carbide micro-channel alkylation reactor and application method thereof
PendingCN108126637AImprove temperature distributionBoost octaneChemical/physical/physico-chemical microreactorsLiquid hydrocarbon mixtures productionTemperature controlAlkyl transfer
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
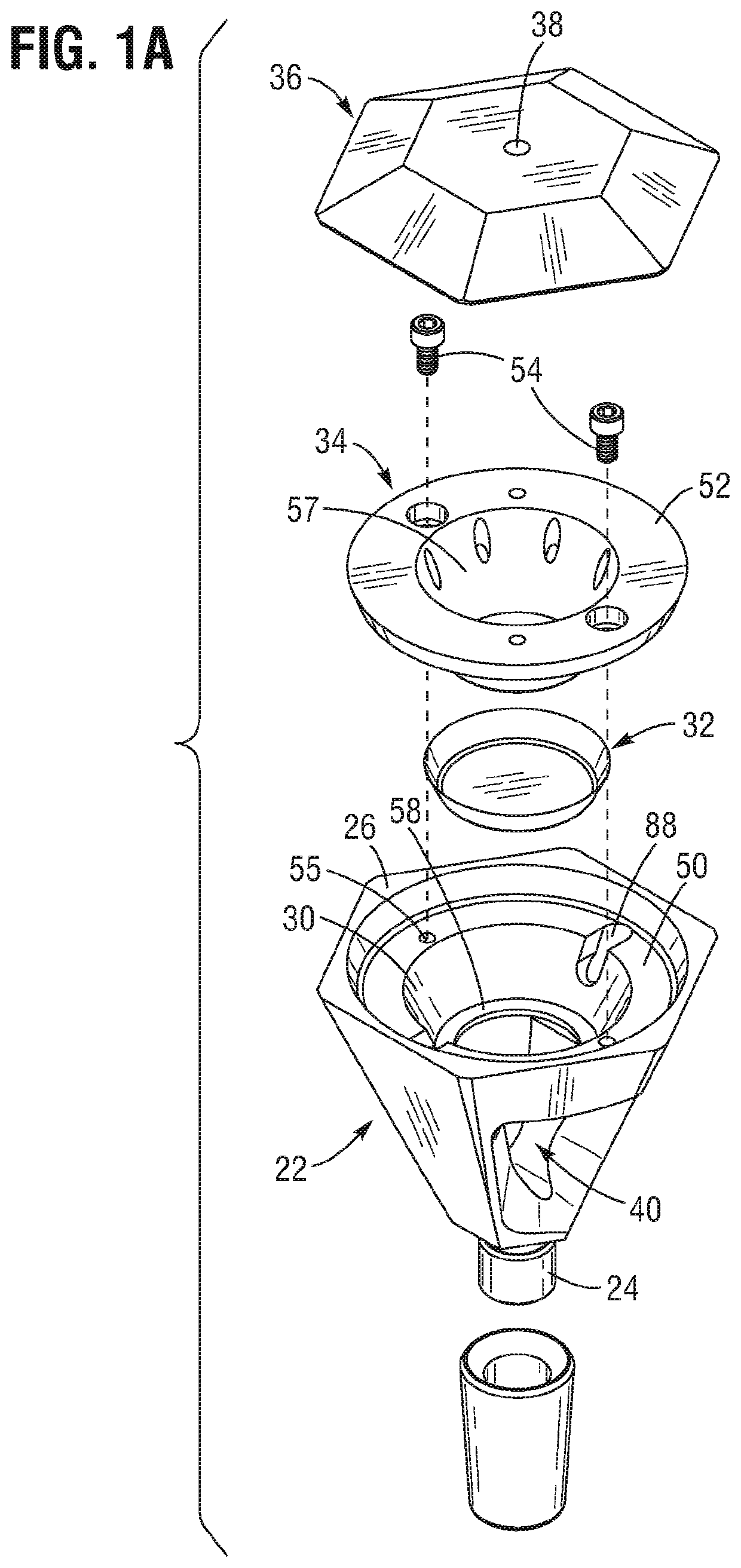
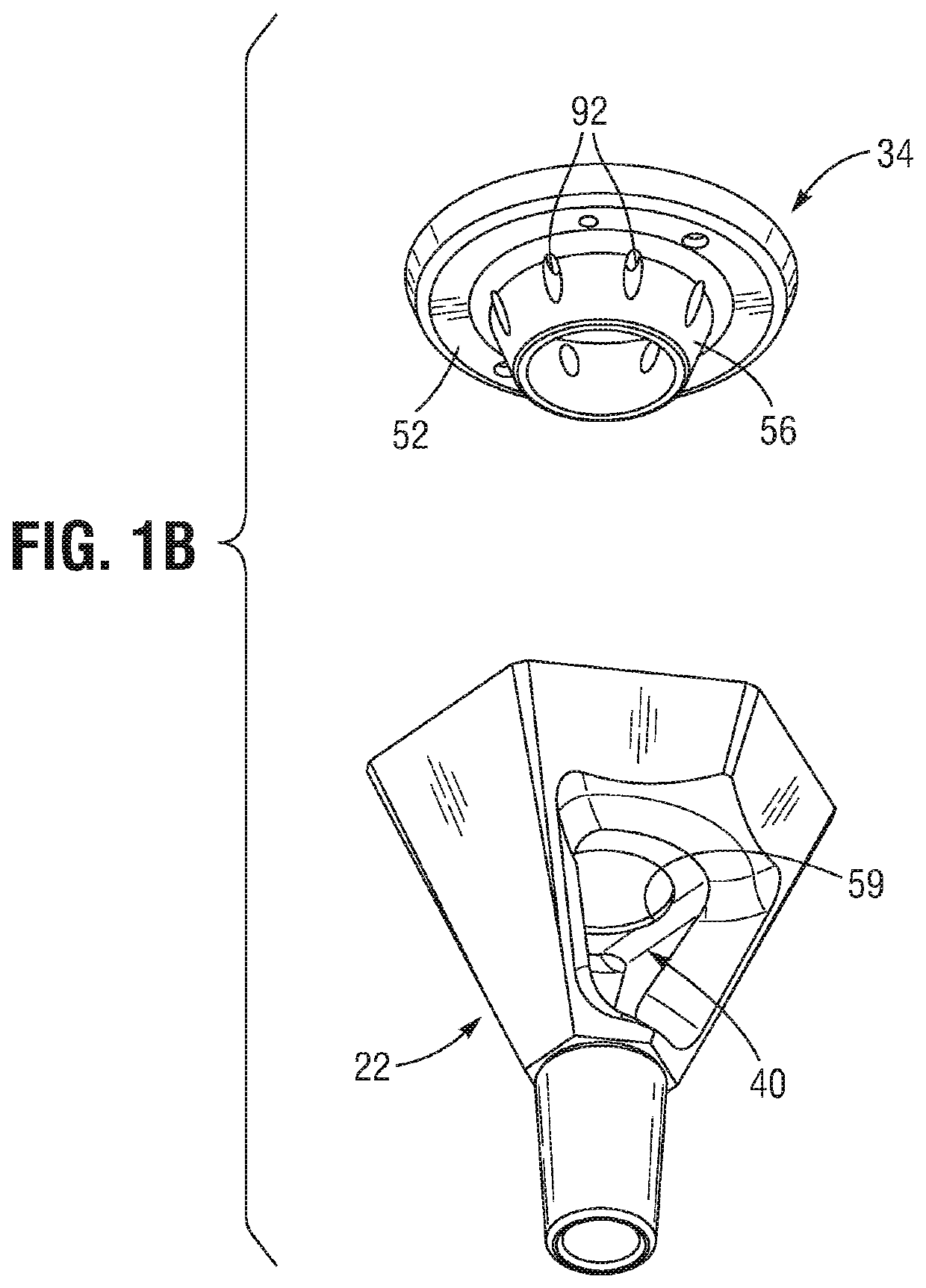
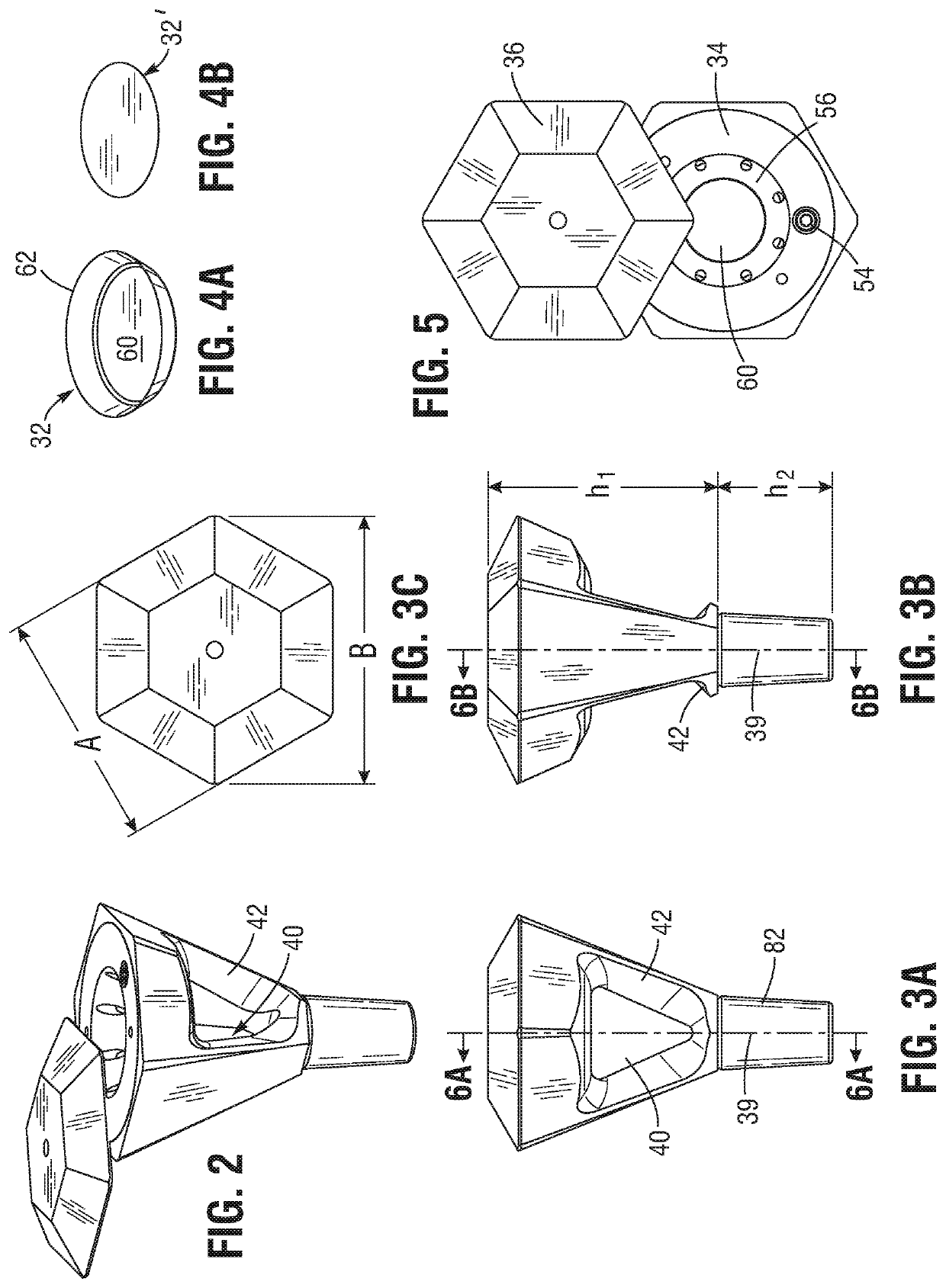
Butane-free smoking device
Owner:ANTHONY DUSTIN
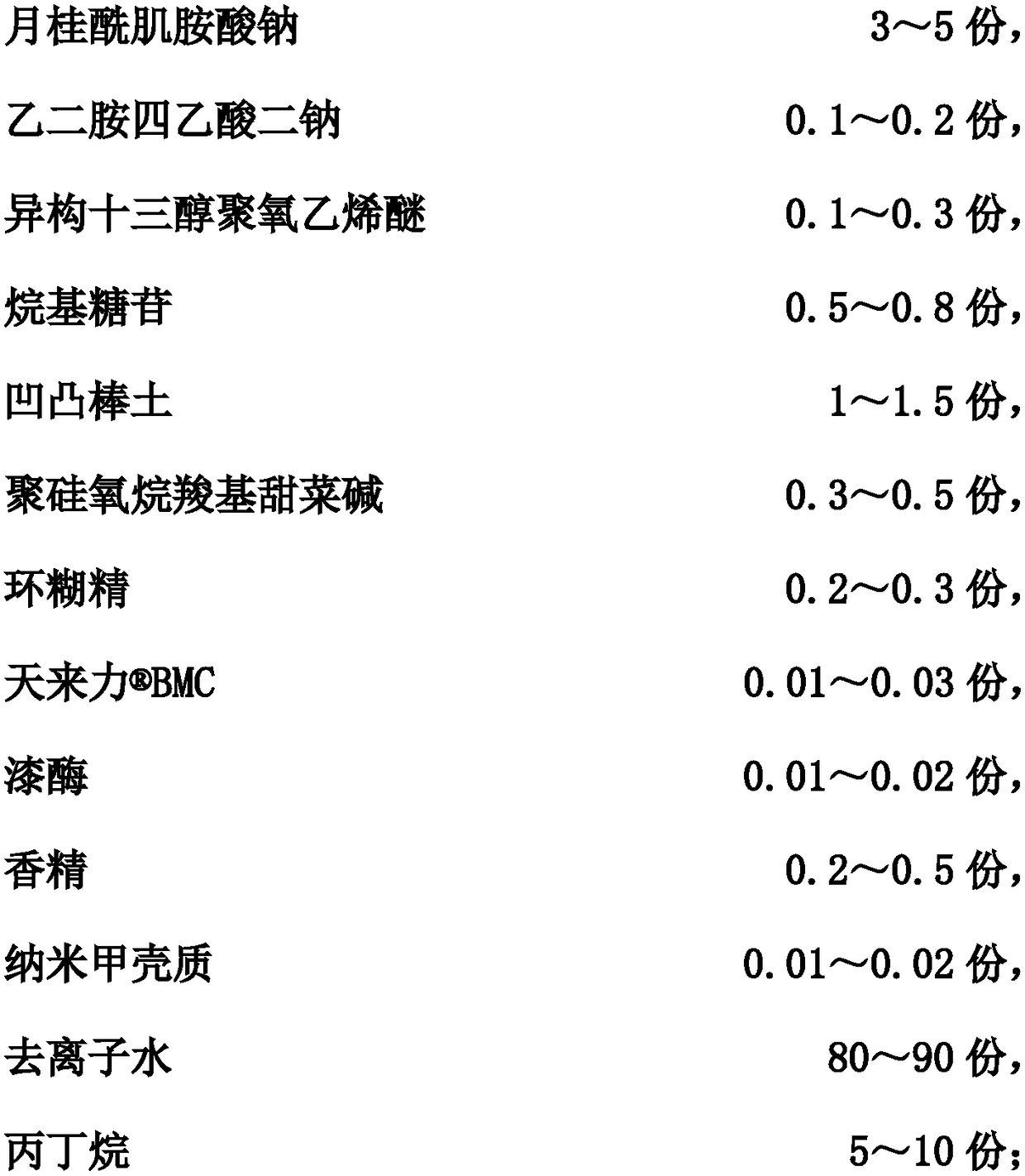
Slow release type photocatalyst bleaching cleaning aerosol
InactiveCN108822998AEasy to useNot corrosiveInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsOrganic detergent compounding agentsBetaineCyclodextrin
Owner:ZHEJIANG LUDAO TECH CO LTD
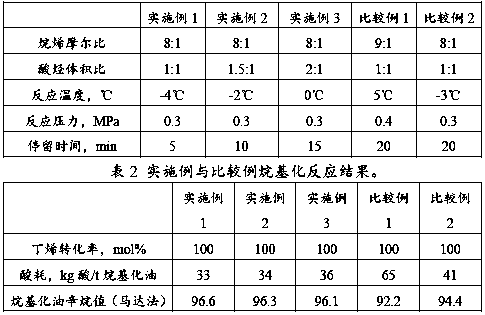
Preparation method of vanadium-phosphorus-oxygen catalyst for regulating and controlling crystal face, and butane oxidation application
ActiveCN112473707AMicroscopically mixed evenlyEase of industrial preparationPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic chemistryO-Phosphoric AcidPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of a vanadium phosphorus oxide catalyst for regulating and controlling a crystal face. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing a supergravity circulating device; adding a mixed solvent of isobutanol and benzyl alcohol into a feed liquid storage area, adding V2O5, heating, preserving heat, starting a motor, an ultrasonic probe and a submerged pump, spraying reaction liquid onto a filler through the submerged pump, returning the reaction liquid to the feed liquid storage area after the reaction liquid passes through the filler, and carrying out reduction reaction for 1-3 hours; cooling to 85-95 DEG C in the supergravity circulating device, adding concentrated phosphoric acid, and heating to 110-115 DEG C; reacting for 3-5 hours to obtain a vanadium-phosphorus-oxygen catalyst precursor; and drying the vanadium-phosphorus-oxygen catalyst precursor in a drying oven at the temperature of 110-130 DEG C for 8-15 hours, and then activating at the temperature of 350-450 DEG C. According to the invention, the crystal face orientation of the prepared catalyst is changed, and a dominant crystal face is converted into a 001 crystal face from an existing 130 crystal face for preparing a vanadium-phosphorus-oxygen catalyst (VO(HPO4).0.5H2O).
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH +1
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap