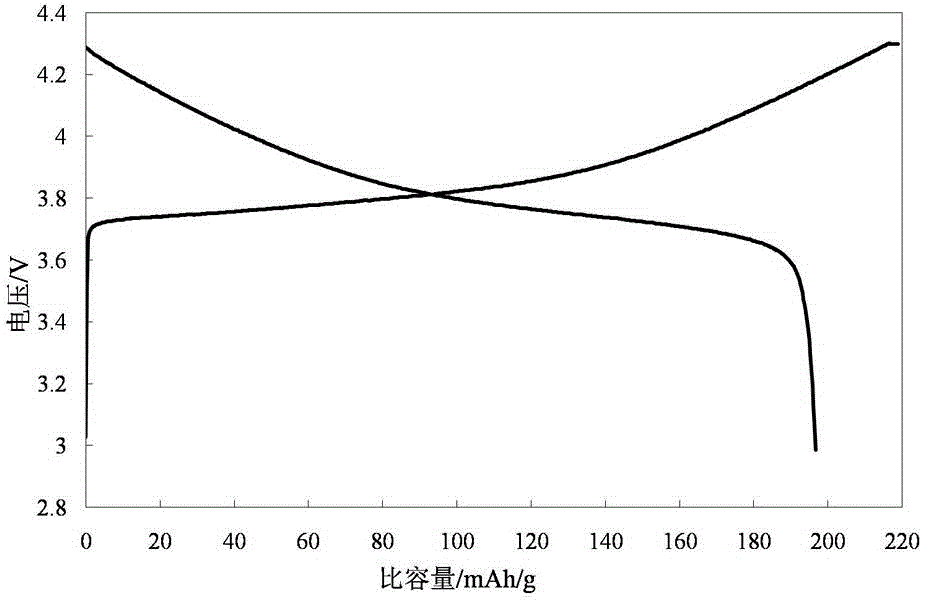
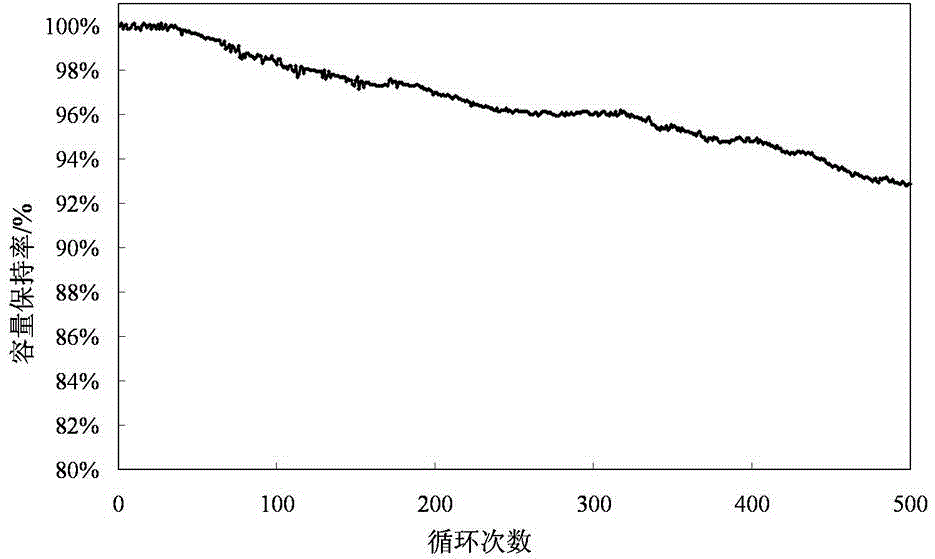
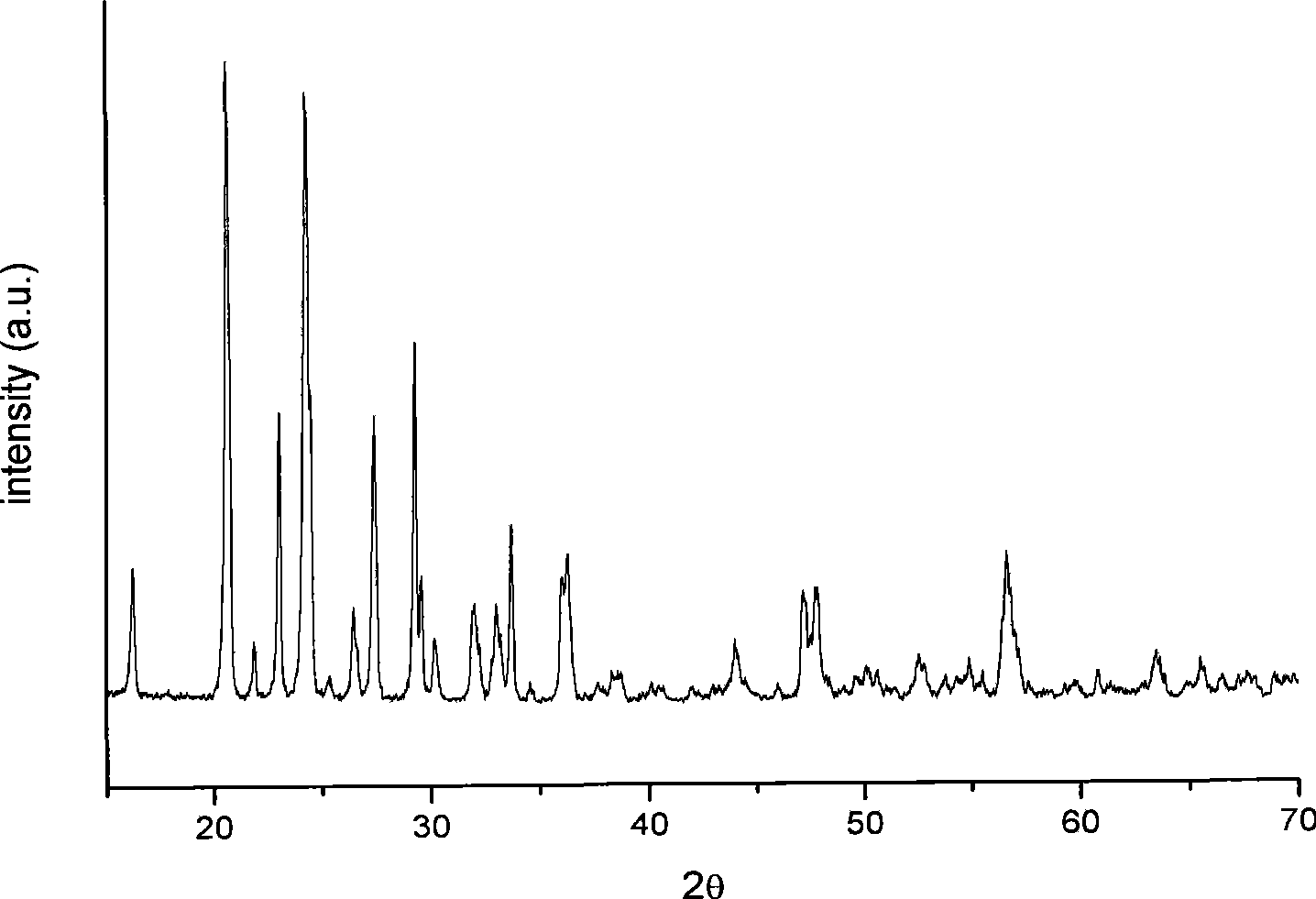
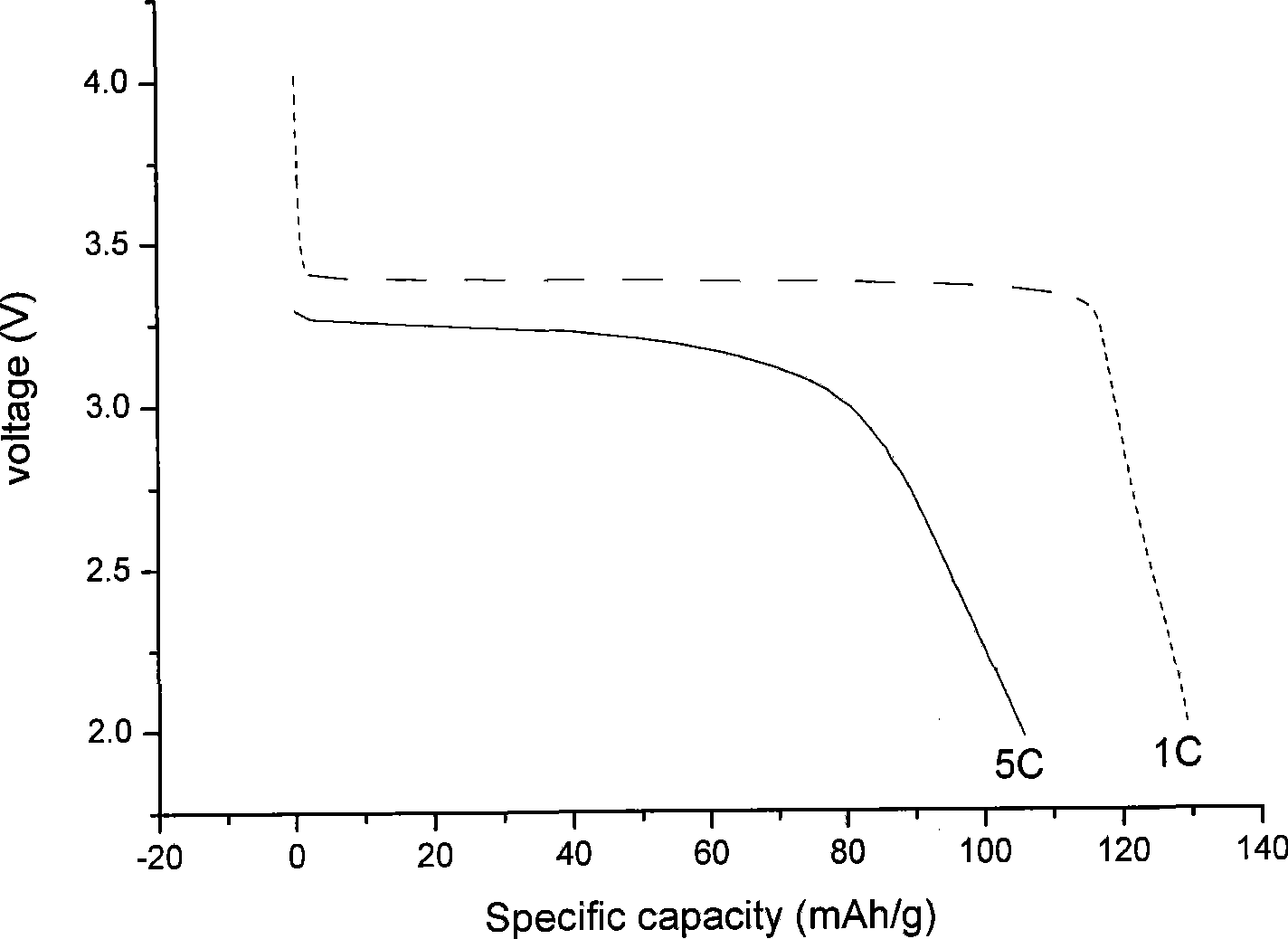
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11 results about "Lithium iron phosphate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Lithium iron phosphate (LFP) is an inorganic compound with the formula LiFePO₄. It is a gray, red-grey, brown or black solid that is insoluble in water. The material has attracted attention as a component of lithium iron phosphate batteries, a type of Li-ion battery. This battery chemistry is targeted for use in power tools, electric vehicles, and solar energy installations. It is also used in OLPC XO education laptops.
Surface coating modified lithium ion battery cathode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104577093AImprove securityNo significant reduction in specific capacityCell electrodesLithium iron phosphatePhysical chemistry
Owner:ZHEJIANG MEIDARUI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Preparation of lithium ionic cell positive pole material lithium ferrous phosphate/carbon composite
InactiveCN101483236ASimple processEase of mass productionElectrode manufacturing processesPhosphorus compoundsCarbon compositesPhosphate
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Low-temperature electrolyte for lithium iron phosphate battery
InactiveCN106129472AImprove low temperature conductivityReduced solvation radiusSecondary cellsElectrolytesLithium vanadium phosphate batteryTetrafluoroborate
Owner:DONGFENG COMML VEHICLE CO LTD
Method for preparing positive pole material for ferrous phosphate lithium battery from low-valence oxygen-containing acid of phosphorus
InactiveCN101332984ALow costWide variety of sourcesCell electrodesPhosphorus compoundsPhosphateFerrous salts
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Heat dissipation module for battery thermal management
ActiveCN110534843AImprove cooling efficiencyUniform temperatureAir-treating devicesSecondary cellsLithium iron phosphateEngineering
The invention discloses a heat dissipation module for battery thermal management. The heat dissipation module comprises a top cover plate, a cooling plate and an outlet pipeline. The top cover plate is provided with two fluid passages. The top cover plate and the outlet pipe are respectively located at the upper and lower ends of the cooling plate. The cooling plate is intenrally provided with a fractal microchannel. The inlet of the fractal microchannel is connected with a fluid pipeline flowing through the pole lug, and the outlet of the fractal microchannel is connected with the outlet pipeline. The cooling plate and lithium iron phosphate battery cells are alternately distributed, and the two sides of each lithium iron phosphate battery cell are attached to the cooling plate. The temperature of the battery module can be accurately controlled, the temperature of the battery module is controlled within a safe range and the temperature distribution is uniform; and the heat dissipationmodule has a compact structure and is beneficial to realize the weight reduction of the whole vehicle.
Owner:CHANGAN UNIV
Large-capacity lithium iron phosphate storage battery
InactiveCN101651231AIncrease capacityIncrease energy densityElectrode manufacturing processesActive material electrodesNameplate capacityLithium iron phosphate
Owner:SICHUAN CHANGHONG ELECTRIC CO LTD
Dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres and preparation method thereof through electrochemical anode oxidation
InactiveCN103556169ASynthesis temperature is lowEasy to embedElectrolysis componentsMicrosphereElectrochemical anodization
The invention discloses dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres and a preparation method thereof through electrochemical anode oxidation, relating to dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres and a method for preparing the dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres through electrochemical anode oxidation, and aiming to solve the problems that iron phosphate micro nanoparticles prepared by the prior art are long in synthesis time, high in synthesis temperature and complex in operation step. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of preparing a mixed solution of phosphoric acid and ammonium fluoride of a certain molar concentration to serve as electrolyte for anode oxidation, and generating the dandelion-shaped iron phosphate microspheres on the surface of an iron foil under conditions of certain current by taking a high-purity iron foil as an anode and a platinum sheet as a cathode. The iron phosphate obtained by the invention is used as a precursor when being used for preparing lithium iron phosphate.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Big data extraction and calculation method for capacity imbalance degree of lithium iron phosphate battery system
PendingCN111239607AStable M-shaped bimodal characterThe M-shaped bimodal feature is completely preservedElectrical testingLithium iron phosphateElectrical battery
The invention discloses a big data extraction and calculation method for the capacity imbalance degree of a lithium iron phosphate battery system. The method comprises the following specific steps: setting screening conditions, screening voltage and power values, obtaining a voltage-electric quantity curve, obtaining a broken line fitting curve of the voltage-electric quantity acquisition data, carrying out smooth fitting processing on the broken line fitting curve to obtain a voltage-electric quantity / voltage curve of the lithium iron phosphate battery, and carrying out calculation accordingto the voltage-electric quantity / voltage curve of the lithium iron phosphate battery to obtain imbalance degree delta SOC values of different batteries so that the calculation of the capacity imbalance degree is completed. According to the method, the M-shaped double-peak characteristic presented by the derivation curve can be stabilized, and the calculated amount of big data processing can be reduced on the premise that the precision of key characteristic parameters is not reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN KING LONG UNITED AUTOMOTIVE IND CO LTD
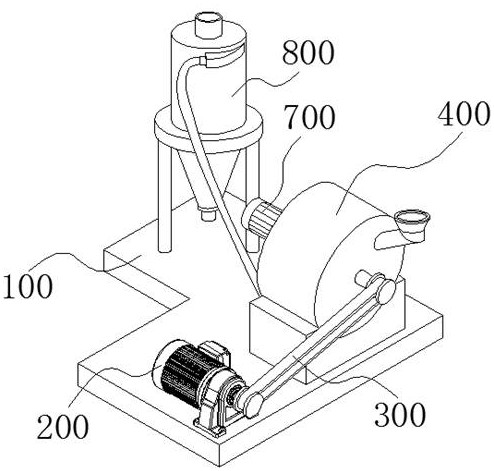
Lithium iron phosphate battery crushing device and crushing method
PendingCN114471840AImprove crushing qualityEliminate the problem that dead corners cannot be smashedWaste accumulators reclaimingGrain treatmentsLithium iron phosphateStructural engineering
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
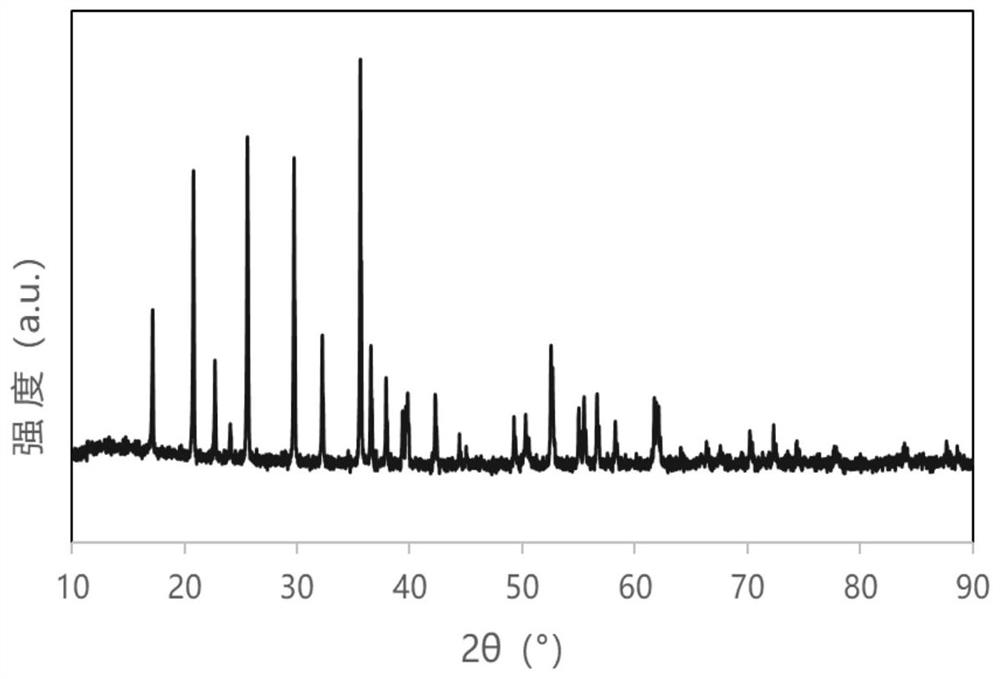
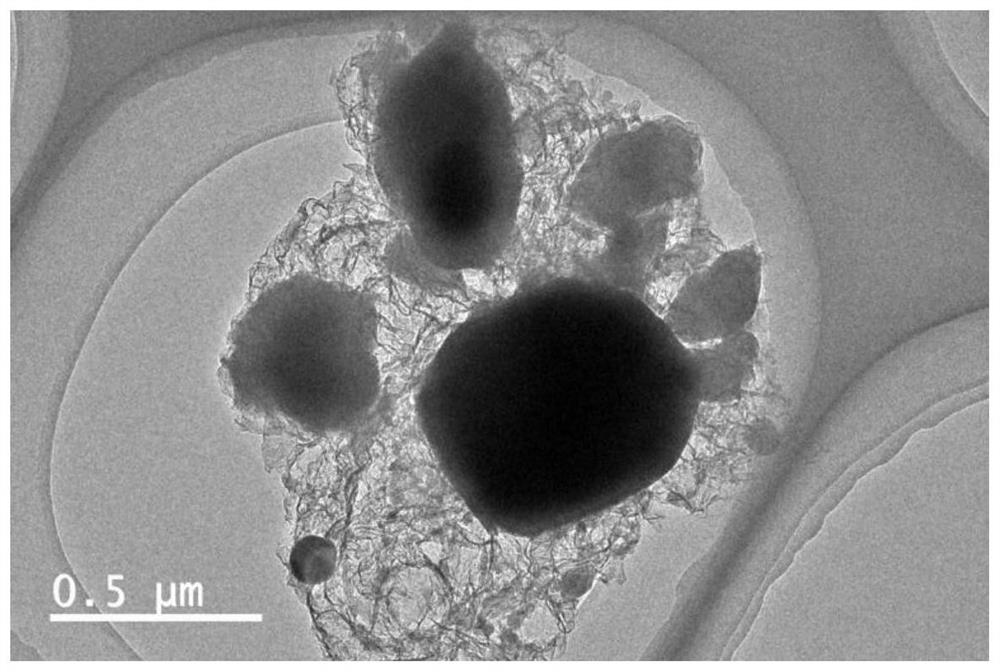
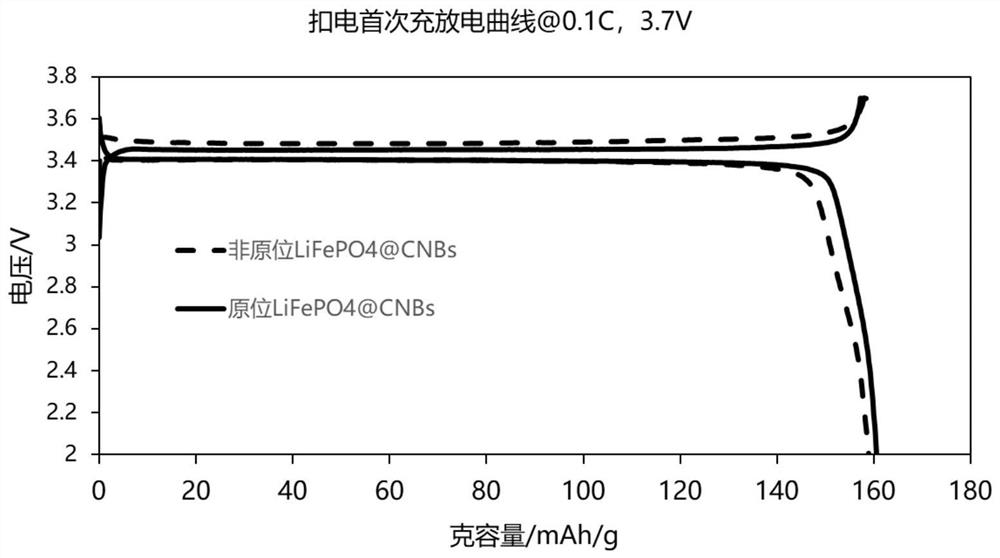
Lithium iron phosphate/carbon nanobelt composite material, preparation method and lithium ion battery
PendingCN114314554AImproved magnification performanceImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesLithium iron phosphatePhysical chemistry
Owner:SUNWODA ELECTRIC VEHICLE BATTERY CO LTD
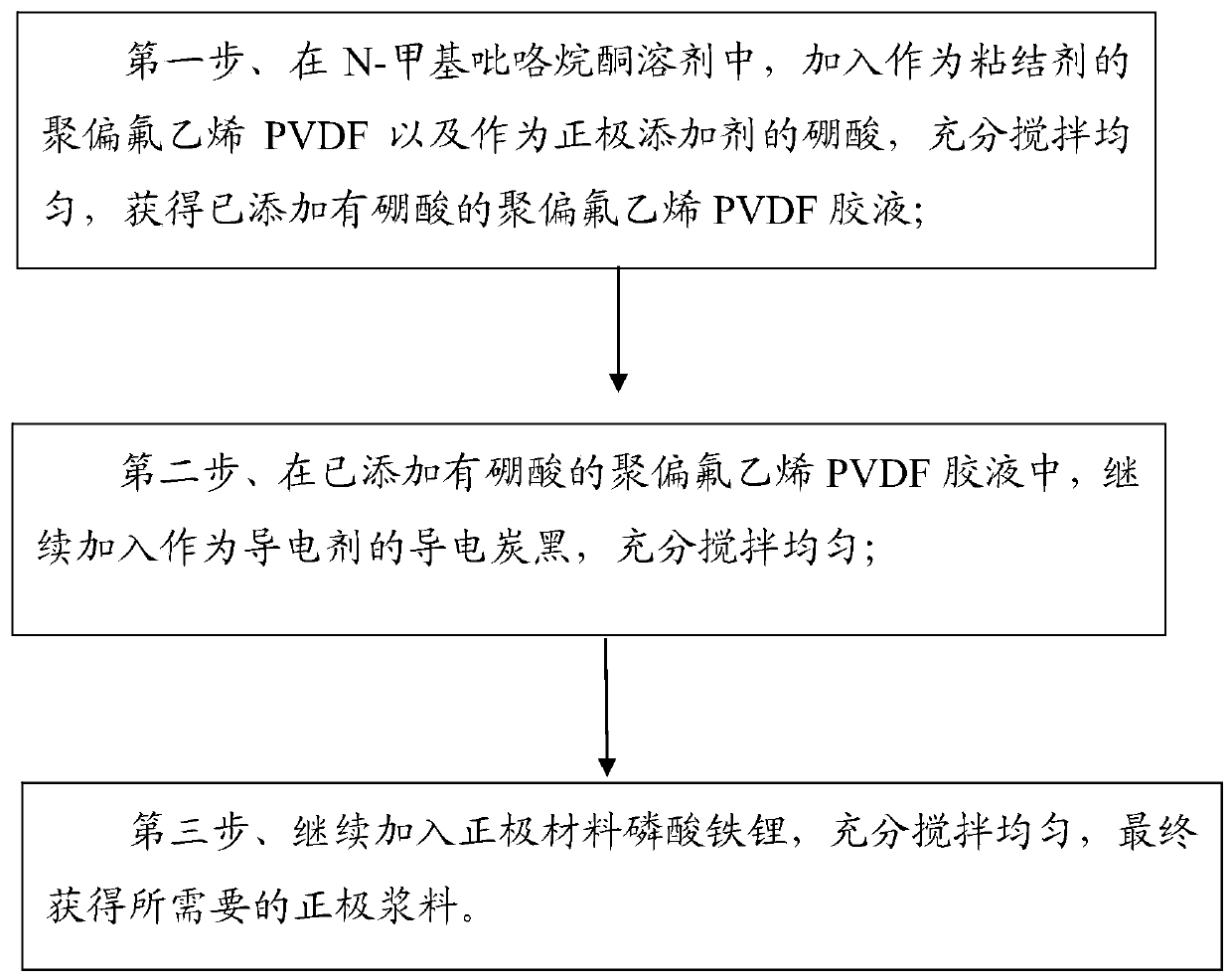
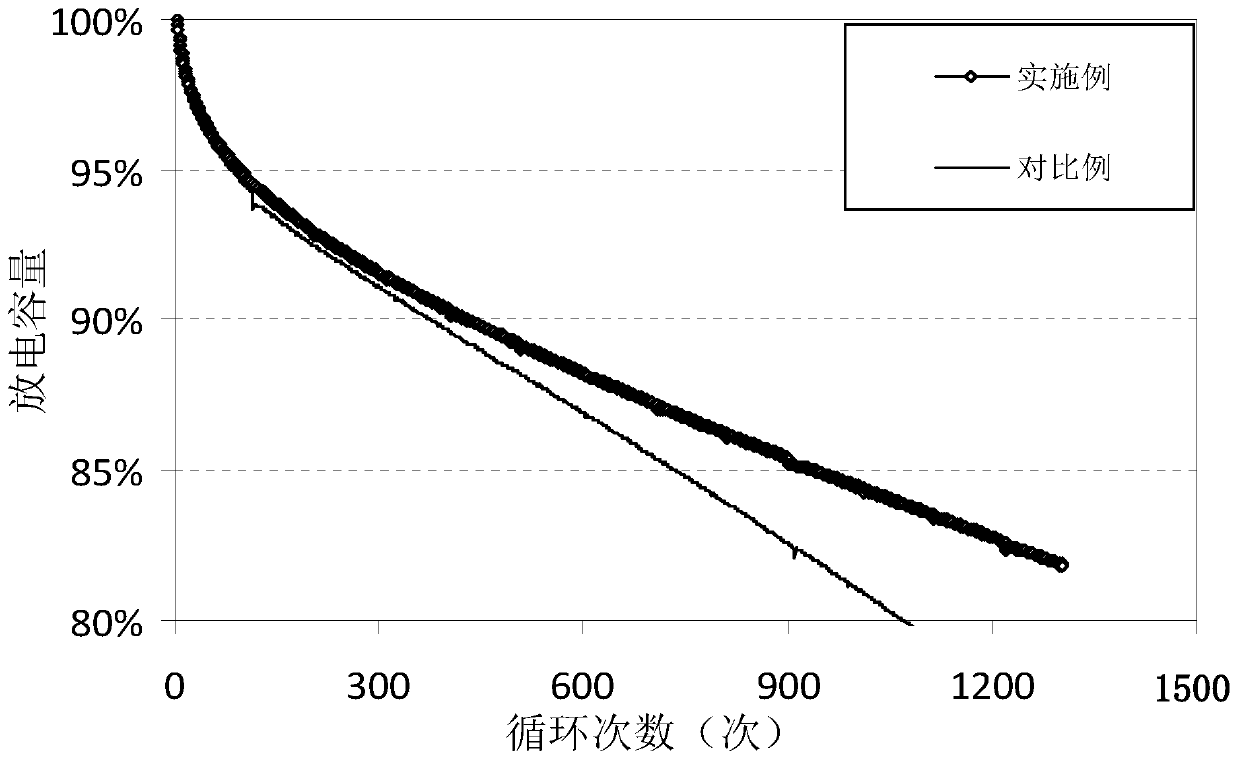
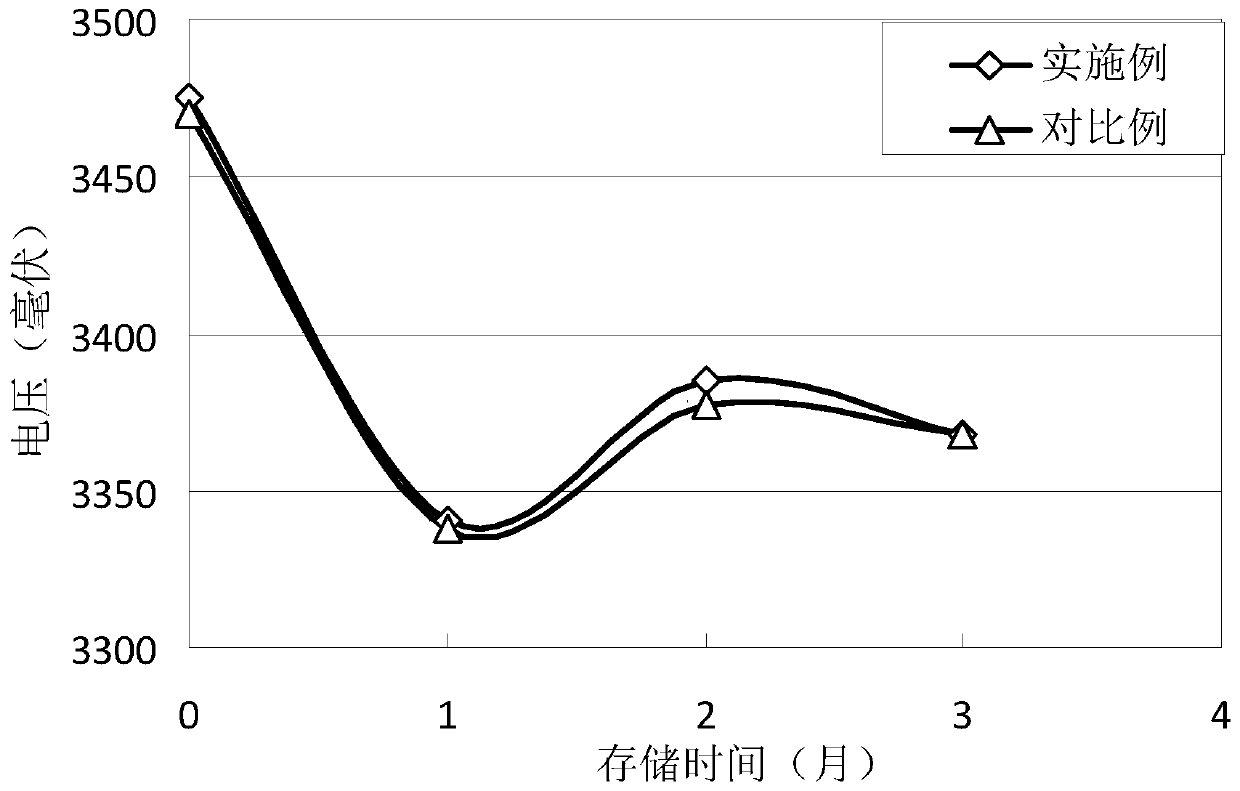
Positive electrode slurry and preparation method thereof, positive plate and lithium iron phosphate battery
InactiveCN110943218AImprove high temperature circulationEasy to storeElectrode manufacturing processesLi-accumulatorsSolid componentPyrrolidinones
Owner:TIANJIN LISHEN BATTERY
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap