Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
38results about "Electric devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
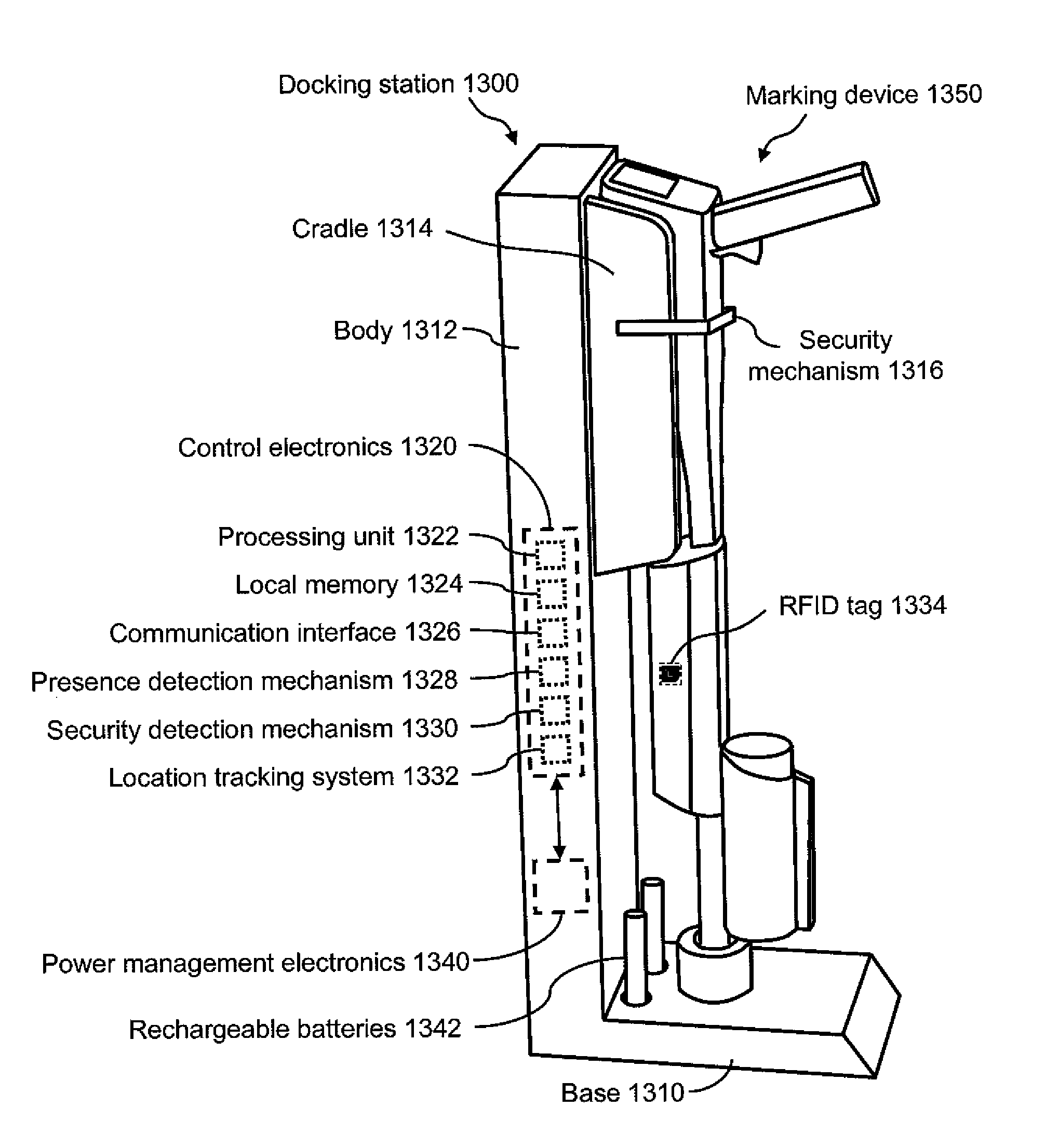
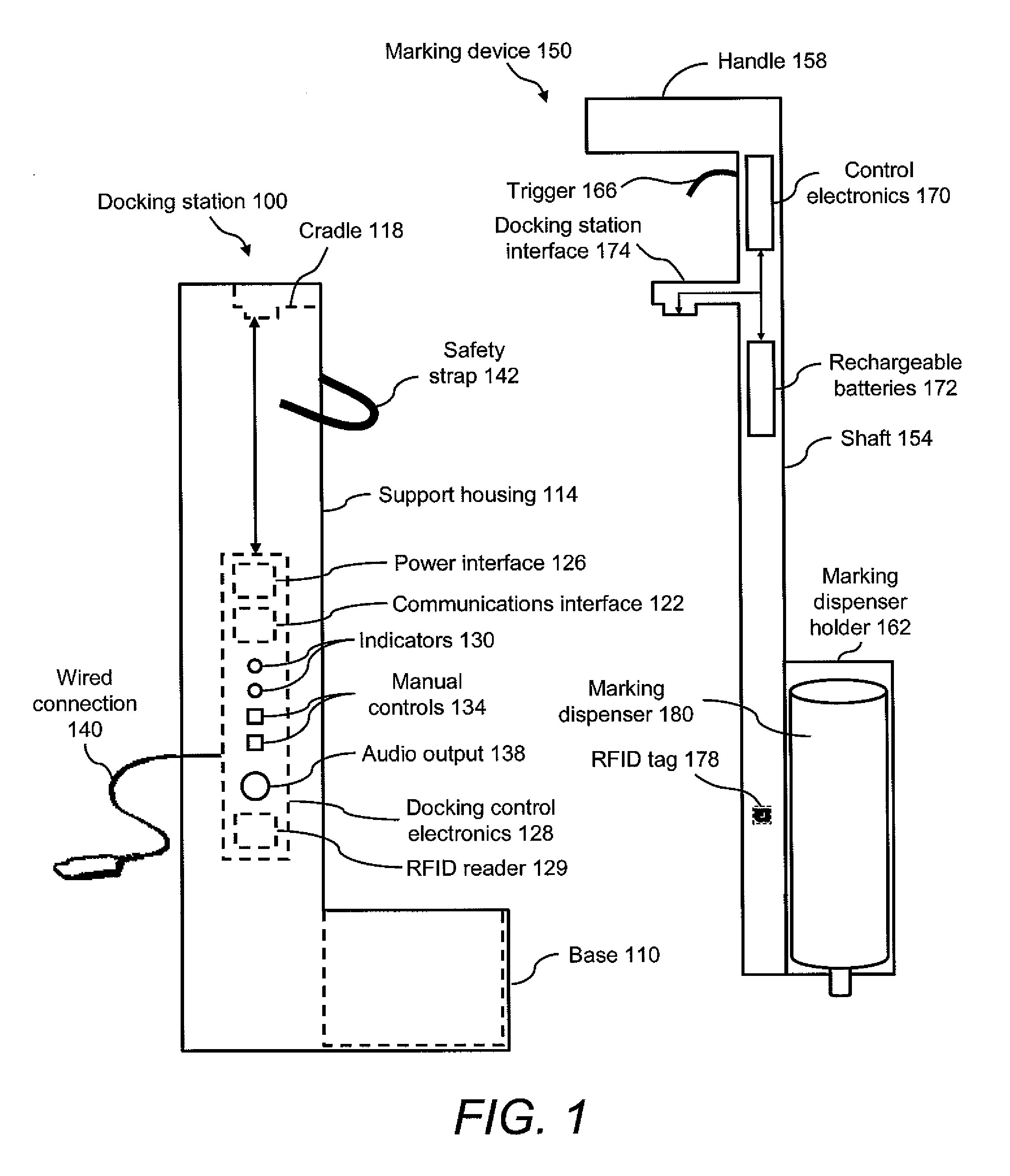
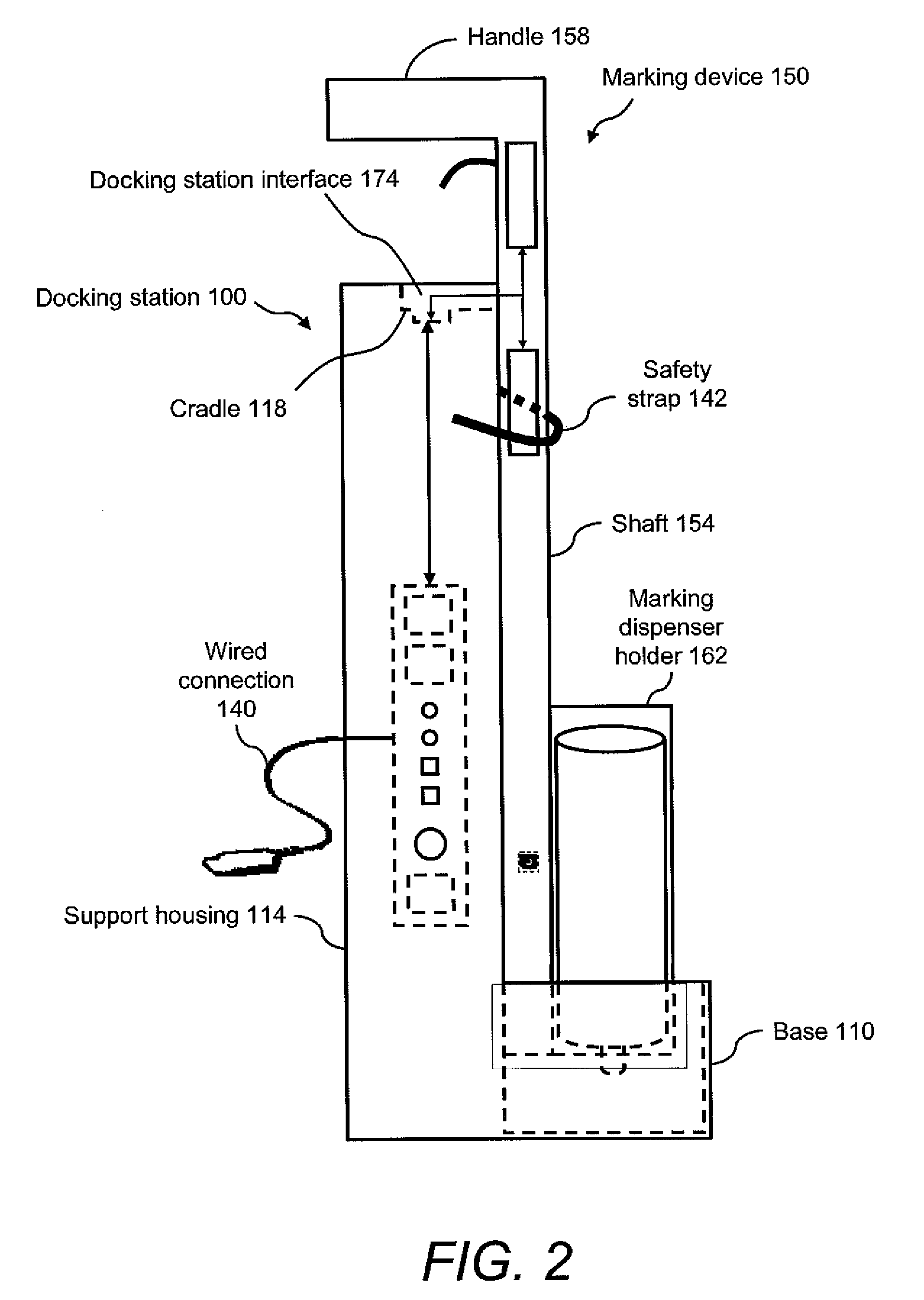
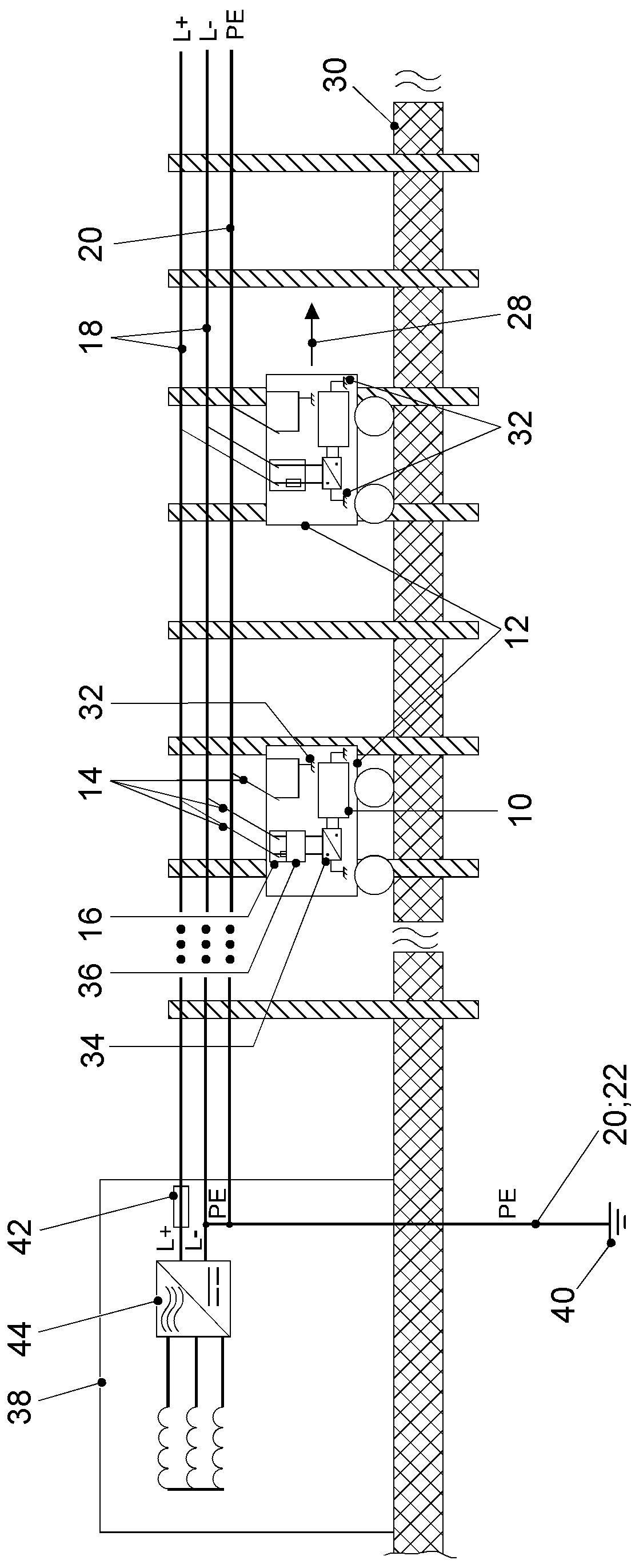
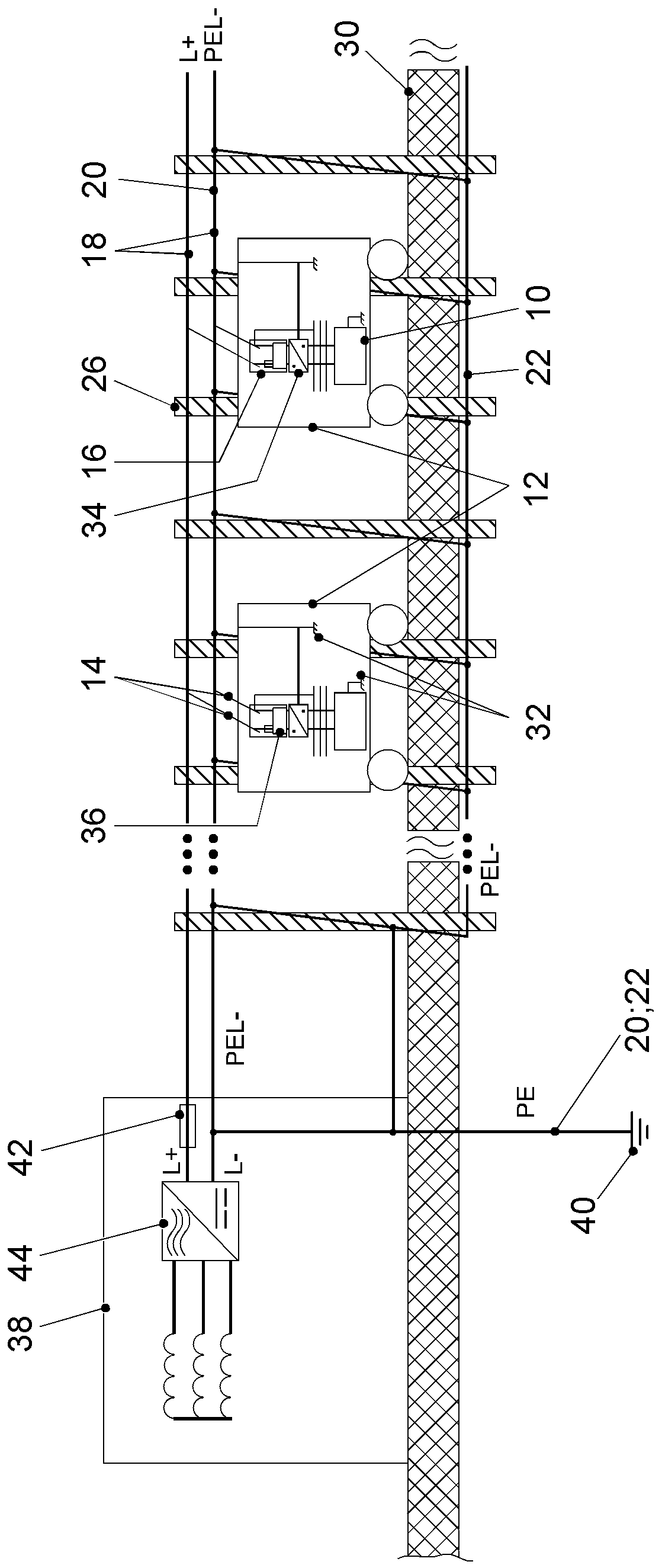
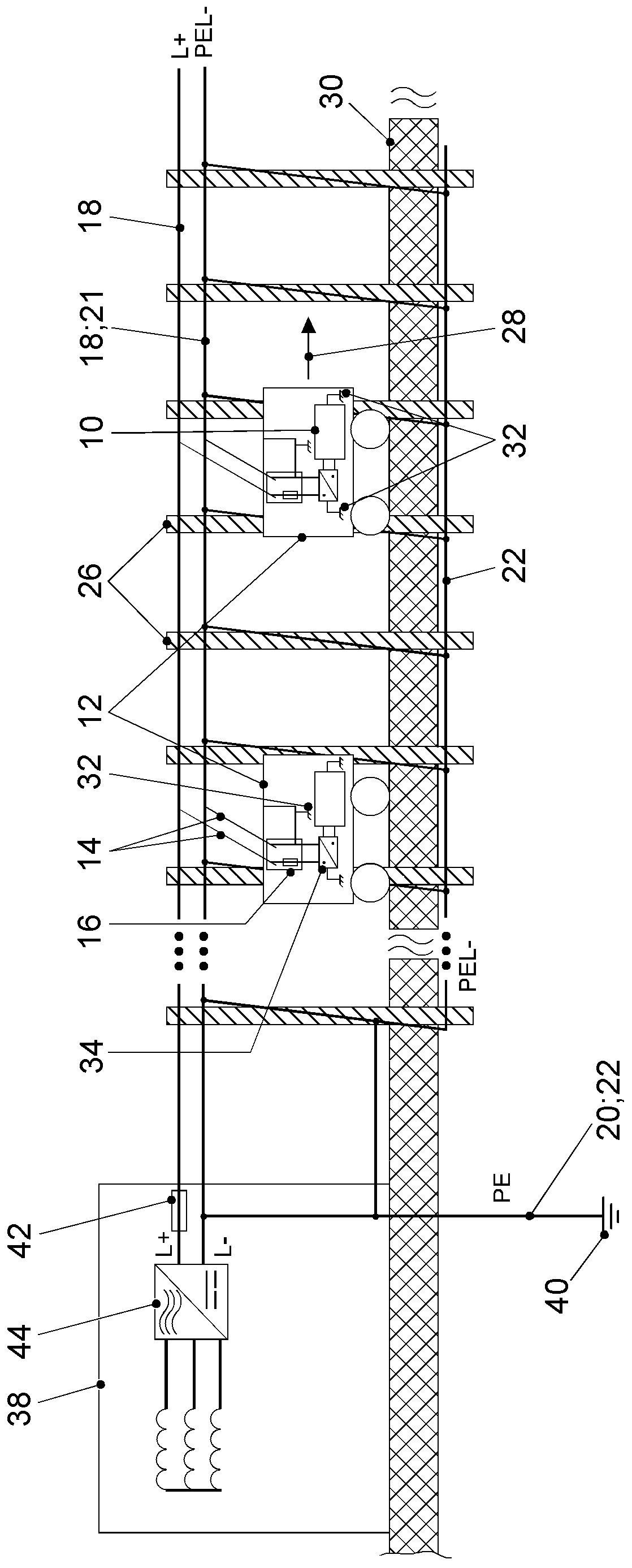
Marking device docking stations having security features and methods of using same
Owner:CERTUSVIEW TECH LLC
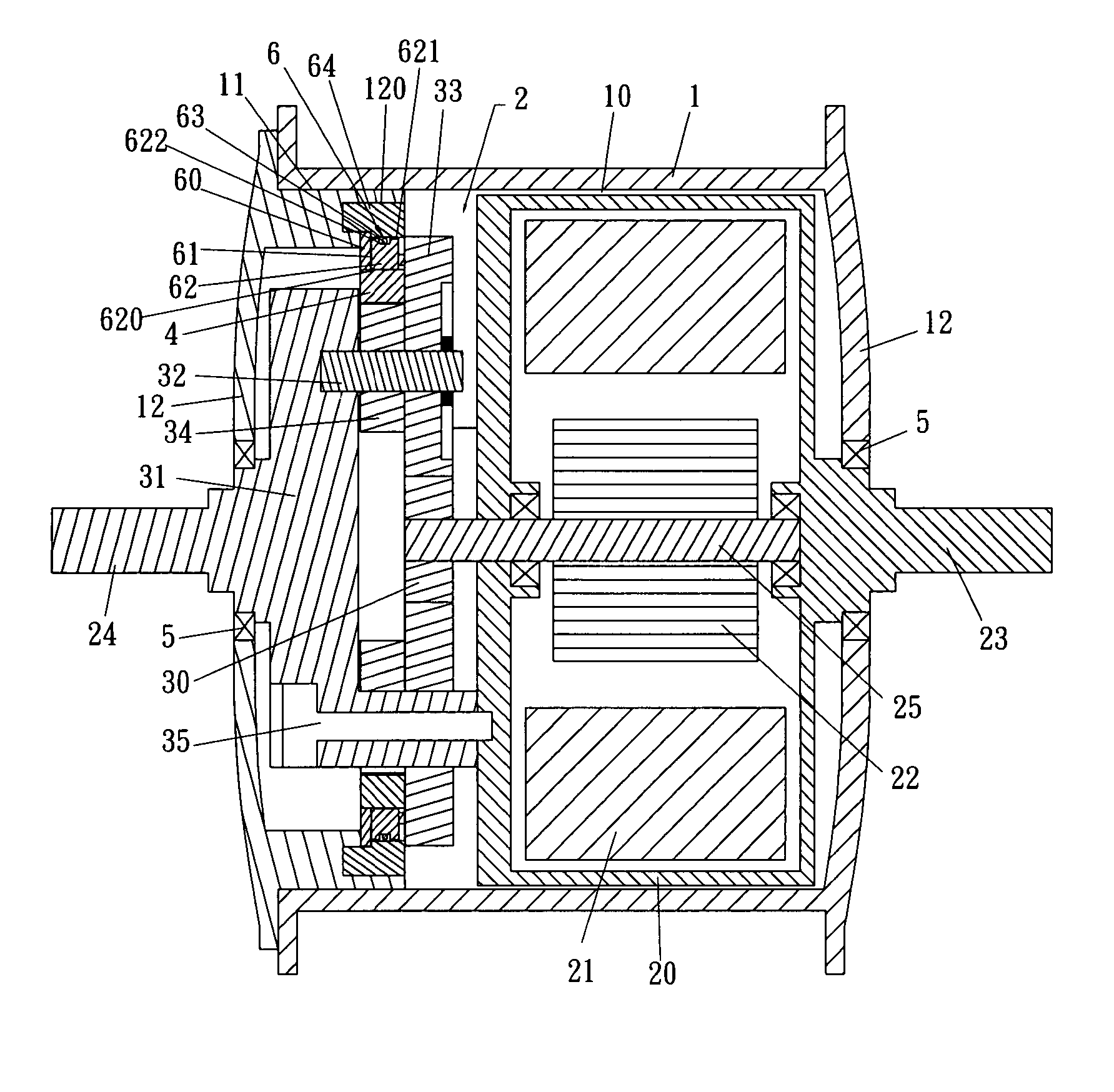
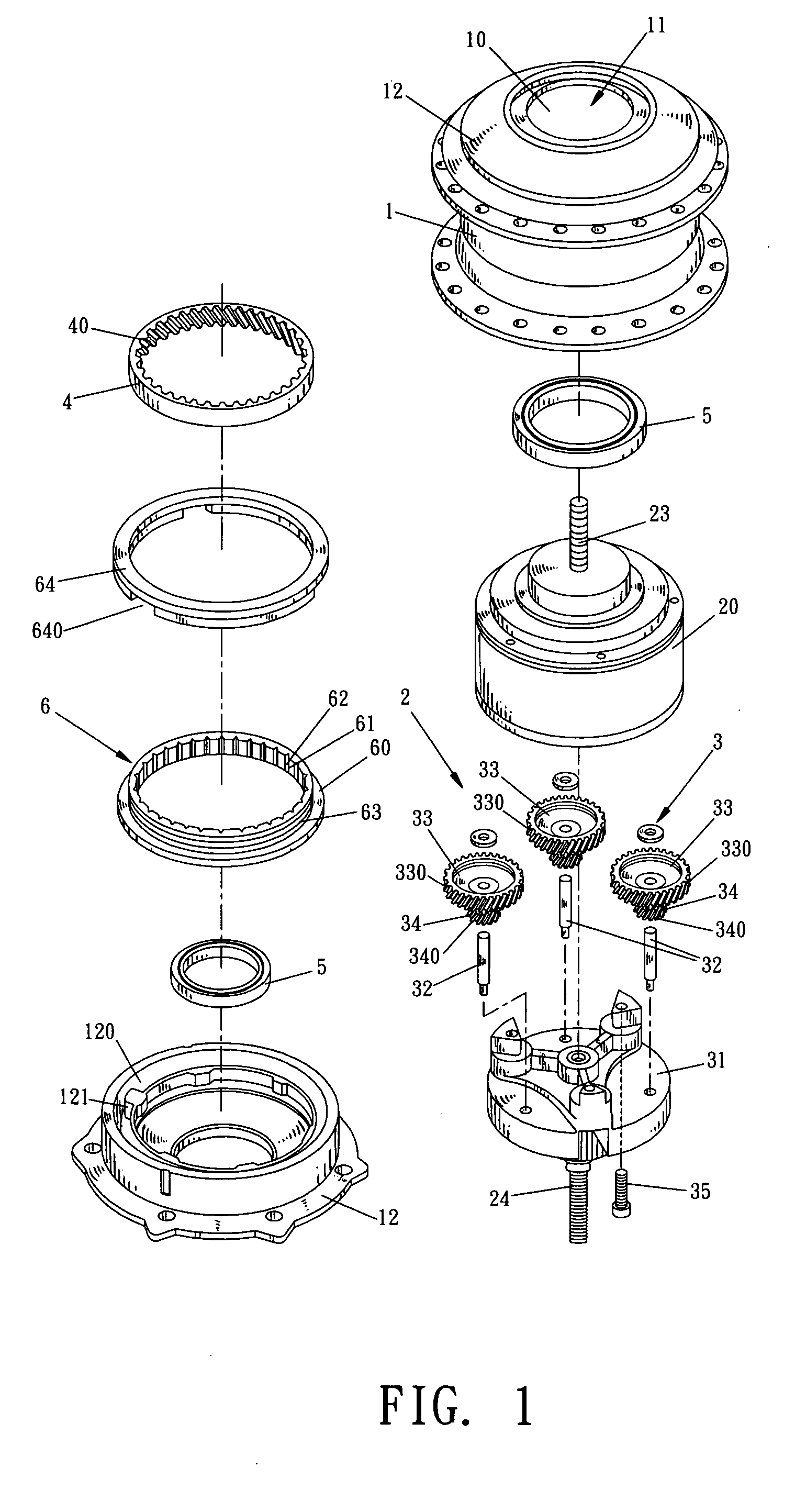
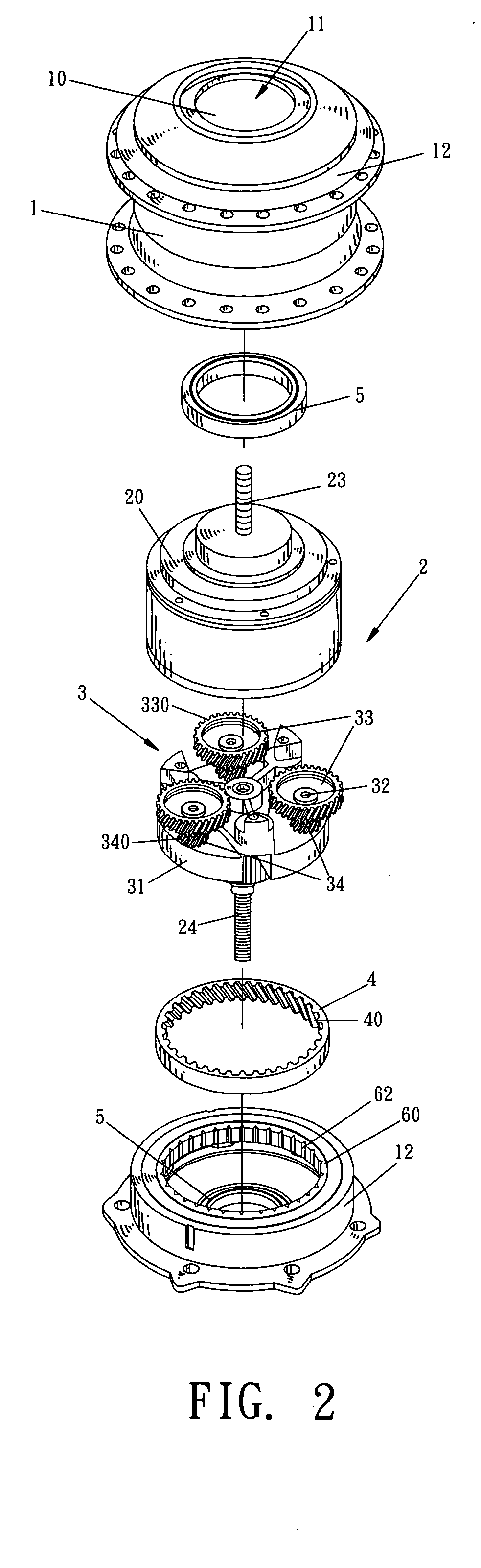
Hub motor mechanism
An electrically driven hub includes an electrical mechanism including an electrical motor and a planetary gear system connected to the electrical mechanism. A first fixed shaft is connected to the stator of the electrical motor and a second fixed shaft is connected to a second end of the stator of the electrical motor. The first and second fixed shafts are connected to the vehicle frame. A one-way clutch is connected between a cover of the hub and the planetary gear system so that the hub is rotated when the planetary gear system is activated by the motor.
Owner:LO CHIU HSIANG
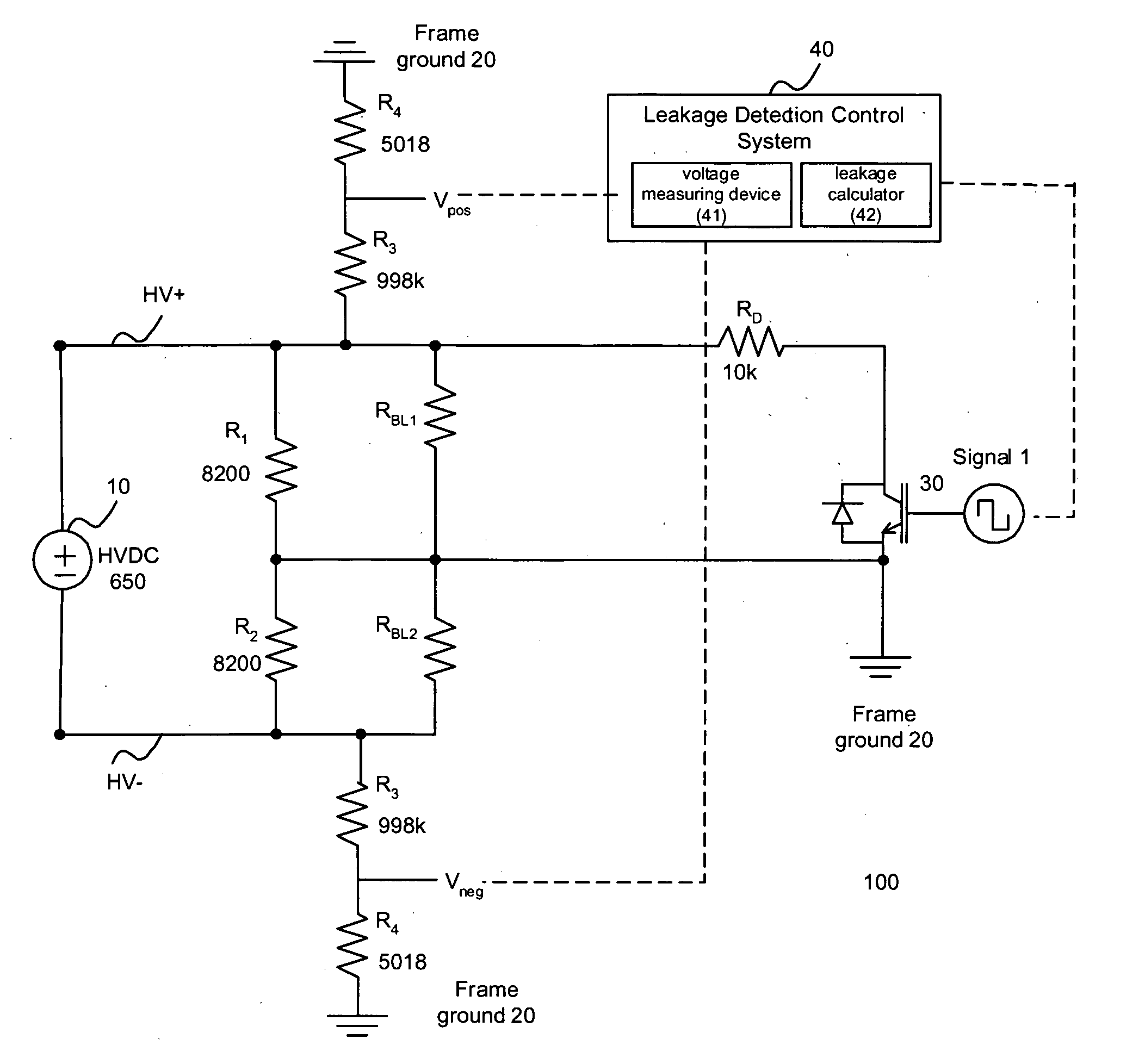
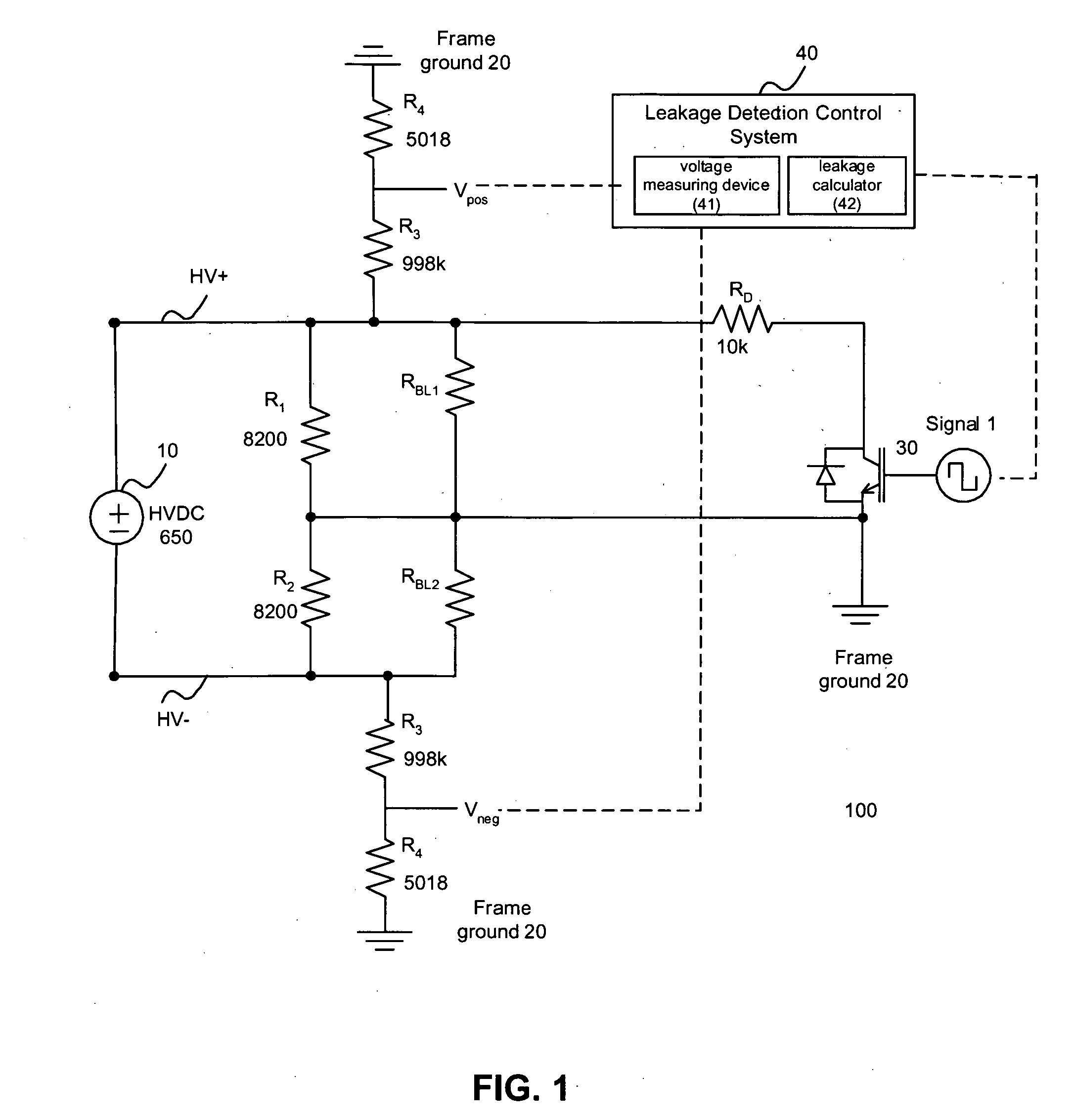
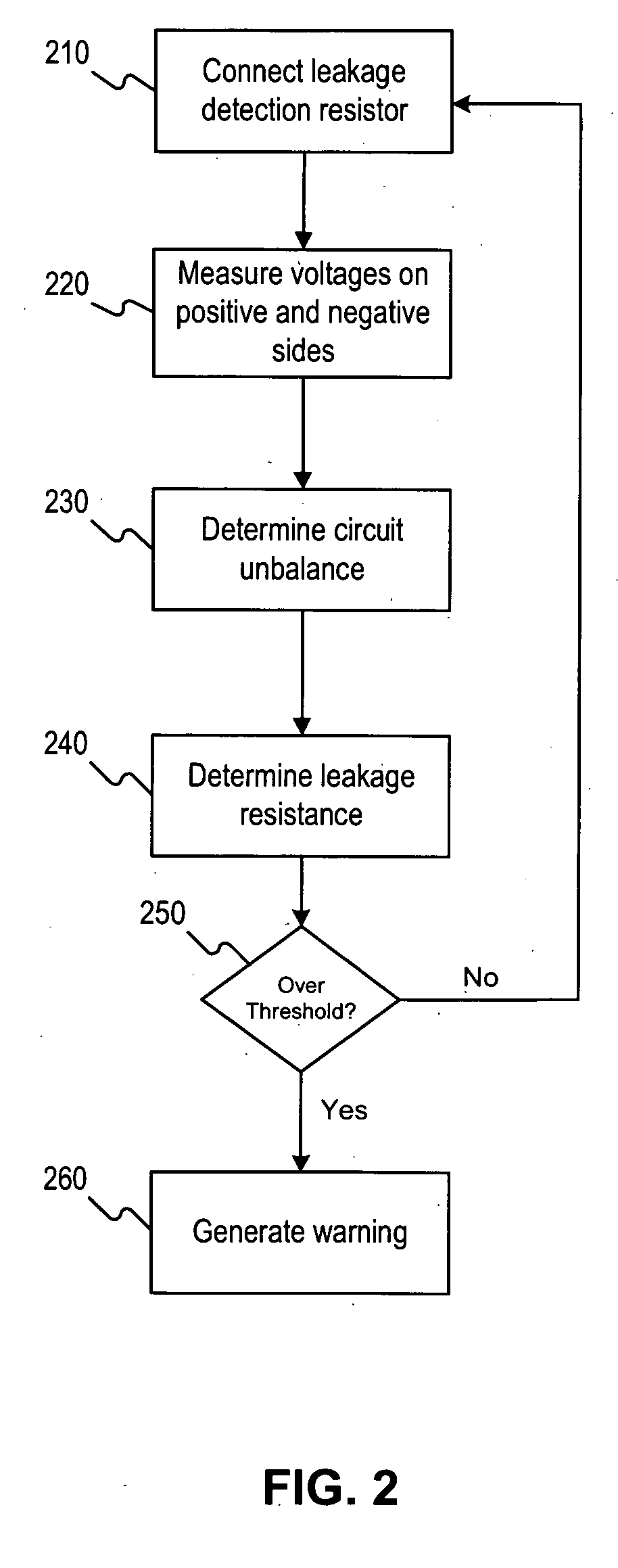
Systems and methods for electrical leakage detection
ActiveUS20080129308A1Hybrid vehiclesVehicle fittingsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC +1
Automated meter reading system
ActiveUS20080195562A1Data processing applicationsElectric devicesTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Owner:ELSTER ELECTRICTY LLC
Power unit and safety circuit having the same
ActiveUS20090051226A1Accurate graspEnsure safetyDc network circuit arrangementsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical connection
A power unit including a plurality of series-connected battery modules and a safety circuit.A service plug is inserted from the side of a terminal board of a battery pack, thereby establishing an electrical connection among battery modules. A connector is provided on a back of a terminal cover by way of a projecting section, and a second safety switch is activated by attachment of a terminal cover and insertion of the connector to the terminal board, thereby establishing an electrical connection among the battery modules. Even when the service plug is attached at the time of completion of maintenance without attachment of the terminal cover, the battery modules are still kept in an unconnected state by means of a second switch, and energization, which would otherwise arise with exposed terminals, is prevented.
Owner:GRUPO PETROTEMEX DE C V +1
In-wheel actuator and in-wheel assembly comprising the same
An in-wheel assembly is provided, and the in-wheel assembly includes an in-wheel actuator and a wheel. The in-wheel actuator includes a driving motor; a decelerator which is disposed inside the driving motor and configured to reduce a rotational speed of the driving motor; and a hollow shaft which is disposed inside the driving motor and configured to transfer a rotational force of the driving motor to the decelerator, which is accommodated in a hollow of the hollow shaft, and circulates fluid inside of the driving motor with respect to a surface of the decelerator when driven to rotate by the driving motor. The wheel accommodates the in-wheel actuator and receives a rotational speed reduced by the decelerator to rotate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Electric vehicle
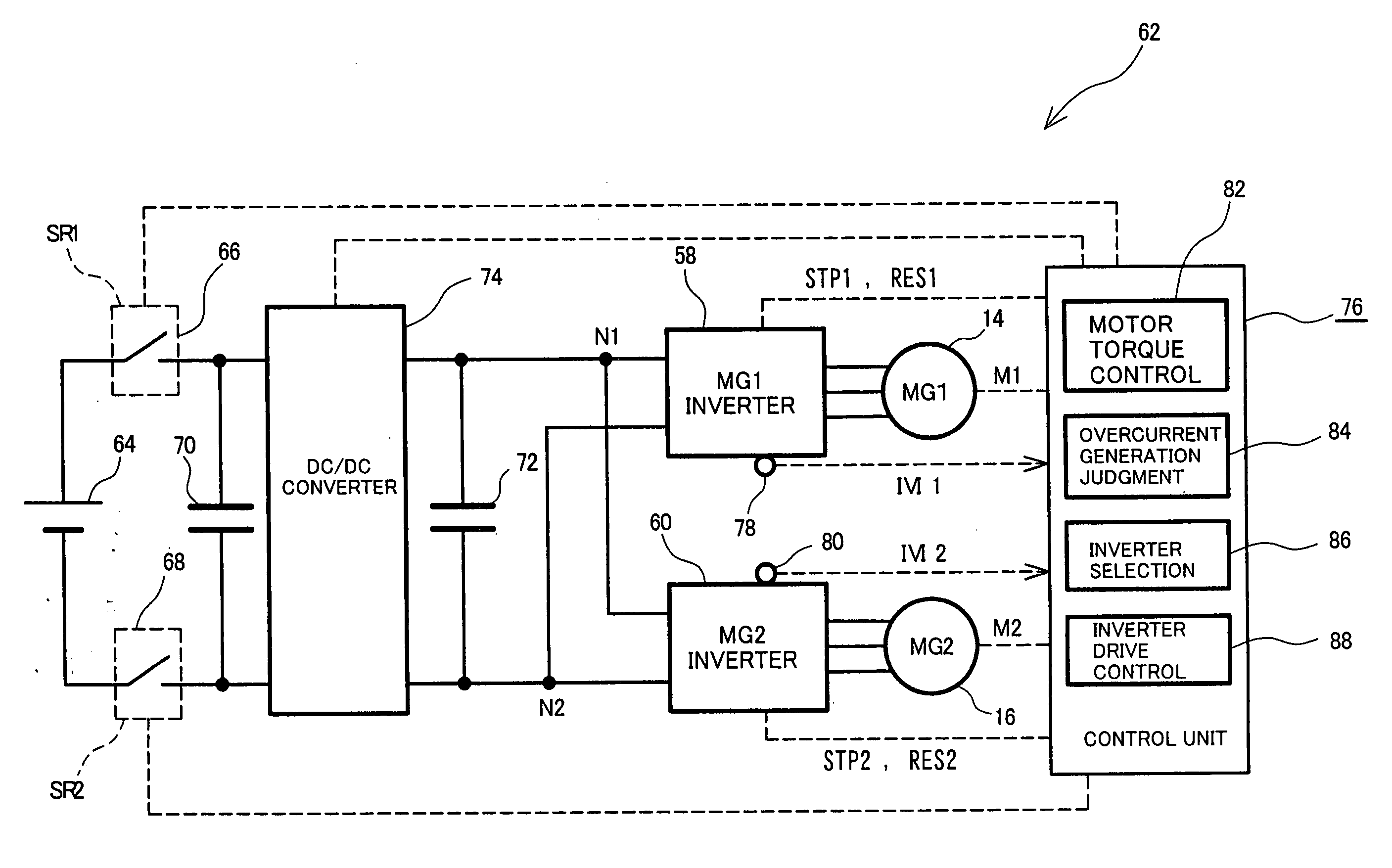
InactiveUS20100027170A1Efficient implementationSafe evacuationConversion with intermediate conversion to dcElectrical testingOvercurrentElectric vehicle
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
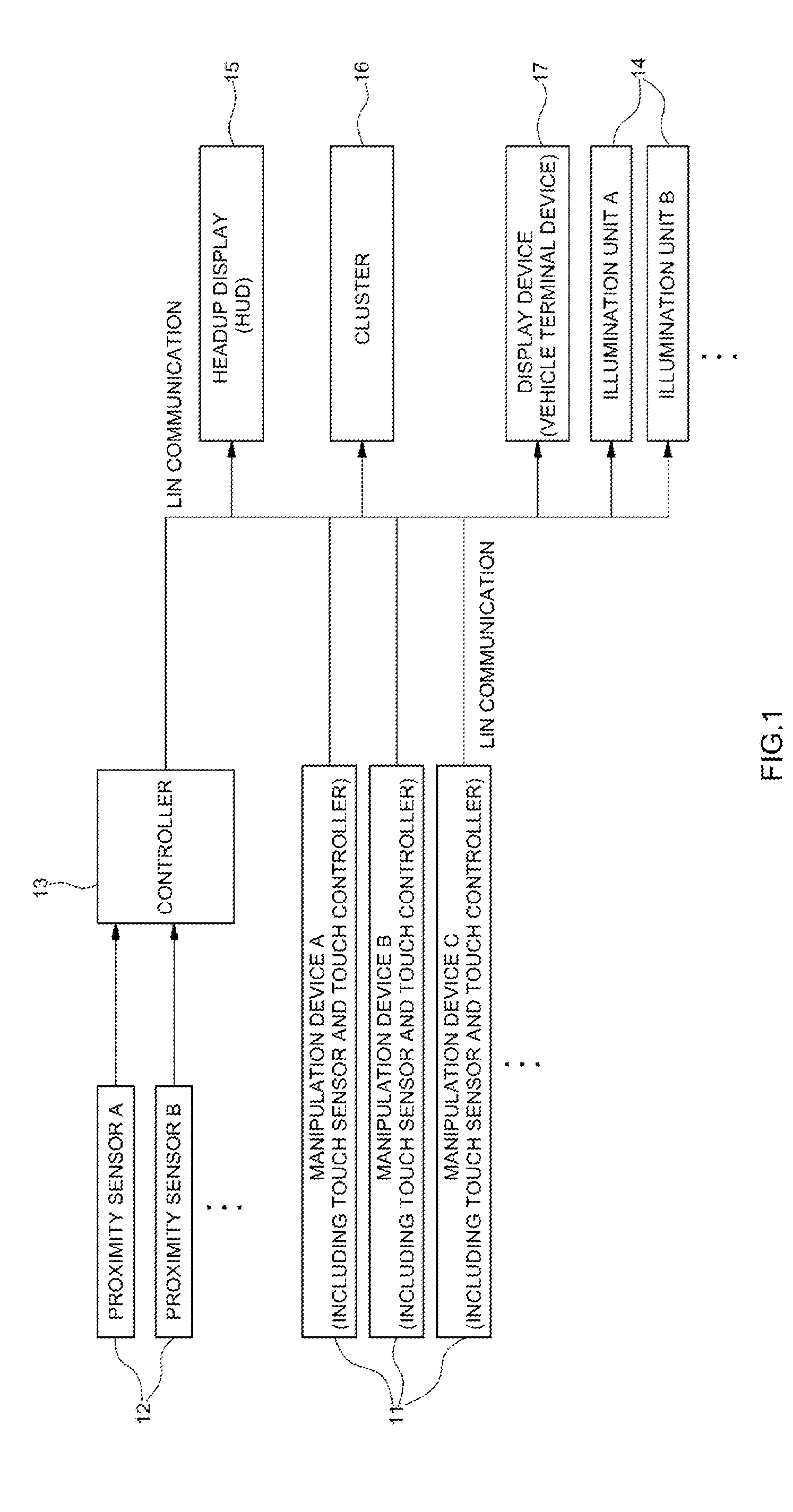
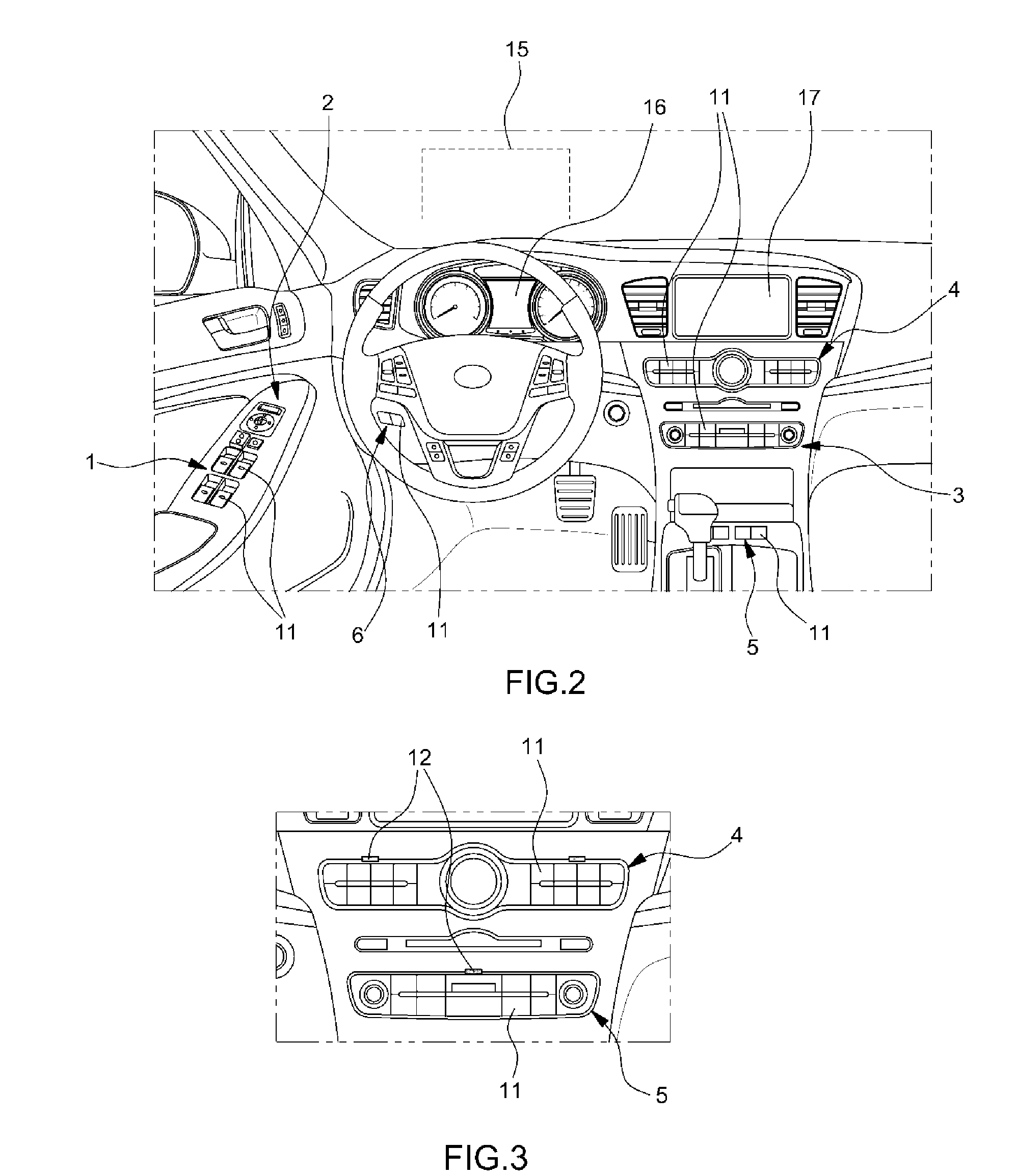
System for providing vehicle manipulation device information
InactiveUS20140368029A1Improving convenience in manipulation and driving stabilityImproving in manipulationContact mechanismsElectric devicesBiomedical engineeringProximity sensor
A system for providing vehicle manipulation device information provides information about a manipulation device such as a switch or a button to a user in advance, before the user manipulates a device mounted on a vehicle, thus improving convenience in manipulation and driving stability. The system includes a proximity sensor installed in a manipulation portion having the manipulation device for manipulating the device mounted on the vehicle to sense an object that approaches the manipulation portion. The system also includes a controller that receives an approach sensing signal from the proximity sensor, and outputs a control signal for displaying manipulation device information of the manipulation portion, and a display unit for displaying the manipulation device information of the manipulation portion.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD
Protection arrangement for an electric vehicle
ActiveUS20160130851A1Maintenance of such closeLarge capacityCharging stationsElectric devicesElectrical energy storageCurrent collector
Owner:VOLVO LASTVAGNAR AB
Stand-Alone Renewable-Energy Generating Device Including Emission Savings Sensor, Retrofit Emissions Savings Sensor for such a Device, and Method
InactiveUS20110213506A1Increase motivationLevel controlPV power plantsCommunication interfaceNetworked system
Owner:CHANGERS
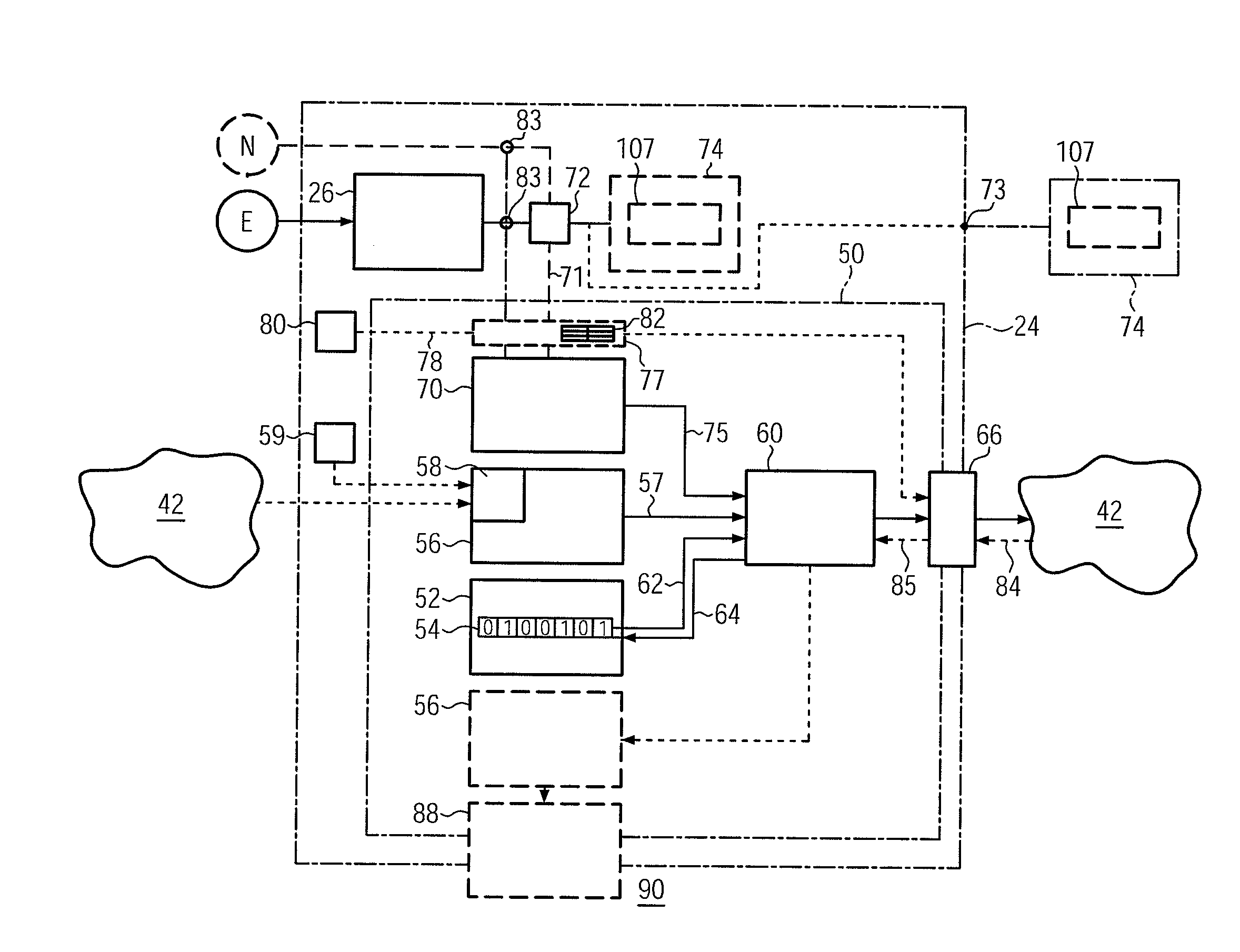
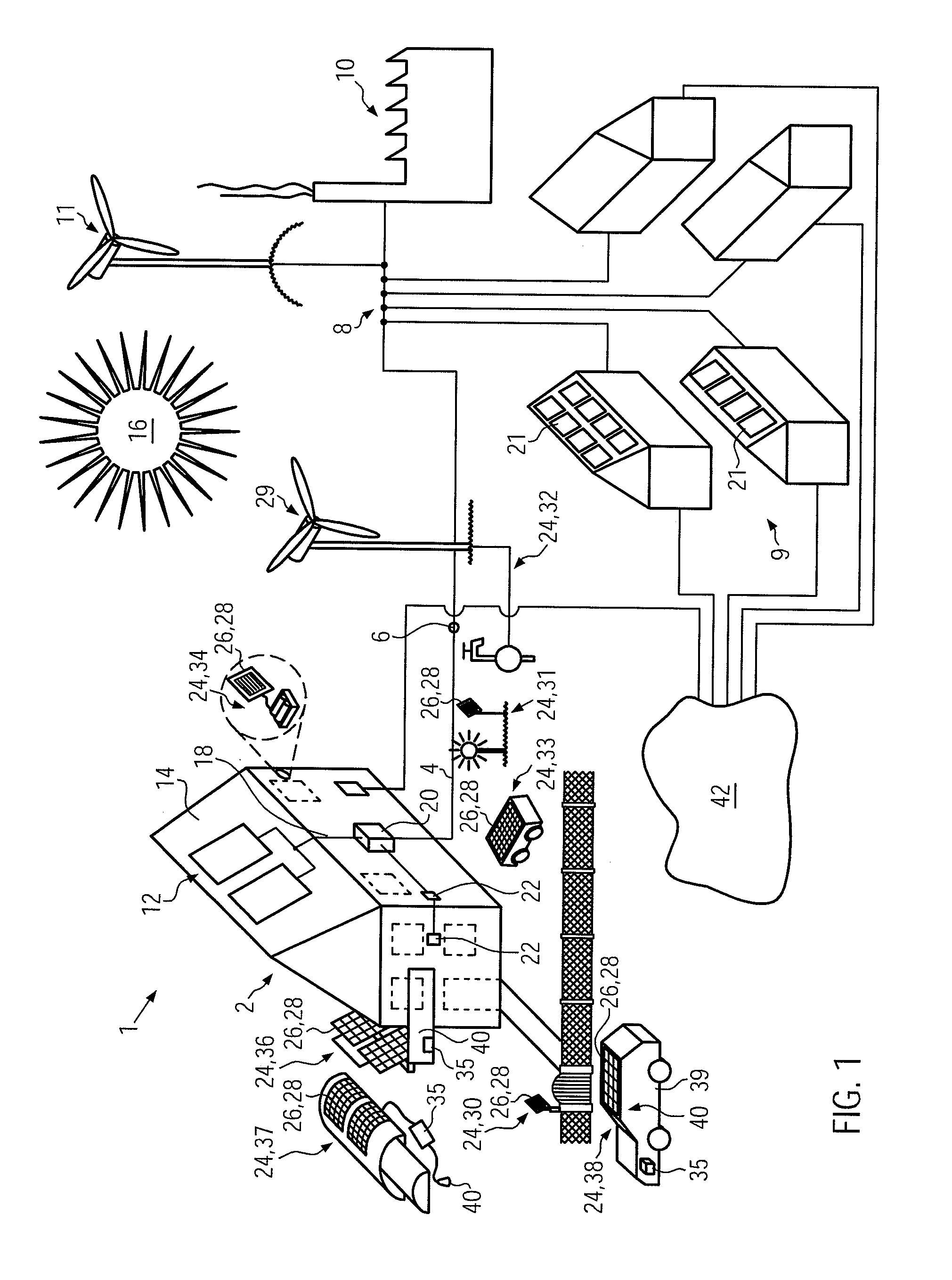
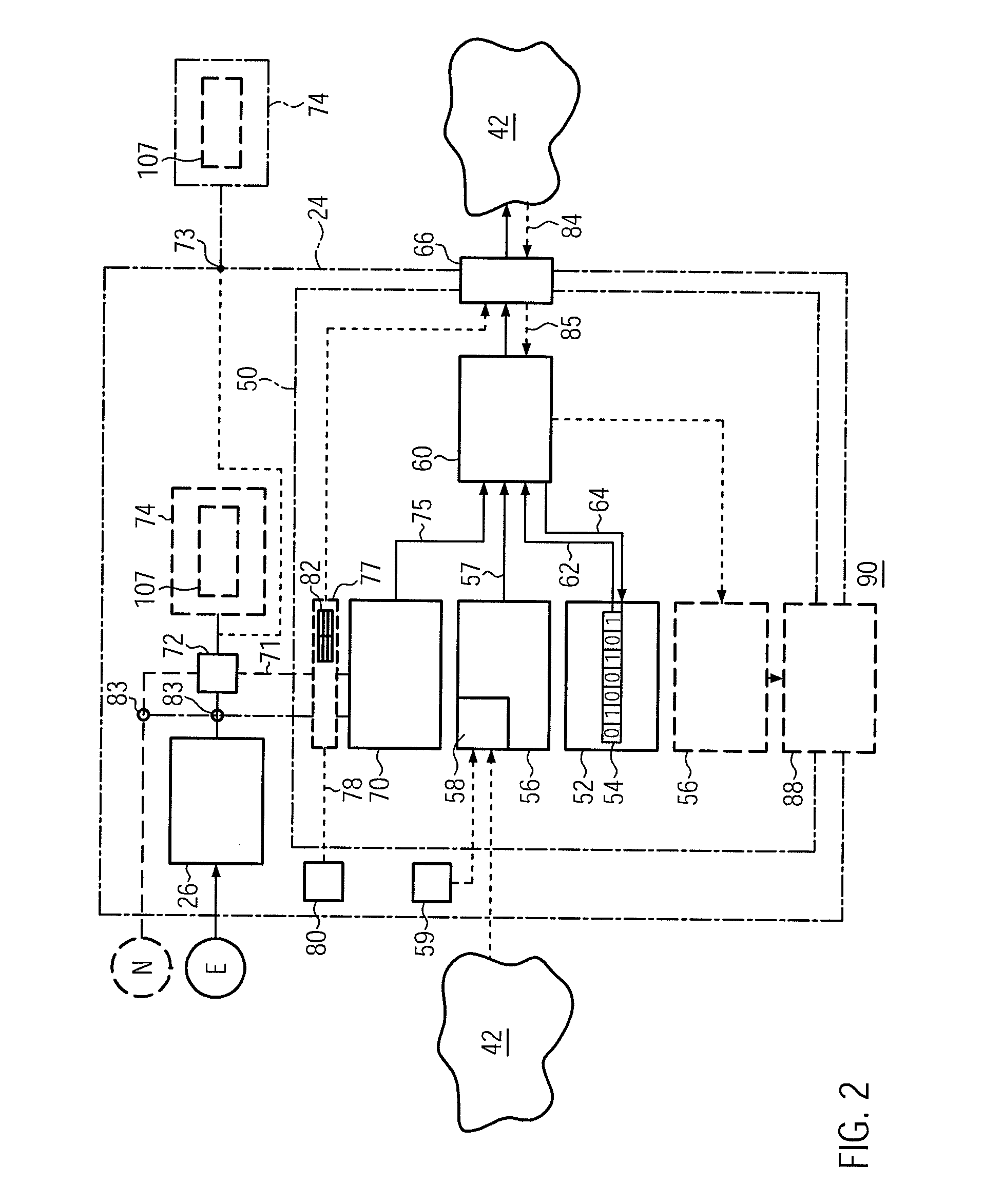
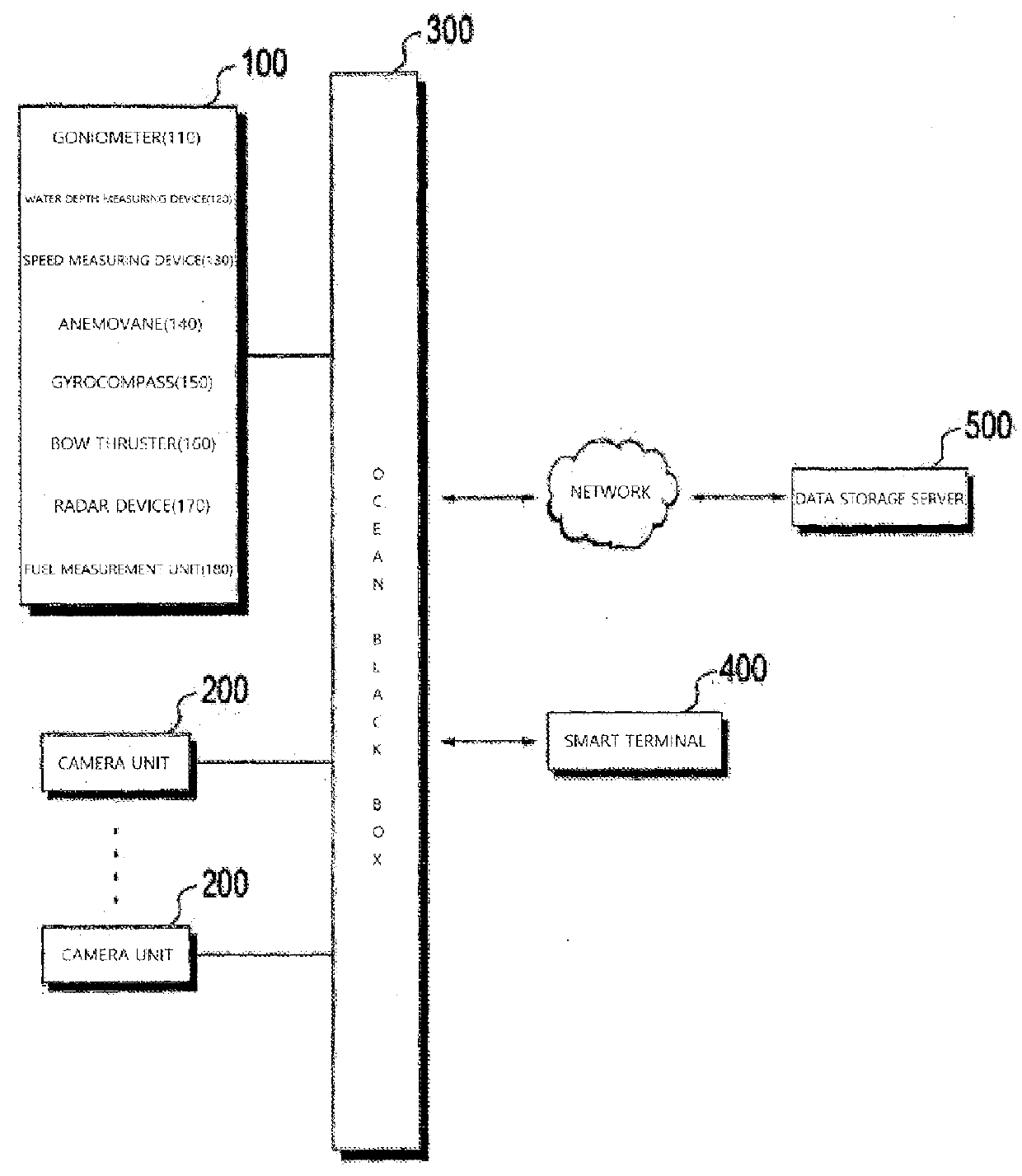
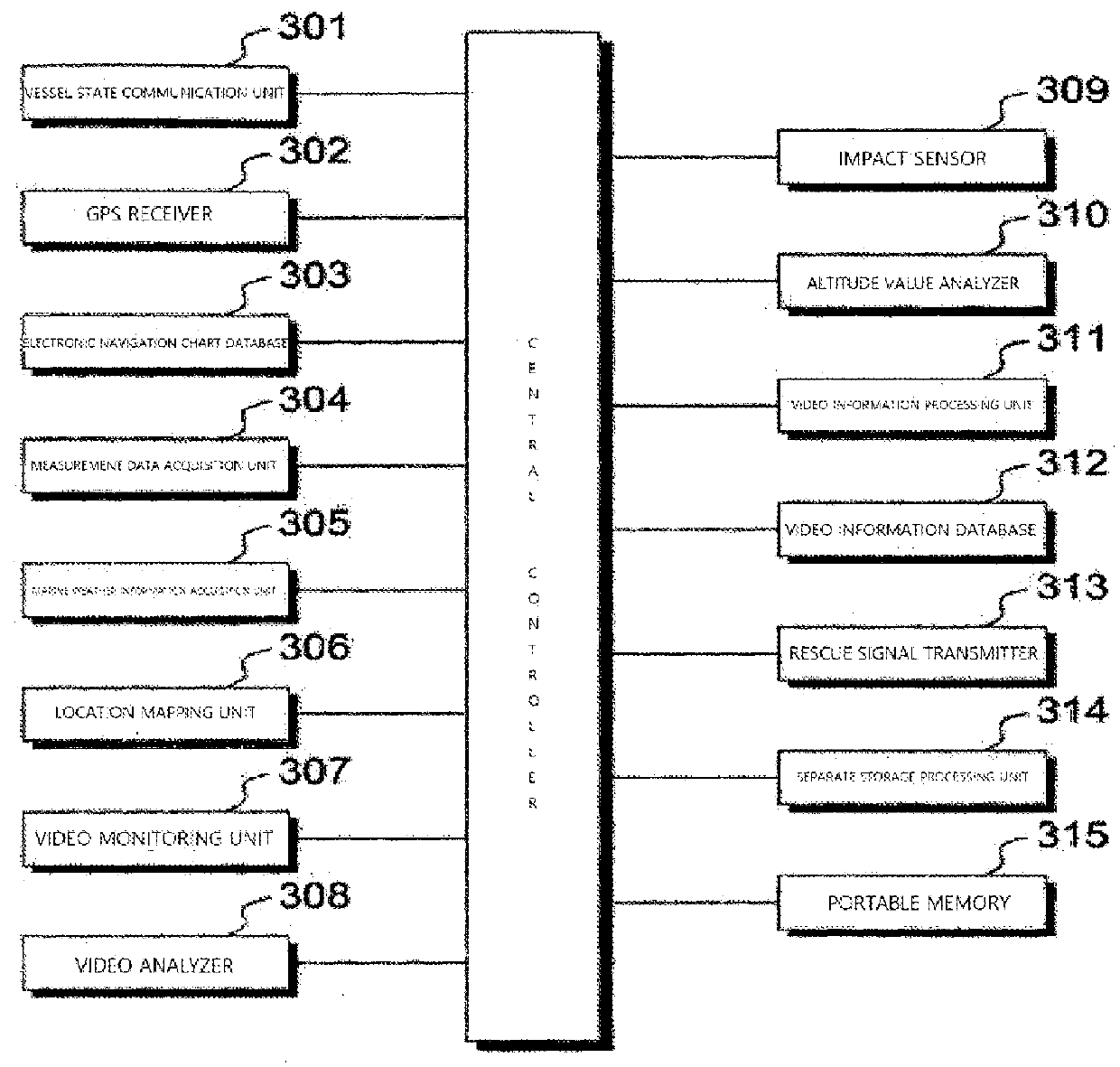
Black box system for leisure vessel
InactiveUS20160031536A1Improve portabilitySpeed controllerElectric devicesSimulationMarine navigation
Owner:BONC INOVATORS
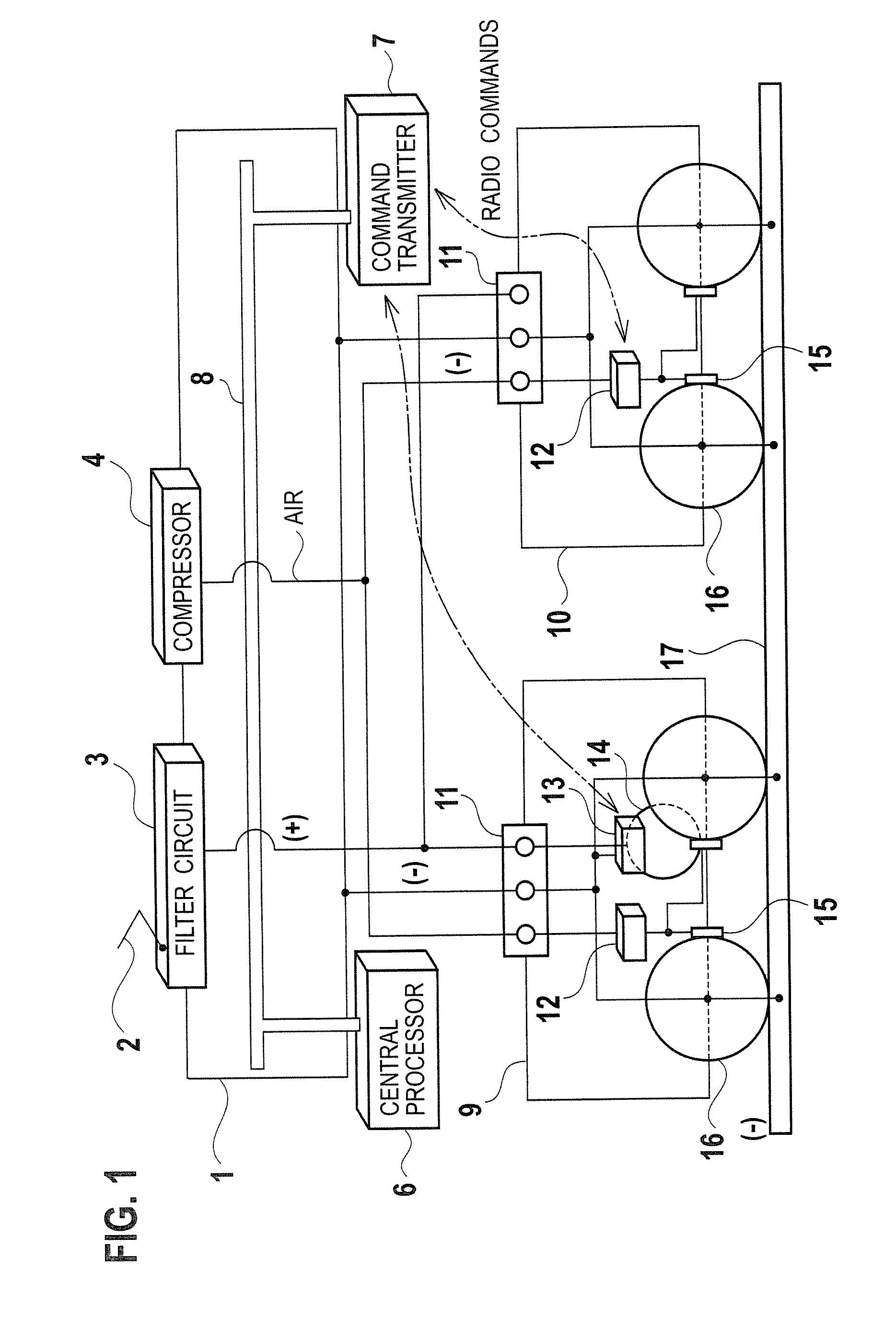
System and method for activating and deactivating a remotely controlled vehicle starter
ActiveUS20090178639A1Simple and economical to manufactureFrequency-division multiplex detailsDigital data processing detailsTelecommunicationsControl engineering
A system for activating and deactivating a remotely controlled vehicle starter includes a handheld mobile communication device having at least a speaker mounted therein and a wireless transmitter having at least a start switch mounted therein. A first wire connects a negative voltage supply path to the speaker circuit with a negative voltage supply path to the start switch circuit. A variable resistor is provided and has a pair of end terminals. There is a second wire having each of a first end thereof electrically connected to a positive voltage supply path to the speaker circuit and an opposed second end thereof electrically connected to one terminal end of the variable resistor. A third wire is also provided to connect an opposed end terminal of the variable resistor to a positive voltage supply path to the start switch.
Owner:GALLARZO JOSE L
Electrical power steering apparatus
InactiveUS20140174844A1Avoiding possible electrical shockMaintain securitySpeed controllerElectric devicesElectric power steeringElectrical battery
A motor control circuit includes a power relay, a converter division, a smoothing condenser, a control circuit and a motor drive circuit, and is connected to a battery as high voltage power and to an electrical motor. The battery is connected with a driving battery having the high voltage such as 288V etc. A step down circuit reduces the high voltage to a low voltage such as 36V etc., charges a low voltage charge device and supplies drive power to the motor drive circuit. When the vehicle collision is occurred, the control circuit detects the collision by a value of detected acceleration, a power change relay is turned on to change to the power source from the low voltage charge device after voltage of the smoothing condenser is reduced, thereby connecting the low voltage to the motor drive circuit.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
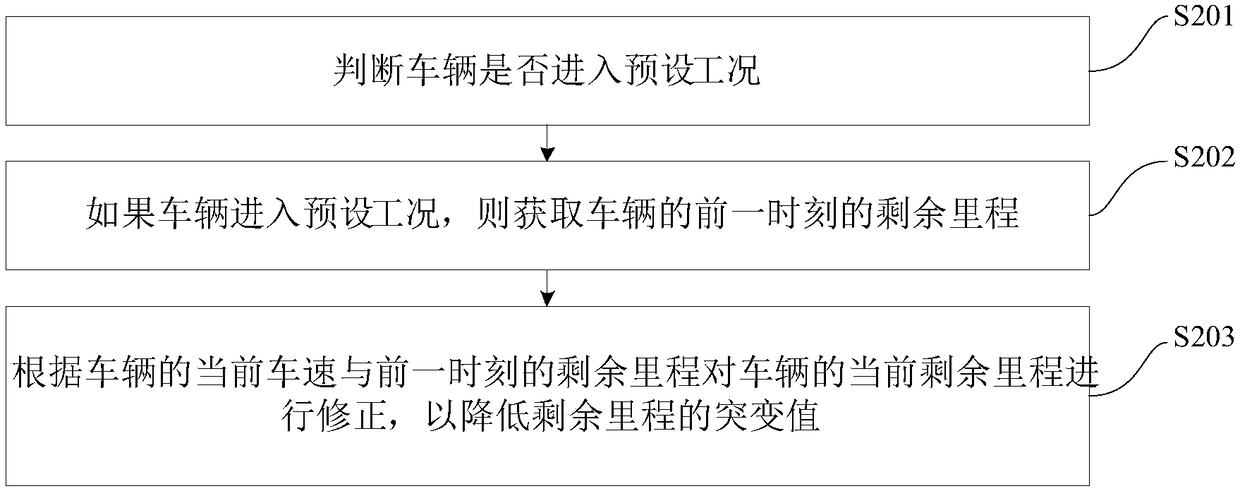
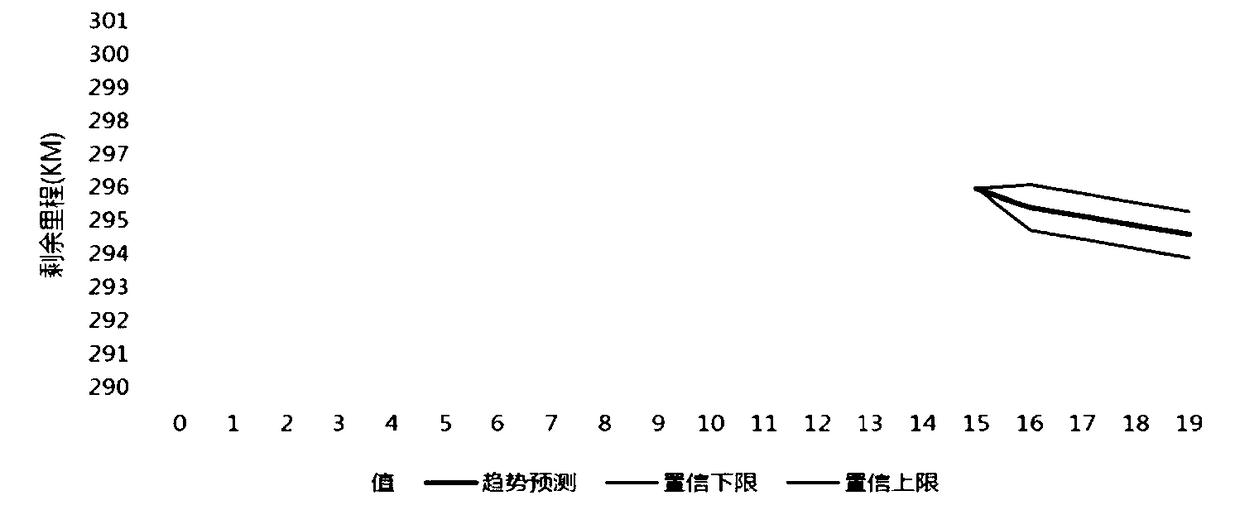
Electric vehicle remainder range detection method and device and vehicle with electric vehicle remainder range detection device
InactiveCN108482128AImprove experienceReduce Mutation ValueElectric devicesVehicular energy storageEngineeringElectric vehicle
Owner:国机智骏汽车有限公司
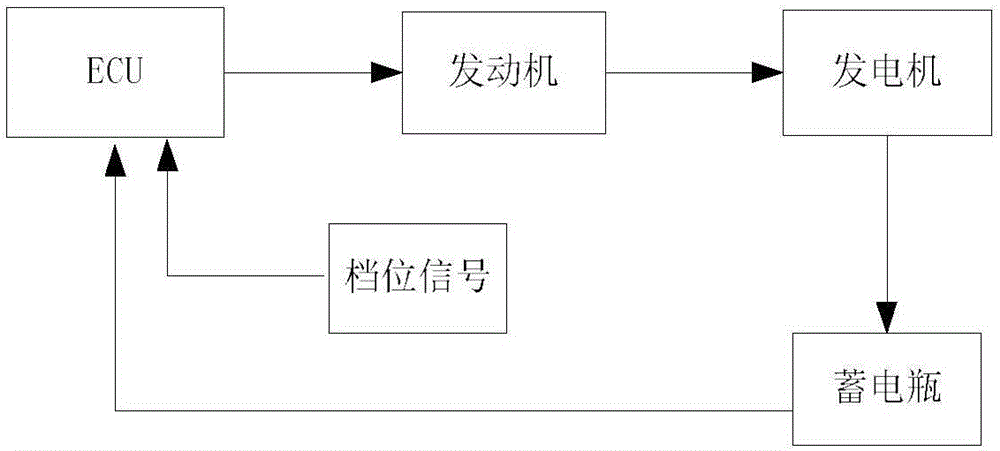
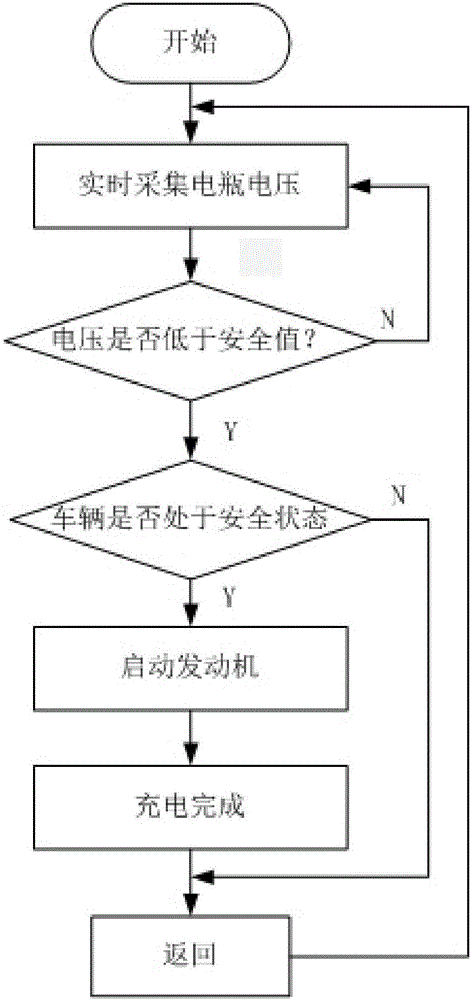
Intelligent system preventing power lack for automobile battery
Owner:成都雅骏汽车制造有限公司
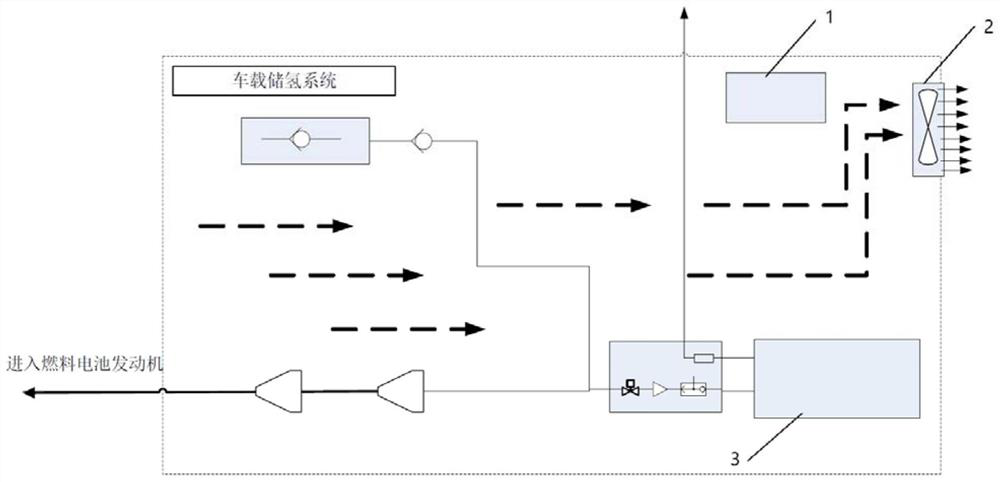
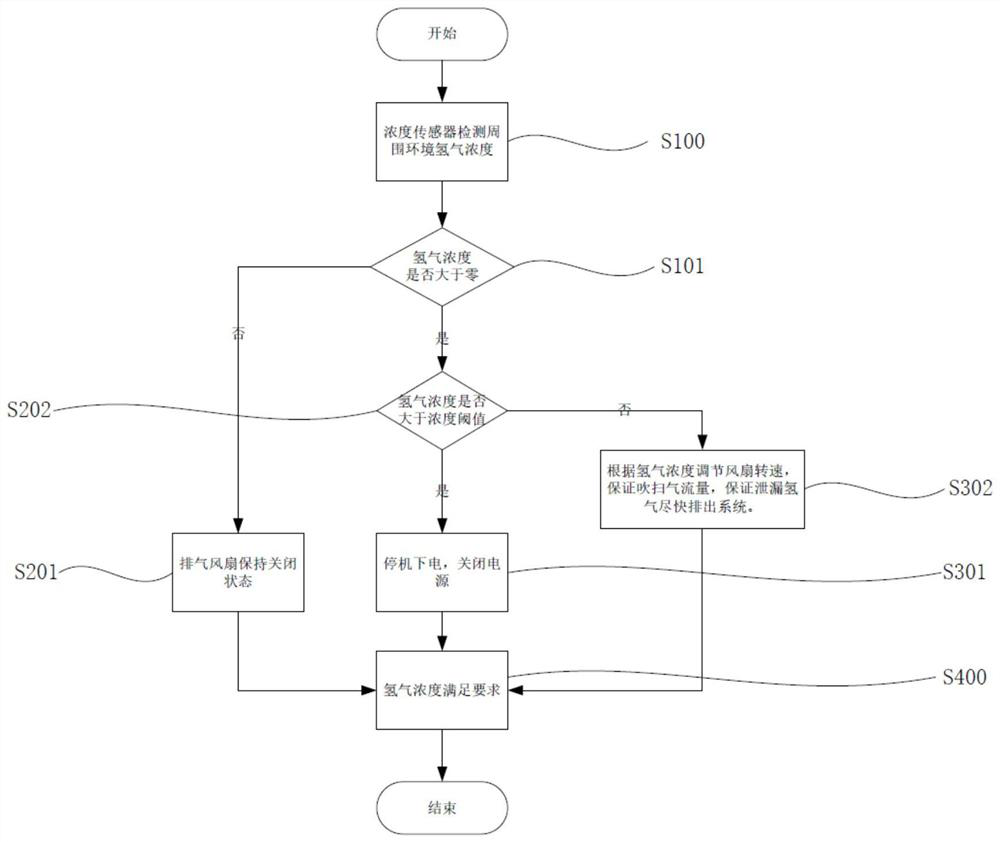
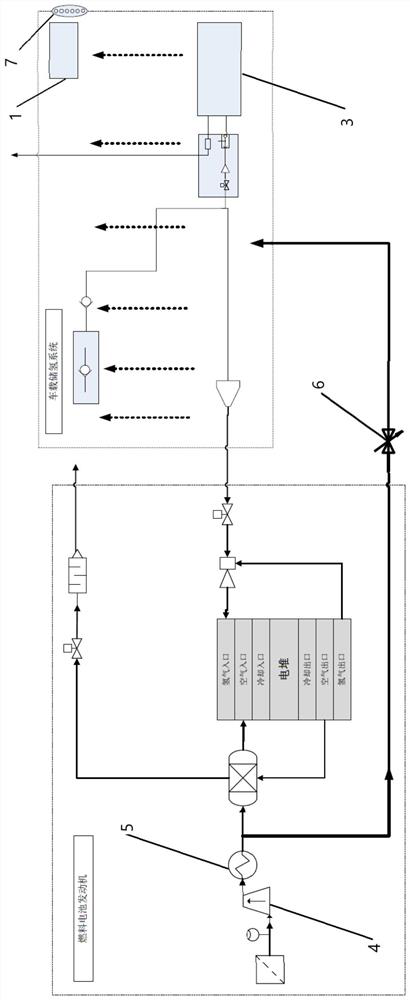
Vehicle-mounted hydrogen storage system device and control method thereof
Owner:CHINA FIRST AUTOMOBILE
Battery emergency disconnection system based on accurate measurement and use method
ActiveCN111817256AIncrease current coverageReduced risk of thermal runawayElectric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical batteryBattery cell
The invention discloses a battery emergency disconnection system based on accurate measurement. The battery emergency disconnection system comprises a high-voltage electric load, a processor unit anda battery, wherein the battery is electrically connected with a burning explosion type fuse and a copper bar; the burning explosion type fuse is electrically connected with a high-voltage electric load through the processor unit, the copper bar is electrically connected with a temperature sensor through the processor unit, meanwhile, the copper bar and the temperature sensor are electrically connected with a relay, and the relay is electrically connected with the high-voltage electric load. According to the battery emergency disconnection system, the loss of charging and discharging of the battery is reduced through an alternative scheme, the action time of the fuse is prolonged, the current coverage range of the fuse for battery protection is increased, and the thermal runaway risk of thebattery due to overcurrent is reduced.
Owner:DELU TECH CO LTD
Electric rolling stock driving apparatus
InactiveUS20080011185A1Improve reliabilityEasy to manufactureElectric devicesLocomotivesMotorized vehicleTruck
Owner:BRIAN INVESTMENTS +1
Electric leakage detection device for in-vehicle power supply system, and hydraulic shovel
InactiveCN105960595AThere is no leakage detectionCircuit monitoring/indicationAC motor controlIn vehicleMeasurement point
An electric leakage detection device for an in-vehicle power supply system includes: a detection signal generation unit for applying an AC voltage to a voltage application point on a wire connecting a power conversion circuit and a power supply, said power conversion circuit converting the power from the power supply to AC power and supplying the AC power to an electric motor; a voltage measurement unit for measuring the voltage at a voltage measurement point between said detection signal generation unit and said voltage application point; and an electric leakage detection unit for detecting, when a control device for said electric motor is providing said electric motor with an instruction for holding a constant rotation angle, whether or not electric leakage is present between said power conversion circuit and said electric motor depending on the voltage at said voltage measurement point measured by said voltage measurement unit.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
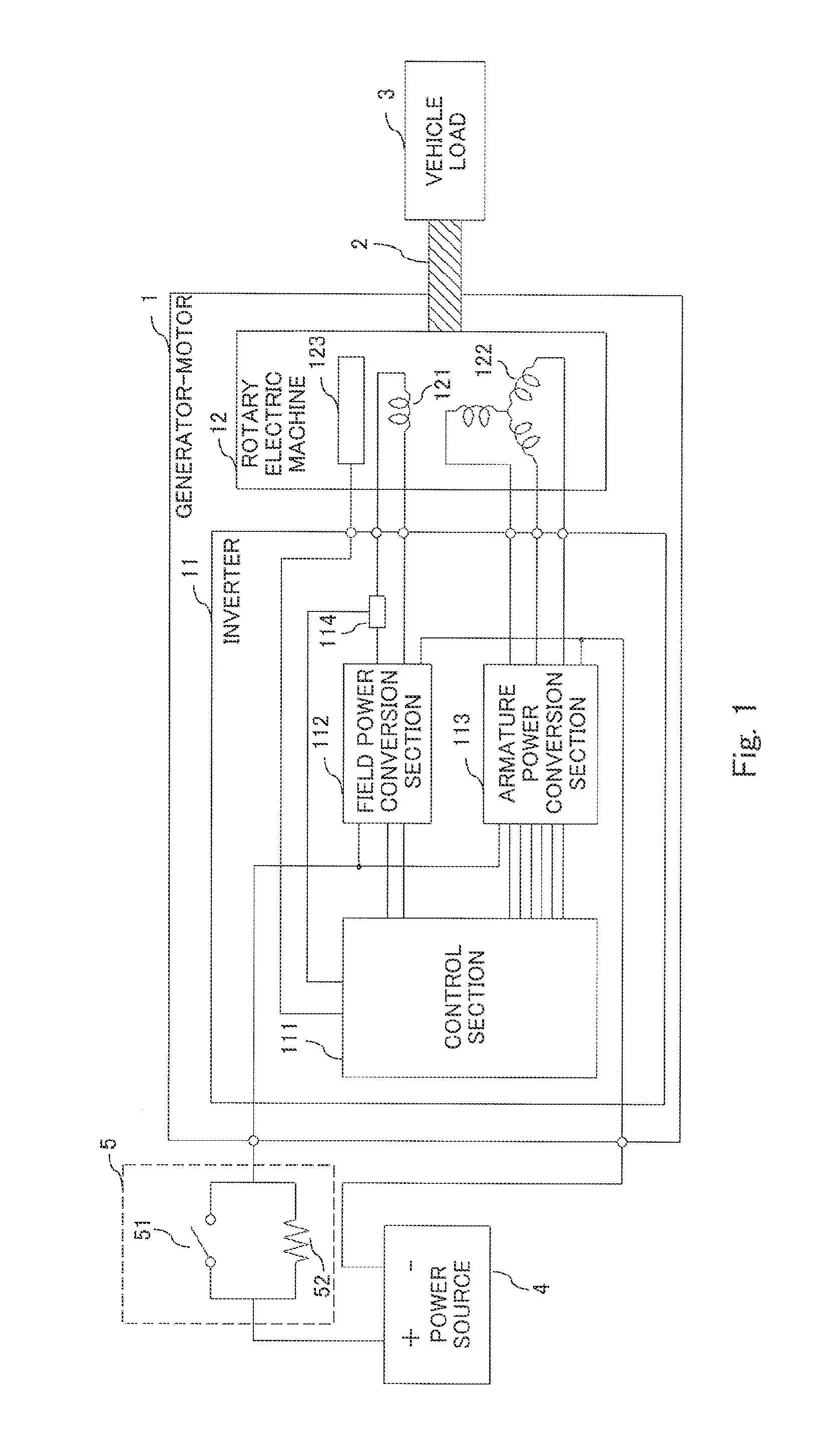
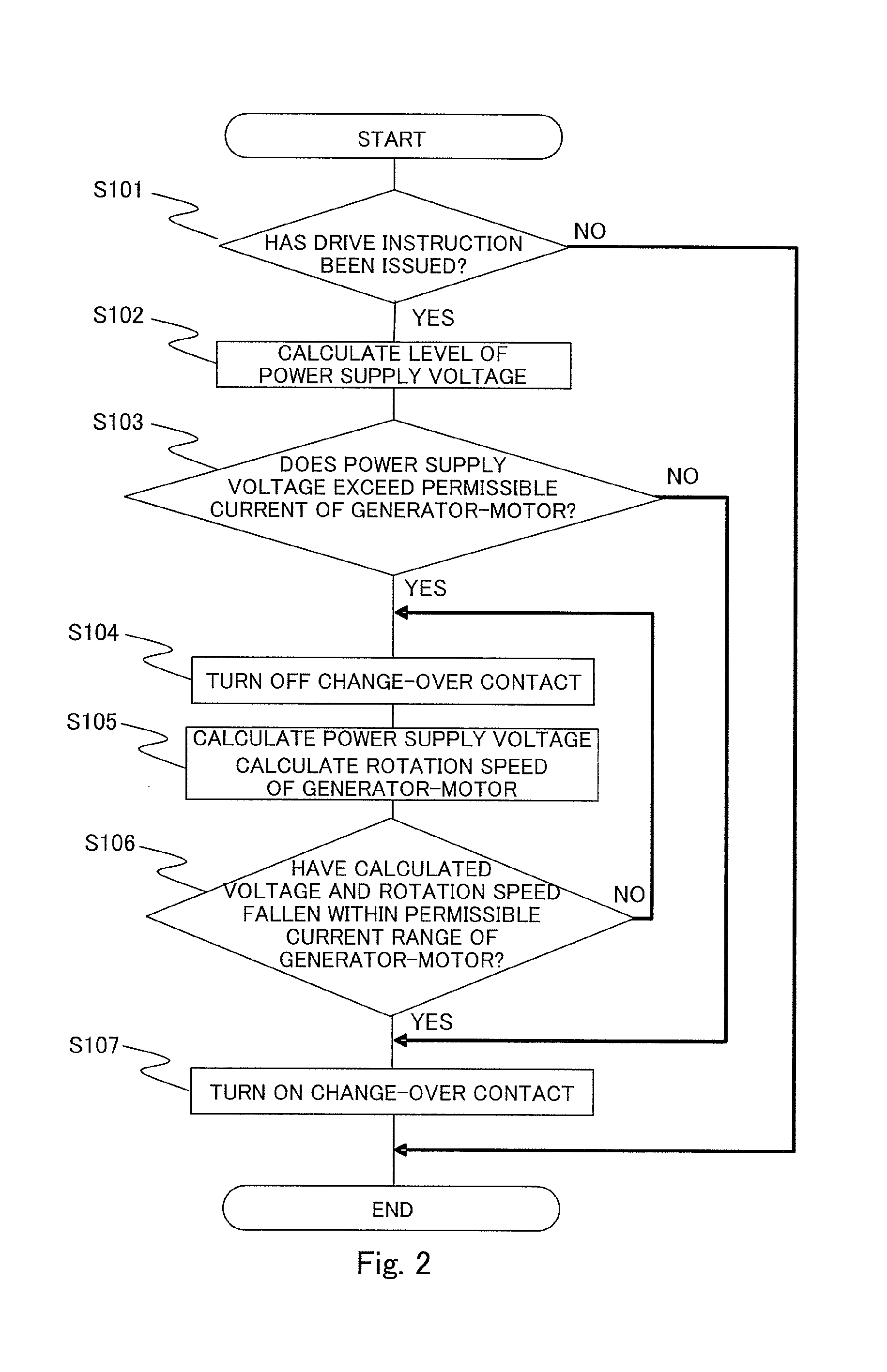
Control device for generator-motor and control method for generator-motor
ActiveUS20140001841A1InexpensiveElectric motor controlElectric devicesDriving currentElectric machine
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Micro-discharge power dynamic tracking method
Owner:北京优诺信创科技有限公司
Campus electric appliance fault detection method, background server and system
ActiveCN114295928AImprove maintenance efficiencyImprove accuracyElectric devicesElectrical testingEmbedded systemServer
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAOLUN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Driving apparatus for electric vehicle
Owner:LG MAGNA E POWERTRAIN CO LTD
Charging device for electric vehicle
ActiveCN103986199AAvoid power outagesBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsElectrical batteryCharge control
A charging device for an electric vehicle is disclosed. A mal-operation detection unit detects whether a start operation part is operated mistakenly by an electric vehicle user; when mal-operation is detected by the a charging control unit during processes where batteries in the electric vehicle are charged by an external power source arranged outside the electric vehicle, the batteries are kept being charged.
Owner:SUZUKI MOTOR CORP
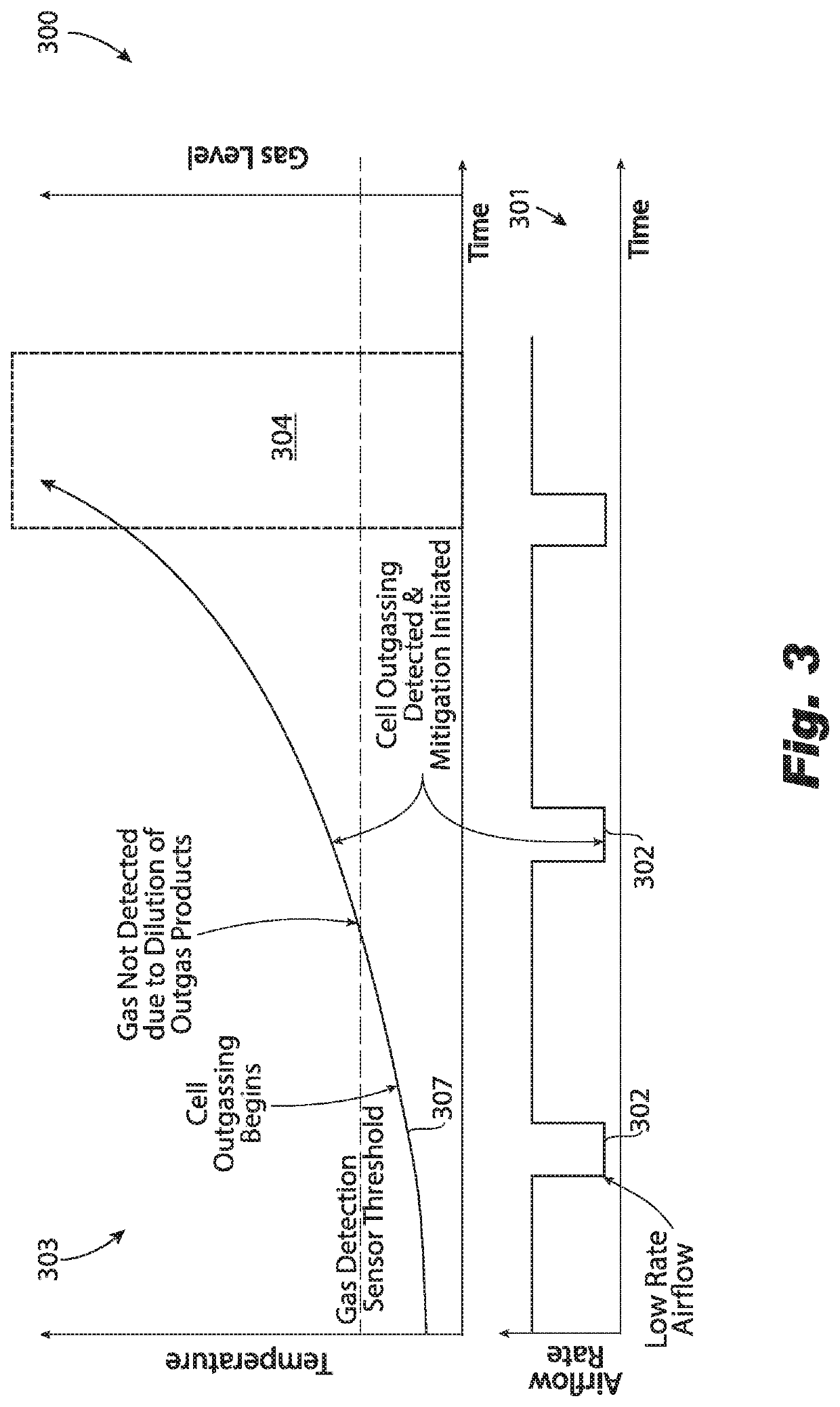
Systems and methods for battery ventilation
PendingUS20210098763A1Increase cooling airflowCell temperature controlSecondary cell gas removalParticulatesThermodynamics
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
A control system for a vehicle
ActiveCN109548401ADo not exceed yaw safety limitAssociation with control/drive circuitsSpeed controllerElectric machineControl system
A control system for a vehicle having a first wheel arranged to be driven by a first electric motor and a second wheel arranged to be driven by a second electric motor, wherein the first wheel and thesecond wheel are transversely located on the vehicle relative to each other, the control system comprising a first controller associated with the first electric motor and a second controller associated with the second electric motor, wherein the first controller includes means for estimating a first power value for the power applied to the second wheel by the second electric motor when the secondelectric motor is placed in a first motor configuration and means for estimating a second power value for the power applied to the second wheel by the second electric motor when the second electric motor is placed in a second motor configuration, wherein upon the occurrence of a predetermined condition the first controller is arranged to determine a first power differential between the power being applied to the first wheel by the first electric motor and the first power value and a second power differential between the power being applied to the first wheel by the first electric motor and the second power value, wherein if the first controller determines that if either the first power differential or the second power differential is greater than a predetermined value the first controlleris arranged to adjust the torque generated by the first electric motor or if both the first power differential and the second power differential are less than a predetermined value the first controller is arranged to maintain the torque generated by the first electric motor.
Owner:PROTEAN ELECTRIC LIMITED
System for electric vehicle integrated with road
ActiveCN111319516ALower resistanceReduce power lossRail devicesElectric devicesElectrical conductorEnergy supply
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
Power systems for three-phase permanent magnet motors
The system has a three-phase inverter (1) connected to primary ends (2a-2c) of windings (3a-3c) of three phases of a permanent magnet three-phase motor (4). A three-phase isolation contactor (9') is placed on two of the windings between the inverter and the respective primary end. Secondary ends (5a-5c) of the windings are connected to a common point (6), and a neutral double contactor (11) is placed on the two windings between the point and the respective secondary end. The contactors (9', 11) are respectively placed between the ends (2a, 5a) and the ends (2c, 5c). An independent claim is also included for a method for deactivating a permanent magnet four-phase motor for a railway vehicle in case of an internal defect.
Owner:ALSTOM TRANSPORT TECH SAS
High-safety power machine for electric vehicle
InactiveCN114132159AReduce impactReduce vibrationElectric devicesNon-rotating vibration suppressionSpontaneous combustionElectric vehicle
Owner:汪立钢
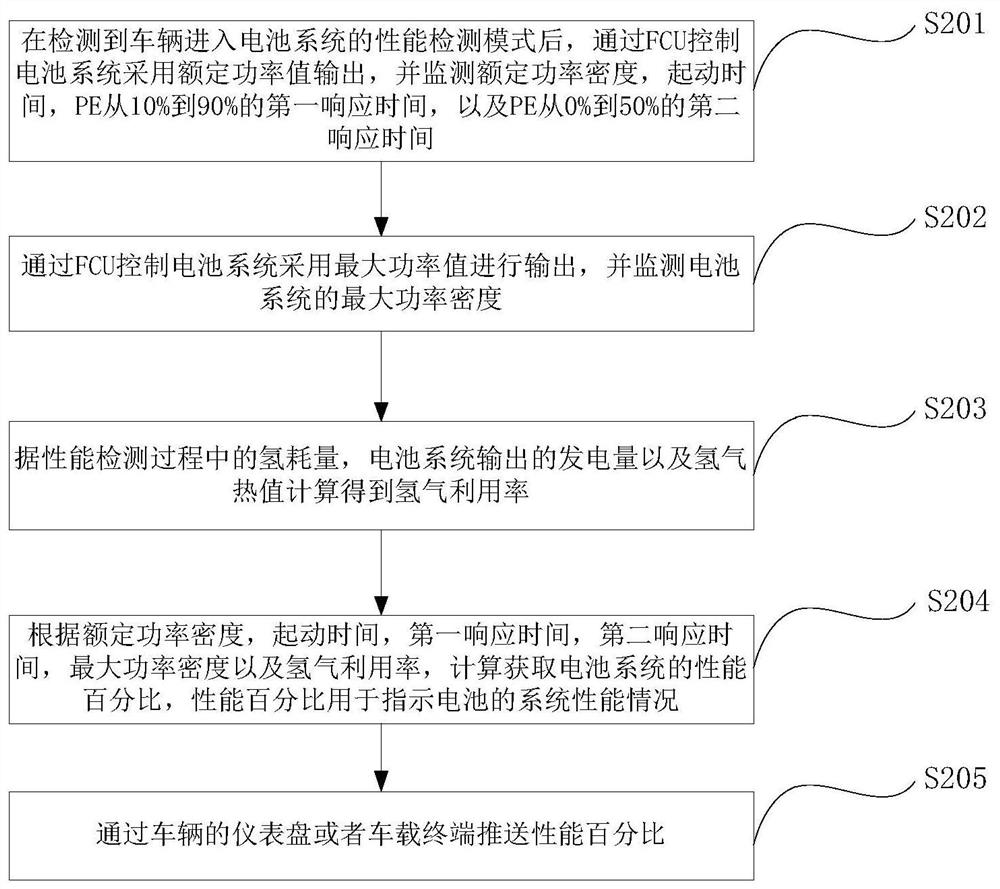
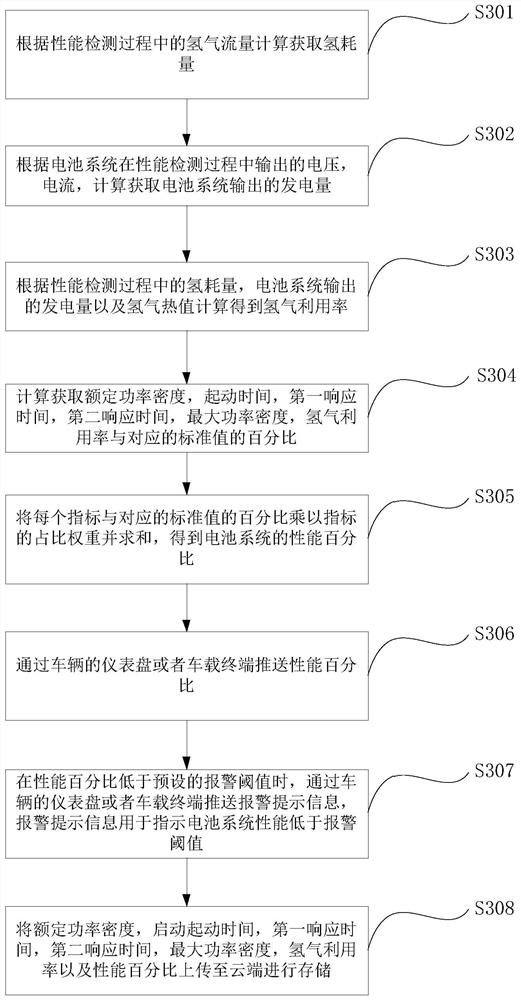
Hydrogen fuel cell system performance detection method and device, equipment and medium
ActiveCN113910909AElectric devicesElectric vehicle charging technologyIn vehicleAutomotive engineering
Owner:WEICHAI POWER CO LTD
Popular searches
Electric energy management Special data processing applications Electric propulsion Control devices Battery/fuel cell control arrangement Information technology support system Electric propulsion mounting Electric machines Toothed gearings Emergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnection
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap