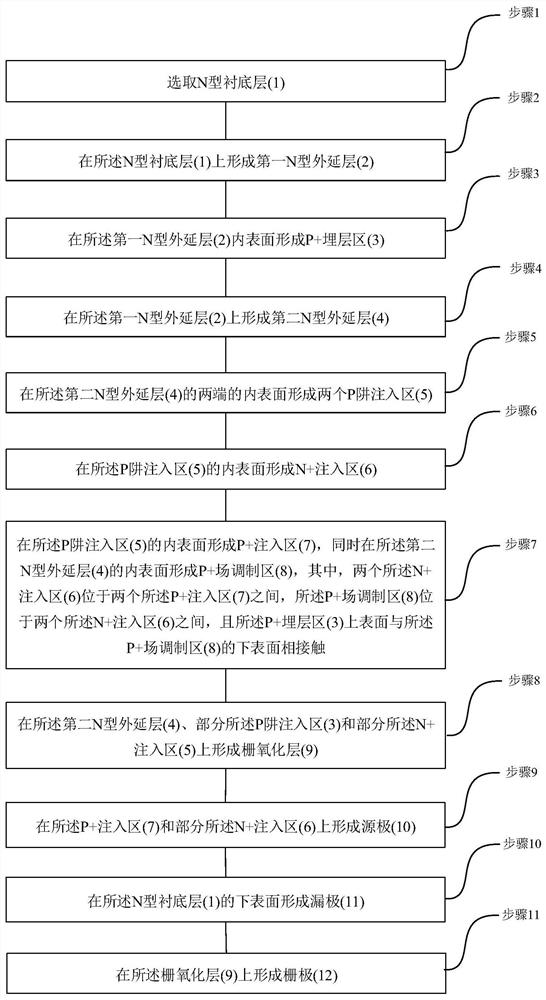
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
21 results about "MOSFET" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET), also known as the metal–oxide–silicon transistor (MOS transistor, or MOS), is a type of field-effect transistor that is fabricated by the controlled oxidation of a semiconductor, typically silicon. It has a covered gate, whose voltage determines the conductivity of the device. This ability to change conductivity with the amount of applied voltage can be used for amplifying or switching electronic signals. The MOSFET was invented by Egyptian engineer Mohamed M. Atalla and Korean engineer Dawon Kahng at Bell Labs in November 1959. It is the basic building block of modern electronics, and the most widely manufactured device in history, with an estimated total of 13 sextillion (1.3 × 10²²) MOSFETs manufactured between 1960 and 2018.
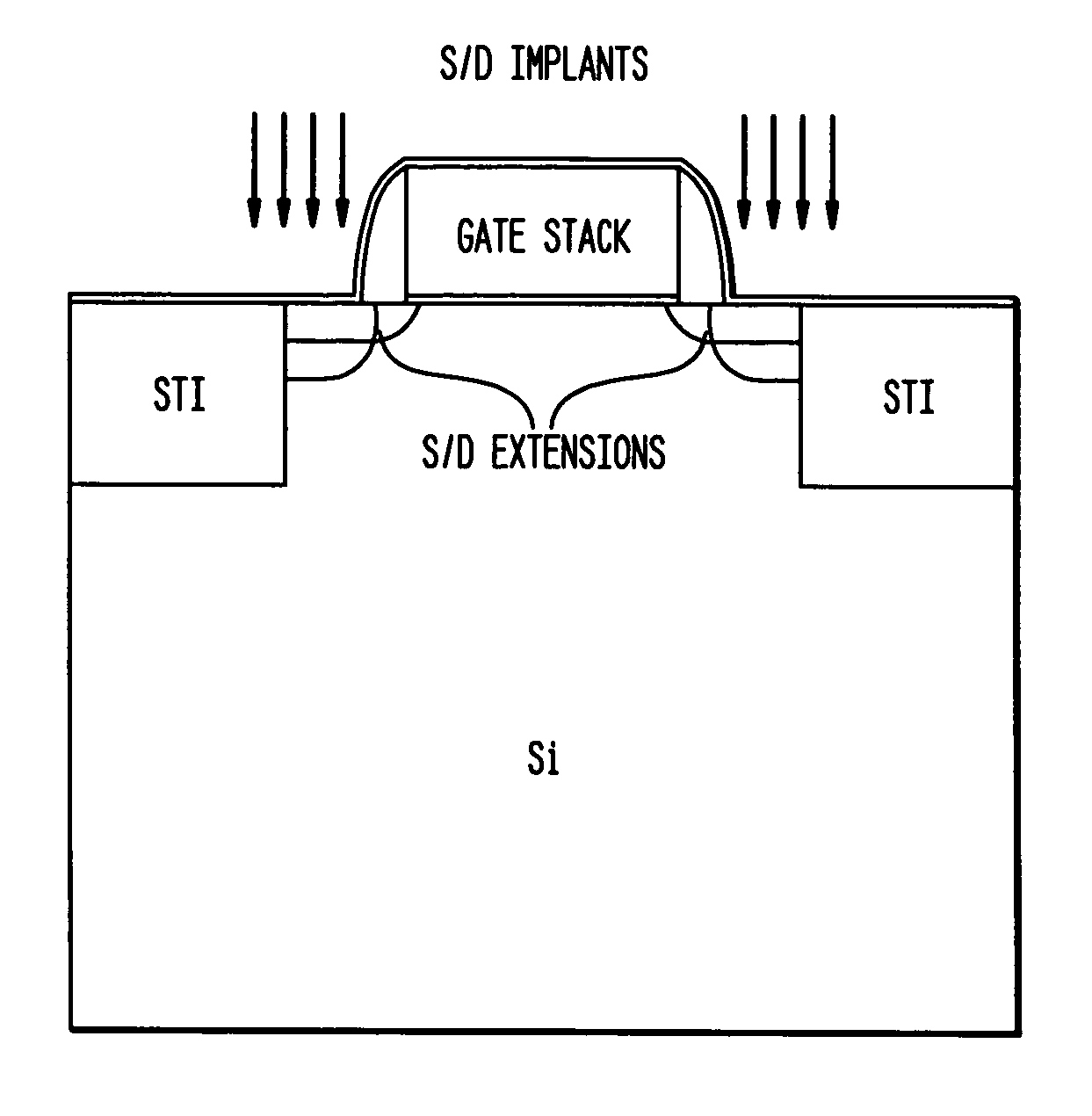
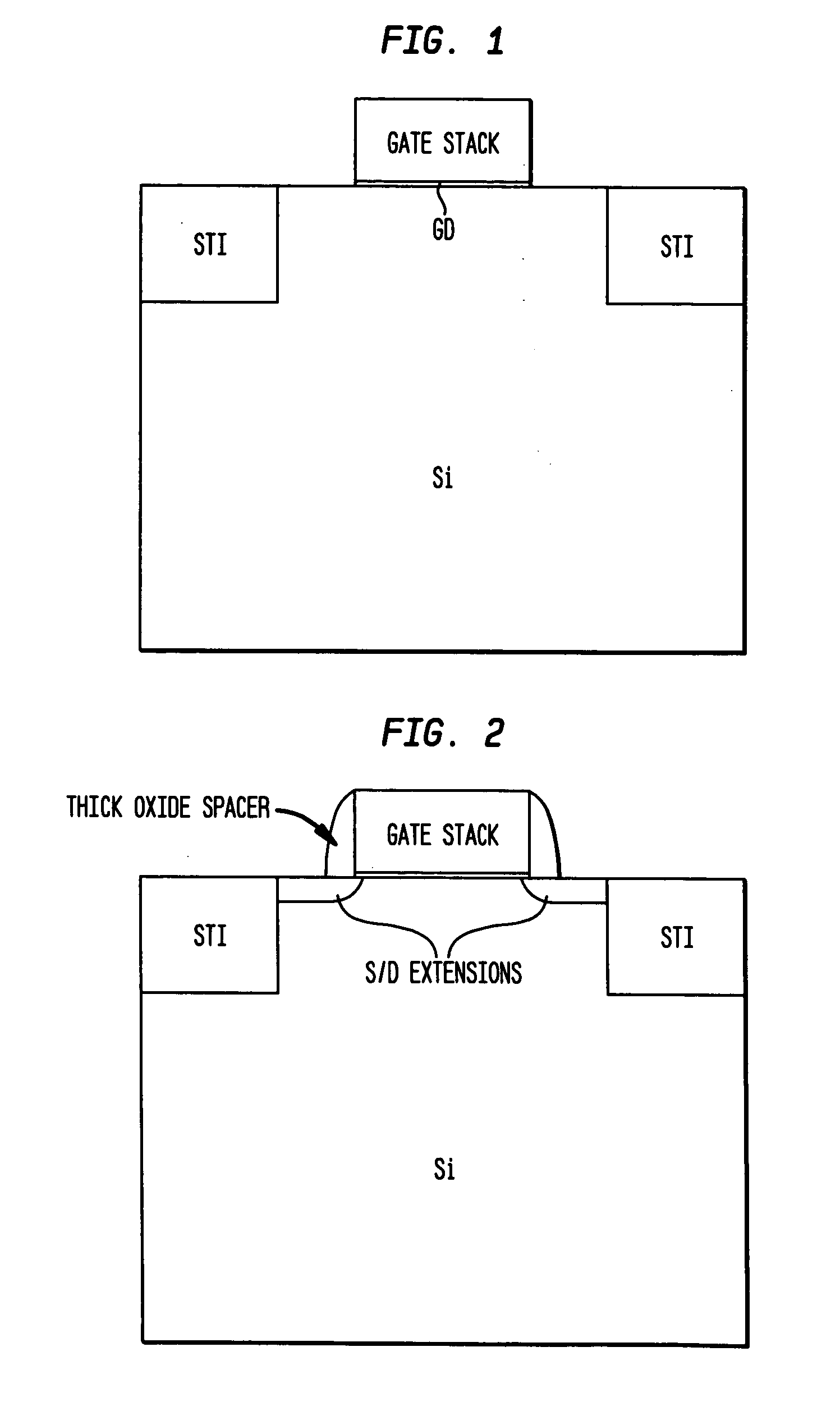
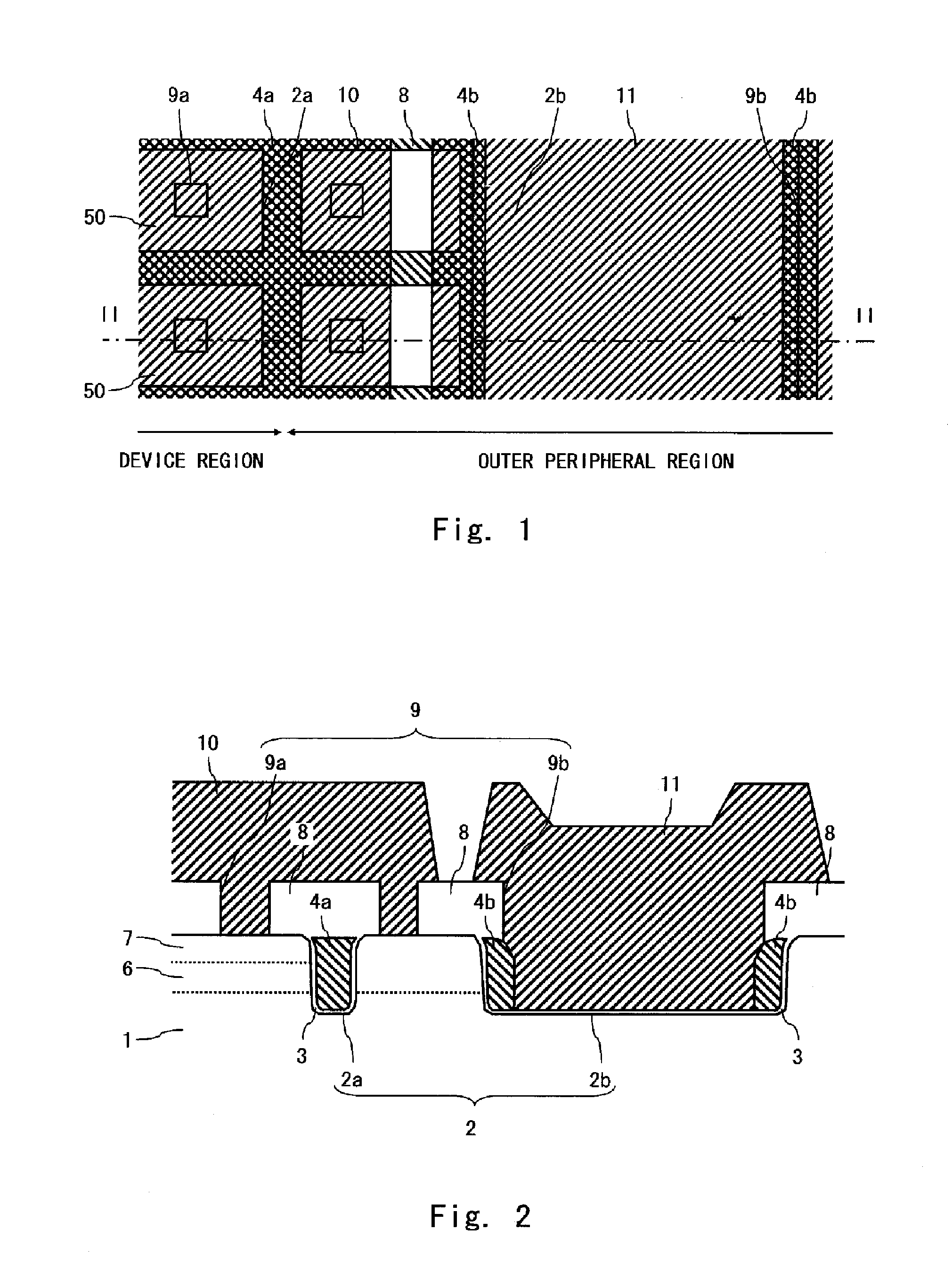
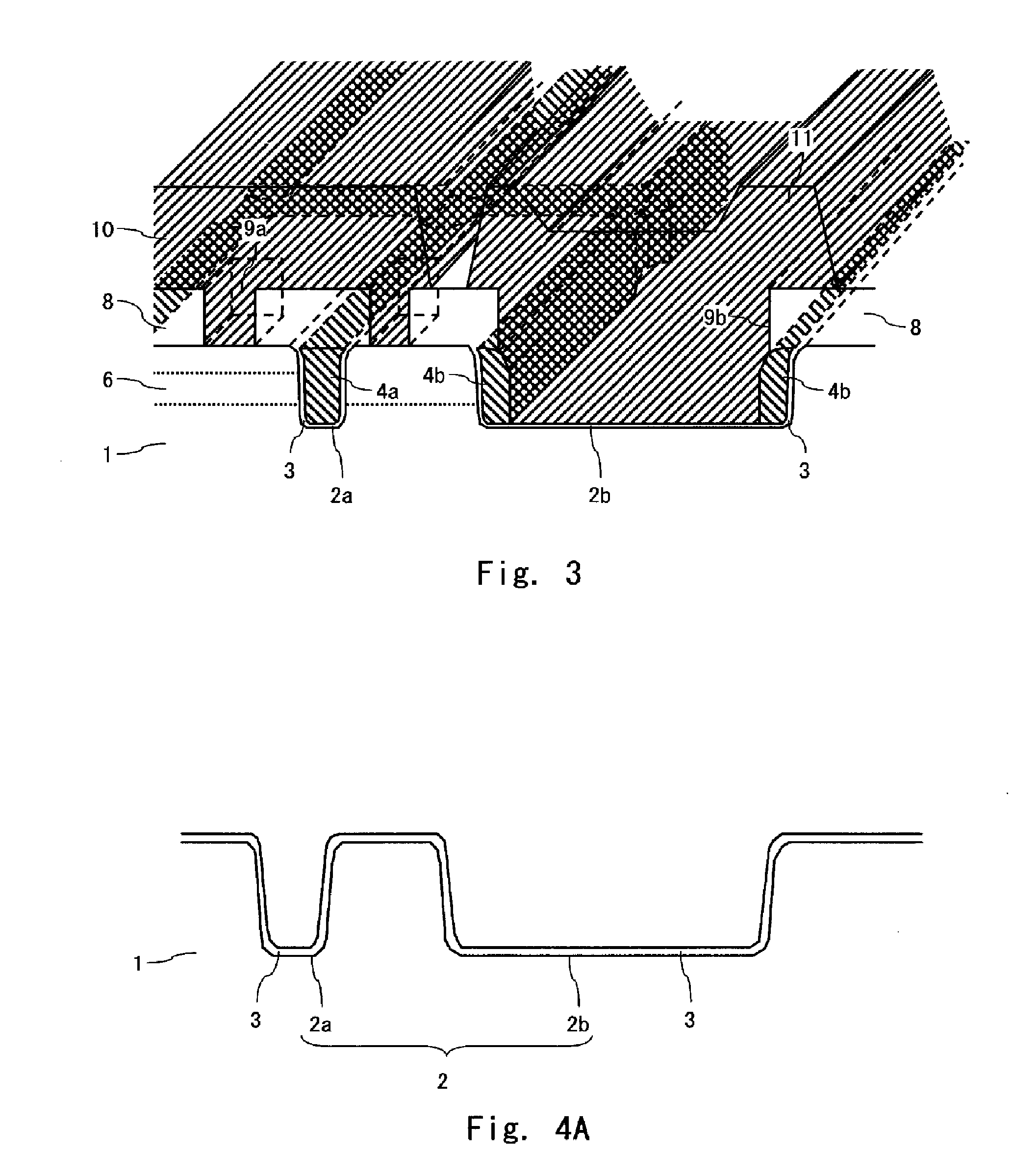
Low-K gate spacers by fluorine implantation
InactiveUS7227230B2Reduce capacitanceReduce Overlap CapacitanceTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETPhysics
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
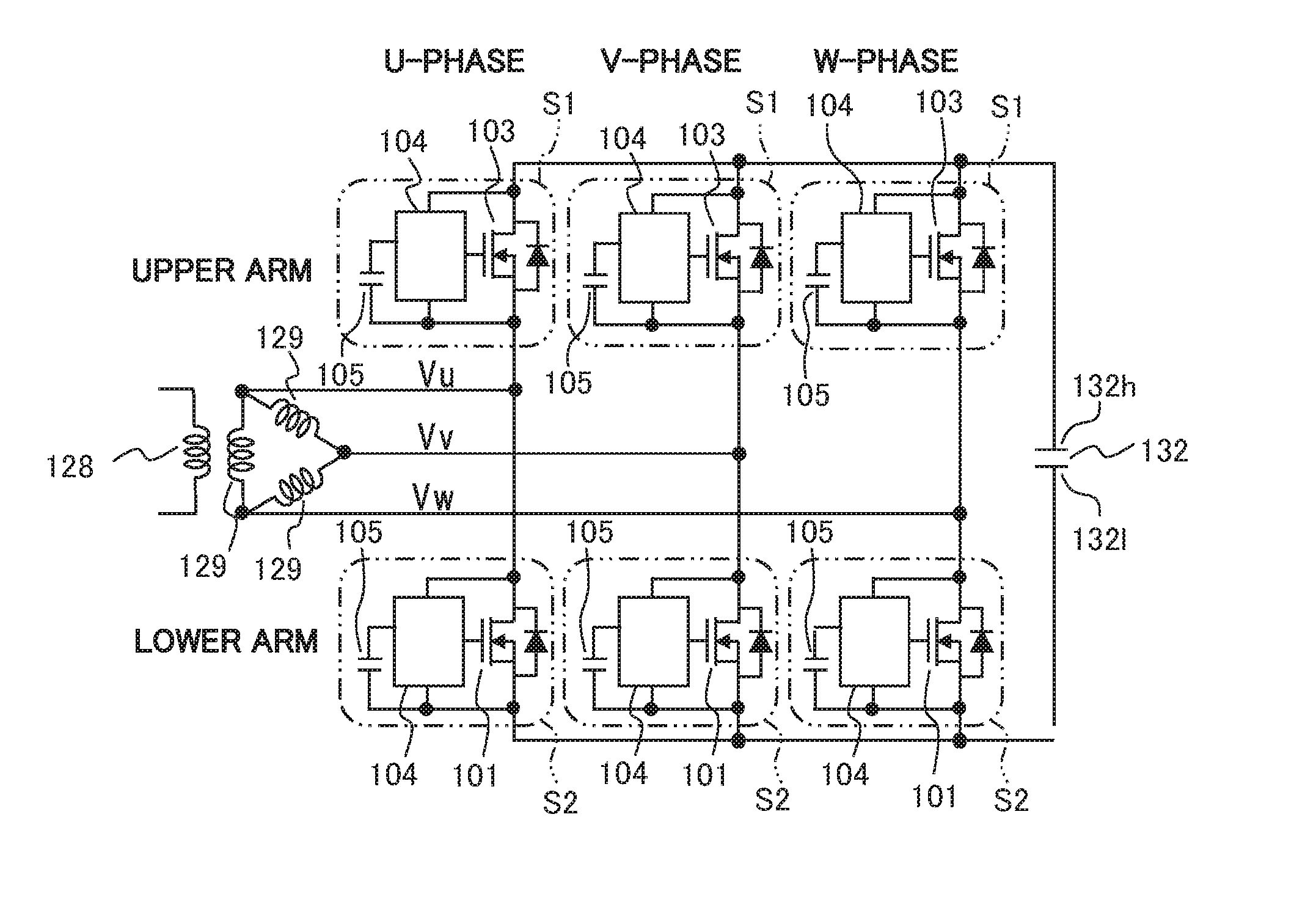
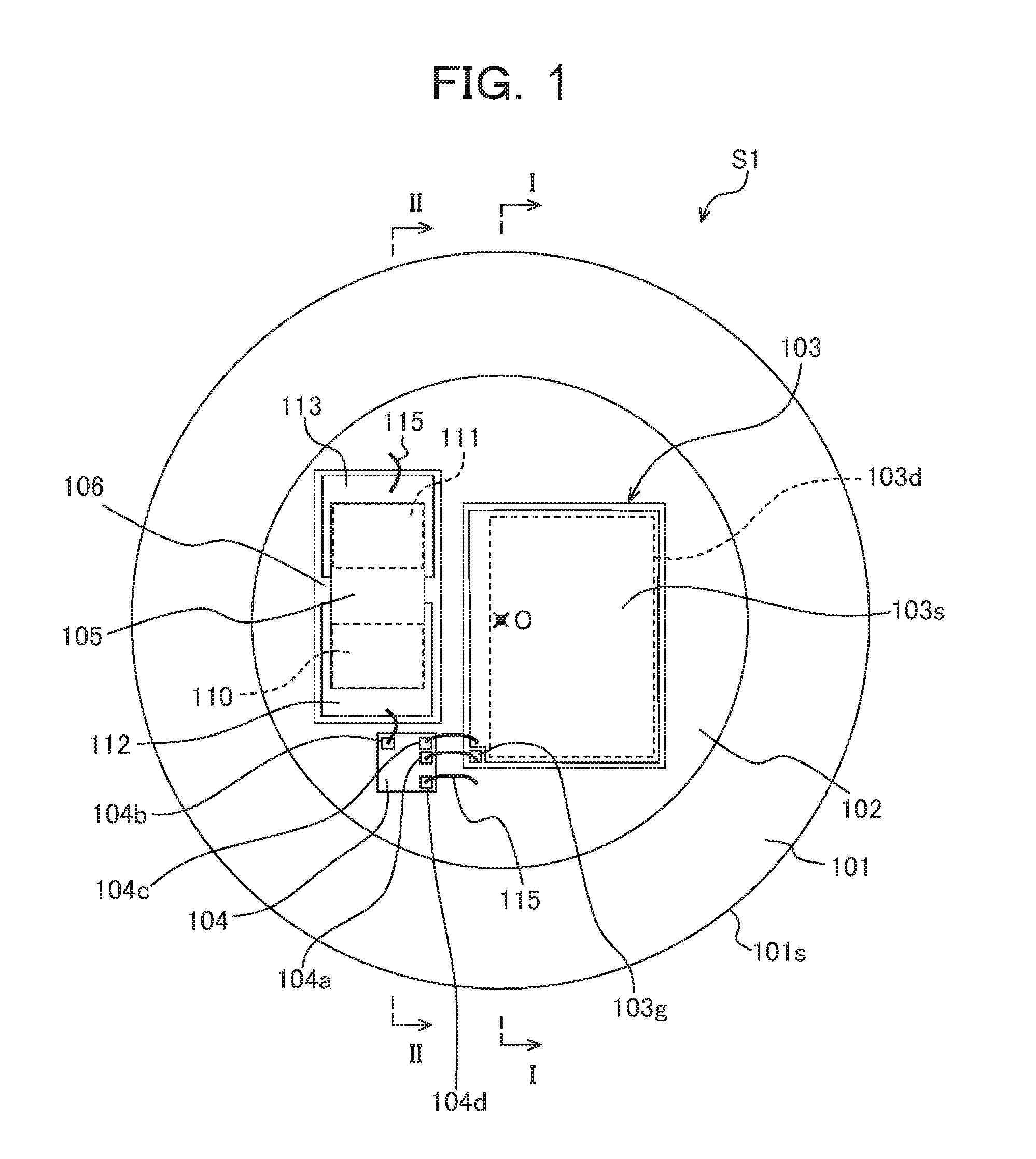
Semiconductor Device, and Alternator and Power Conversion Device Which Use Same
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
High frequency control of a semiconductor switch
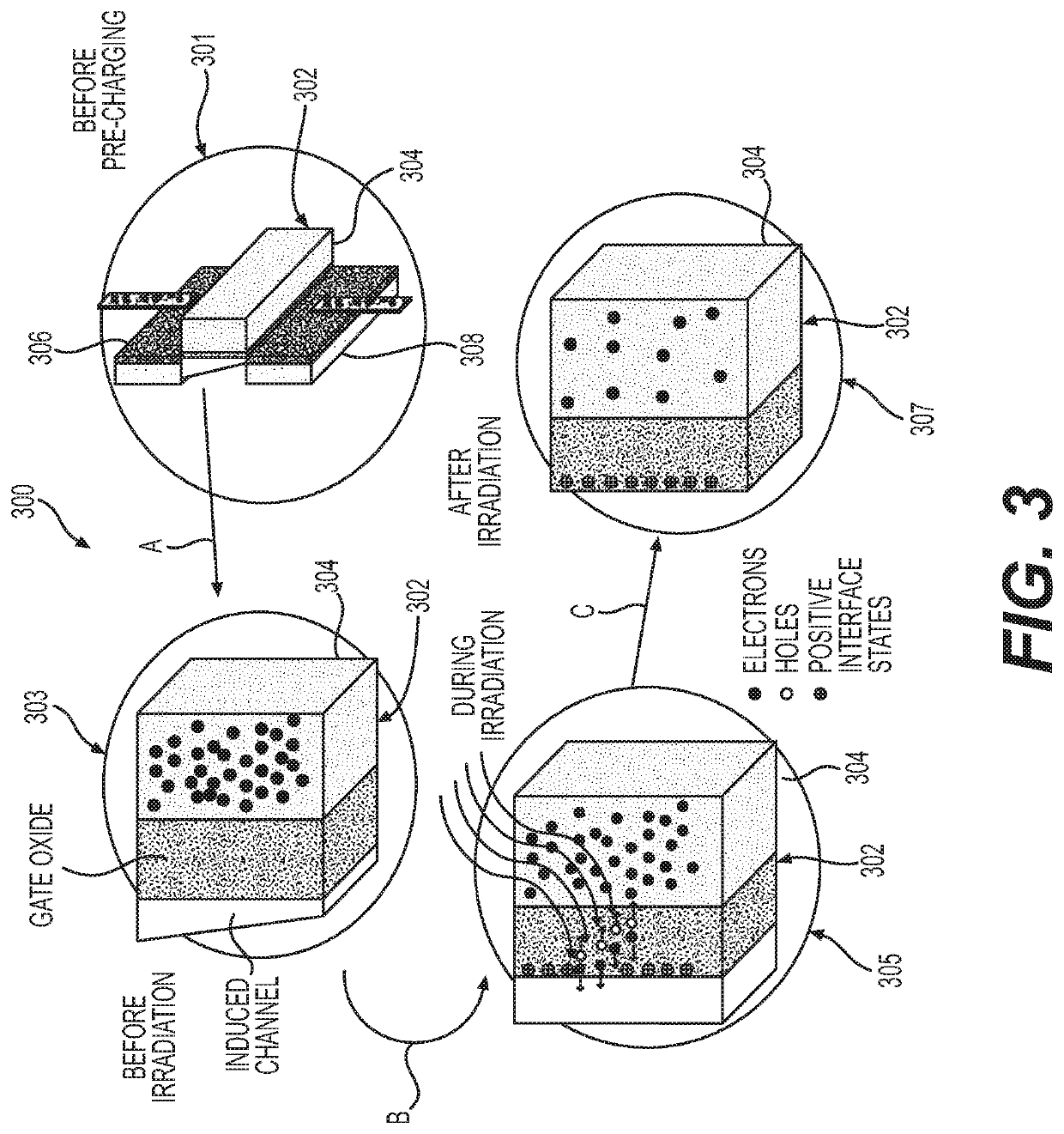
InactiveCN1849748AIncrease the switching frequencyFast driveTransistorElectronic switchingMOSFETPre-charge
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20100258863A1Low costSimplify wafer manufacturing processSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETSemiconductor
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Semiconductor device having electrostatic protection circuit
This invention discloses a semiconductor device including a first buffer MOSFET of a first conductivity type, a second buffer MOSFET of a second conductivity type, an ESD protection circuit, an external input terminal, and a control circuit. The external input terminal capacitively couples to a terminal to which a second potential is applied, and receives the first potential or second potential in a normal operation mode. The control circuit includes a prebuffer which controls the gates of the first and second buffer MOSFETs on the basis of the potential of the external input terminal in the normal operation mode and fixes the external input terminal to the second or first potential by capacitive coupling upon ESD surge application, thereby fixing the gate of the second buffer MOSFET to the second or first potential and turning off the second buffer MOSFET.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
RGB synchronous intelligent light string
ActiveCN108278566AColor effect switchingIncrease diversityLight source combinationsElectric circuit arrangementsMOSFETTransformer
The invention discloses an RGB synchronous intelligent light string. The RGB synchronous intelligent light string comprises an intelligent power supply, a controller, light strings and a main circuit,wherein the plurality of light strings are connected in parallel with the main circuit; the intelligent power supply is connected with the controller; the controller is connected with the main circuit; a 220 V voltage is accessed into one end of an IP44 plug; the other end of the plug is accessed into a resistance wire for current protection, a piezoresistor for voltage limiting control, a filterfor noise filtration and signal separation and a filtering circuit for high-frequency resistance and low-frequency passing; an output end of the filtering circuit is connected to an input end of an MOSFET and a DCDC transformer; the DCDC transformer outputs direct current of which the voltage is changed into a driver and an IRF; the IRF is connected with a program module, a remote control module,a WiFi module and a Bluetooth module; a signal output by the IRF passes through a driving module; the driving module and an output end of the DCDC transformer are connected to the input end of the MOSFET; and an output end of the MOSFET is connected to an end part of the main circuit. The RGB synchronous intelligent light string can simultaneously control the colors of the plurality of light strings to improve a decorative effect.
Owner:JIANGSU LEDCO LIGHTING TECH CO. LTD
Separately excited DC machine controller of electric automobile
InactiveCN103647486AReasonable structure layoutReduce volumeField or armature current controlCapacitanceMOSFET
Owner:TIANJIN QINGYUAN ELECTRIC VEHICLE
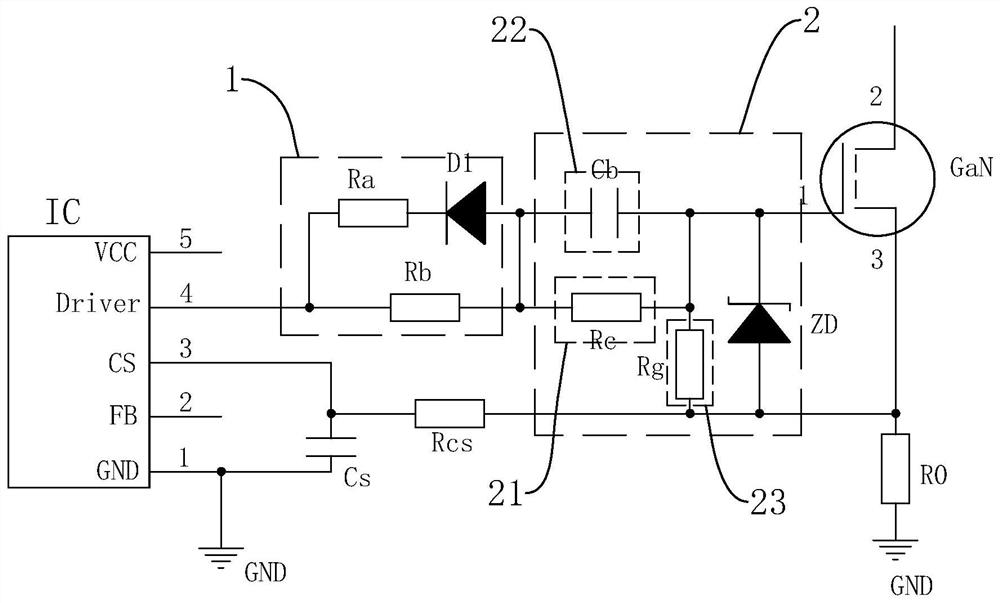
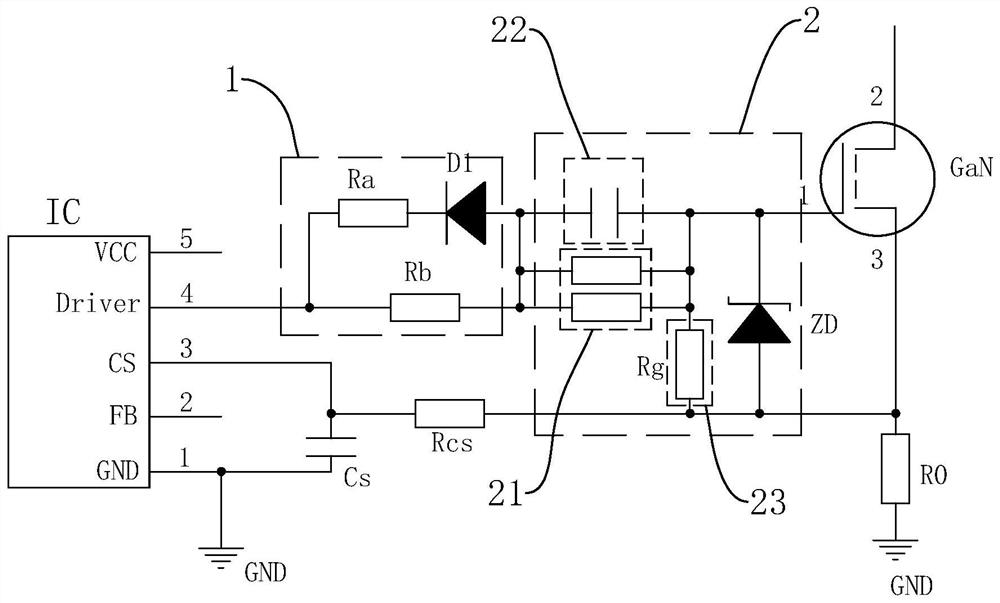
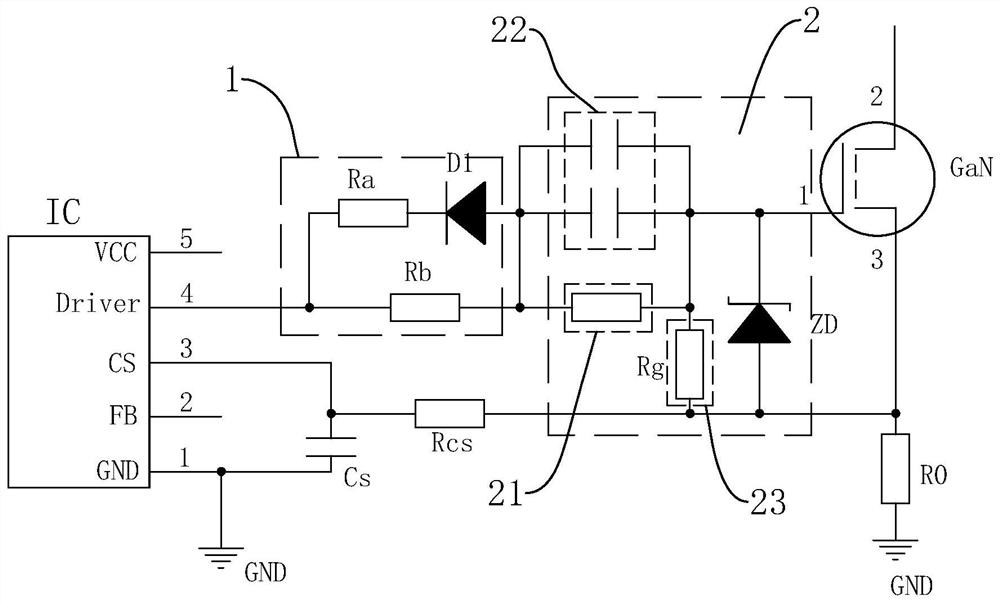
GaN compatible driving circuit
Owner:SHENZHEN FAHOLD ELECTRONICS CO LTD
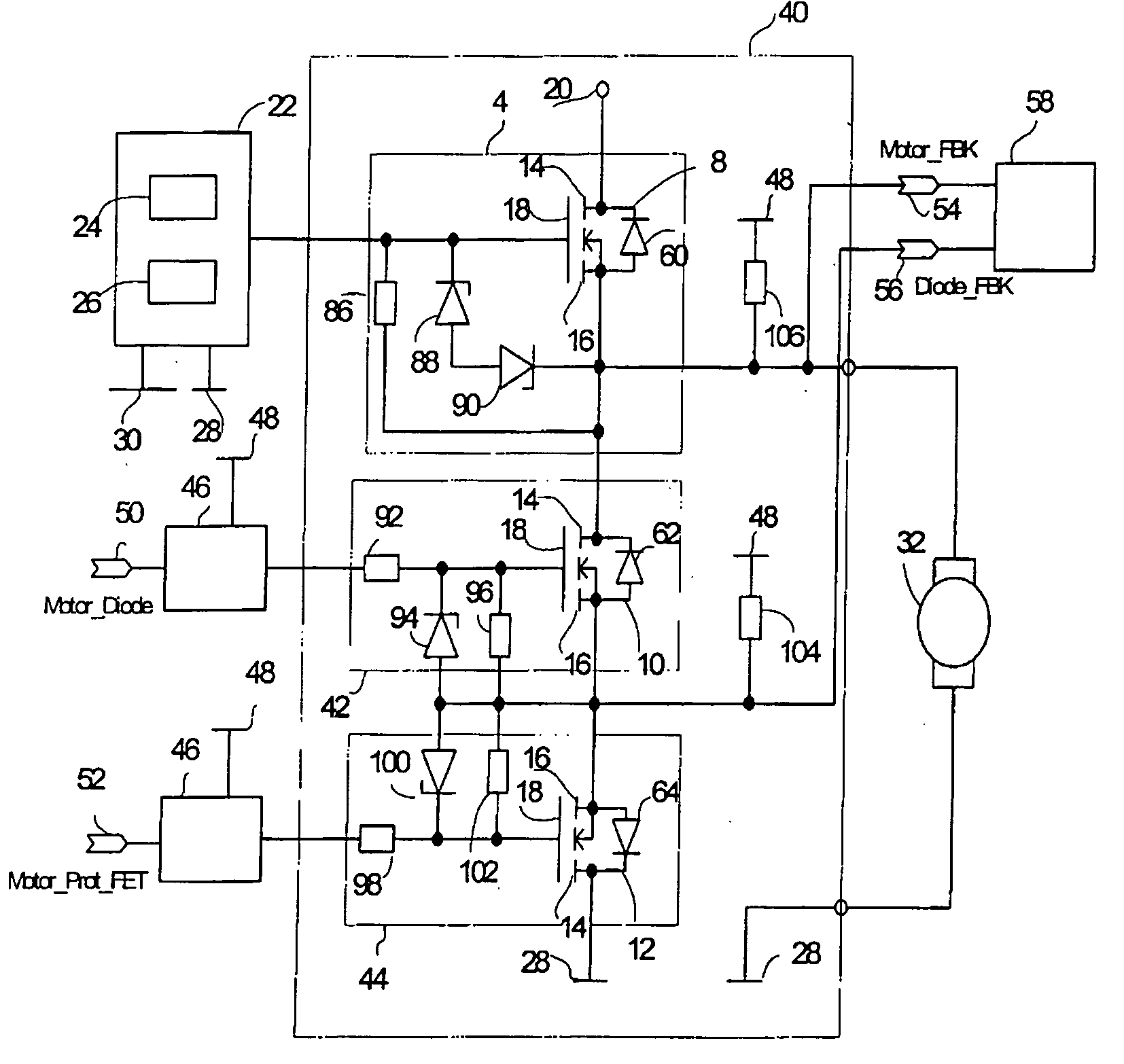
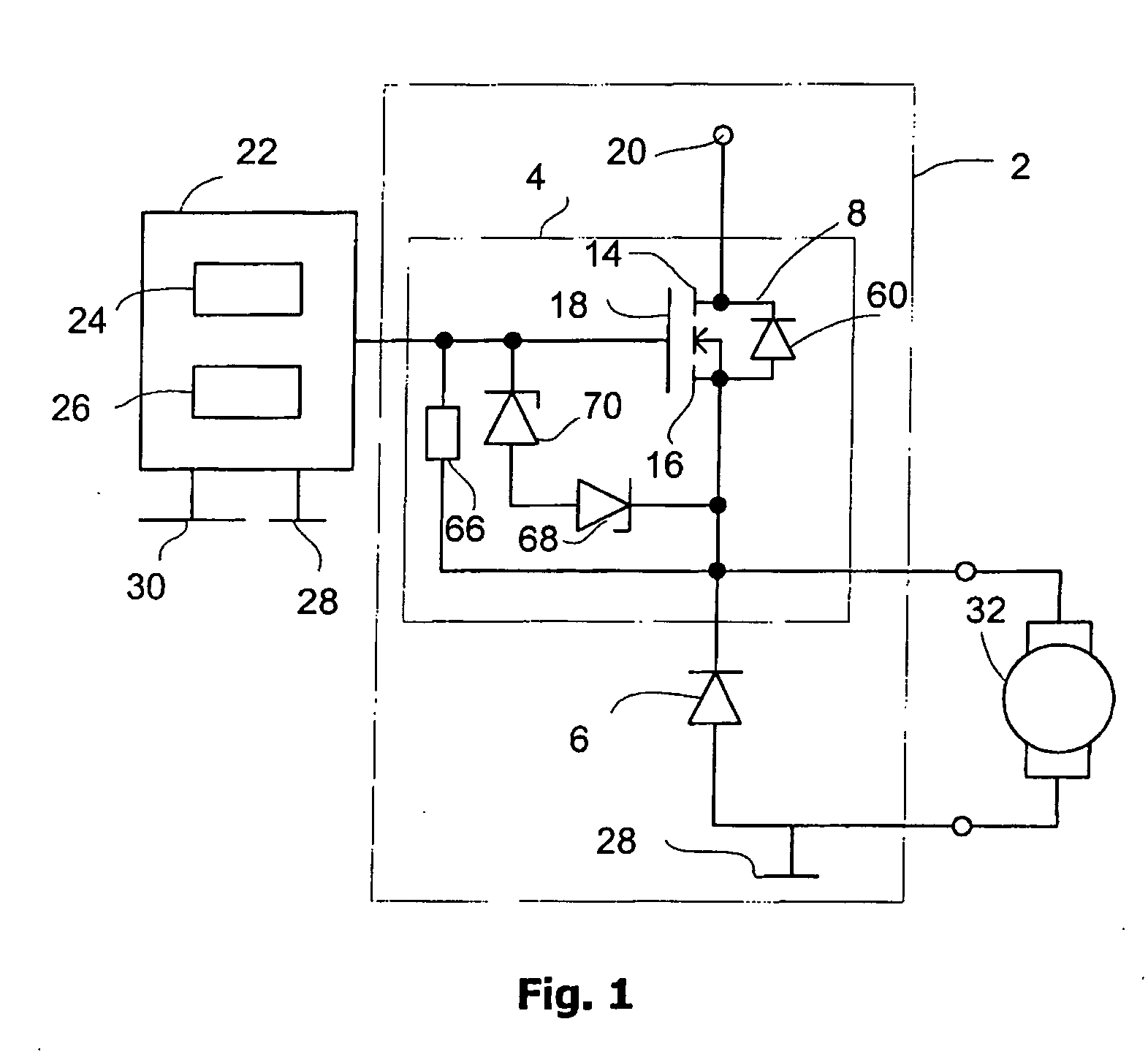
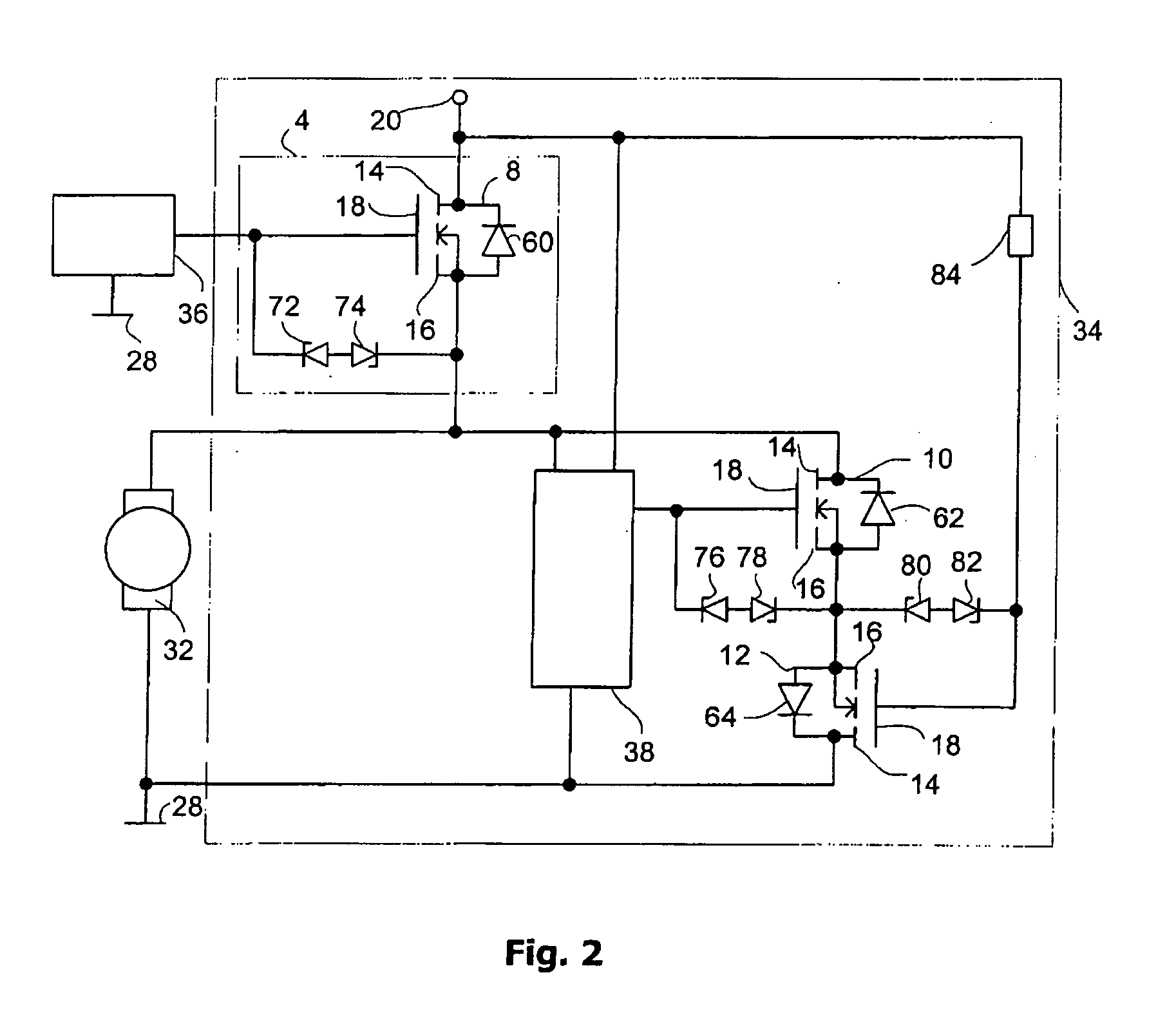
Motor Control Circuit With Malfunction Monitoring
ActiveUS20090219659A1Electric motor controlEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionMOSFETMotor control
Owner:LUCAS AUTOMOTIVE GMBH
Method for monitoring fluctuation of MOSFET gate line end cutting process
InactiveCN110488575APhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusMOSFETEngineering
Owner:SHANGHAI HUALI INTEGRATED CIRCUTE MFG CO LTD
MOSFET (Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) device for reducing electric field intensity of oxide layer and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114530380AReduce peak electric fieldAvoid Surface Breakdown PhenomenaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETElectrical field strength
Owner:瑶芯微电子科技(上海)有限公司
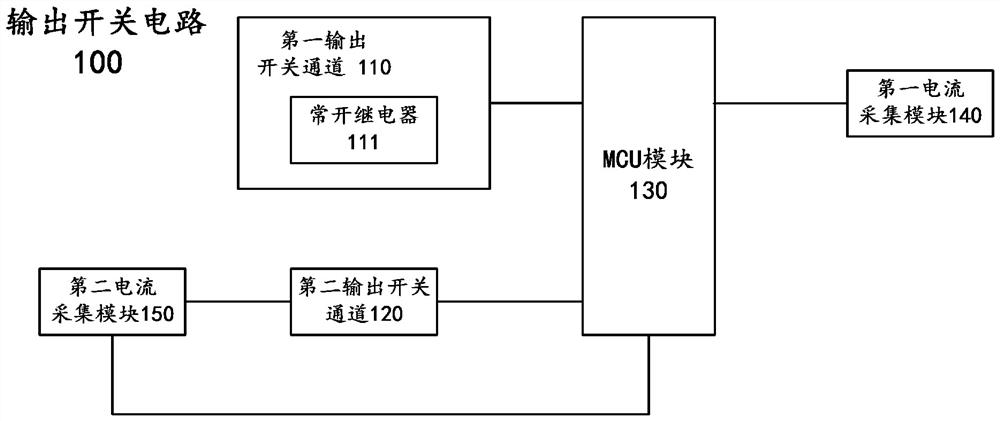
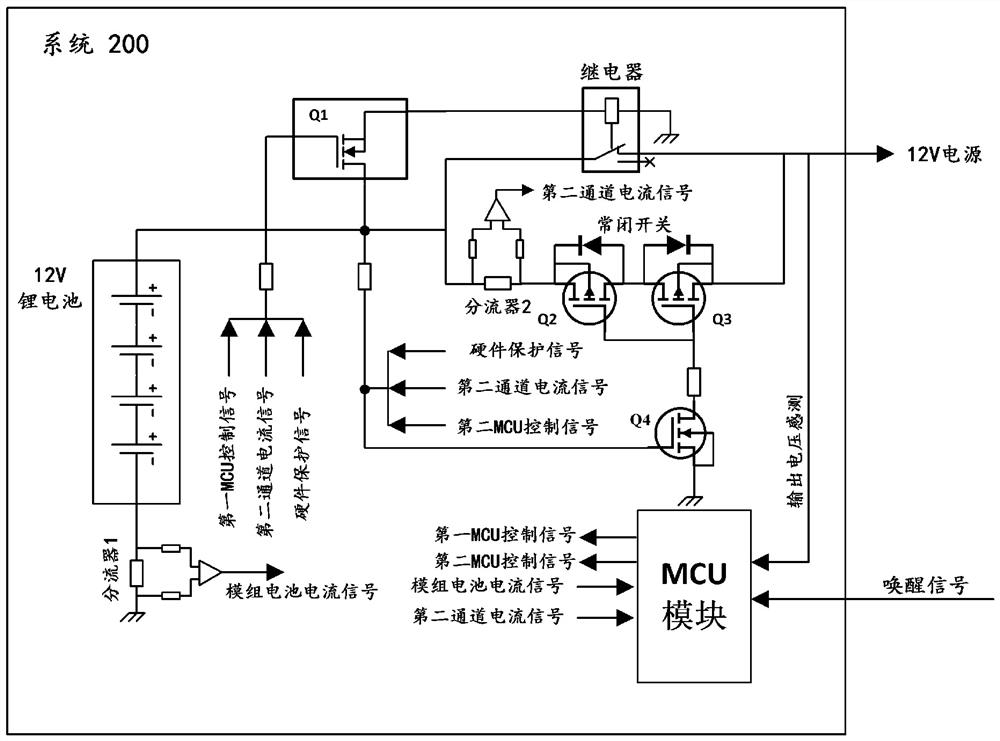
Output switch circuit of vehicle-mounted 12V lithium battery, power supply system and automobile
Owner:SAIC GENERAL MOTORS +1
Alternating current-direct current conversion circuit and power conversion device
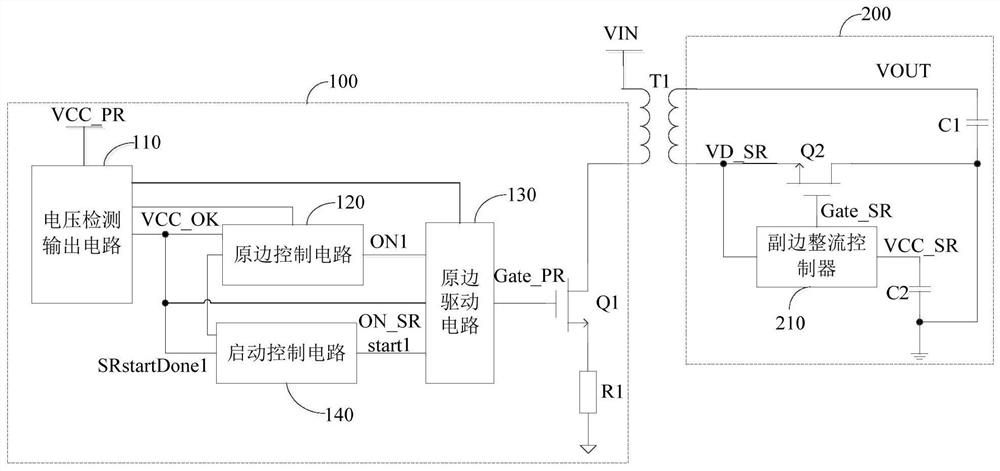
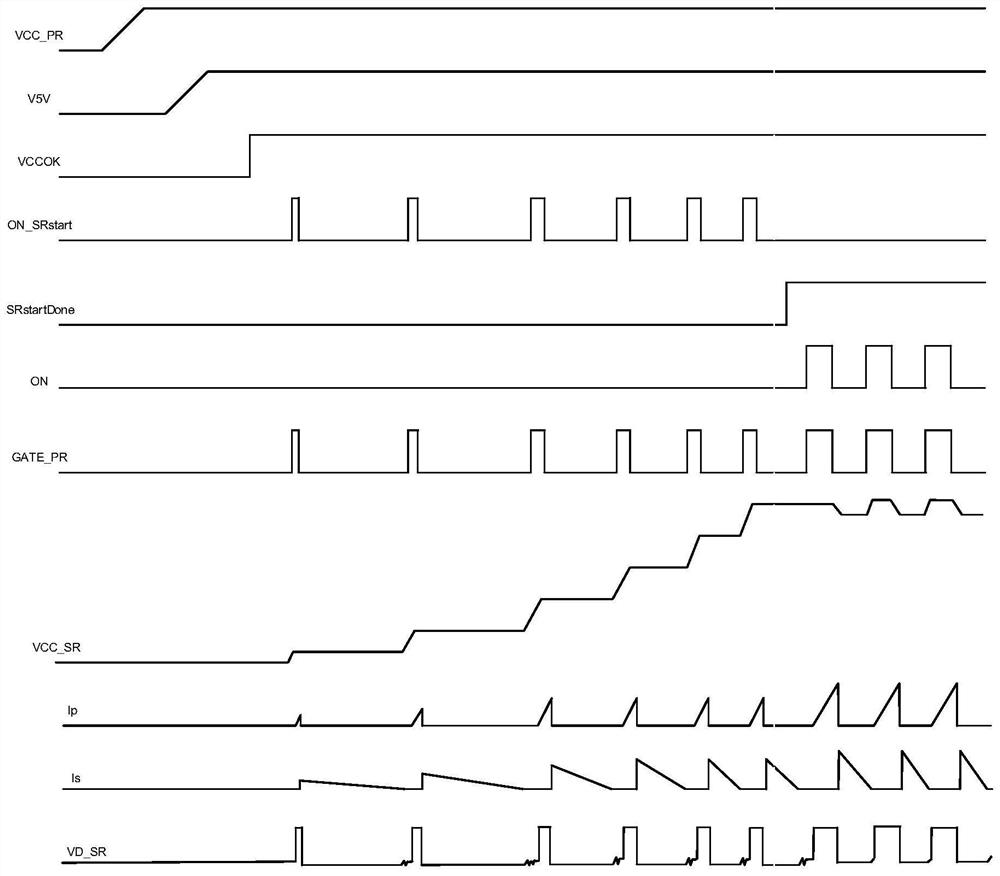
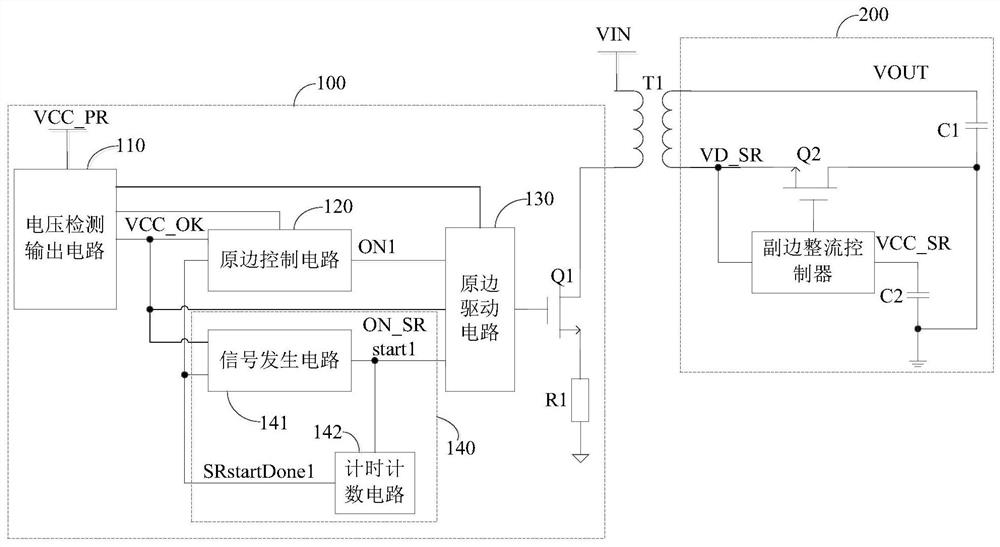
PendingCN113972847AAddressing Excessive StressHigh drive reliabilityEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionMOSFETControl signal
Owner:茂睿芯(深圳)科技有限公司
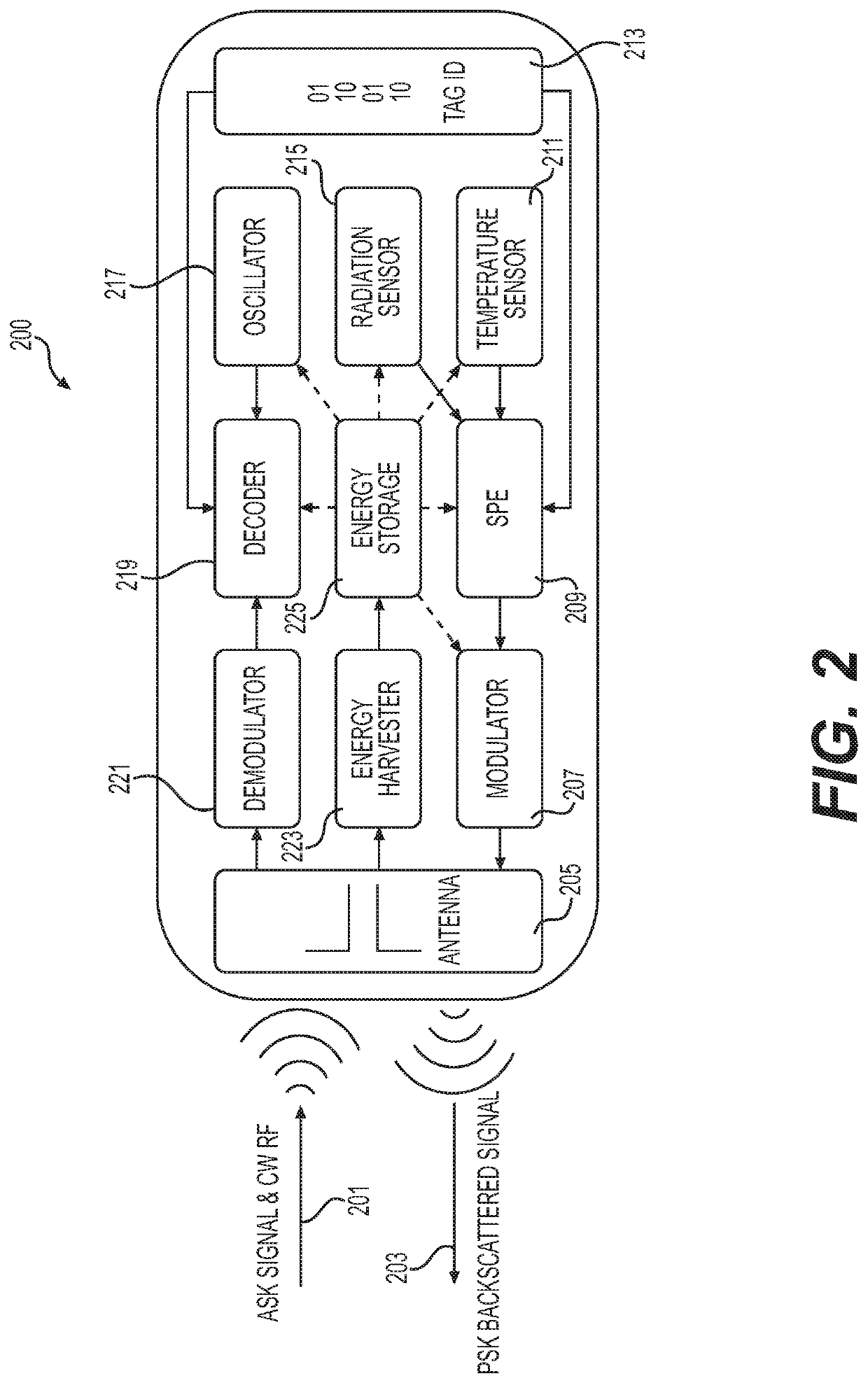
Low power dual-sensitivity fg-mosfet sensor for a wireless radiation dosimeter
Owner:BEST THERATRONICS
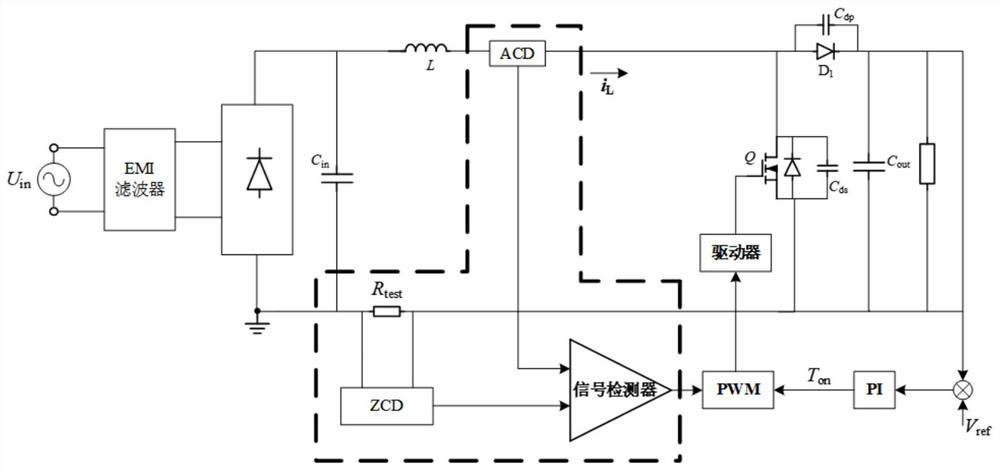
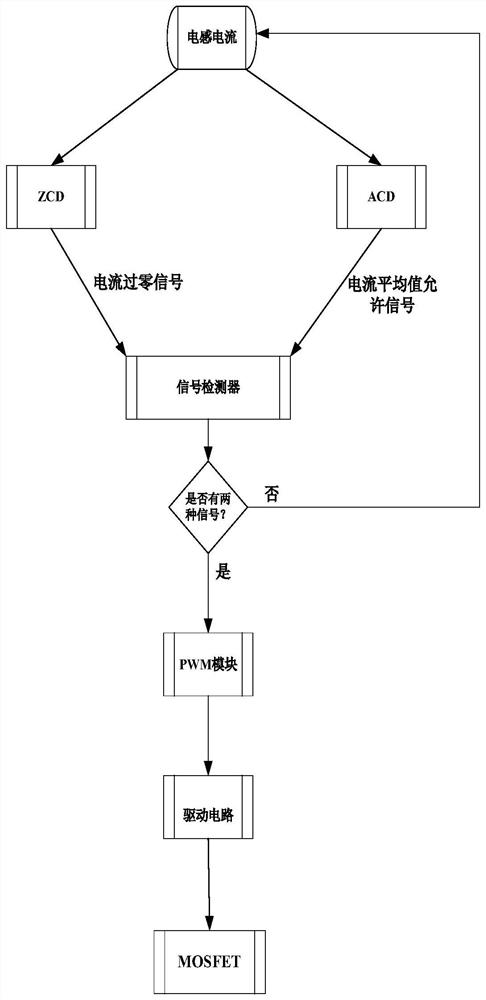
Resonance current suppression method based on synchronous detection of average value and instantaneous value of current
PendingCN114531023AReduce the impactReduce distortionEfficient power electronics conversionPower conversion systemsMOSFETDevice type
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS +1
High efficiency switch-mode power amplifier
ActiveCN101107775APower amplifiersMOSFETElectron mobility
Owner:CREE INC
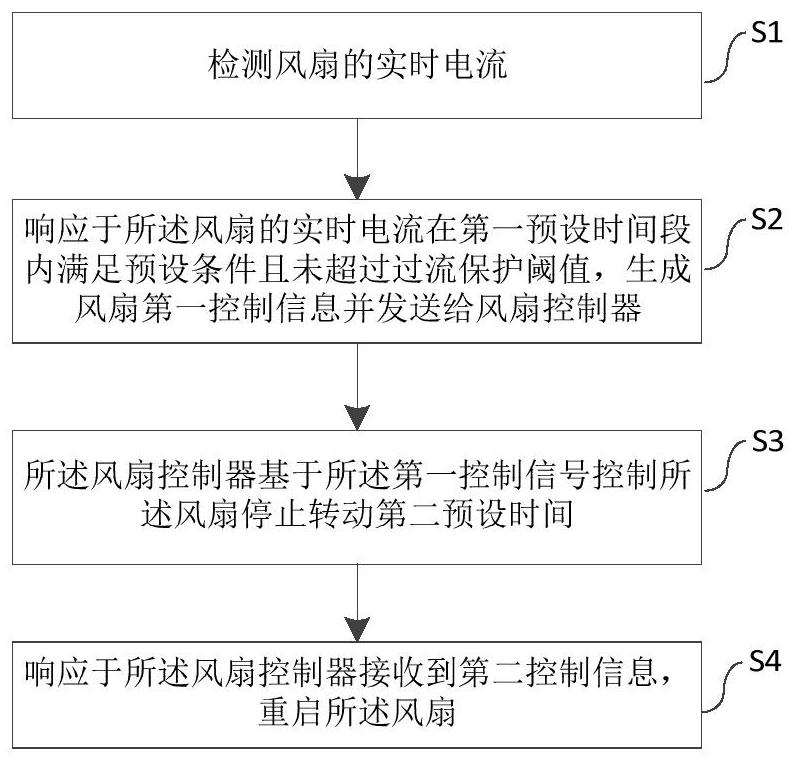
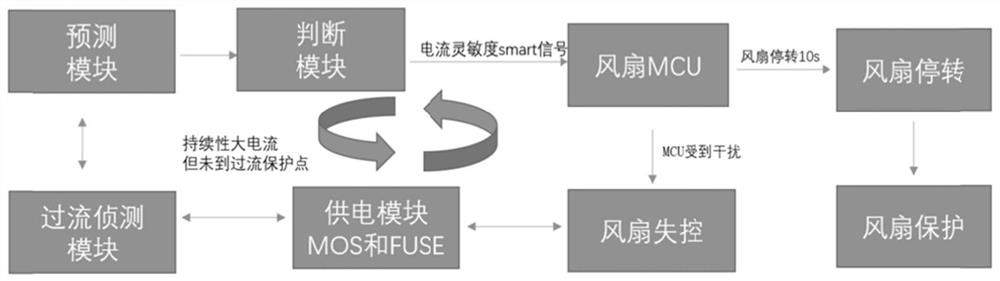
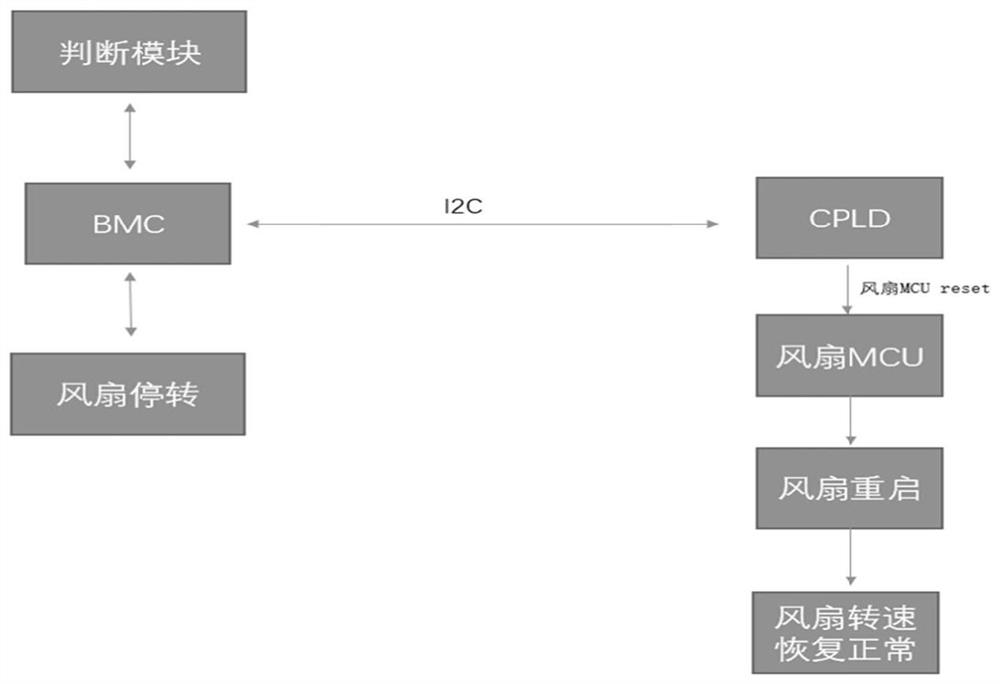
Fan control method, system and equipment and medium
PendingCN114489290ADigital data processing detailsNon-redundant fault processingMOSFETComputer equipment
Owner:SUZHOU LANGCHAO INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
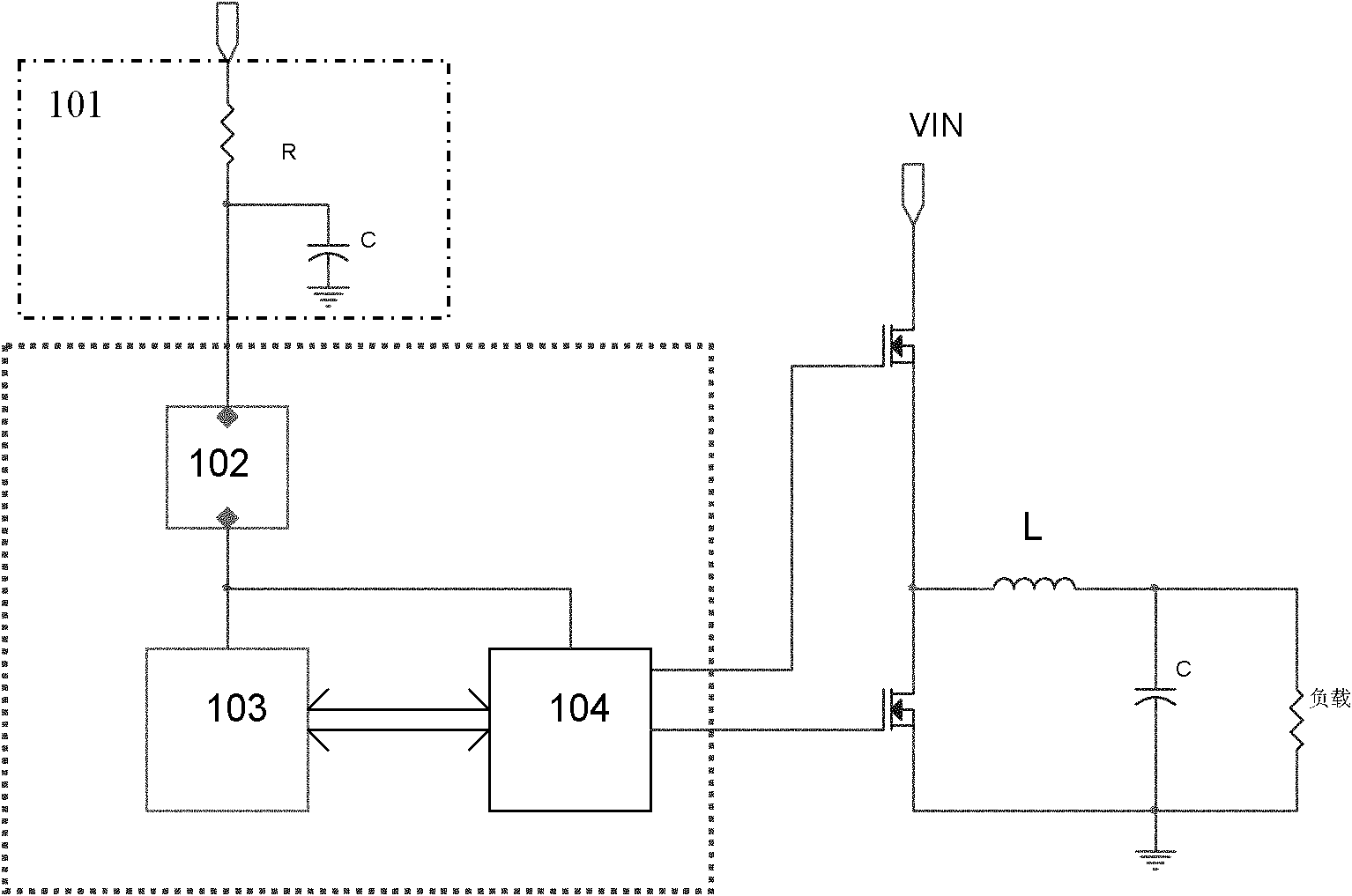
MOSFET gate crosstalk clamping circuit, control method and controller
PendingCN112688289AReduce sizeEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentMOSFETHemt circuits
The invention relates to the technical field of electric control, and in particular relates to an MOSFET gate crosstalk clamping circuit, a control method and a controller. The circuit comprises an MOSFET driving unit, an anti-interference unit and a driving chip; the gate pole of the MOSFET driving unit is connected with the first driving end of the driving chip, the first end of the anti-interference unit is connected with the gate pole of the MOSFET driving unit, and the second end of the anti-interference unit is connected with the negative pressure end or the grounding end of the driving chip; the anti-interference unit is used for receiving crosstalk voltage caused in the switching process of the MOSFET; and the driving chip is used for controlling the anti-interference unit to reduce the crosstalk voltage. The gate electrode of the MOSFET driving unit is isolated and clamped through the circuit, and the crosstalk voltage of the gate electrode is effectively suppressed.
Owner:SUZHOU INOSA UNITED POWER SYST CO LTD
Switching power supply control system of multiple voltage levels
InactiveCN102035414AExpand the range of selectionGuaranteed control accuracyAc-dc conversionMOSFETPower control system
Owner:成都成电硅海科技股份有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap