Methods of producing seed crystal substrates and group 13 element nitride crystals, and seed crystal substrates
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples a1
to A7
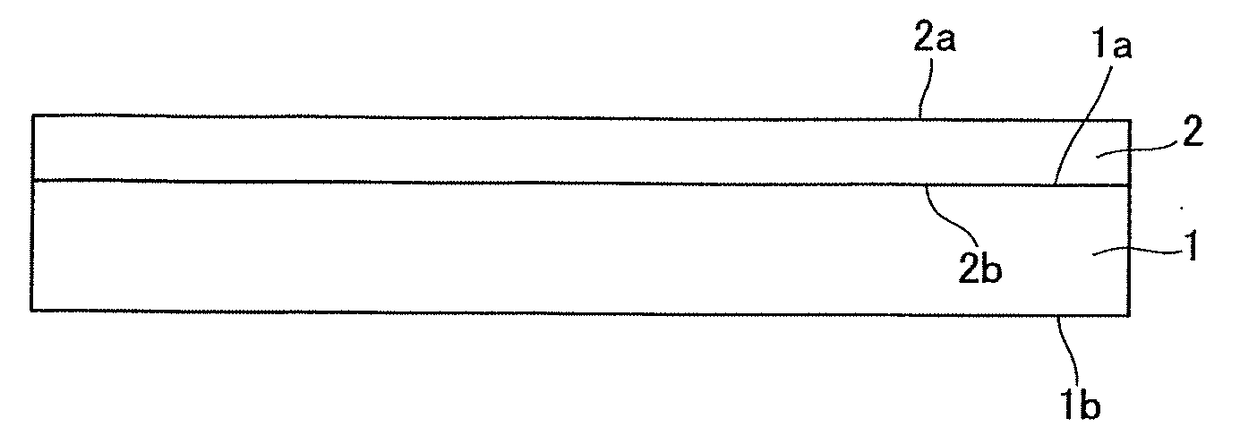
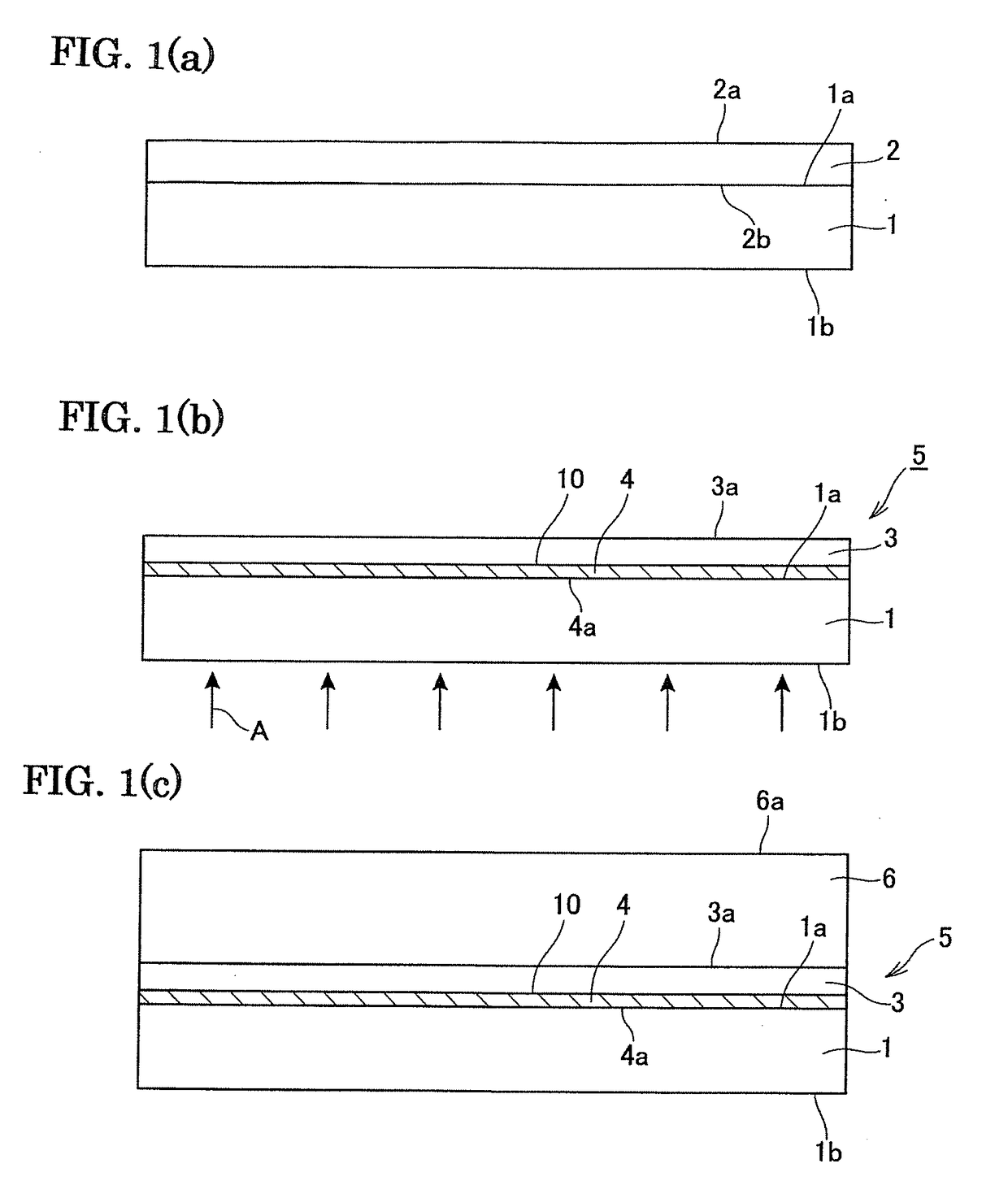
[0075]A c-plane body 1 of sapphire single crystal with a diameter of 4 or 6 inches and a thickness of 1.3 mm was put in an MOCVD apparatus (metal organic chemical vapor deposition apparatus), and heated at 1150° C. for 10 minutes in hydrogen atmosphere to perform the cleaning of the surface of the body. Then, the temperature of the body was lowered to 500° C., and the gallium nitride layer was grown to a thickness of 20 nm using TMG (trimethyl gallium) and ammonia as raw materials to provide the underlying layer. Next, the temperature of the body was raised up to 1100° C., and a seed crystal layer 2 of gallium nitride was grown to a thickness of 4 μm using TMG and ammonia as raw materials.
[0076]Then, laser light was irradiated from the side of the sapphire body 1 to form the altered portion.
[0077]As a laser light source, it was used a pulse laser using a third harmonic wave (wavelength of 355 nm) of Nd:YAG laser. The repetition frequency was made 10 Hz, the pulse width was made...
example b1
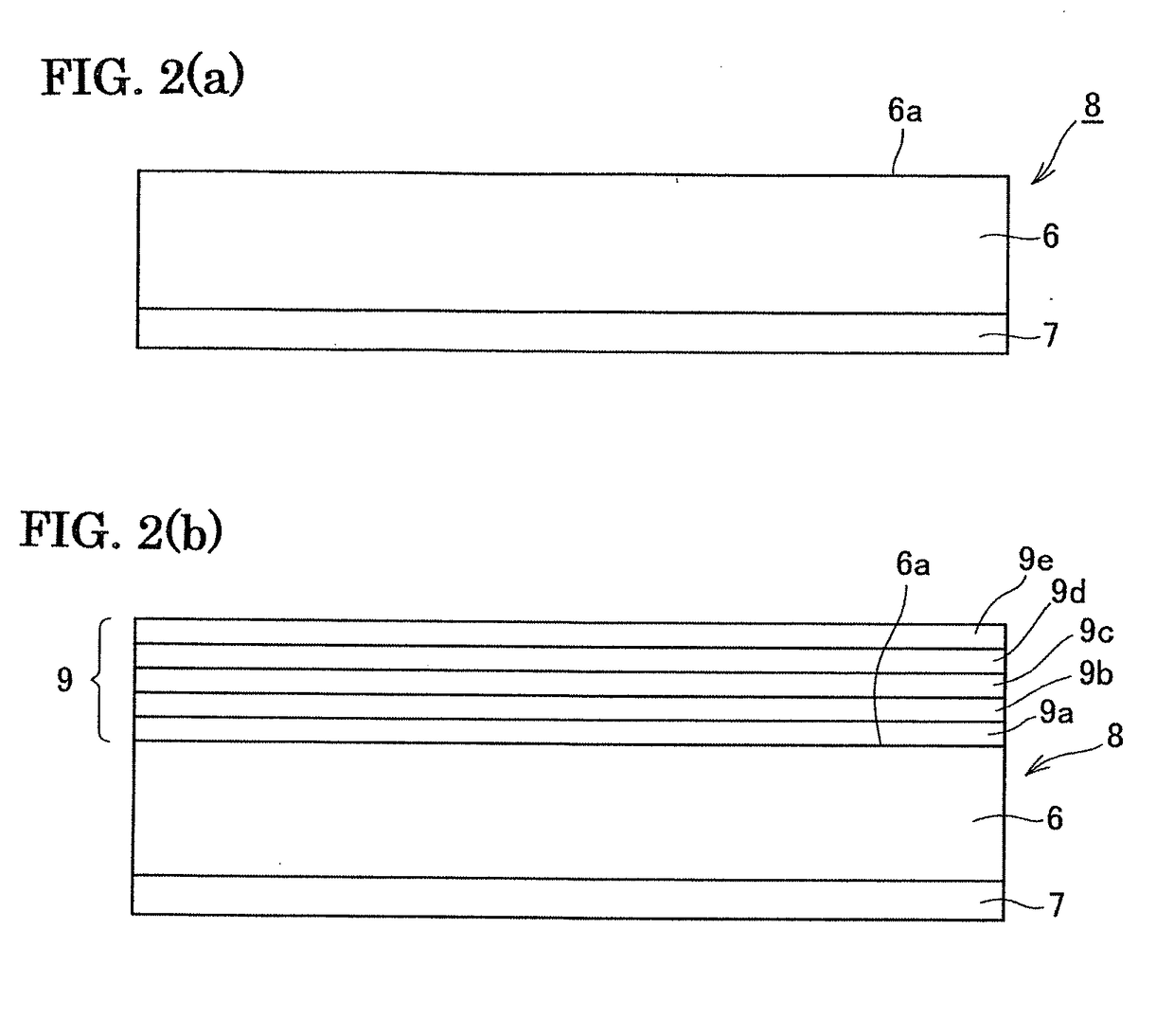
[0091]The seed crystal substrate was produced and gallium nitride layer was grown thereon as the Example A3. Then, the supporting body was processed by grinding so that the gallium nitride crystal layer was separated to obtain a free-standing substrate. Then, the yield of the cooling step, the yield of the separation by grinding and amount of bowing of the free-standing substrate after the separation were measured and shown in table 2.
examples c1 to c6
[0094]The seed crystal substrate was produced and gallium nitride crystal layer was grown as the Example A. However, according to the present examples, the thickness of the gallium nitride layer was made as large as 1400 μm, so that the gallium nitride crystal layer was separated from the supporting body due to spontaneous separation during the cooling step.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap