Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
19 results about "Analyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An analyte, component (in clinical chemistry), or chemical species is a substance or chemical constituent that is of interest in an analytical procedure.
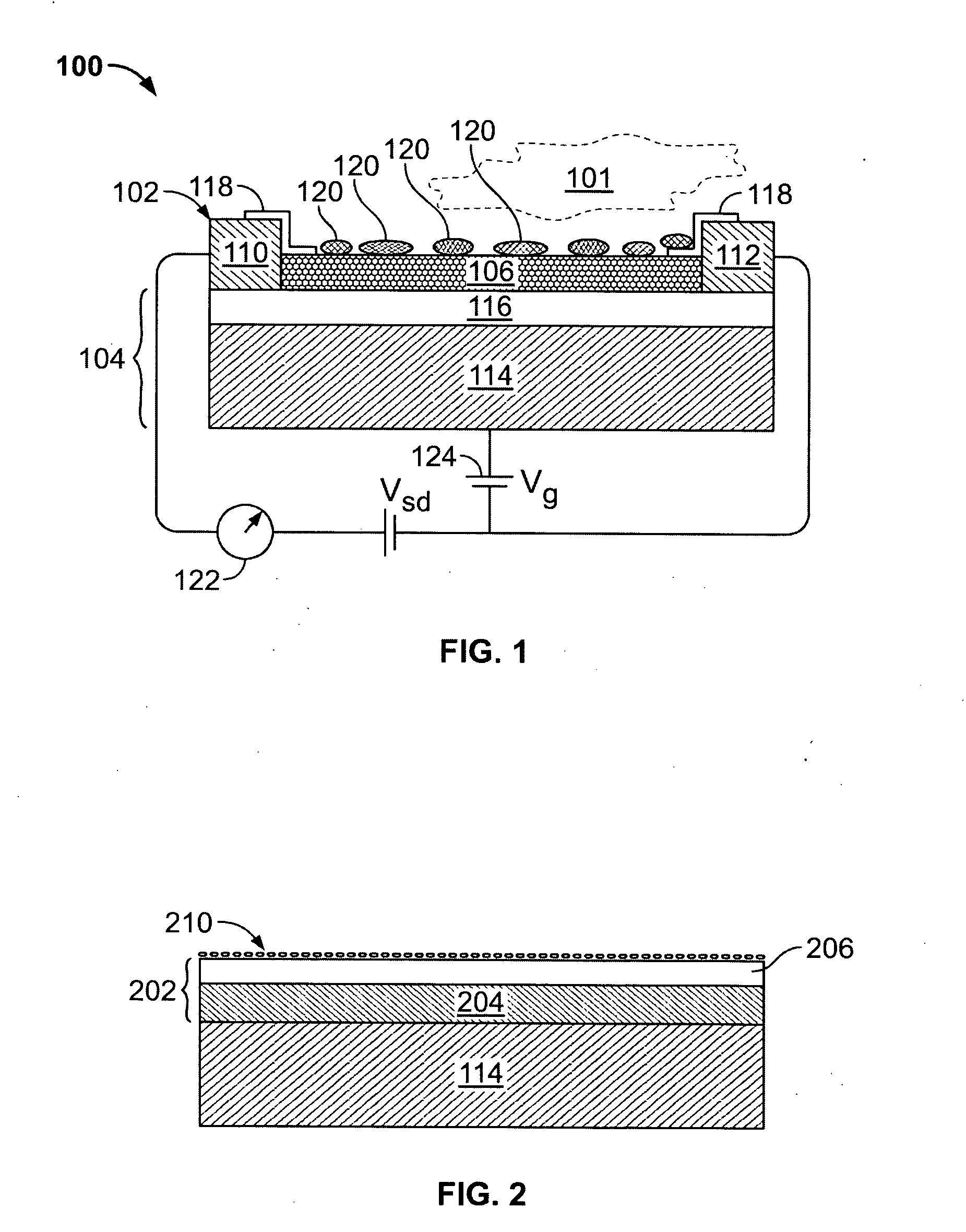
Device and method for determining analyte levels
InactiveUS7110803B2Reducing and eliminating phenomenonEliminate and significantly delay environmental stress crackingWithdrawing sample devicesMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteImplanted device
Owner:DEXCOM
Remotely communicating, battery-powered nanostructure sensor devices
InactiveUS20060055392A1Increase rangeReduce power consumptionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansNanosensorsElectricityAnalyte
Owner:NANOMIX
Methods and systems for utilizing quantitative imaging
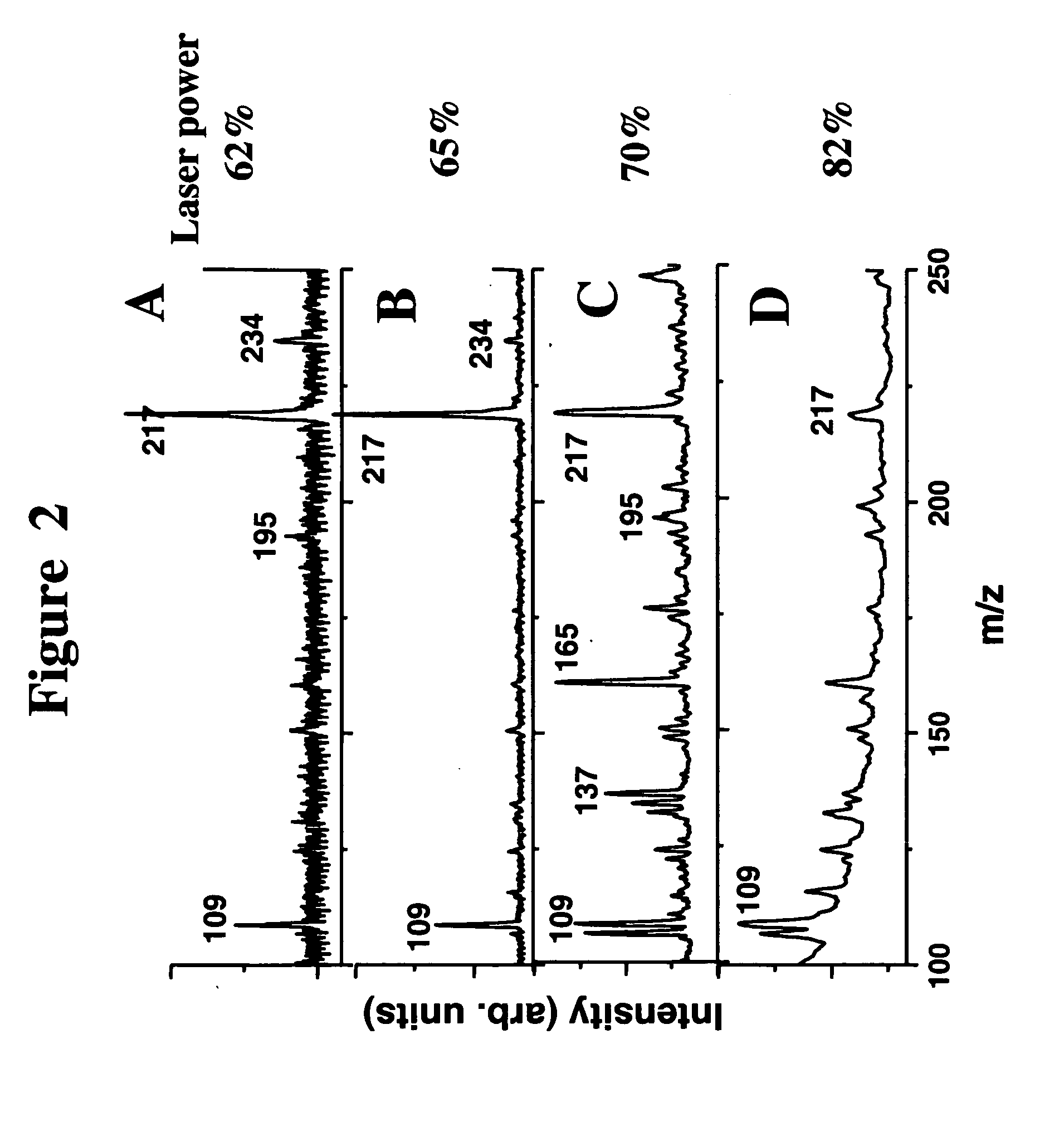
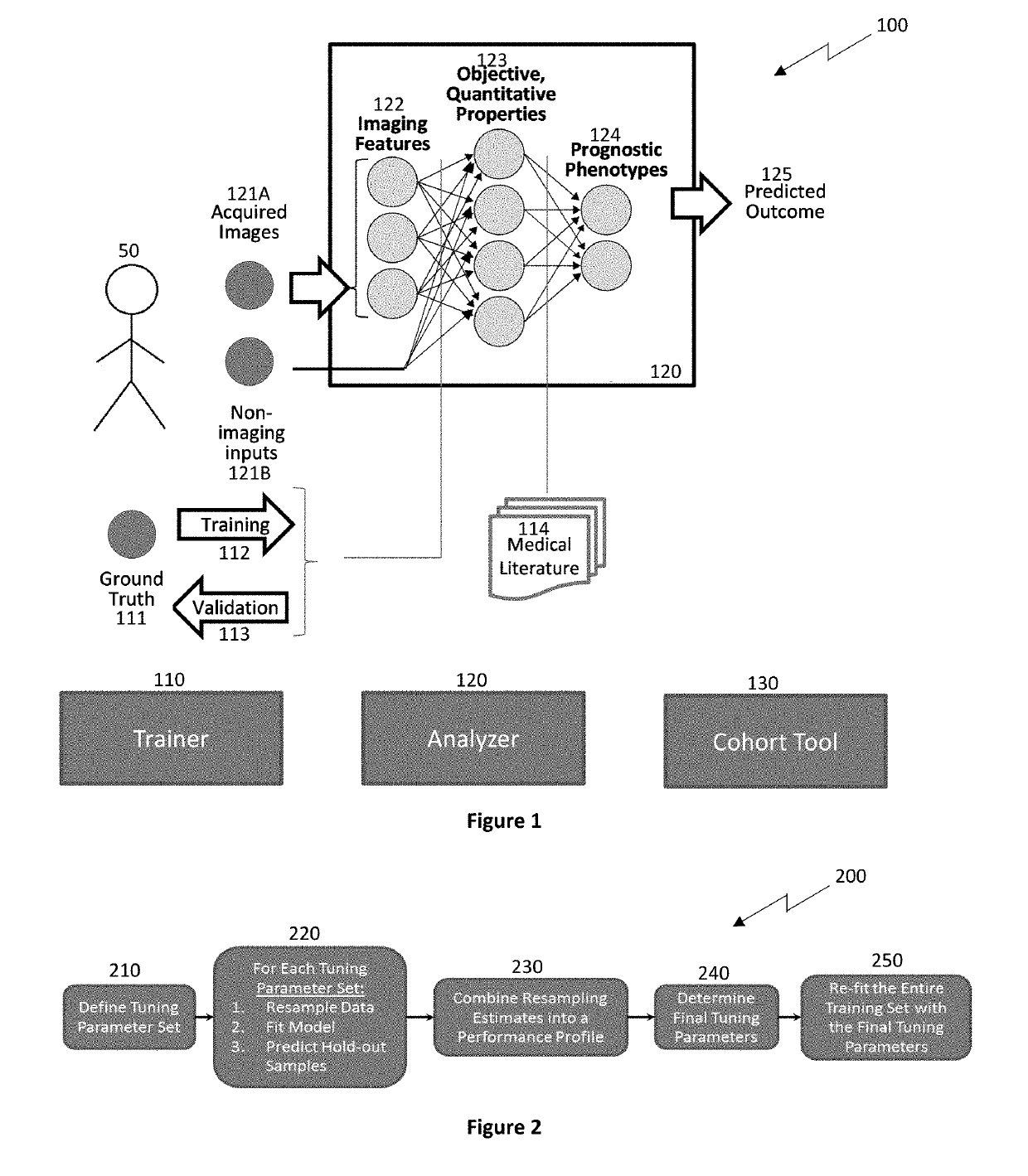
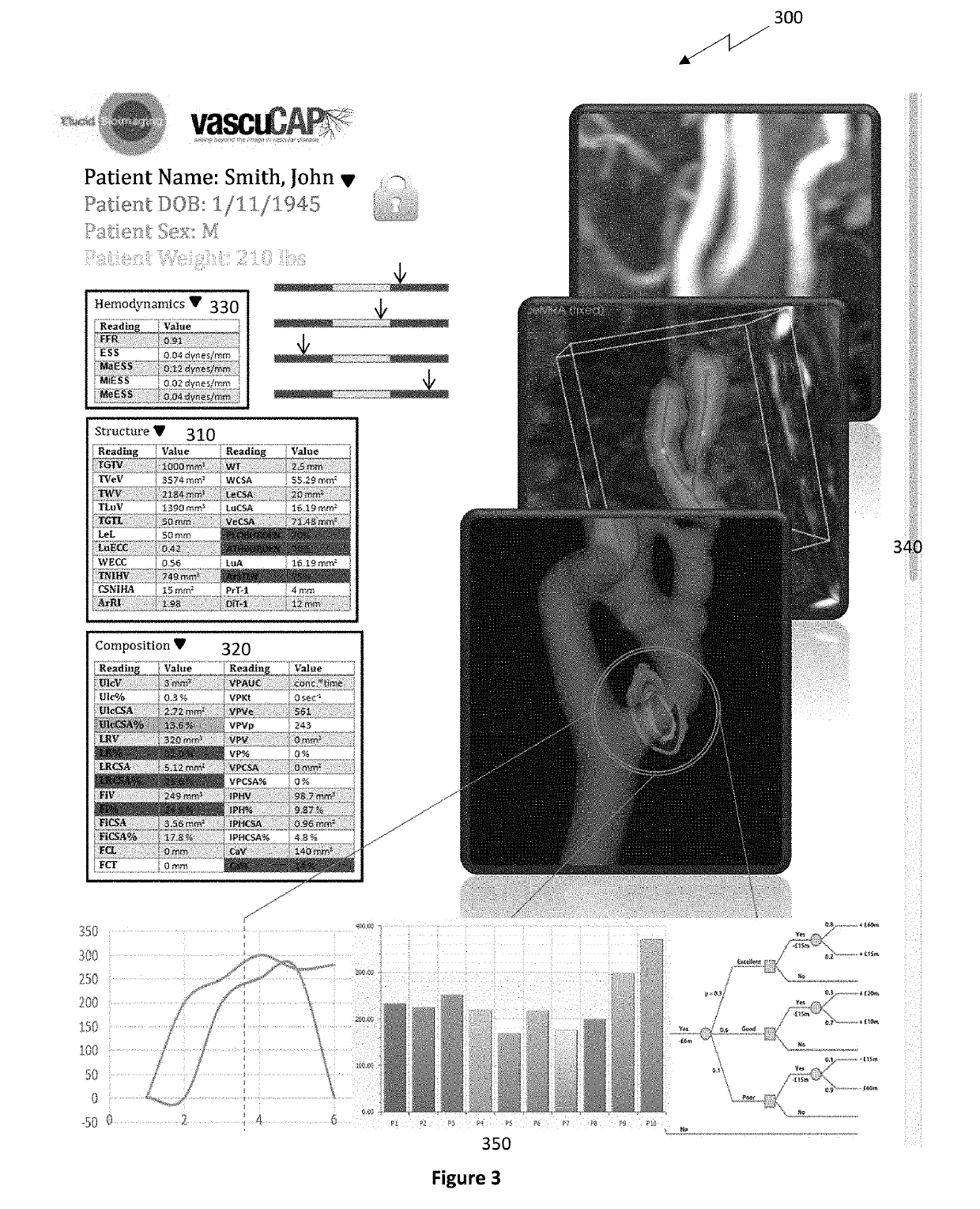
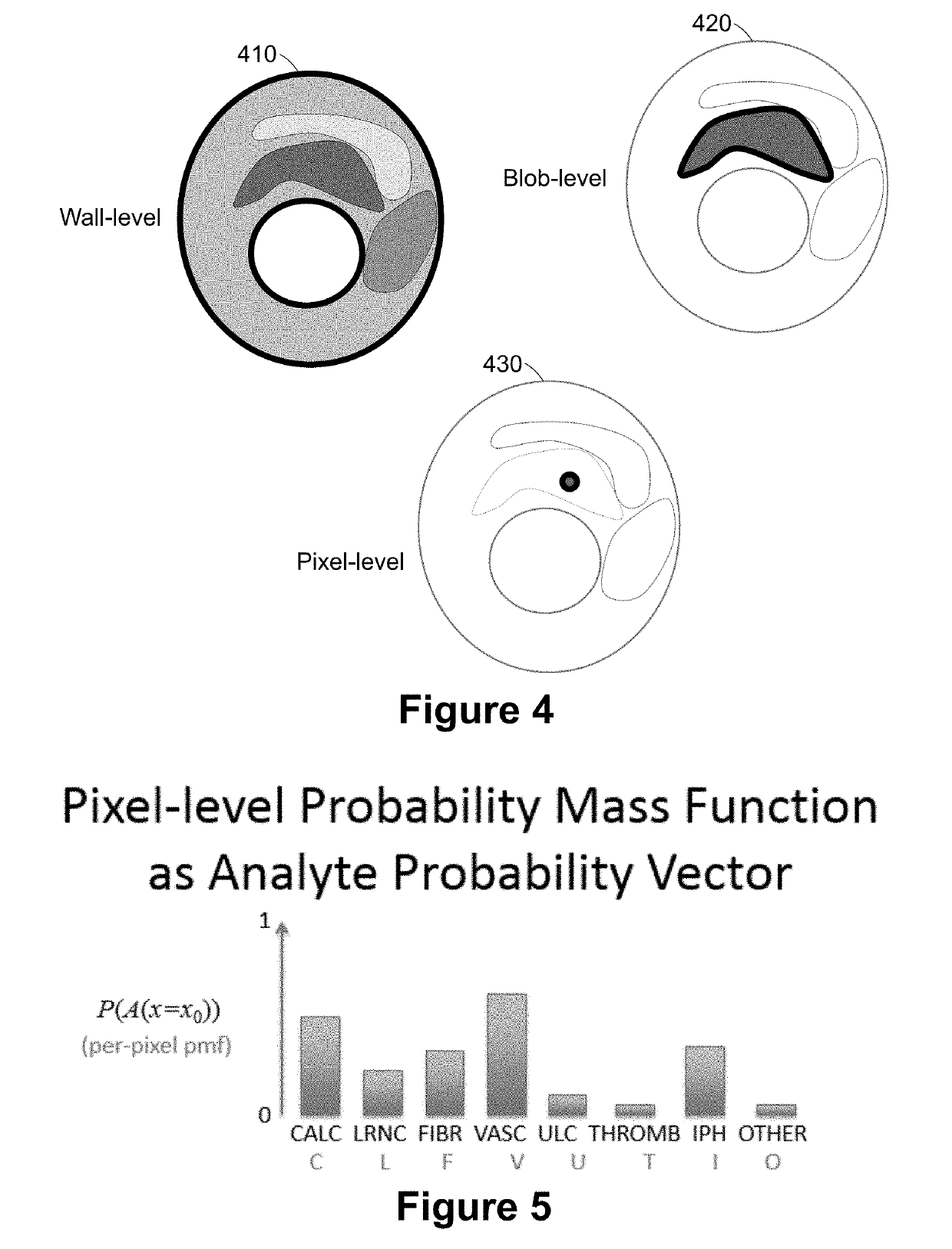
Systems and methods for analyzing pathologies utilizing quantitative imaging are presented herein. Advantageously, the systems and methods of the present disclosure utilize a hierarchical analytics framework that identifies and quantify biological properties / analytes from imaging data and then identifies and characterizes one or more pathologies based on the quantified biological properties / analytes. This hierarchical approach of using imaging to examine underlying biology as an intermediary to assessing pathology provides many analytic and processing advantages over systems and methods that are configured to directly determine and characterize pathology from underlying imaging data.
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
Matrix for MALDI analysis based on porous polymer monoliths
InactiveUS20050023456A1Ion sources/gunsIsotope separationTime-of-flight mass spectrometryAnalyte
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods and systems for utilizing quantitative imaging
ActiveUS20190180438A1Favorable vascular wall transcriptomic profileHigh prevalenceImage enhancementImage analysisPathology diagnosisAnalyte
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
Sample element for use in material analysis
InactiveUS20050106749A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAbsorption ratioAnalyte
A system and method are provided for determining a concentration of an analyte in a material sample. The method includes providing a sample element with a sample chamber at least partially defined by at least one window formed from a material having greater than about 1% wavelength-domain variation in absorbtivity of electromagnetic radiation incident thereon. The method further includes employing the sample element with an analyte detection system which determines the concentration of the analyte with clinically acceptable accuracy.
Owner:OPTISCAN BIOMEDICAL
Novel standard reference solutions
Owner:BIONOSTICS
Devices, methods and systems for low volume microarray processing
InactiveUS6913931B2Reduction and elimination of liquid retention interfaceAvoid the needMaterial nanotechnologyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsAnalyteFluorescence
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Quantitative imaging for detecting histopathologically defined plaque fissure non-invasively
Systems and methods for analyzing pathologies utilizing quantitative imaging are presented herein. Advantageously, the systems and methods of the present disclosure utilize a hierarchical analytics framework that identifies and quantify biological properties / analytes from imaging data and then identifies and characterizes one or more pathologies based on the quantified biological properties / analytes. This hierarchical approach of using imaging to examine underlying biology as an intermediary to assessing pathology provides many analytic and processing advantages over systems and methods that are configured to directly determine and characterize pathology from underlying imaging data.
Owner:ELUCID BIOIMAGING INC
Using asymmetrical flow focusing to detect and enumerate magnetic particles in microscale flow systems with embedded magnetic-field sensors
InactiveUS20090001024A1Water/sewage treatment by magnetic/electric fieldsFiltration separationMagnetic markerAnalyte
Improved detection and enumeration of magnetic particles in a flowing stream by enveloping the particle-containing sample stream with buffer streams from the sides and from the top, thus individualizing the particles and navigating the sample stream as a single-file flow into the proximity of sensors embedded underneath the flow channel. At the same time, larger physical size of the flow channel alleviates problems such as channel clogging. Magnetic particles can represent any analyte of interest, such as biomolecules or bacterial cells, which are labeled with magnetic labels.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND INC
Ion mobility spectrometer with parallel drift gas and ion carrier gas flows
ActiveUS20070023647A1Takes effortObtain goodTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteIonization chamber
Owner:DRAGER SAFETY
Methods for detecting and quantifying non-polar analytes with high sensitivity
Owner:WATERS TECH CORP
Functionalized support for analytical sample preparation
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
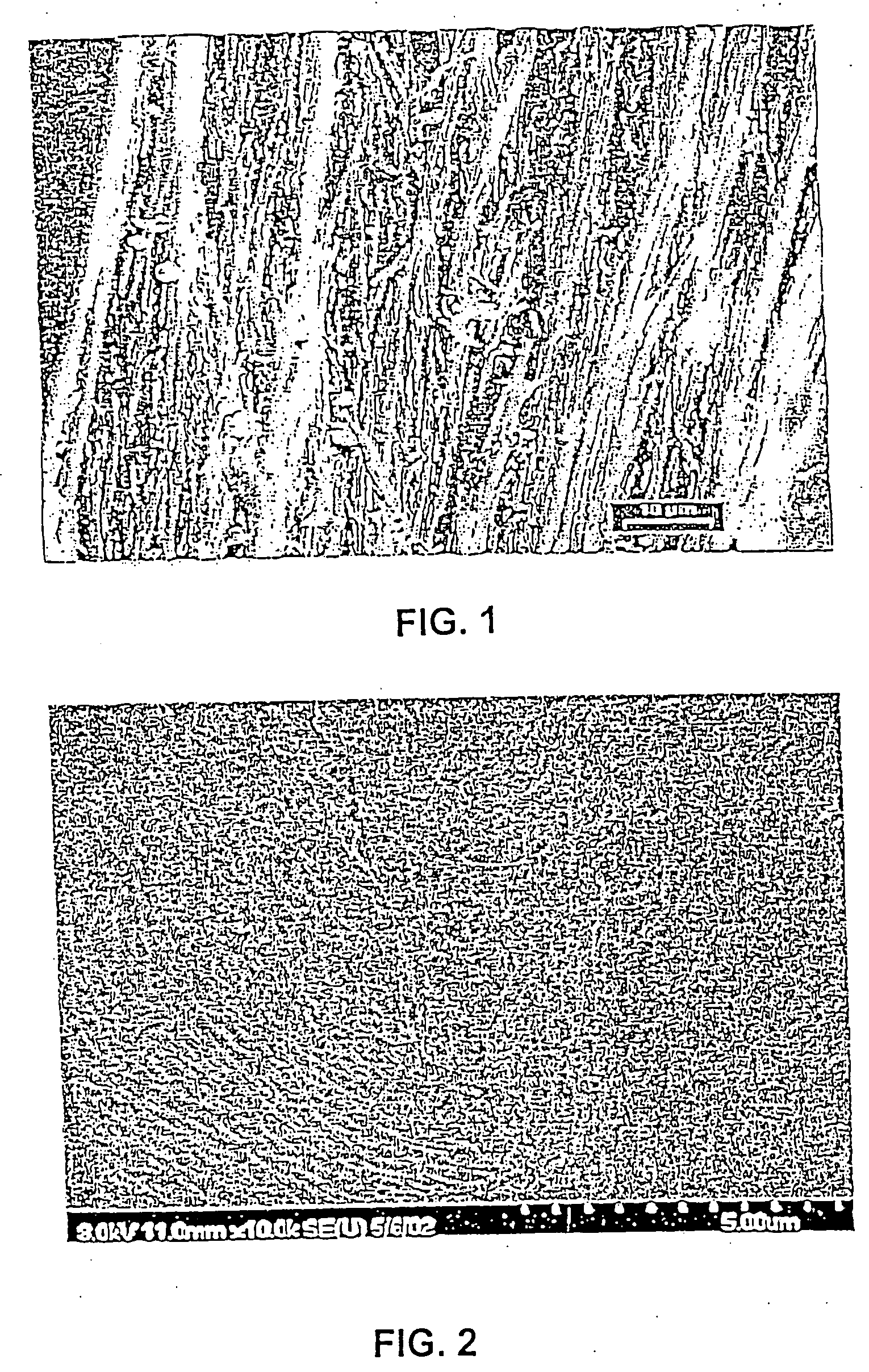
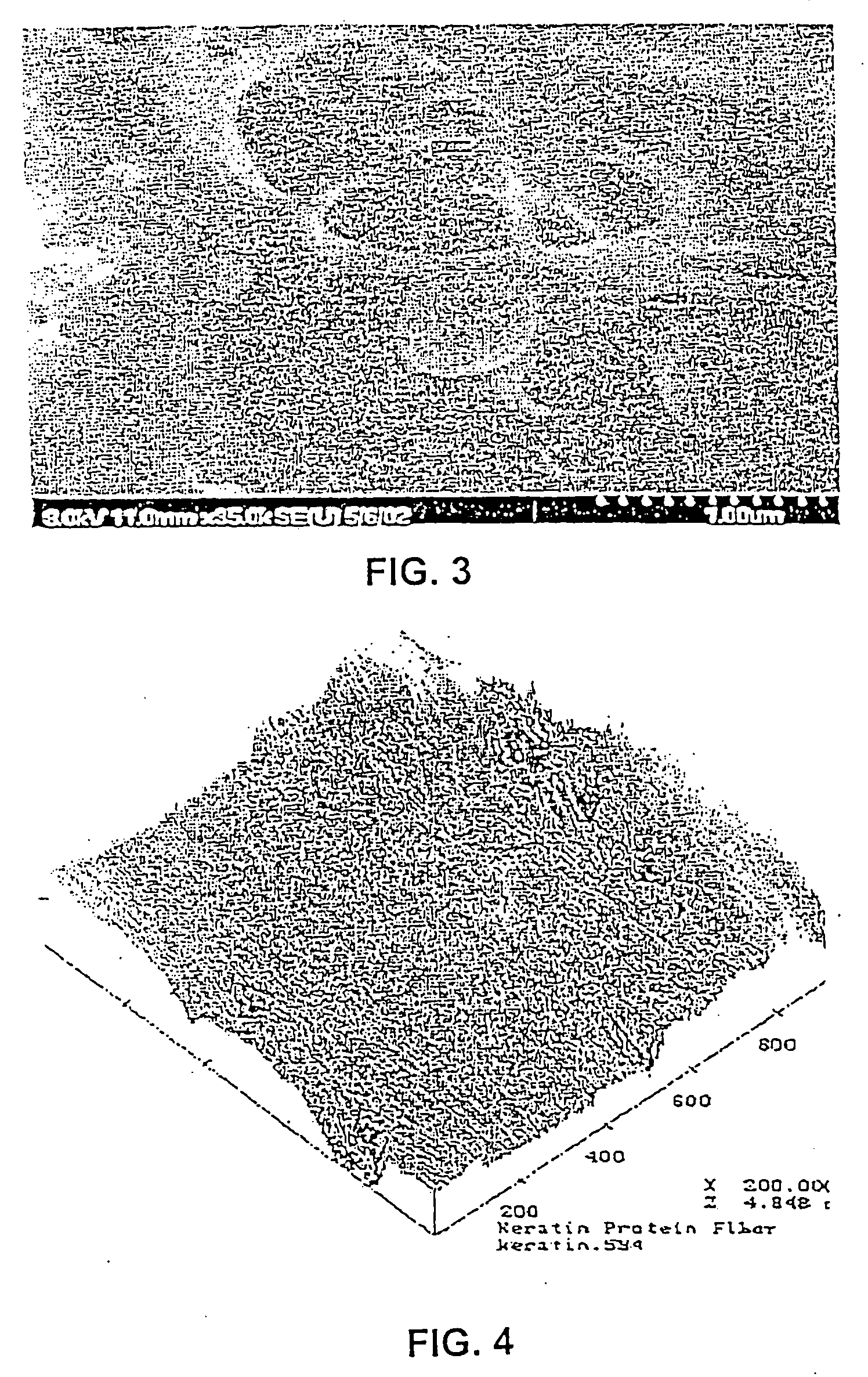
Use of fibrous protein fibers for chemical sensing and radiation detection
InactiveUS20060194198A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsReference sampleAnalyte
Owner:LICATA CARLO
Measurement system with optical referencing
ActiveUS20090304247A1Improve accuracyAccurate assessmentInvestigating moving sheetsCharacter and pattern recognitionSpatially resolvedAnalyte
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
Analyte concentration measuring method, particle containing agglutinated fluorescent material, and inspection device
InactiveUS20190226988A1Satisfactory detection sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFluorescence/phosphorescenceAggregation-induced emissionAnalyte
This analyte concentration measuring method including:preparing a mixed solution by mixing a sample solution containing an analyte, with a solution containing aggregation-induced emission fluorescent material-containing particles that have a binding partner which binds with the analyte and that agglutinate and fluoresce when the analyte binds to the binding partner;measuring the fluorescence intensity generated from the aggregation-induced emission fluorescent material-containing particles in the mixed solution; andcomparing a fluorescence intensity calibration curve for analyte concentration with the fluorescence intensity, and associating the fluorescence intensity with the analyte concentration in the mixed solution. Employing agglutinating-luminescent-material-containing particles enables measurements to be carried out with a satisfactory detection sensitivity while suppressing background fluorescence.
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD +1
Optical disc assemblies for performing assays
InactiveUS7054258B2Filamentary/web record carriersScattering properties measurementsAnalyteComputer science
Owner:VINDUR TECH
Device and method for determining a level or concentration of an analyte in a person's blood from one or more volatile analytes in the person's breath
PendingUS20220139557A1Improve patient wellbeingEasy to monitorKernel methodsMedical automated diagnosisMicrocontrollerDisease
Owner:SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Reduction of interferences in immunoassays
PendingUS20200400654A1Easy to detectReliable resultsBiological testingAssay labelsAnalyteChemical compound
The present invention relates to a method for determining an analyte in a sample, comprising a) contacting said sample with at least a first and a second detector compound; b) determining the amount of complexes comprising at least one detector compound; and, c) determining said analyte in a sample based on the result of step b), wherein said first detector compound comprises a first binding moiety and a first label, and said second detector compound comprises a second binding moiety and a second label, and wherein the first label and the second label are non-identical. The present invention further relates to a kit for detecting an analyte in a sample, comprising at least a first and a second detector compound for said analyte, wherein said first detector compound comprises a first binding moiety and a first label, and said second detector compound comprises a second binding moiety and a second label, and wherein the first label and the second label are non-identical; and to a device for determining an analyte in a sample, comprising at least a first and a second detector compound for said analyte, wherein said first detector compound comprises a first binding moiety and a first label, and said second detector compound comprises a second binding moiety and a second label, and wherein the first label and the second label are non-identical; and means for determining at least one signal obtained from said first label and said second label; and to the use of a composition comprising at least a first and a second detector compound for detecting an analyte, wherein said first detector compound comprises a first binding moiety and a first label, and said second detector compound comprises a second binding moiety and a second label, and wherein the first label and the second label are non-identical.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap