Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5 results about "Nuclease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A nuclease (also archaically known as nucleodepolymerase or polynucleotidase) is an enzyme capable of cleaving the phosphodiester bonds between nucleotides of nucleic acids. Nucleases variously effect single and double stranded breaks in their target molecules. In living organisms, they are essential machinery for many aspects of DNA repair. Defects in certain nucleases can cause genetic instability or immunodeficiency. Nucleases are also extensively used in molecular cloning.
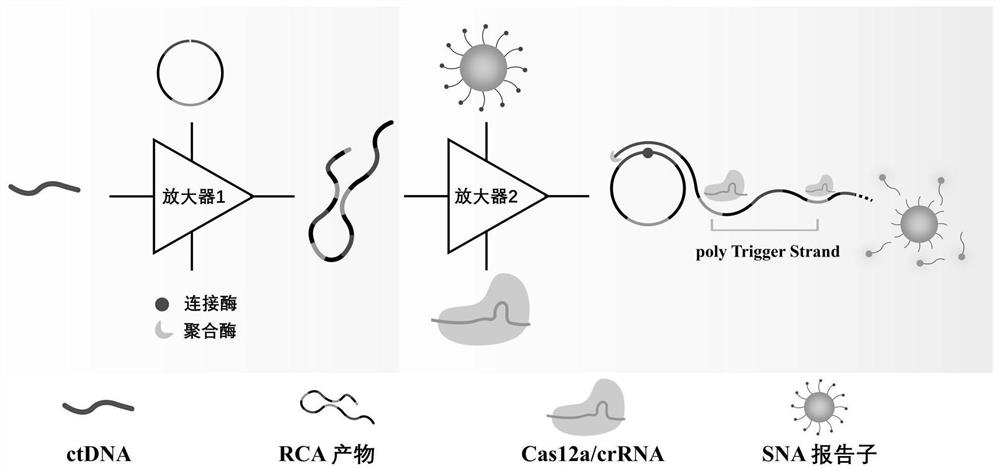
Preparation method of paper-based photocathode biosensor for detecting microRNA
ActiveCN110376259AIncrease surface areaGood photosensitizationMaterial electrochemical variablesPhotocathodeOxygen
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
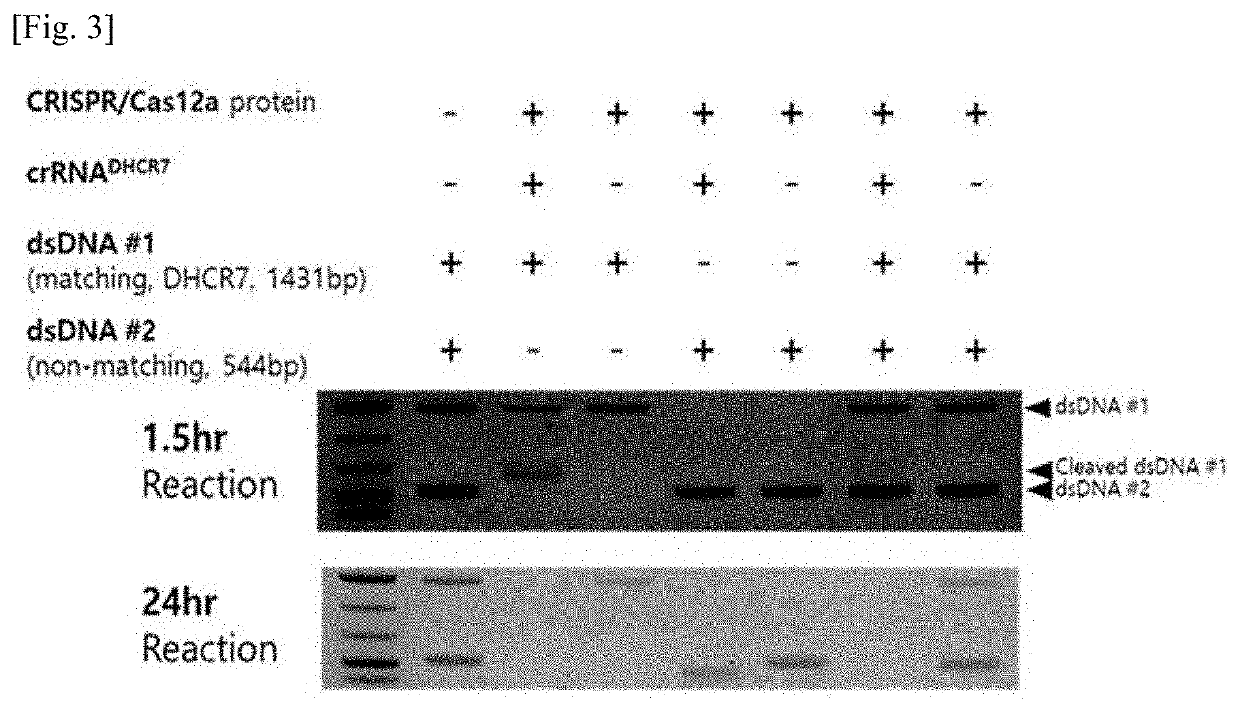
Pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases and a coding gene and application thereof. The pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases (TALEN) is obtained by merging a pair of DNA identifying proteins with two different source subunits of a Fok1 DNA incision enzyme respectively, and two adjacent locuses on a prion protein gene (PRNP) exon2 of a goat or a sheep can be identified in specificity mode. When the pair of transcriptional activation subsample effect factor nucleases is simultaneously transferred into a host cell, the nucleases can shoot targets of the exon2 locuses of a host cell PRNP gene and enable the target shooting locuses to have genic mutation so as to perform targeted modification on the PRNP gene of the goat or sheep. The nucleases have the advantages of being strong in specificity, high in target shooting efficiency and accuracy and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
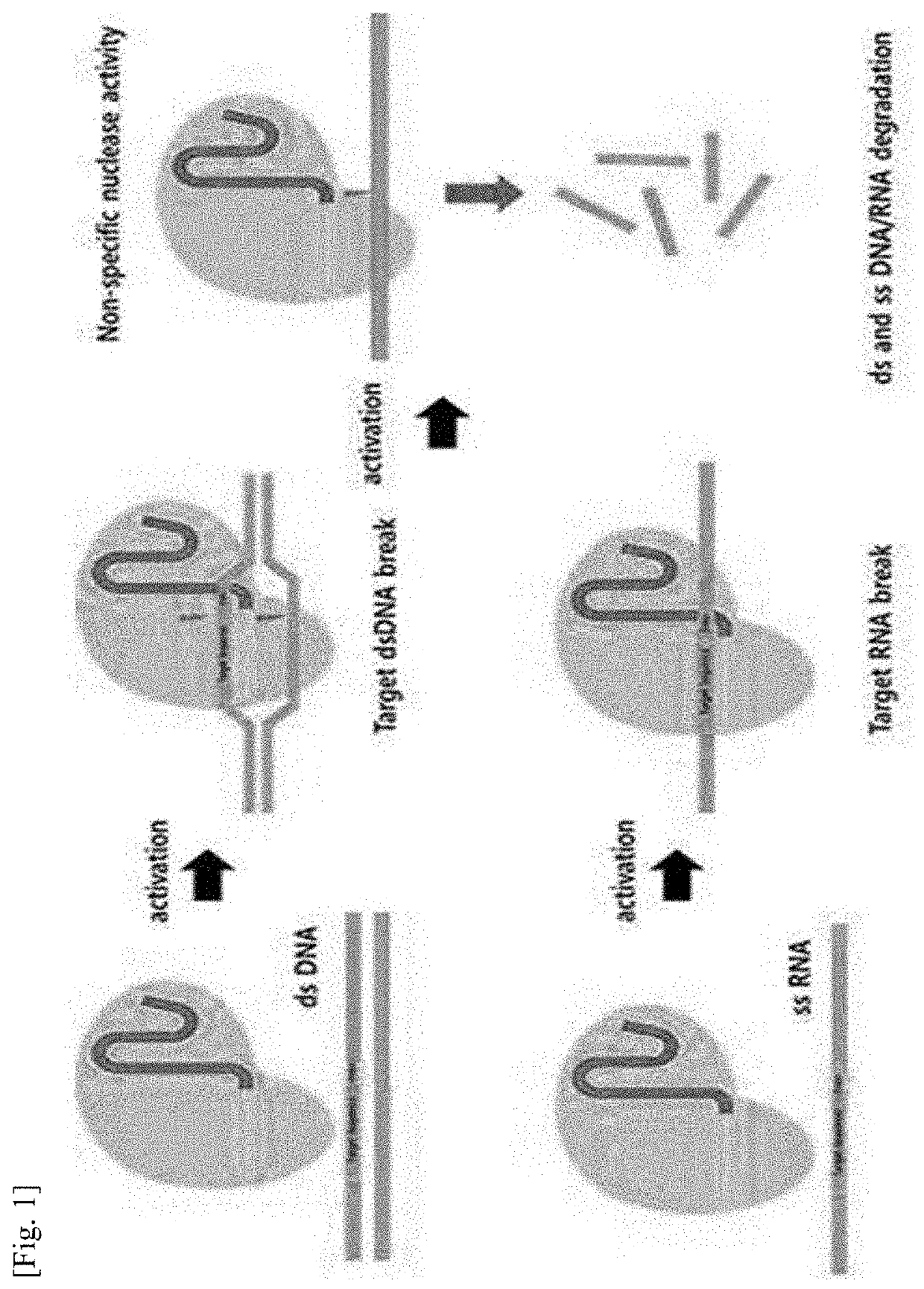
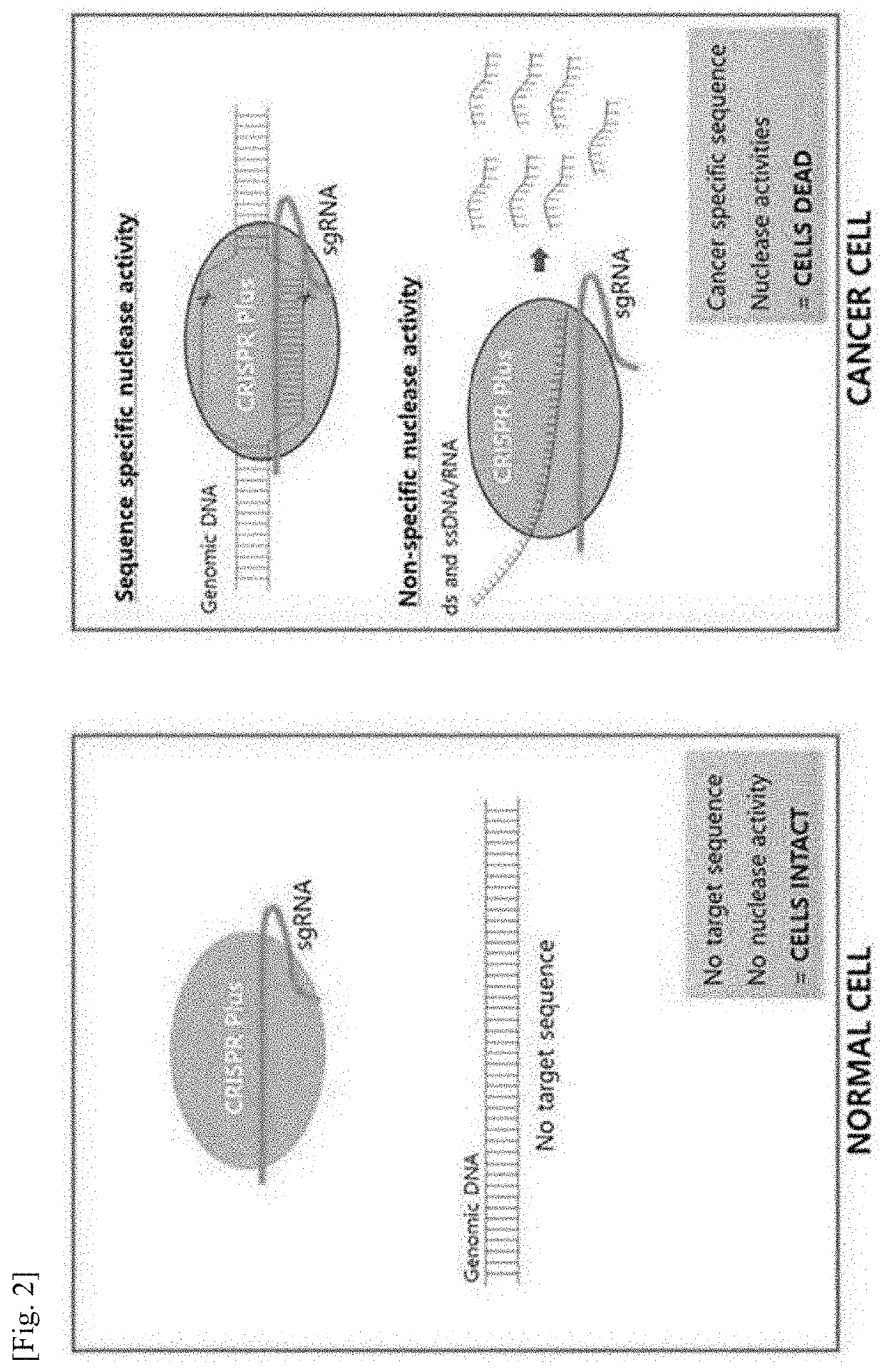
Pharmaceutical composition for treating cancer, containing guide RNA and endonuclease as active ingredients
PendingUS20210128697A1Strong specificityEfficient killingOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAnticarcinogenCancer cell
Owner:G FLAS LIFE SCI
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap