Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
10 results about "Liquid nitrogen" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Liquid nitrogen—LN₂—is nitrogen in a liquid state at an extremely low temperature (−195.79 °C (77 K; −320 °F) boiling point at sea level). Nitrogen was first liquefied at the Jagiellonian University on 15 April 1883 by Polish physicists, Zygmunt Wróblewski and Karol Olszewski. It is produced industrially by fractional distillation of liquid air.
Method for efficient ultralow temperature cryopreservation of turbot sperms
InactiveCN103348966AImprove permeabilityLow toxicityDead animal preservationGenetic diversityGermplasm
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
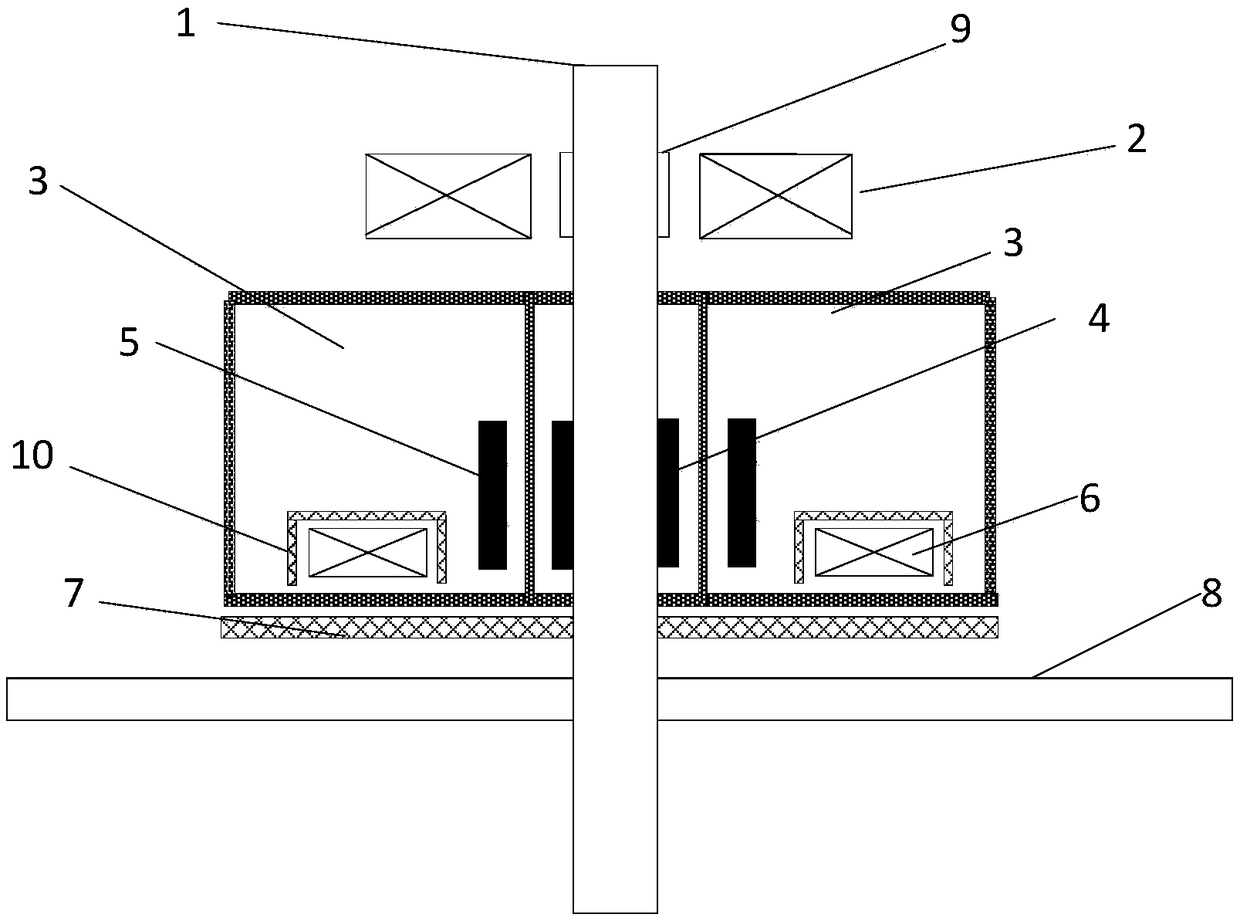
Automatic liquid nitrogen filling refrigeration device of high-temperature superconducting magnet
InactiveCN107068323AReduce gapReduce lossesSuperconducting magnets/coilsNitrogenHigh temperature superconducting
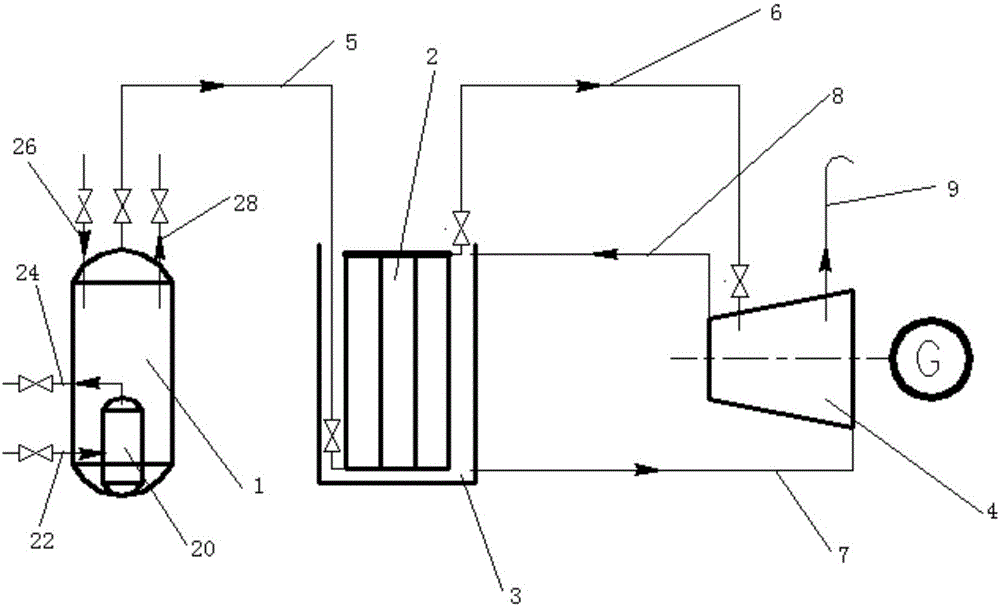
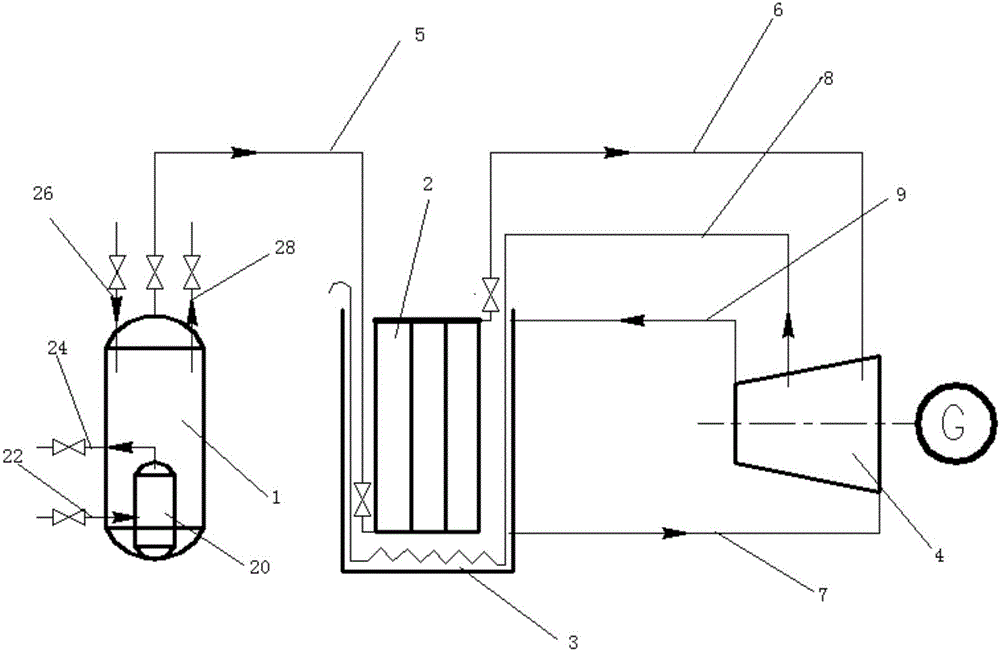
The invention relates to an automatic liquid nitrogen filling refrigeration device of a high-temperature superconducting magnet. The refrigeration device comprises a magnet cooling dewar flask, a nitrogen evaporation pipeline, a liquid nitrogen pipeline, a liquid nitrogen communication vessel and an outside liquid nitrogen vessel, wherein the magnet cooling dewar flask comprises an inner liner and an outer liner; a vacuum interlayer is formed between the inner liner and the outer liner; the outer liner is connected with an upper end cover of the magnet cooling dewar flask by flange bolts; a permanent magnet is arranged above the upper end cover; cold conducting discs are respectively arranged on the two outer sides of the top of the inner liner; the high-temperature superconducting magnet generating a suspension force with the permanent magnet is arranged above the cold conducting discs; the nitrogen evaporation pipeline penetrates through the tops of the outer liner and the inner liner; the liquid nitrogen pipeline penetrates through the bottoms of the outer liner and the inner liner; the nitrogen evaporation pipeline is connected with one port at the top of the liquid nitrogen communication vessel by a first hose; a port at the bottom of the liquid nitrogen communication vessel is connected with the liquid nitrogen pipeline by a second hose; and another port at the top of the liquid nitrogen communication vessel is connected with a port of the outside liquid nitrogen vessel by a third hose.
Owner:SICHUAN FEICHUANGNENGDA TECH CO LTD
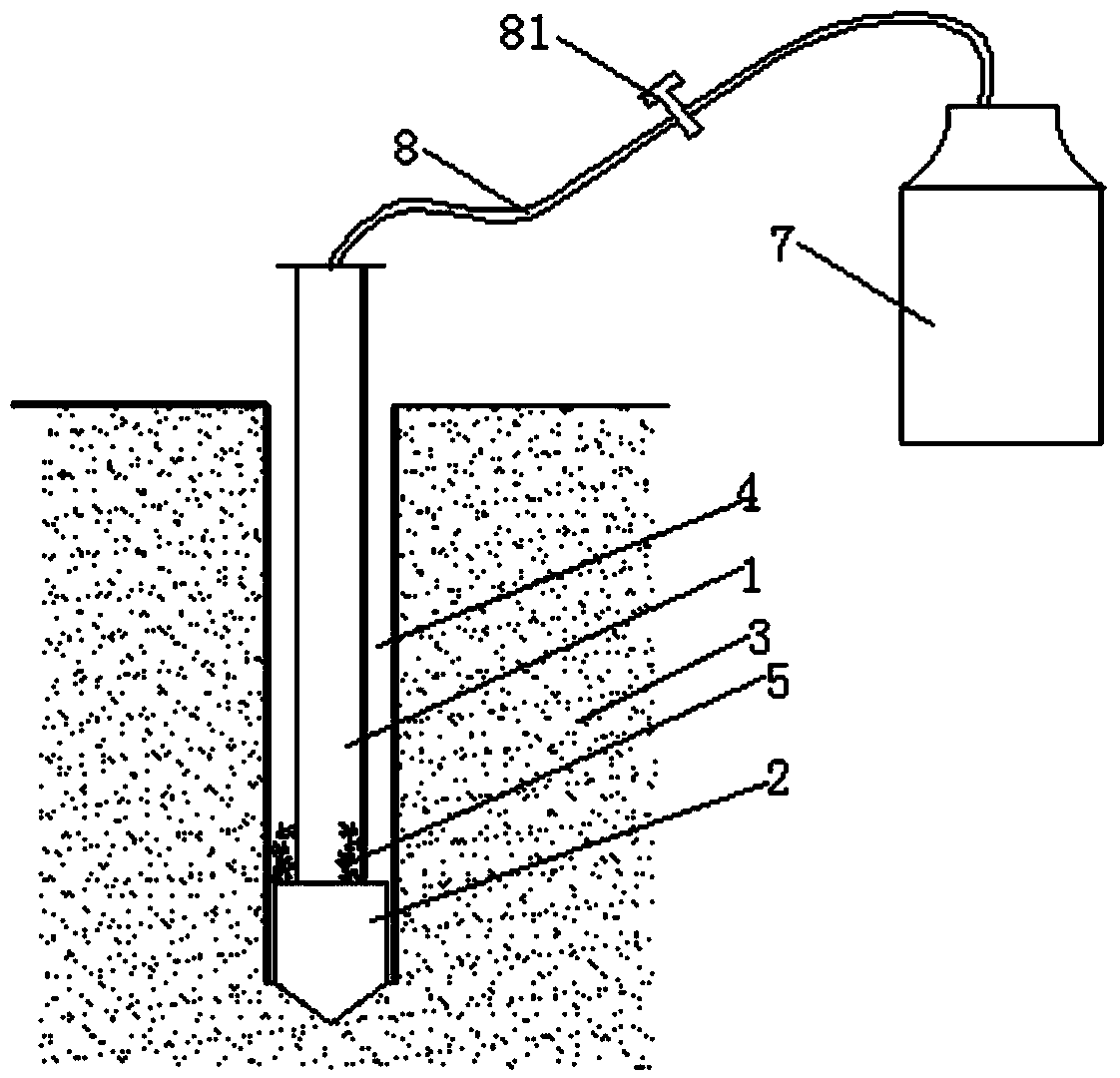
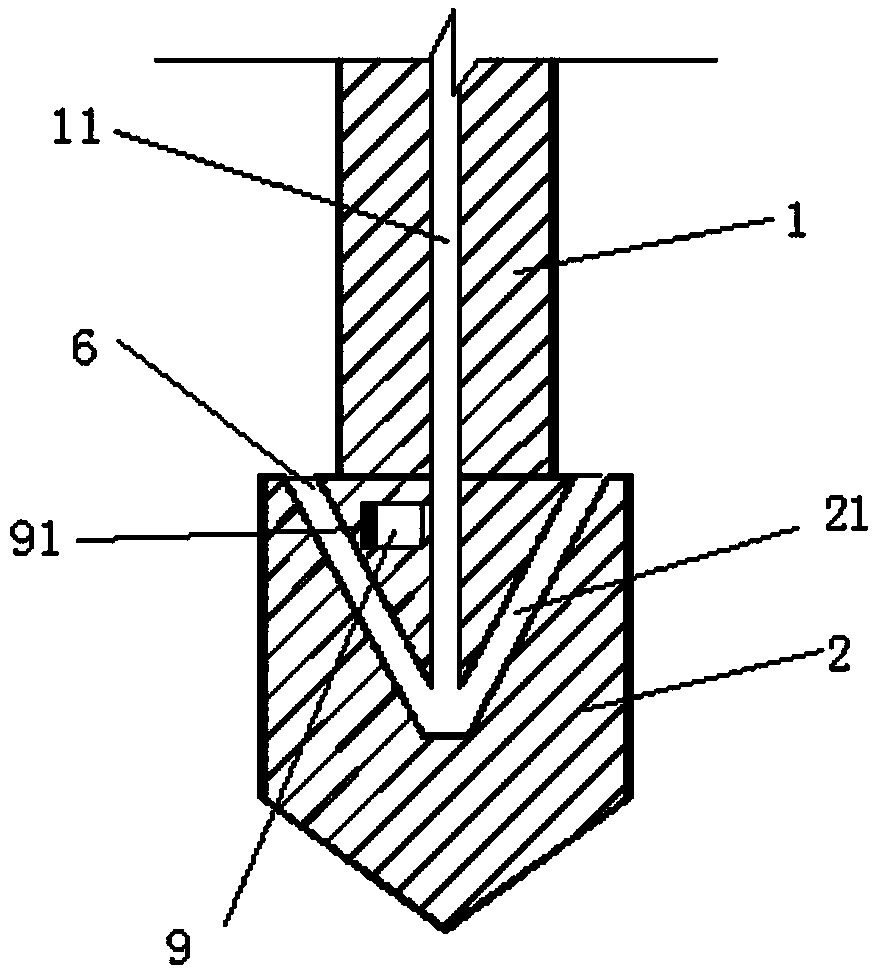
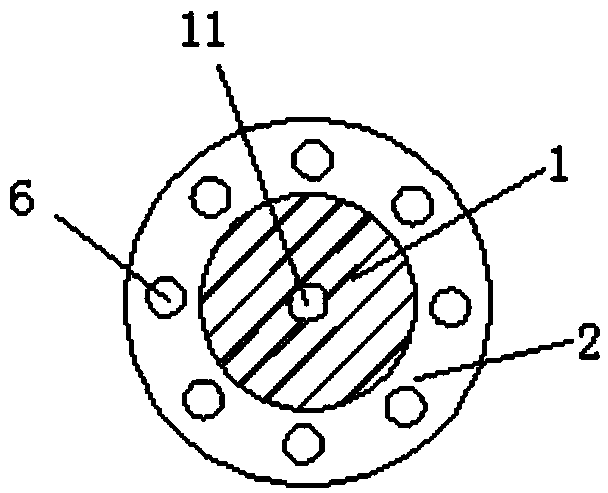
Device for quickly drilling in frozen earth and construction method thereof
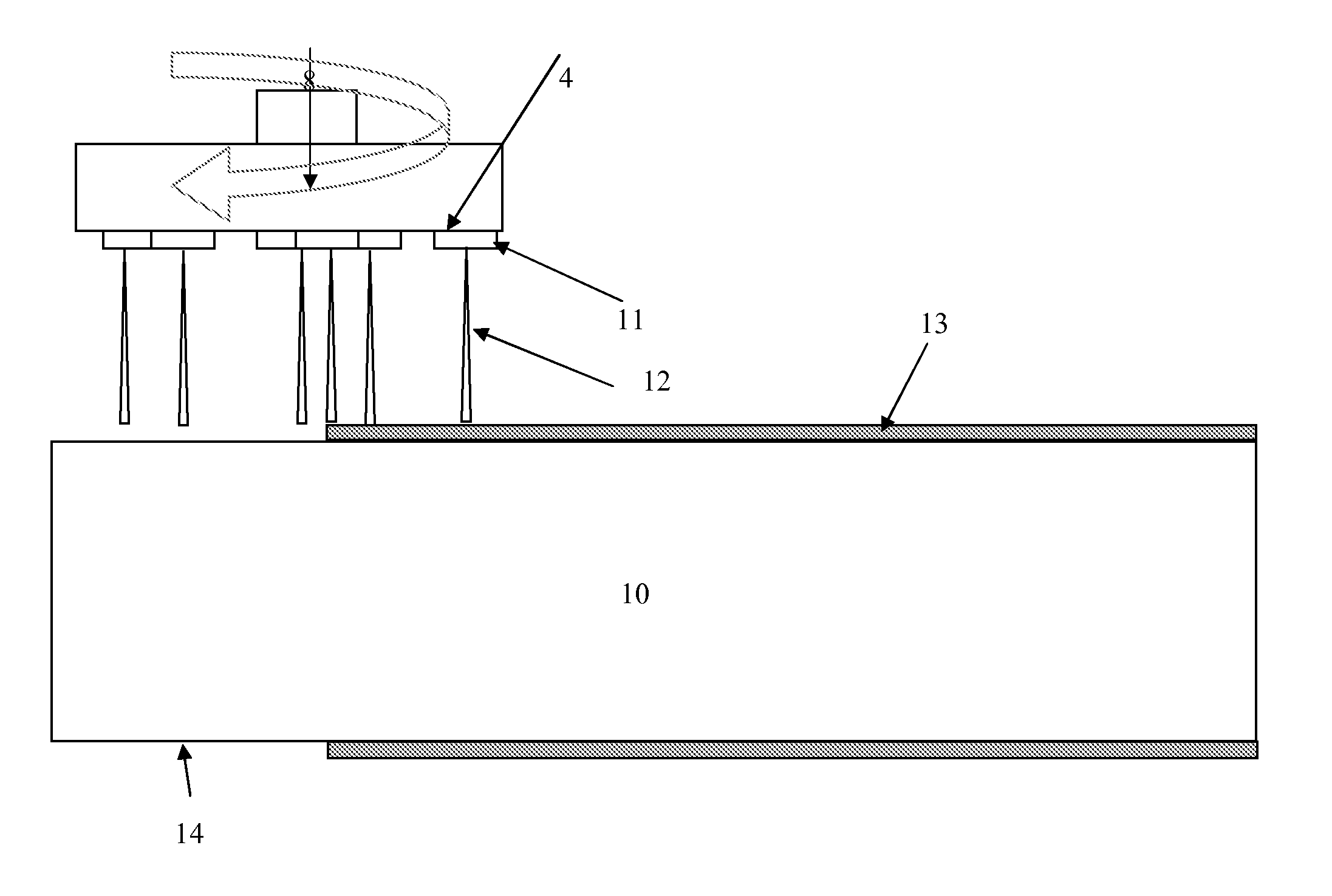
ActiveCN104110221AHigh speedDecrease phenomenonEarth drilling toolsDrill bitsNitrogenLiquid nitrogen
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
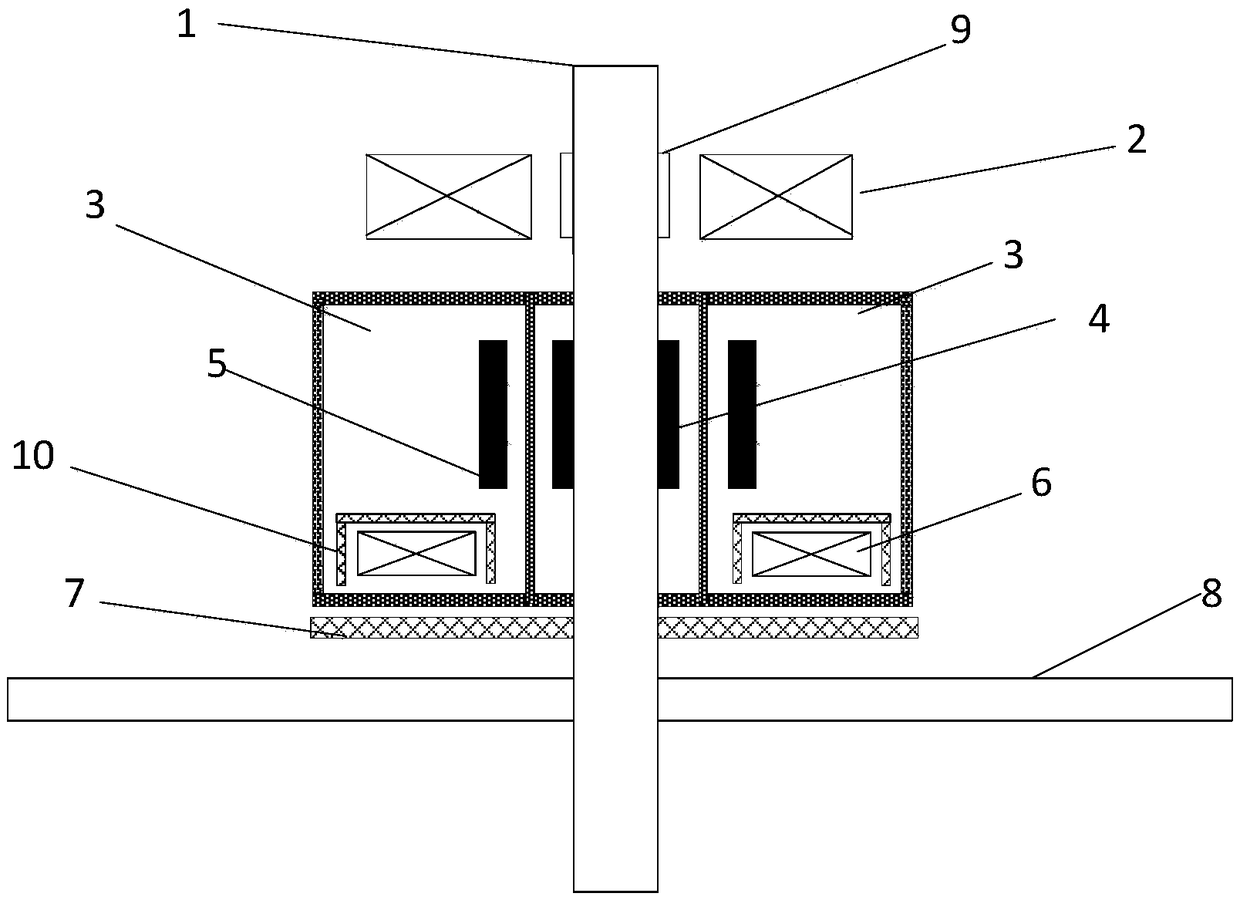
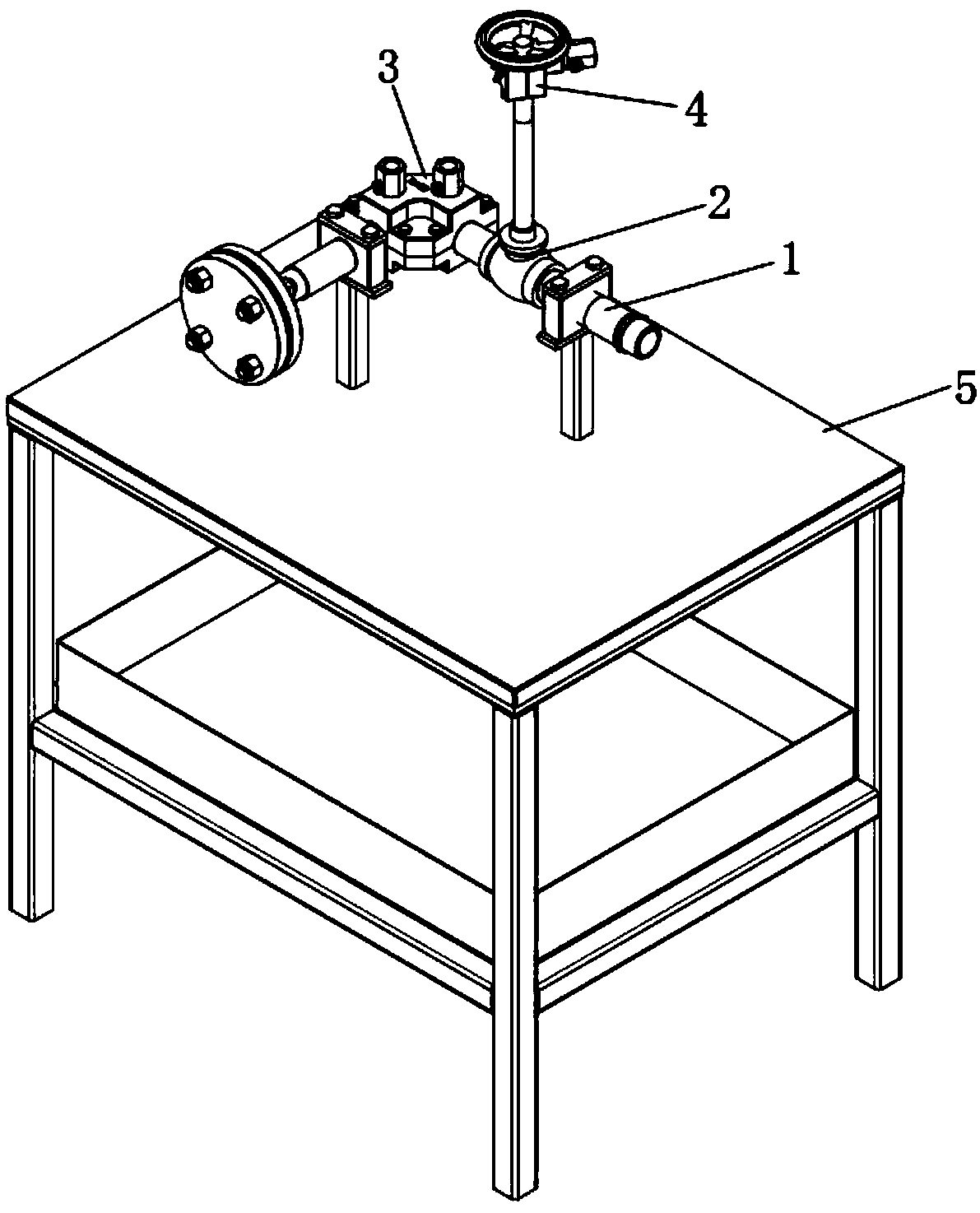
Device for measuring thermoelectric performance in wide temperature range
InactiveCN1837801AGuaranteed accuracyAvoid mutationElectrical testingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectricityMeasurement device
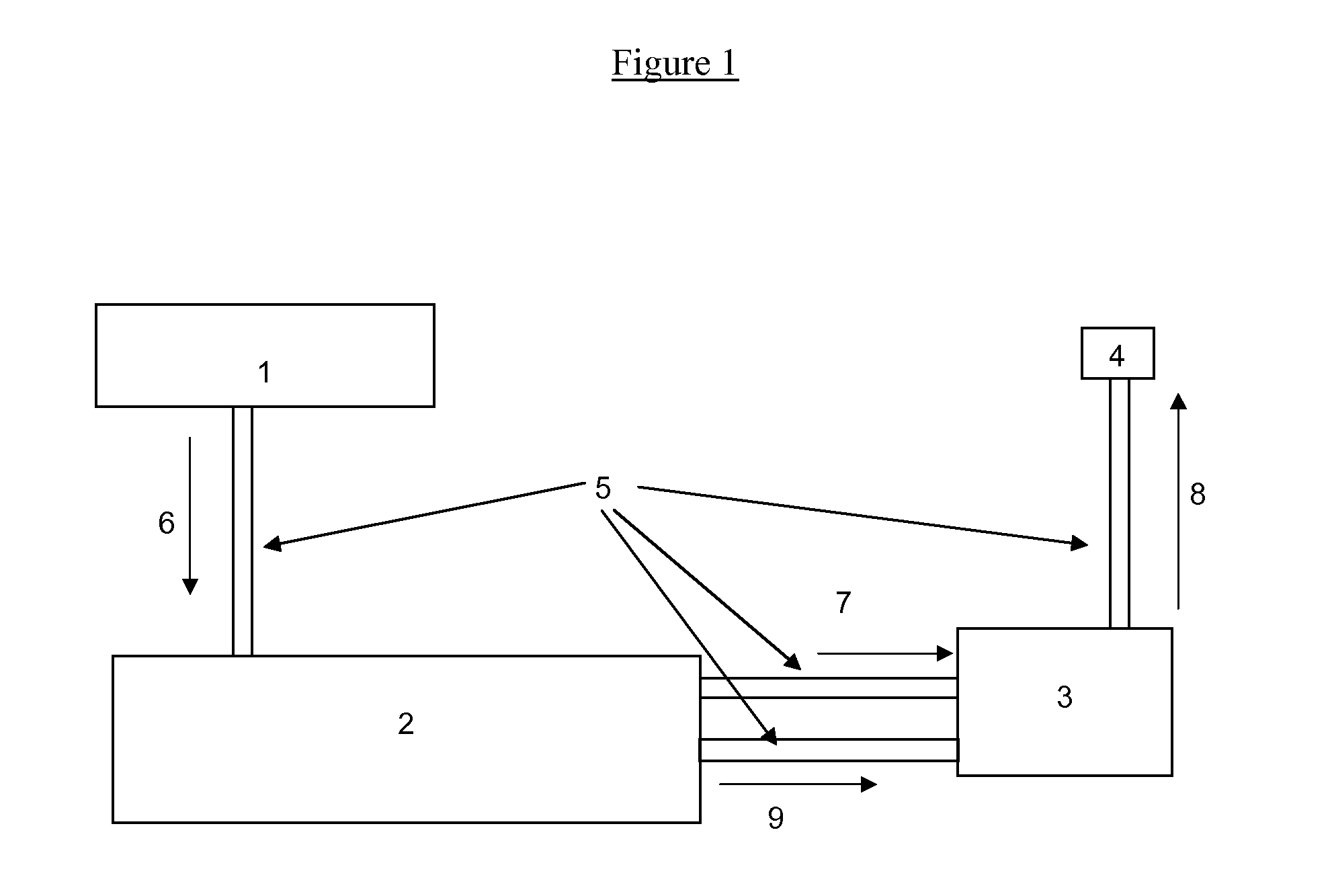
This invention relates to a device for measuring thermoelectric performance in wide temperature range, which comprises a measuring platform (5); a sealed vacuum chamber (2) with a vacuumizing device, a heater (9) and a liquid nitrogen cavity (7) connected to the lower ends of an inlet pipe (4) and an outlet pipe (6). Wherein. Both upper ends of (4) and (6) are outside of the chamber (2); there is an insulating layer (8) between (5) and (7). This invention can measure property continually.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
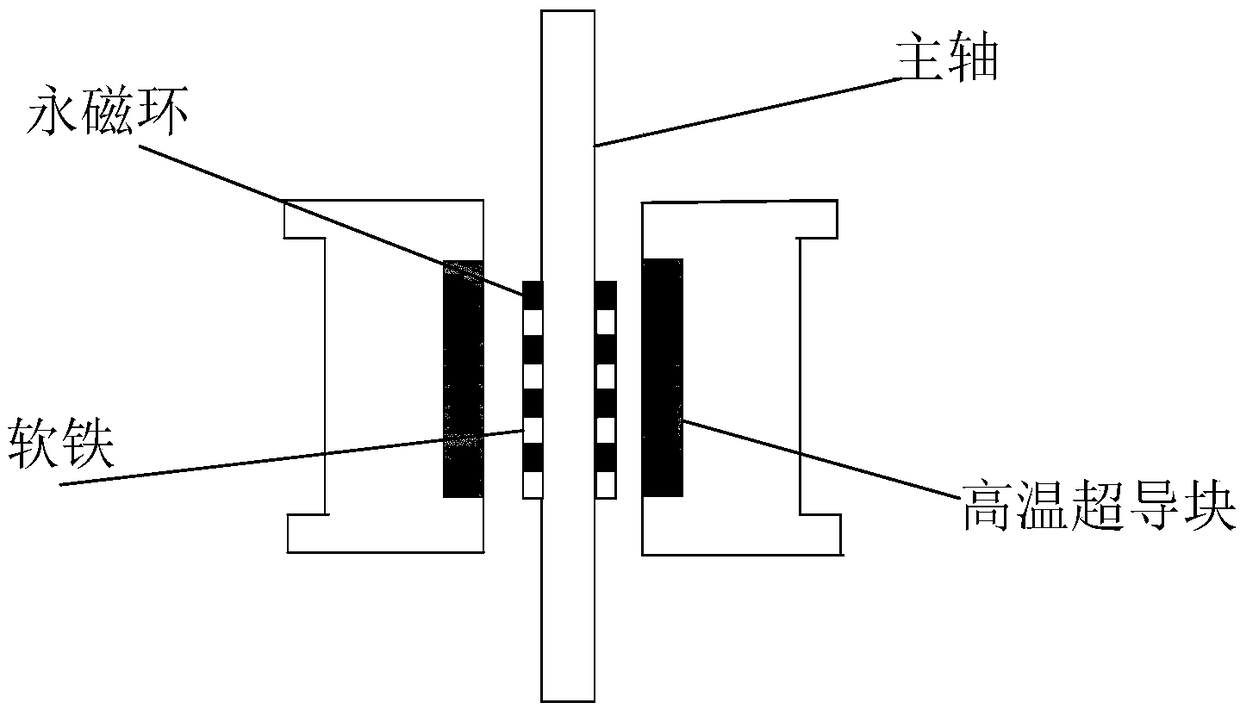
Flywheel energy storage mixed type superconducting magnetic bearing
ActiveCN108869543ASuppression of radial swingIncreased complexityMagnetic bearingsEngine componentsSuction forceSuperconducting magnetic bearing
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Low temperature liquefaction vehicle fuel tanker operation box pipeline equipment plugging simulation test bench
PendingCN109459225AMachine part testingFluid-tightness measurement using fluid/vacuumGas cylinderEngineering
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPECIAL EQUIP INSPECTION & TECHN RES
Mobile energy station and energy utilization method
ActiveCN105715952AGuaranteed stabilityImprove securityPressure vesselsSteam engine plantsNitrogenProduct gas
Owner:ENN SCI & TECH DEV
Method for extracting chitosan from oyster shells
The invention discloses a method for extracting chitosan from oyster shells. The method includes the steps of firstly, using clean water to clean waste oyster shells to remove silt and impurities on the surfaces of the oyster shells; secondly, drying and crushing the oyster shells obtained in the first step to obtain oyster shell powder; thirdly, sequentially performing low-temperature freezing and low-temperature lyophilization, and then using liquid nitrogen as the grinding medium to perform low-temperature crushing under the temperature from minus 80 DEG C to minus 120 DEG C by using an ultralow-temperature crusher; fourthly, adding purified water into materials obtained in the third step, evenly mixing, and processing in a high-pressure homogenizing machine; fifthly, performing acid treatment, to be more specific, soaking materials obtained in the fourth step into diluted hydrochloric acid, washing until neutrality is achieved, centrifuging, and drying to obtain chitin; sixthly, performing deacetylation, and drying to obtain the chitosan. The method has the advantages that the whole working procedure time is shortened, black impurities in the intermediate working procedure are avoided, and the obtained chitosan is pure white.
Owner:GUANGXI HUANZHU MARINE BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Process for removing a composite coating present on the surface of a gas cartridge
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE
Efficient bleaching process of white cement clinkers
InactiveCN109206031AHigh whitenessIncrease the rate of temperature dropLiquid nitrogenCalcination
The invention discloses an efficient bleaching process of white cement clinkers. The efficient bleaching process of the white cement clinkers comprises the following steps of performing high-temperature firing on the white cement clinkers by a rotary kiln; discharging the white cement clinkers into a grate cooler from the discharging end of the rotary kiln for cooling; after the high-temperature cement clinkers enter the grate cooler, falling the high-temperature cement clinkers onto a first grate bed for cooling; performing sharp cooling on the cement clinkers in the first grate bed through providing mixed liquid nitrogen and air; cooling the cement clinkers to 600 to 800 DEG C; then, falling the cement clinkers onto a second grate bed to be cooled; performing air cooling in the second grate bed completely through the air; cooling the cement clinkers to 80 to 100 DEG C; discharging the cement clinkers out of the grate cooler. The invention aims at providing the efficient bleaching process of the white cement clinkers so as to solve the problems of whiteness improvement limitation and more heat consumption requirement during white cement clinker calcination.
Owner:JIANGXI YINSHAN WHITE CEMENT CO LTD
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap