Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about "Position/direction control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
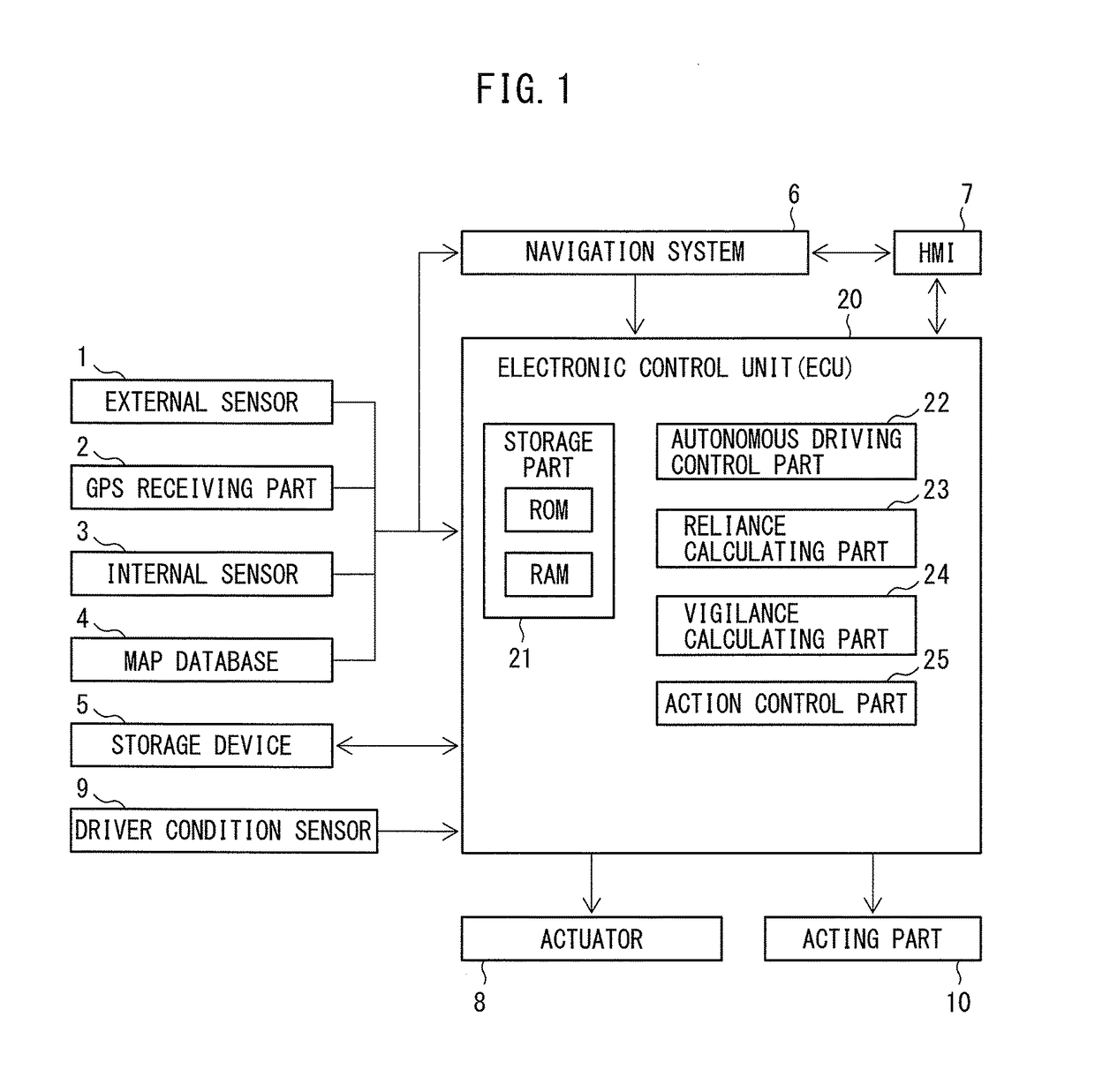
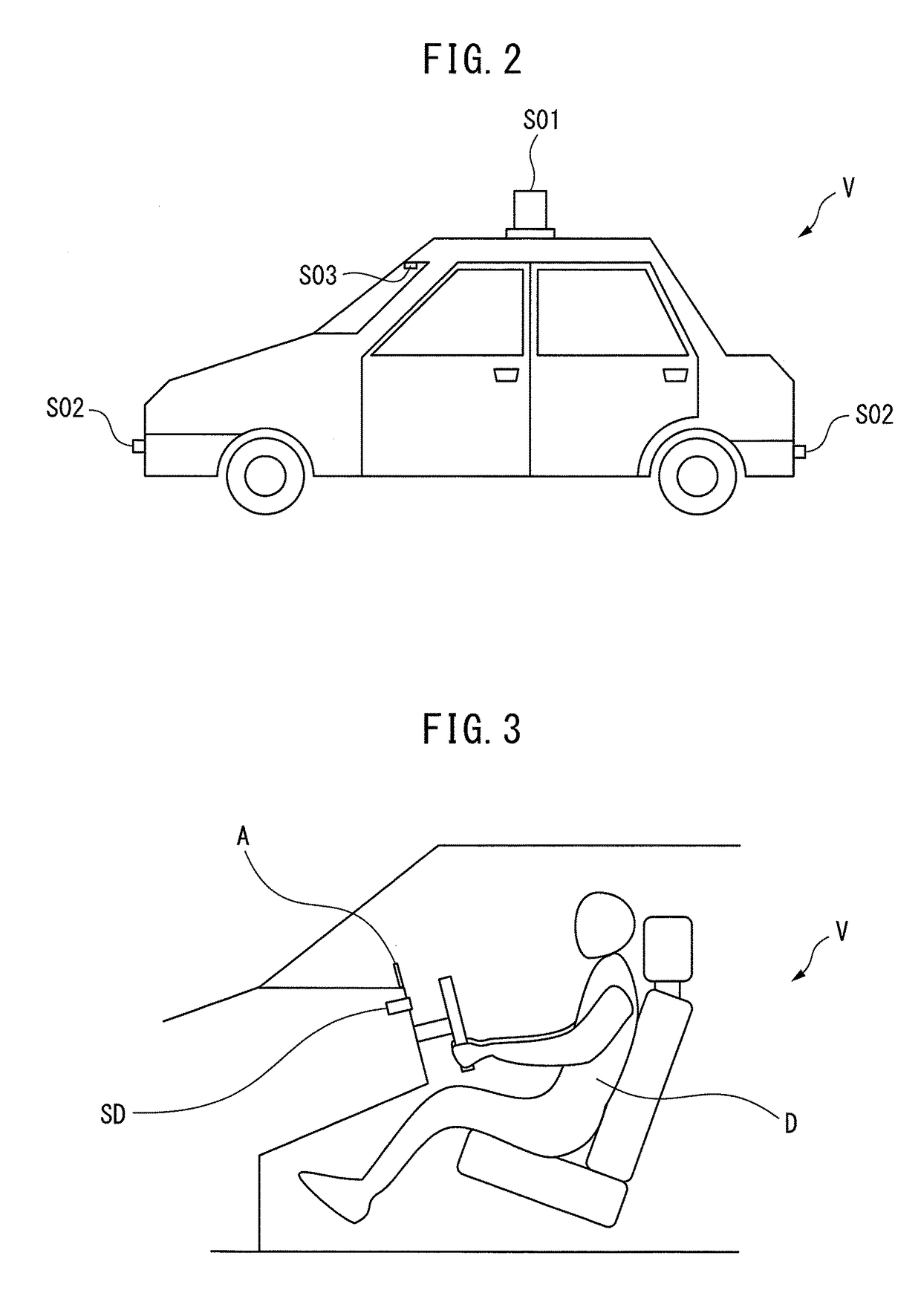
Determining when to drive autonomously
ActiveUS8718861B1Instruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlSimulationArtificial intelligence
Owner:WAYMO LLC
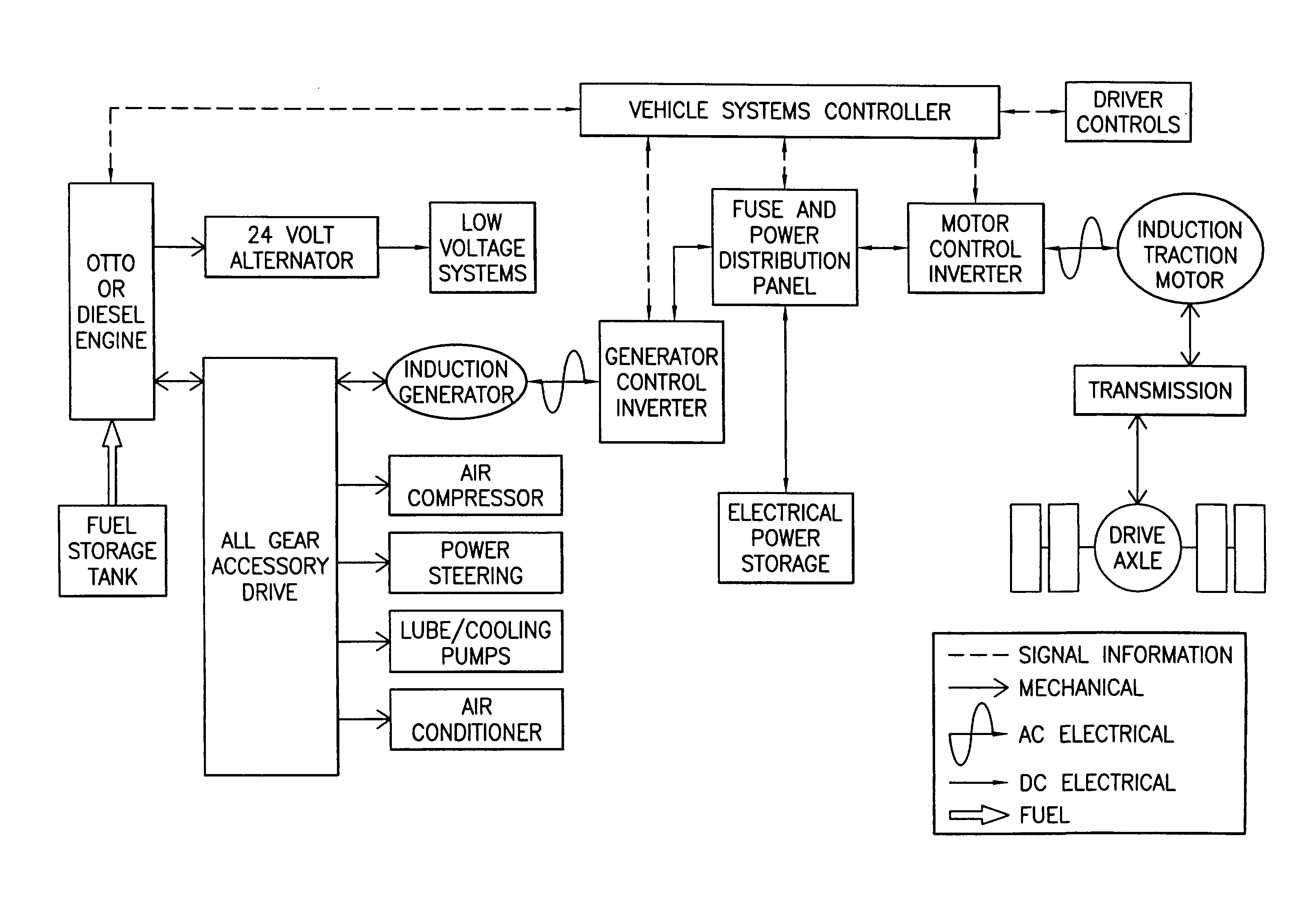
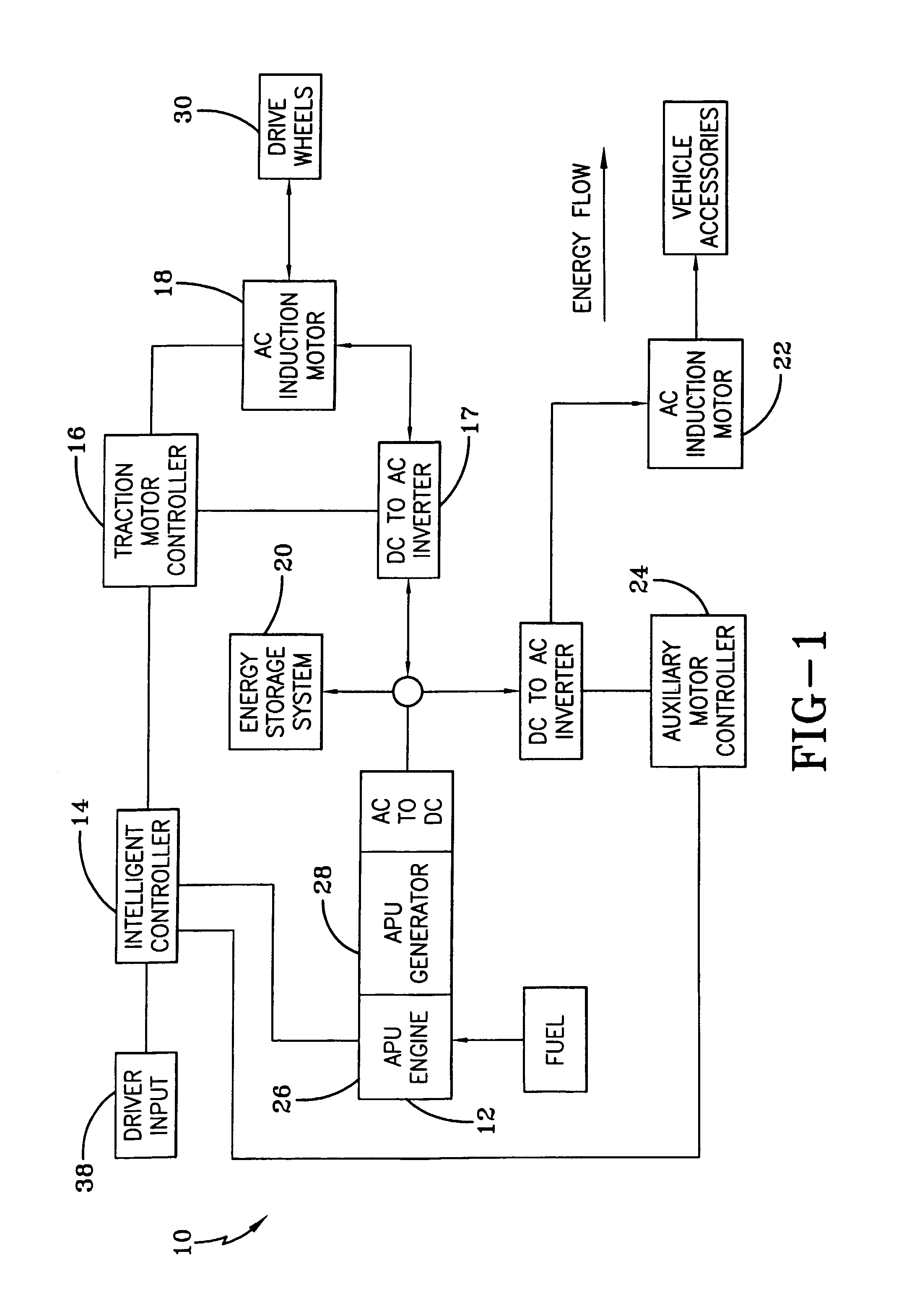
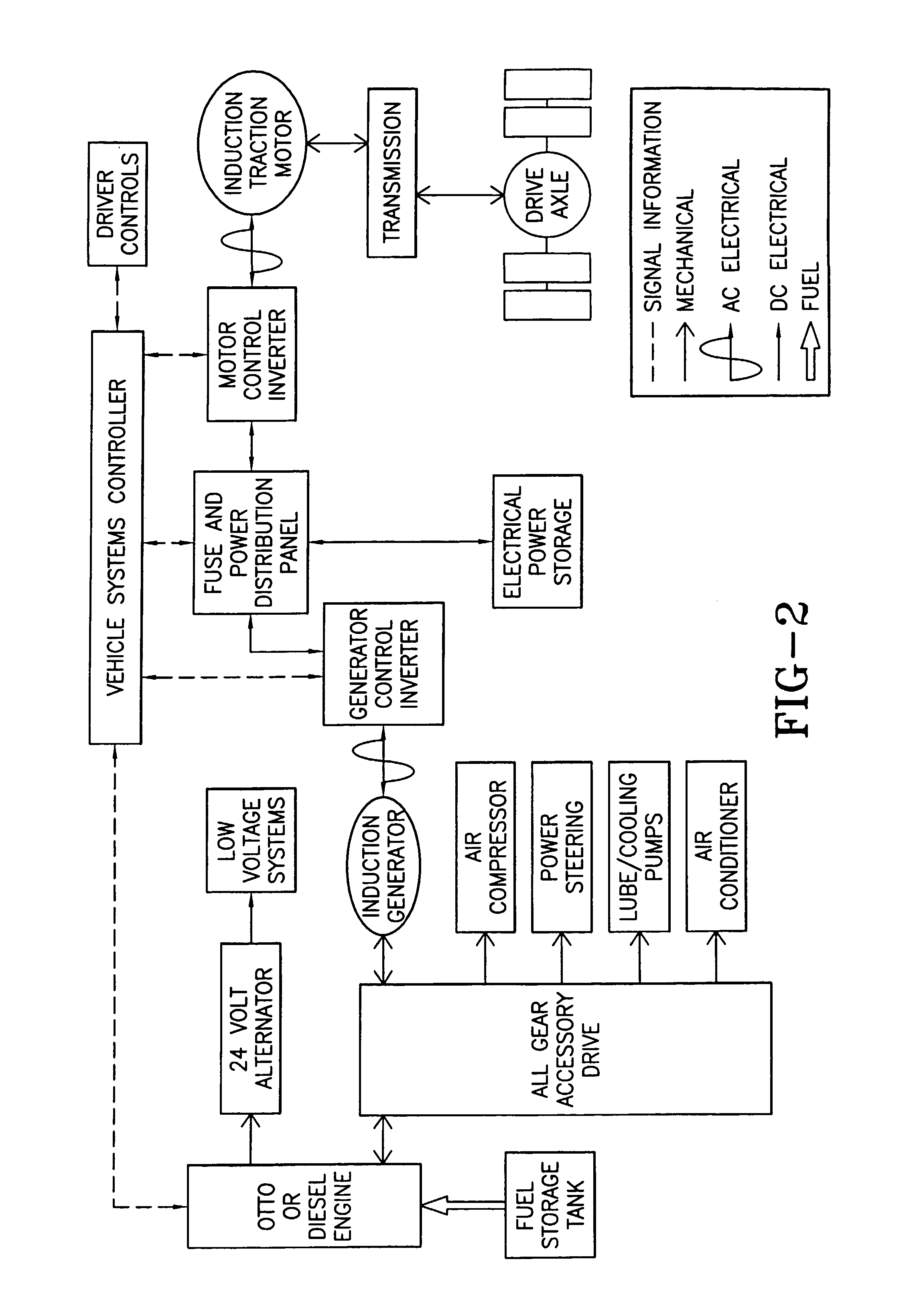
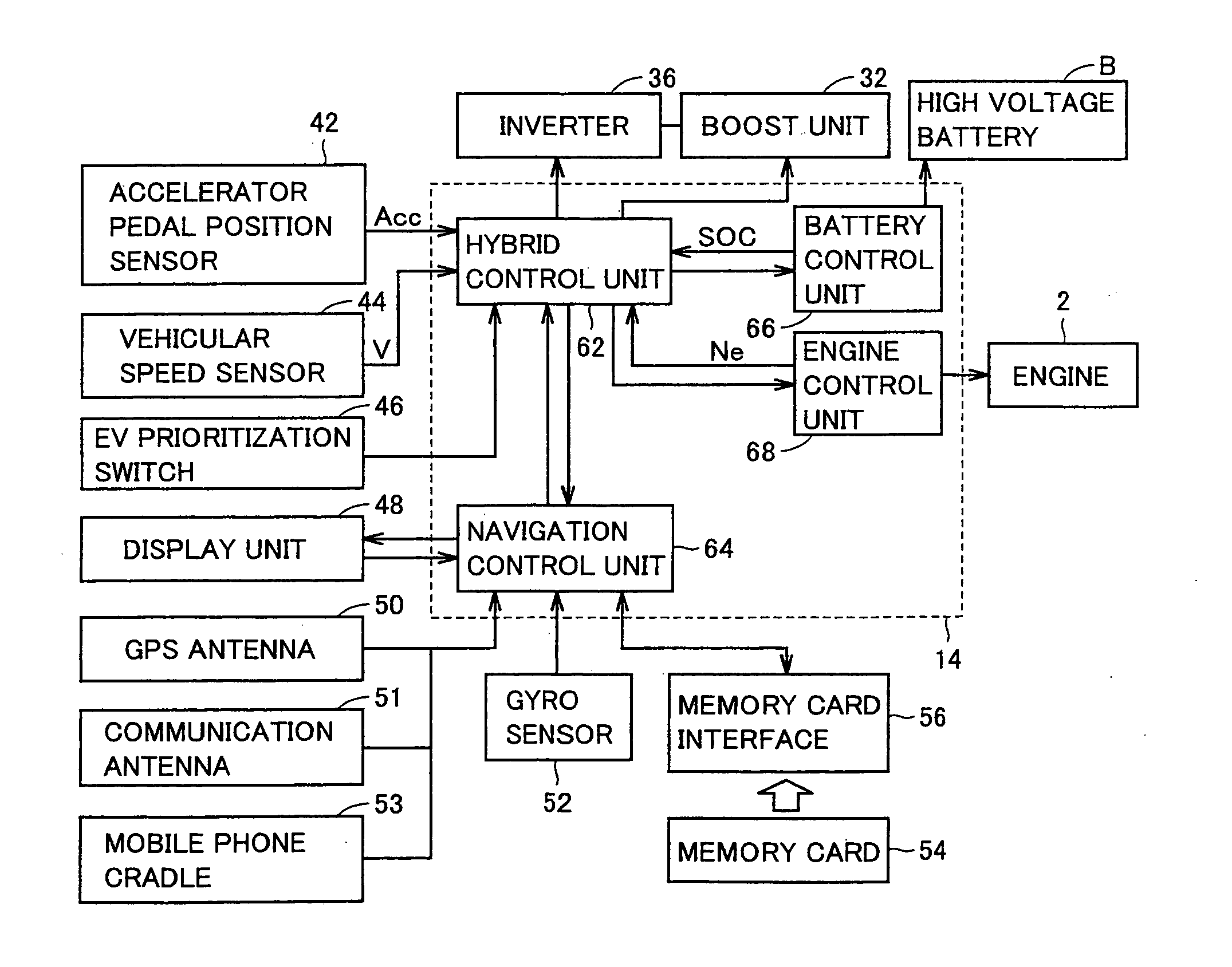
Hybrid electric vehicle
InactiveUS7252165B1Poor vehicle performanceImprove variationDigital data processing detailsVehicle sub-unit featuresLow voltageAuxiliary power unit
Owner:BOWLING GREEN STATE UNIV
Jackknife Condition for Backing up of a Vehicle Attached to a Long Wheelbase Dual Axle Trailers
A jackknife warning condition controller and control method notifies a driver of a potential jackknife situation while backing up a vehicle with an attached trailer. The vehicle has a front axle with steerable front wheels controlled by the driver and a rear axle with non-steerable rear wheels. The trailer has a front axle with non-steerable front wheels and a rear axle with steerable rear wheels controlled by a trailer steering controller. The jackknife controller receives an operator-controlled vehicle steering angle and a measured hitch angle. The jackknife warning condition controller determines a directional jackknife warning condition and compares the measured hitch angle with the determined directional jackknife warning condition. If the measured hitch angle satisfies the directional jackknife warning condition then a notification is sent to the driver.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
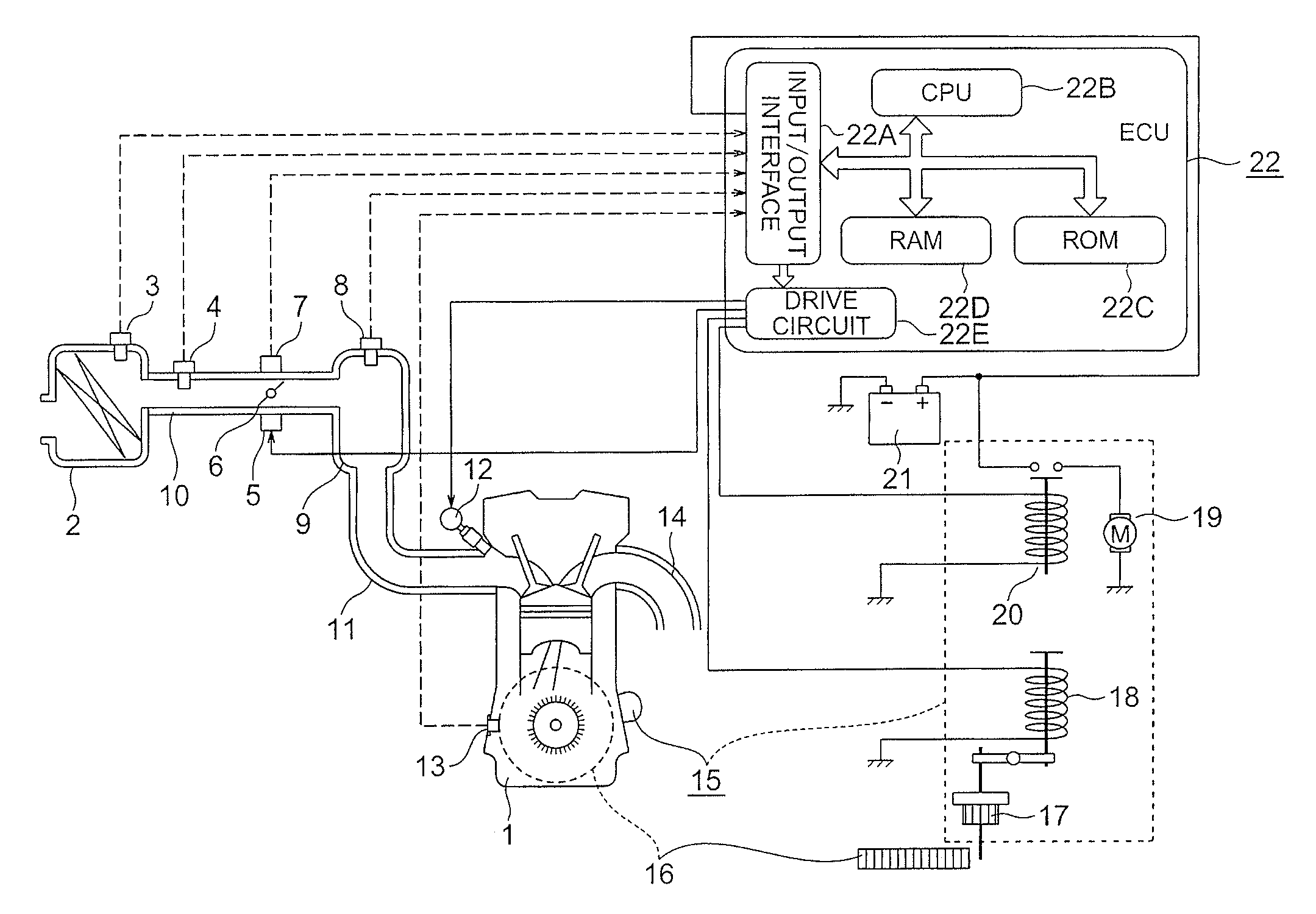
Internal combustion engine control for improved fuel efficiency
ActiveUS20100006065A1Undesirable vibration reductionImprove efficiencyAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlWork cycleFuel efficiency
A variety of methods and arrangements for improving the fuel efficiency of internal combustion engines are described. Generally, an engine is controlled to operate in a skip fire variable displacement mode. Feedback control is used to dynamically determine the working cycles to be skipped to provide a desired engine output. In some embodiments a substantially optimized amount of air and fuel is delivered to the working chambers during active working cycles so that the fired working chambers can operate at efficiencies close to their optimal efficiency. In some embodiments, the appropriate firing pattern is determined at least in part using predictive adaptive control. By way of example, sigma delta controllers work well for this purpose. In some implementations, the feedback includes feedback indicative of at least one of actual and requested working cycle firings. In some embodiments, the appropriate firings are determined on a firing opportunity by firing opportunity basis. Additionally, in some embodiments, an indicia of the current rotational speed of the engine is used as a clock input for a controller used to selectively cause the skipped working cycles to be skipped.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
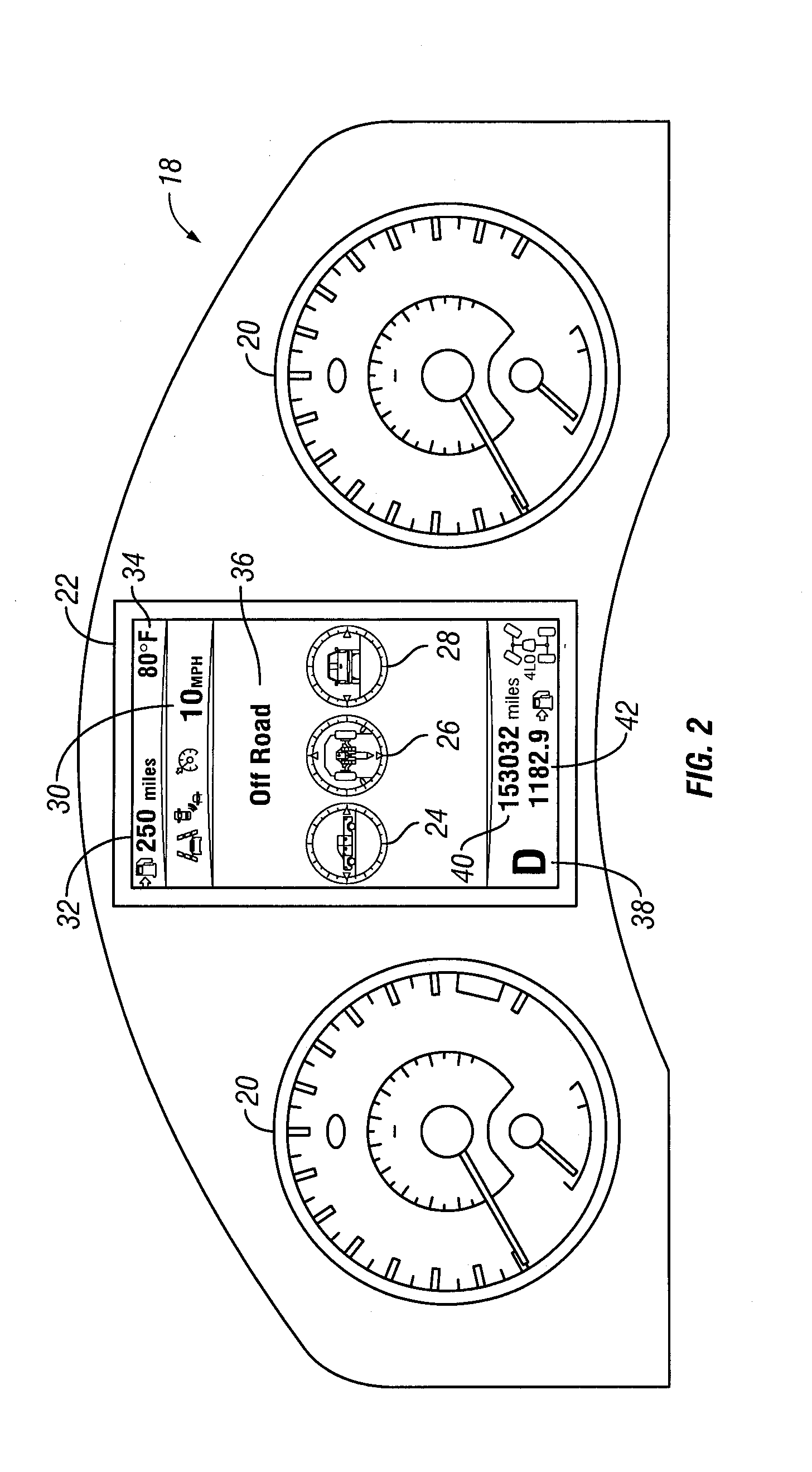
Vehicular display device, method of controlling the same, program, and storage medium having program stored therein
ActiveUS20100010697A1Increase awarenessIncrease mileageInstruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsTravel modeDisplay device
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
Control system and method
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
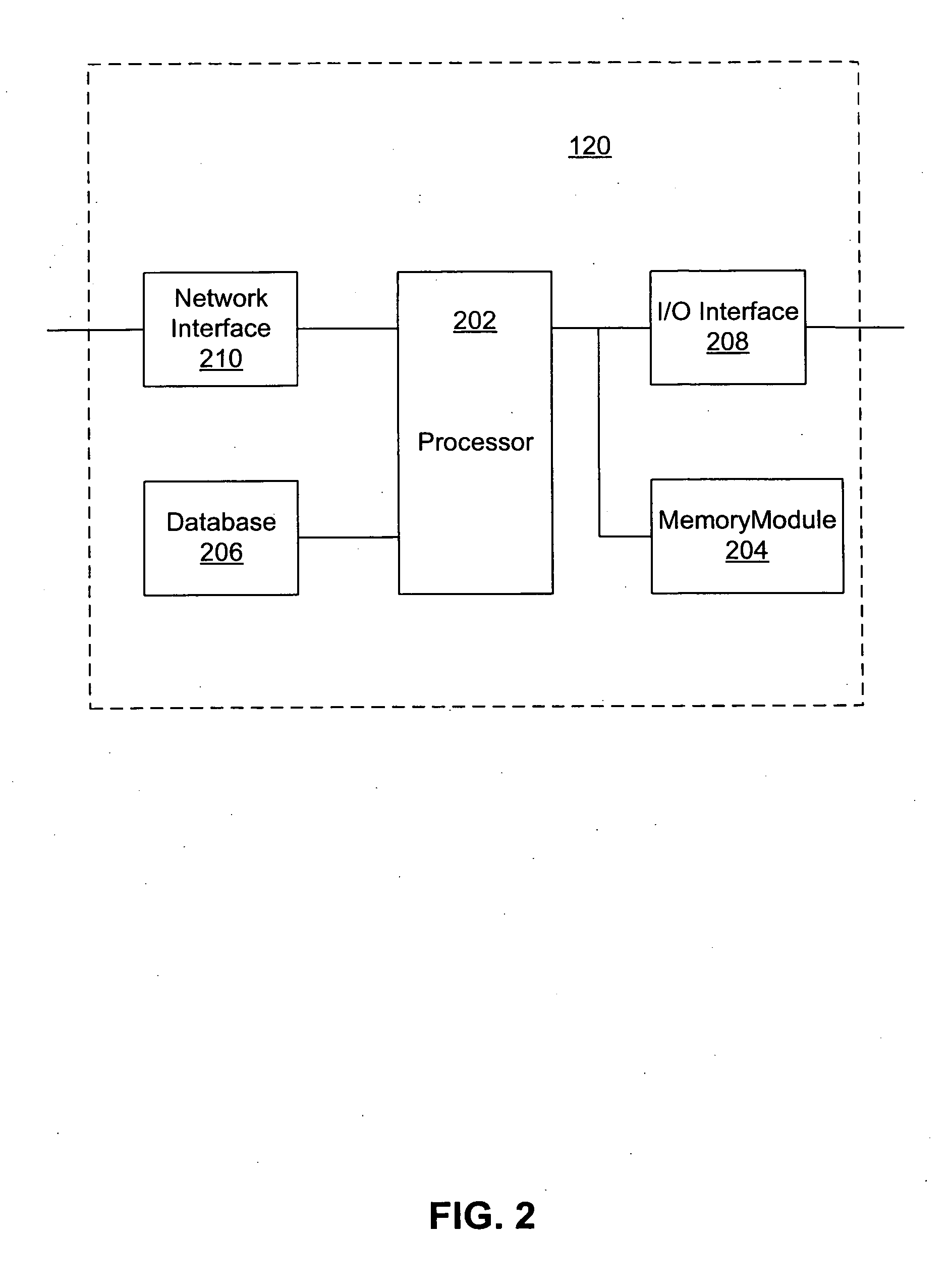
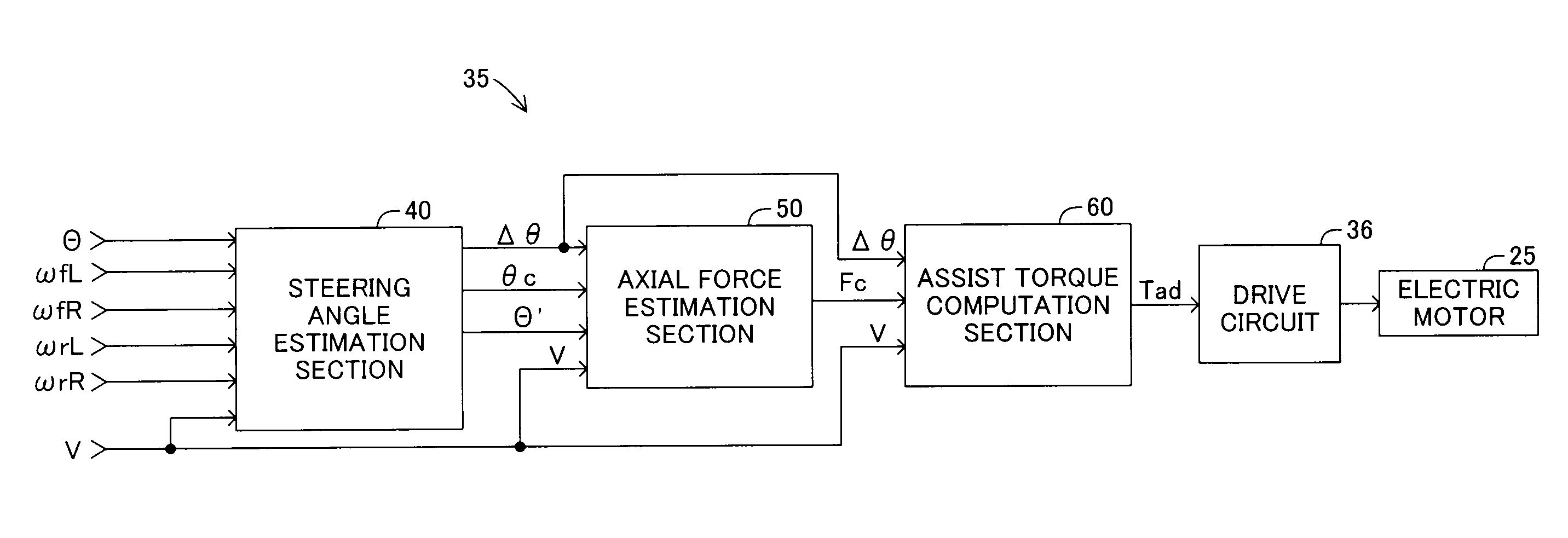
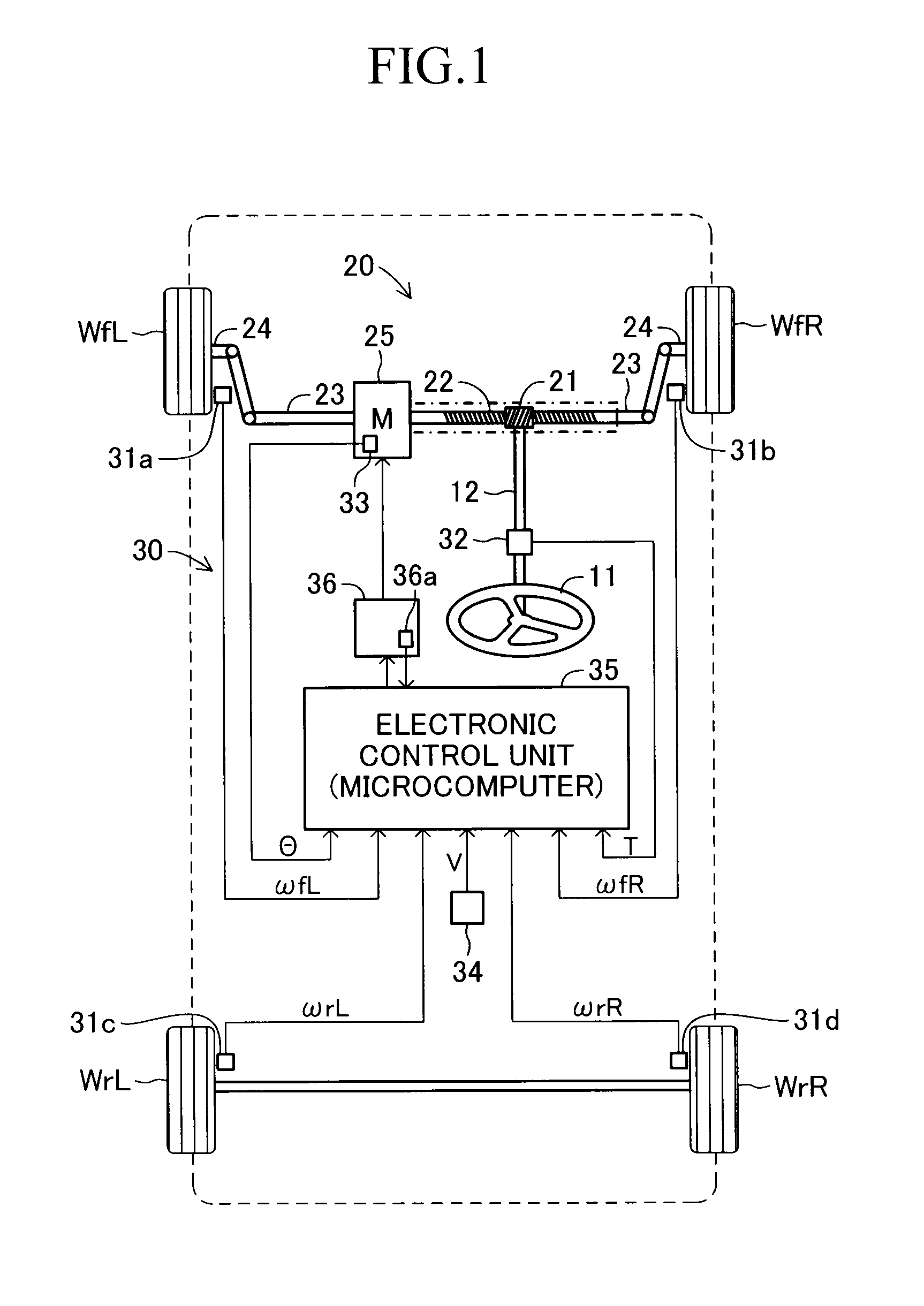
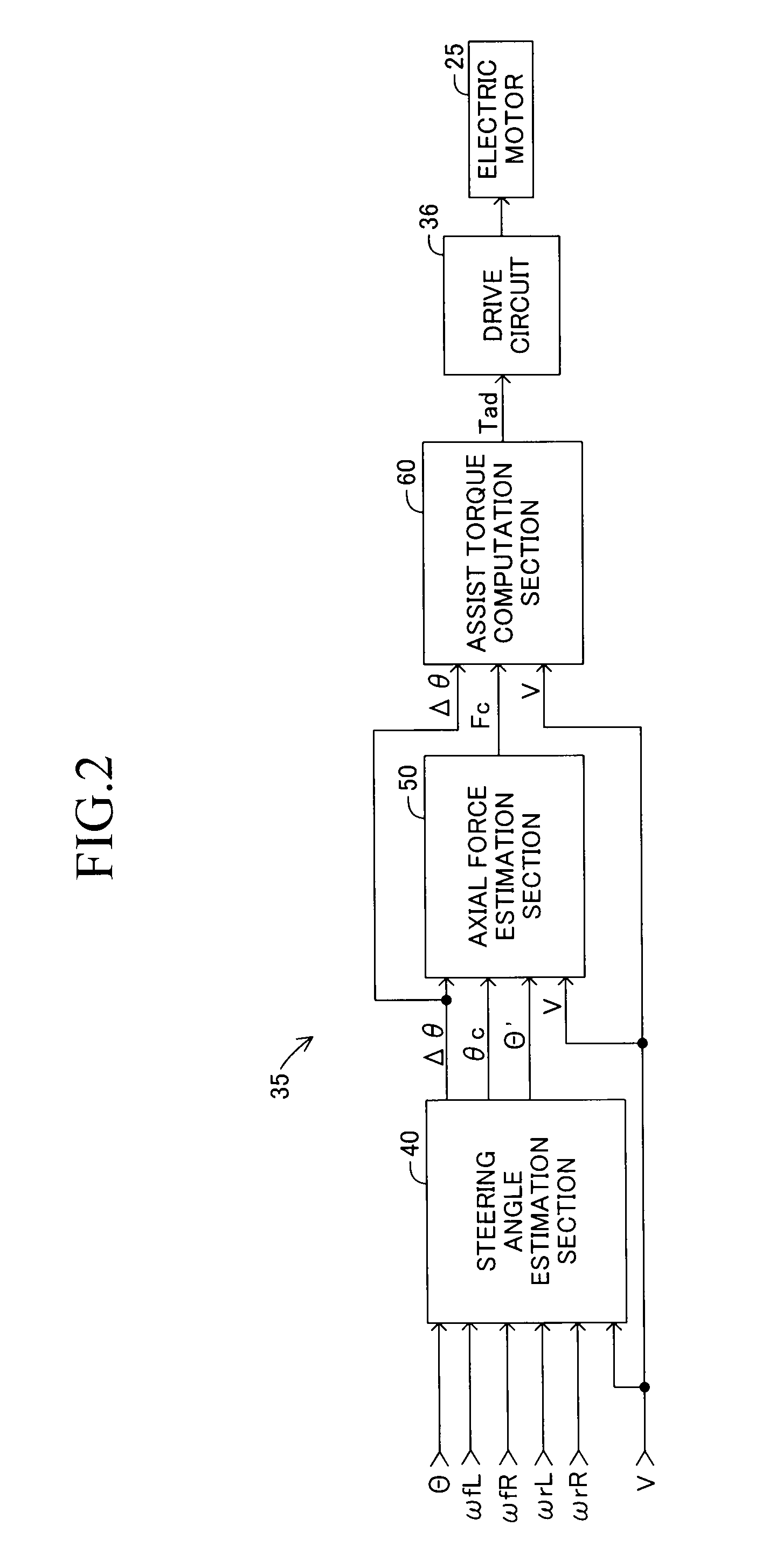
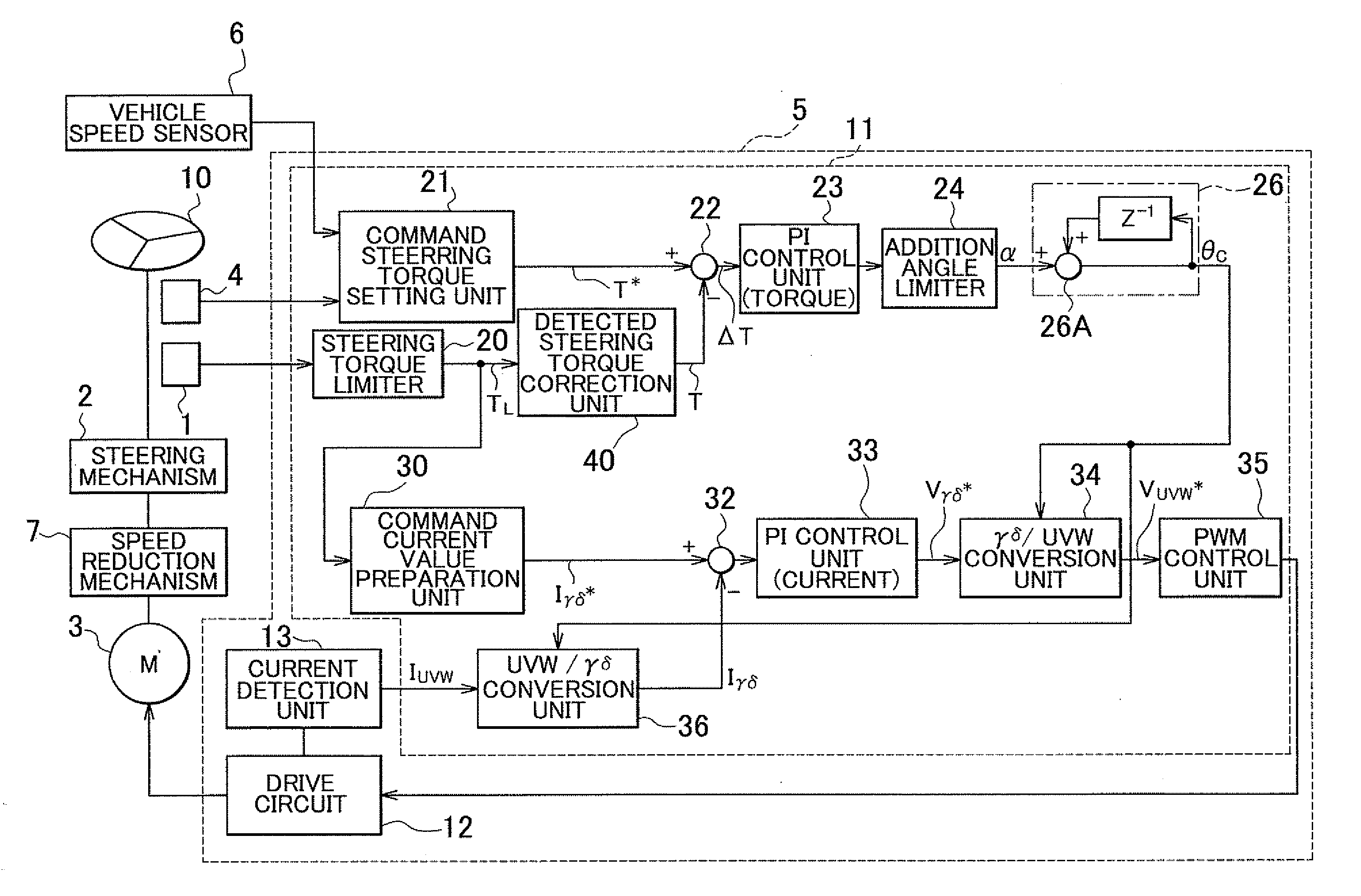
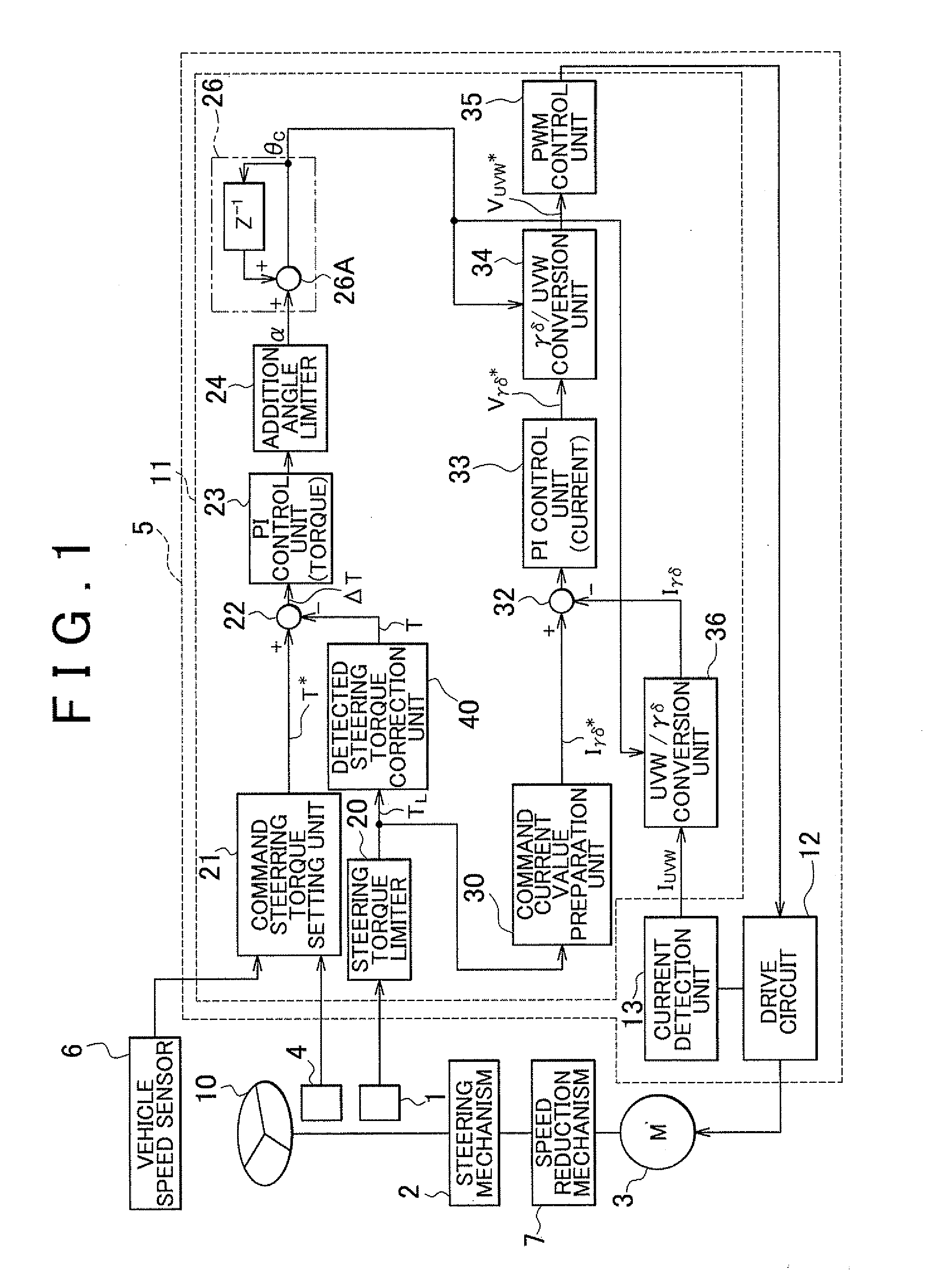
Electric power steering apparatus for vehicle
InactiveUS20120197493A1Steering initiationsAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringHysteresis
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
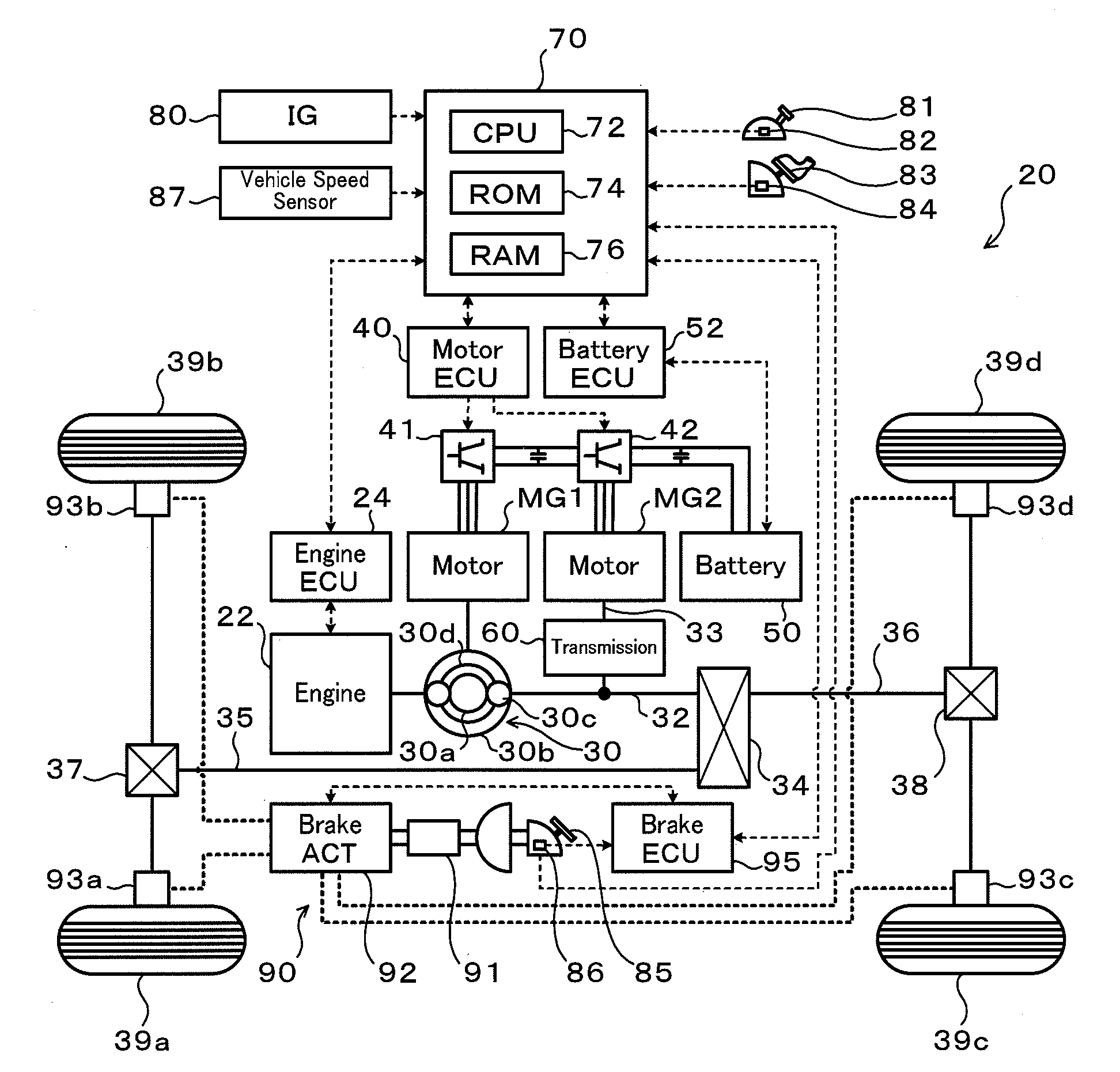
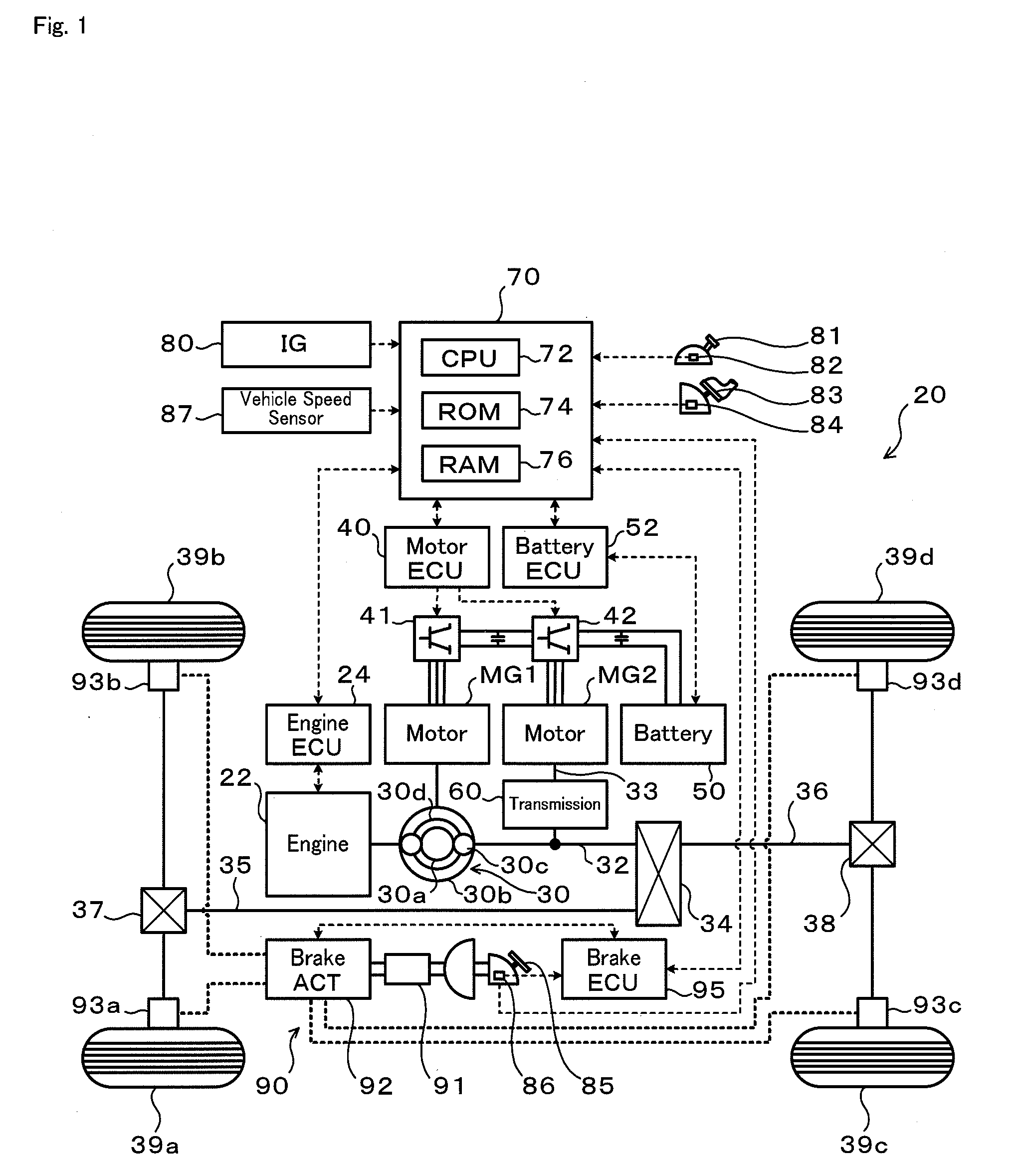
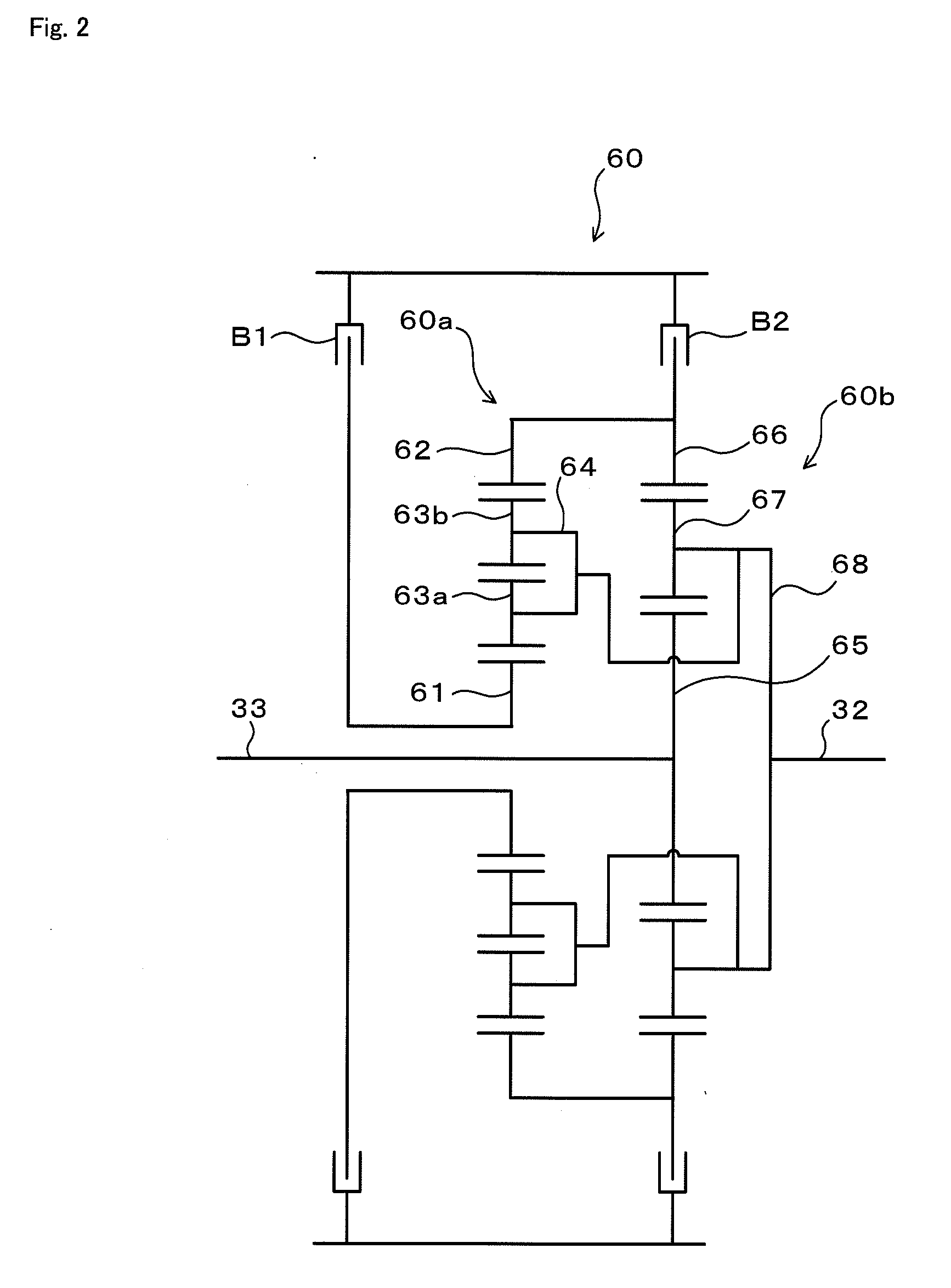
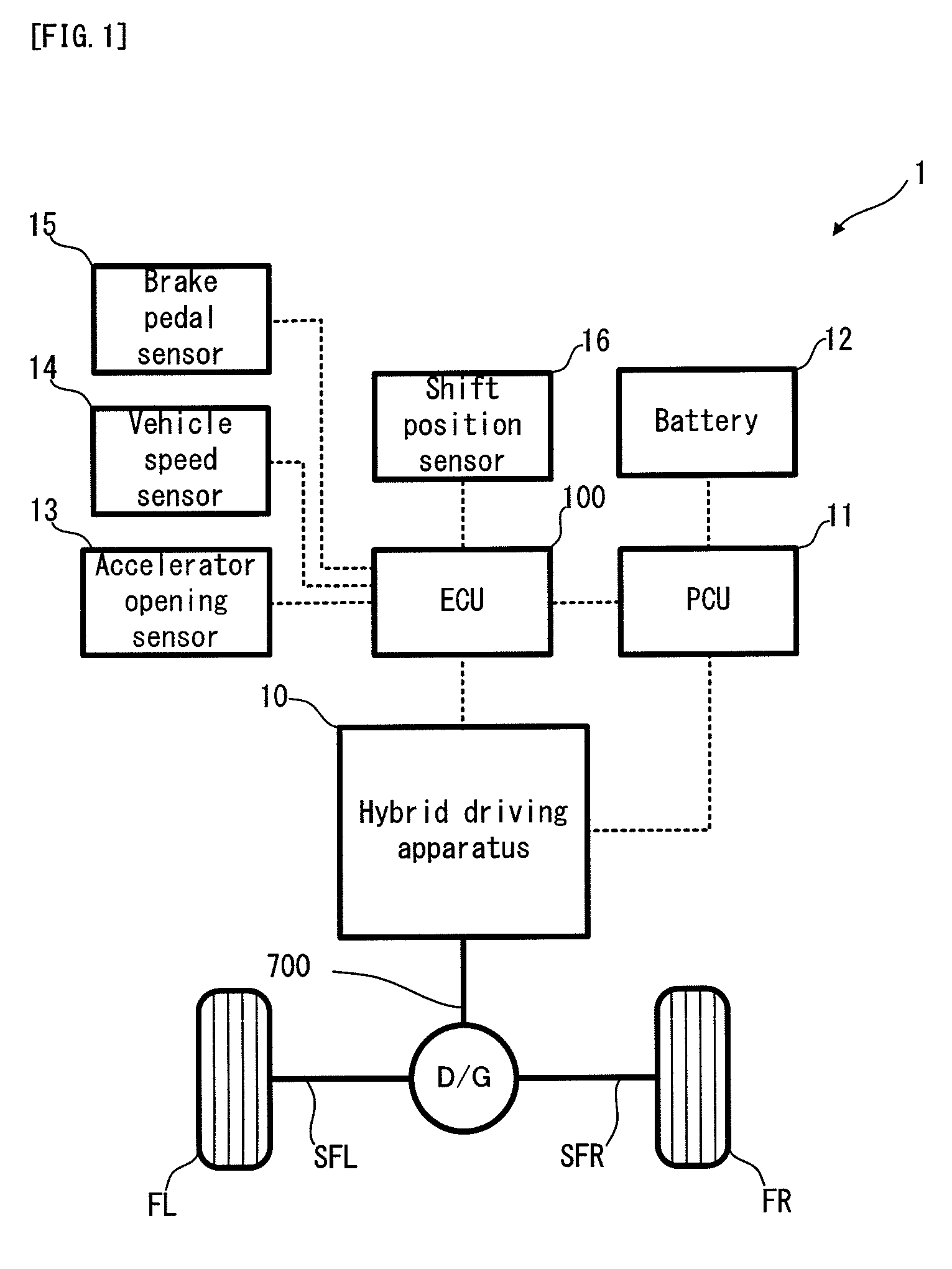
Vehicle and control method thereof, power output apparatus and control method thereof, and driving system and control method thereof
ActiveUS20080185199A1Reduce variationImprove braking effectHybrid vehiclesAnalogue computers for trafficBrake torqueRegenerative brake
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK +1
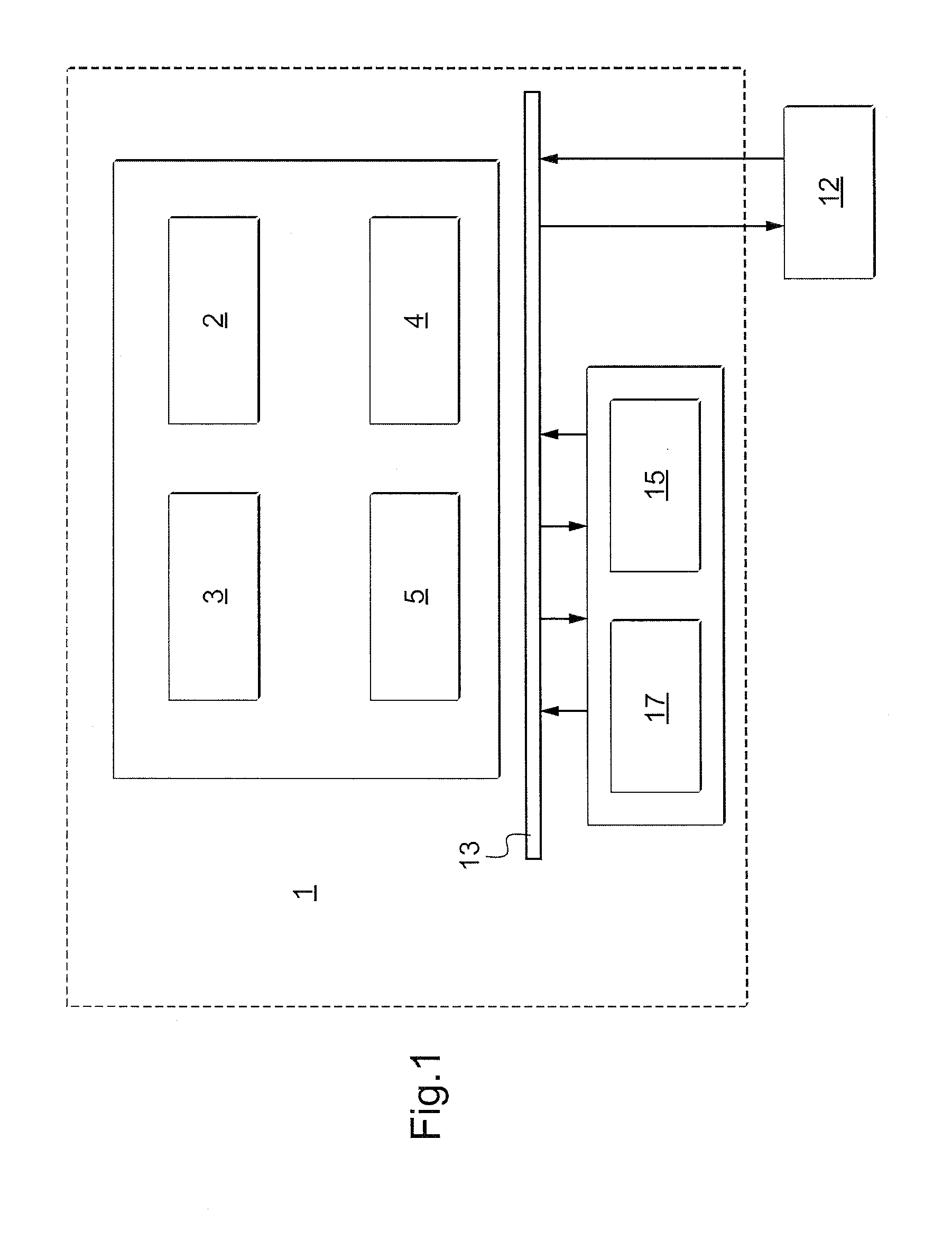
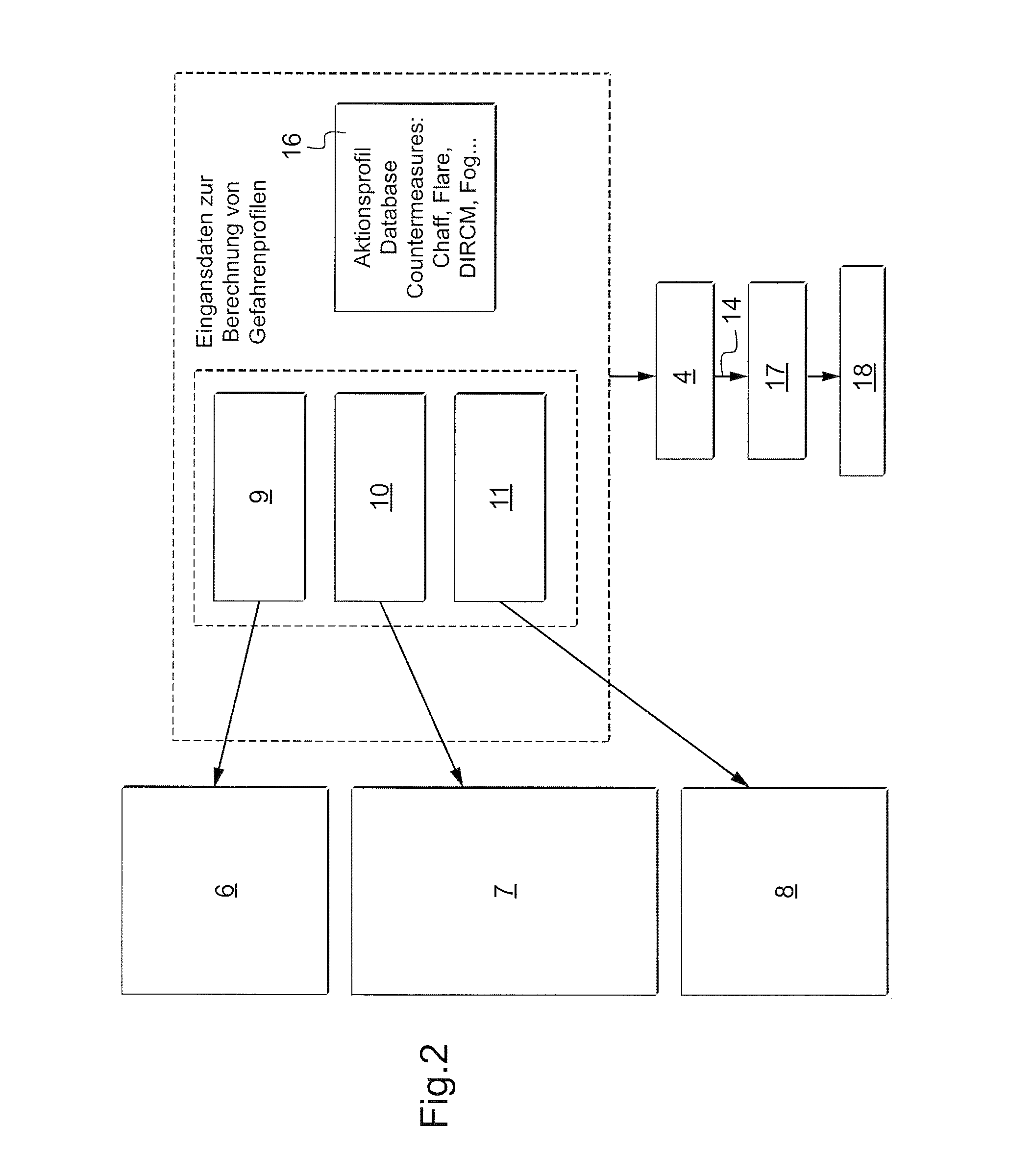
System and method for situation specific generation and assessment of risk profiles and start of suitable action for protection of vehicles
InactiveUS20110196551A1Defence devicesAnalogue computers for trafficRisk profilingData source
Owner:EUROCOPTER DEUT GMBH
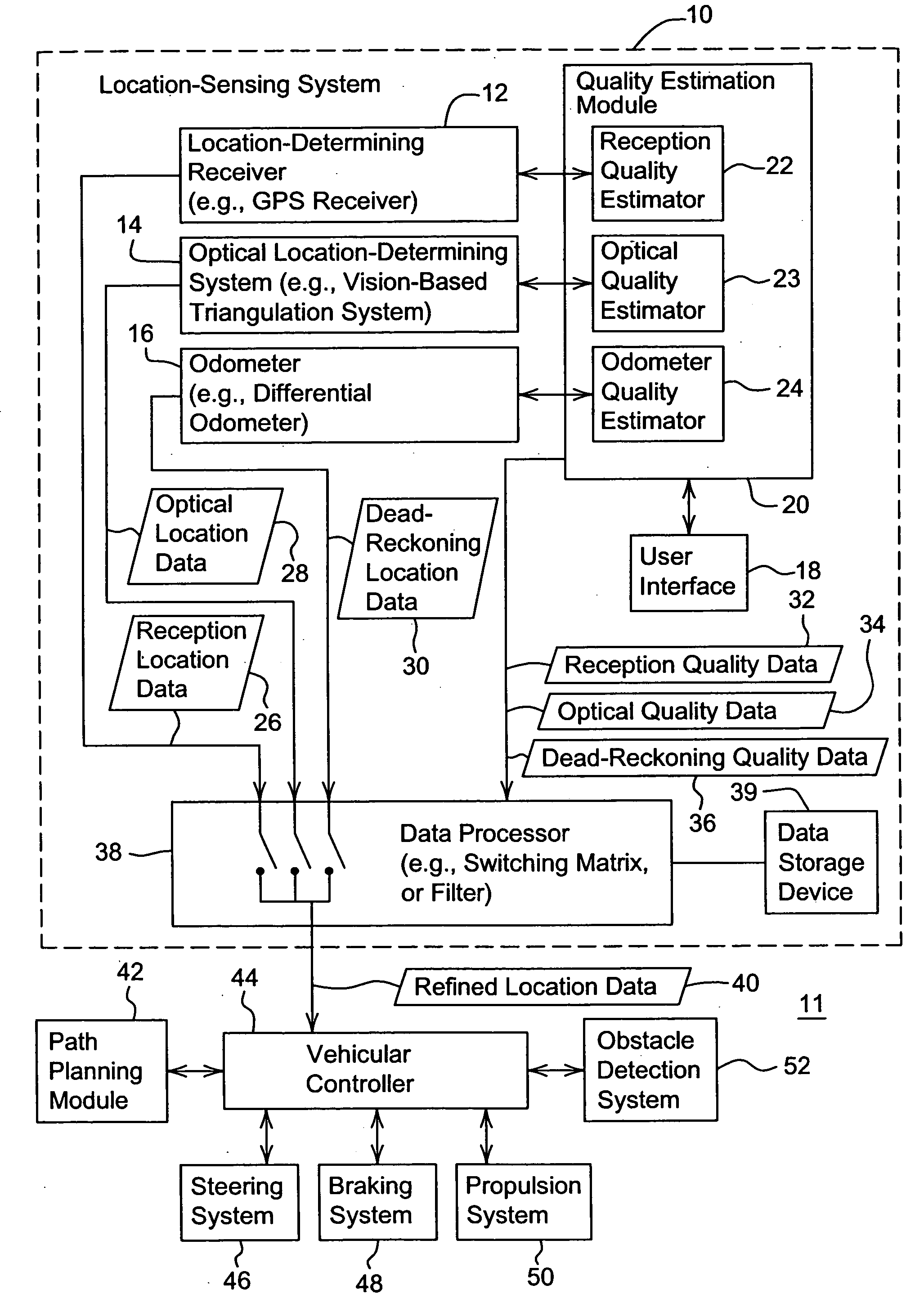
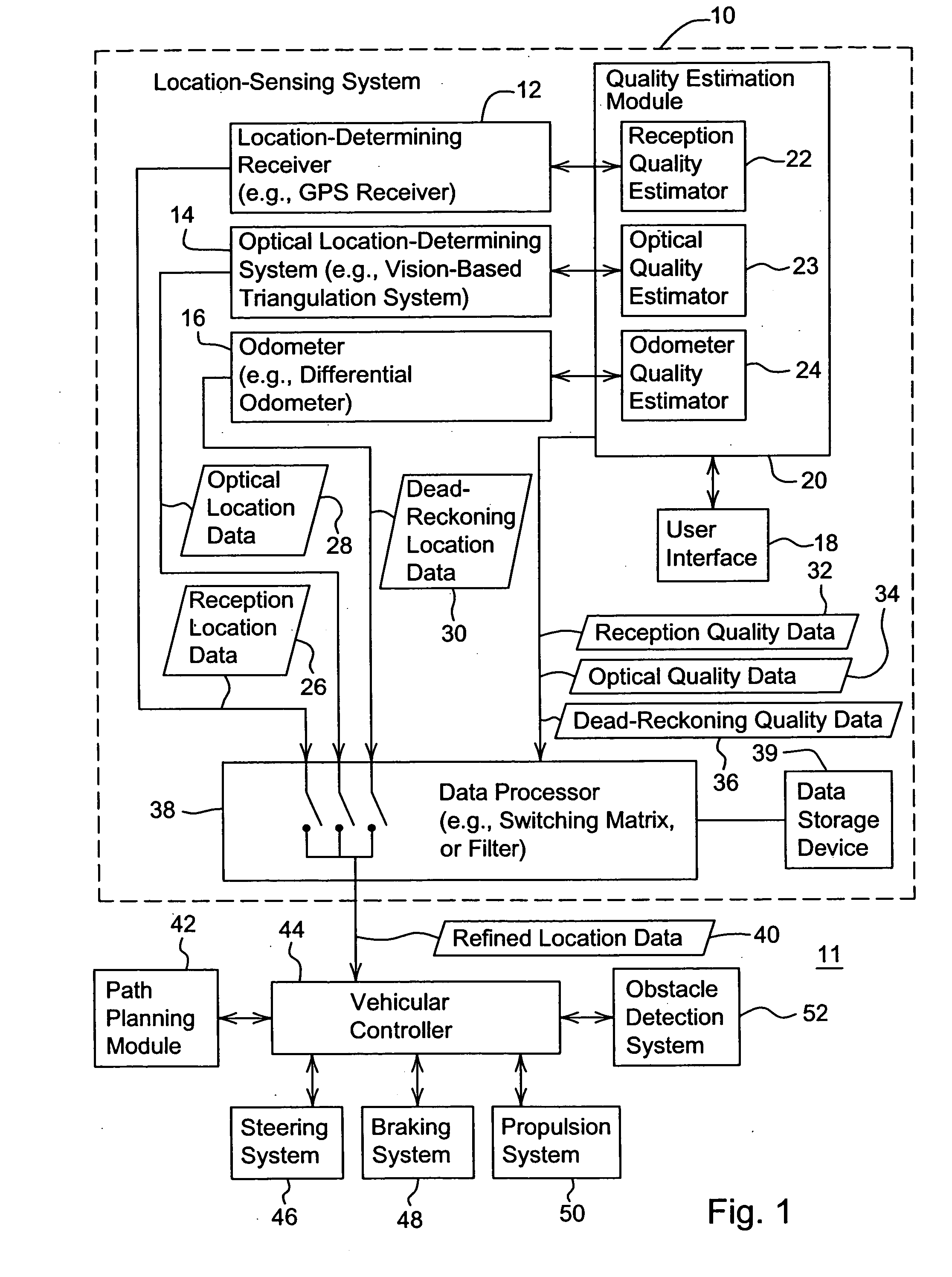
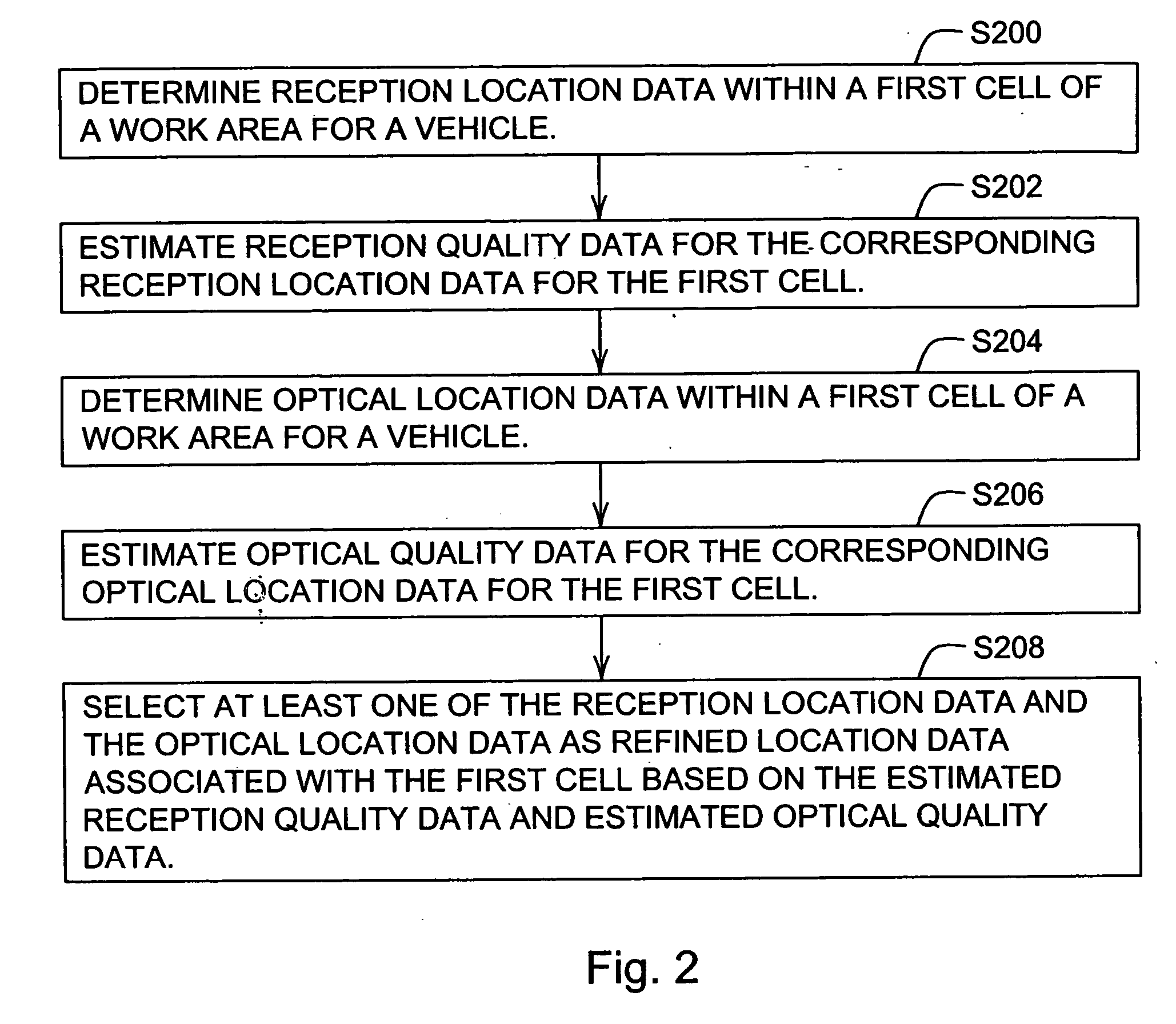
Vehicular navigation based on site specific sensor quality data
ActiveUS20060189329A1Instruments for road network navigationDigital data processing detailsQuality dataData treatment
Owner:DEERE & CO
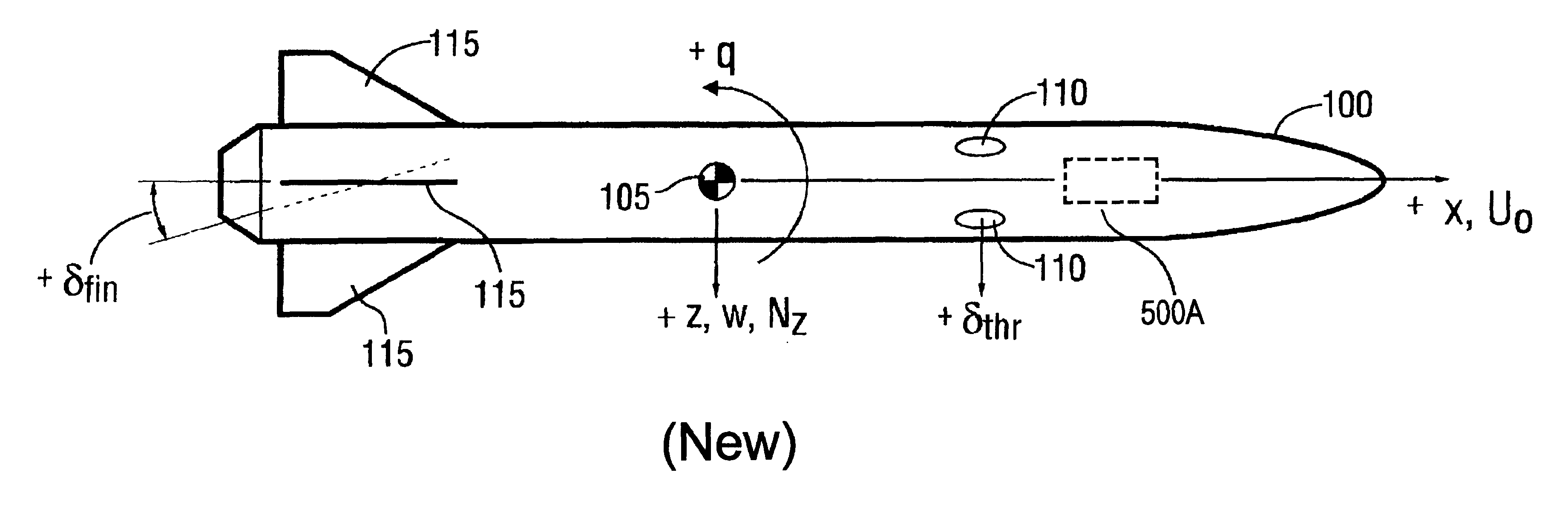
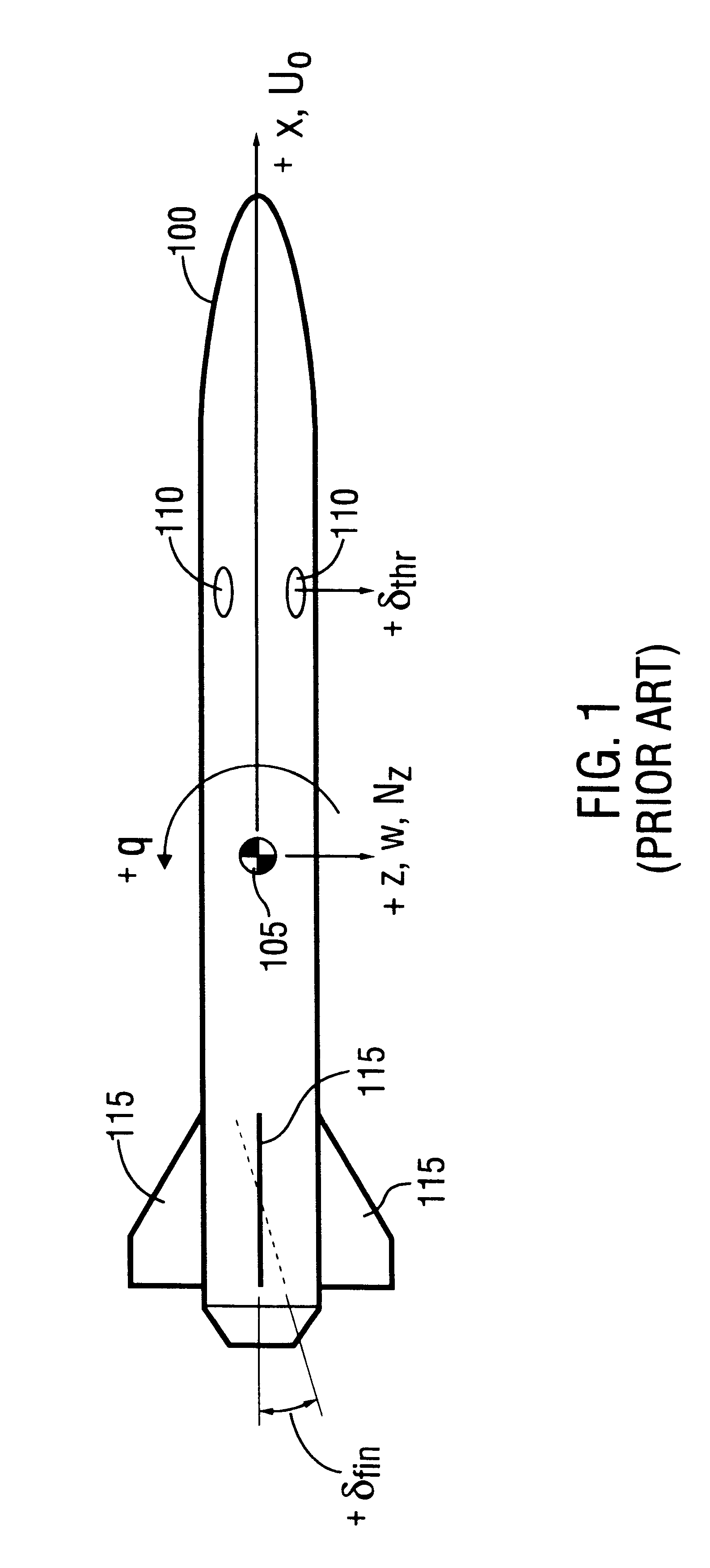
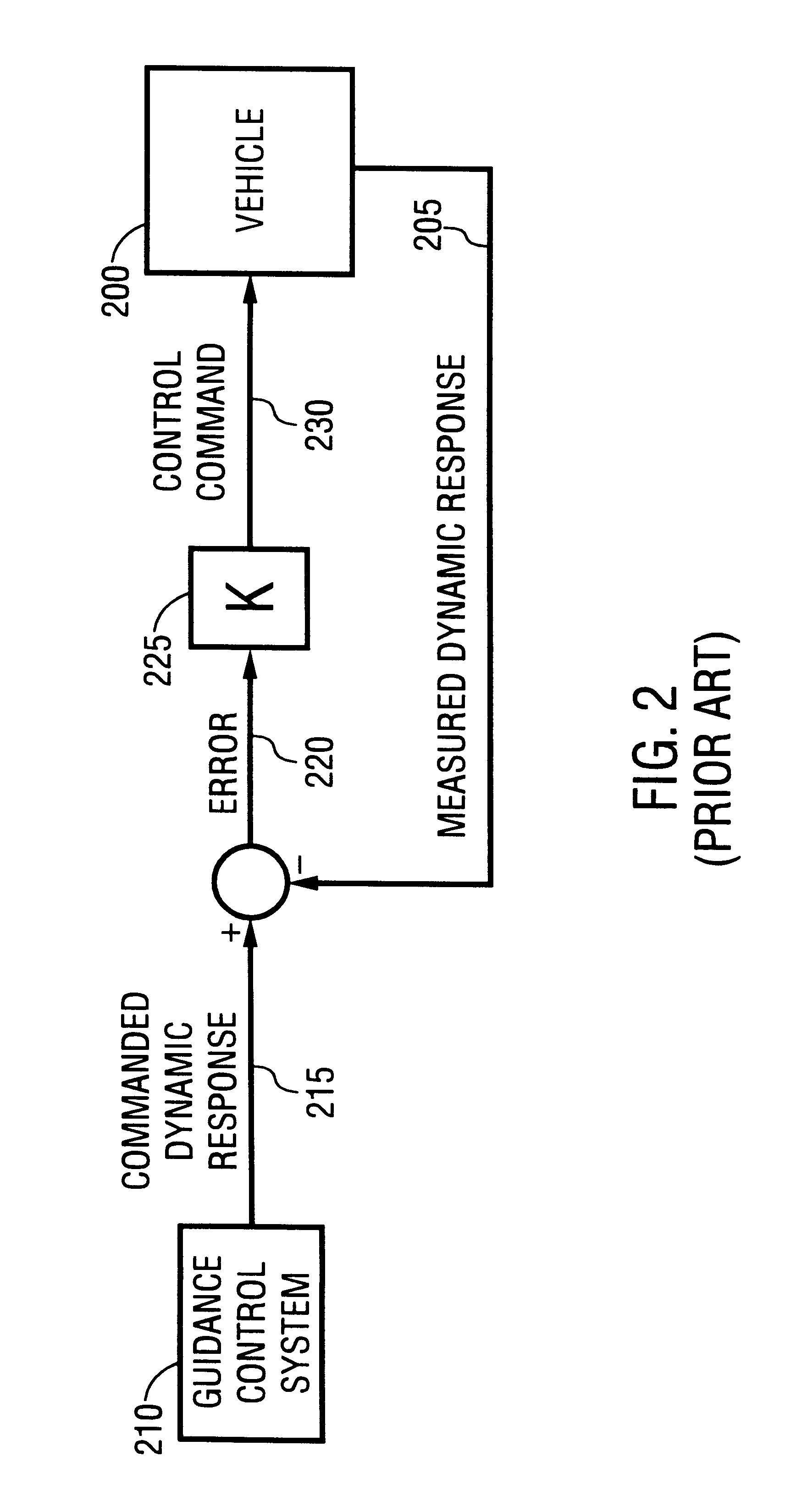
Dual-control scheme for improved missile maneuverability
InactiveUSRE37331E1Improve abilitiesImproved missile divert capabilityDirection controllersDigital data processing detailsNoseDynamic capabilities
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
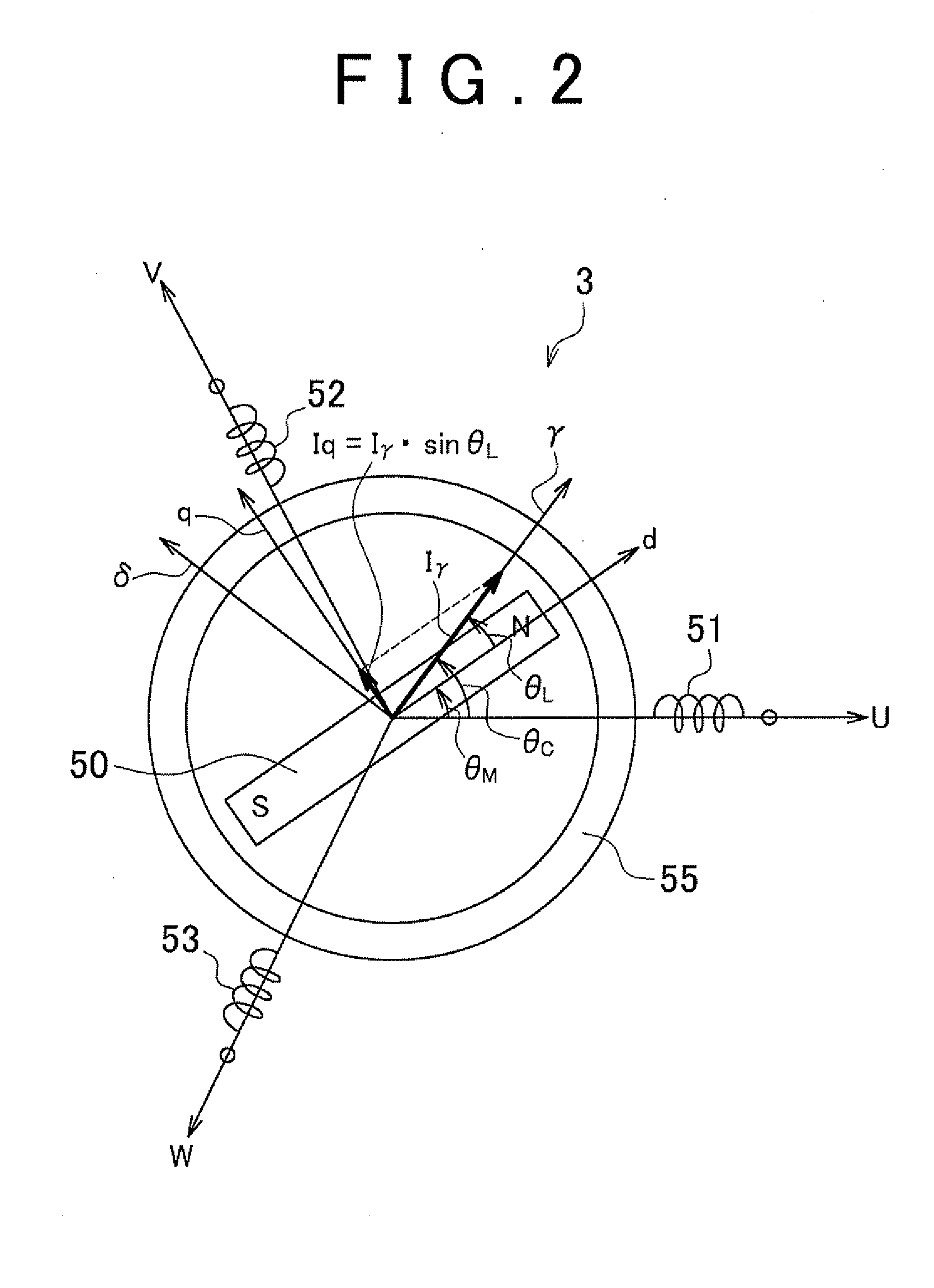
Motor control unit and vehicle steering system
InactiveUS20110112724A1Digital data processing detailsSingle motor speed/torque controlMotor controlControl torque
Owner:JTEKT CORP
Walking assistance moving vehicle
InactiveUS20150066242A1Carriage/perambulator accessoriesDigital data processing detailsMobile vehicleDistance sensors
Owner:FUNAI ELECTRIC CO LTD
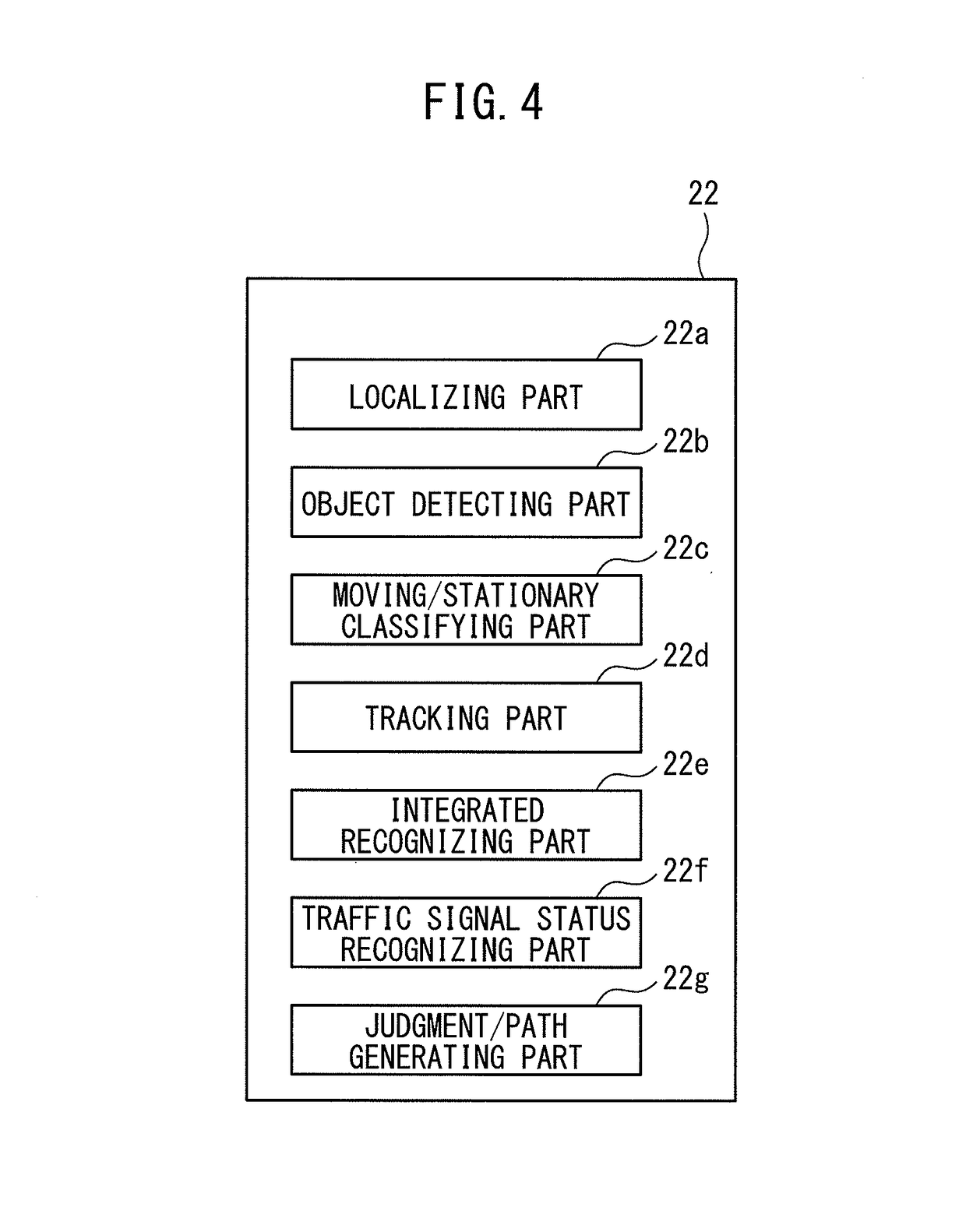
Autonomous driving control system for vehicle
ActiveUS20170261982A1Precise positioningIncrease productionAutonomous decision making processExternal condition input parametersDriver/operatorOperating point
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
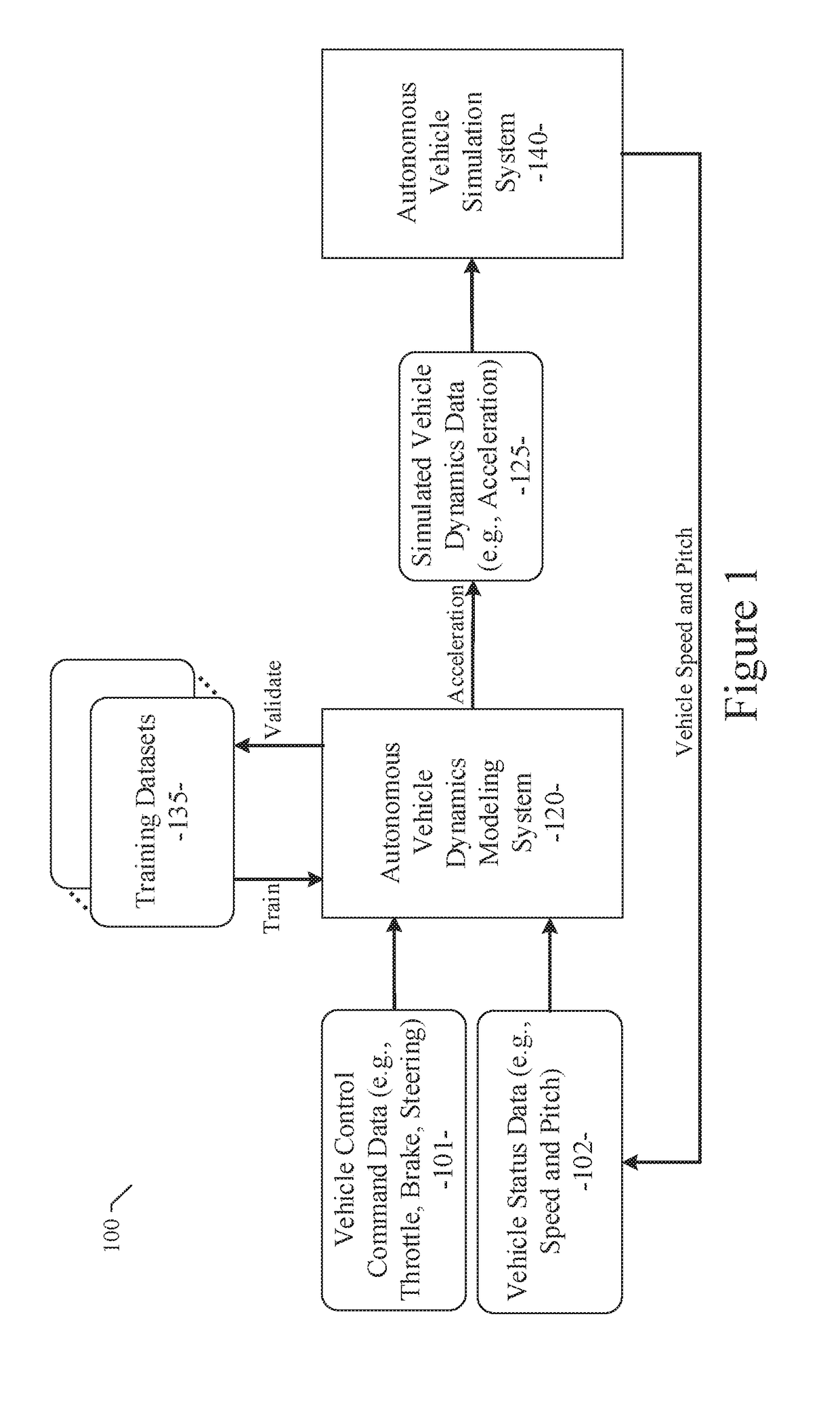
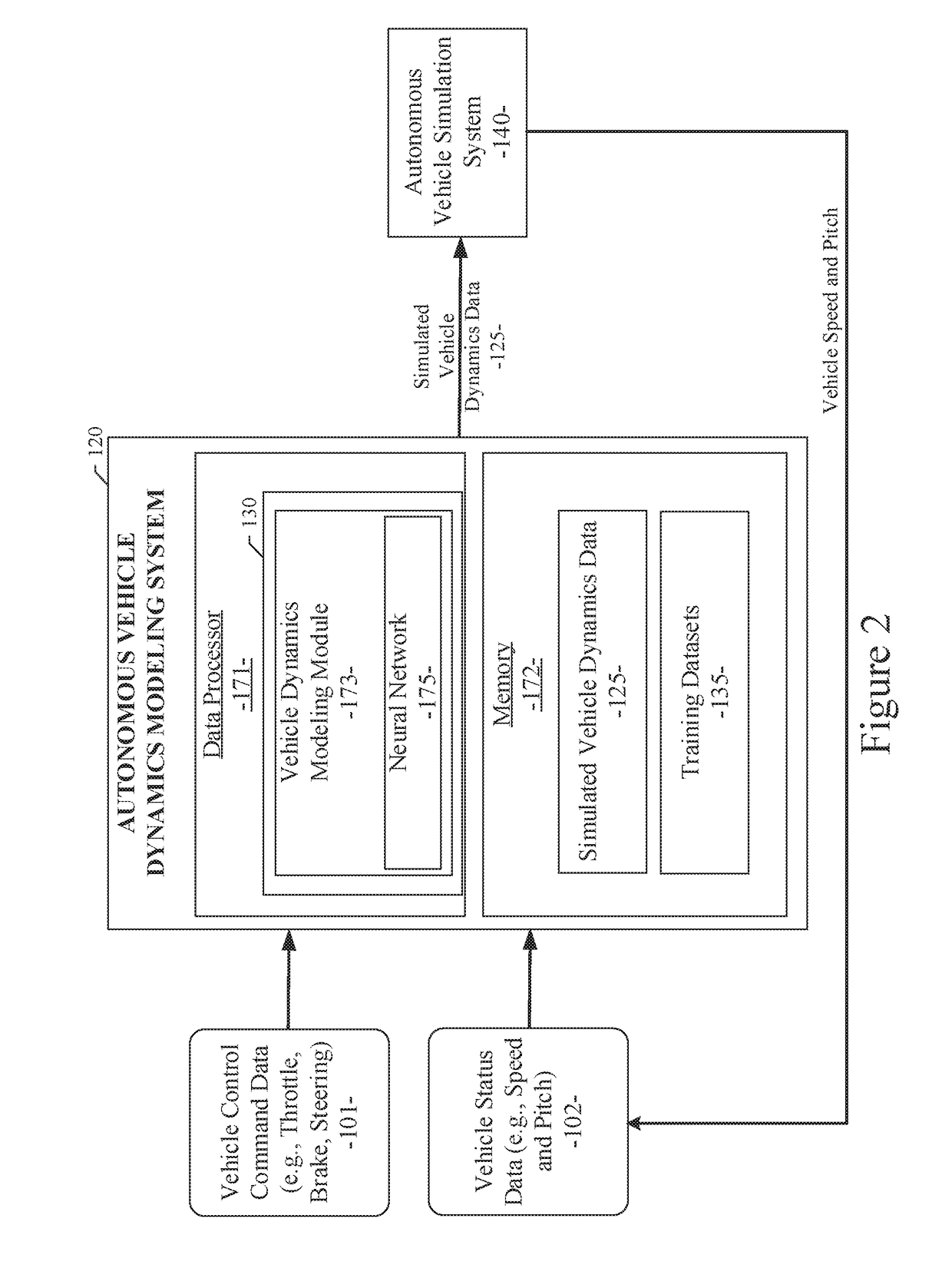
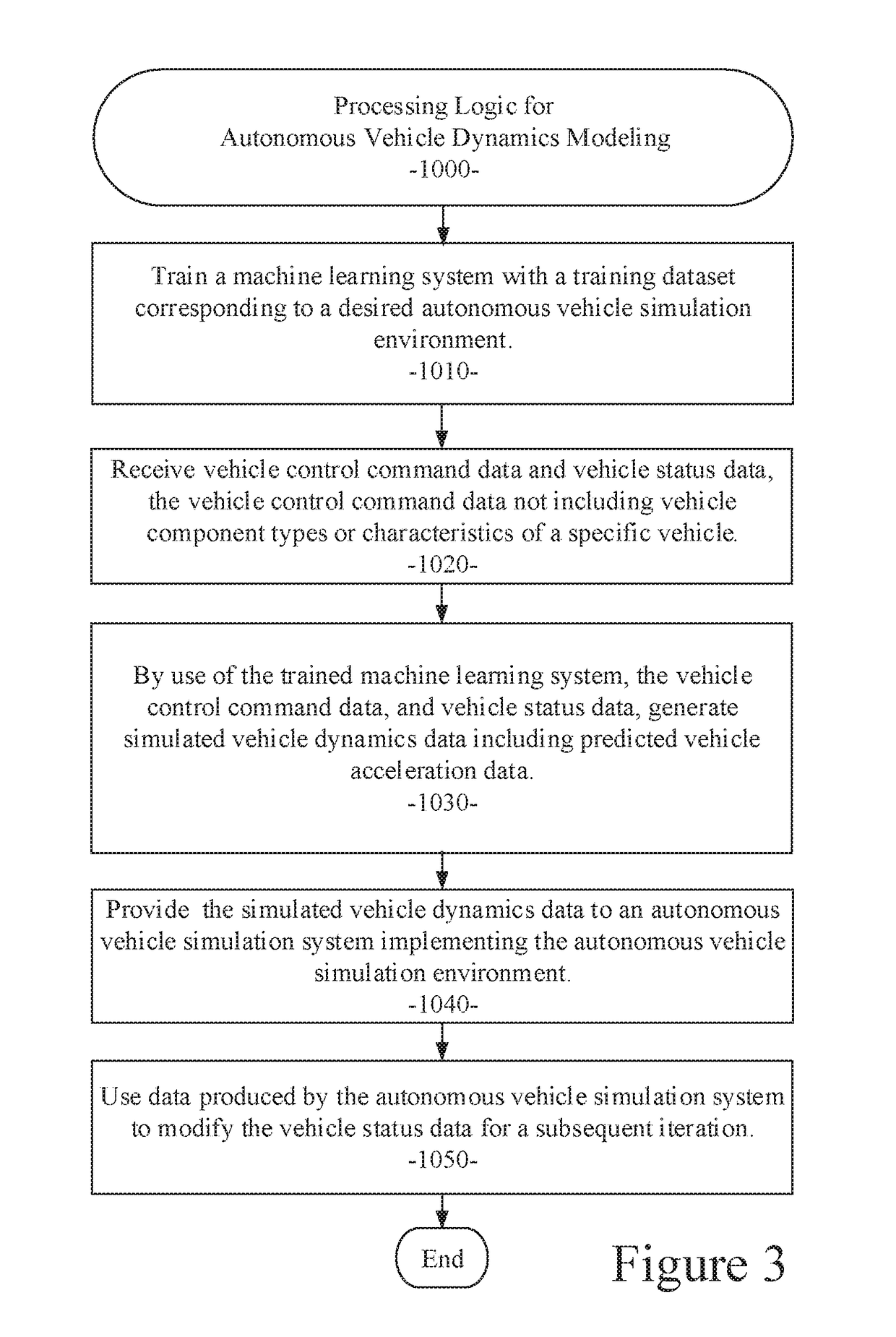
Neural network based vehicle dynamics model
ActiveUS20190049980A1Easy to adaptSave model rebuilding timeAutonomous decision making processSimulator controlVehicle dynamicsData set
Owner:TUSIMPLE INC
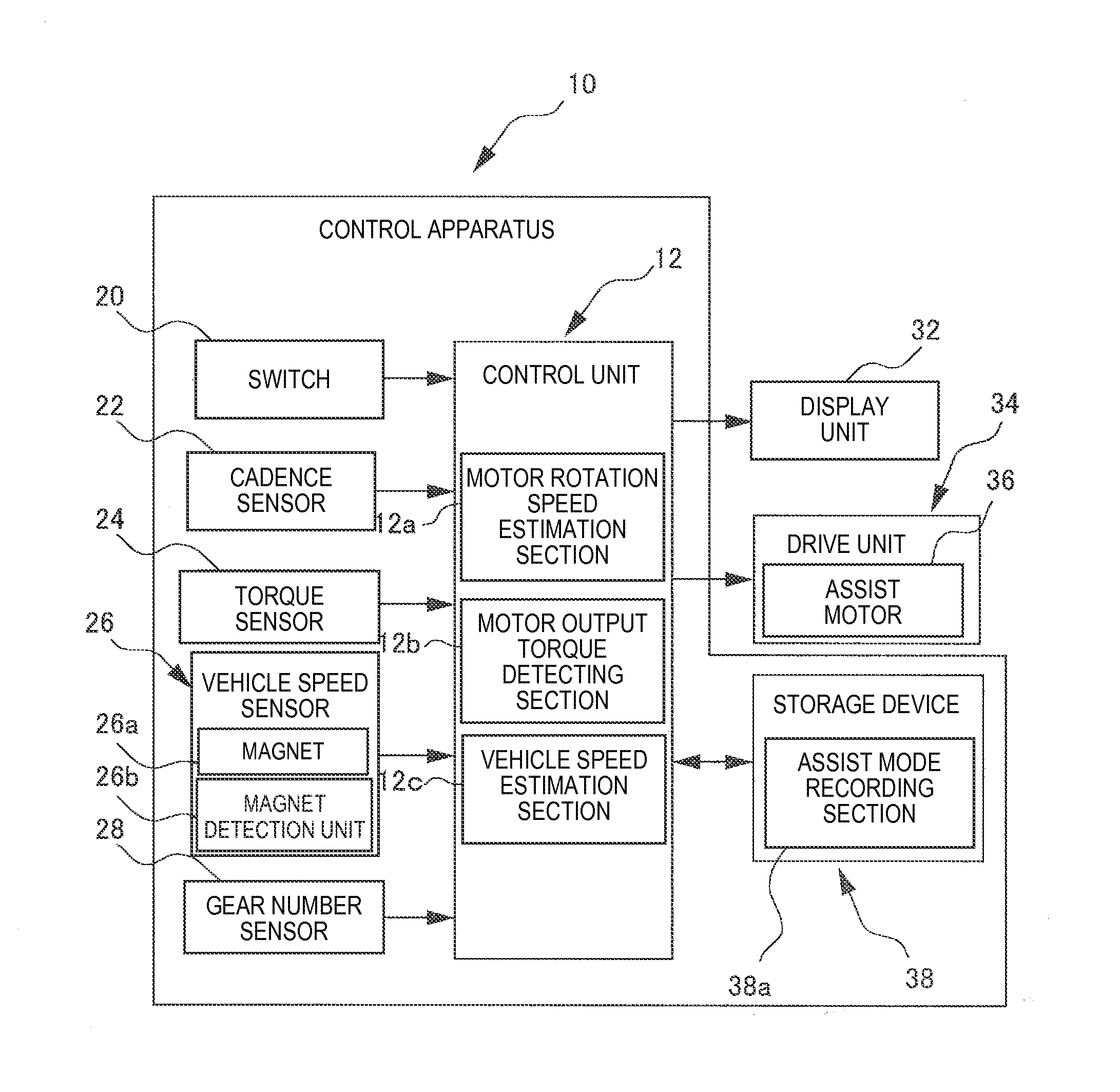
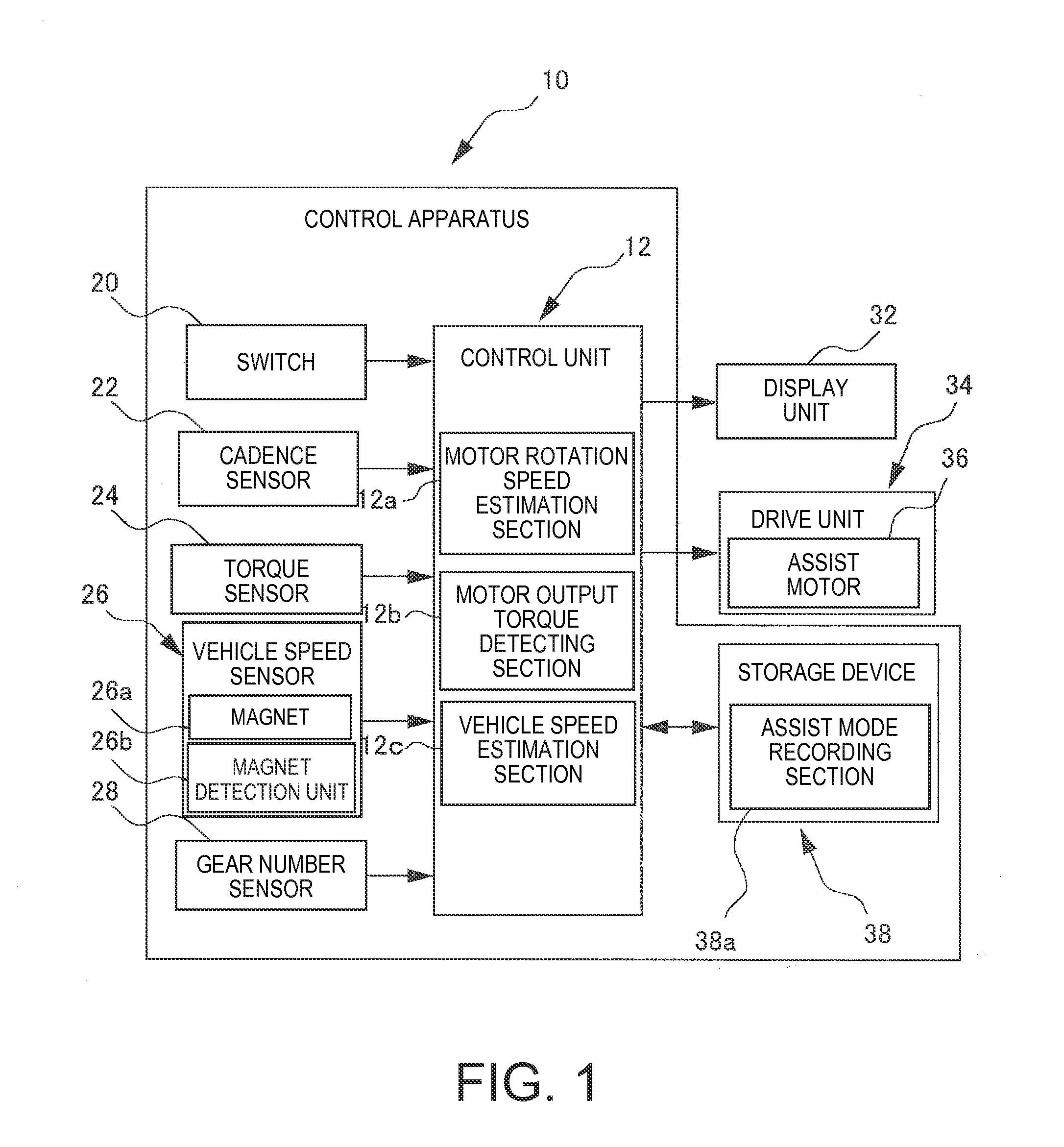
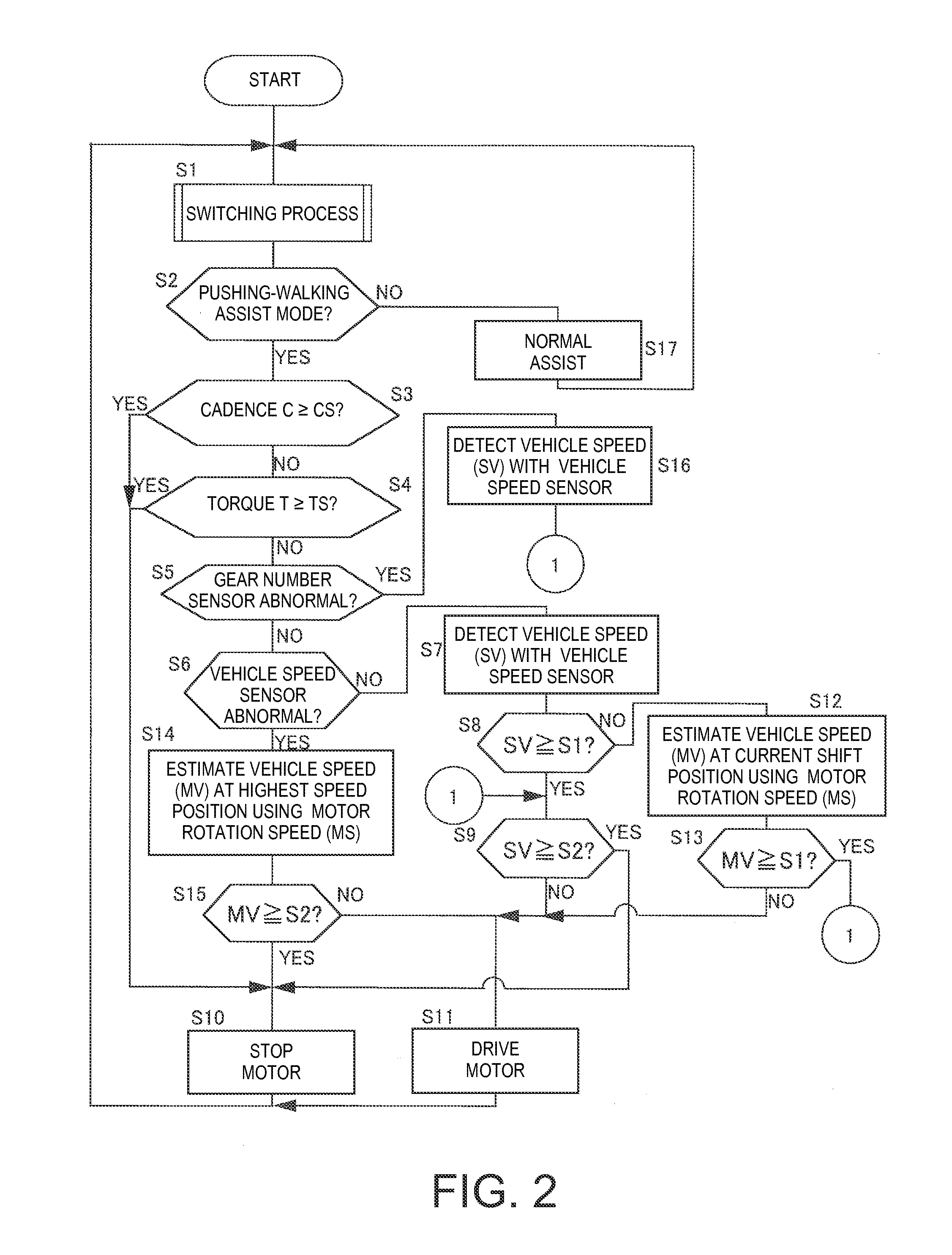
Bicycle control apparatus
ActiveUS20150367750A1Simple configurationSpeed controllerDigital data processing detailsControl unitElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SHIMANO INC
Steering damper with active adjustment of damping characteristics
ActiveUS20140249720A1Robust and reliable methodPrecise changeDigital data processing detailsAutomatic steering controlRelative motionHydraulic fluid
A device adjusts the rotational damping of a steering device such that the rotational damping varies depending on whether the rotational motion about a steering axis is caused by a force acting on the steering device of the vehicle or a force acting on the part(s) of the vehicle contacting the ground. The flow of hydraulic fluid in the steering damper partly or wholly is adjusted by a main valve unit that is coupled together with both an attaching part and a steering device. The opening area of the main valve unit is determined by a relative motion between the attaching part and the steering device such that the flow of the hydraulic fluid in a direction from and to the respective damping chambers of the steering damper is controlled depending on the cause of the rotational movement.
Owner:OHLINS
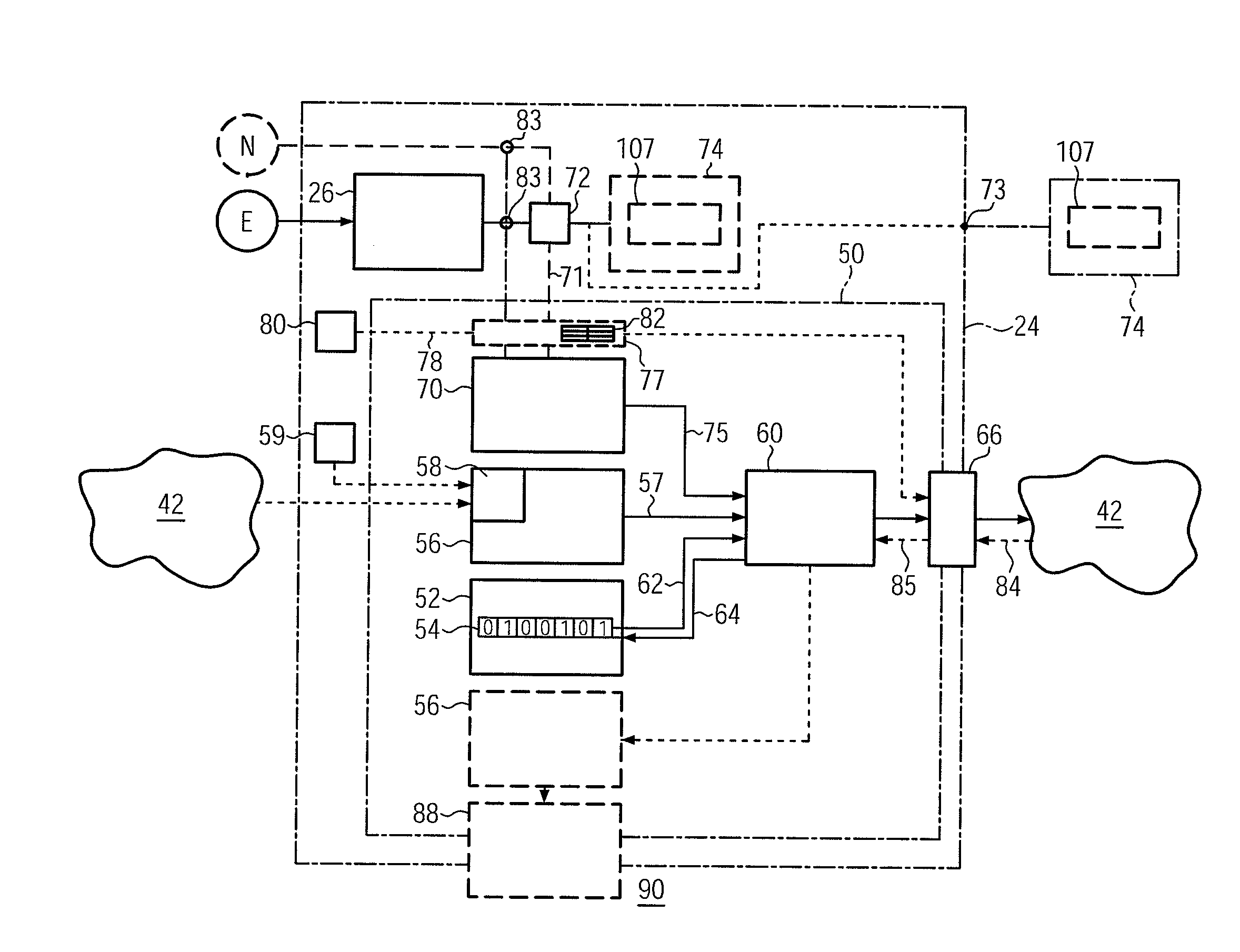
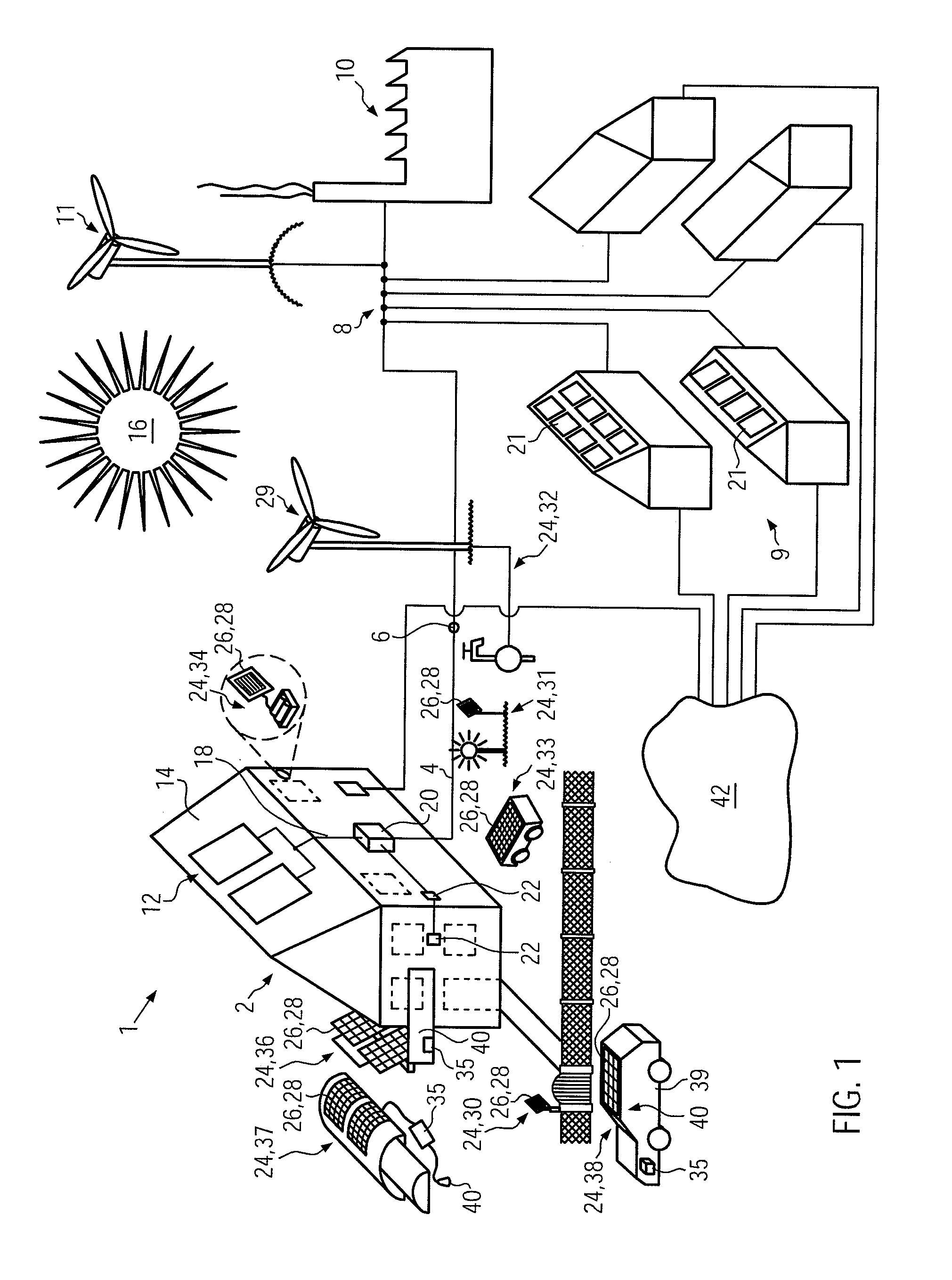
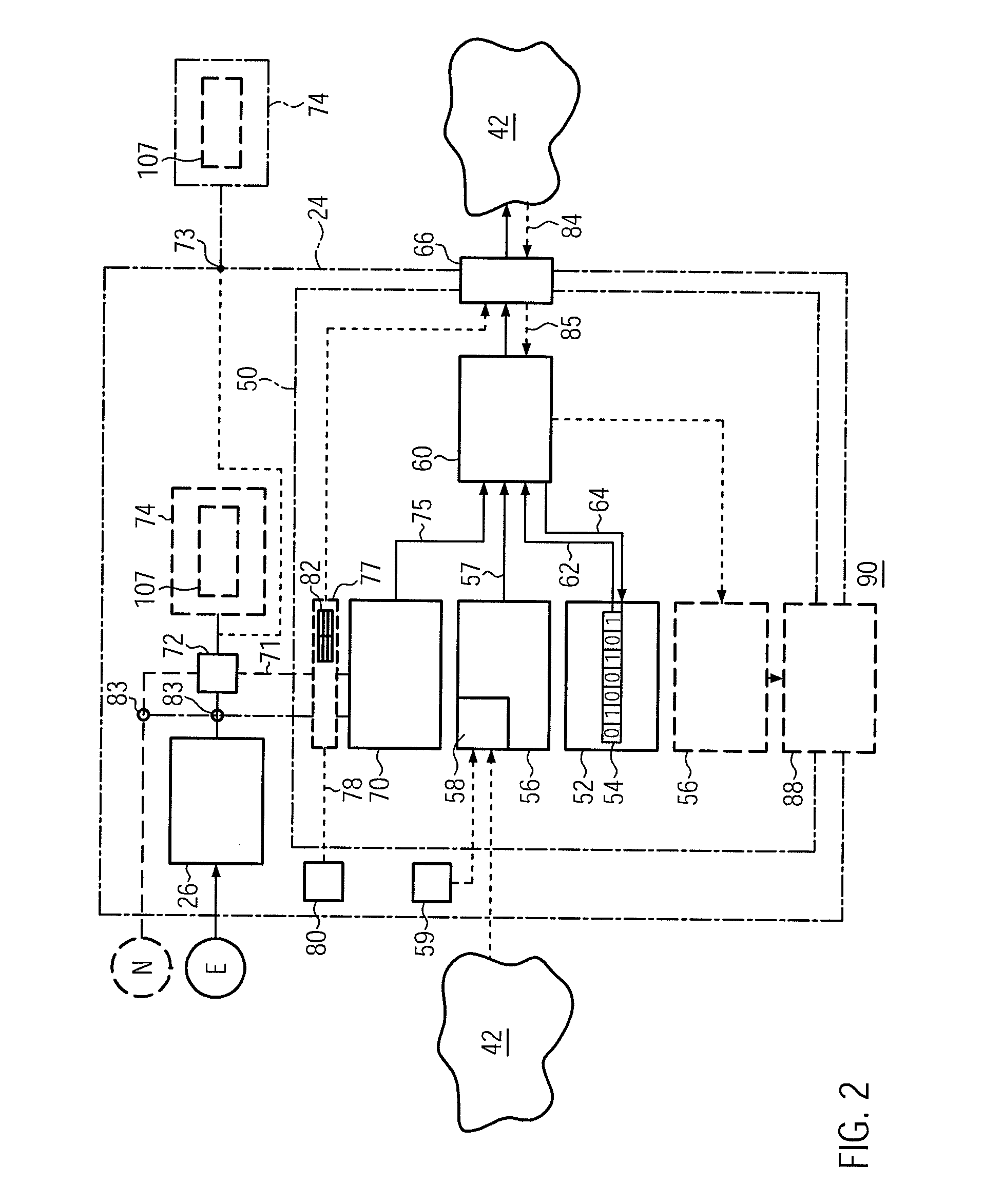
Stand-Alone Renewable-Energy Generating Device Including Emission Savings Sensor, Retrofit Emissions Savings Sensor for such a Device, and Method
InactiveUS20110213506A1Increase motivationLevel controlPV power plantsCommunication interfaceNetworked system
Owner:CHANGERS
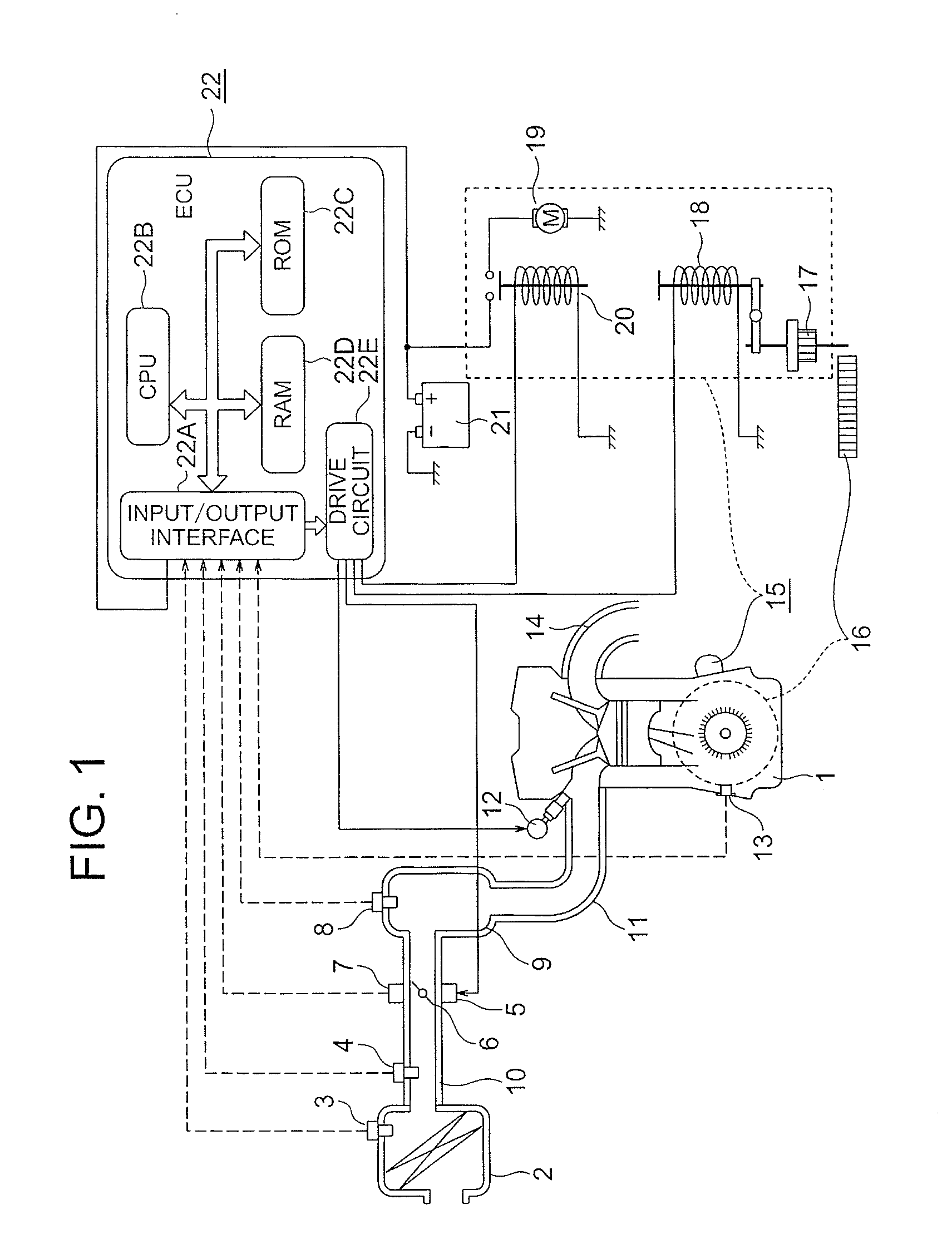
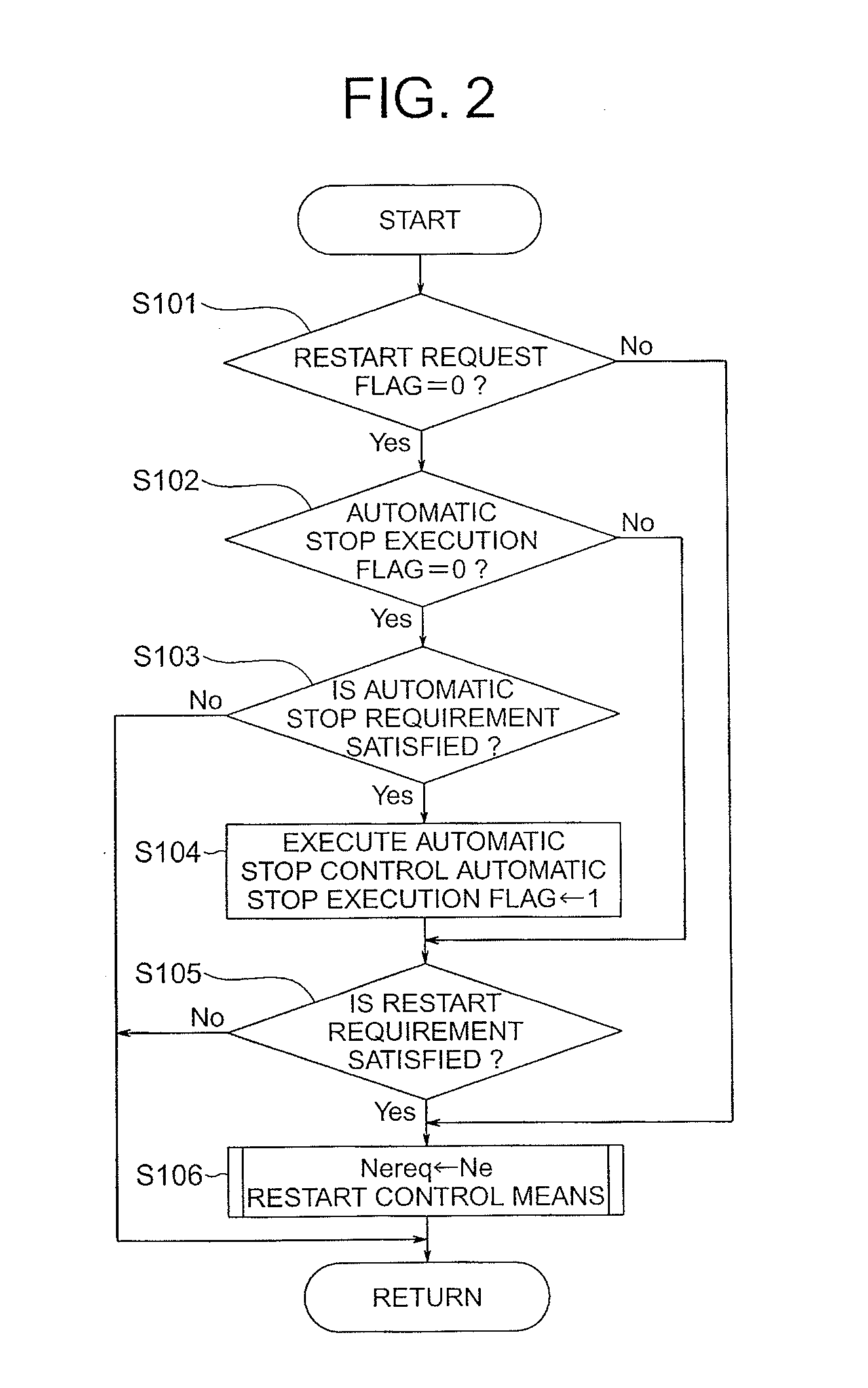
Automatic stop/restart device for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20120290194A1Reliable engagementLow costElectrical controlDigital data processing detailsGear wheelExternal combustion engine
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Vehicle control apparatus
ActiveUS20120053769A1Suppress sudden changesMitigate torque shockHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsElectric machineryControl theory
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for controlling a soil working means based on image processing and related system
ActiveUS20210136993A1Improve abilitiesHigh degreeAutonomous decision making processCharacter and pattern recognitionNerve networkImaging processing
Please replace the Abstract originally filed with the following: The invention relates to a method for controlling a soil working means, based on an image processing. Such a soil working means comprises a locomotion member and a working member. The method comprises the steps of acquiring at least one digital image of the soil by means of digital image acquisition means installed on the working means; processing, by means of an electronic processing unit, the at least one digital image acquired by performing at least one convolution operation on the digital image by means of a trained neural network; obtaining, by means of the electronic processing unit, at least one synthetic soil descriptor based on such a processing; generating, by means of the electronic processing unit, at least one control signal of the locomotion member or of the working member based on the synthetic soil descriptor.
Owner:VOLTA ROBOTS SRL
Method for controlling a hybrid traction assembly and hybrid vehicle controlled according to such a method
ActiveUS20130274984A1Avoid disadvantagesHybrid vehiclesDigital data processing detailsState of chargeHybrid vehicle
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Air-fuel ratio sensor and control apparatus for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20100300418A1Improve responsivenessElectrical controlExhaust apparatusControl layerAtmospheric air
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Four-wheel drive combine with slip control
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P
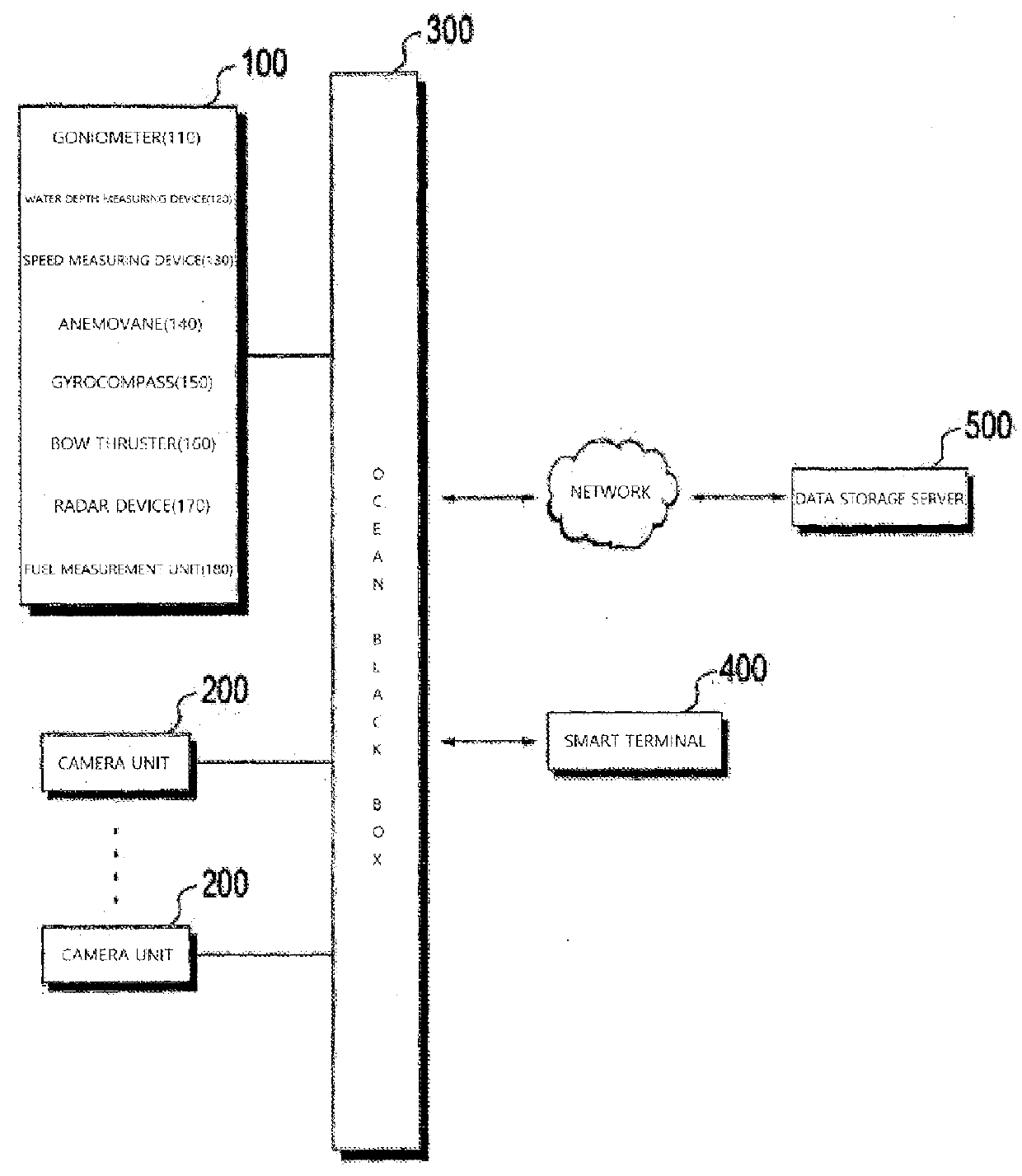
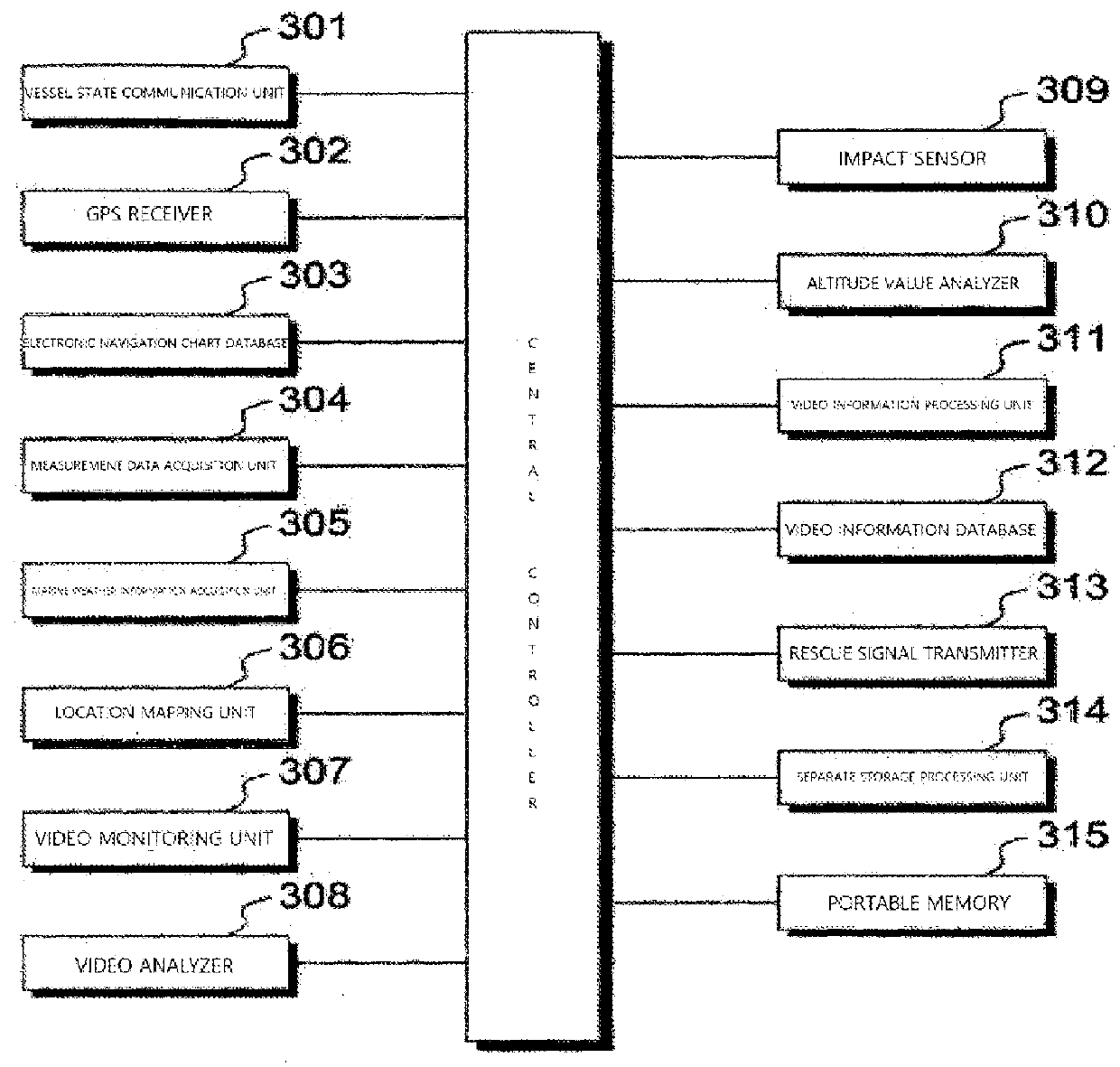
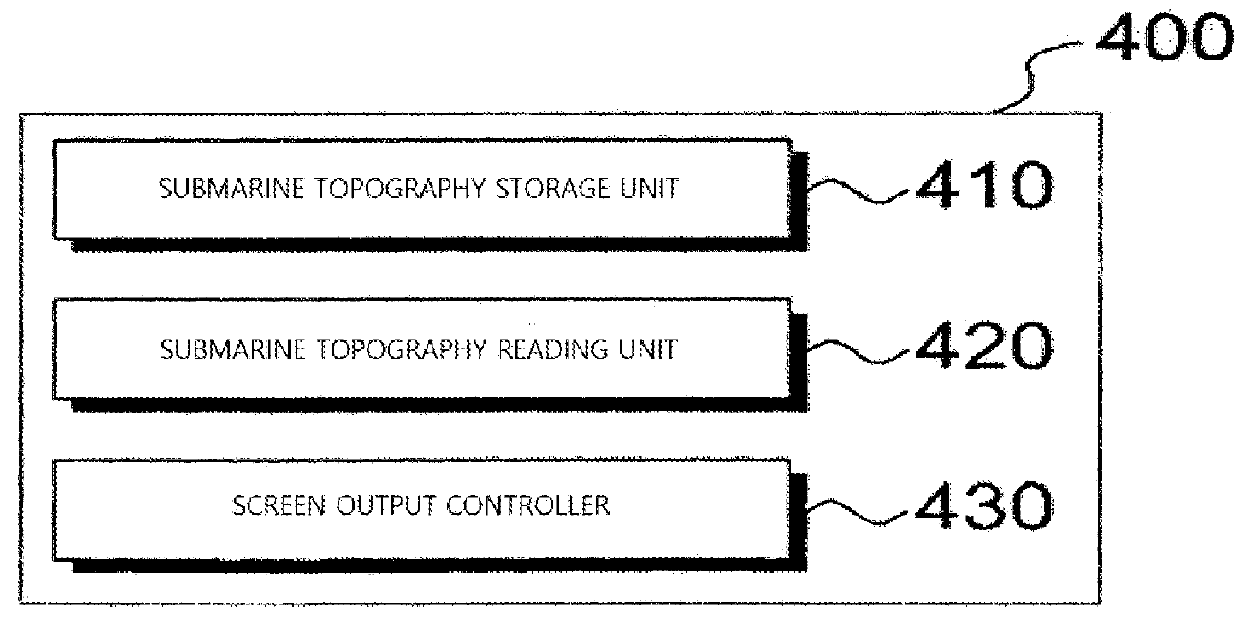
Black box system for leisure vessel
InactiveUS20160031536A1Improve portabilitySpeed controllerElectric devicesSimulationMarine navigation
Owner:BONC INOVATORS
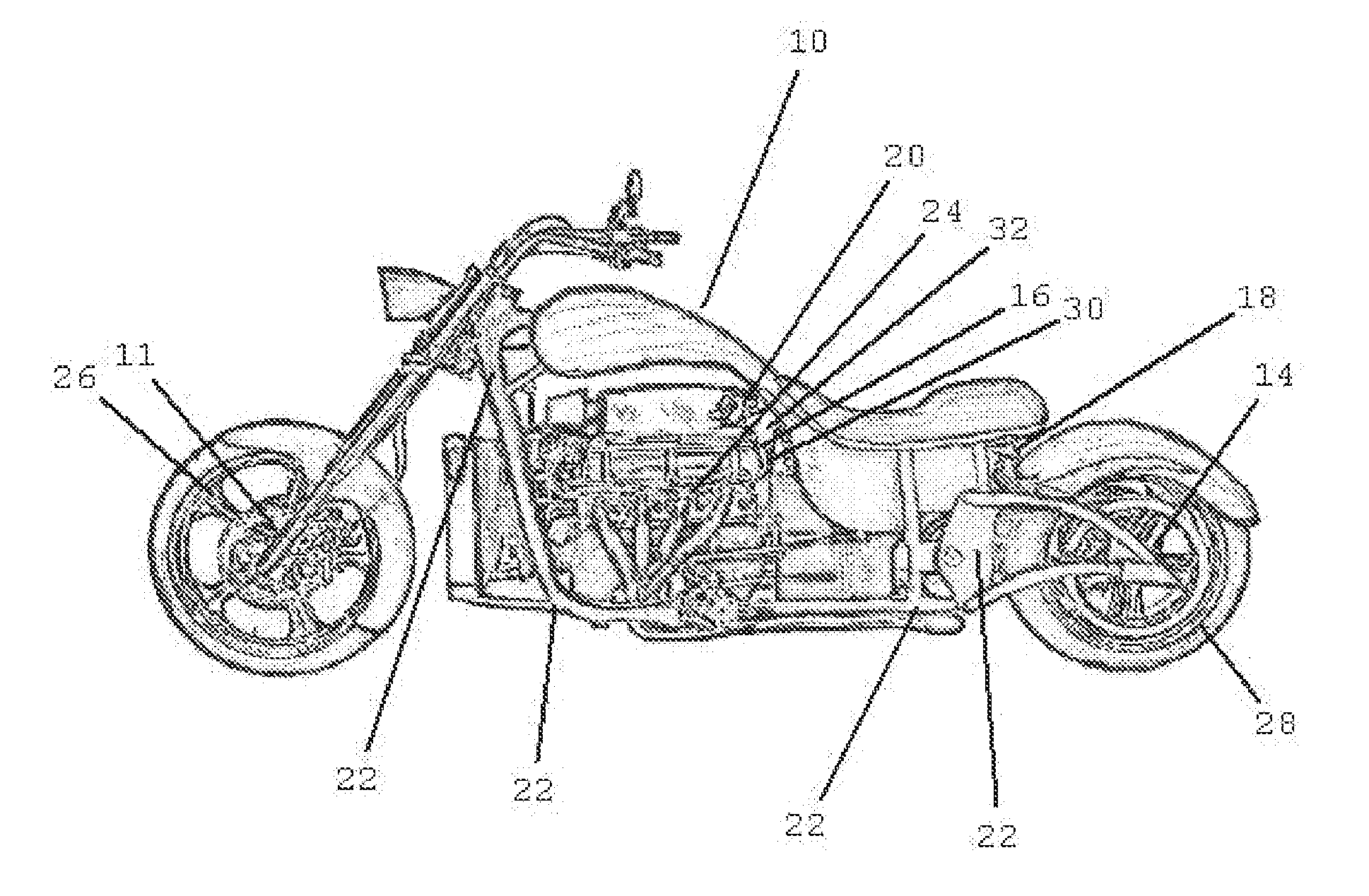
Motorcycle traction control system
InactiveUS20130103281A1Efficient transferReduce throttlingDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsTransmitted powerControl system
Owner:SABERTOOTH MOTORCYCLES
Vehicle orientation indicator
ActiveUS20150212106A1Reliable indicationDigital data processing detailsPropulsion using engine-driven generatorsGravitational forceVehicle orientation
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
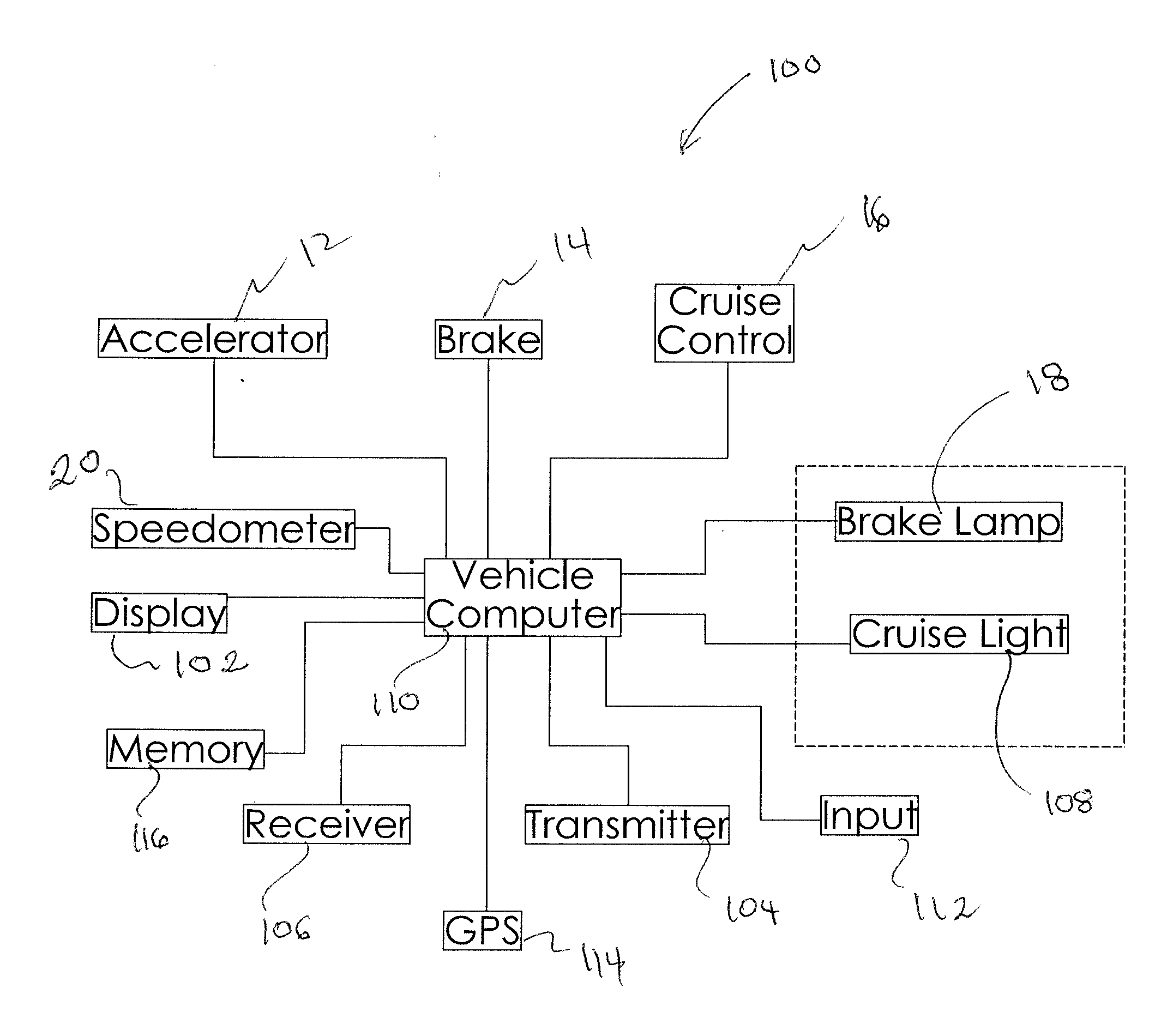
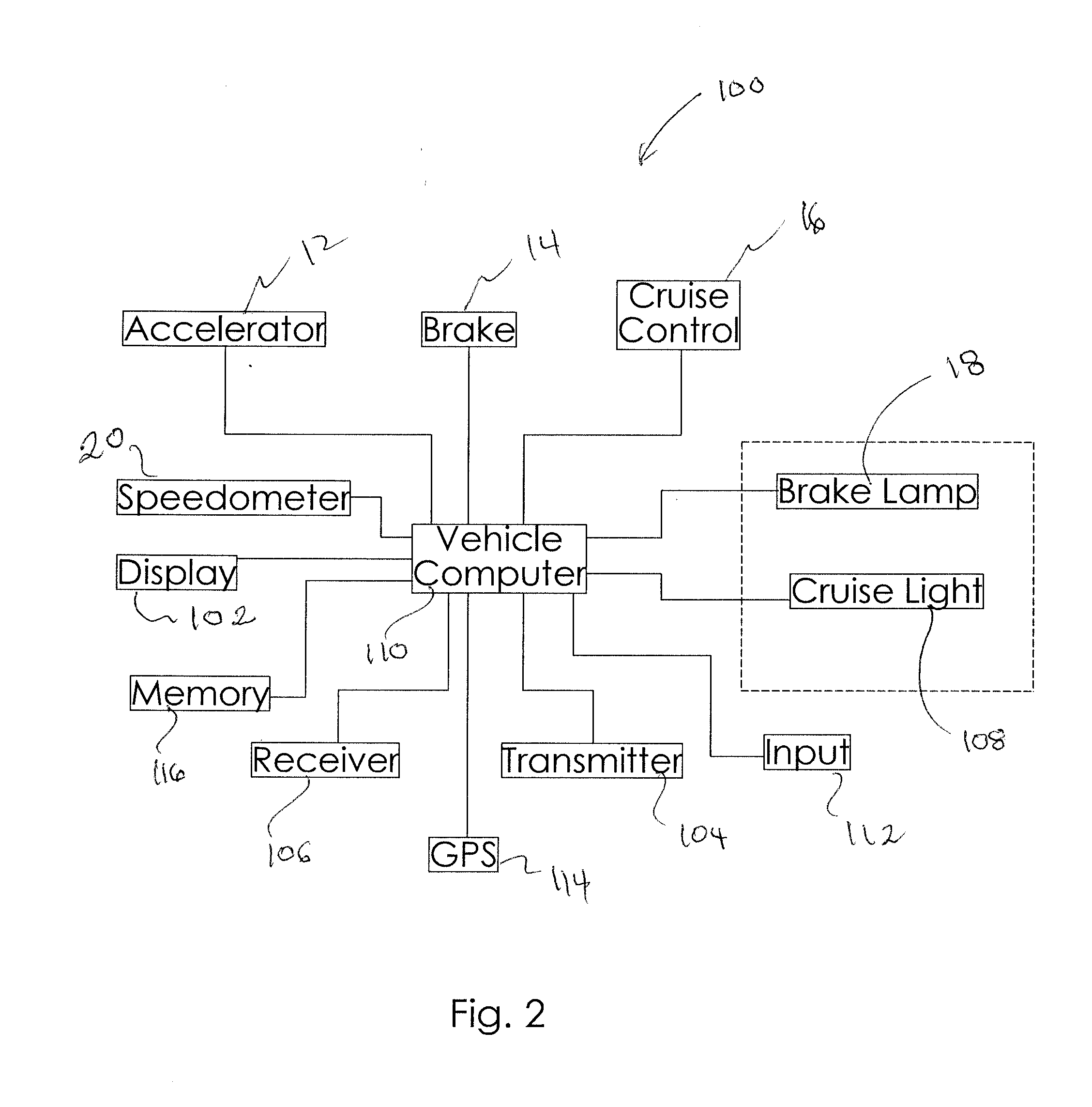
Automobile Communication System
InactiveUS20110307156A1Less fuelImprove protectionDigital data processing detailsAutomatic initiationsCommunications systemCruise control
Owner:VAN NESTE KENNETH J
Braking process for an airplane
InactiveUS20100076623A1Reduce braking possibilityAutomatic braking sequenceDigital data processing detailsJet aeroplaneAirplane
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Imaging device, camera-equipped drone, and mode control method, and program
InactiveUS20200180759A1Unmanned aerial vehiclesRemote controlled aircraftImage transferMode control
An imaging device for use on-board a reconnaissance vehicle comprises an image capturing unit configured to capture images of a photographic area. A control unit communicates via a serial communications interface with a control body unit of the reconnaissance vehicle, and operates in an image photographing mode that receives control information from the control body unit of the reconnaissance vehicle via the serial communications interface and in an image transfer mode that transfers the images to the control body unit of the reconnaissance vehicle via the serial communications interface in accordance with a data transfer protocol. The control unit responds to detecting mode switching conditions to switch autonomously from the image photographing mode to the image transfer mode. Only a single serial communications interface is needed both to control the imaging device and to transfer the captured images from the imaging device in the image transfer mode.
Owner:SONY CORP
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap