Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
11 results about "Synthetic resin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
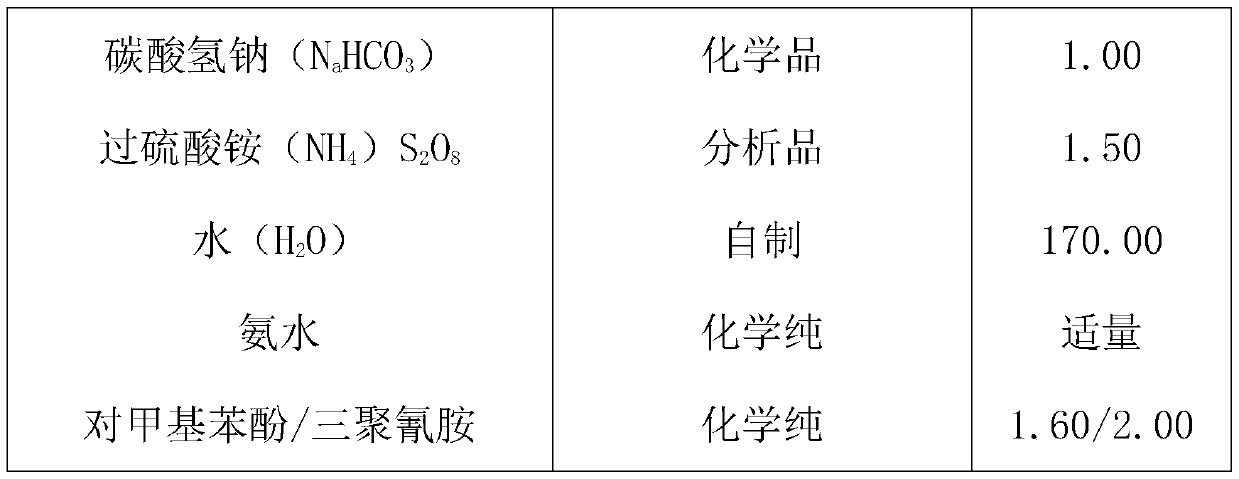
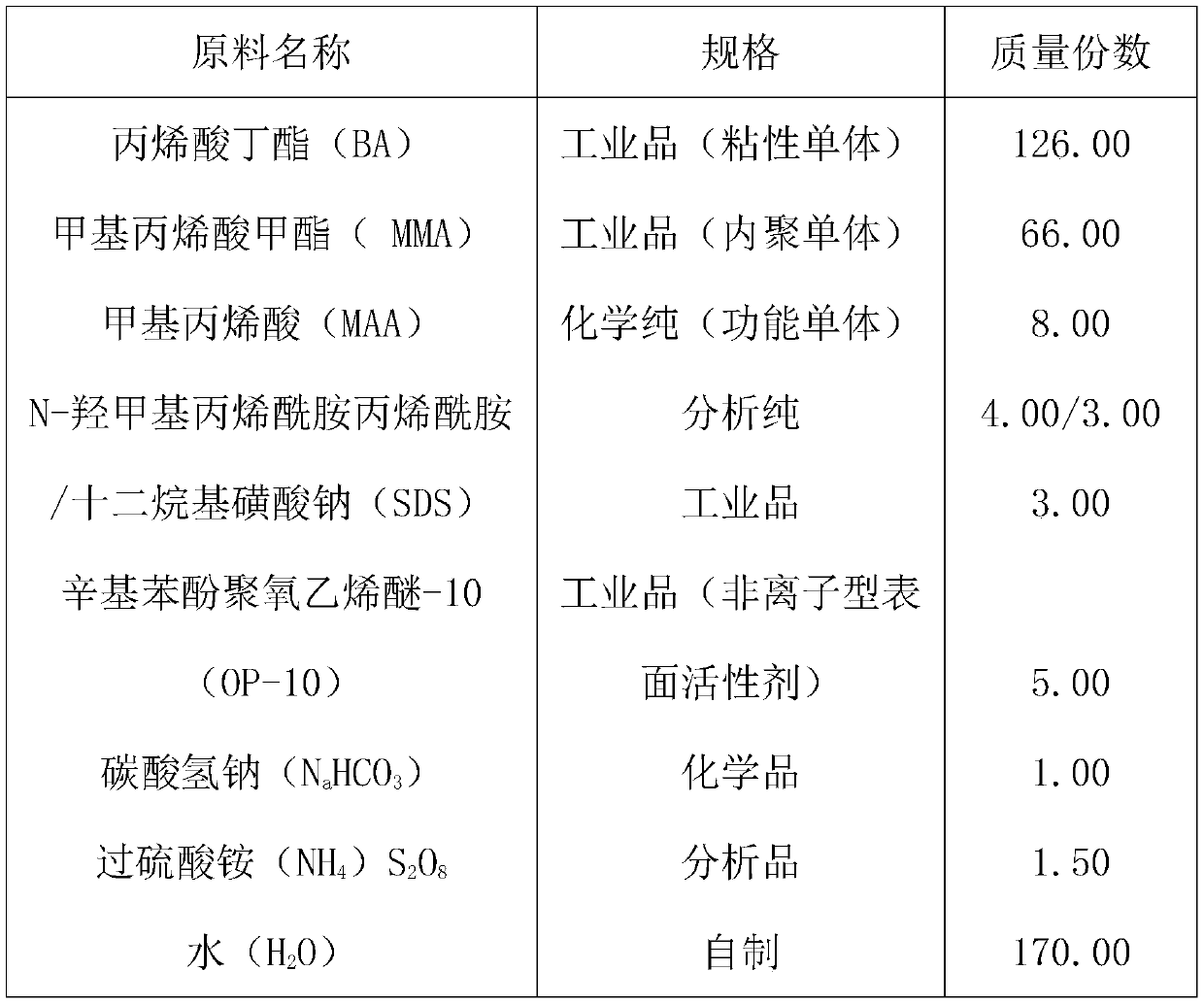
Synthetic resins are industrially produced resins, typically viscous substances that convert into rigid polymers by the process of curing. In order to undergo curing, resins typically contain reactive end groups, such as acrylates or epoxides. Some synthetic resins have properties similar to natural plant resins, but many do not.
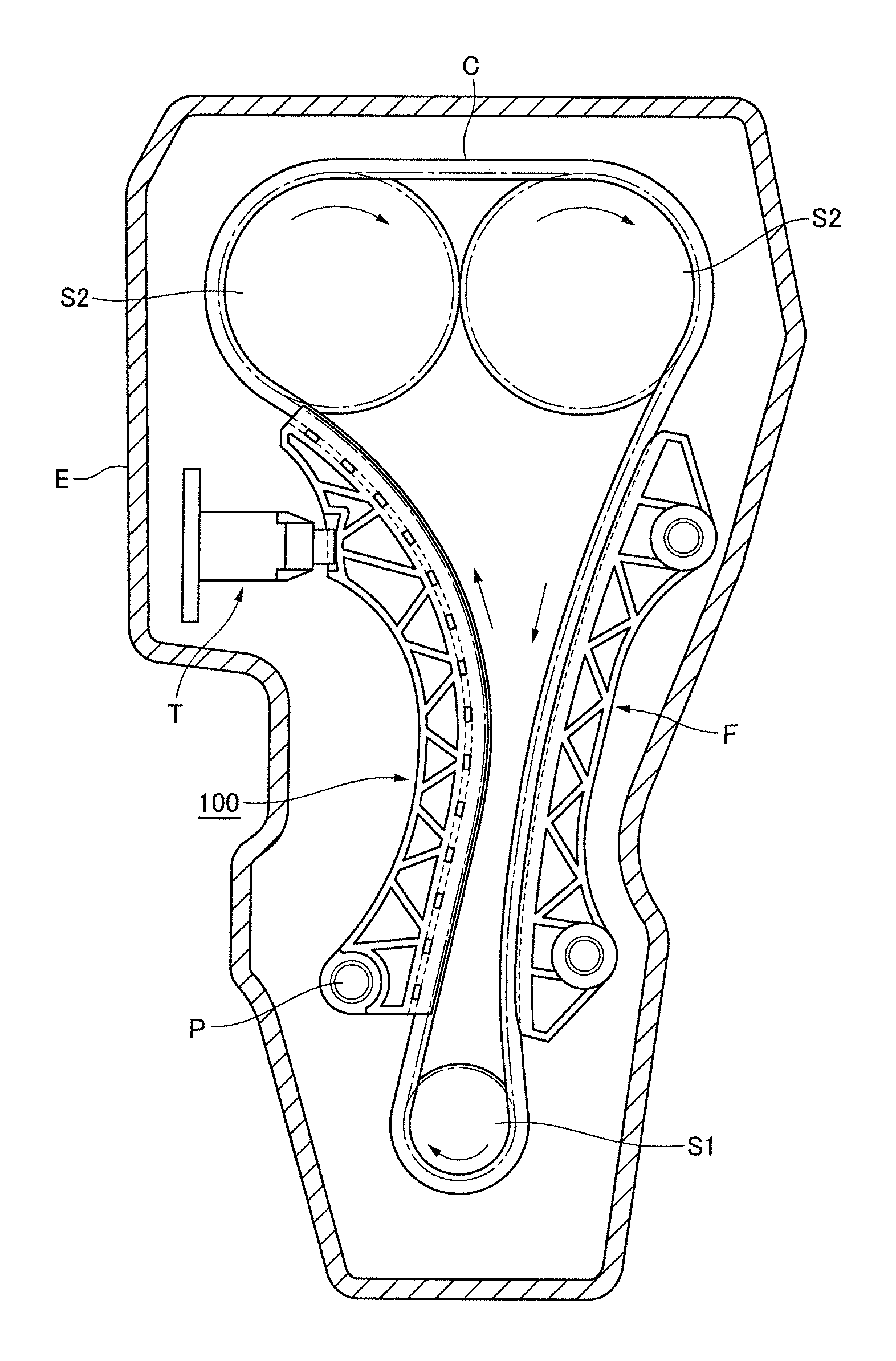
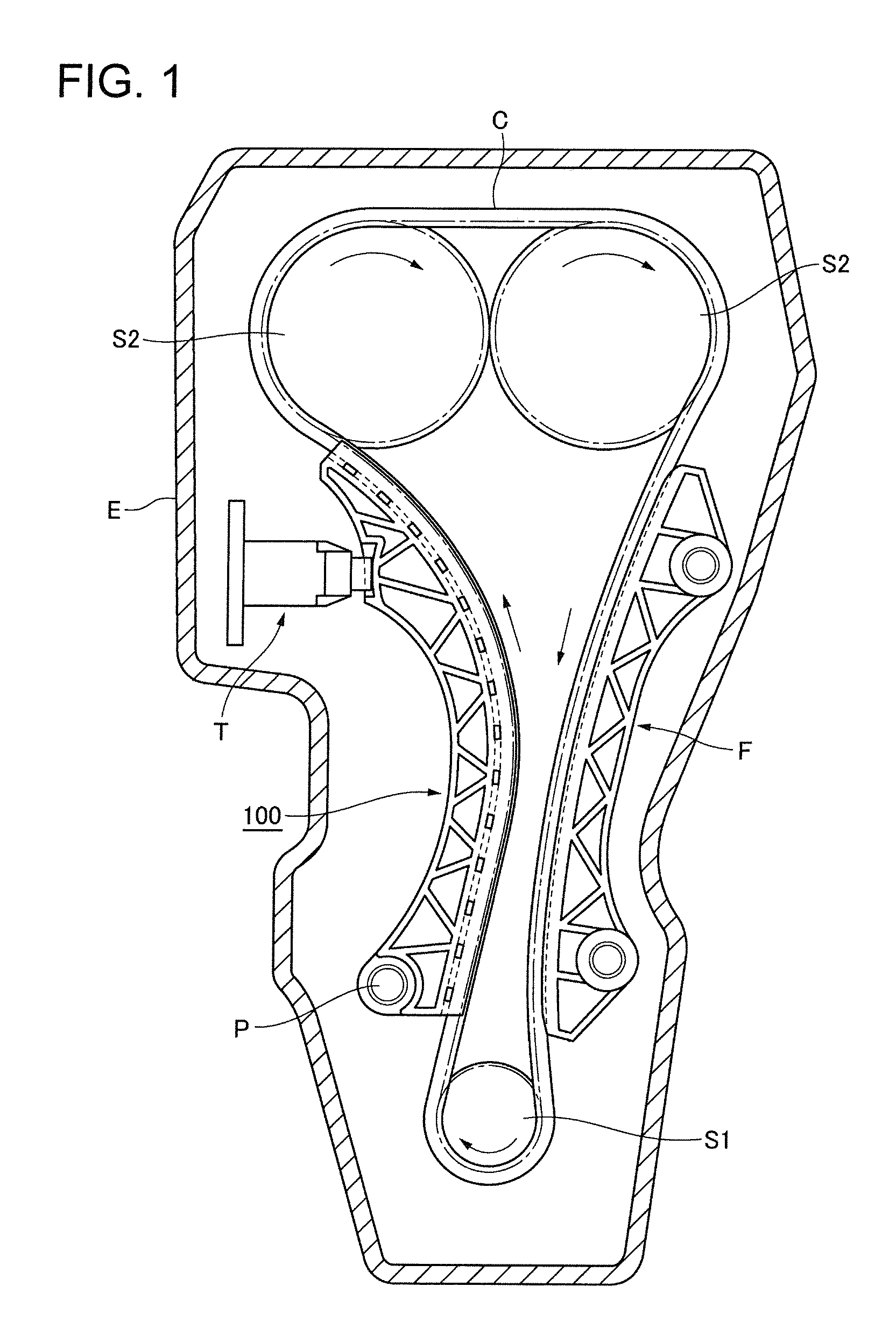
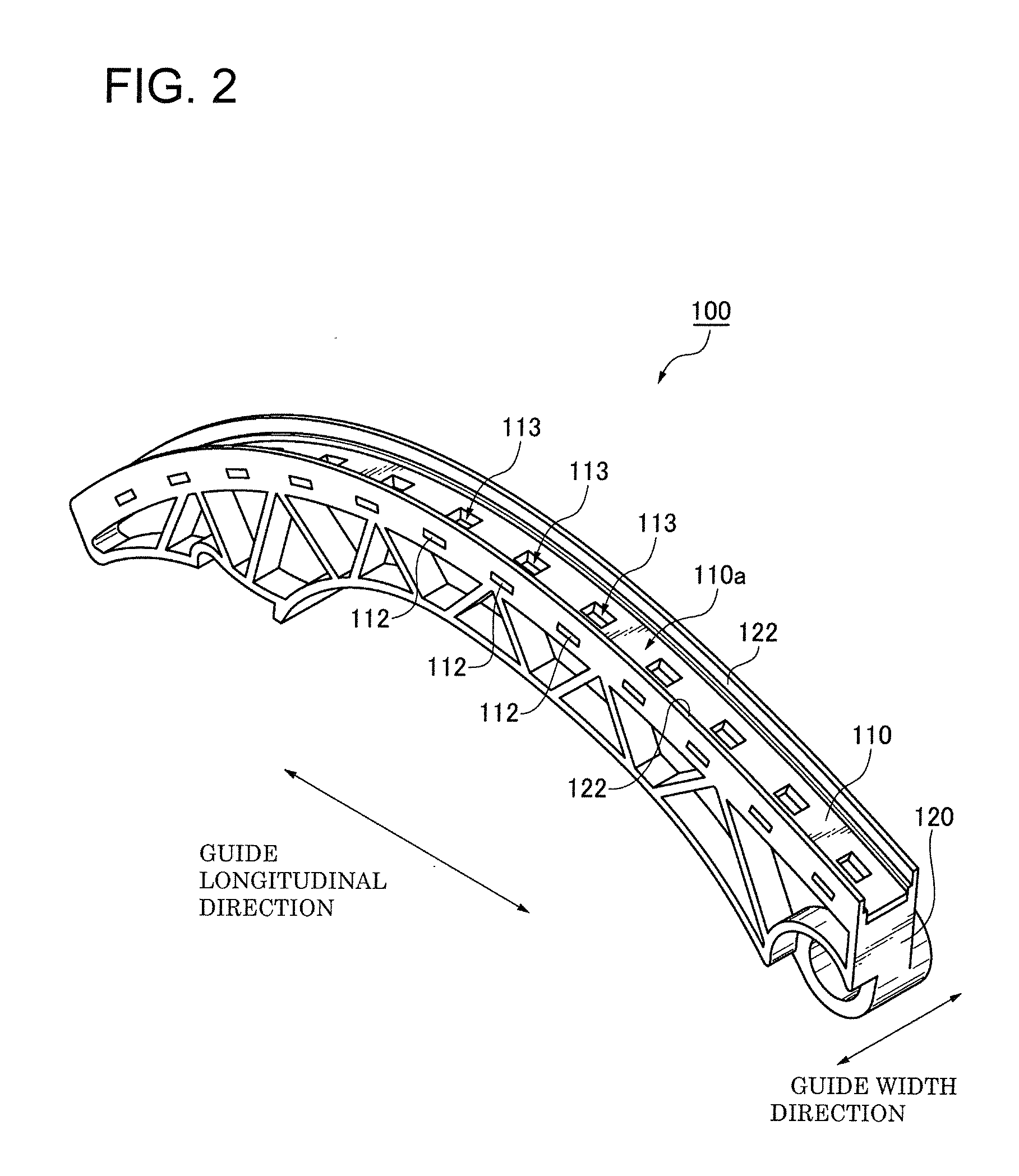
Transmission guide
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
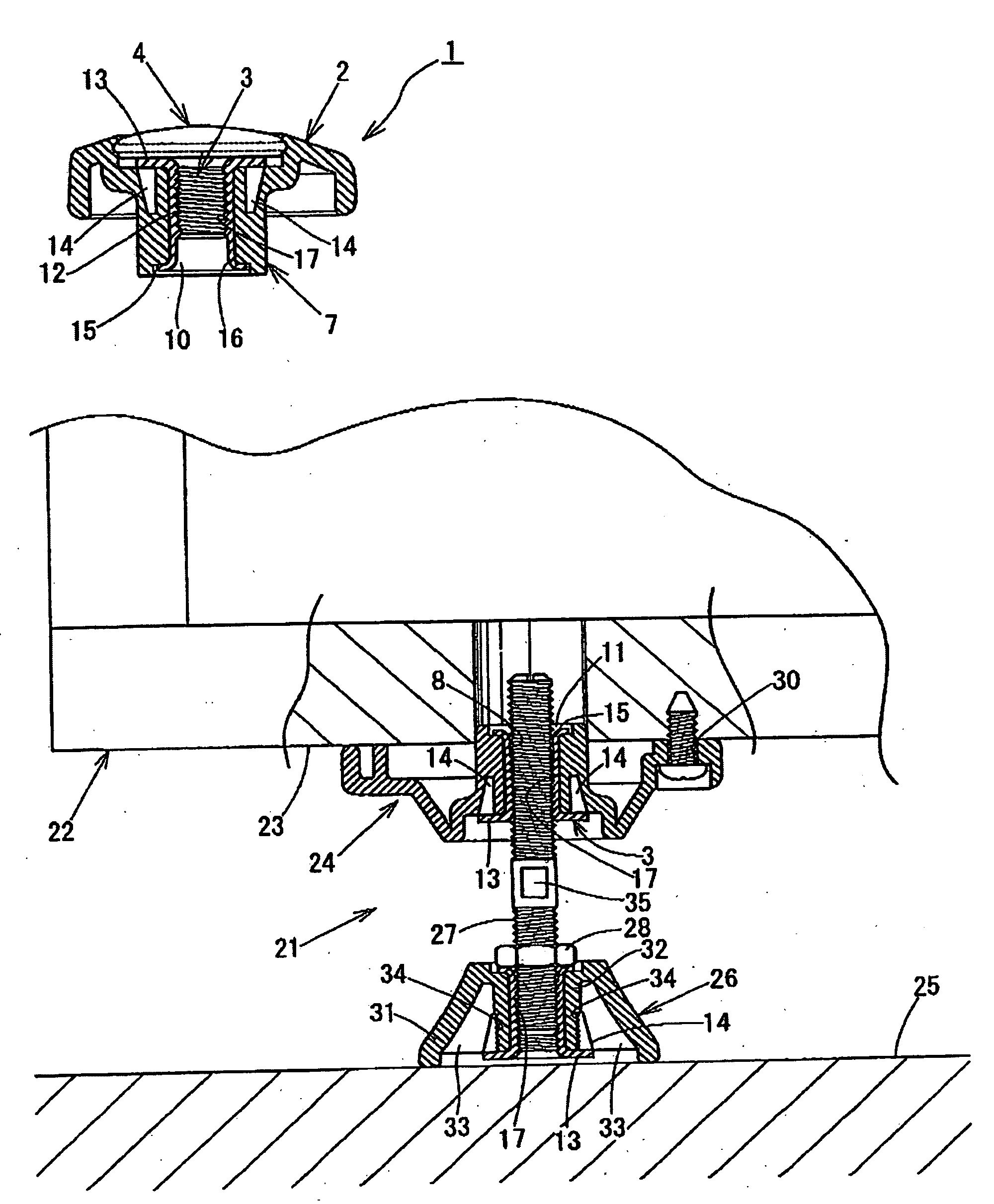
Male fixing member of hook-and loop fastener, and sheet product with the fixing member
InactiveUS20050235462A1Improve productivityEnsure durabilitySnap fastenersRopes and cables for vehicles/pulleyEngineeringSynthetic resin
A first base material having a number of male engaging elements (112) formed of synthetic resin on a surface thereof and a second base material (121) are jointed and secured each other through a column-like joint portion (131). There is provided a male fixing member for sheets, which facilitates attachment operation to clothes or suspension cloths, has a durability, never loses appearance when it is mounted on clothes and allows even an infant to engage or disengage the male fixing members easily by an engagement / disengagement function of a surface fastener.
Owner:YKK CORP
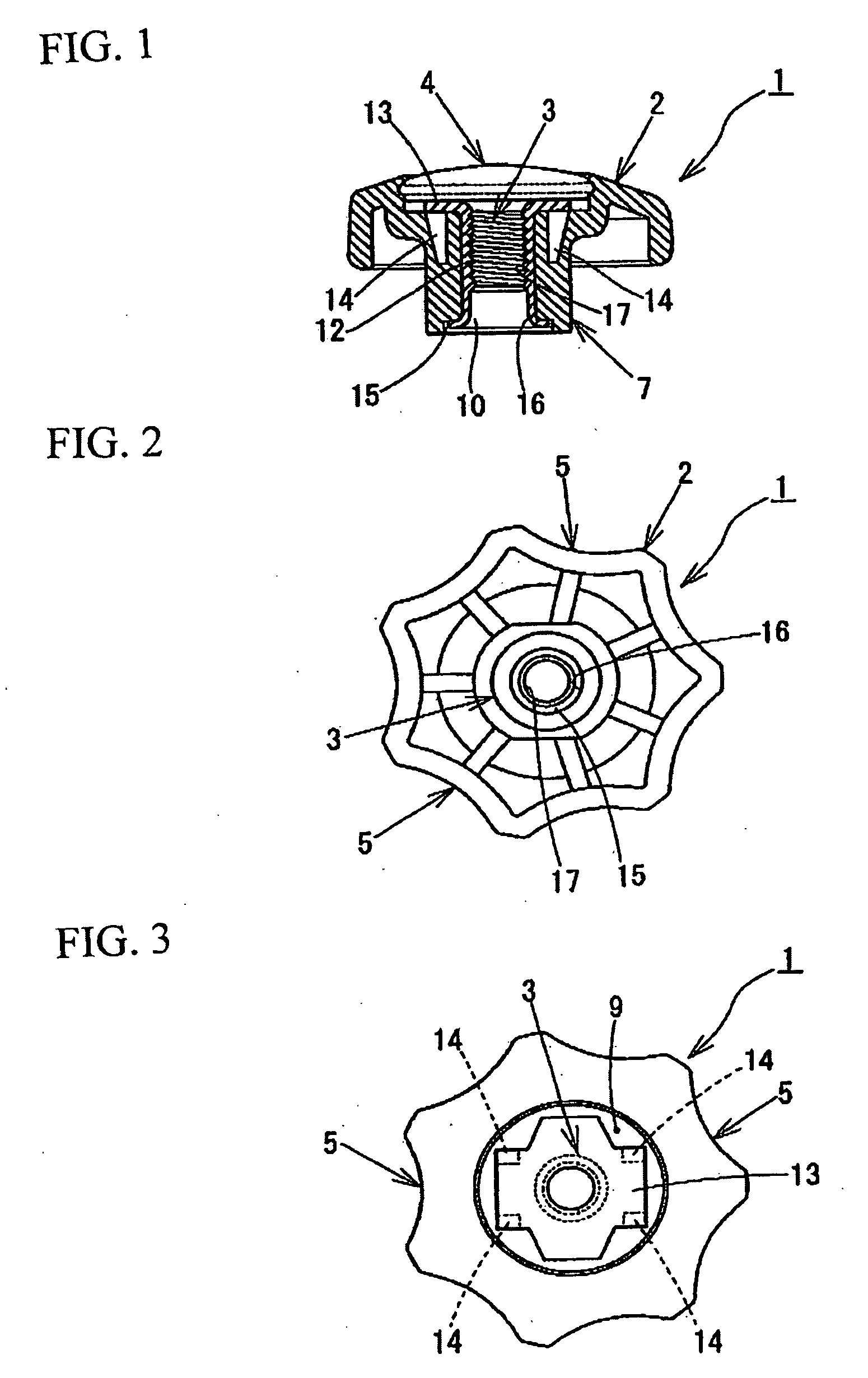
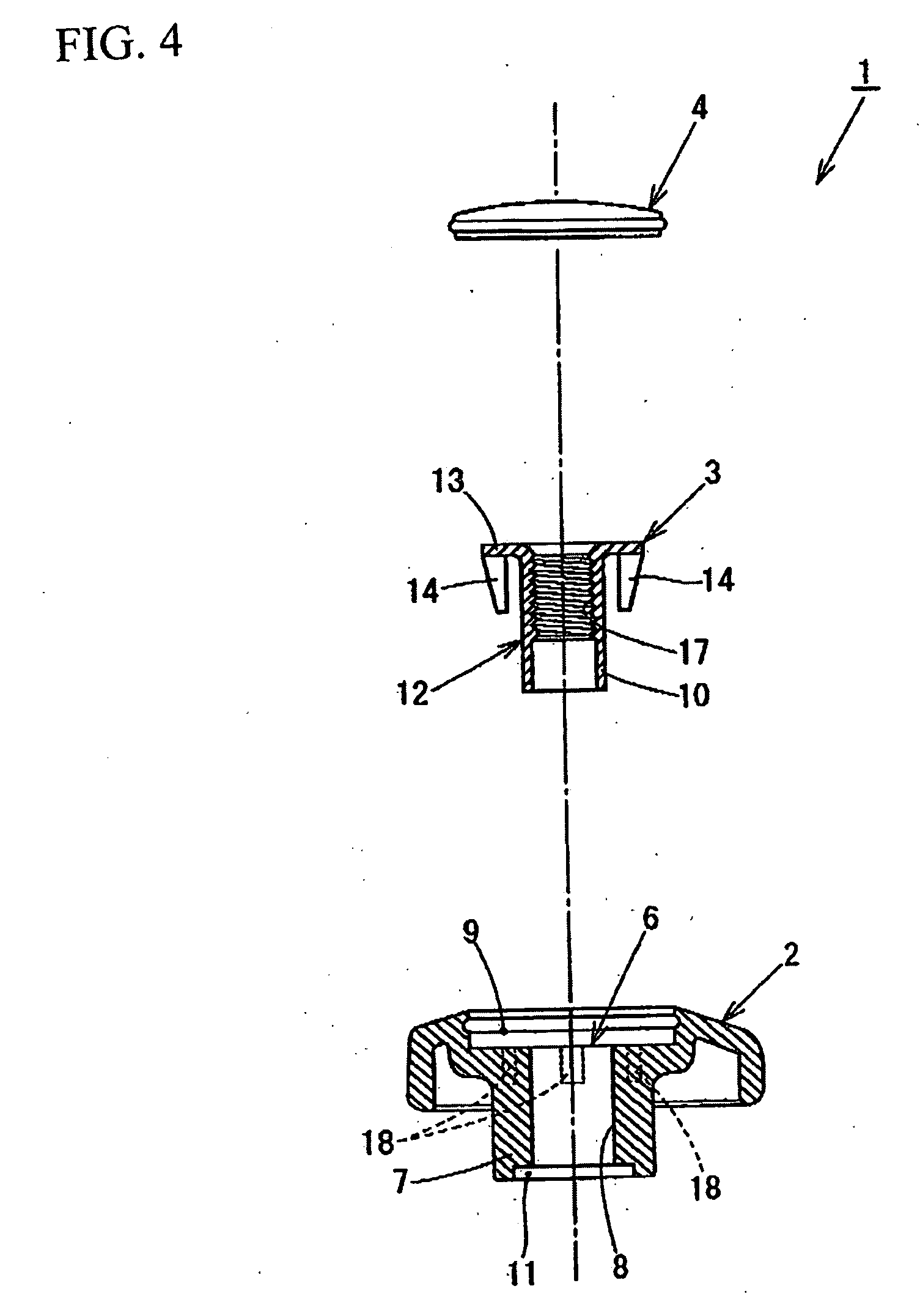
Synthetic resin member having a female screw
Owner:NAGAYAMA ELECTRONICS IND
Molybdenum fibre reinforced resin concrete material
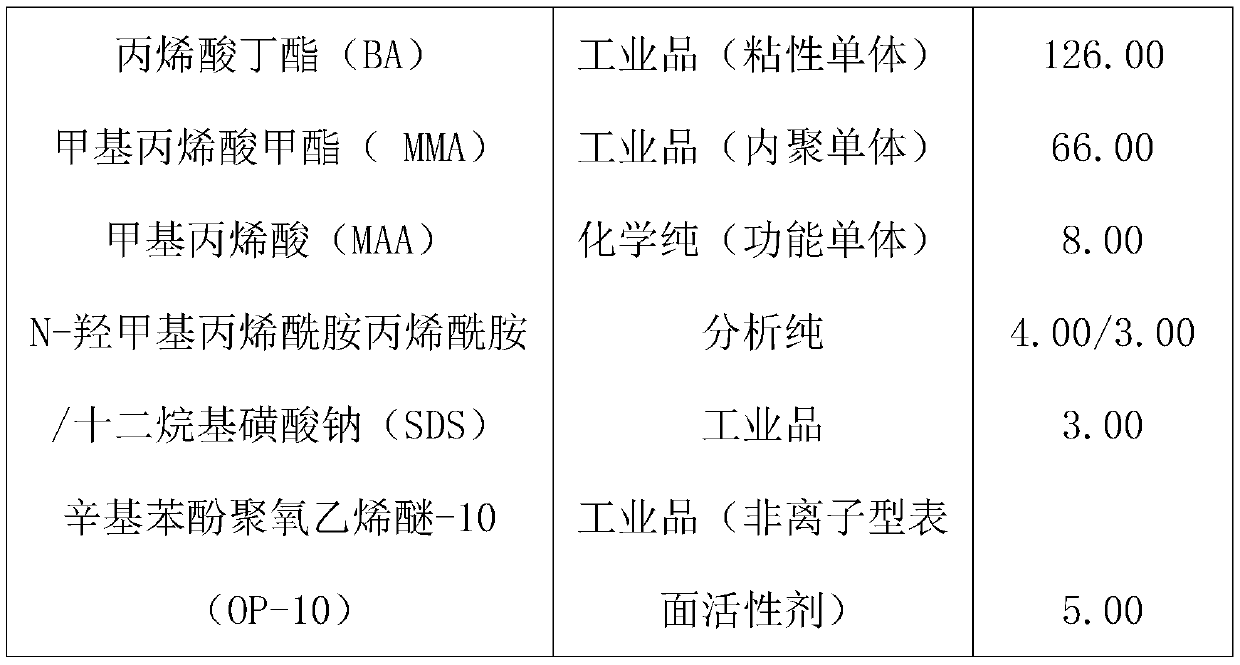
InactiveCN101759397AGood physical and mechanical propertiesHigh compressive strengthKinetosomesResin-Based Composite
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Thermoplastic polymer composition and molded article
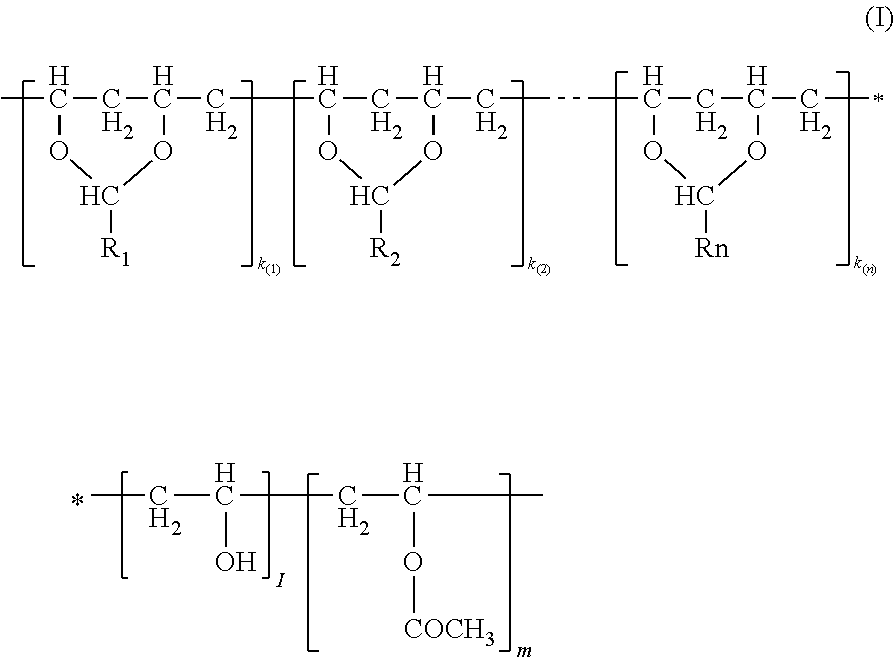
InactiveUS20130122289A1Excellent in flexibility propertyImprove mechanical propertiesNon-fibrous pulp additionNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolyvinyl alcoholGlass transition
Owner:KURARAY CO LTD
Coating material for sealing coal wall of gob-side coal roadway
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
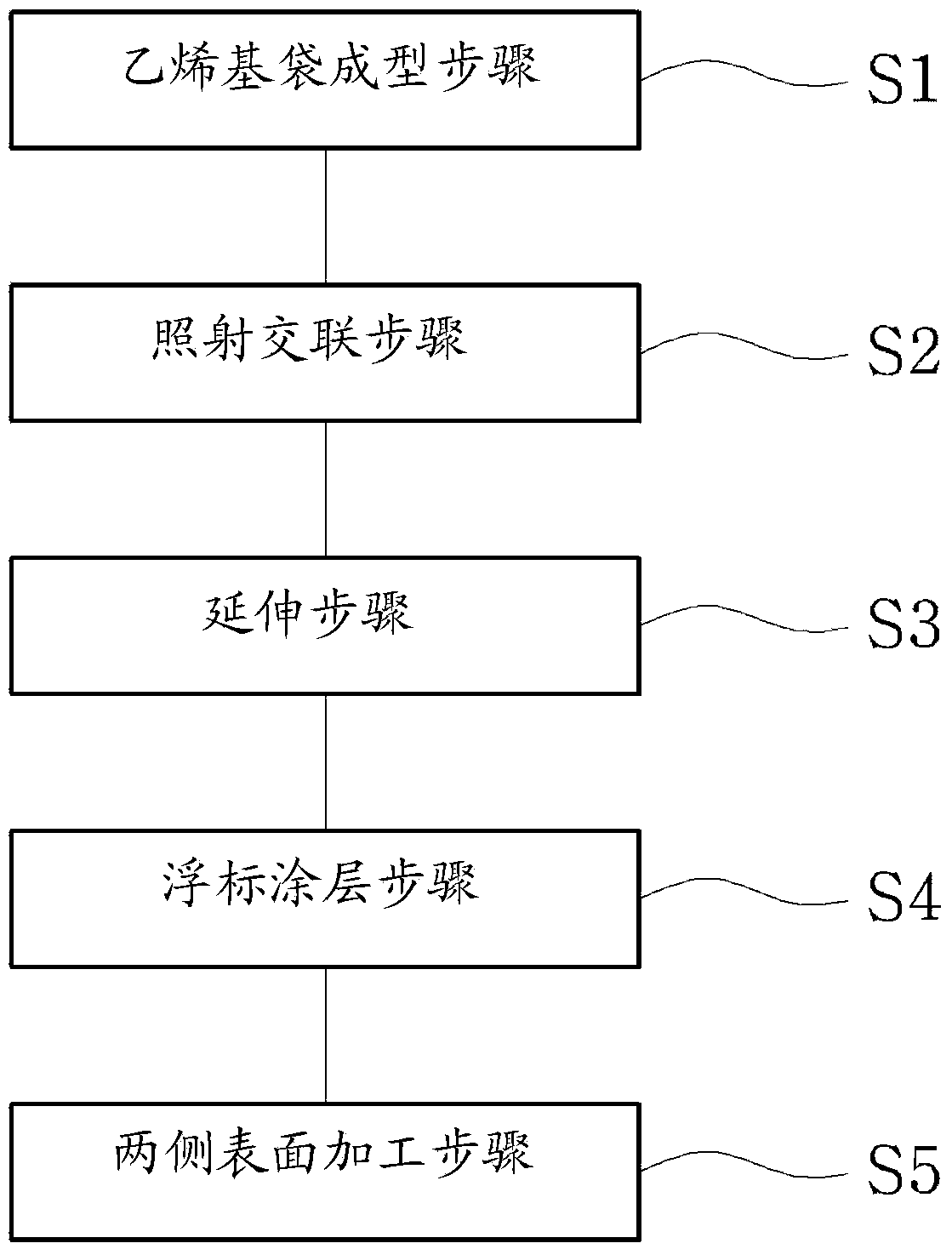
Buoy for aquaculture and manufacturing metho
ActiveCN103563802AImprove COPExtend your lifeClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaAquaculture industryPolystyrene
Owner:广东联塑农业设施科技有限公司
Door
The present invention discloses a door which has sufficient bending strength and is not damaged by moisture. The front panel 10 and the rear panel 20 of the door of the invention are made of glass fiber material. A pair of transverse frames 30a and 30b are made of synthetic resin, and a pair of longitudinal frames 40a and 40b made of wood comprising a plurality of veneers bonded together are fixed between edge portions of the front and rear panels. The upper and lower portions of the longitudinal frames are fixedly bonded to the lower and upper surfaces of each of the transverse frames so that the longitudinal frames are not exposed. In addition, a pair of cover plates 50 made of synthetic resin are attached to the outer side surfaces of the longitudinal frames so that the longitudinal frames are not exposed to the outside. The inner space defined by the frame between the front panel and the rear panel is filled with foaming liquid to form a foam layer.
Owner:TRINITY GLASS INT
Manufacturing method for gas barrier film, and electronic member or optical member provided with gas barrier film
InactiveCN104114287AEfficient preparationThere will be no problem of poor sealingVacuum evaporation coatingSynthetic resin layered productsOrganic solventHigh humidity
The present invention pertains to: a method for producing a gas barrier film that includes at least a base that is formed of a synthetic resin, and a gas barrier layer that is formed on the base, the method comprising a step 1 and 2 below; and an electronic member or an optical member that includes a gas barrier film obtained by the method. In the gas barrier film obtained by means of the present invention, a problem of adhesion failure between the gas barrier layer and the base dose not occur even when the gas barrier film is subjected to high-temperature / high-humidity conditions. [Step 1] that applies a silicon-based polymer compound solution that includes a silicon-based polymer compound and an organic solvent to the base to obtain a film of the silicon-based polymer compound solution, and dries the film by heating to form a layer that includes the silicon-based polymer compound, the base having a gel fraction of 70% or more and less than 98% when immersed in the organic solvent at 23°C for 72 hours; [Step 2] that subjects the layer that includes the silicon-based polymer compound to a plasma treatment to form the gas barrier layer.
Owner:LINTEC CORP
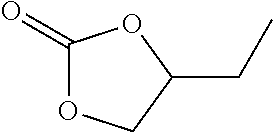
Hardenable synthetic resin comprising considerable proportions of cyclic carbonate groups, as well as/and cyclocarbonate-resin-based fixing systems, the production and use thereof
InactiveUS20160083501A1Increasing bond stressHigh viscosityOrganic chemistryPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesCarbonateSynthetic resin
Owner:FISCHERWERKE ARTUR FISCHER GMBH & CO KG
Wheatstrawplant fibersynthetic resin and preparation process thereof
Owner:安徽科邦树脂科技有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap