Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45results about "Acoustic wave reradiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
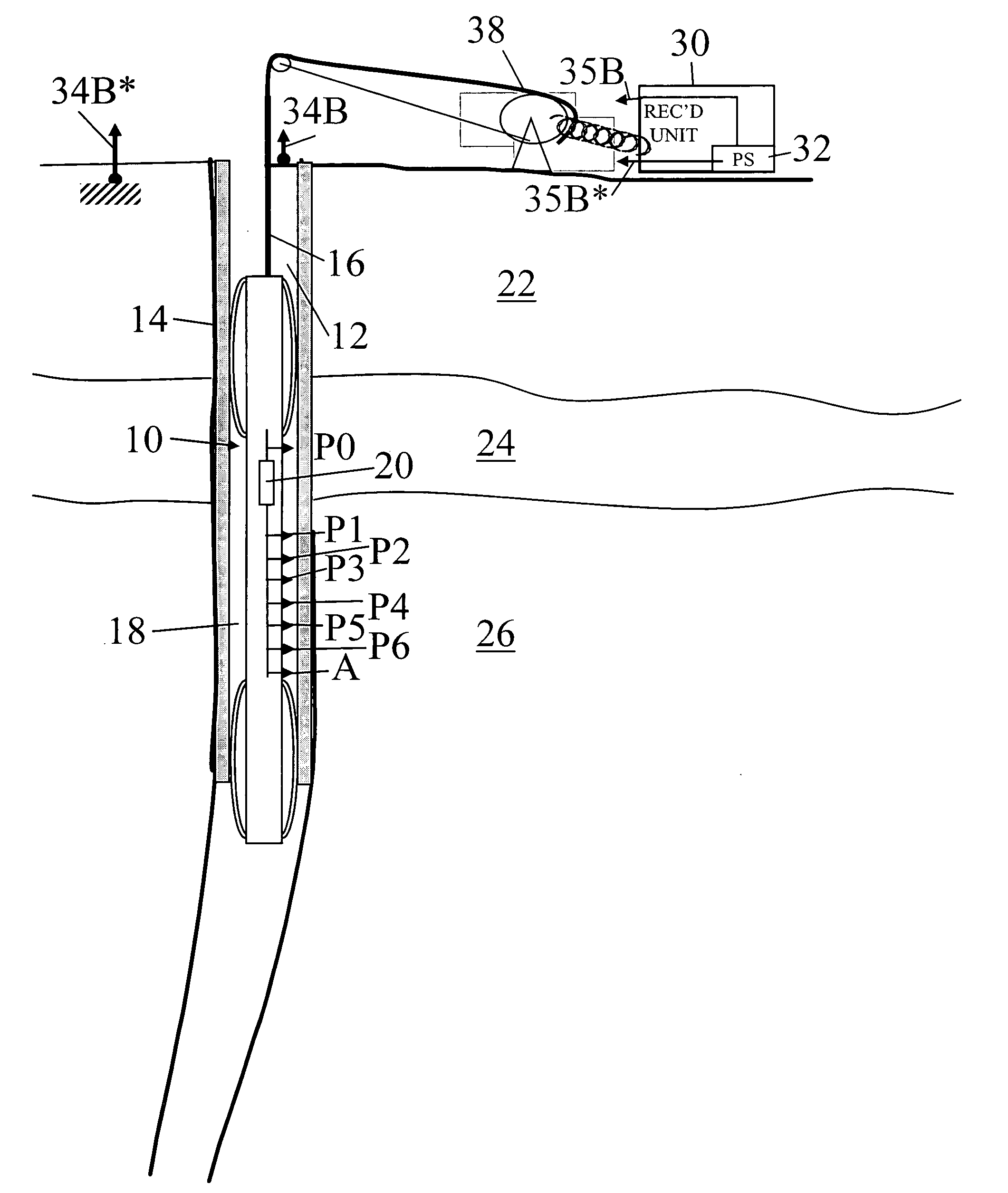
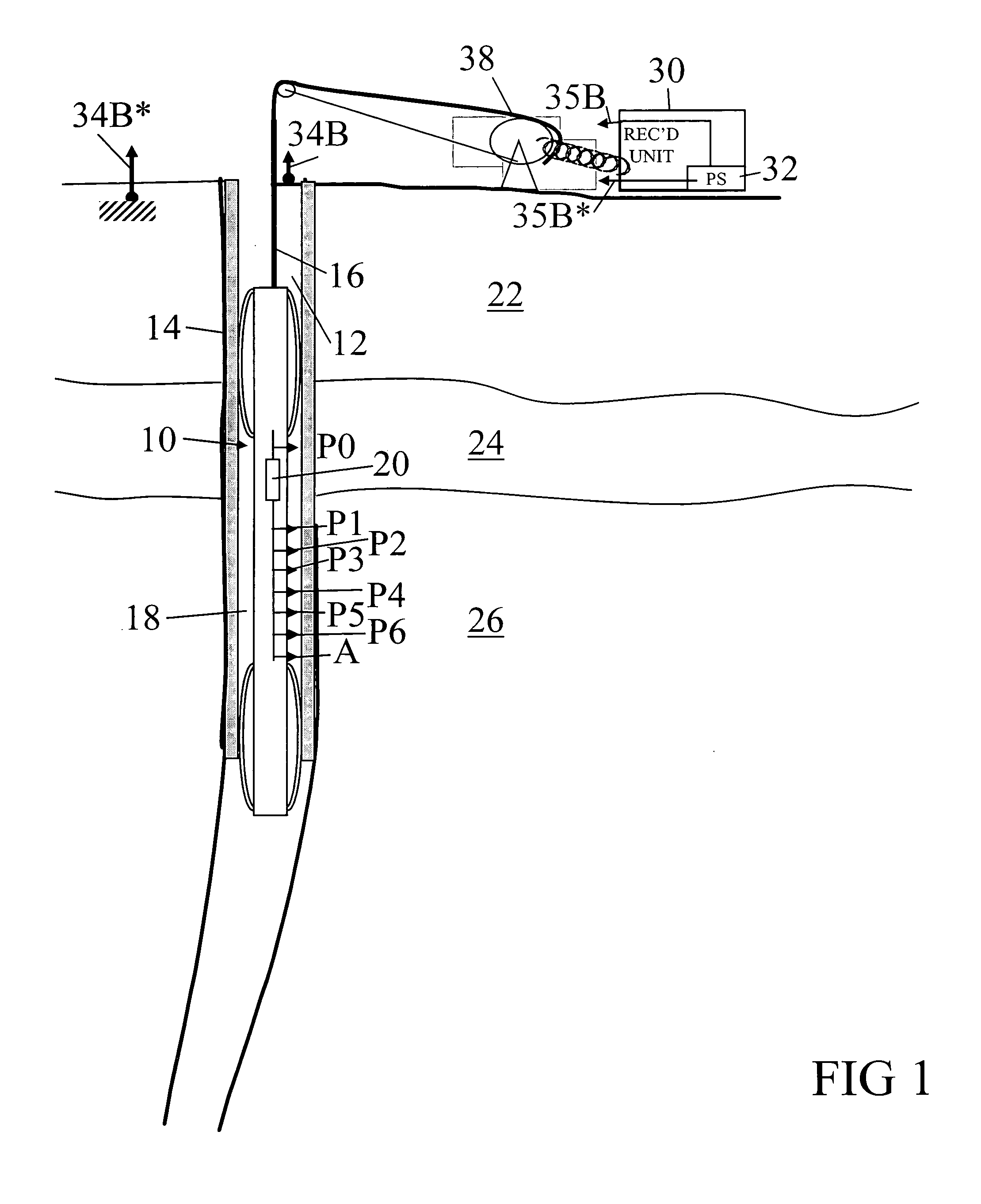
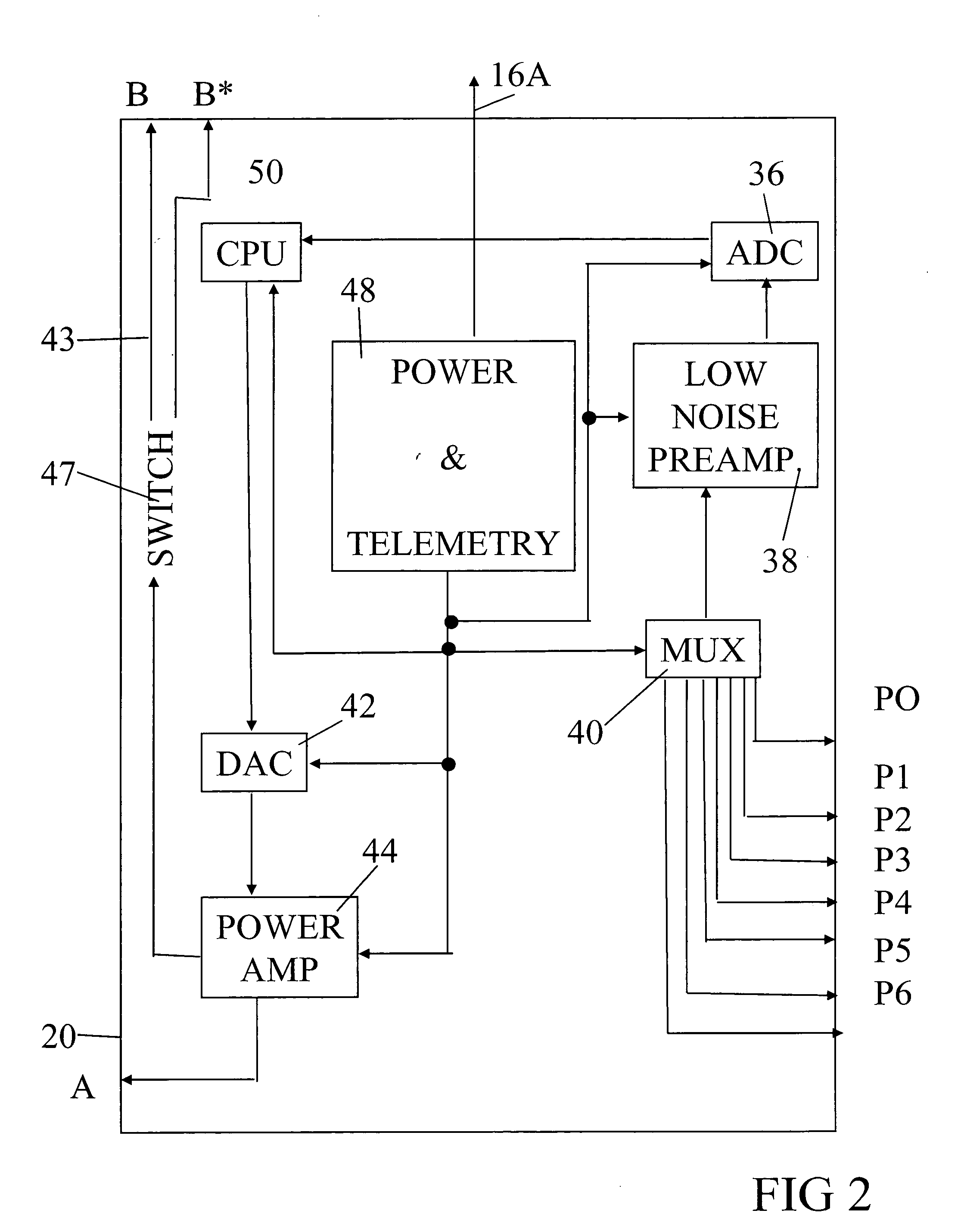
Methods for characterization of petroleum reservoirs employing property gradient analysis of reservoir fluids
ActiveUS20130151159A1Accurate representationElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingConstructionsReservoir fluidPetroleum reservoir
A methodology for reservoir understanding employs analysis of fluid property gradients to investigate and distinguish between non-compartmentalization of the reservoir, compartmentalization of the reservoir, and lack of thermodynamic equilibrium in the reservoir.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System for measuring earth formation resistivity through an electrically conductive wellbore casing
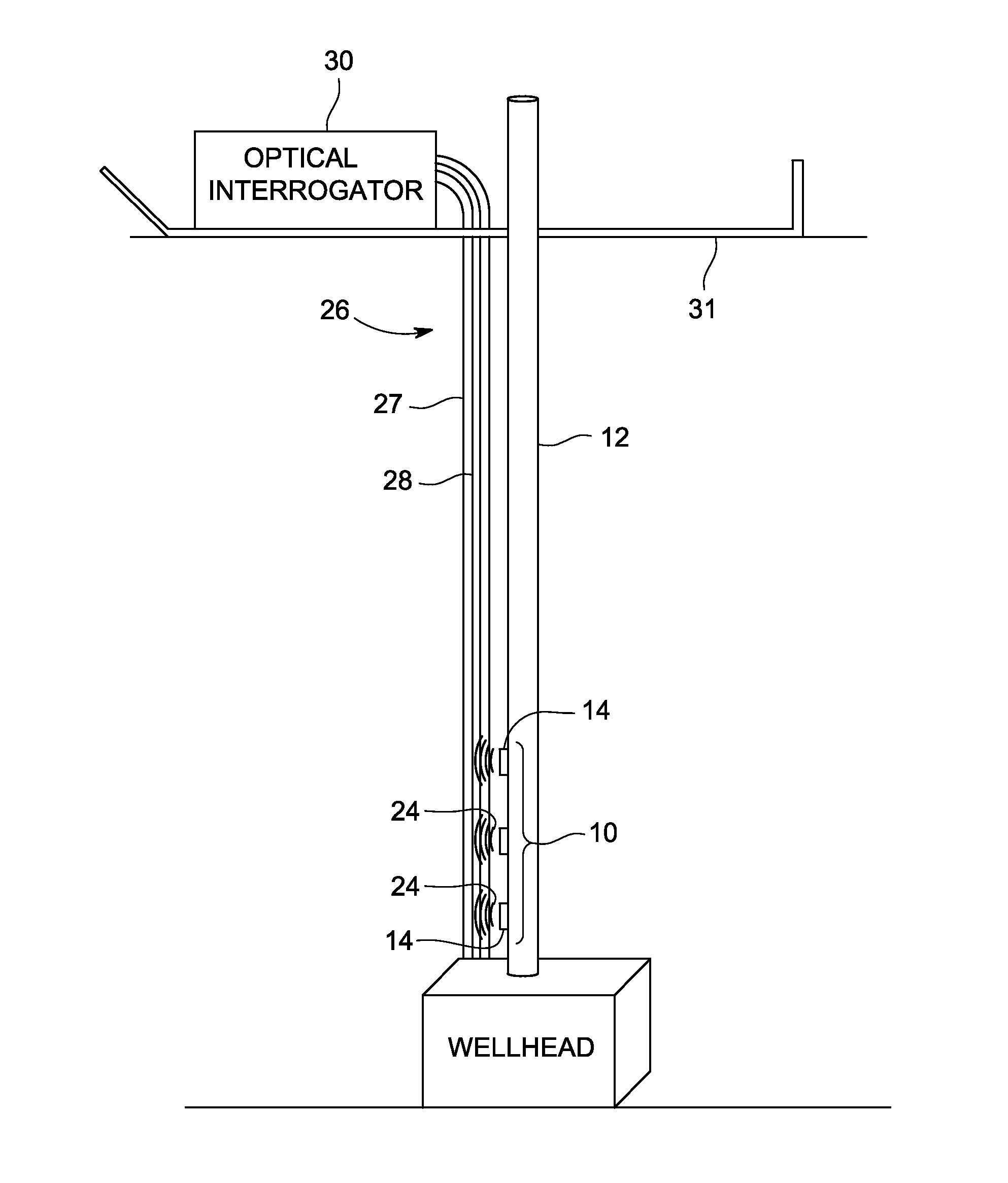
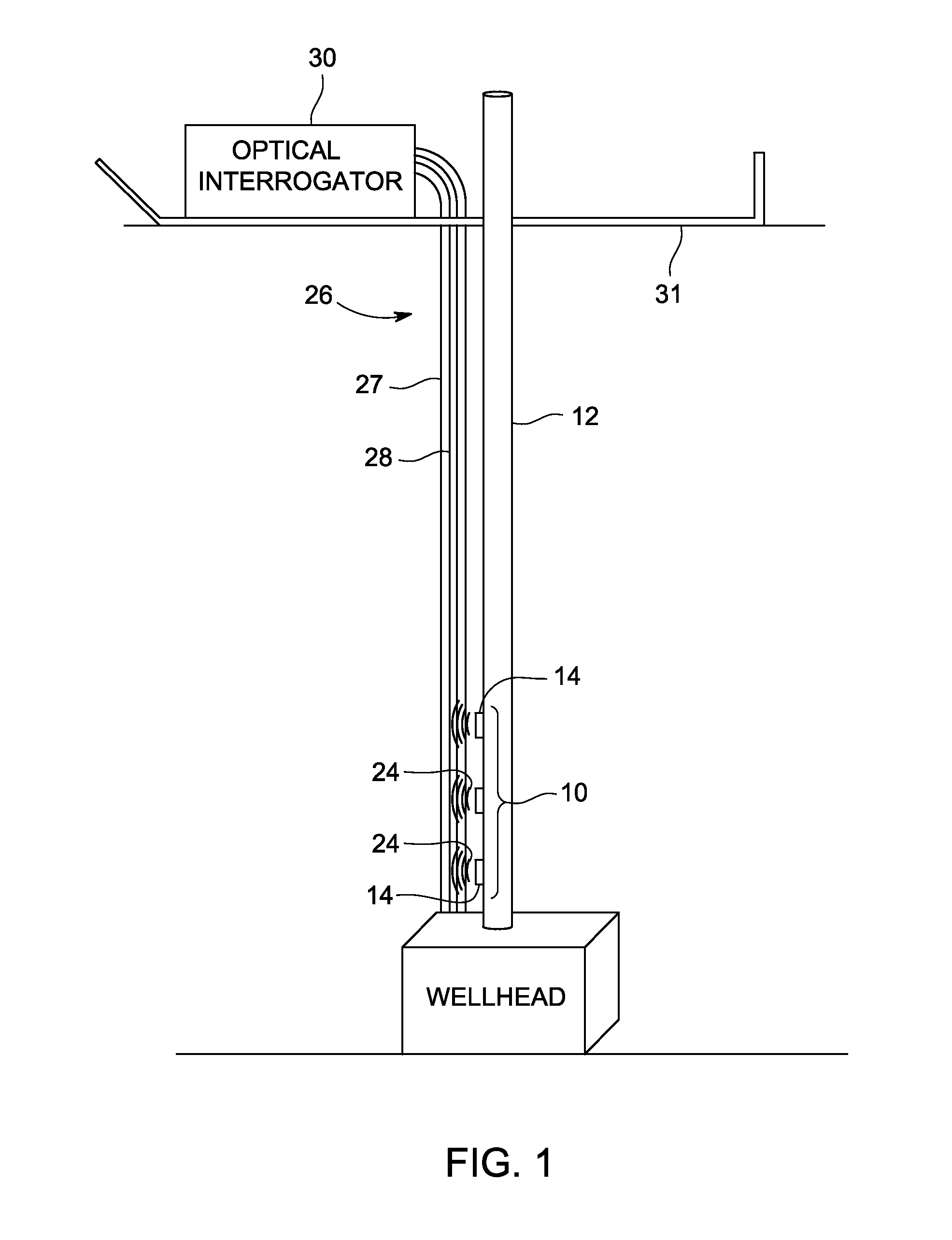
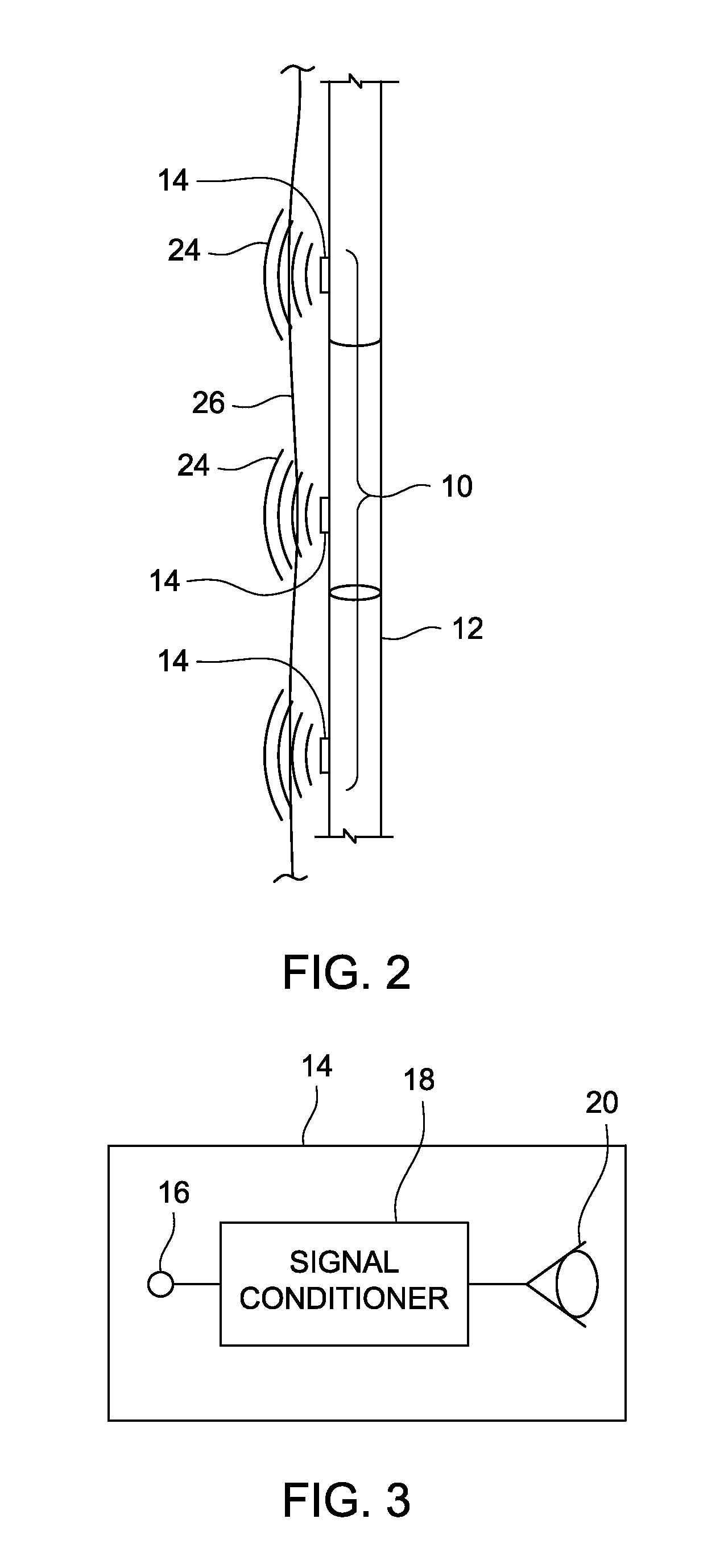
InactiveUS20050264295A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingAcoustic wave reradiationElectricityEngineering
Owner:KJT ENTPR
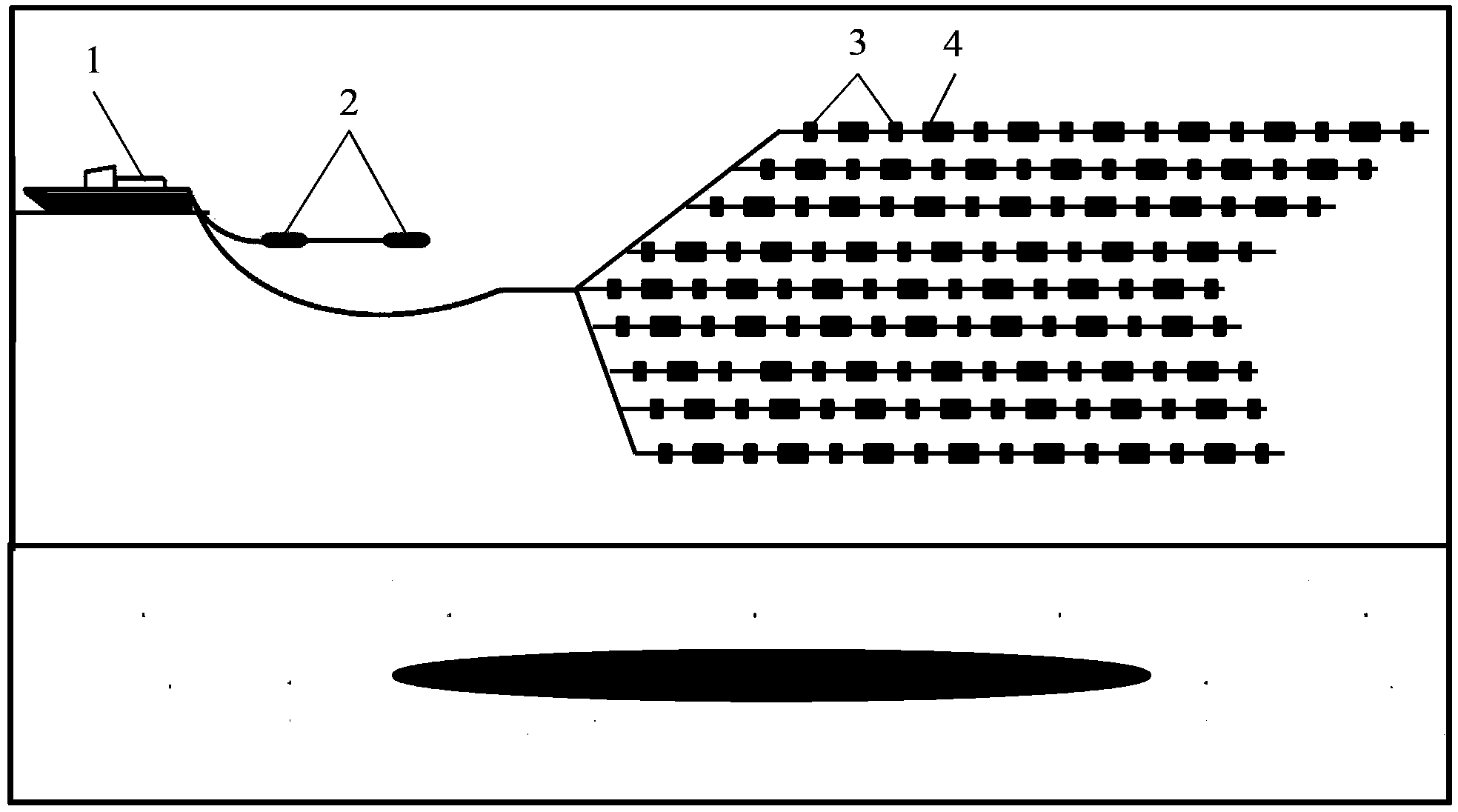
Towrope type ocean controllable source electromagnetism and earthquake data collection system
InactiveCN104280781AImprove reliabilityIncrease the amount of data collectedSeismic signal receiversElectric/magnetic detectionElectric field sensorAccelerometer
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
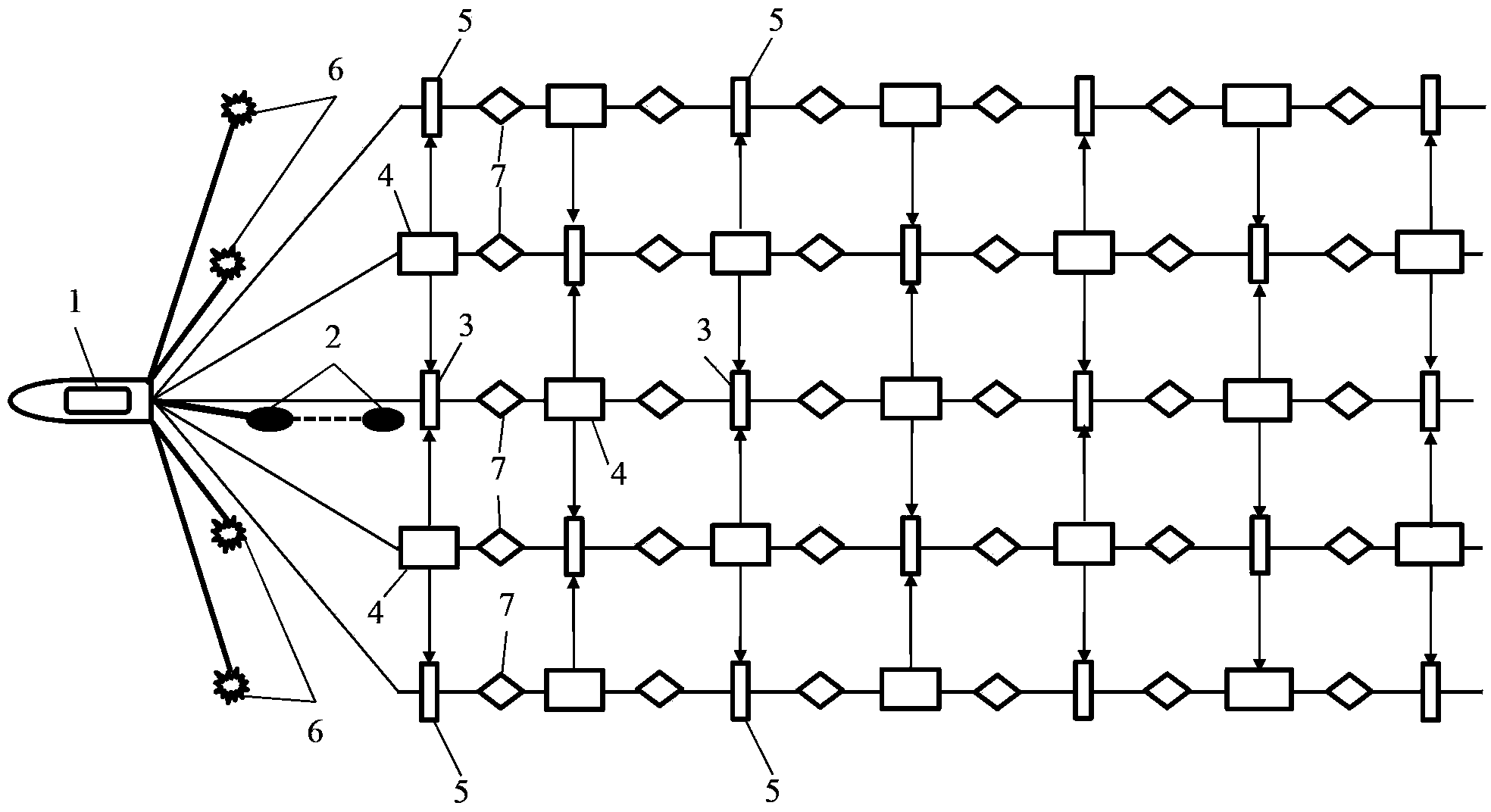
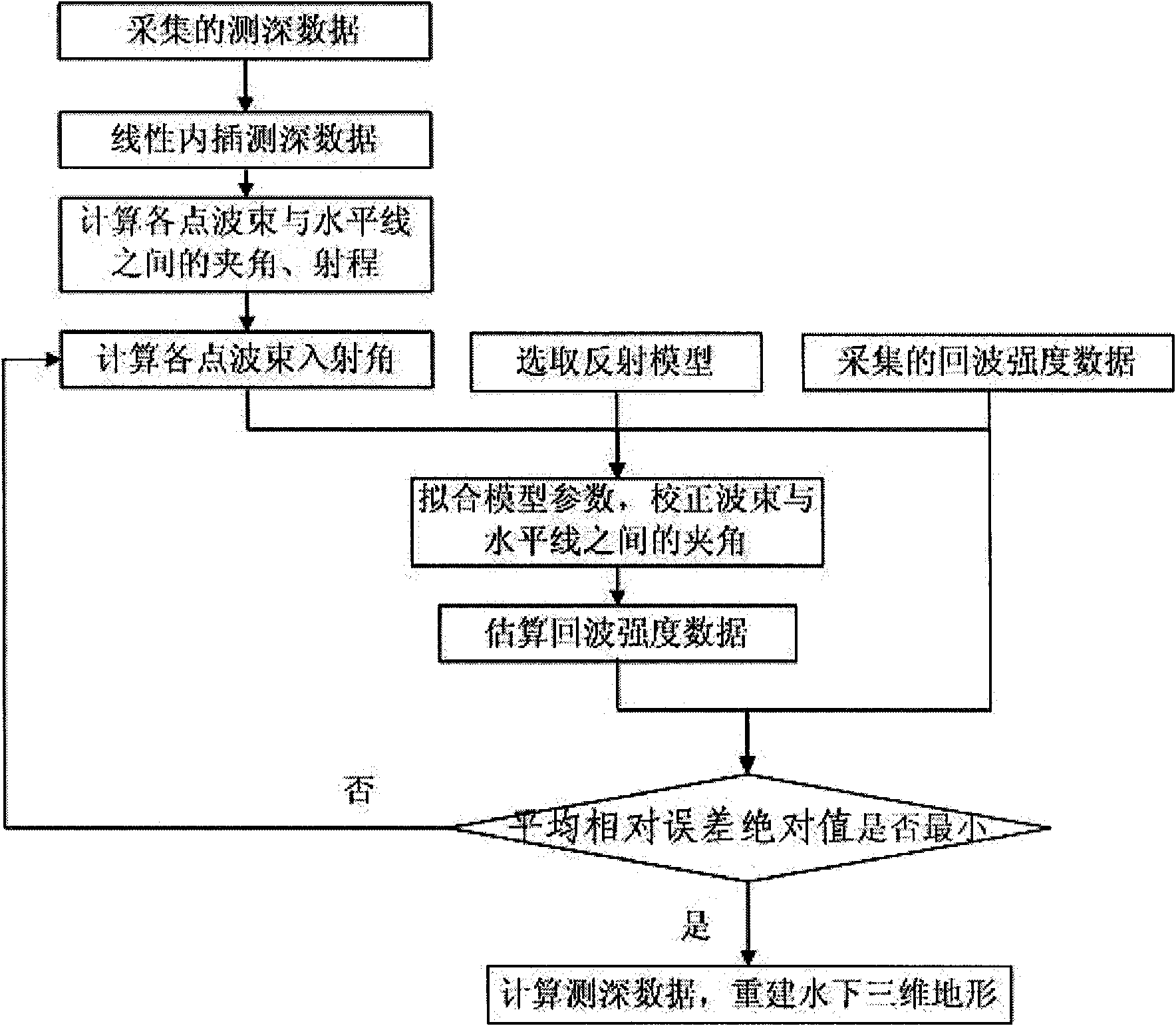
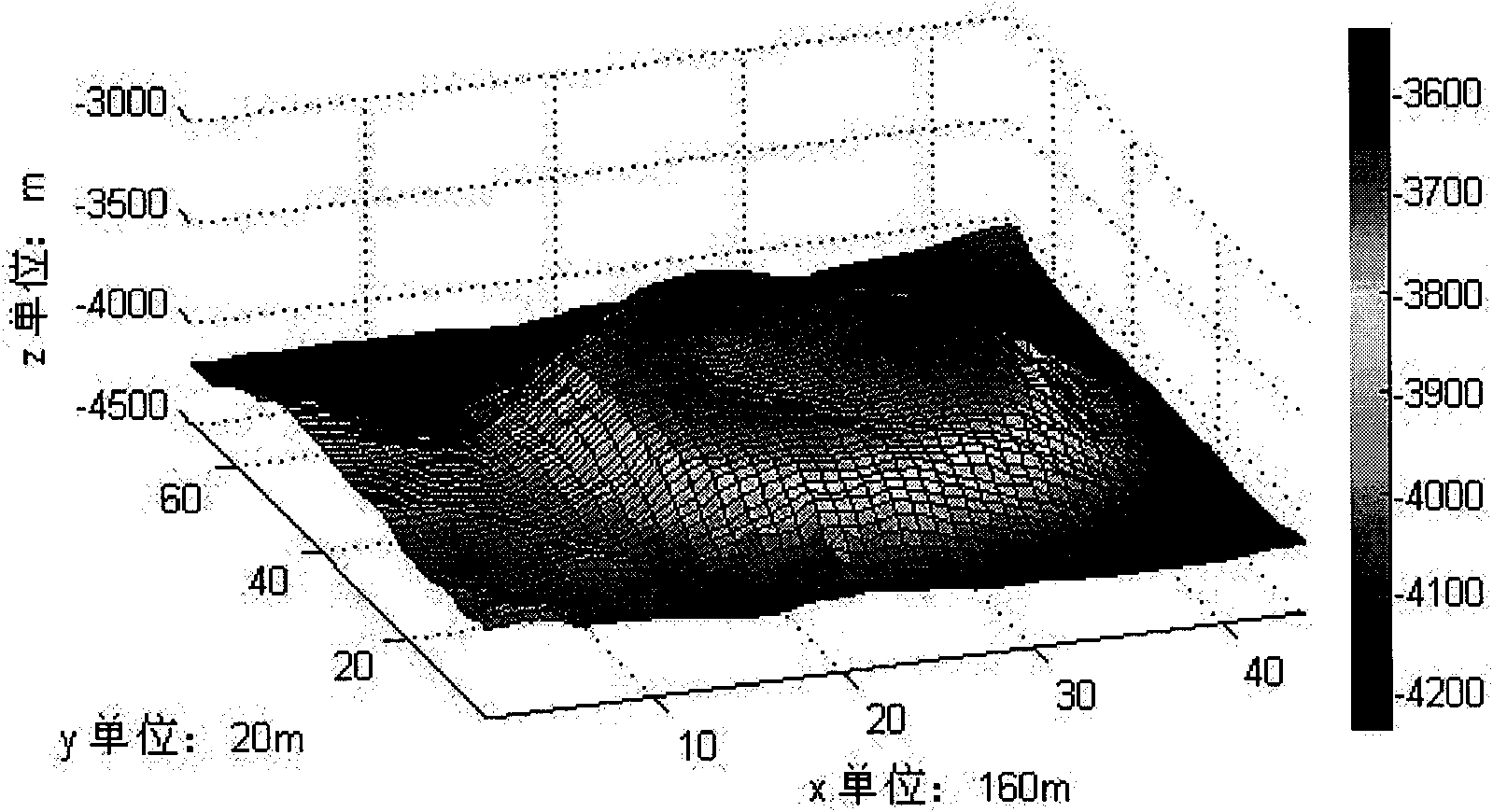
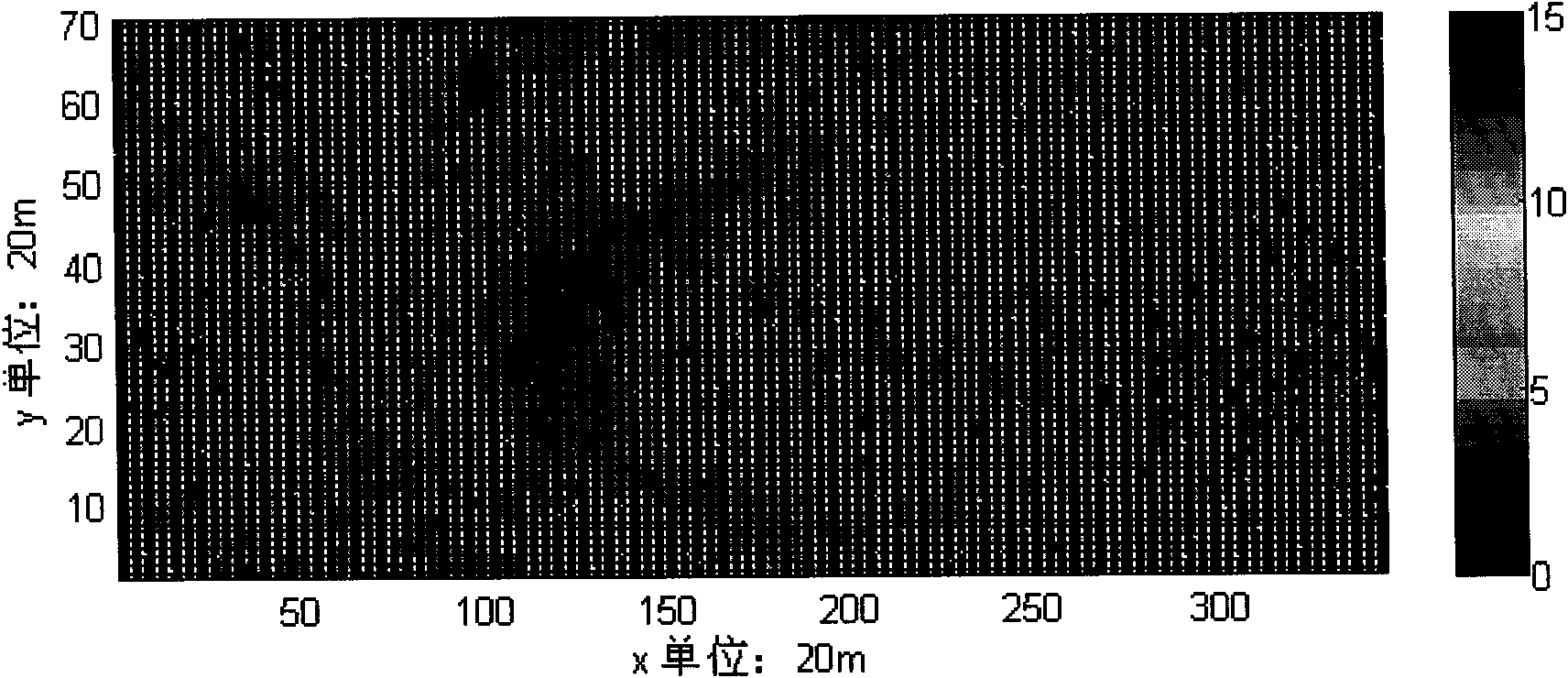
Underwater three dimensional terrain reconstruction method based on multi-beam sonar data
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
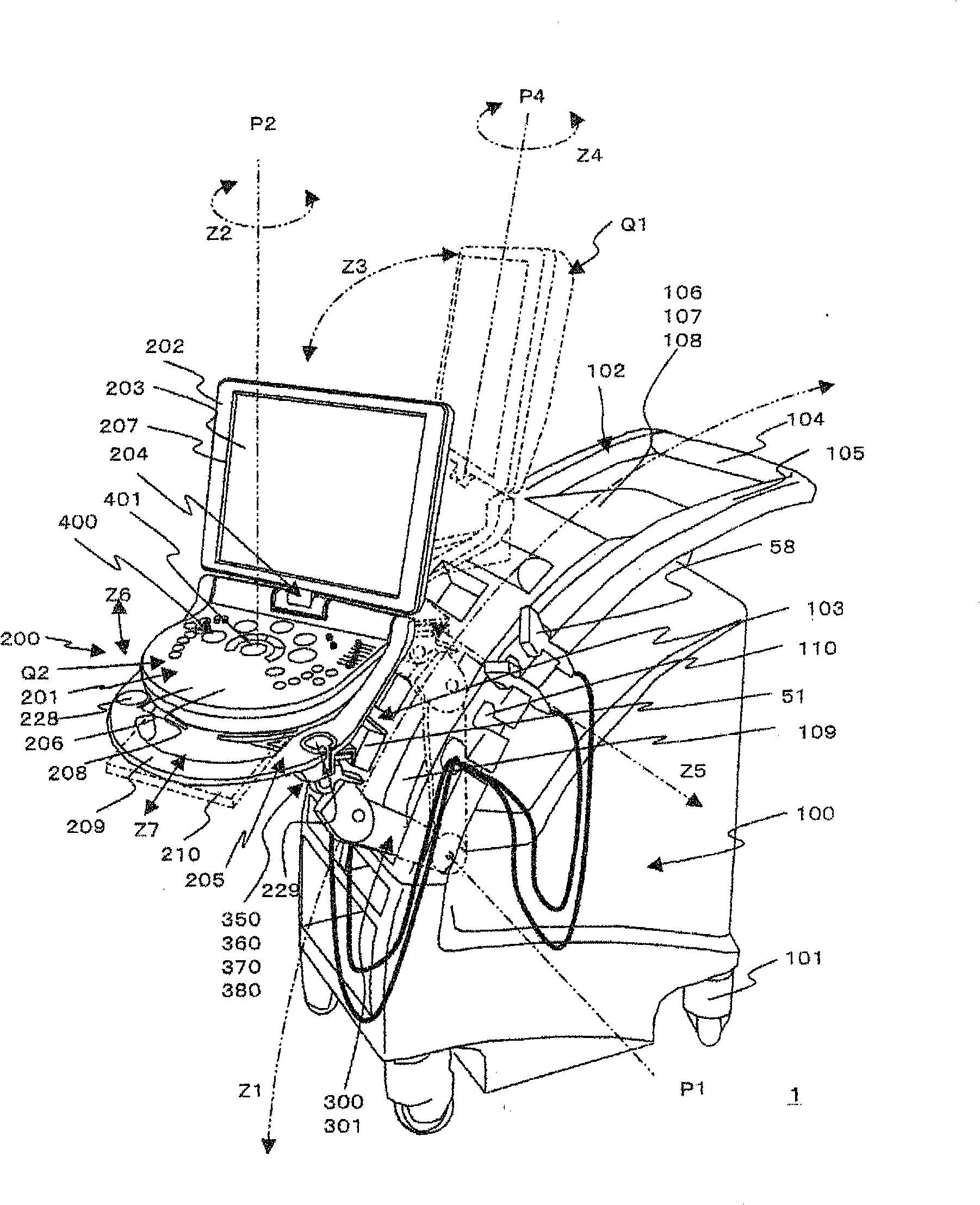
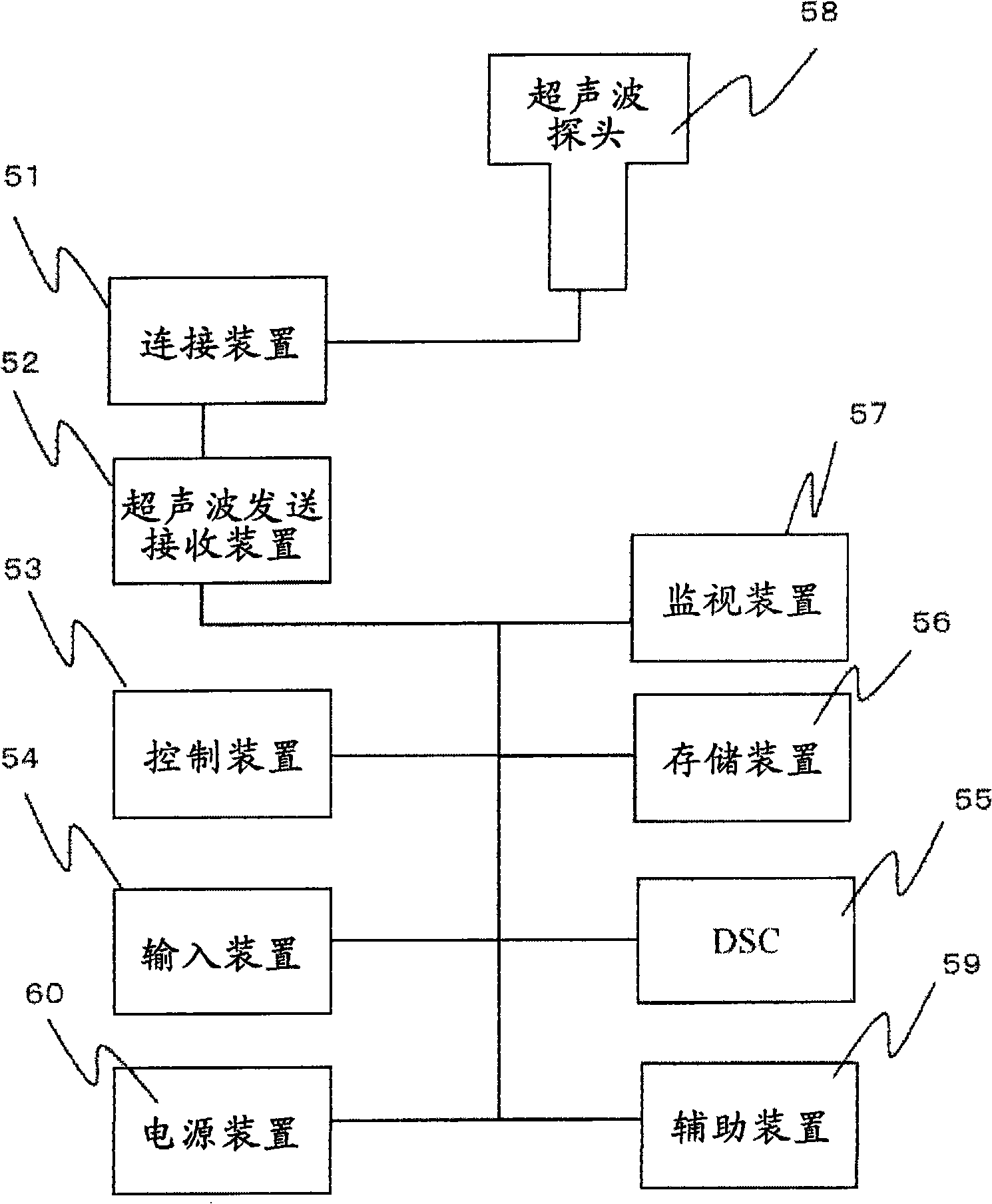
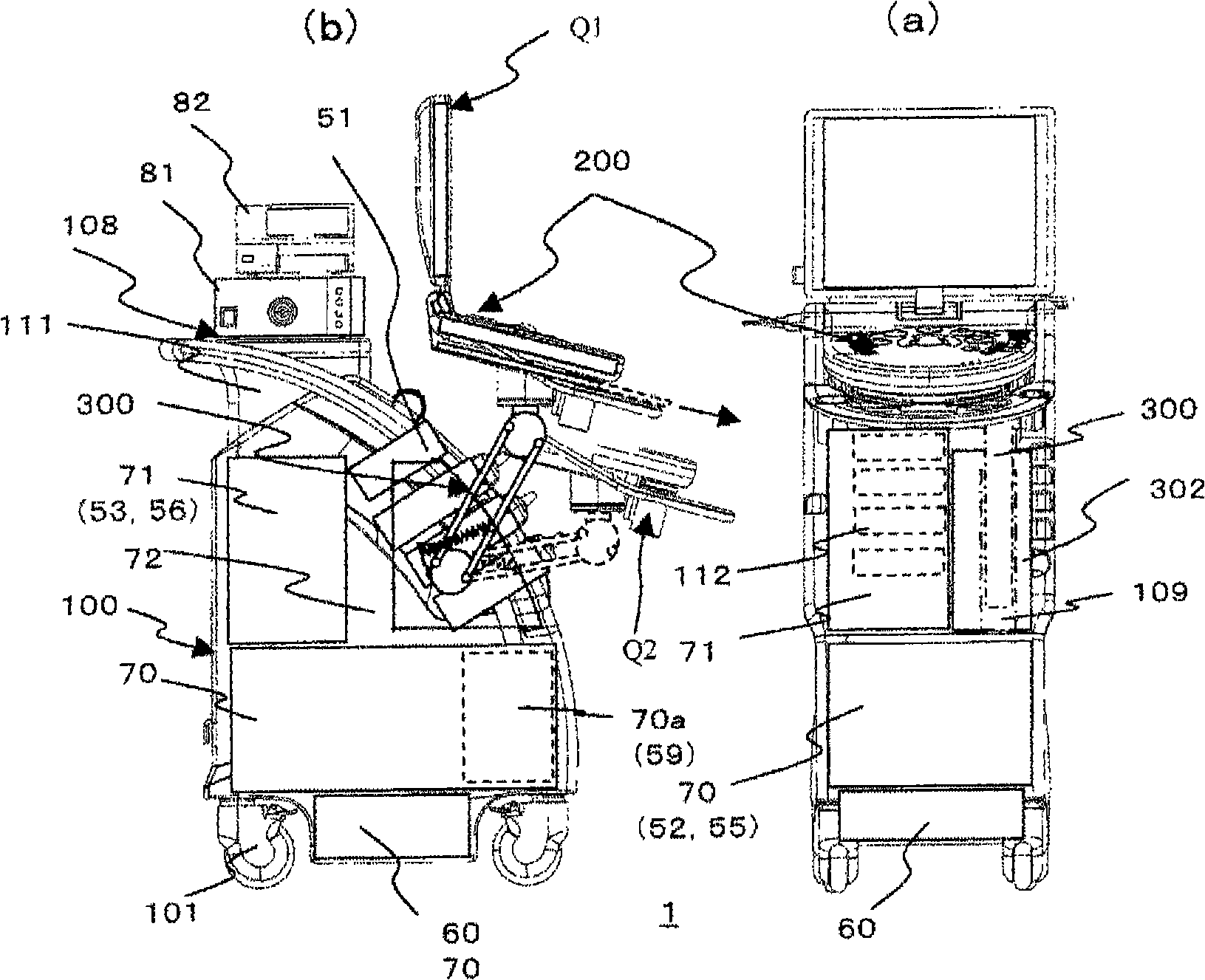
Ultrasonograph
ActiveCN101541246AEasy to operateEasy to moveUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsStanding PositionsOperability
Owner:HITACHI HEALTHCARE MFG LTD
Quick beamforming method capable of improving array resolution and gain
InactiveCN101609150AImprove resolutionOvercoming demandsAcoustic wave reradiationComputation complexityComputation process
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
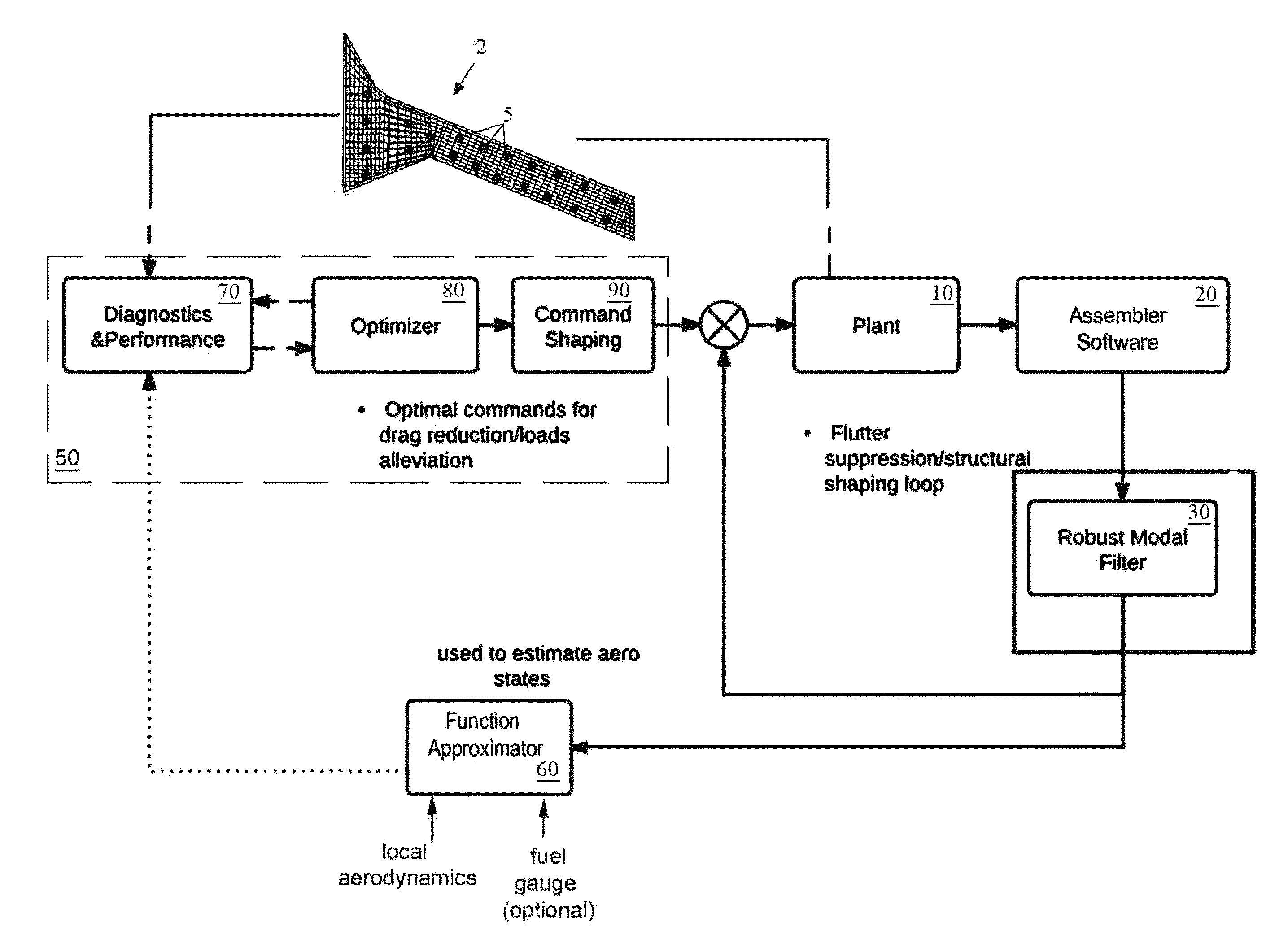
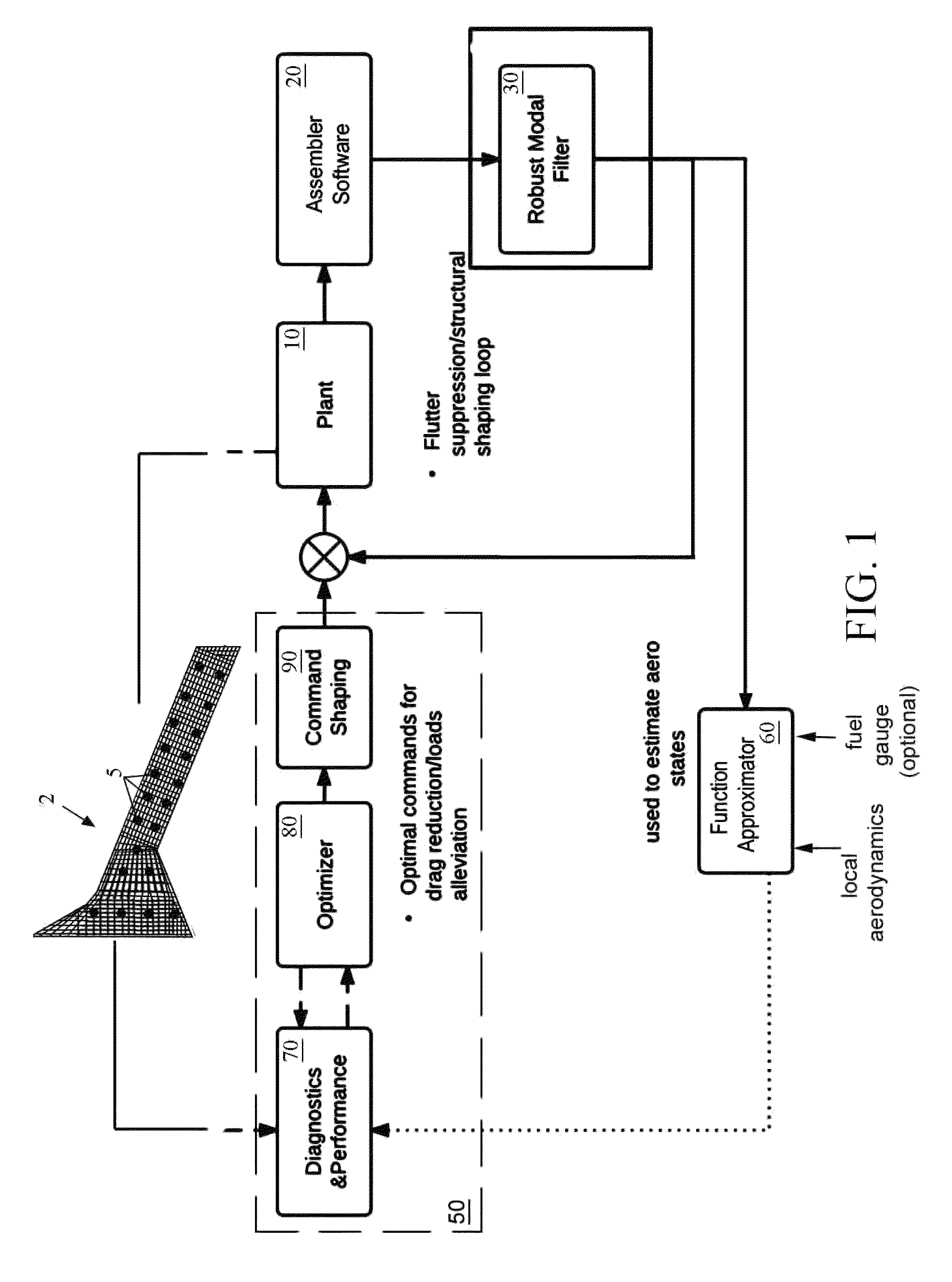
System and method for dynamic aeroelastic control
ActiveUS9073623B1Drag minimizationMaximize fuel efficiencyDetection of fluid at leakage pointPhase-affecting property measurementsSensor arrayStructural monitoring
Owner:NASA
System and method for providing variable ultrasound array processing in a post-storage mode
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Geosteering in Earth Formations Using Multicomponent Induction Measurements
ActiveUS20090018775A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismology for water-loggingGeosteeringPrincipal component analysis
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Sensor device and residual stress detection system employing same
ActiveUS20150300897A1Easy to integrateImprove reliabilityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesTransducerData acquisition
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
NMR MAS inflow bernoulli bearing
ActiveUS20060082371A1Improve stabilityIncrease stiffnessMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic measurementsAxial pressureSurface velocity
Owner:DOTY SCI
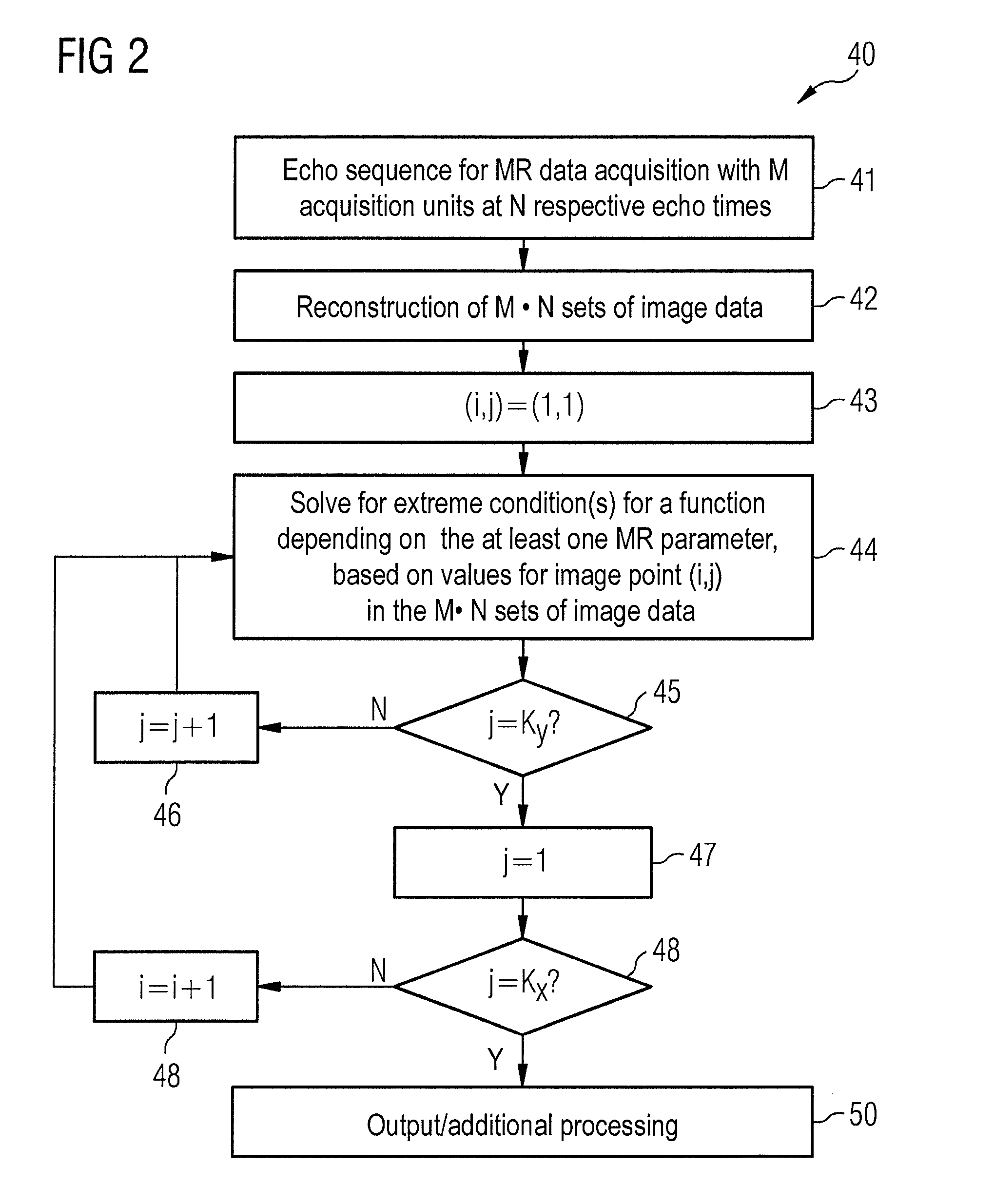
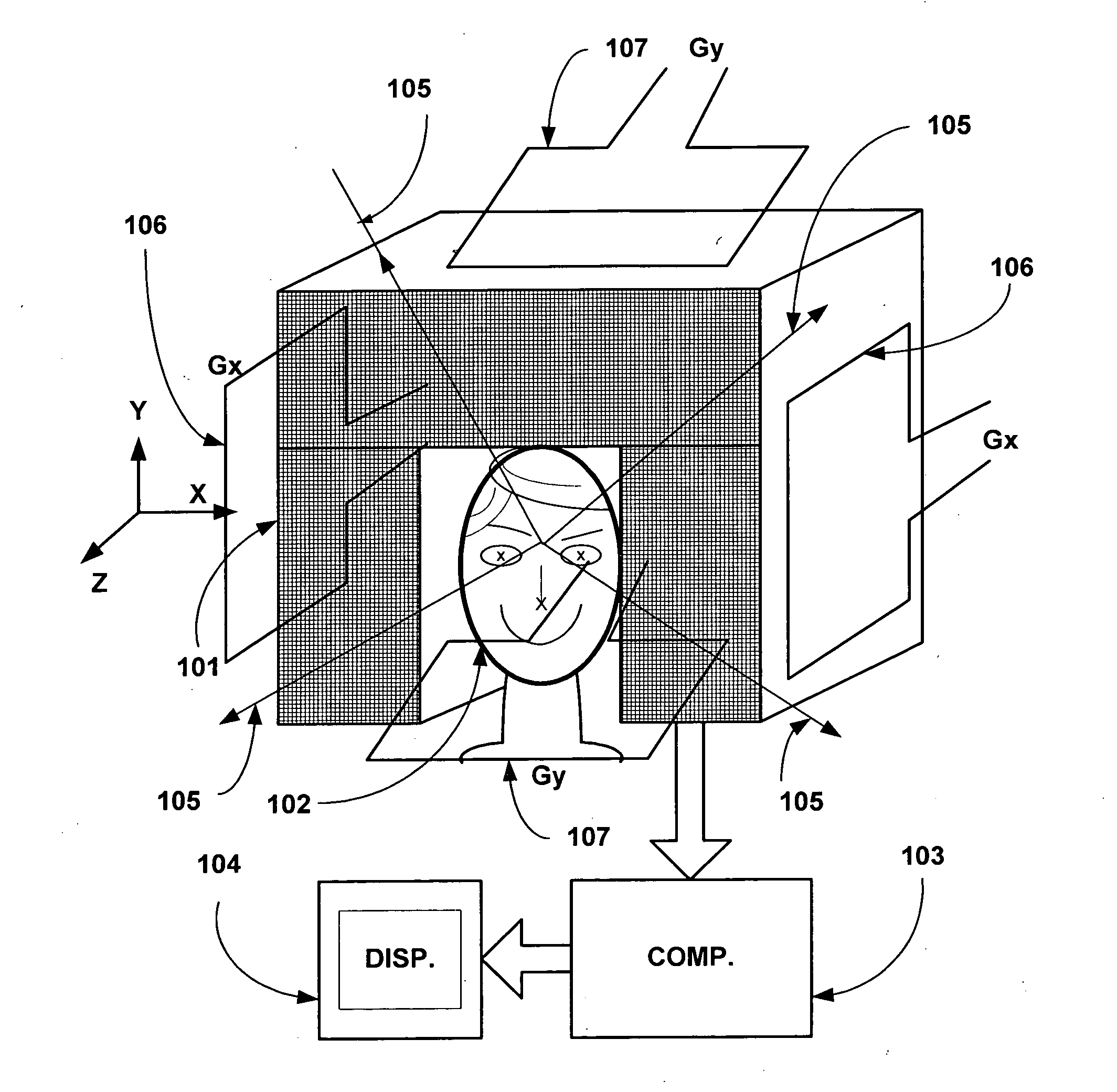
Method and device to process complex image data
InactiveUS20120224757A1Reduce disadvantagesSimplified determinationCharacter and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase differenceImage resolution
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
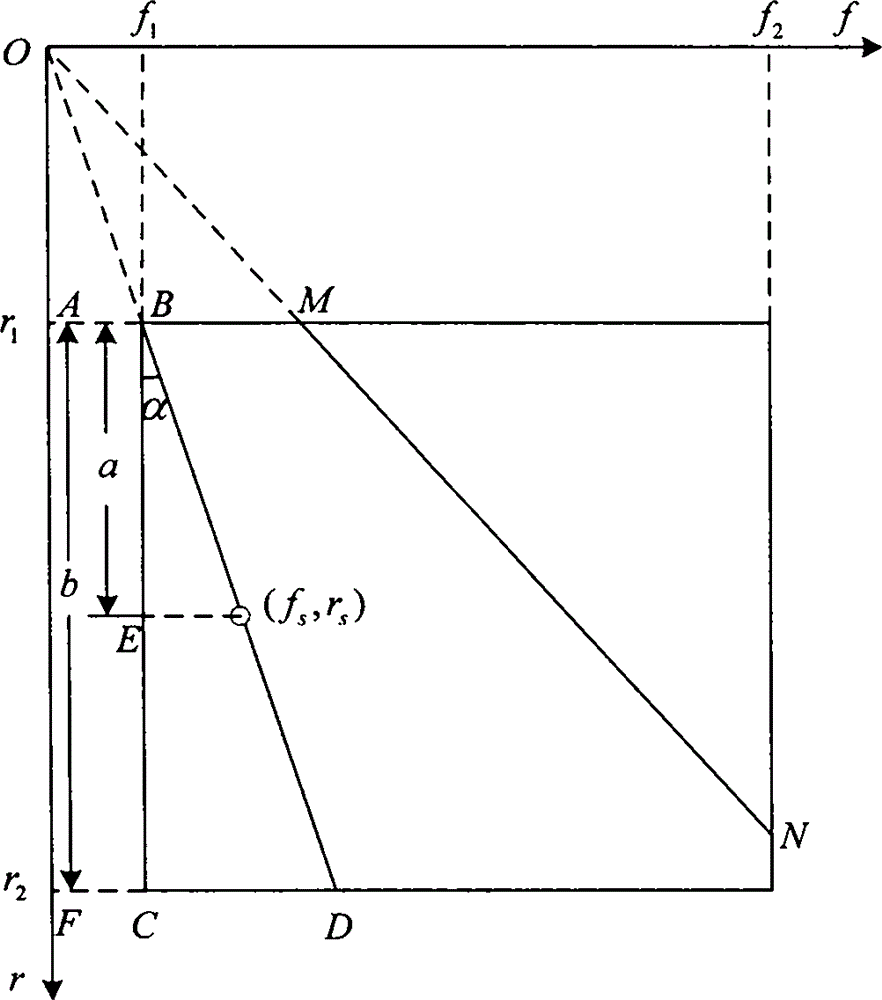
Single horizontal array passive speed measurement and distance measurement device based on sound field interference fringe and method
Owner:中国人民解放军92232部队
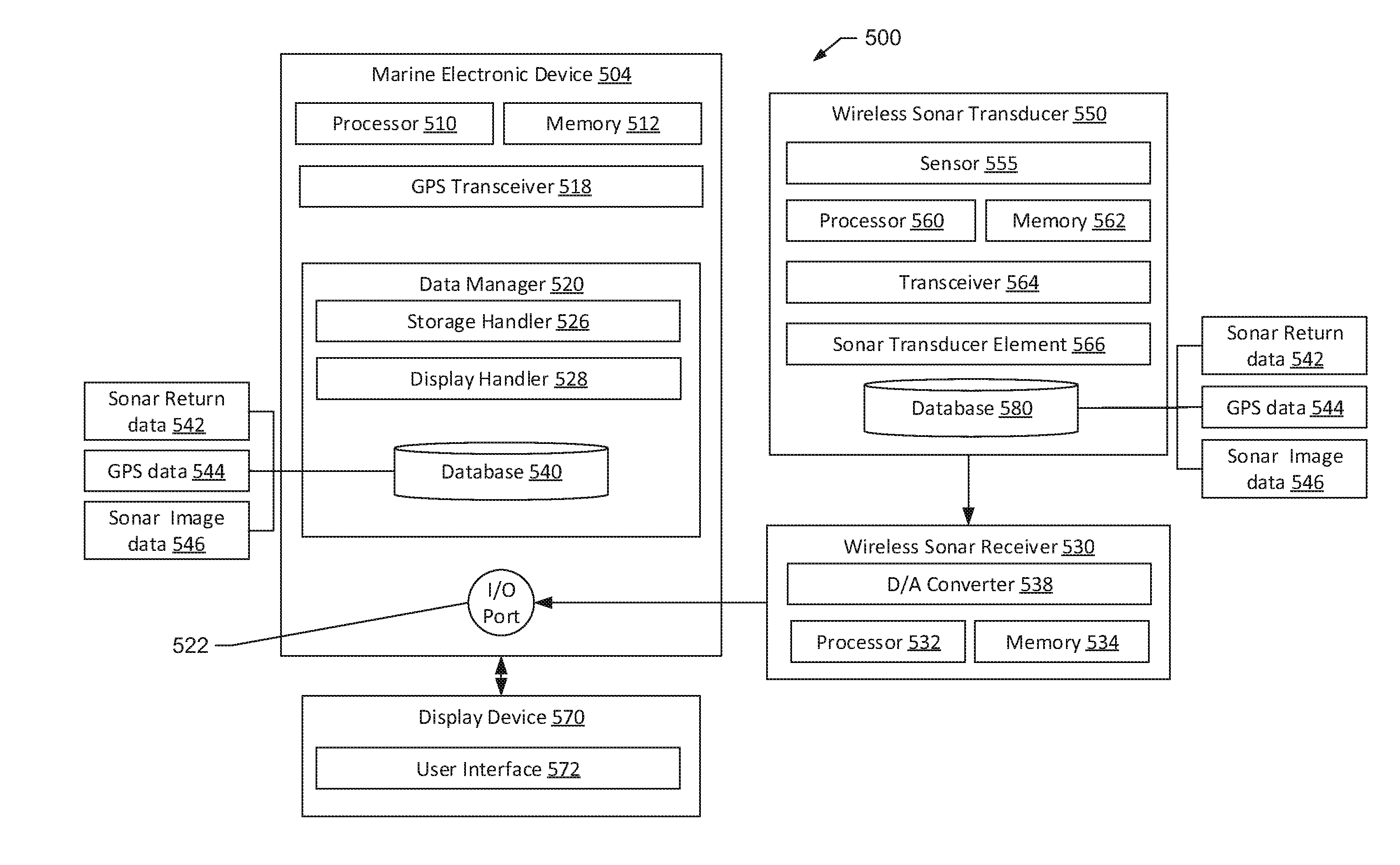
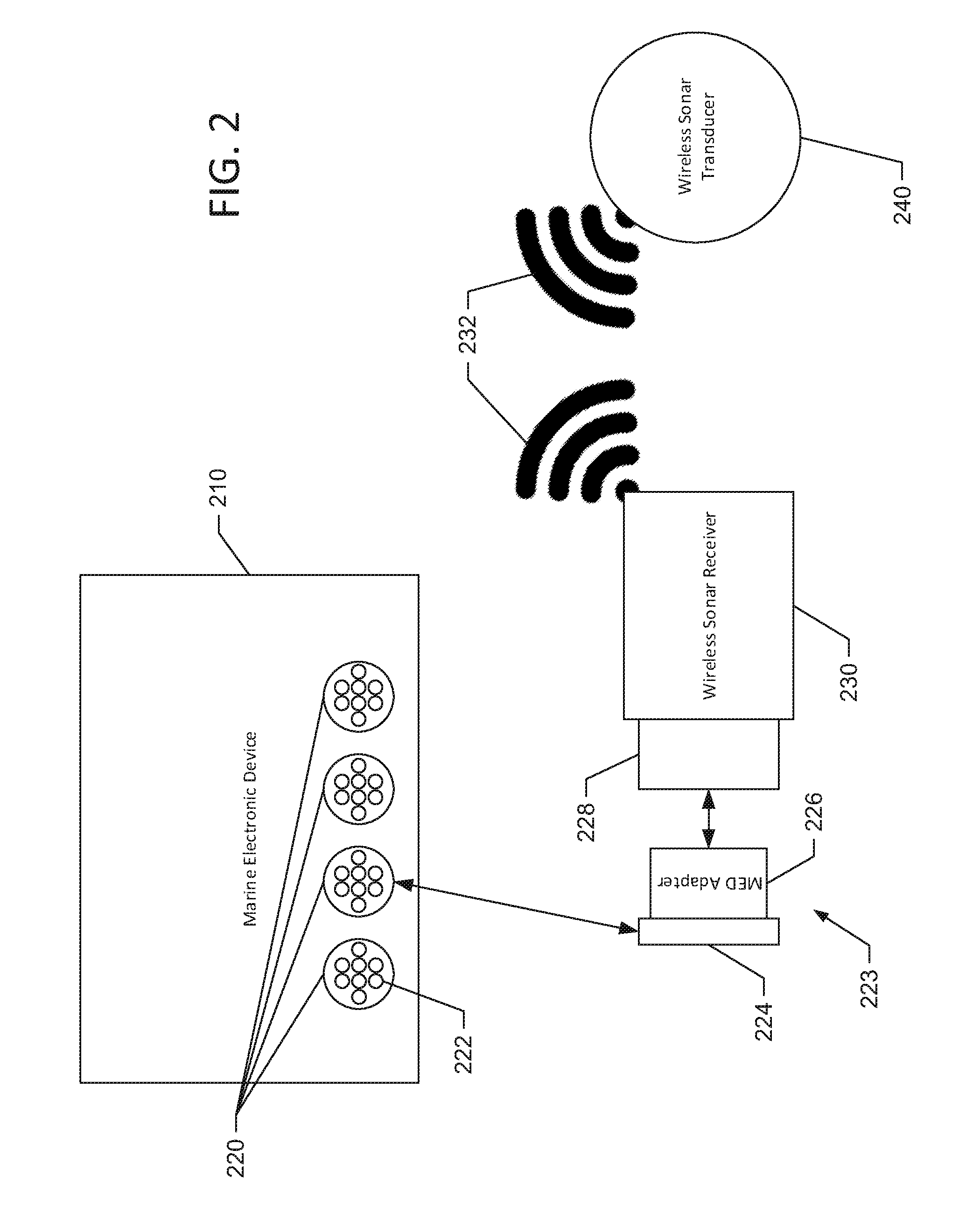
Wireless sonar receiver
Owner:NAVICO HLDG
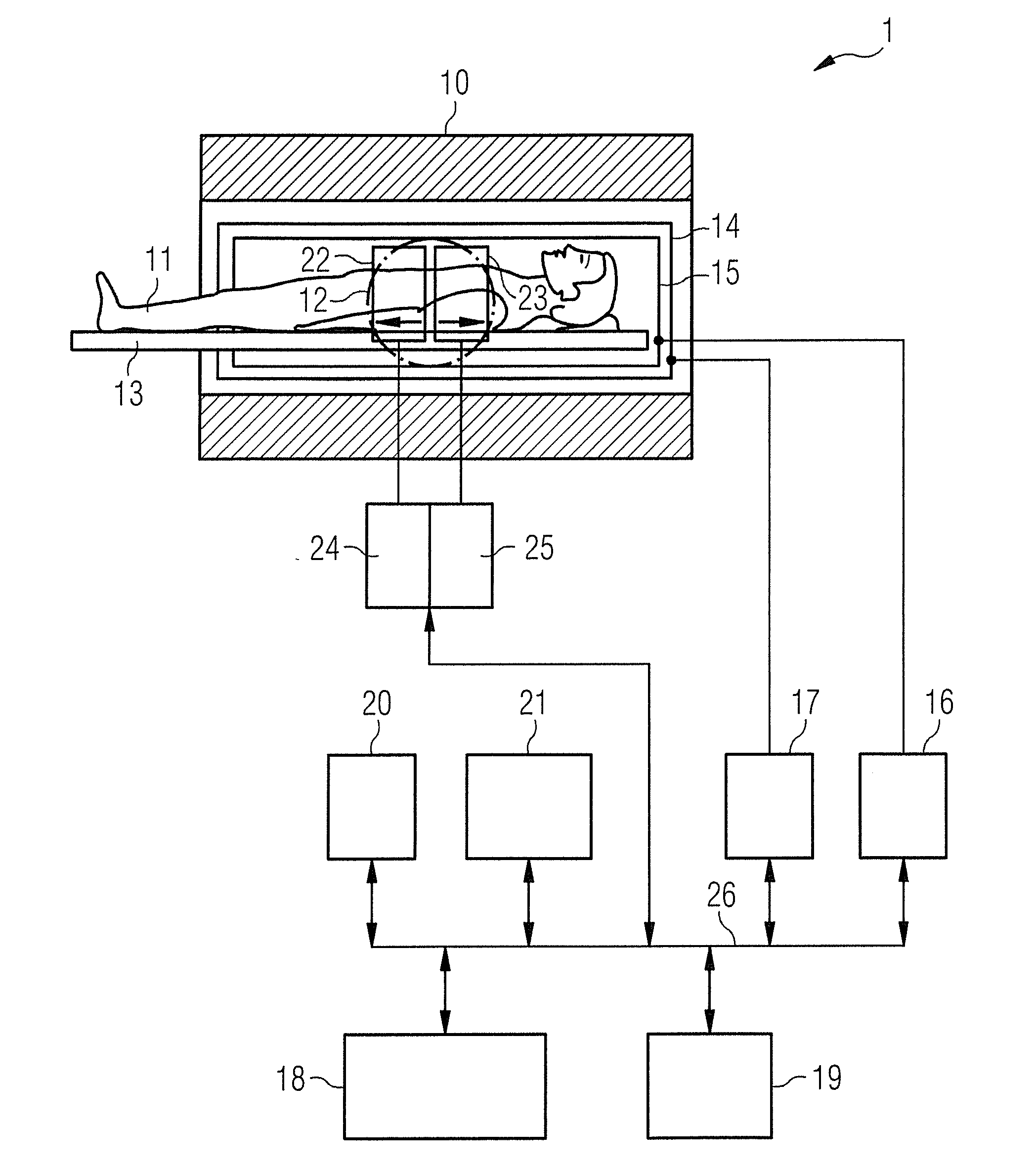
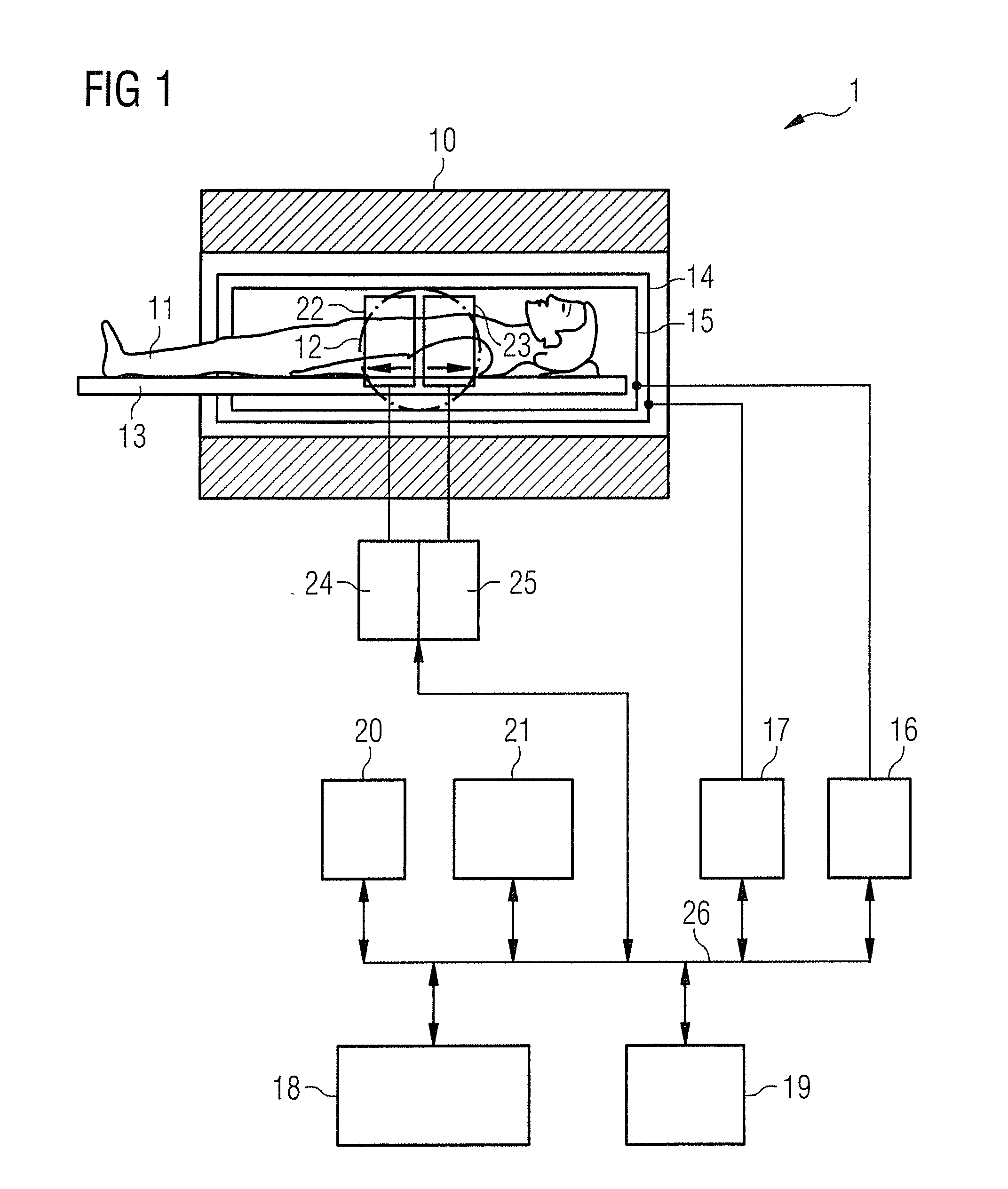
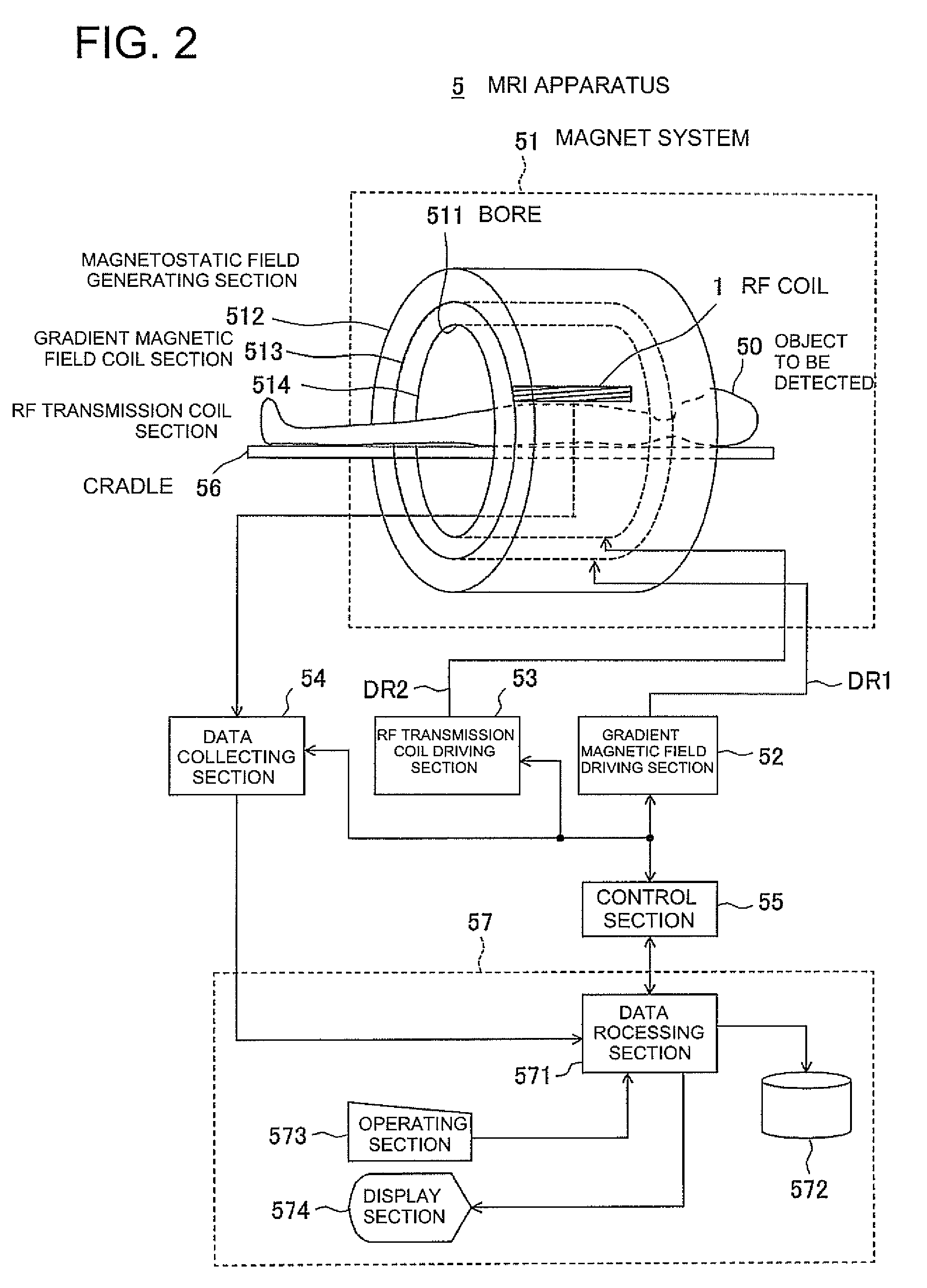
MRI apparatus
InactiveUS20080211496A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging conditionOrder set
An MRI apparatus for performing an MRI examination to an object by sequentially applying an imaging method group, which is constituted by time-sequentially arranging a plurality of different imaging methods, to each of the imaging methods, has an imaging method group setting unit, a performing order setting unit and an imaging condition setting unit. The imaging method group setting unit sets the imaging method group. The performing order setting unit sets a performing order as a performing order of the imaging methods constituting the imaging method group. The imaging condition setting unit sets an imaging condition to each of the imaging methods. The workflow setting unit obtains an examination history data corresponding to the imaging method group, the performing order and the imaging condition from the examination history data previously stored to a storage unit, and sets a first workflow relating to the MRI examination by estimating an imaging time of each of the imaging methods in the performing order based on the obtained examination history data.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Acoustically-responsive optical data acquisition system for sensor data
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Resistive type space debris detection device and method
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Apparatus and method for decreasing bio-effects of magnetic gradient field gradients
ActiveUS20110089947A1Decrease bio-effectsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMagnetic field gradient
Owner:WEINBERG MEDICAL PHYSICS
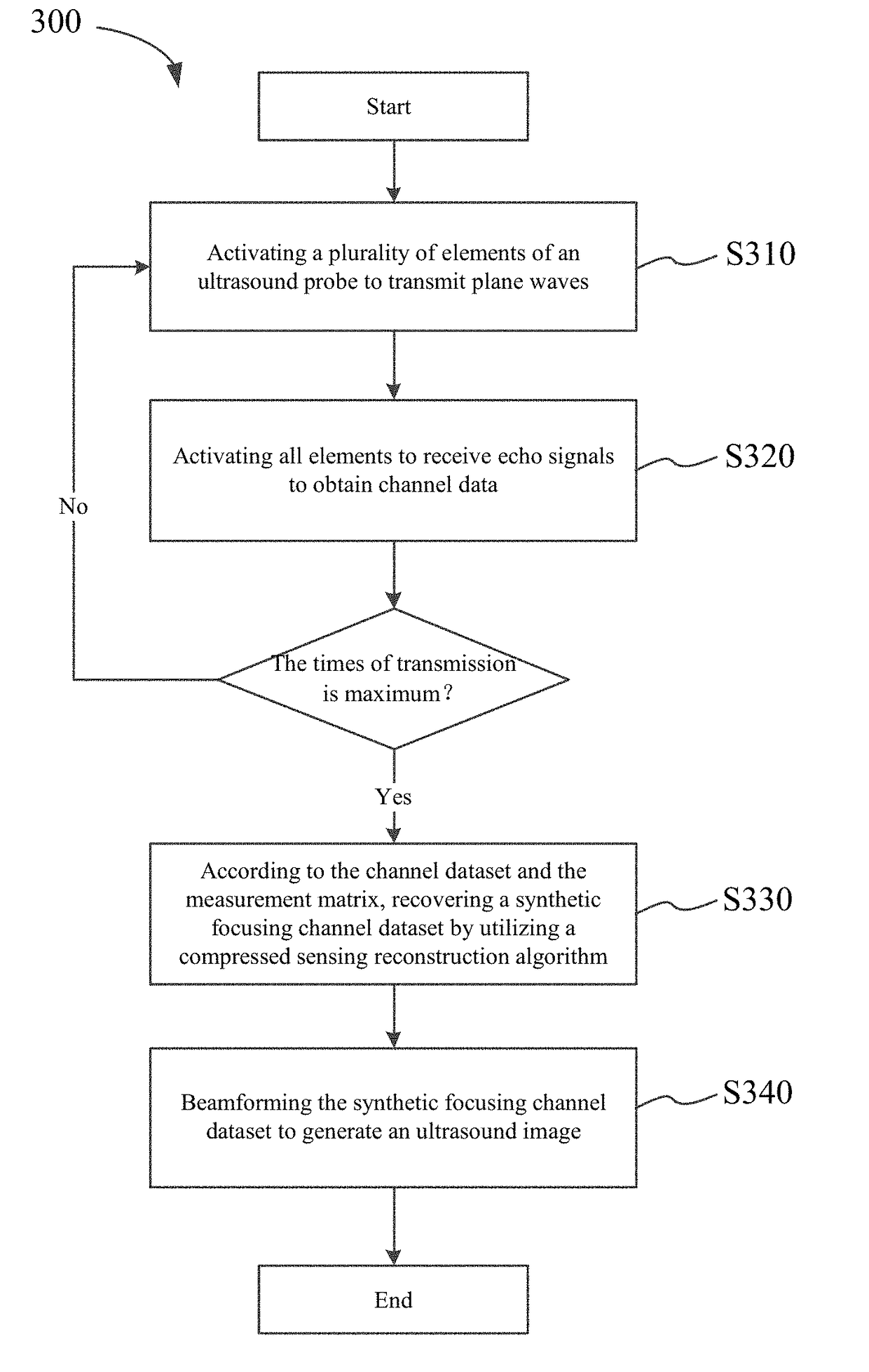
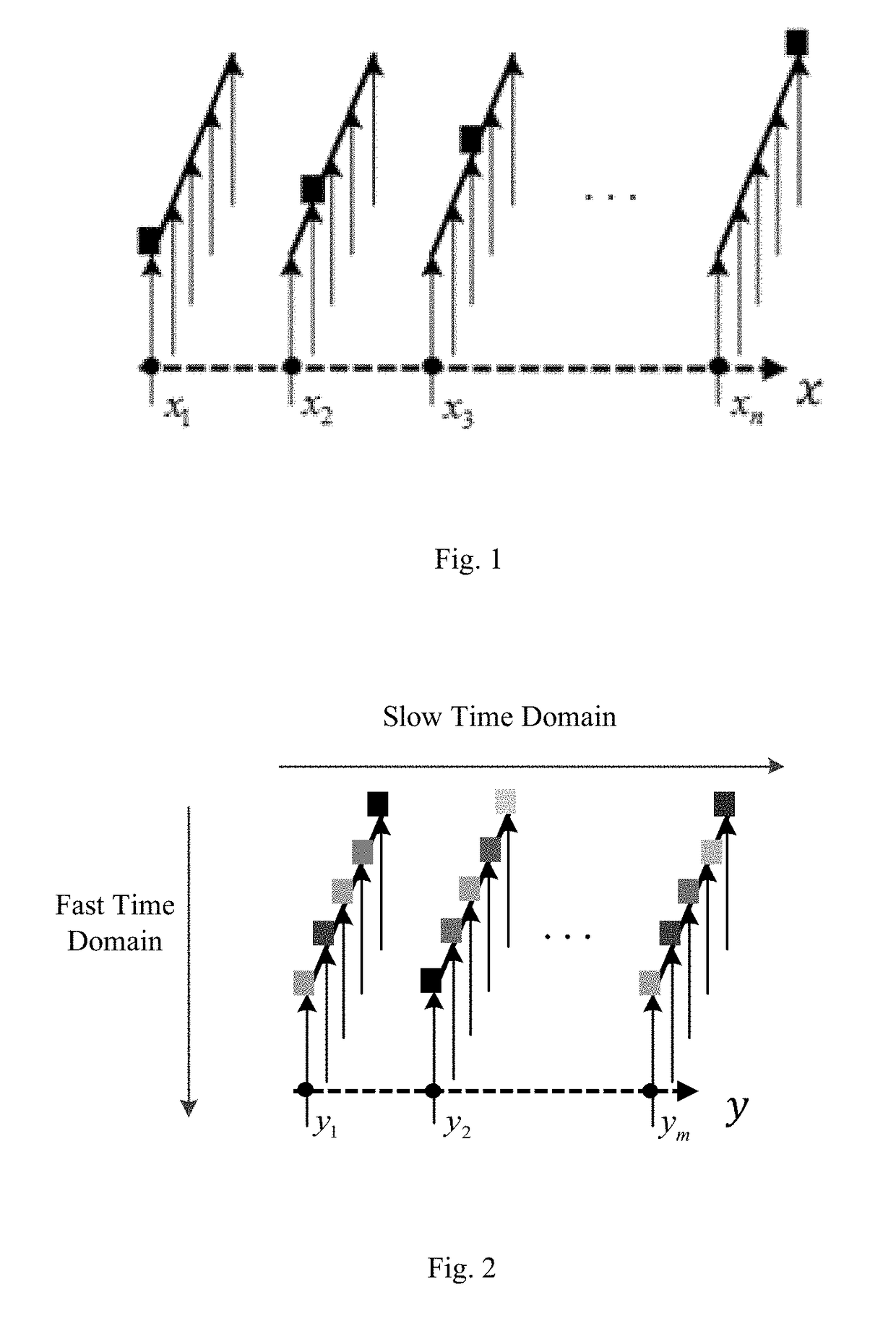
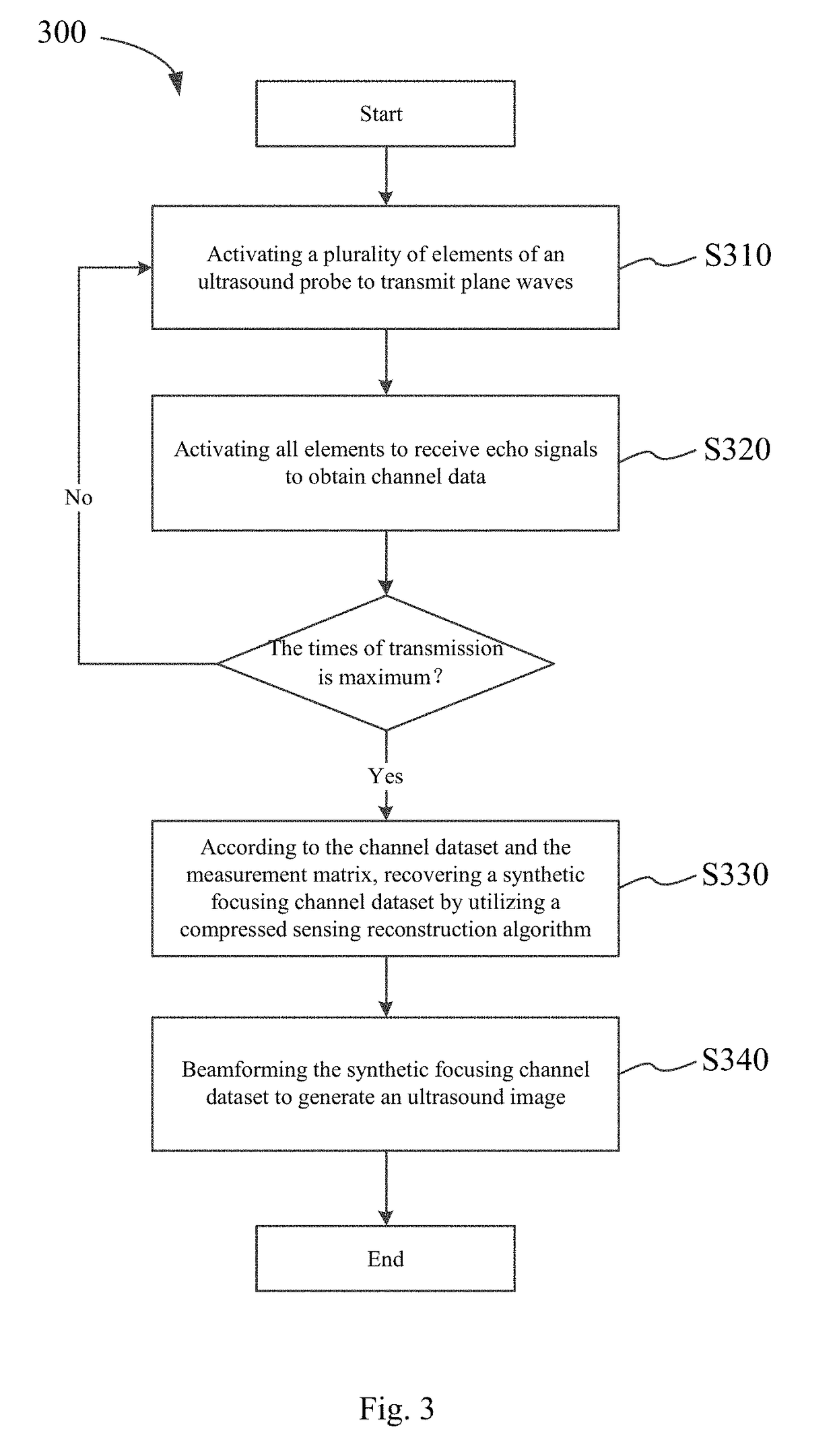
Method and device for ultrasonic imaging by synthetic focusing
ActiveUS20170336500A1High resolutionIncrease frame rateReconstruction from projectionOrgan movement/changes detectionChannel dataSonification
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method to Assess Uncertainties and Correlations Resulting From Multi-Station Analysis of Survey Data
InactiveUS20140244176A1Programme controlElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingCovariance matrixEnvironmental geology
A system, method and computer-readable medium for a drilling a borehole is disclosed. Errors associated with multi-station survey measurements are obtained and partitioned into a set of estimated errors and a set of considered errors. A post-fit covariance matrix is determined from the estimated errors and includes the effects of the considered errors on the estimated errors. A drilling parameter of a drill string in the borehole may be altered using the determined post-fit covariance matrix.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
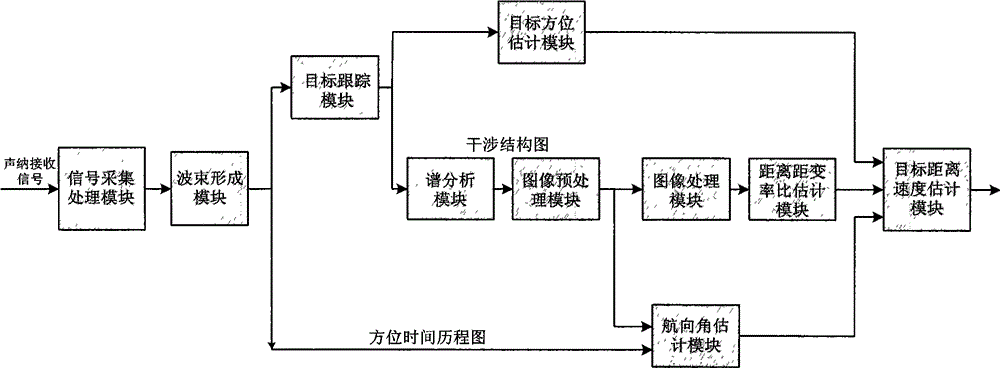
Sonar detection device for three-dimensional space of mine gob
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF SAFETY SCI & TECH
Rotary sonar fish finder
Owner:SUZHOU SLAITE ELECTRONICS TECH
Magnetic resonance scanner with wireless transmission of signals
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Ultrasound breast screening device
InactiveUS20100204580A1Diagnostic probe attachmentOrgan movement/changes detectionActive matrixRelative motion
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
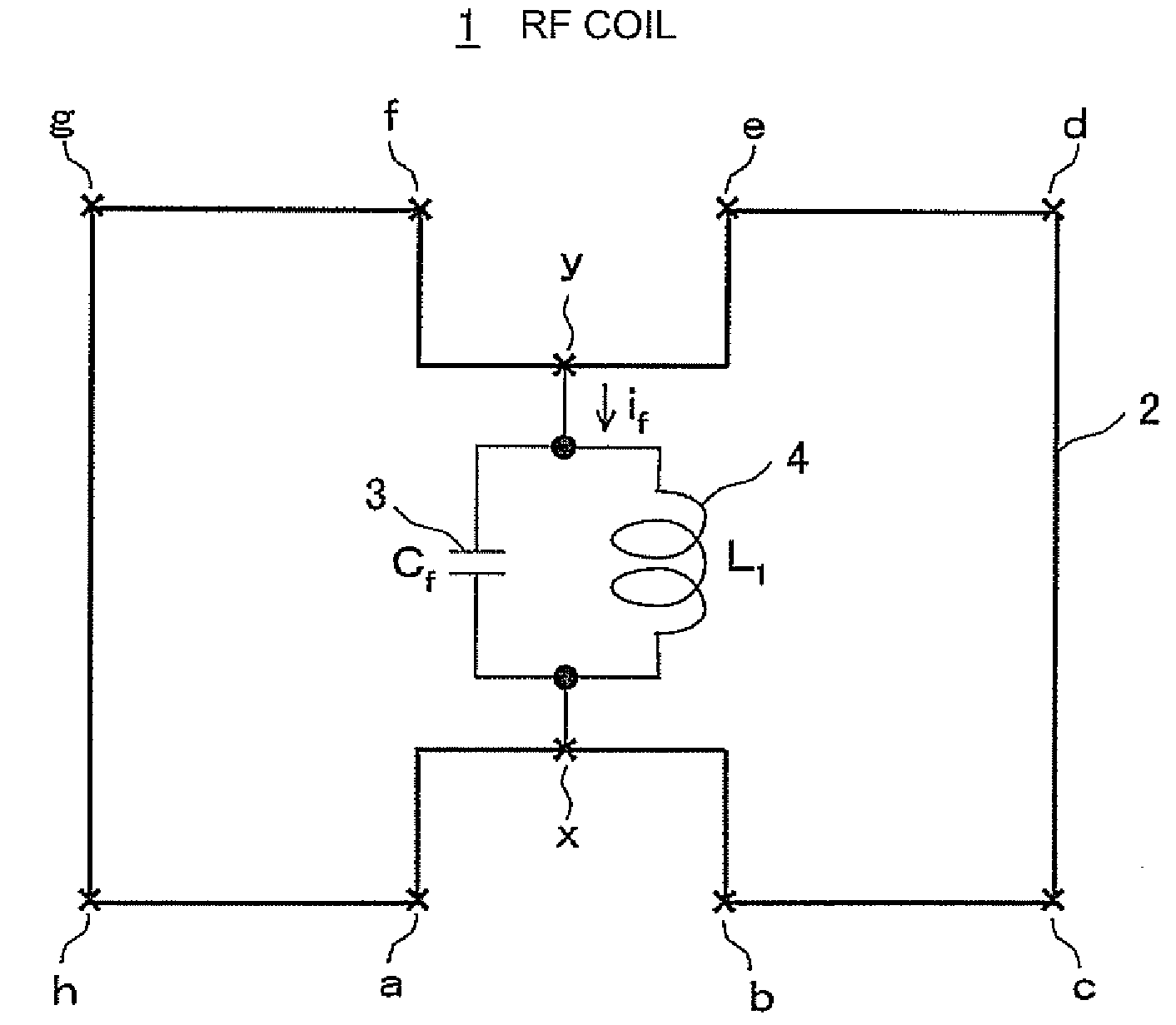
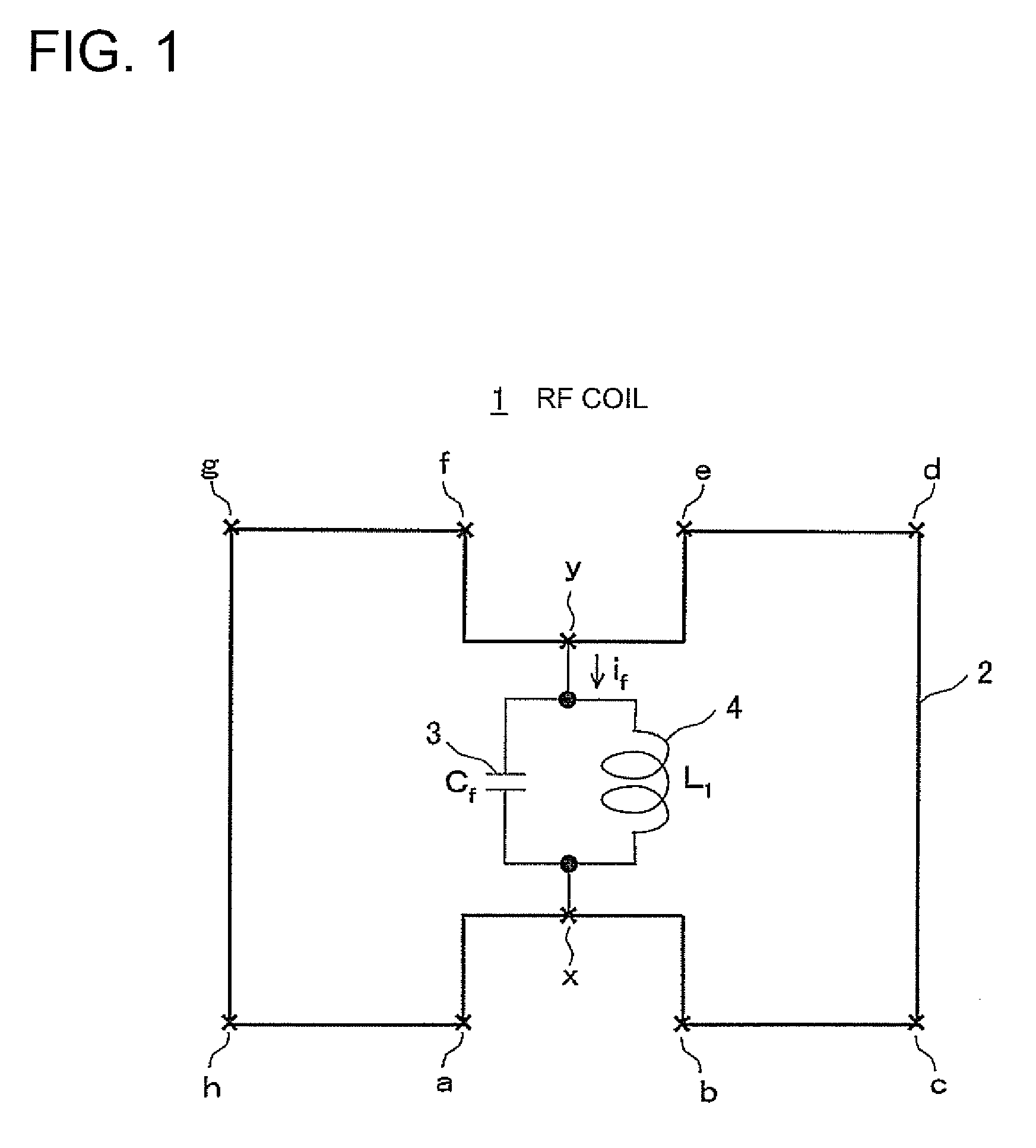
RF coil for MRI apparatus, method of using RF coil for MRI apparatus, and MRI apparatus
InactiveUS20080111549A1Reduce in quantityImprove transmission efficiencyElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceElectrical impedance
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Methods and apparatuses for 3D magnetic density imaging and magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20120126811A1Faster and cheapAvoid frequencyDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionDensity distributionMagnetization
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
Road obstacle detector
InactiveCN106093953AReduce lossesAccurate measurementAcoustic wave reradiationControl signalComputerized system
The invention provides a road obstacle detector. The road obstacle detector comprises an ultrasonic wave range finding sensor, a control unit, a computer system, an alarm device and a power supply device, wherein the ultrasonic wave range finding sensor includes an ultrasonic wave emitter and an ultrasonic wave receiving device; the ultrasonic wave emitter is used for emitting an ultrasonic wave signal to a front portion; the ultrasonic wave receiving device is used for receiving a reflected ultrasonic wave signal; the control unit calculates a difference value of time for emitting the ultrasonic wave signal and time for receiving the reflected ultrasonic wave signal, compares the difference value and a preset time difference value and determines whether there is an obstacle in front of a road, and if there is the obstacle, the control unit further calculates an obstacle height; the computer system receives the obstacle height and compares the obstacle height with a preset height threshold, if the obstacle height is greater than the preset height threshold, a vehicle can not pass through and an alarm control signal is emitted; the alarm device emits an alarm signal according to an alarm control signal; and the power supply device provides power for an internal source of the vehicle and the ultrasonic wave range finding sensor. By using the detector of the invention, an early warning effect can be reached so that unnecessary losses during a vehicle running process are reduced.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG UNIVERSITY
Robot capable of automatically overturning and walking
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Ultrasonic ranging system based on single-chip microcomputer
InactiveCN104459700ADirectionalReduce consumptionAcoustic wave reradiationDisplay deviceHemt circuits
Owner:刘铮
Microwave sensor
InactiveCN102478673AStrong penetrating powerEasy to install secretlyDetection using electromagnetic wavesAcoustic wave reradiationAcoustic wavePower circuits
Owner:高丽韵
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap