Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10 results about "Charge carrier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, a charge carrier is a particle or quasiparticle that is free to move, carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric charges in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons, ions and holes. In a conducting medium, an electric field can exert force on these free particles, causing a net motion of the particles through the medium; this is what constitutes an electric current. In conducting media, particles serve to carry charge...
Method of forming an epitaxial layer for raised drain and source regions by removing surface defects of the initial crystal surface
ActiveUS20060003533A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantCharge carrier
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Low temperature formation of backside ohmic contacts for vertical devices
InactiveUS6909119B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsOhmic contact
A semiconductor device is disclosed that includes a semiconductor substrate having a first surface and a second surface and a first conductivity type and at least one epitaxial layer on the first surface of the semiconductor substrate. The epitaxial layer is formed of a material with a dissociation temperature below that of the semiconductor substrate. A zone of increased carrier concentration is in the semiconductor substrate and extends from the second surface of the semiconductor material toward the first surface. A layer of metal is deposited on the second surface of the semiconductor substrate and forms an ohmic contact at the interface of the metal and the zone of increased carrier concentration.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Semiconductor device and method for producing the same, and power supply
InactiveCN102637650AReduce deteriorationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCharge carrierSemiconductor chip
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Material construction for enhancing optical property and temperature stability of self-organizing quantum point
InactiveCN101308888AImprove optical property temperature stabilityOptical properties Good temperature stabilityLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersCushioningElectron hole
Disclosed is a material structure which is capable of improving optical temperature stability of self-organized quantum dots. The material structure comprises a substrate; a cushioning layer is arranged on the substrate to conceal the defect of the substrate so as to make the growth surface plane; a quantum well layer is arranged on the cushioning layer to generate stress relaxation during the growth and guides the stress relaxation to the quantum dot layer above so as to reduce the thickness of the wetting layer; a barrier layer is arranged on the quantum dot layer and is capable of restricting the current carrier in the quantum dot layer to avoid the weakening of optical temperature stability of the quantum dot material caused by thermally excited transition; a quantum dot layer is arranged on the barrier layer and generates electron hole pairs and radiates composite light when being excited; a cover layer is arranged on the quantum dot layer and is used to change the optical property of the quantum dots and to increase the level spacing between the ground state and the excited state.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor device for electrostatic discharge protection
ActiveUS20150091056A1Speed up triggeringSpeedTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceDevice material
Owner:SOFICS BVBA
Method for manufacturing stable high temperature-resistant hydrogen end group conducting channel on diamond surface
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
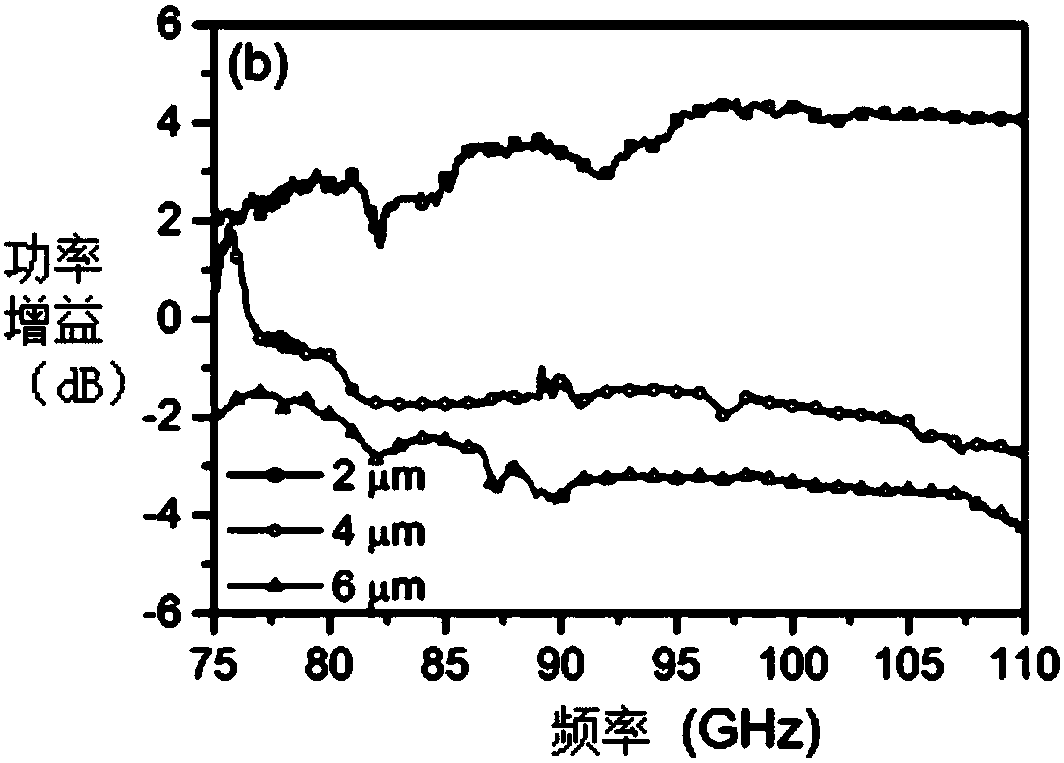
Planar coriolis millimeter wave, terahertz power amplifier and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107819071AHigh frequencyHigh gainBulk negative resistance effect devicesRadarCharge carrier
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
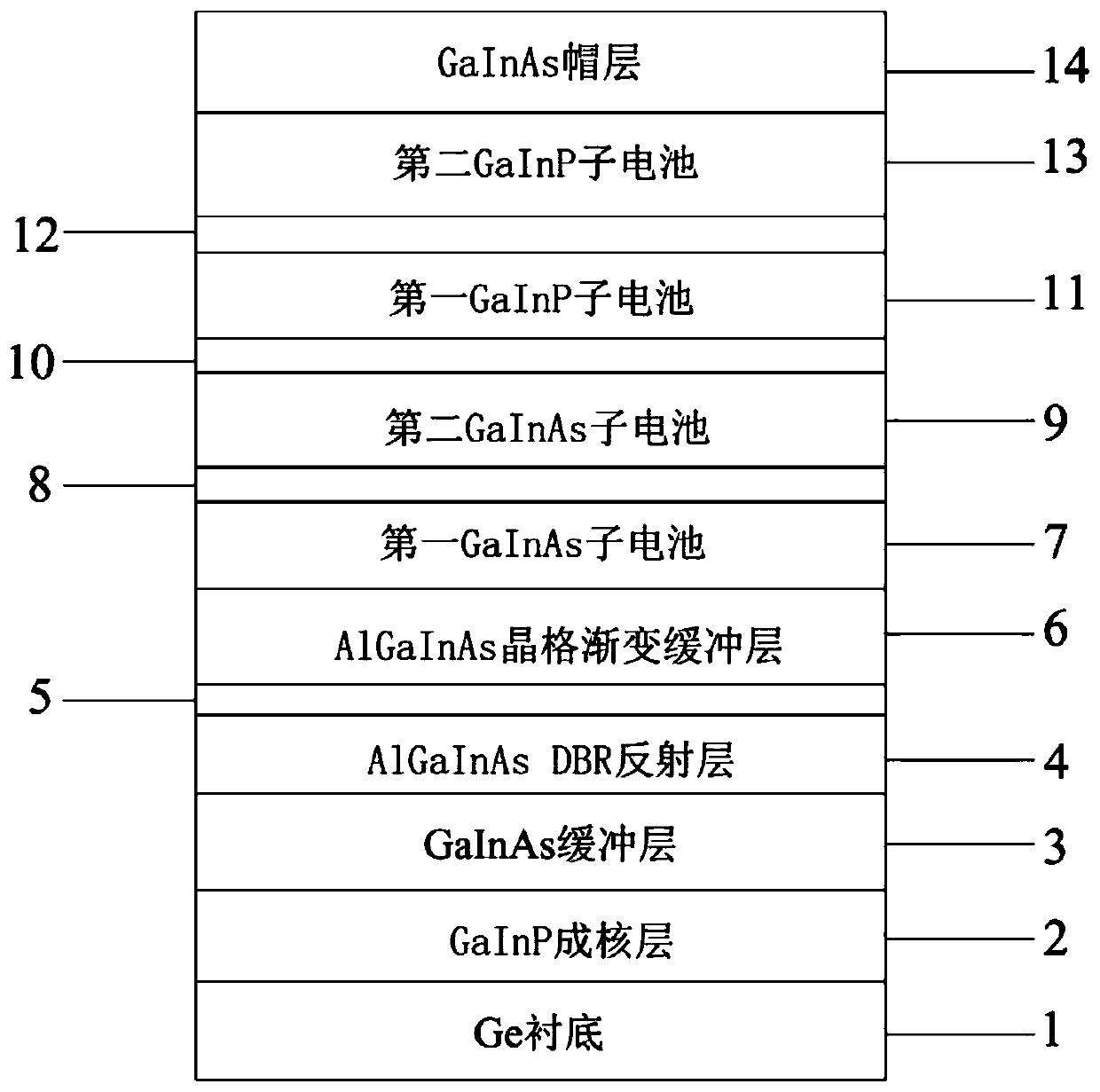
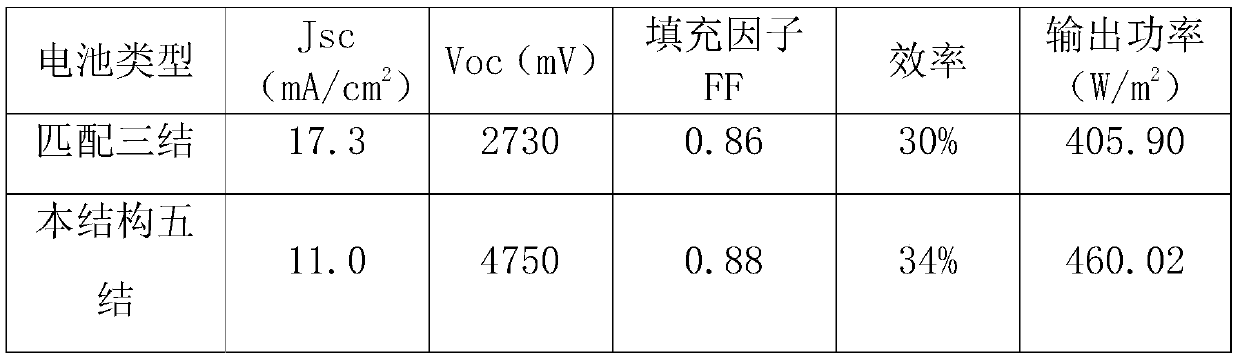
Lattice mismatched five-junction solar cell and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110491965AAchieve growthImprove conversion efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationLattice mismatchCharge carrier
Owner:ZHONGSHAN DEHUA CHIP TECH CO LTD
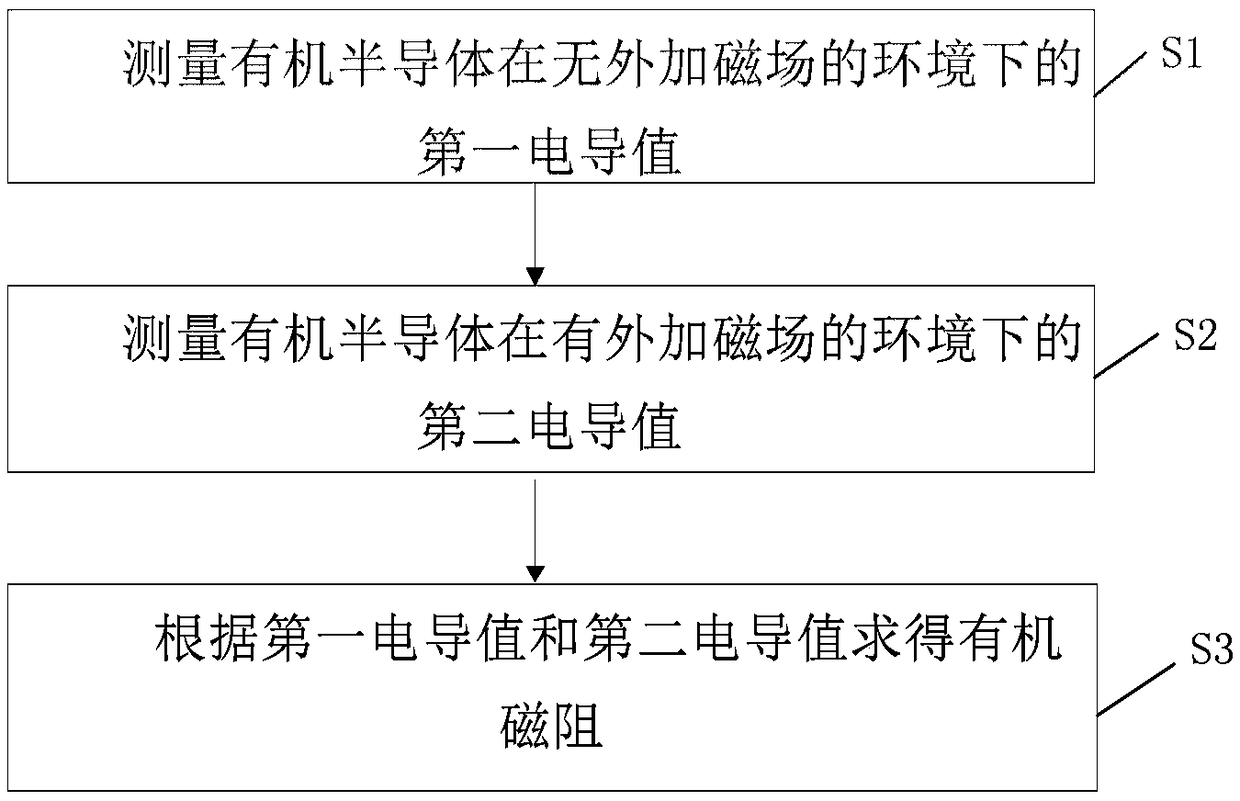
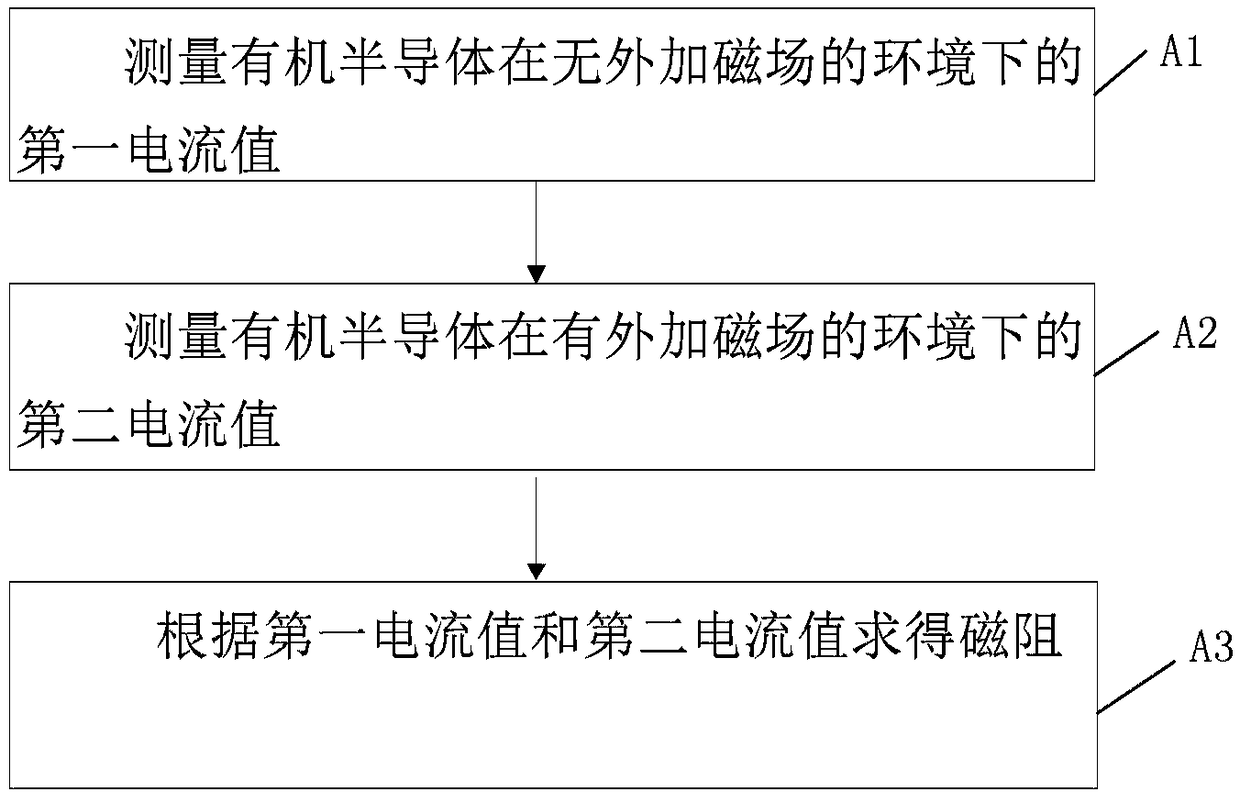
Method for measuring organic magnetic resistance of organic semiconductors
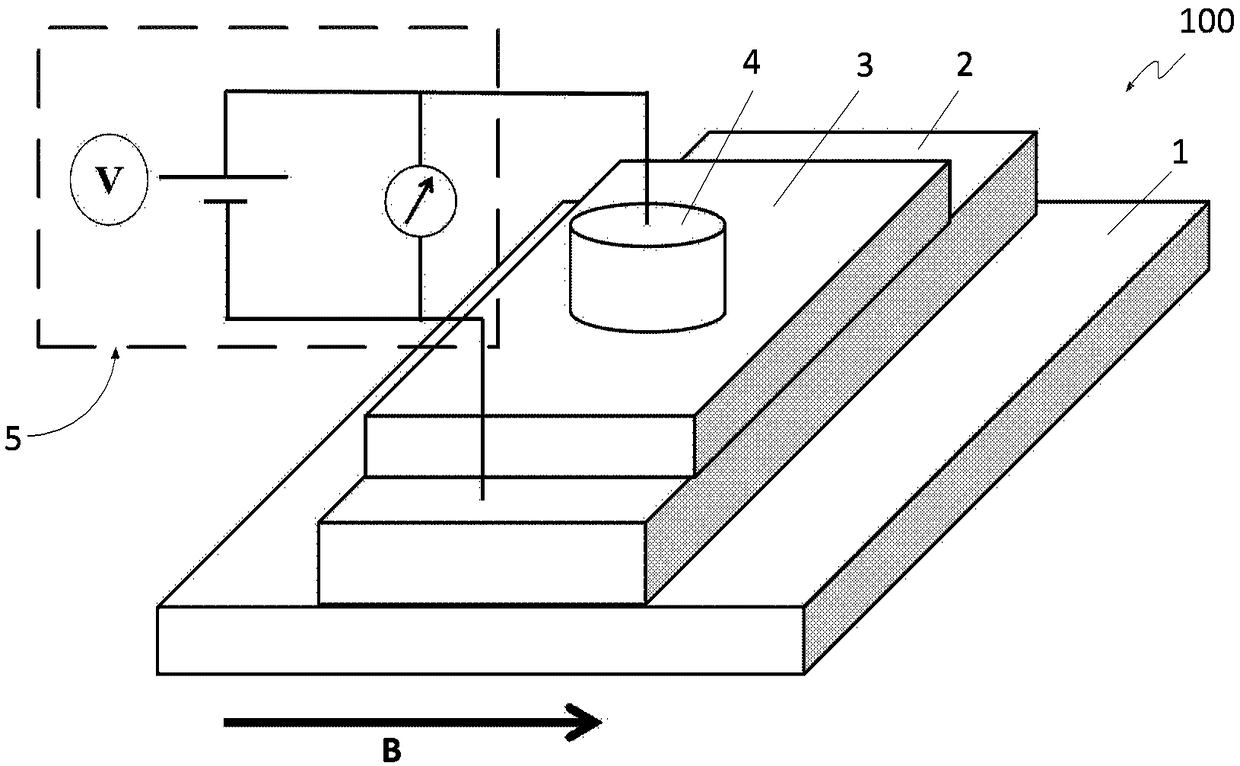
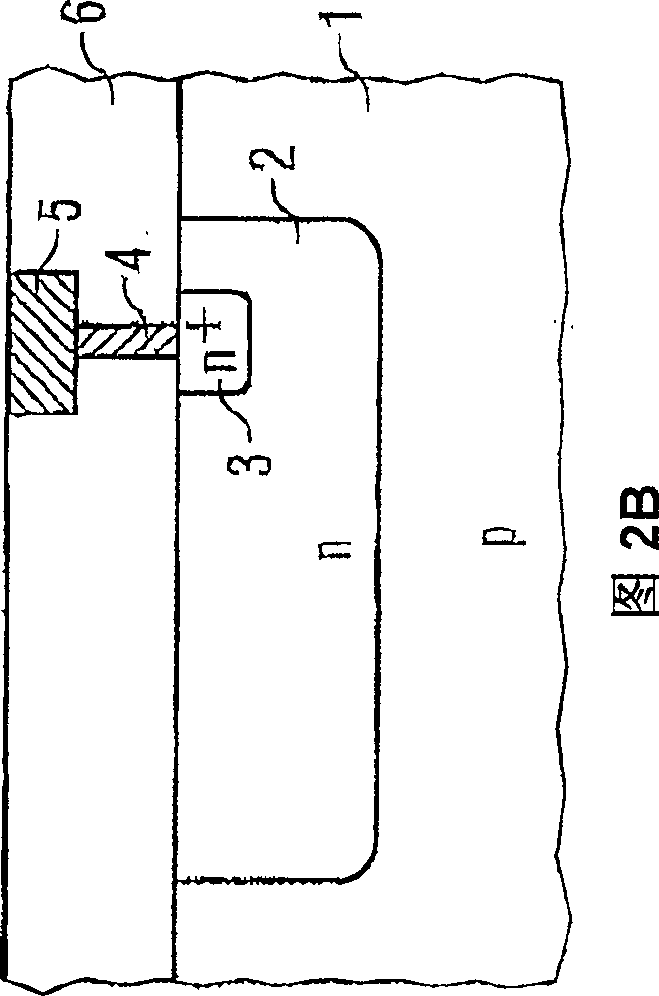
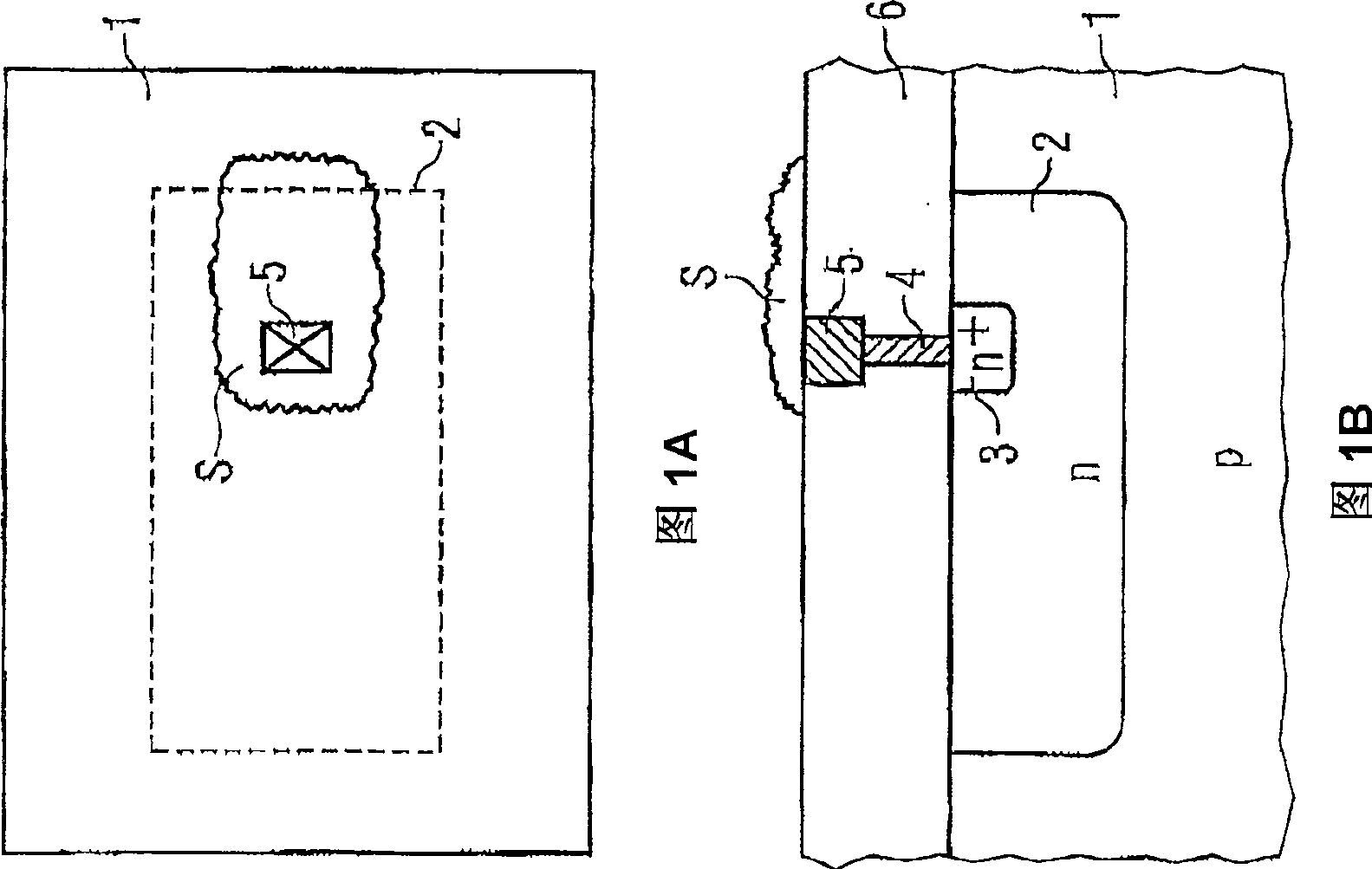
InactiveCN109061529AMagnetic measurementsMagnetoresistanceCharge carrier
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid-state circuit assembly
InactiveCN100483732CSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSolid-stateCharge carrier
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap