Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
584 results about "Biomedical engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare purposes (e.g. diagnostic or therapeutic). This field seeks to close the gap between engineering and medicine, combining the design and problem solving skills of engineering with medical biological sciences to advance health care treatment, including diagnosis, monitoring, and therapy. Also included under the scope of a biomedical engineer is the management of current medical equipment within hospitals while adhering to relevant industry standards. This involves equipment recommendations, procurement, routine testing and preventative maintenance, through to decommissioning and disposal. This role is also known as a Biomedical Equipment Technician (BMET) or clinical engineering.
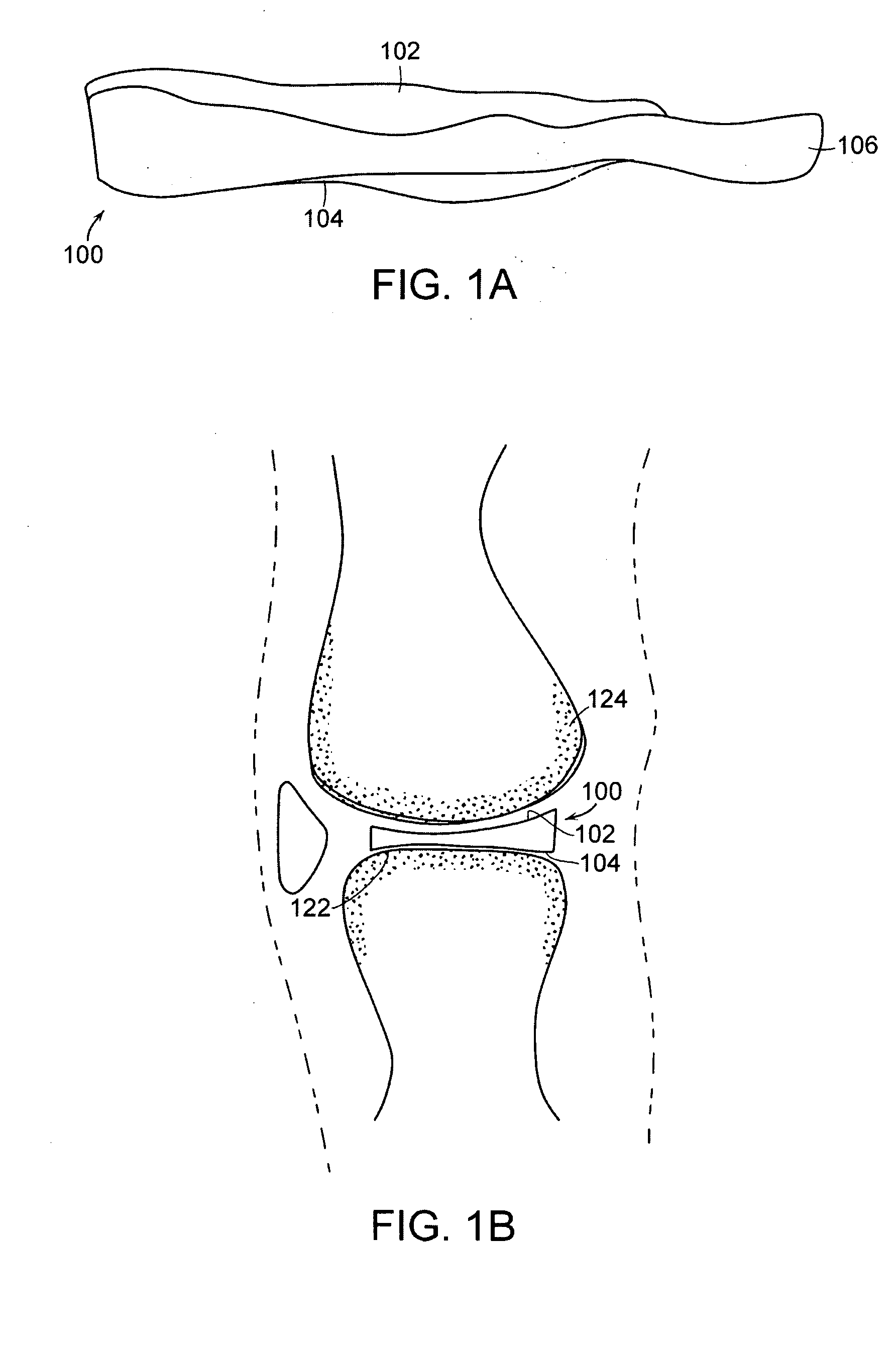
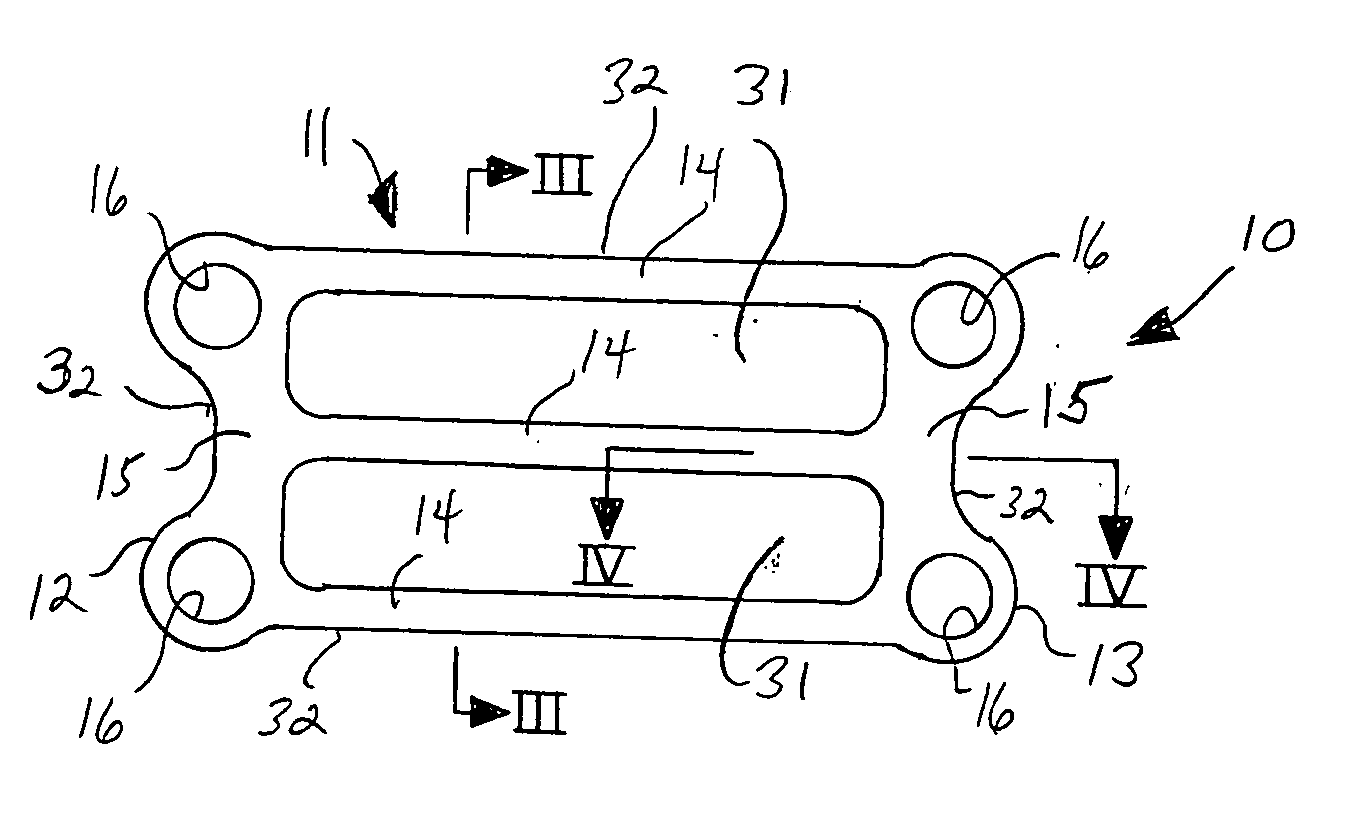
Prosthetic cardiac valve formed from pericardium material and methods of making same
ActiveUS20070233228A1Barrier to undesired abrasionPrevent and minimize valve leakageCell electrodesHeart valvesProsthetic valveProsthesis
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
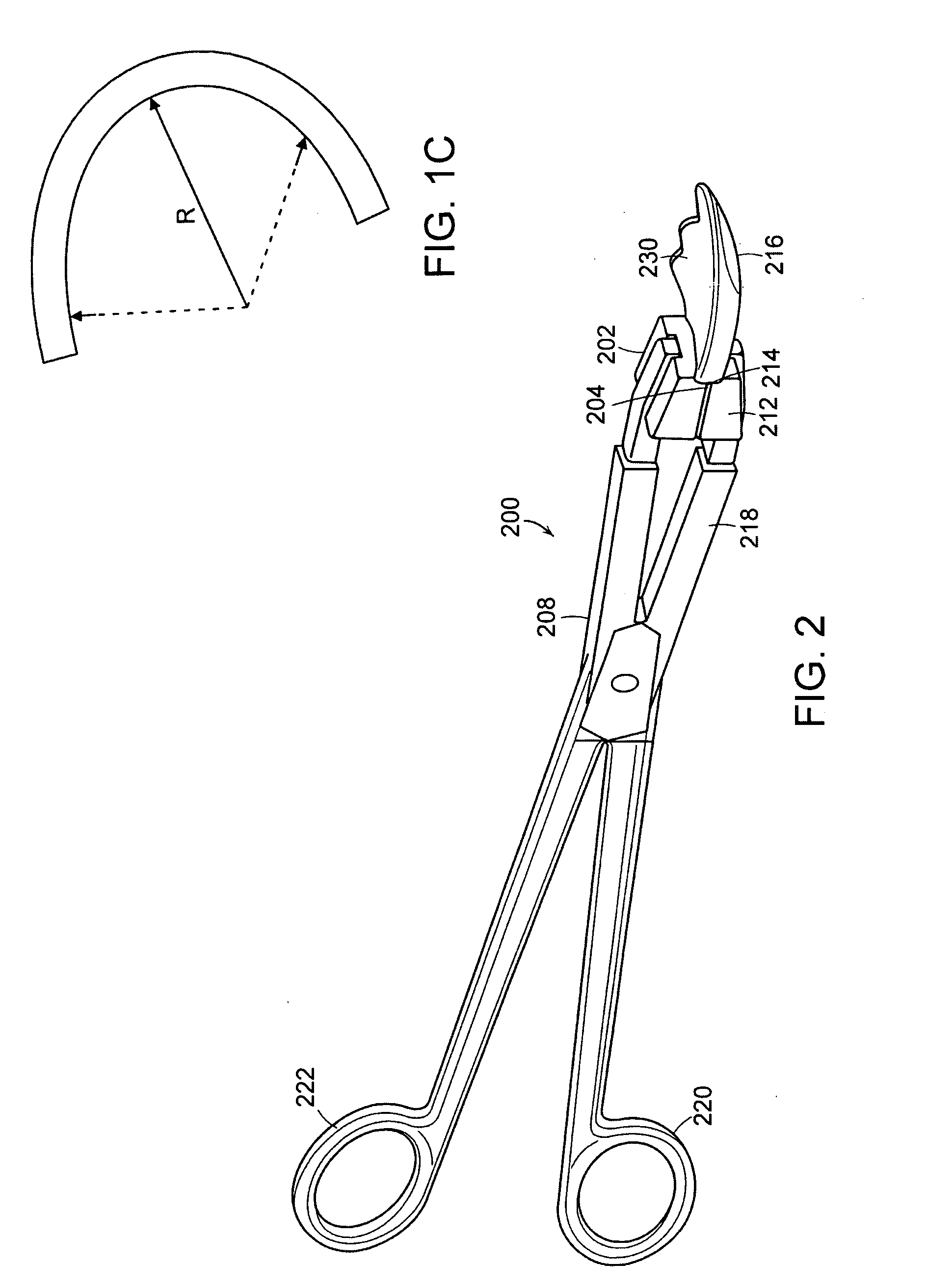
Implant Grasper
InactiveUS20070156171A1Improve gripReduce the possibilityKnee jointsSurgical forcepsBiomedical engineering
Owner:CONFORMIS
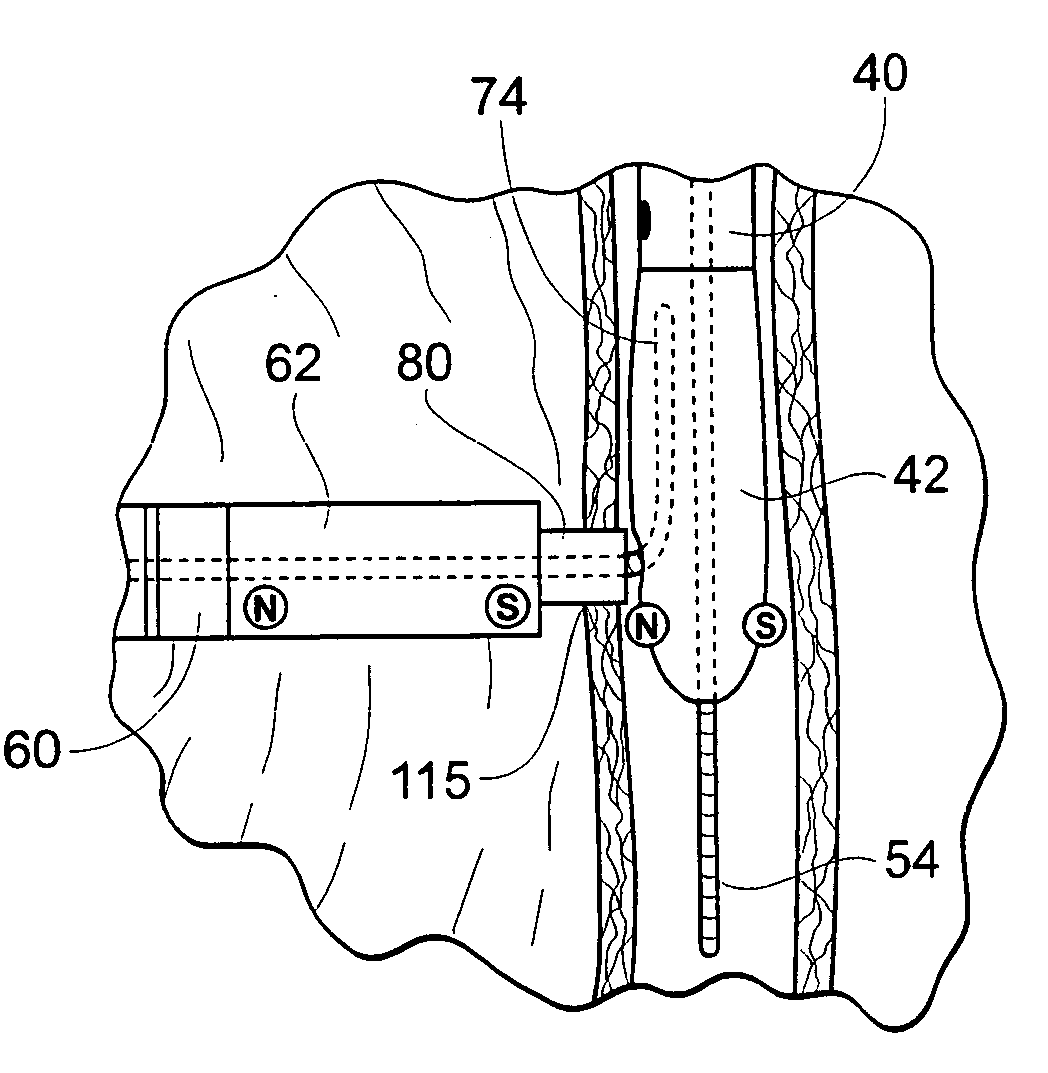
Devices, systems, and methods for reshaping a heart valve annulus, including the use of magnetic tools
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
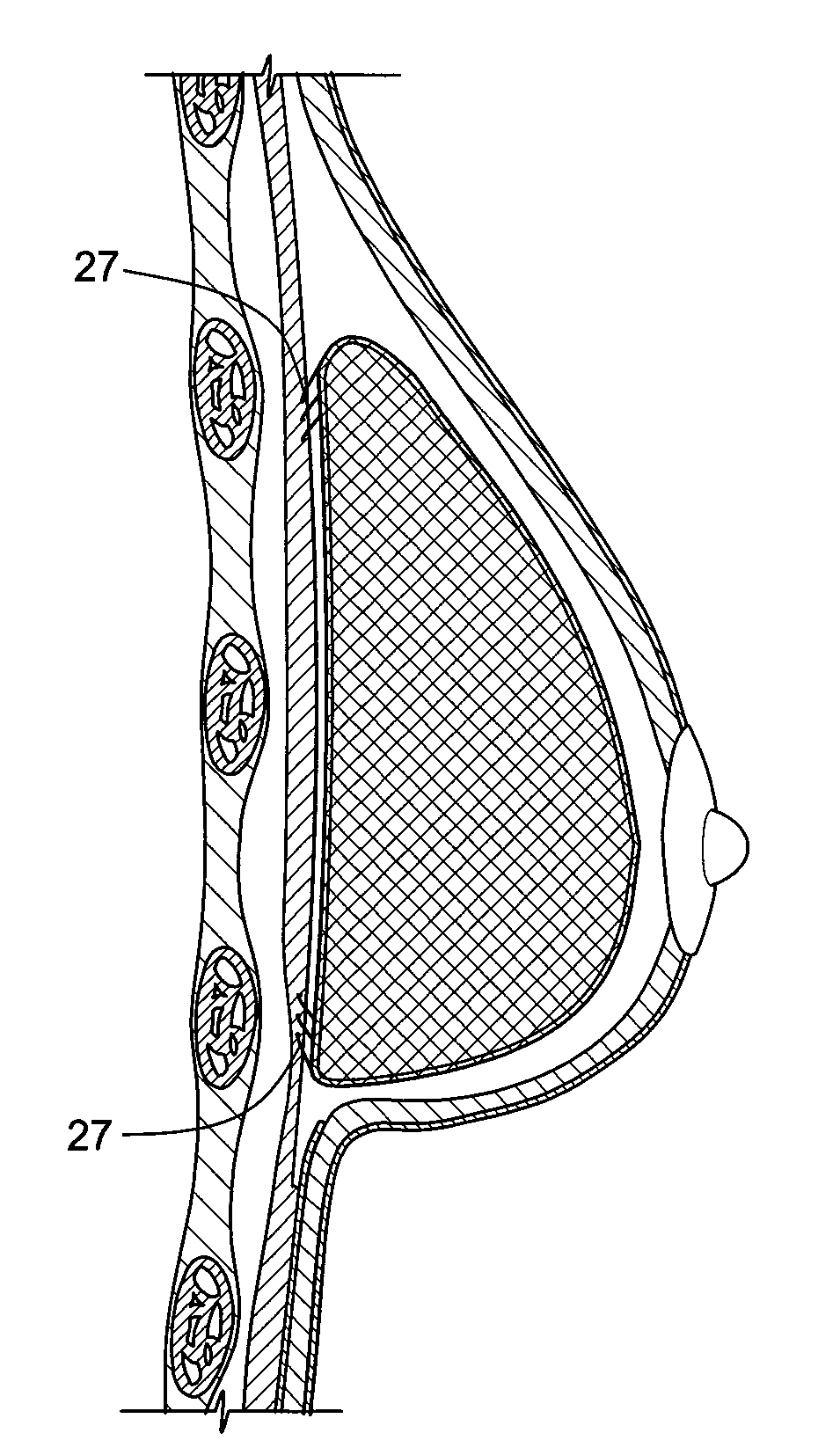
I-beam configuration bone plate
InactiveUS20060015103A1Sufficient strength and rigidityReducing strength and rigidityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringBone plate
A bone plate having a first opposing end containing screw-receiving apertures and a second opposing send containing screw-receiving apertures, the first opposing end and the second opposing end being joined by a plurality of bridging members, the bridging members having an I-beam configuration in cross-section and defining at least one opening in the main body of the bone plate.
Owner:KLS MARTIN LP
Anchor Element For Knotless Fixing Of Tissue To A Bone
Owner:KARL STORZ GMBH & CO KG +1
Smart drapes for collision avoidance
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
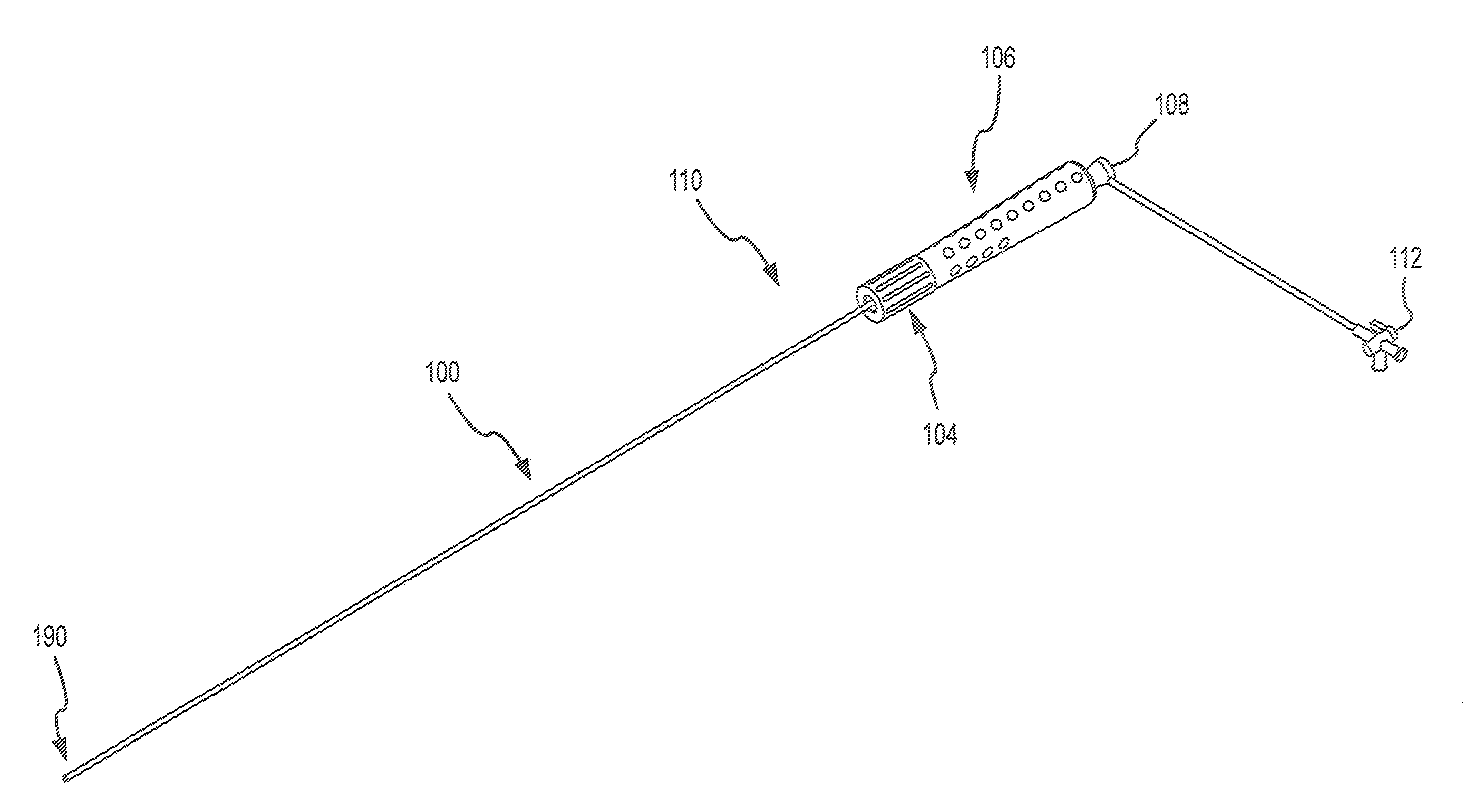
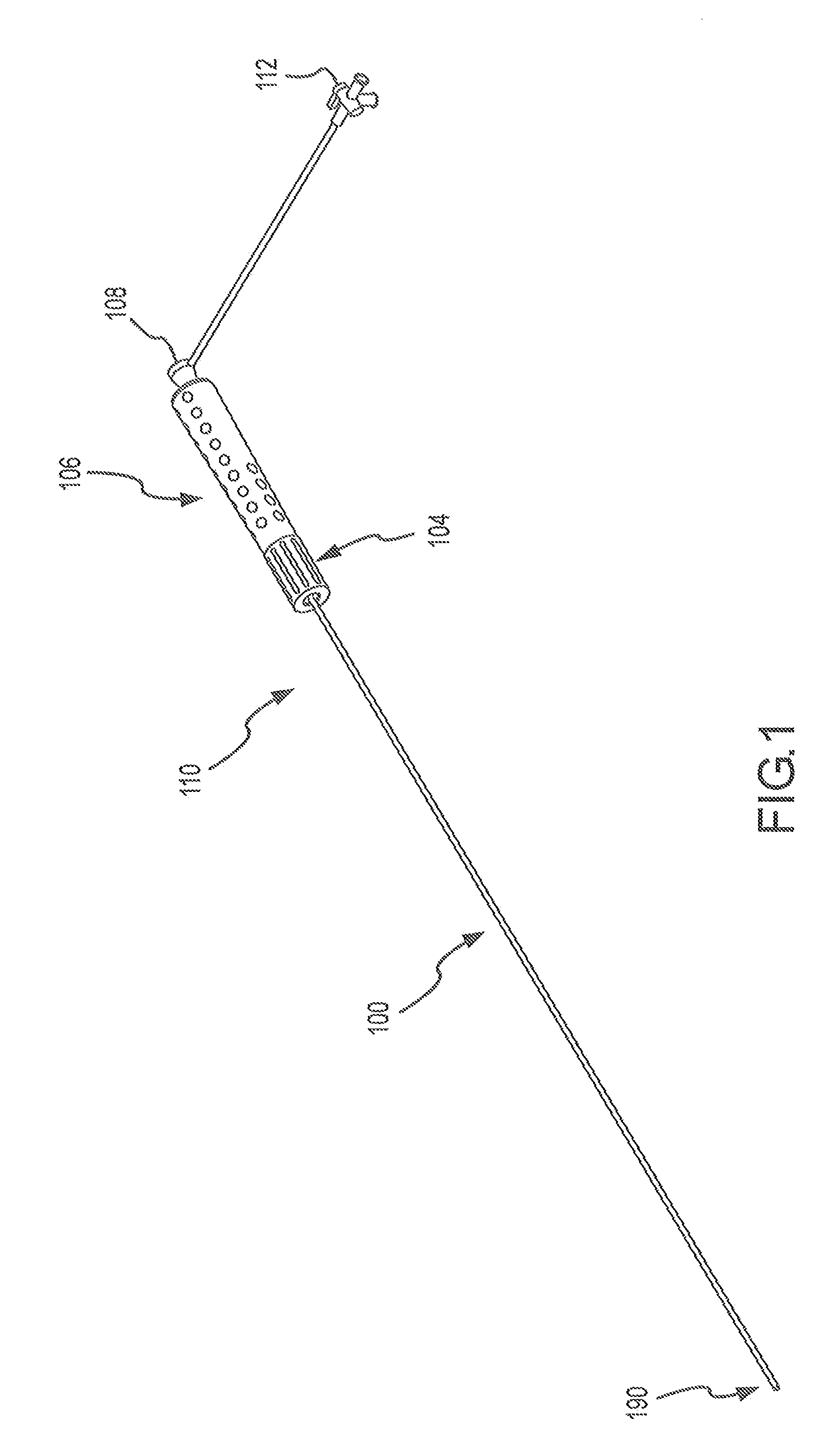
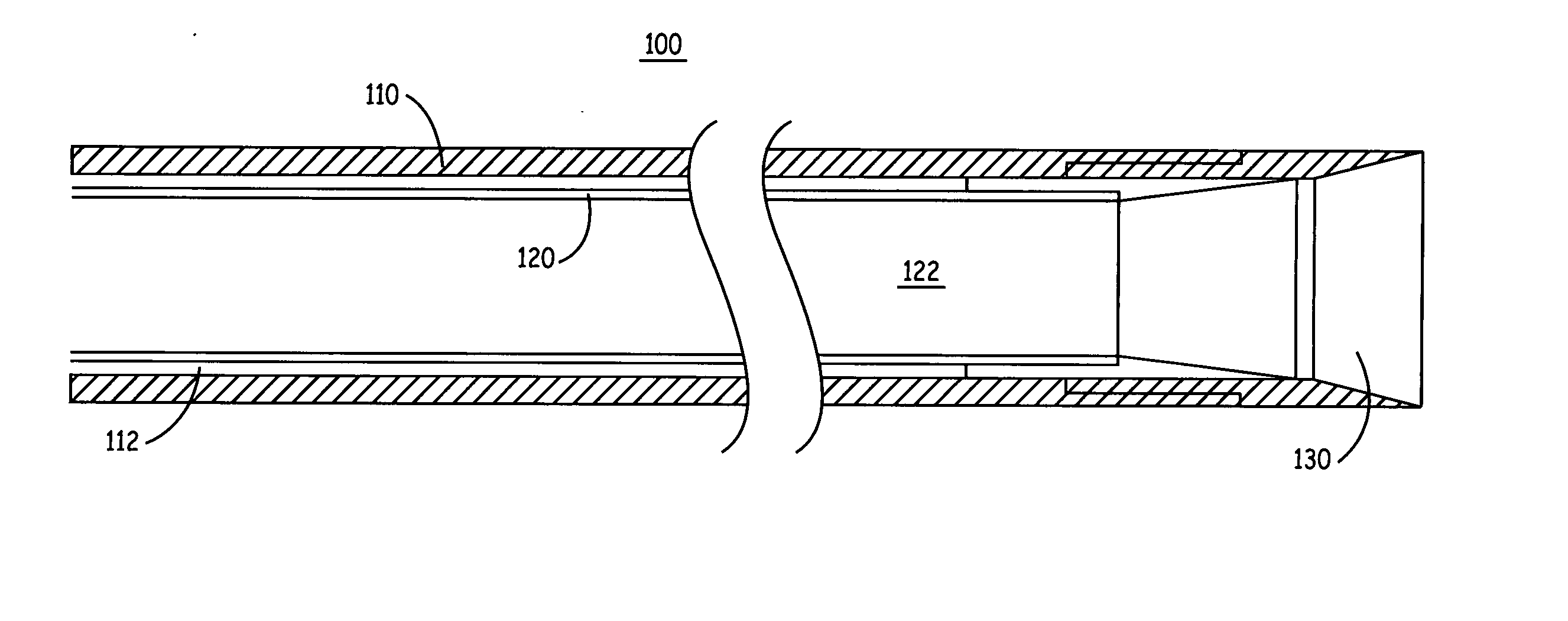
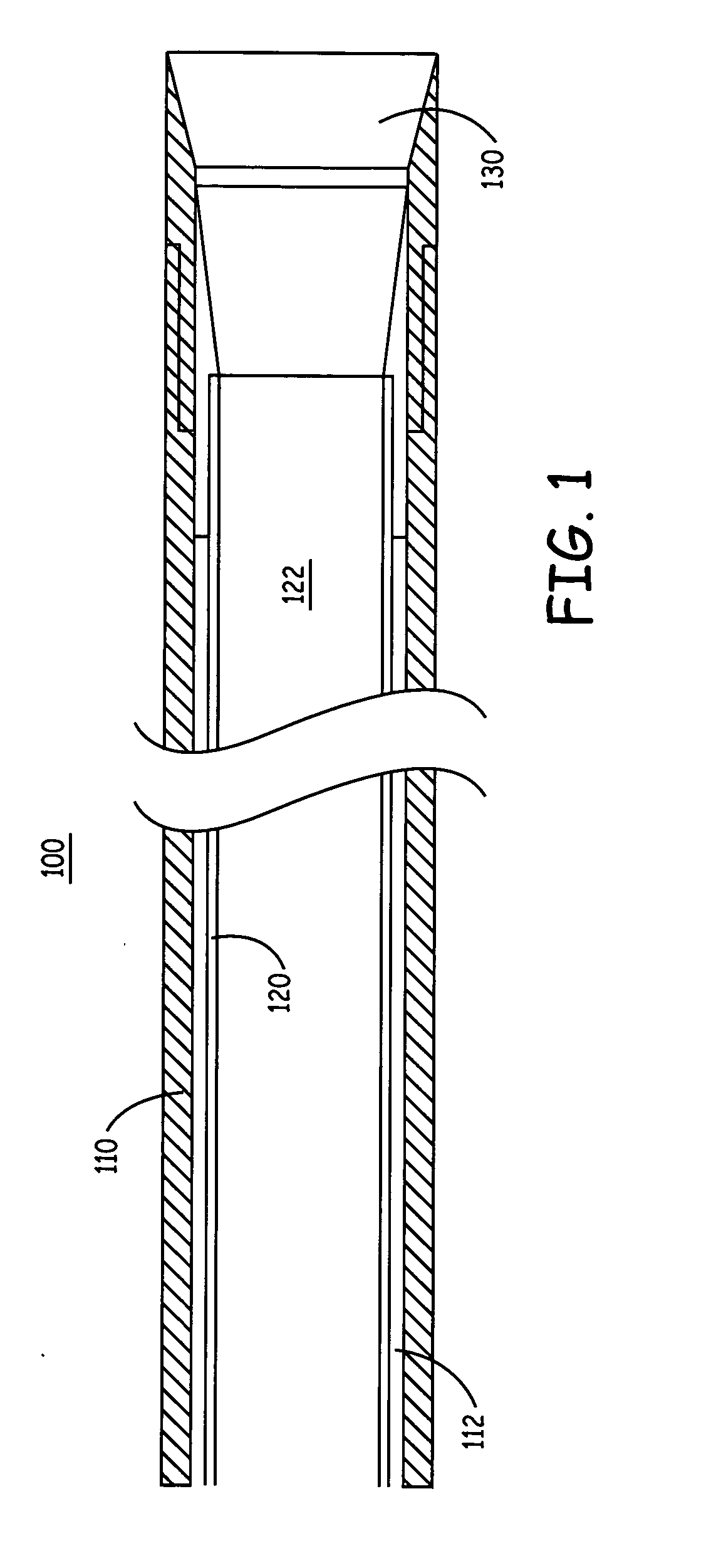
Catheter and introducer catheter having torque transfer layer and method of manufacture
ActiveUS20090024110A1Increase flexibilityExcellent kink resistanceCatheterCoatingsLumen DiameterUltimate tensile strength
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Gastric retention controlled drug delivery system
ActiveUS20040180088A1Maintain physical integrityFast swellingOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderControlled drugsControl release
The present invention provides a gastric retention controlled drug delivery system comprising: (a) a controlled release core comprising a drug, a highly swellable polymer and a gas generating agent, said core being capable of swelling and achieving floatation rapidly while maintaining its physical integrity in gastrointestinal fluids for prolonged periods, and (b) a rapidly releasing coat composition comprising the same drug as in the core and pharmaceutically acceptable excipients, wherein the coating composition surrounds the core such that the system provides a biphasic release of the drug in gastrointestinal fluids.
Owner:SUN PHARMA INDS
Growth stimulating wound dressing with improved contact surfaces
InactiveUS20080177253A1Non-adhesive dressingsWound drainsWound dressingSurface roughness
A wound contact device comprising a permeable material and a wound contact layer having voids extending through the contact layer to a depth in the permeable material. The wound contact layer can comprise a thin sheet or film forming a generally flat and smooth wound contact surface having essentially no discontinuities or gaps. The wound contact layer can comprise a thin sheet of highly calendered fabric forming a wound contact surface having a mean surface roughness in the range of about 0 microns to about 200 microns. In progressive wound healing, an embodiment of the wound contact device having the fabric contact surface is used in earlier healing stages and an embodiment of the wound contact device with film contact surface is used in later healing stages. The wound contact device is particularly useful in wound dressings for use in suction-assisted wound therapy.
Owner:BOEHRINGER TECH
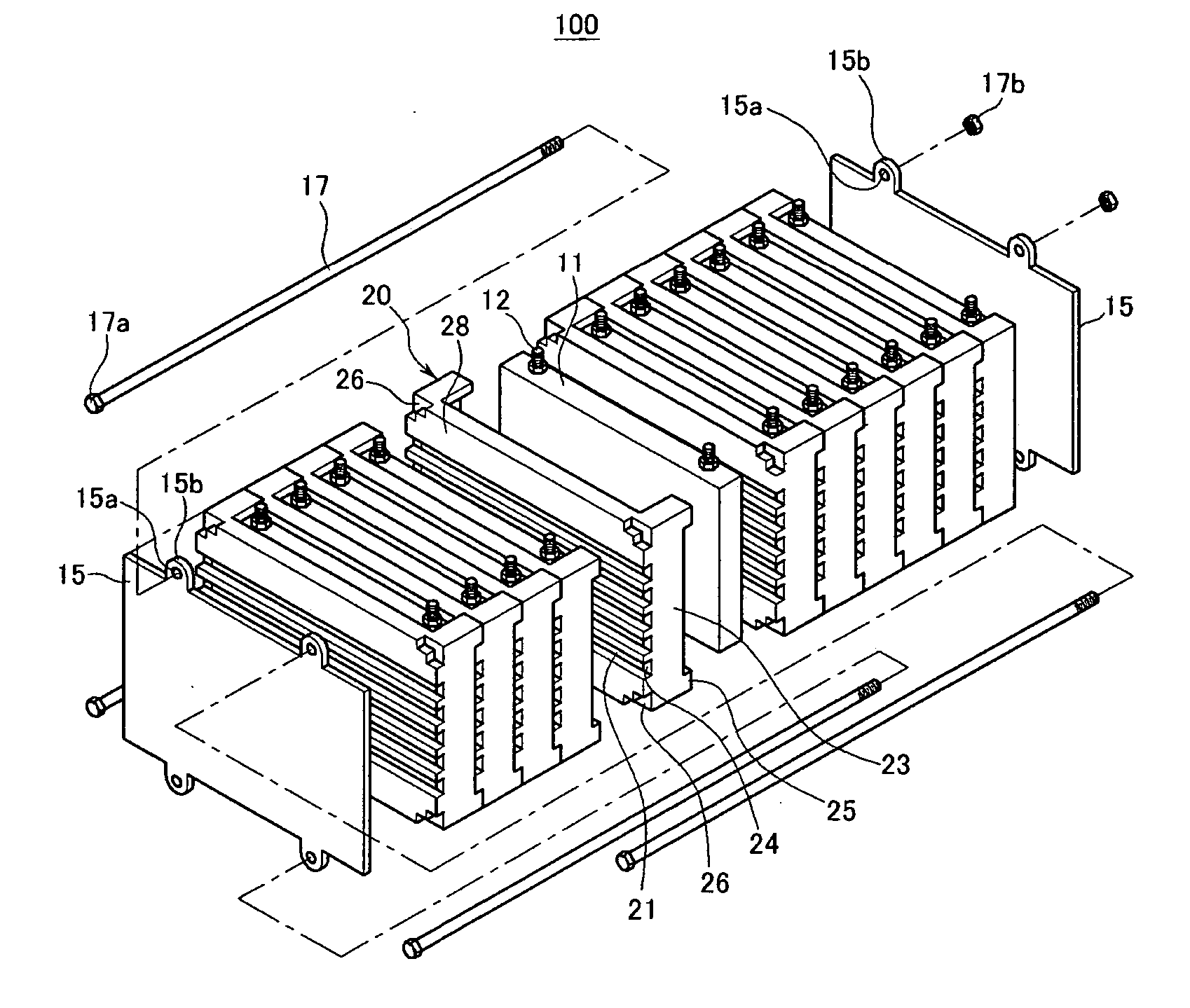
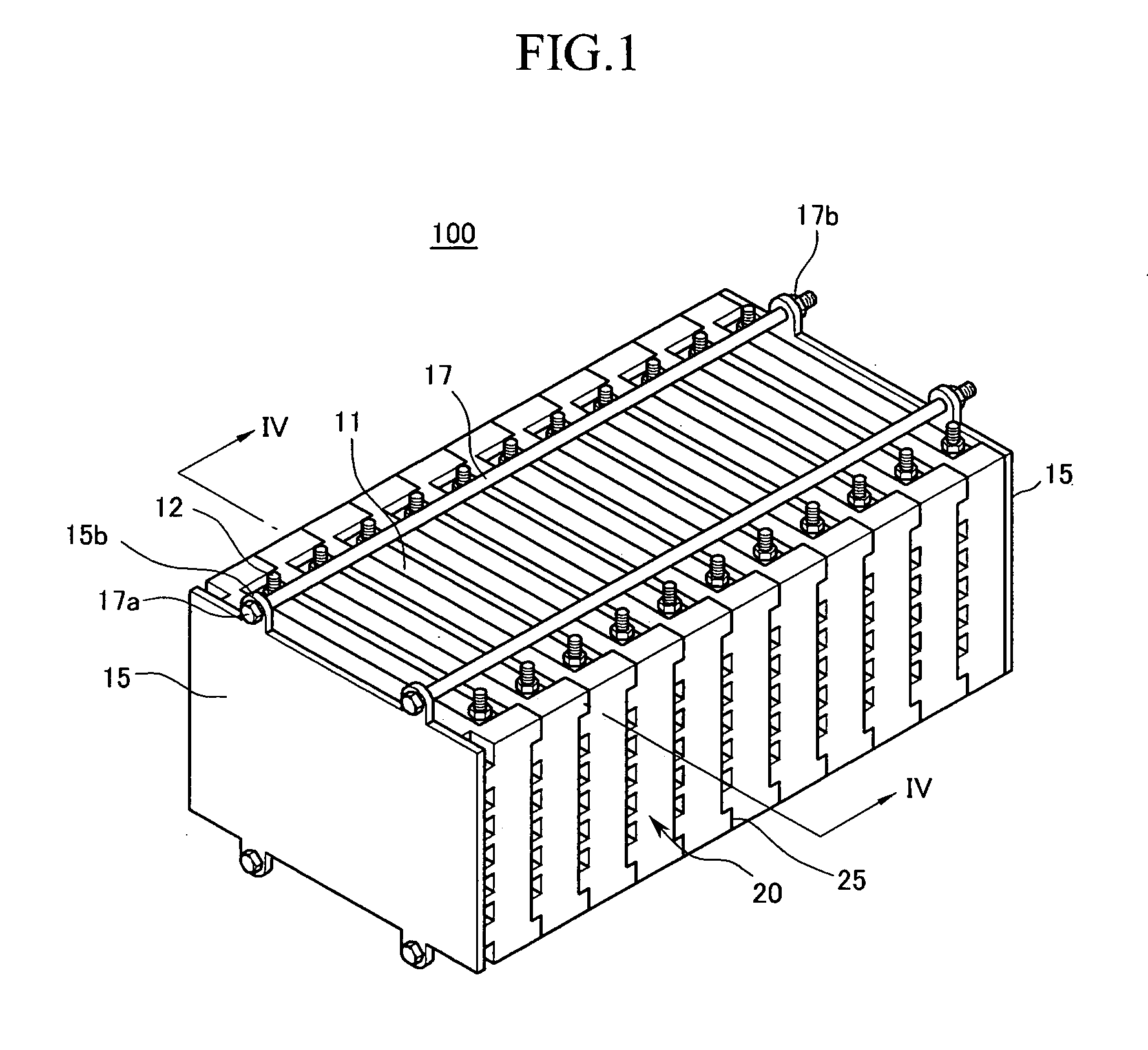
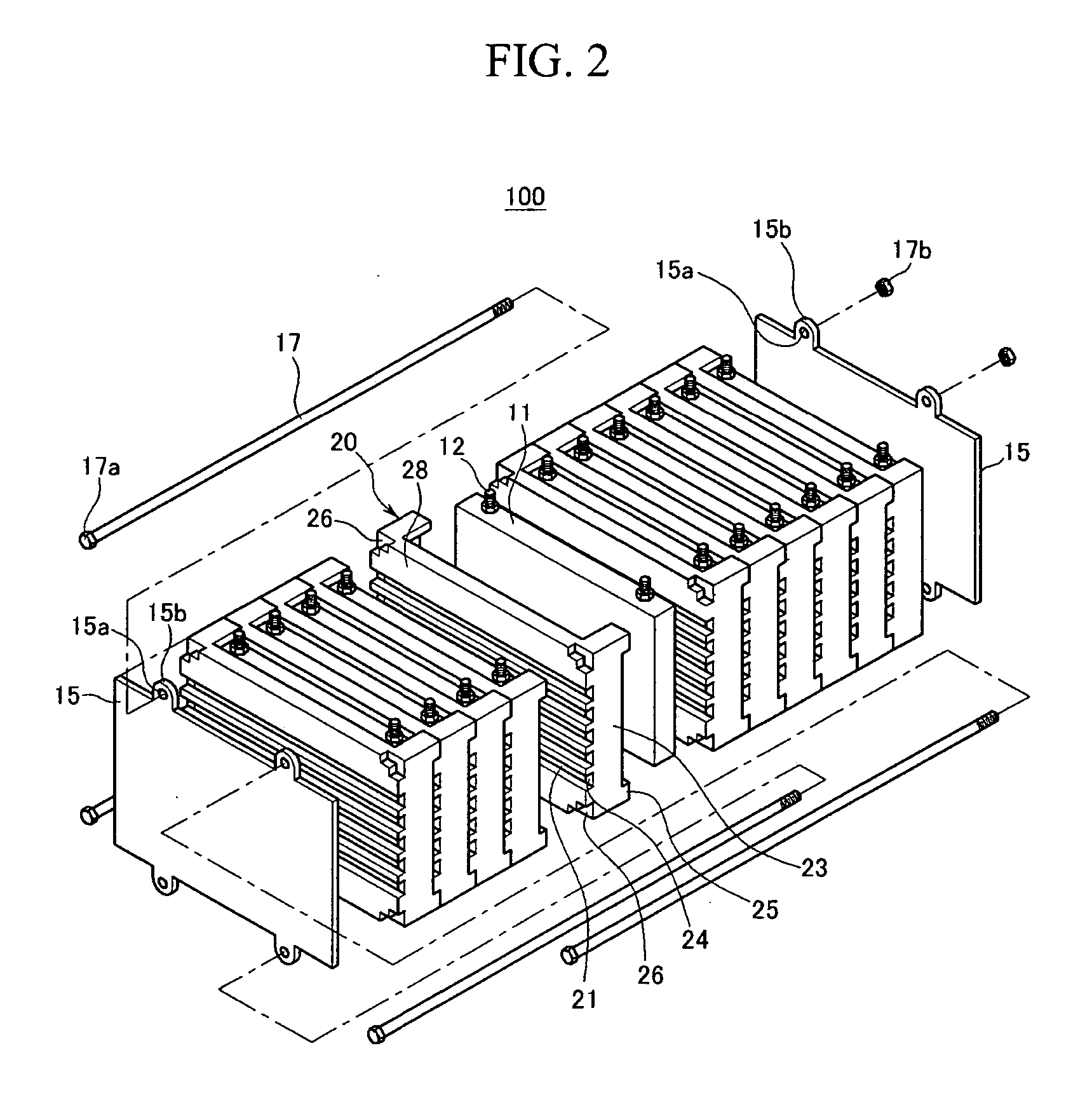
Battery module with improved cell barrier between unit cells
ActiveUS20070037051A1Improved unit cell cooling performanceEasy to makePrimary cell to battery groupingFinal product manufactureBiomedical engineering
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Electrosurgical device and methods
Owner:AVENT INC
Intervertebral implant
ActiveUS20070191959A1Easy to insertEasy to manufactureInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical instrumentBiomedical engineering
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Minimally invasive coring vein harvester
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Medical lead with flexible distal guidewire extension
InactiveUS7313445B2Reduce displacementIncrease thrustTransvascular endocardial electrodesExternal electrodesActive fixationBiomedical engineering
An implantable medical lead is provided with a distal guidewire extension. A flexible distal guidewire extension, which may take the form of a helically wound wire around a tapered core, extends from the distal end of a lead body. The extension may exit a tip electrode, which may be a generally rounded electrode or an active fixation electrode. The distal guidewire extension is preferably insulated, but may be provided with an uninsulated segment for serving as an electrode.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
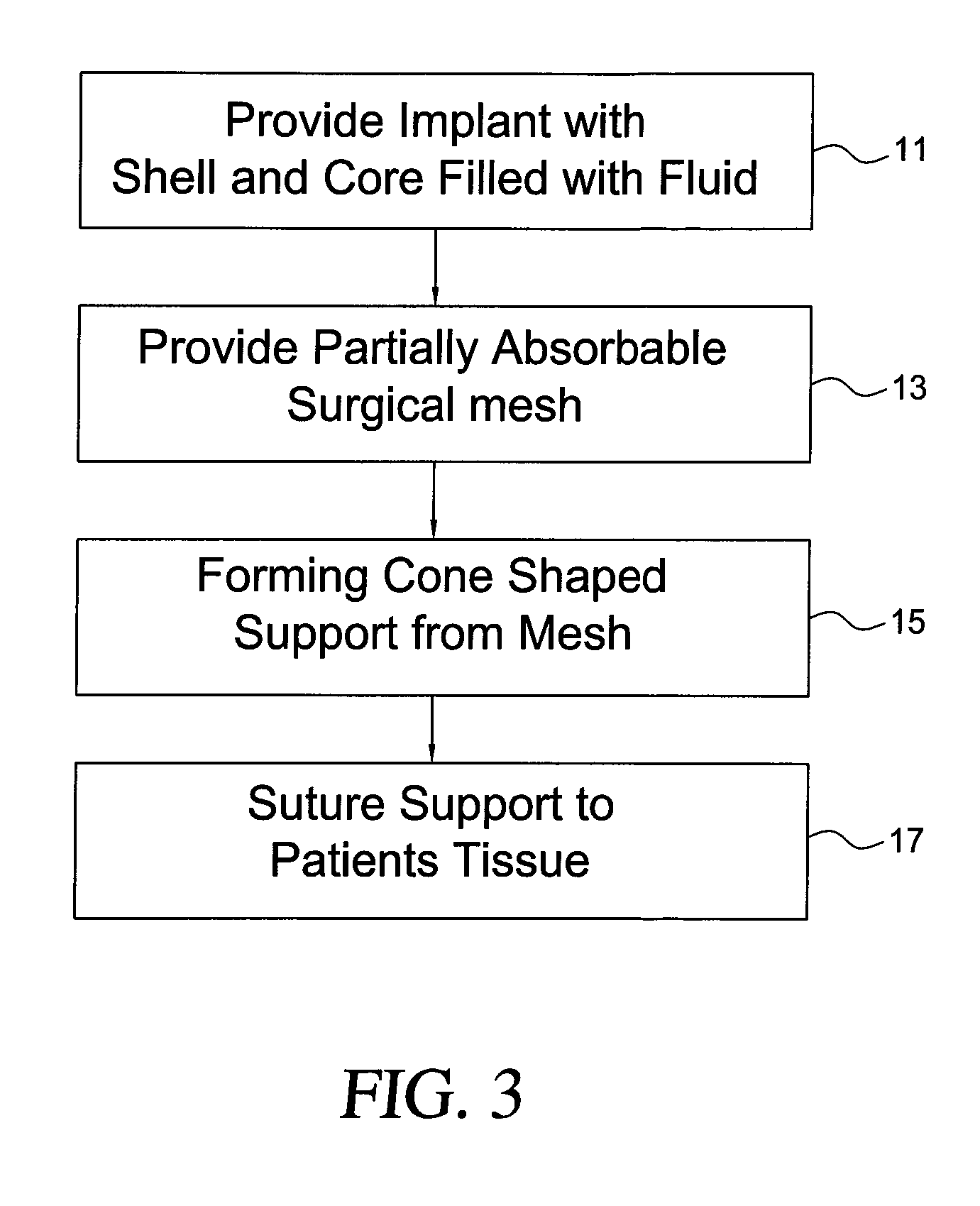
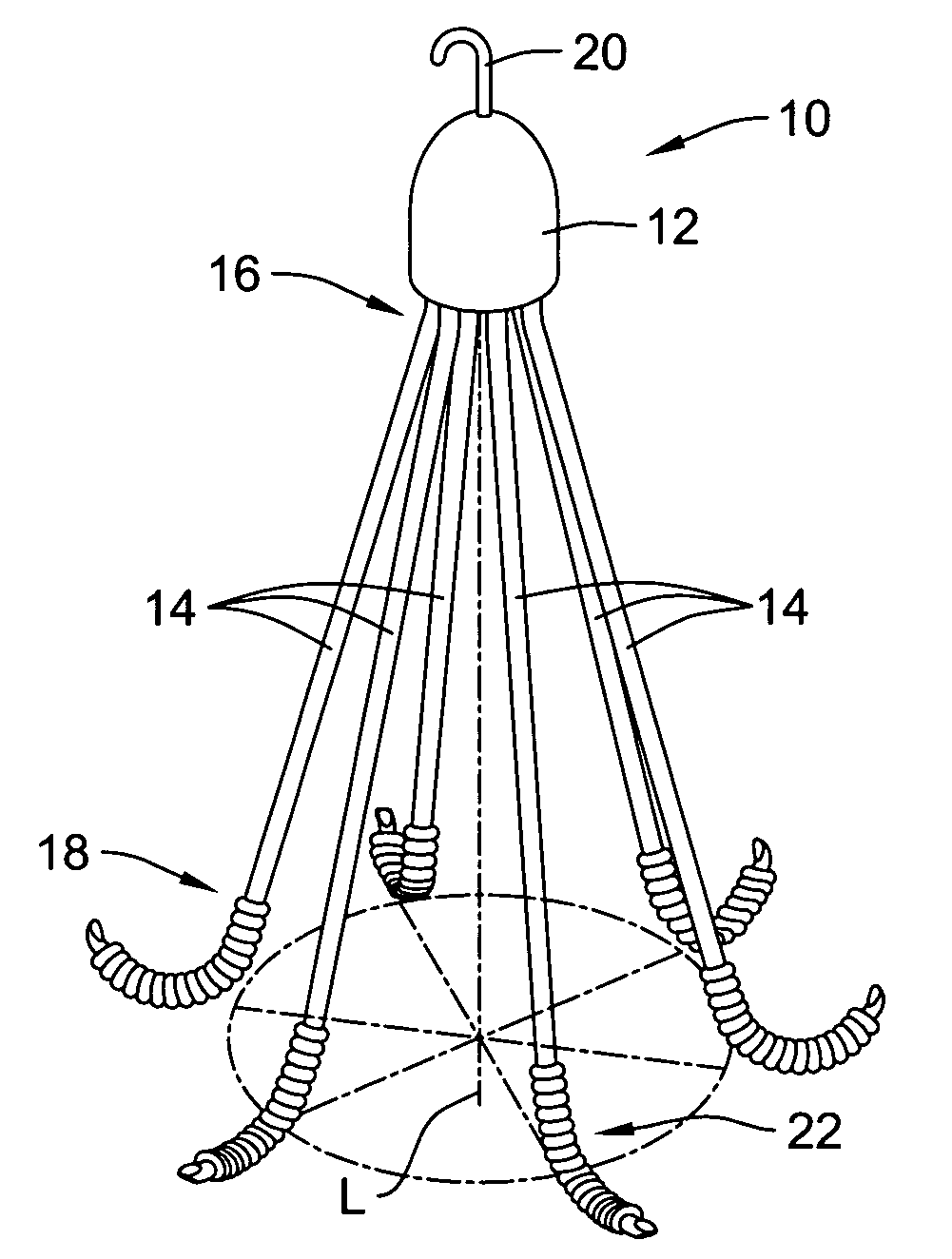
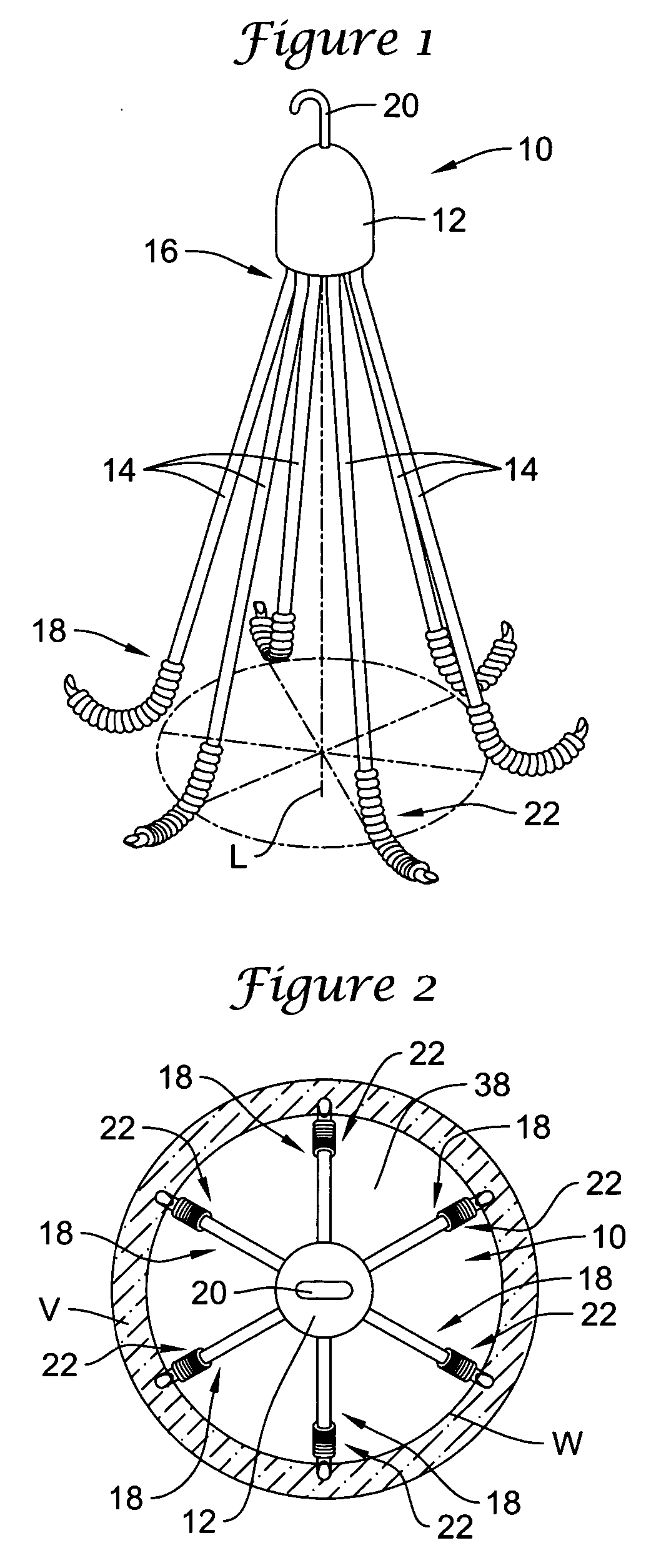
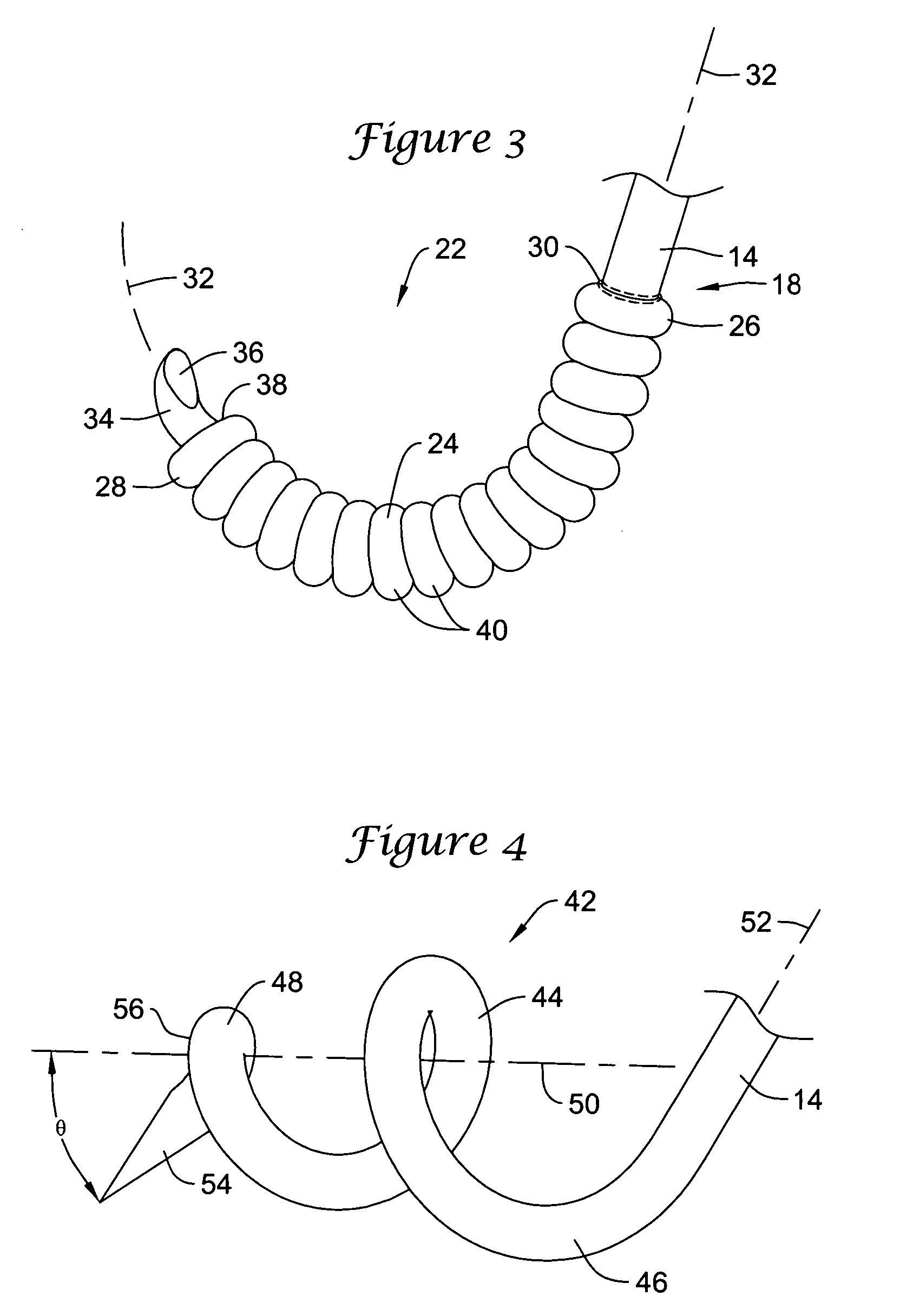
Self supporting and forming breast implant and method for forming and supporting an implant in a human body
Owner:TECHNO INVESTMENTS
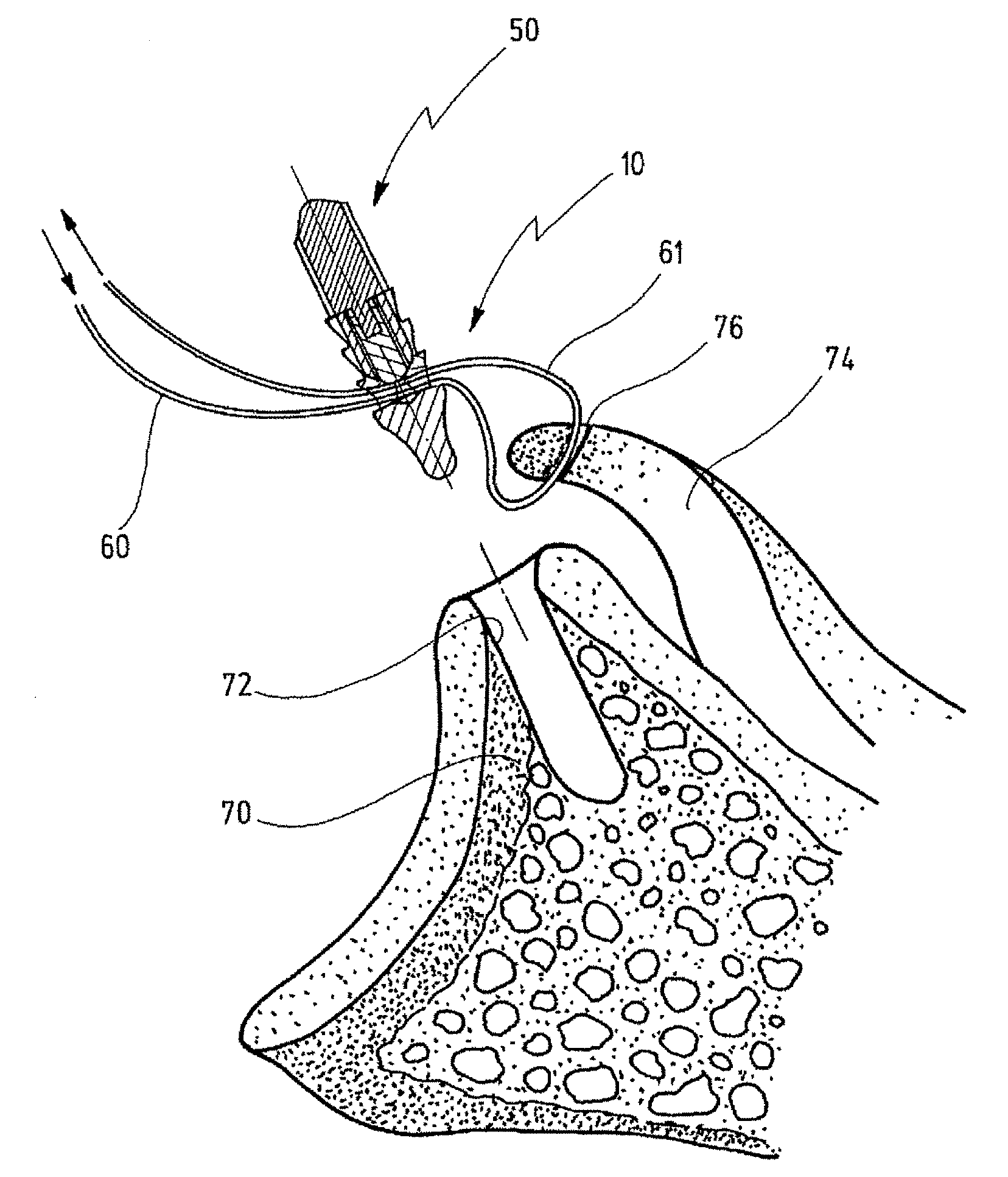
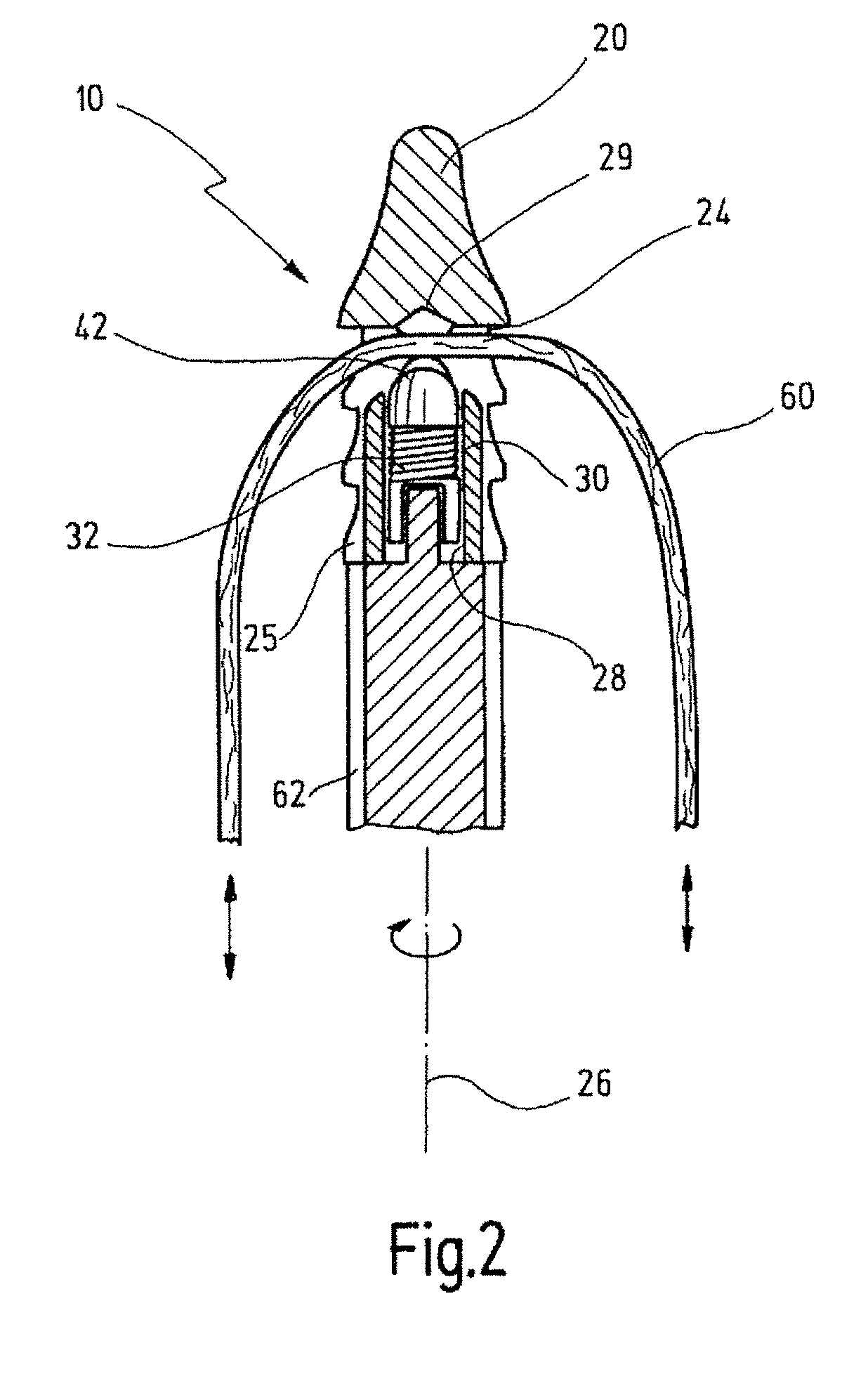
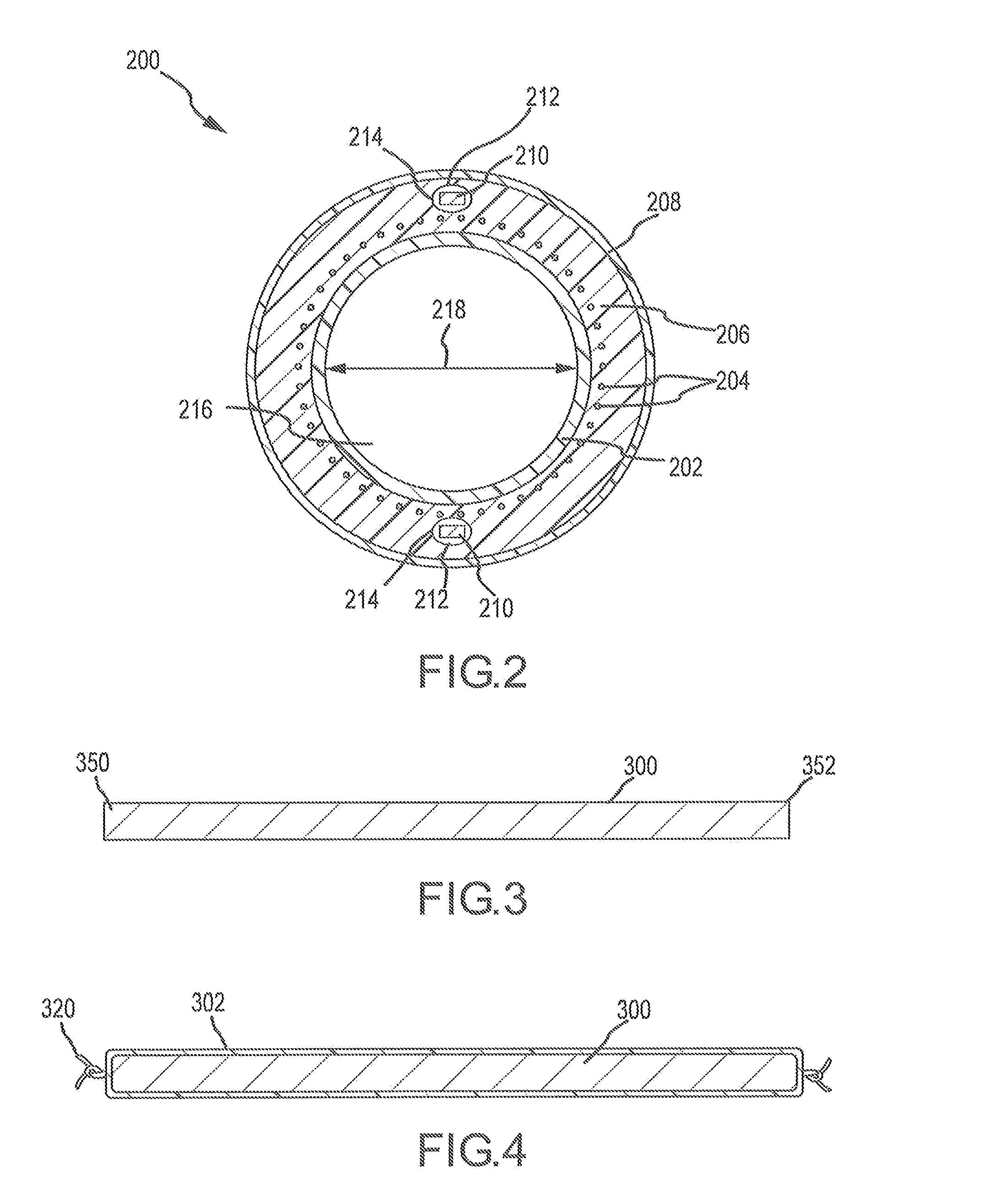
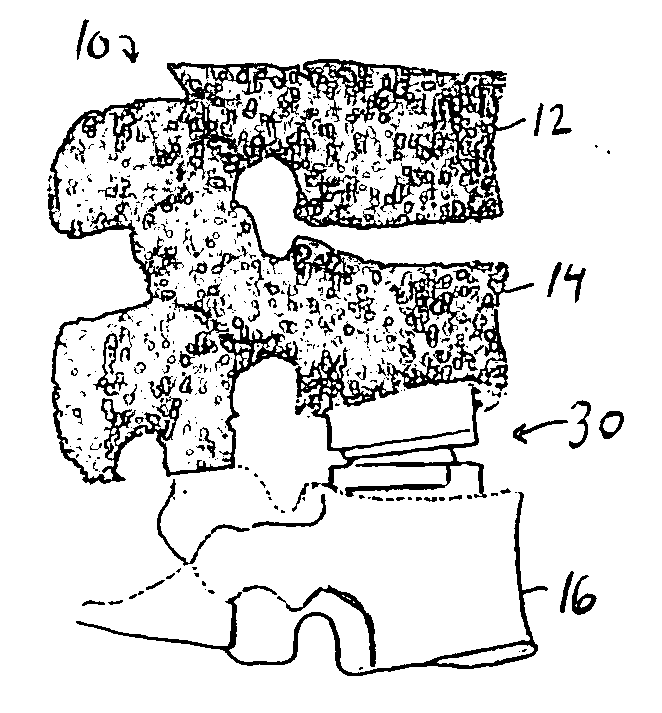
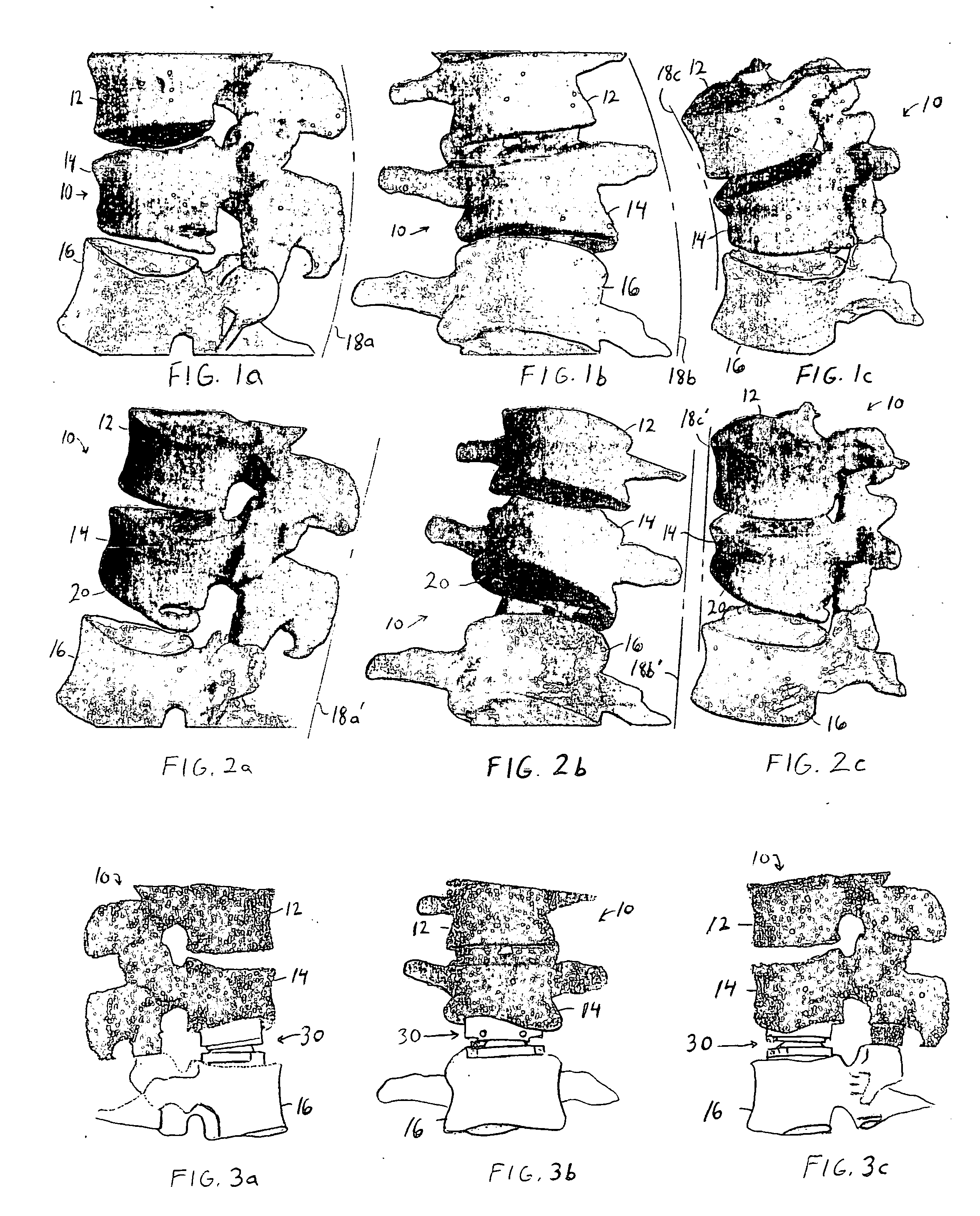
Bone grafts
A spinal spacer 300 for engagement between vertebrae is provided which includes a body 301 formed of a bone composition. The body 301 includes a first end 311, an opposite second 315 end, a superior face 335 defining a superior vertebral engaging surface 337 and an inferior face 338 defining an inferior vertebral engaging surface 340. At least one of the vertebral engaging surfaces defines a set of migration resistance grooves 350. Each of the grooves 350 includes a first face 355 defining an angle of no more than about 90 degrees relative to the engaging surface 340 and a second opposing sloped face 360. The first and second faces 355, 360 define an arcuate pocket 370 therebetween for trapping vertebral bone to resist migration of the spacer 300. In one embodiment, the grooves 350 are arranged in series in that all of the second faces 360 slope in the same direction.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method and apparatus for the control and monitoring of shape change in tissue
ActiveUS7416550B2Surgical instruments for heatingShape changeOptical property
A method of electroforming tissue comprises creating stress in the tissue; and causing a direct current to flow in the tissue to change the stress, strain, or intrinsic mechanical properties including shape of the tissue. Force is mechanically applied to the tissue to create external stresses or material parameters of the tissue are used to create internal stresses in the tissue by causing a current to flow in the tissue. The method further comprises the step of monitoring the stresses in the tissue and controlling the current flowing in the tissue according to the stresses therein by monitoring impedance, the optical properties, the pH, acoustic properties of the tissue, the gas formation in the tissue, the color of the tissue as caused by a chemical dye disposed therein or as caused by electroplating a material thereon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Apparatus for producing semiconductors and other devices and cleaning apparatus
InactiveUS6035871AWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorBiomedical engineering
Provided is an apparatus for producing semiconductor and other devices, which can improve the quality of deposited films and increase the yield of produced devices in comparison with the conventional apparatus. The apparatus of the invention comprises a plurality of dry treatment chambers (7a, 7b, 7c, 7d, 7e), a transfer room (6) interconnecting the dry treatment chambers (7a, 7b, 7c, 7d, 7e), loading / unloading chambers (8a, 8b, 8c, 8d), and a cleaning apparatus (13). The transfer room (6) and the cleaning apparatus (13) are directly or indirectly connected to each other.
Owner:ALPS ALPINE CO LTD
Retrievable intravascular filter with bendable anchoring members
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
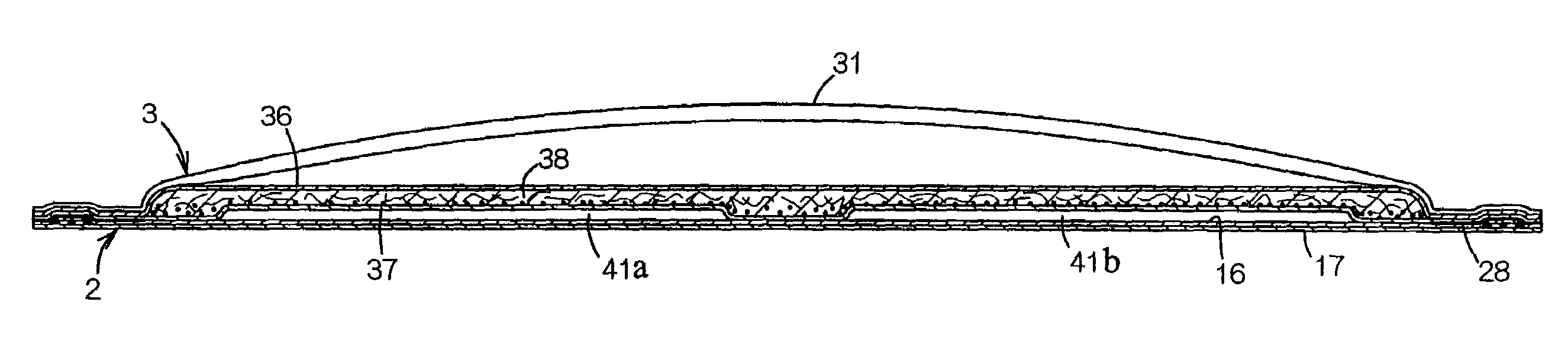
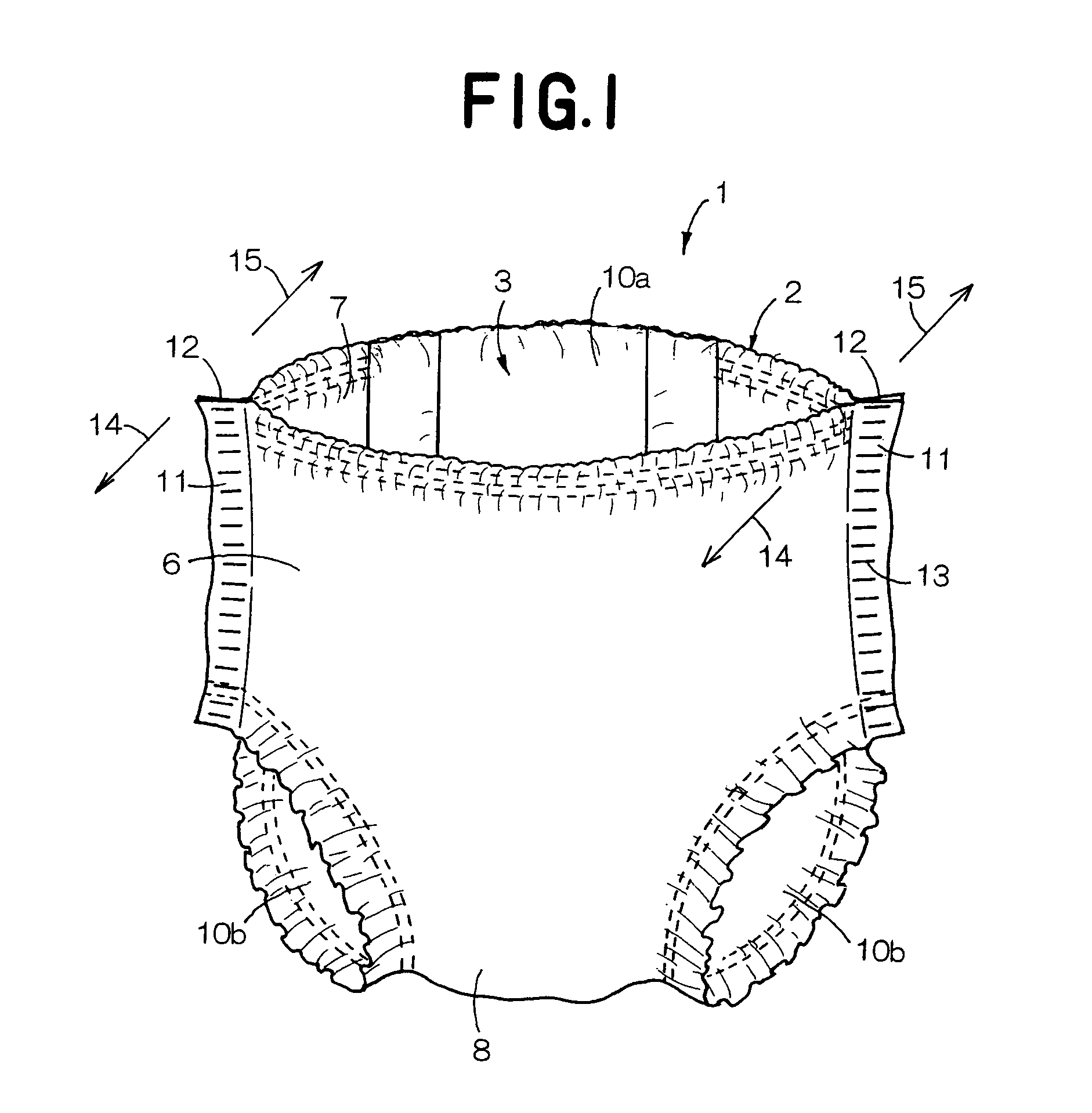
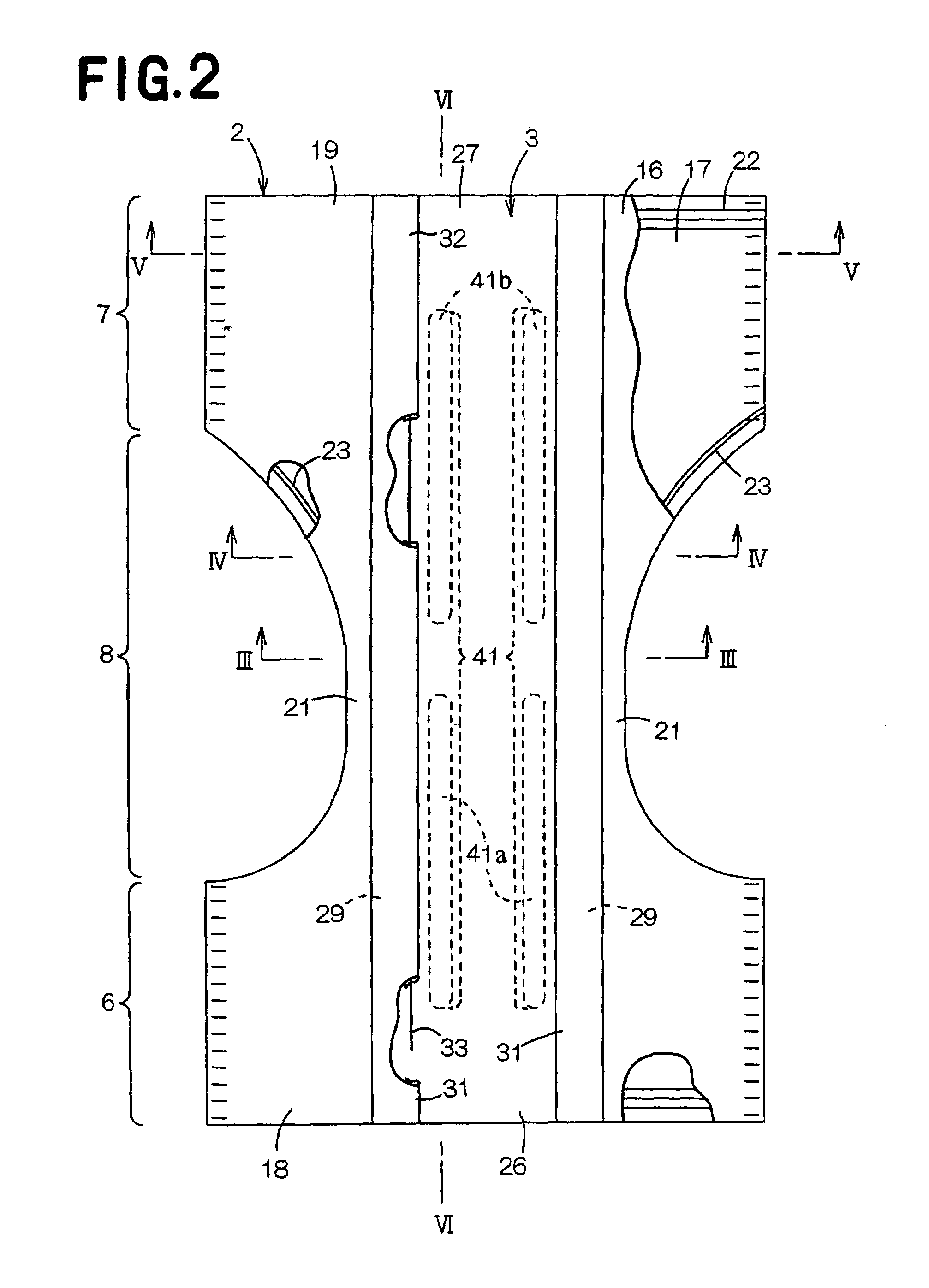
Disposable diaper
Owner:UNI CHARM CORP
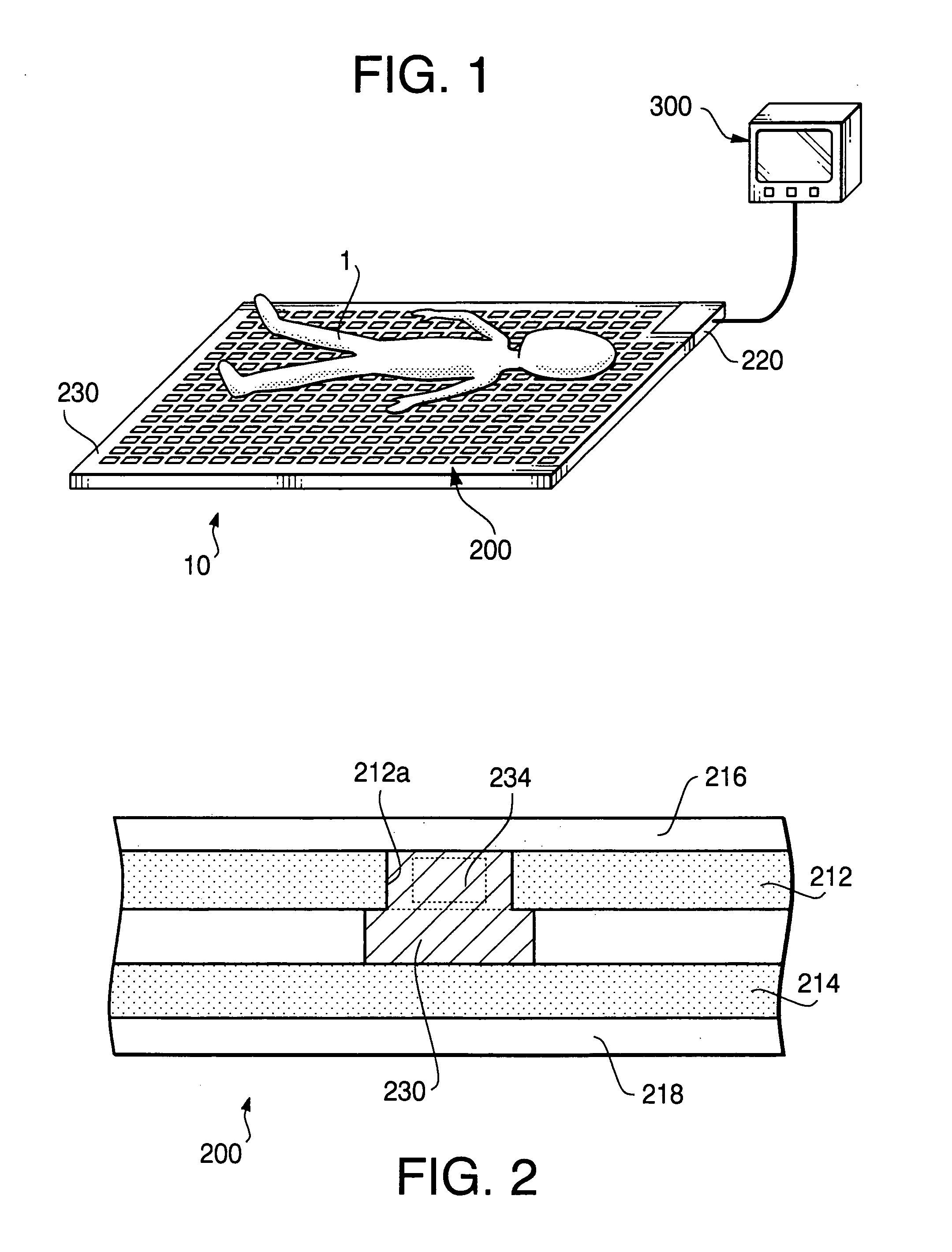
Pressure detecting mat and antidecubitus system provided with the same
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
System for detecting catheter electrodes entering into and exiting from an introducer
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Solid implant
Owner:KU DAVID N
Self-contouring spinal rod
Owner:AESCULAP AG
Skin treating device
Owner:LRC PROD LTD
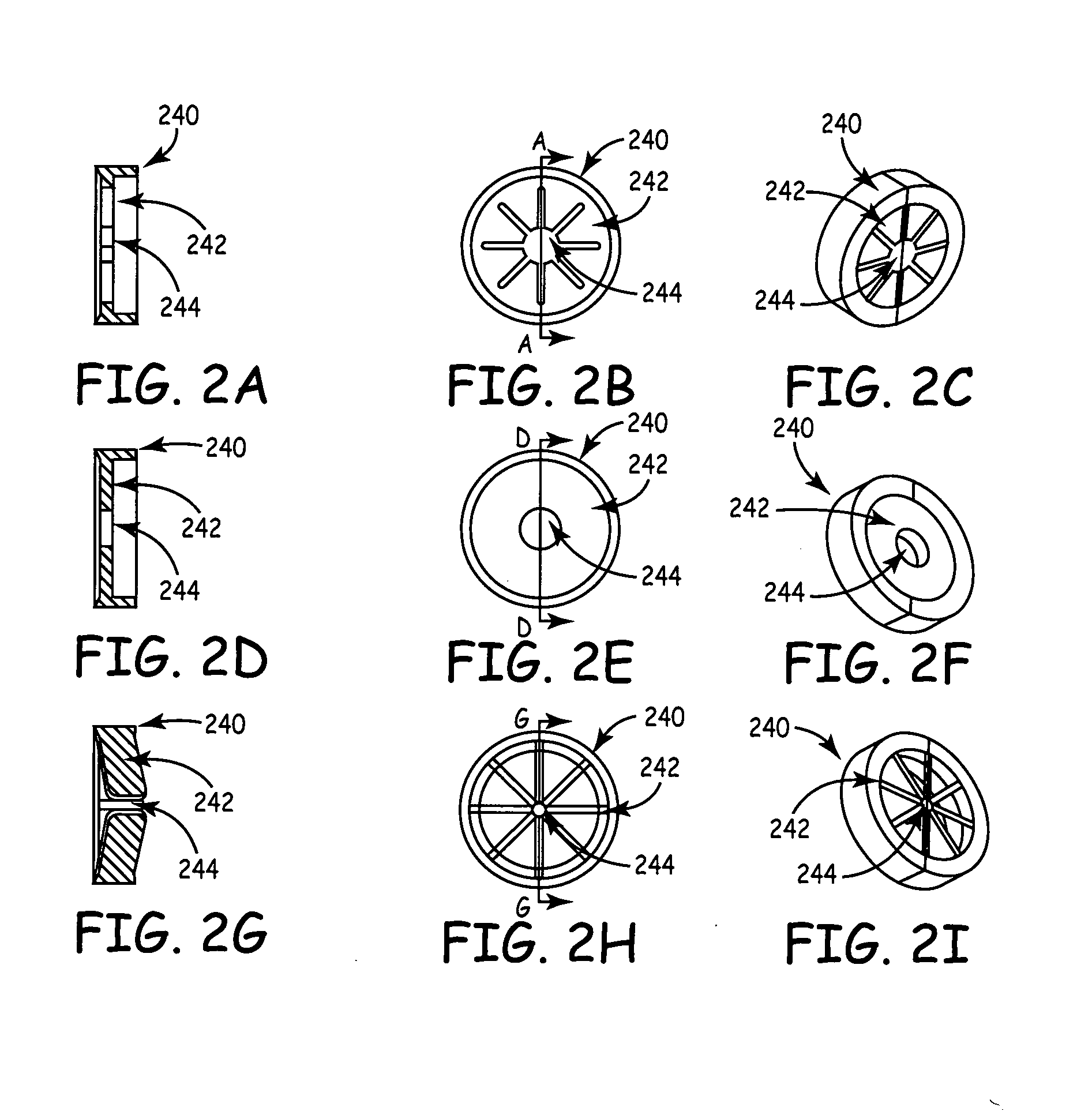
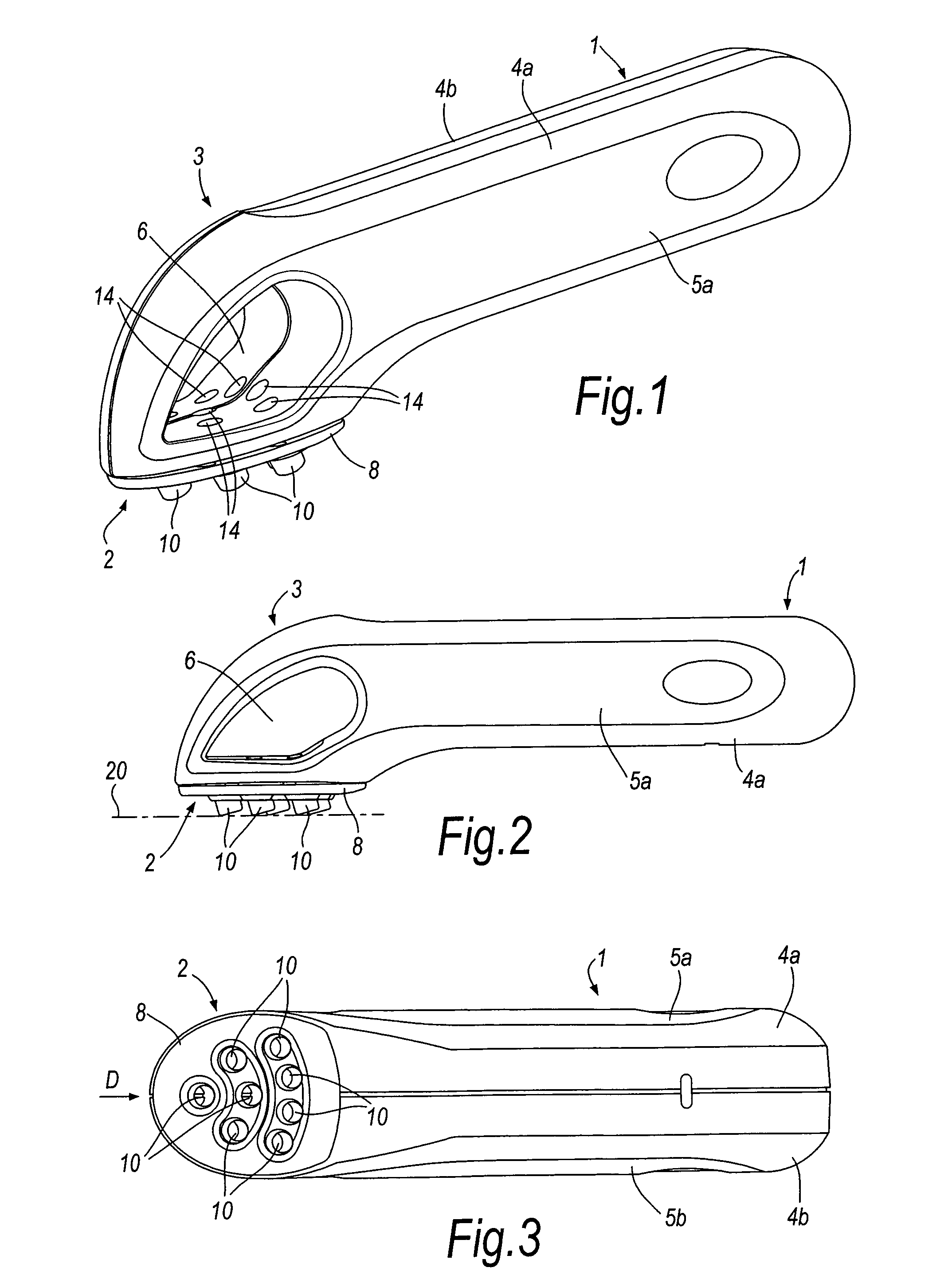
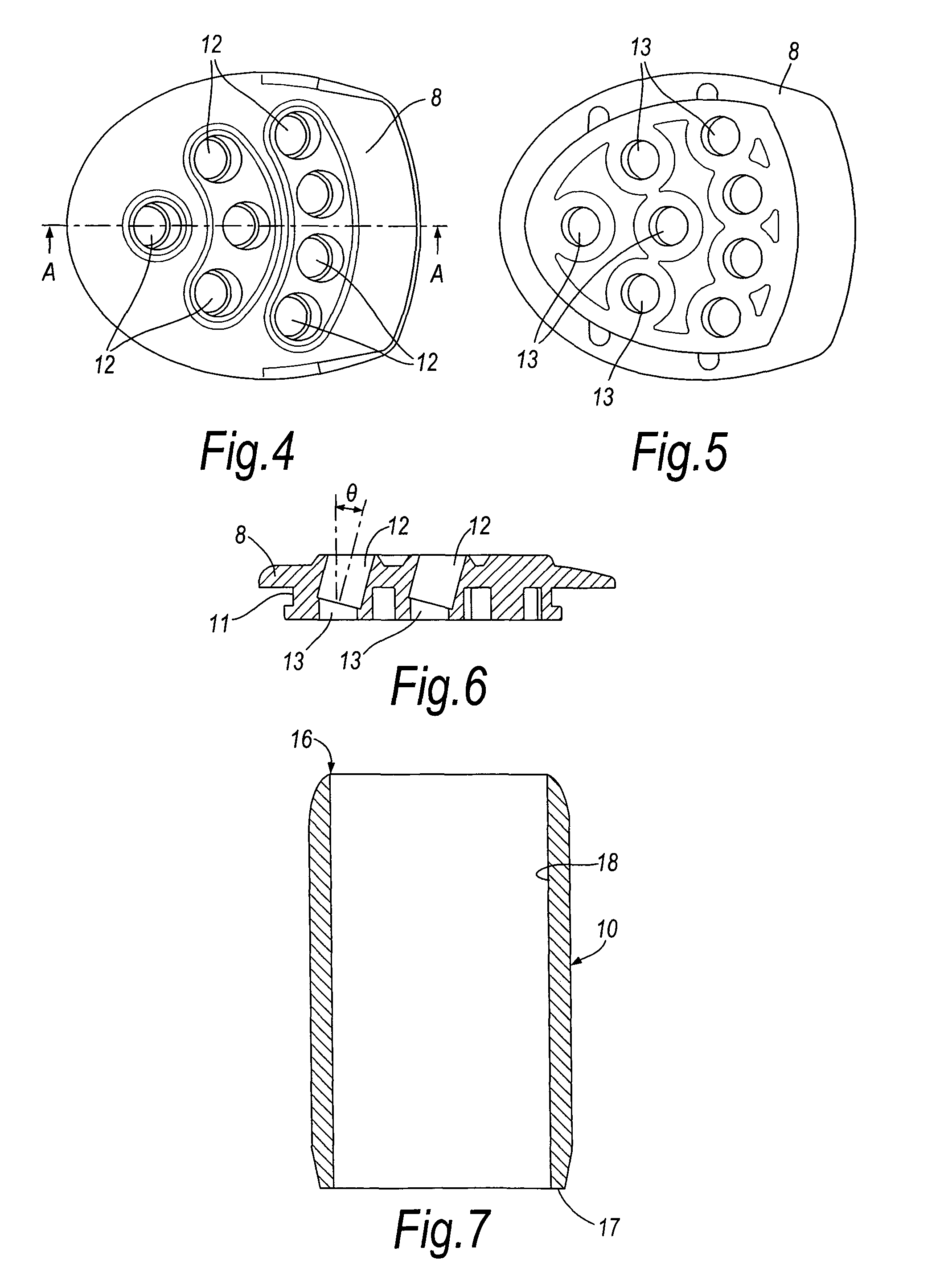
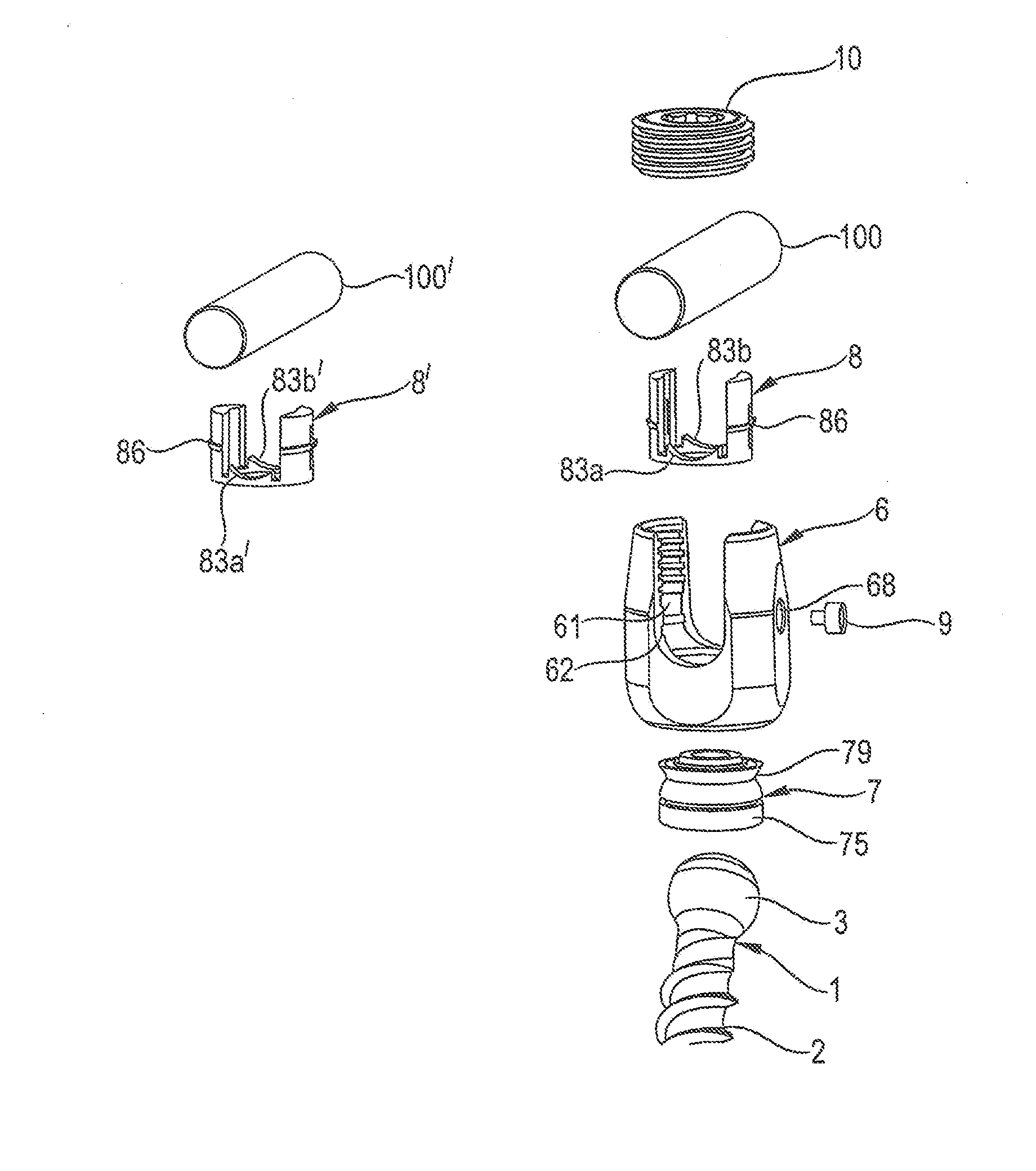
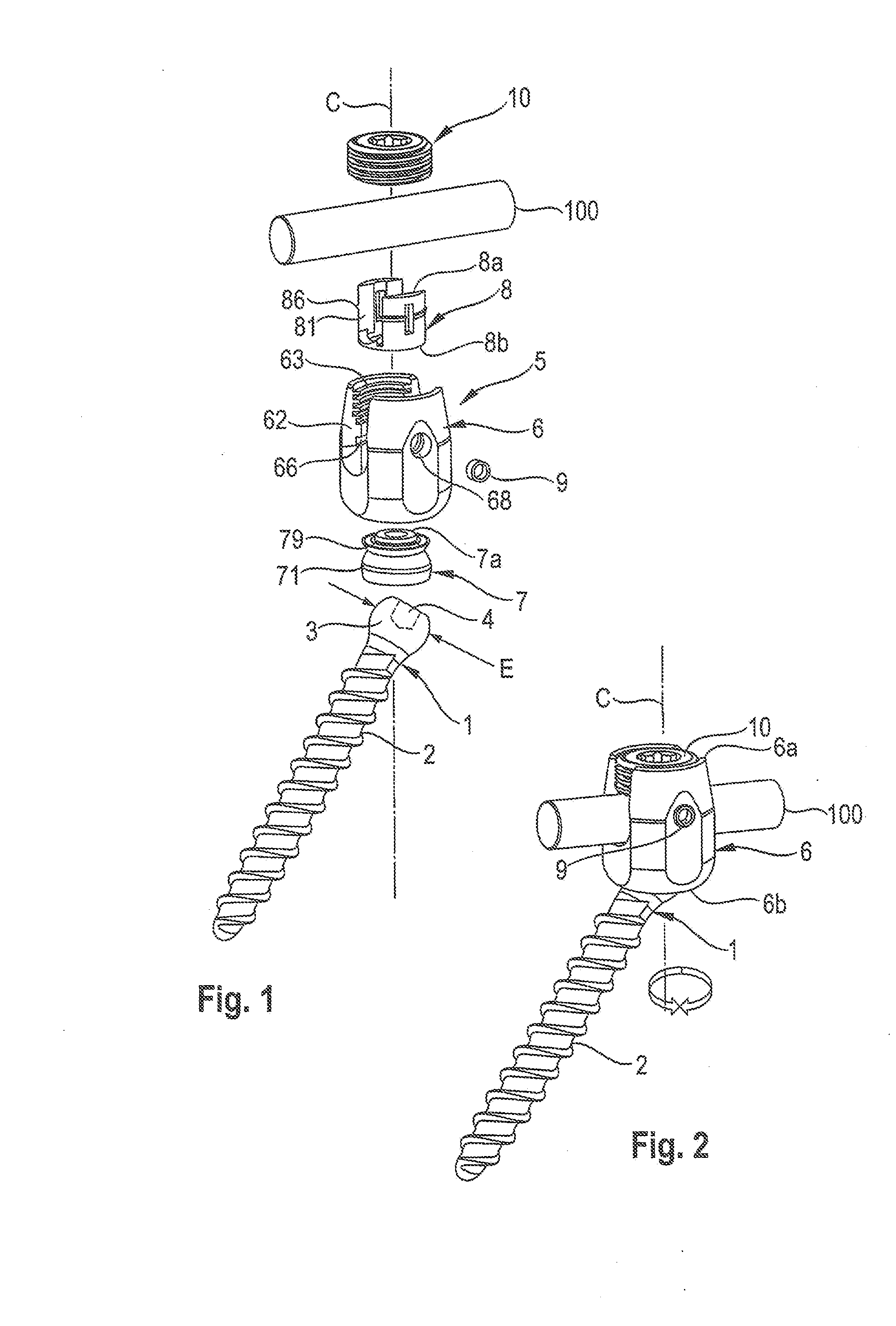
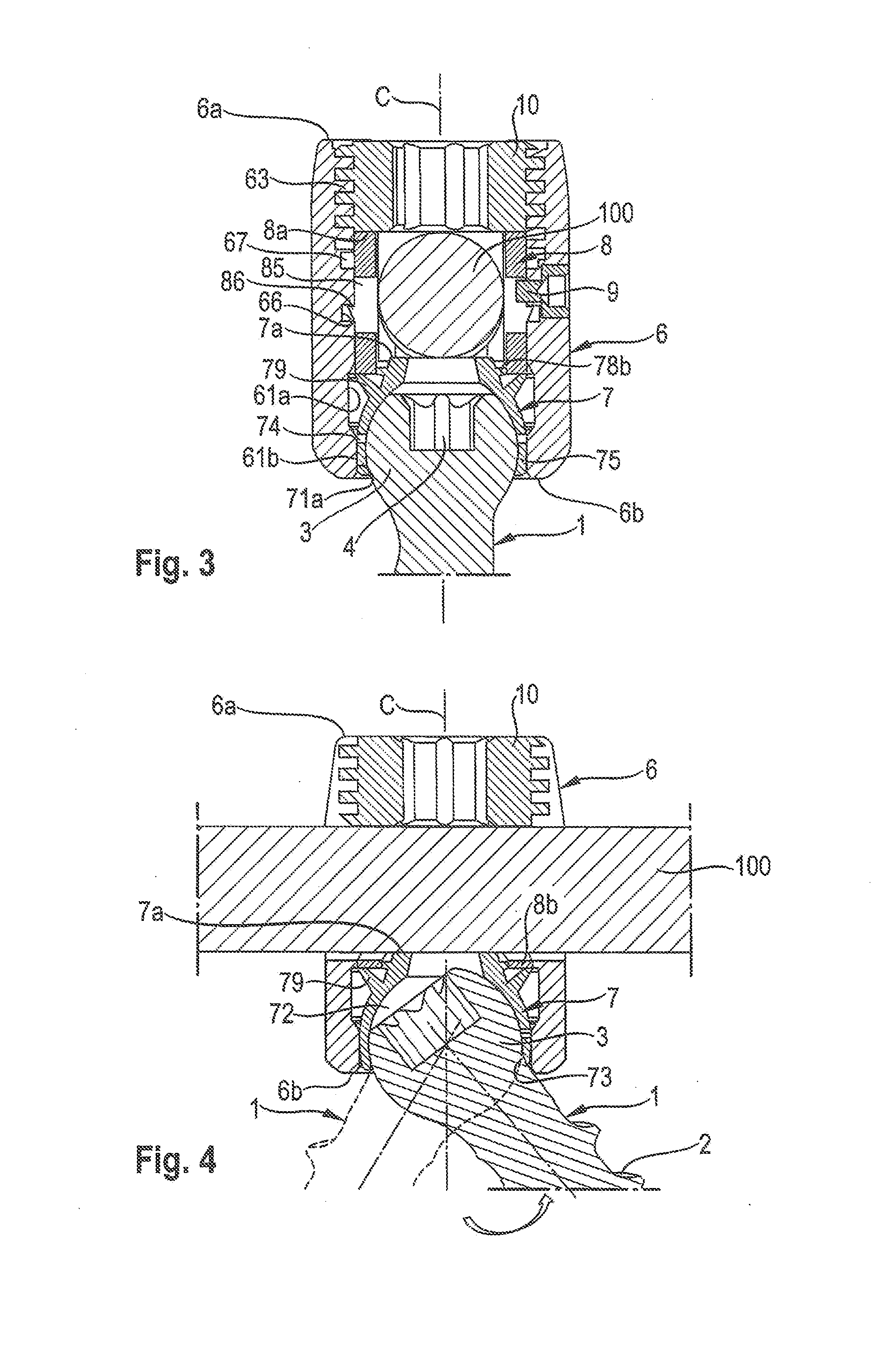
Coupling assembly for coupling a rod to a bone anchoring element, kit of such a coupling assembly different rod receiving elements and bone anchoring device
ActiveUS20150032162A1Achieve modularityLow costInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsBiomedical engineeringBone material
An instrument for inserting a bone anchoring element into a bone is provided, the instrument including a shaft (2) having an end portion (23, 23′) for engaging the bone anchoring element and for transferring torque to the bone anchoring element (1, 1′) and a longitudinal axis defining an axis of rotation (R);a cutting member (4, 4′) connected to the shaft (2) with cutting portions (45) that are configured to cut bone material;wherein the cutting member (4, 4′) has an outer diameter (D) defined by the cutting portions (45) that is substantially the same or larger than an outer diameter (dd) of a receiving part (500) of the polyaxial bone anchor in a region at a bottom end (500b) of the receiving part.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Magnetic resonance imaging interference immune device
InactiveUS20080129435A1Impedence networksTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsBiomedical engineeringVoltage
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
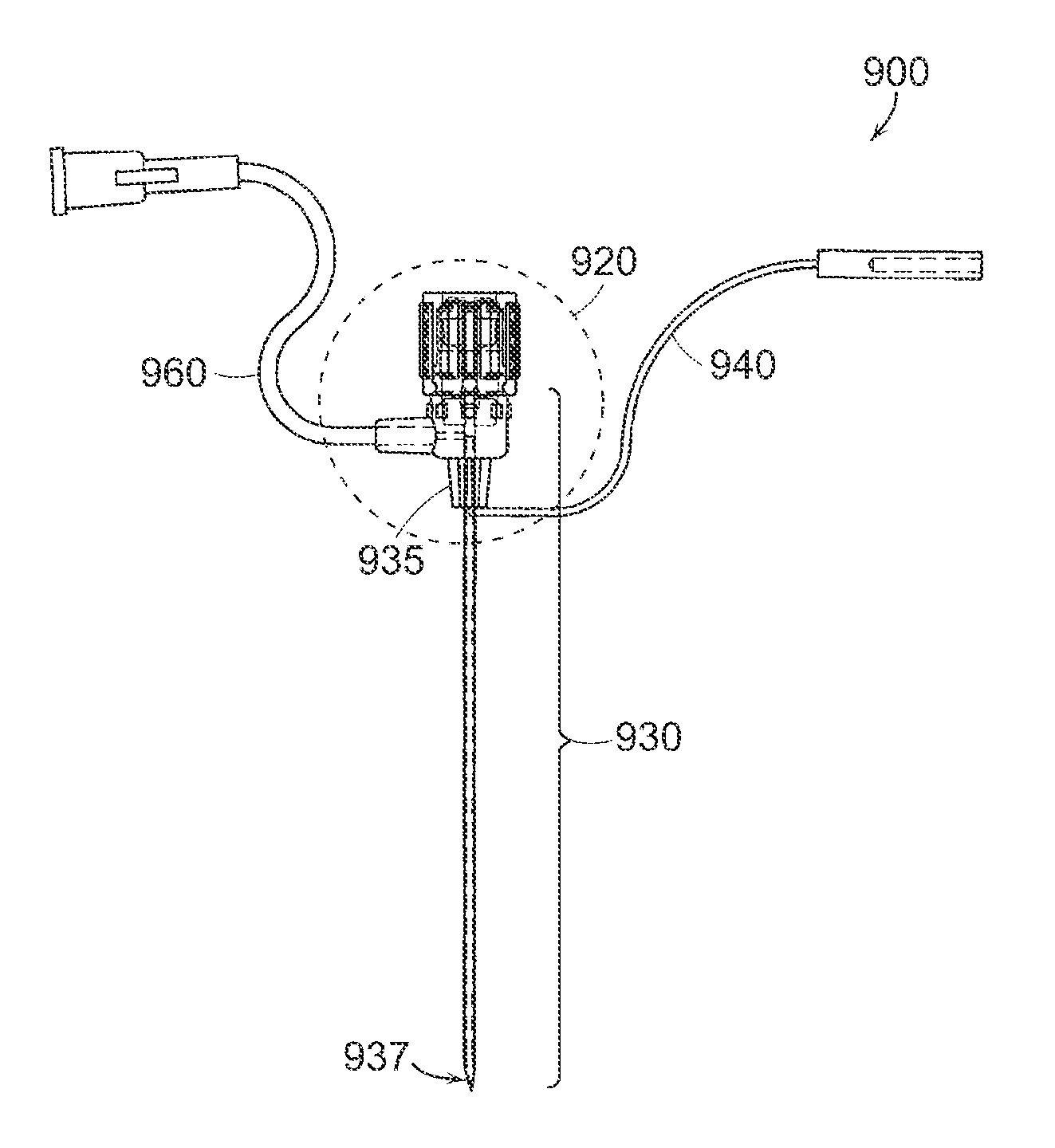
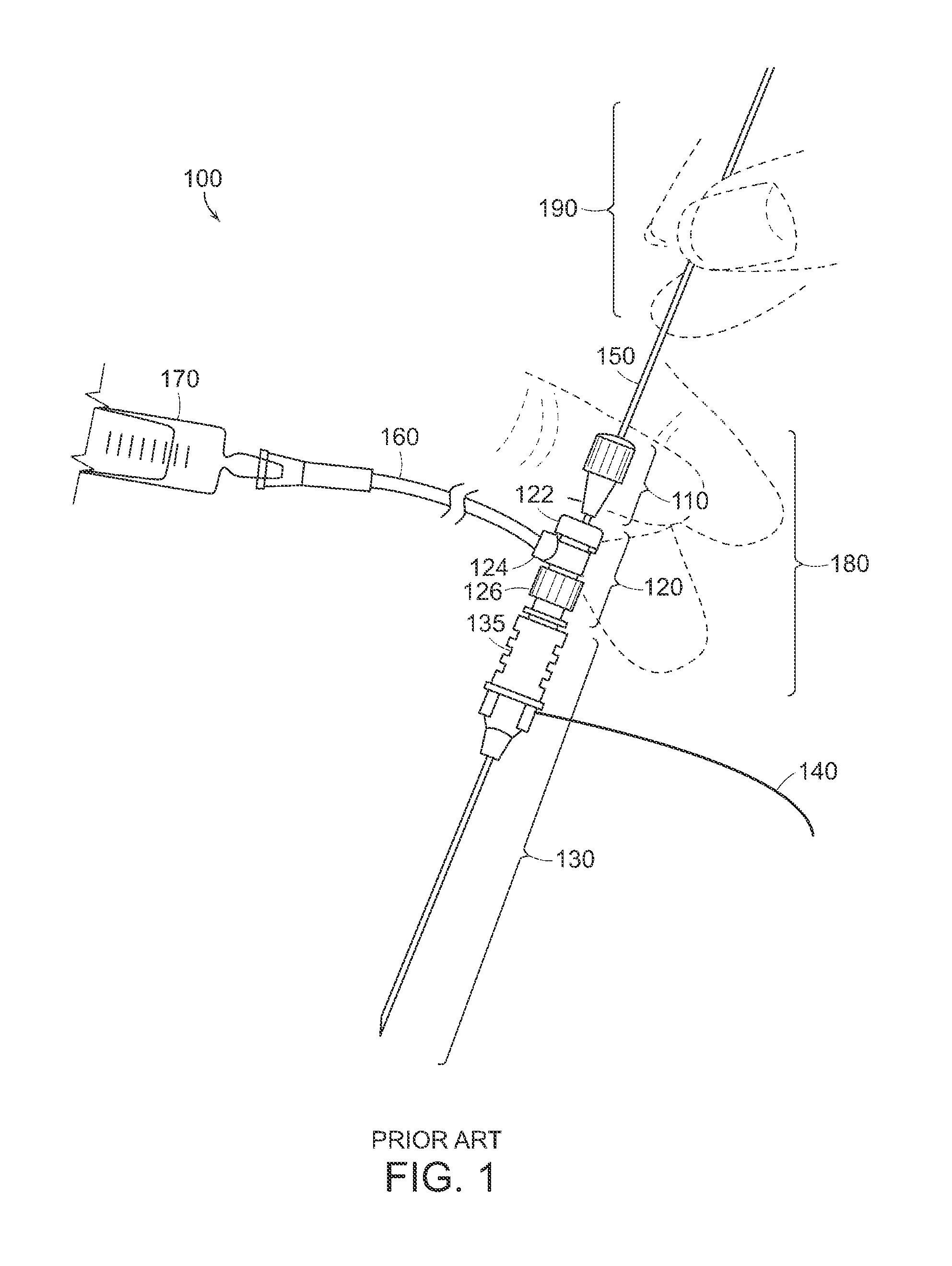
Catheter system and method for administering regional anesthesia to a patient
ActiveUS7120487B2Easy to controlMinimize movementSpinal electrodesAnaesthesiaEngineeringCatheter introducer
Owner:NELSON DAVID A
Customizing an intervertebral implant
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap