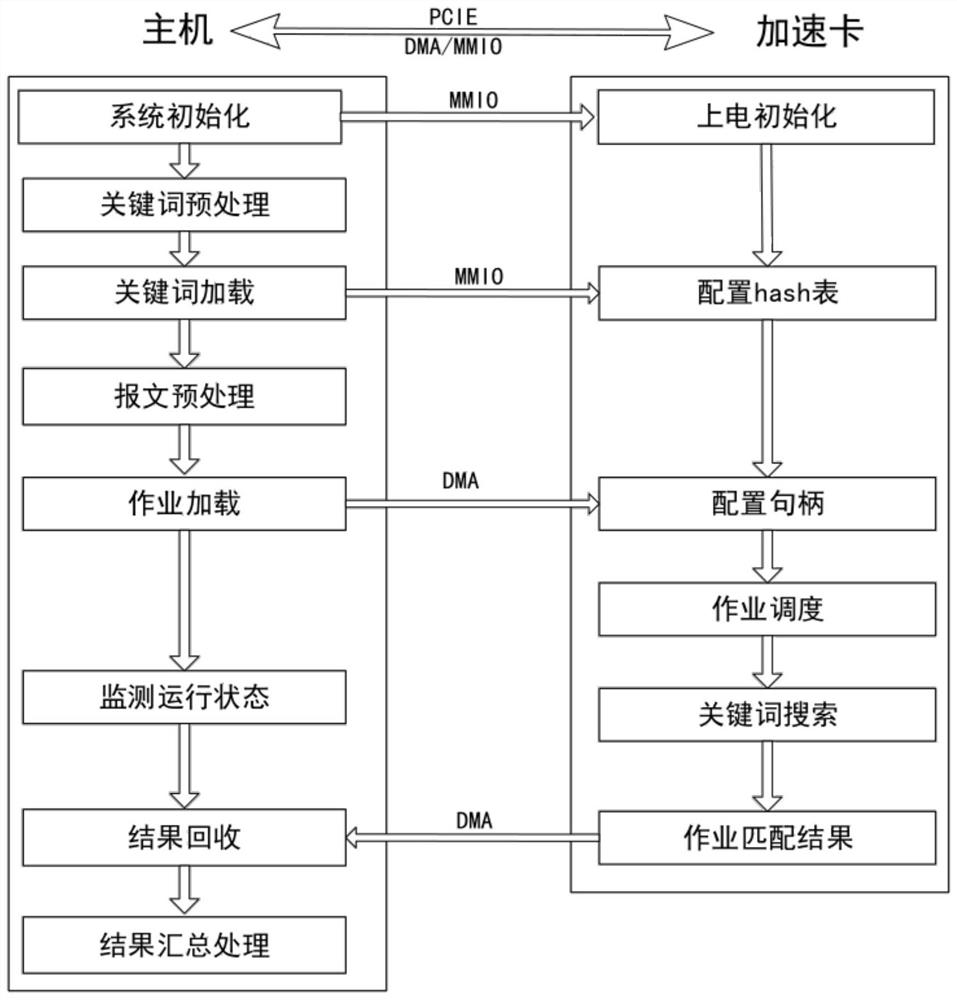
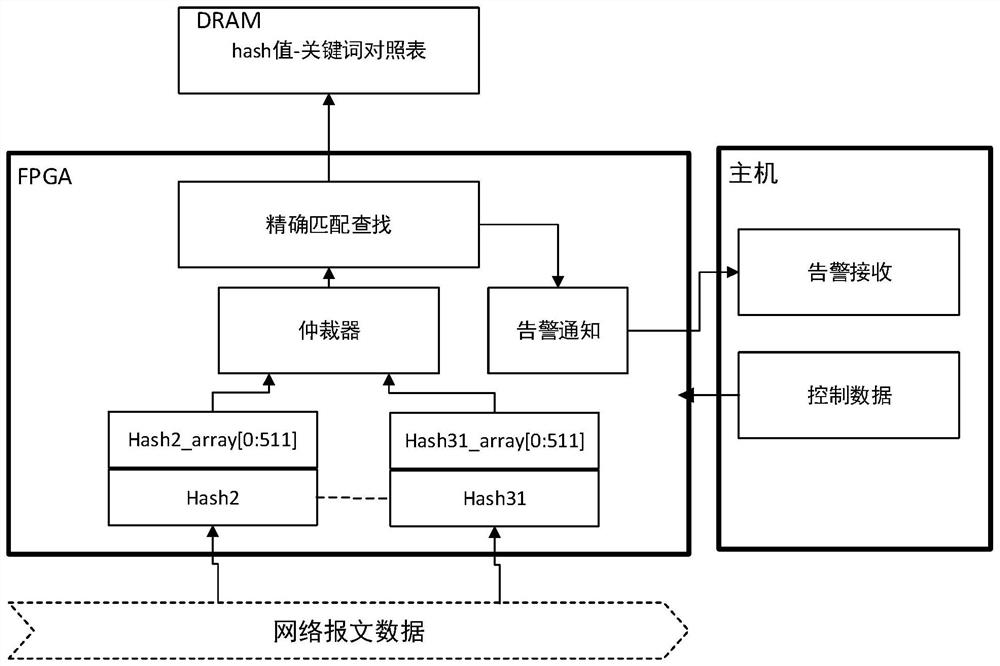
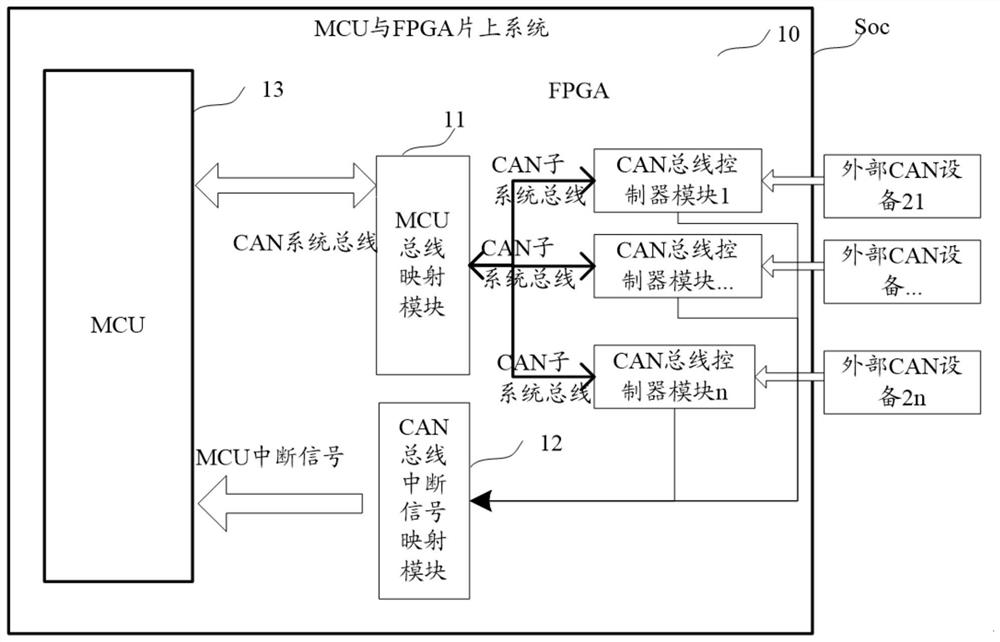
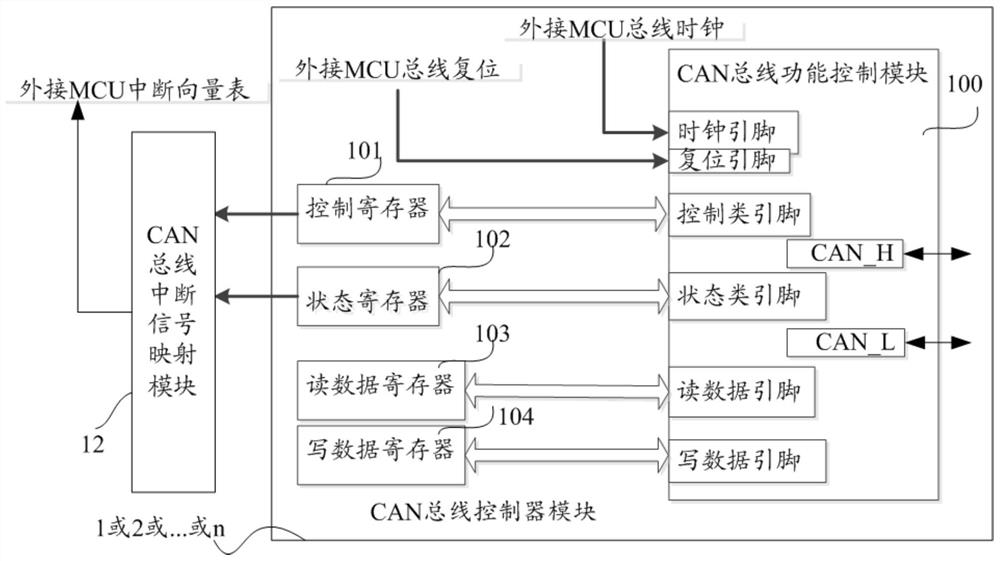
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
15 results about "Field-programmable gate array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturing – hence the term "field-programmable". The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language (HDL), similar to that used for an Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC). Circuit diagrams were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation tools.
Method to match input and output timestamps in a video encoder and advertisement inserter
InactiveUS20130083859A1Color television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionComputer graphics (images)Video processing
A method, a video processing system, and an electronic device are disclosed. A video transcoder may decode a compressed video data frame creating a decoded video data frame. The video transcoder may embed a network presentation timestamp in the decoded video data frame. The video transcoder may re-encode the decoded video data frame creating a transcoded video data frame. A field programmable gate array may compare the network presentation timestamp with a transcoder presentation timestamp to determine a timestamp offset.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
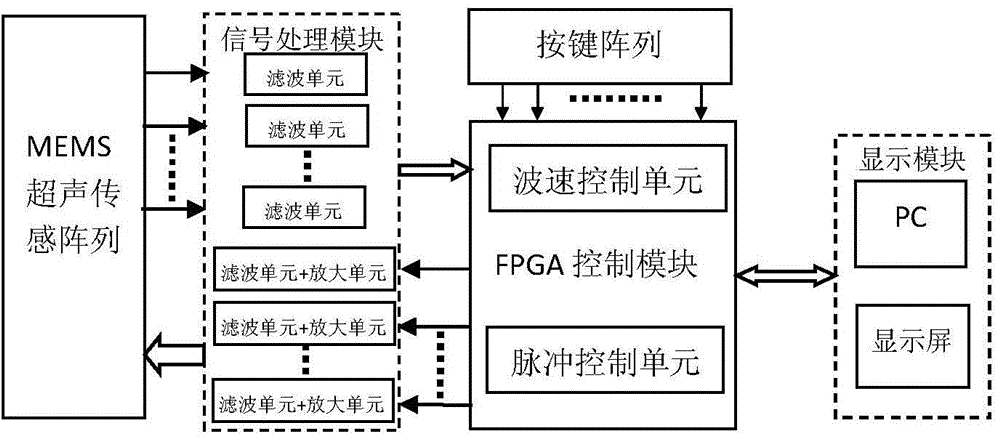
Ultrasonic phased array detector with low power consumption and capability of transforming styles of arrays
InactiveCN104820023AEasy to exploreGood choiceMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesHardware structureUltrasonic sensor
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
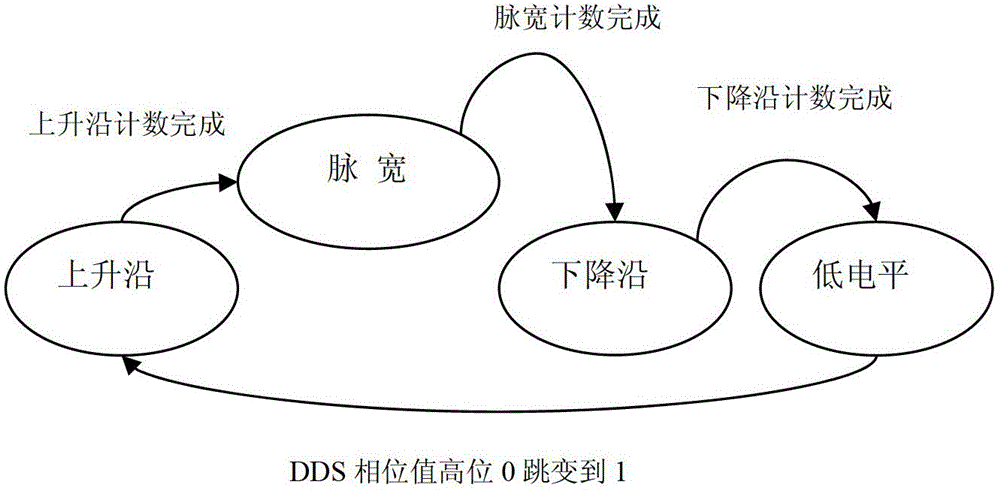
Wide-dynamic high-accuracy and edge time adjustable impulse wave producing method
ActiveCN102723931ASimplify complexityLower slew rateElectric pulse generatorWave shapePulse wave
Owner:UNI TREND TECH (CHINA) CO LTD
Method for processing consistency of sum-difference channel signal transmission delays through automatic calibration
InactiveCN102163980AMonitor shows calibration resultsTo achieve the purpose of delay difference calibrationBaseband system detailsDigital signal processingPeak value
The invention provides a method for processing the consistency of sum-difference channel through automatic calibration in a double-channel monopulse mechanism, and when the method is applied to the process of extracting angular error signals by using a sum-difference cross-correlation algorithm, the peak values of sum and difference signals subjected to cross-correlation can be improved effectively, thereby obtaining the maximum angular error detection sensitivity. The method is implemented by the technical scheme which comprises the following steps: in a digital signal processing module in a field-programmable gate array (FPGA) chip, inputting sum signals by a memory (first in first out FIFO1) controlled by a high-speed system clock, and inputting difference signals by a memory (FIFO2) controlled by another high-speed system clock; in a digital signal processor (DSP) chip, designing a logic control program for the whole phase calibration process, wherein the logic control program is used for receiving a phase calibration command issued by application software and controlling the read-write retardation change of the FIFO1 and the FIFO2; and through combining the DSP program with a position (pitching) phase shifter, automatically organizing a process to complete the calibration on sum-difference channel delays, thereby calibrating the sum-difference channel delays to be consistent.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
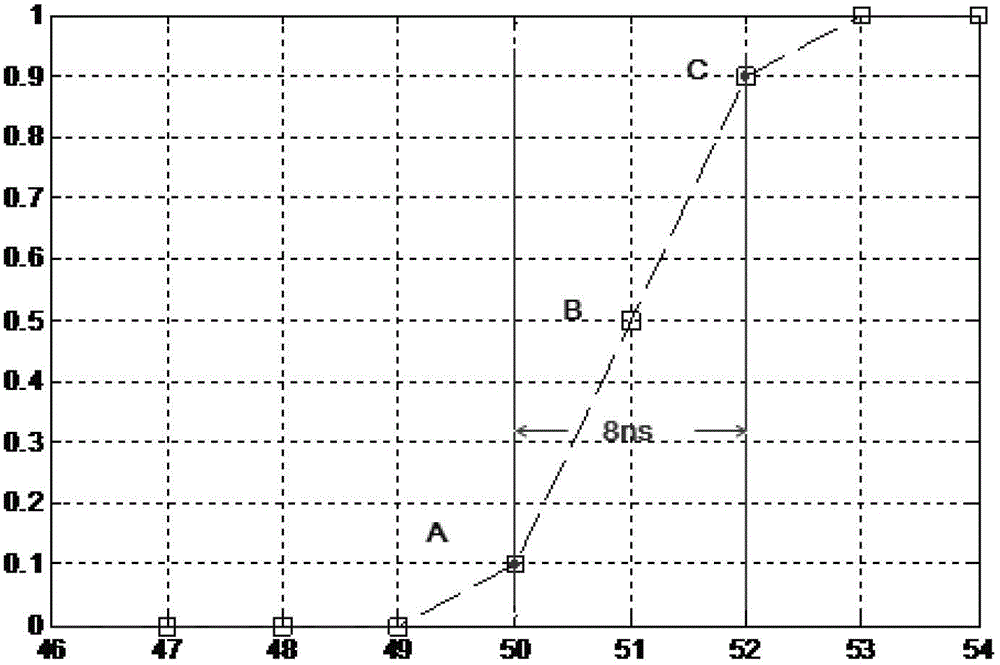
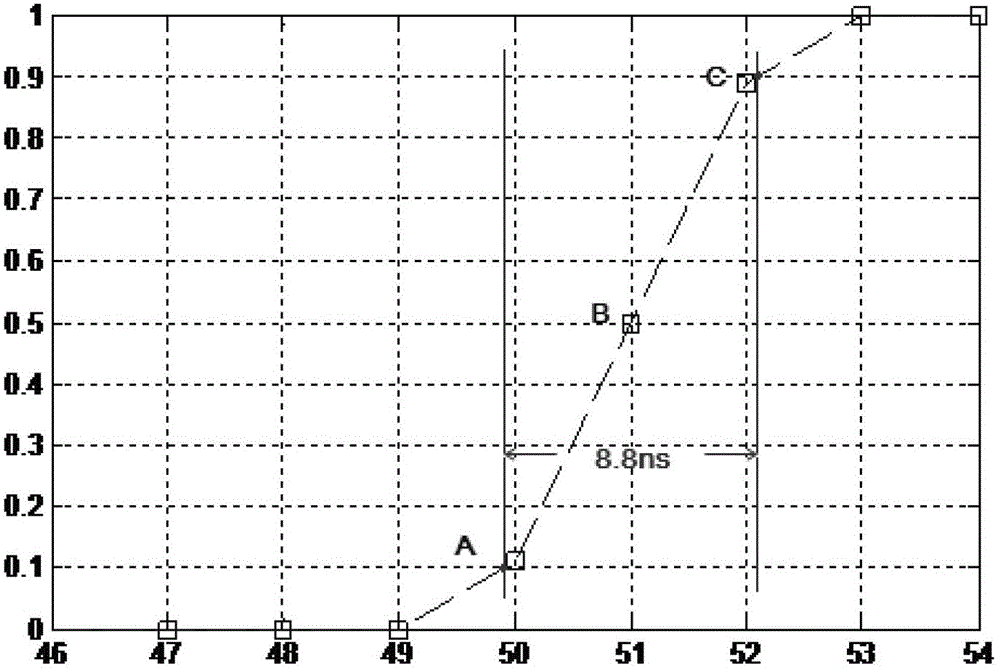
Method, device and frequency meter for measuring pulse width
ActiveCN103176059AAvoid measurement errorsPulse characteristics measurementsFrequency meterField-programmable gate array
The embodiment of the invention provides a method, a device, and a frequency meter which are used for measuring a pulse width. The method for measuring the pulse width includes: utilizing a to-be-measured signal which is delayed by a local standard clock to sample a front end error and a rear end error between an original signal to be measured and the to-be-measured signal which is delayed by a local standard clock; utilizing the local standard clock to record a high level time value of the original signal to be measured; and utilizing the sum of the time value and the front end error to subtract the rear end error to obtain the pulse width of the original signal to be measured. The method, the device, and the frequency meter which are used for measuring the pulse width enables the front end error and the rear end error to be directly obtained during the pulse width measuring process and utilize the carry chain resource inside the FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array), so that the measuring error caused by wiring delay is avoided and the accurate measurement of the pulse width is achieved.
Owner:RIGOL
Position sensor-free control technology for four-phase doubly salient motor
InactiveCN102904502ASolve the problem of high terminal voltage THD valueGuaranteed sineSingle motor speed/torque controlElectronic commutatorsTerminal voltageEngineering
The invention discloses a position sensor-free control method for a four-phase doubly salient motor. During electric running of the four-phase doubly salient motor, counter potential vectors differ from each other by 90 degrees in sequence in a d-q coordinate system. The control method comprises the following steps of: partitioning N (N is a natural number of more than 2) rotating speed ranges for designing wave filters of corresponding cut-off frequencies, only acquiring the terminal voltages of any two adjacent phases, entering a subtractor for removing direct current bias, judging the rotating speed of a motor according to a potential zero crossing point at a certain moment, deciding to enter a wave filter of a certain cut-off frequency through the rotating speed ranges, and acquiring the waveform of potential passing through the wave filter by using a DSP (Digital Signal Processor); establishing a phase shift angle comparison table of a wave filter which corresponds to a certain range specific to different rotating speeds in the range for performing DSP inquiry and corresponding accurate phase shift; and obtaining a practical phase change position through a zero crossing comparator, performing DSP computation, and outputting a driving signal to a switch tube by using an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) to complete phase change. The four-phase doubly salient motor can work in a wide rotating speed range.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Detection circuit capable of detecting a plurality of arbitrary-combination keys by low cost, and processing method
ActiveCN109298331AReduce manufacturing costProgramme controlComputer controlMicrocontrollerPush pull
Owner:郭玉森
Method for processing optical fiber I/O (input/ output) out-of-order frames based on field programmable gate array
Owner:无锡北方数据计算股份有限公司
Movement tracking device of human-computer interaction
InactiveCN103480137AEasy to operateHigh positioning accuracySensing record carriersSport apparatusDisplay deviceHuman–robot interaction
Owner:JIANGSU MEILUN IMAGING SYST
Integrated circuit with bit error test capability
InactiveUS20070159234A1Reduce the impact of the signalAffect performanceDigital circuit testingError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorApplication-specific integrated circuitField-programmable gate array
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Efficient keyword filtering method for FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
PendingCN114297368AFast searchReduce false alarm rateDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsComputer architectureEngineering
Owner:无锡宏创盛安科技有限公司
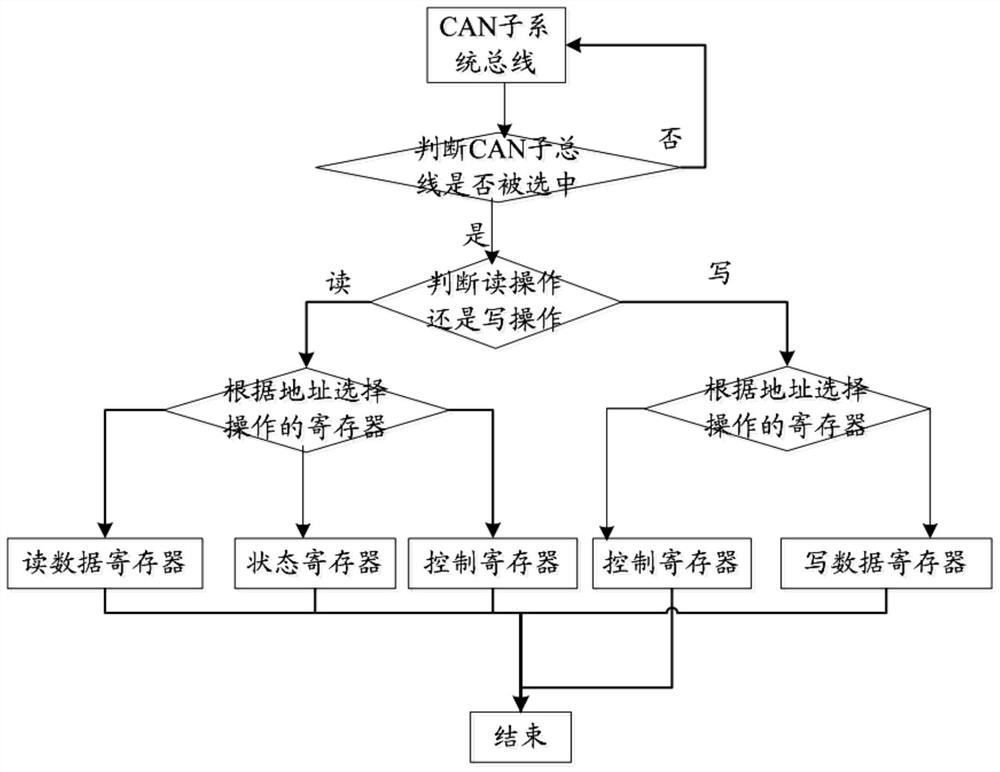
CAN bus communication control system and communication system
ActiveCN112039745AImprove scalabilityImprove acceleration performanceBus networksArea networkCommunications system
Owner:GOWIN SEMICON CORP LTD
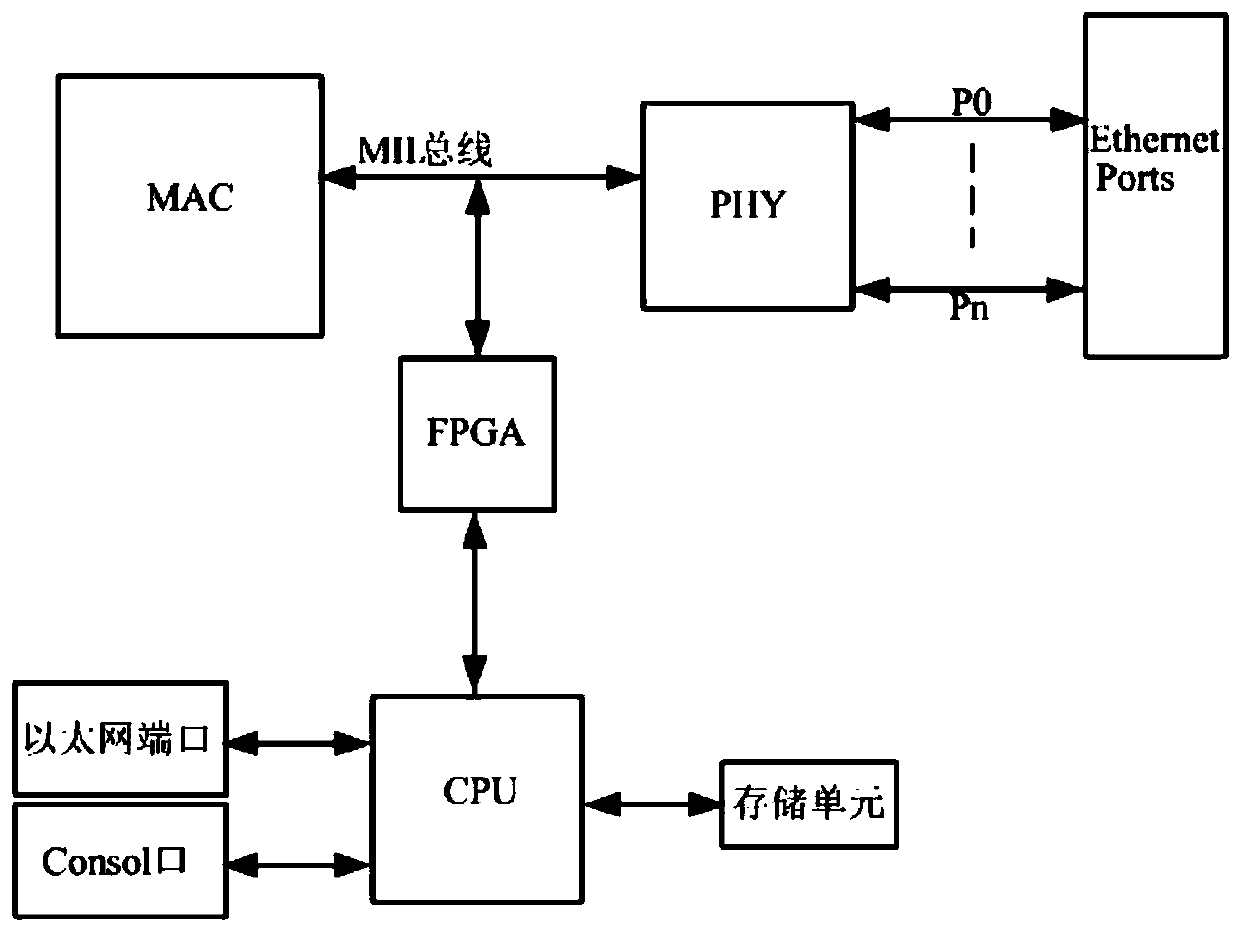
Method for acquiring, monitoring and analyzing Ethernet signal line speed
InactiveCN110430099AImprove diagnostic capabilitiesReduce maintenance costsData switching networksWire speedPhysical layer
Owner:深圳市三旺通信股份有限公司
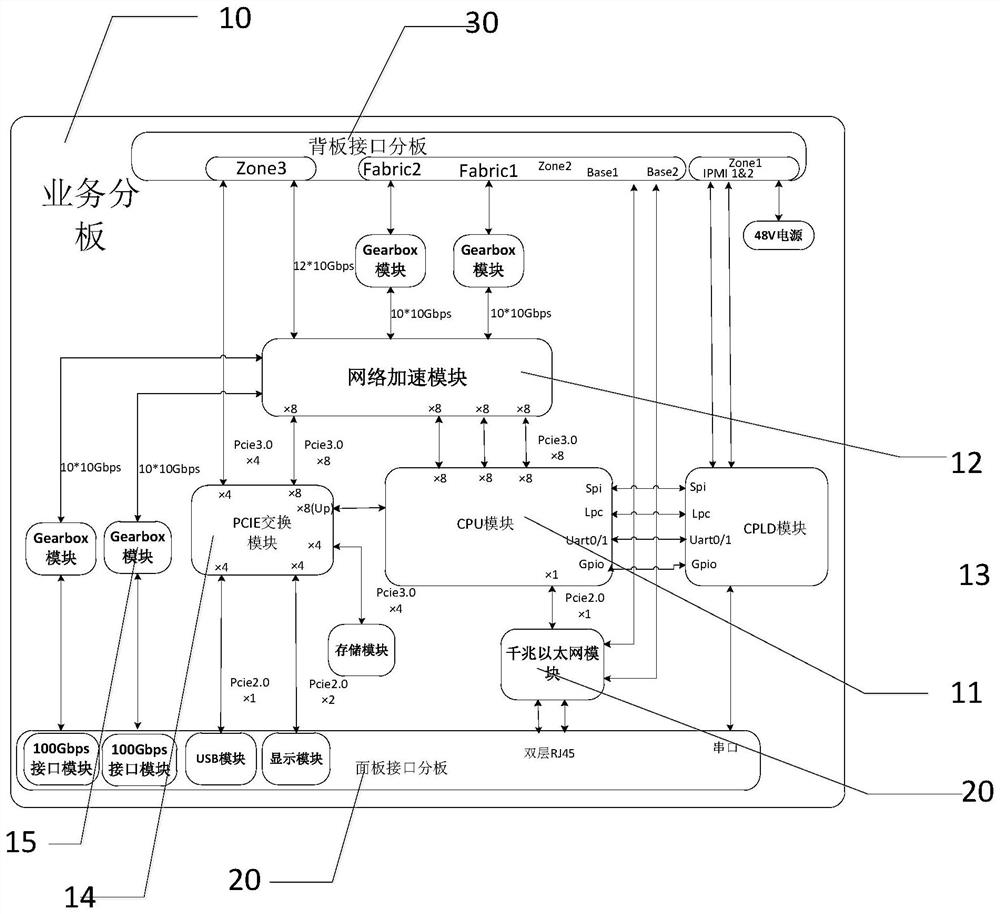
ATCA board card
PendingCN114116588AData switching detailsElectric digital data processingGigabit EthernetField-programmable gate array
Owner:HUNAN RONGTENG NETWORK TECH CO LTD
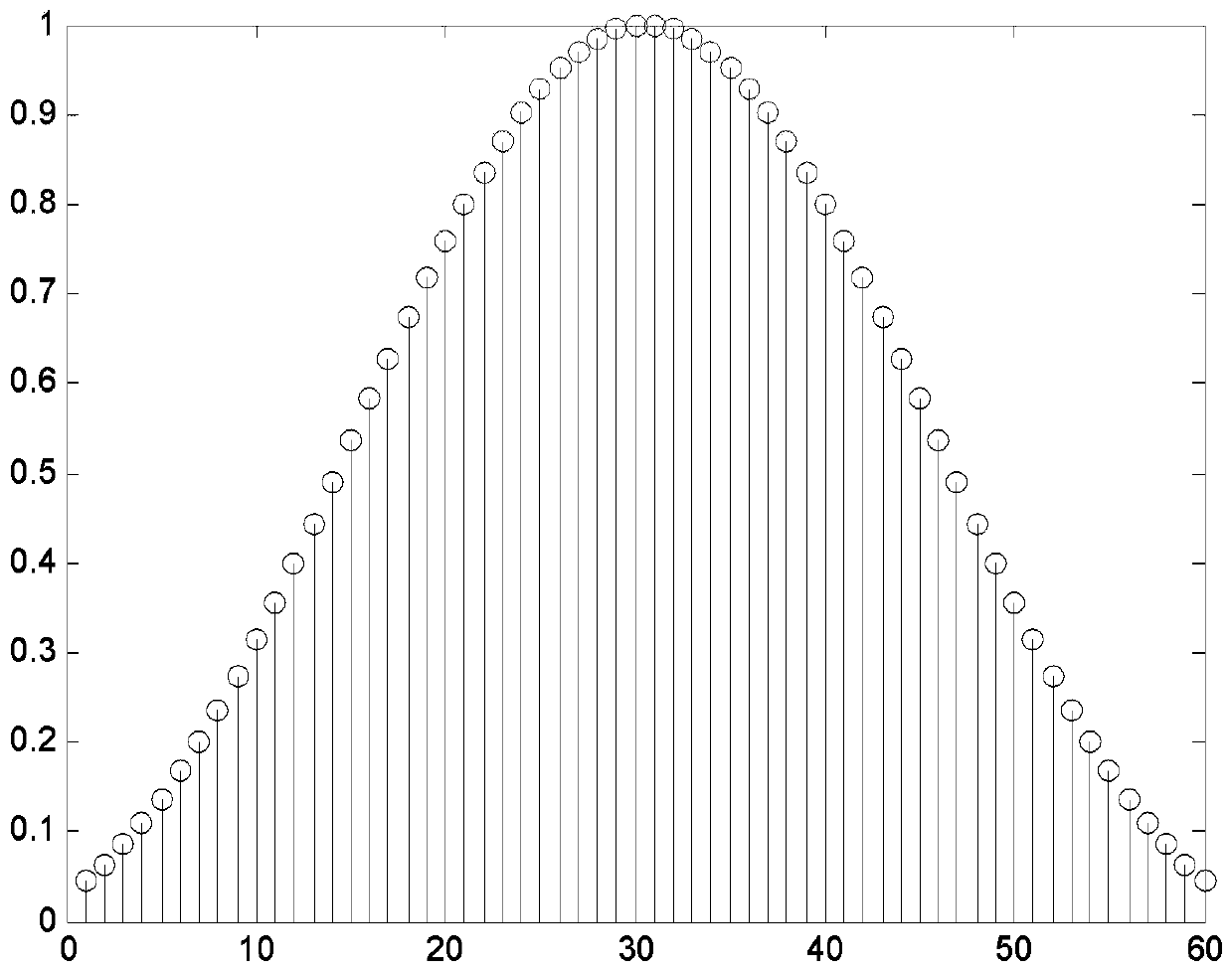
Dual-band spectrum data acquisition method and device
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap