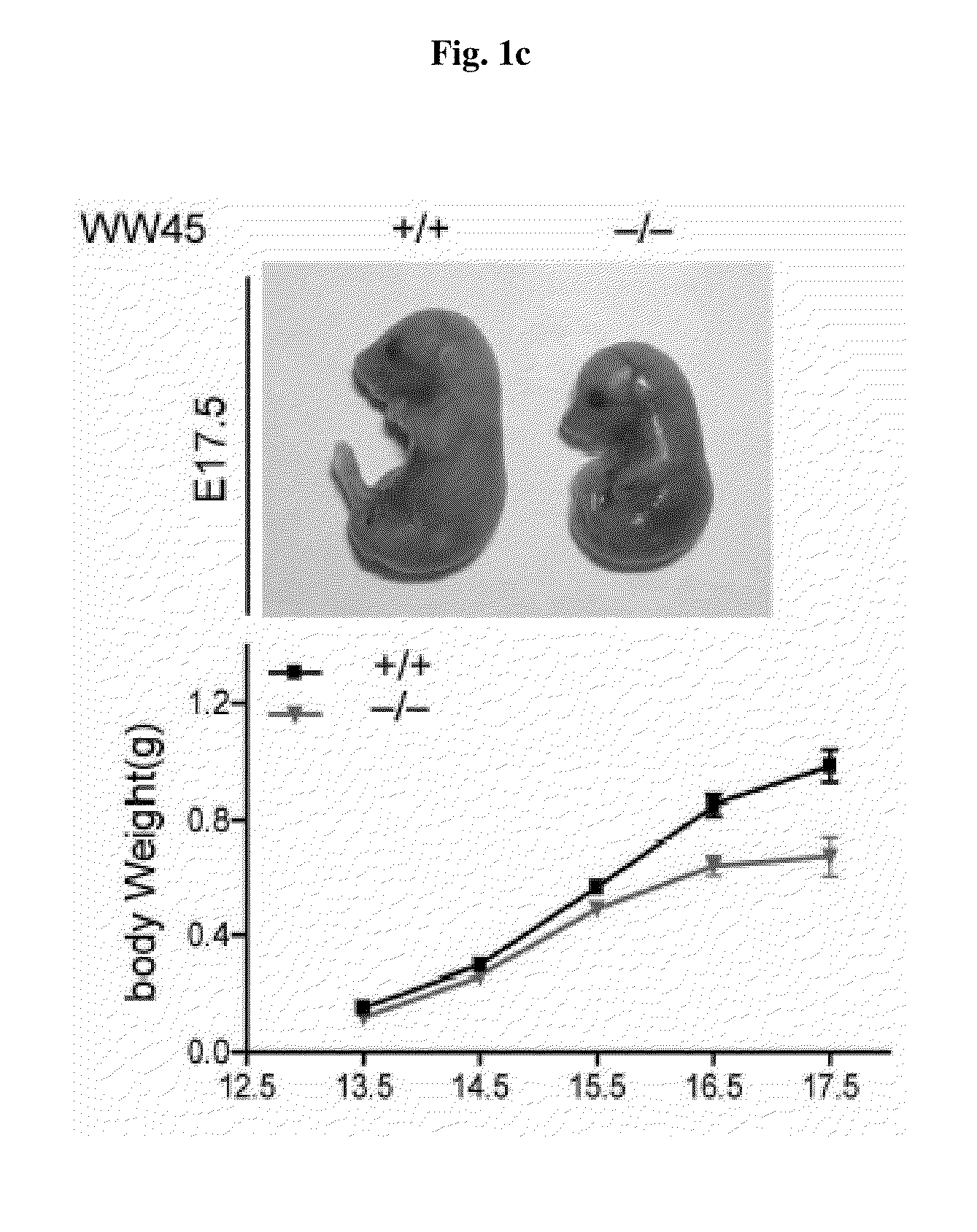
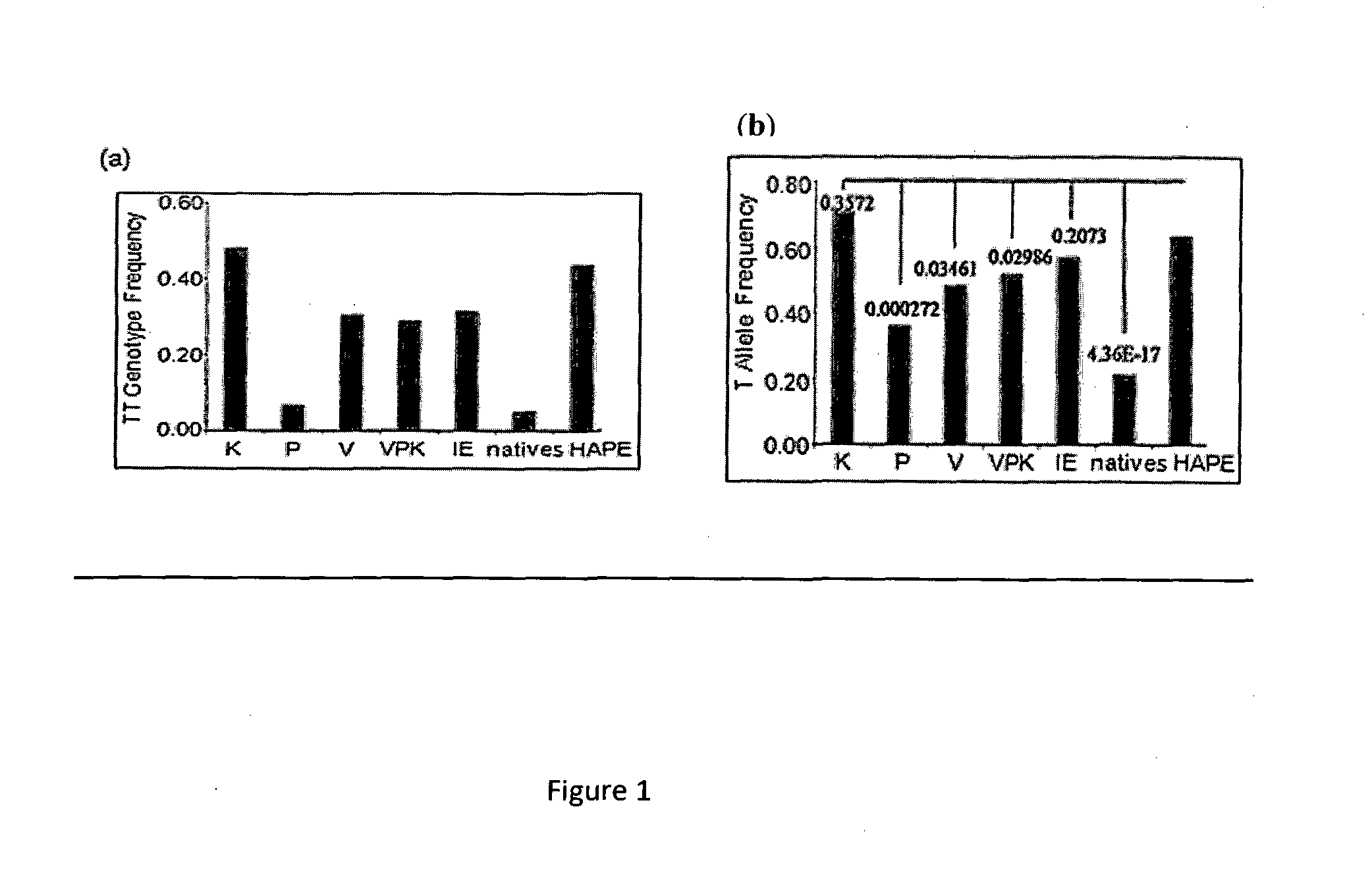
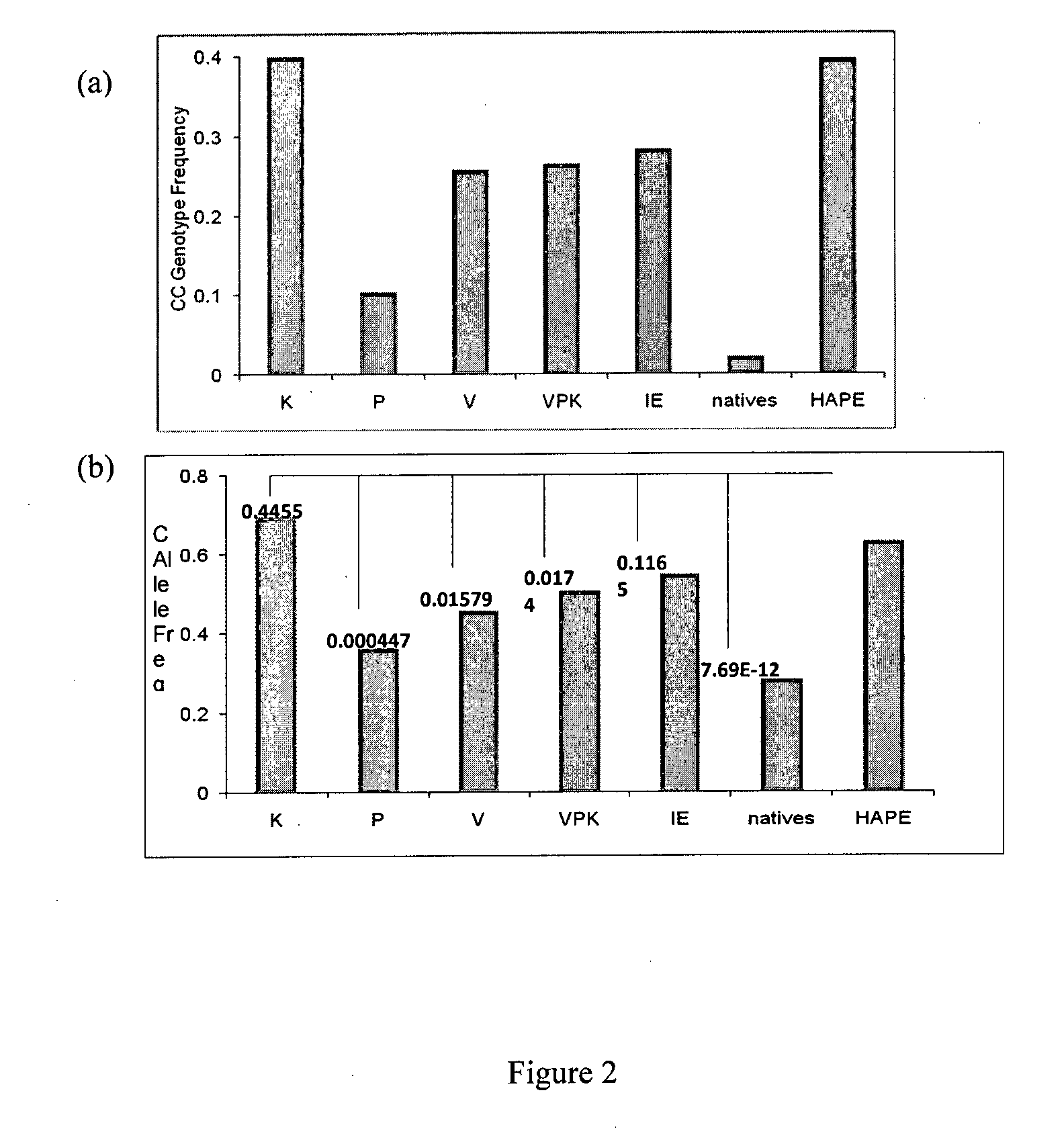
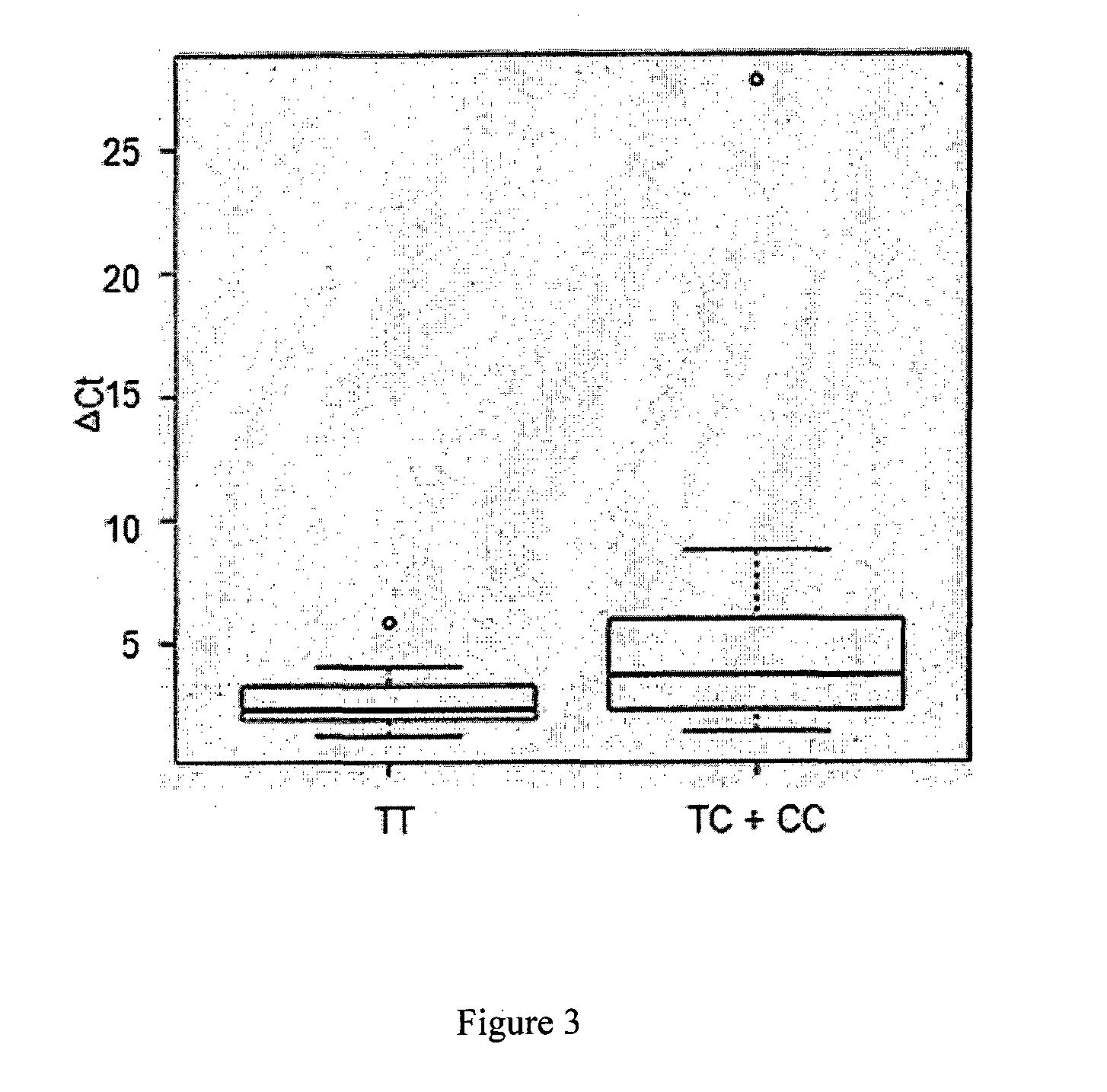
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
23 results about "Organism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In biology, an organism (from Greek: ὀργανισμός, organismos) is any individual entity that propagates the properties of life. It is a synonym for "life form". Organisms are classified by taxonomy into specified groups such as the multicellular animals, plants, and fungi; or unicellular microorganisms such as a protists, bacteria, and archaea. All types of organisms are capable of reproduction, growth and development, maintenance, and some degree of response to stimuli. Humans are multicellular animals composed of many trillions of cells which differentiate during development into specialized tissues and organs.
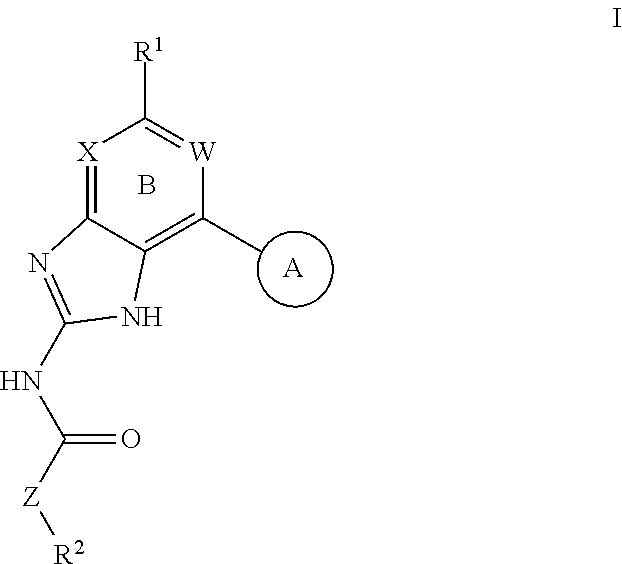
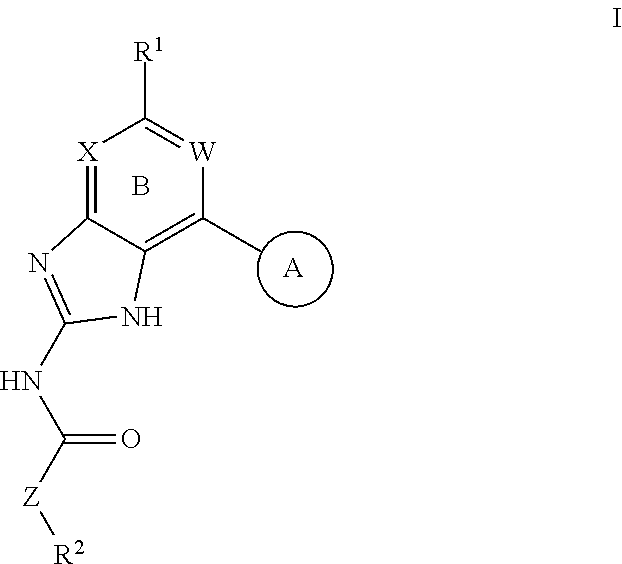
Gyrase Inhibitors and Uses Thereof
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
Denitrifying phosphorus removal bacteria bacillus cereus H-hrb01 and screening method and application
ActiveCN102827787AEasy to waterExcellent water indicatorsBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyChemical oxygen demand
Owner:HIT YIXING ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
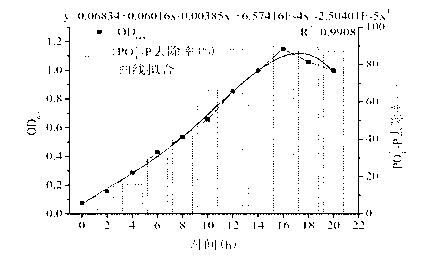
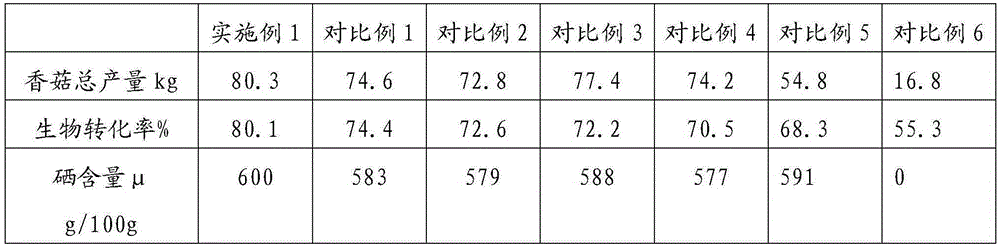
Selenium-enriched mushroom grass culture medium and method for producing selenium-enriched shiitake mushrooms
InactiveCN105585361ASignificant increase in production and incomeSignificant resistance to lodgingHorticultureFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyMonopotassium phosphate
Owner:井冈山井祥菌草生态科技股份有限公司
Soil improvement method for planting blueberries
The invention relates to a soil improvement method, in particular to a soil improvement method for planting blueberries. The method mainly solves the technical problems that existing blueberry planting soil improvement measurements affect soil organism conditions, are high in cost and have toxic action on blueberry roots. The method includes the steps that firstly, fermented furfural residues are evenly applied to soil to be improved in summer, and turning plough is performed to make the fermented furfural residues and the soil fully mixed; secondly, after 1-1.5 months, peat, saw dust and organic fertilizer are applied to the soil, and turning plough is performed to make the peat, the saw dust and the organic fertilizer fully mixed with the soil; thirdly, manual weeding is performed; fourthly, soil plowing and ridging are performed in the spring of the next year, and the improvement to the soil for planting blueberries is completed. The pH value of the improved soil is 4.5-4.8, nutrient status of the soil is improved, and the survival rate of transplanted biennial blueberries and the survival rate of six-year-growing-period blueberries can reach 95-96% and 96-97% respectively. The method is used for blueberry cultivation.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
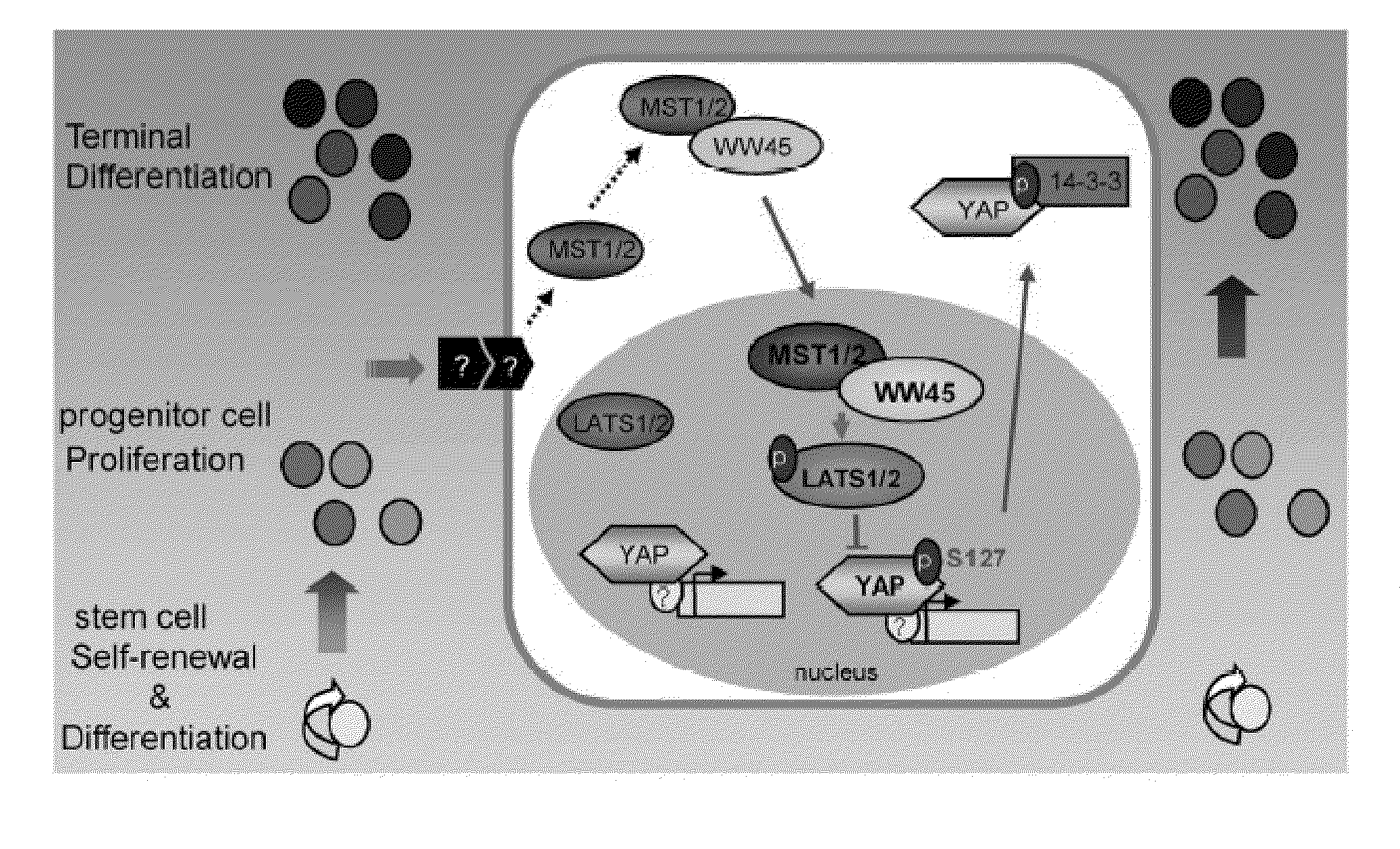
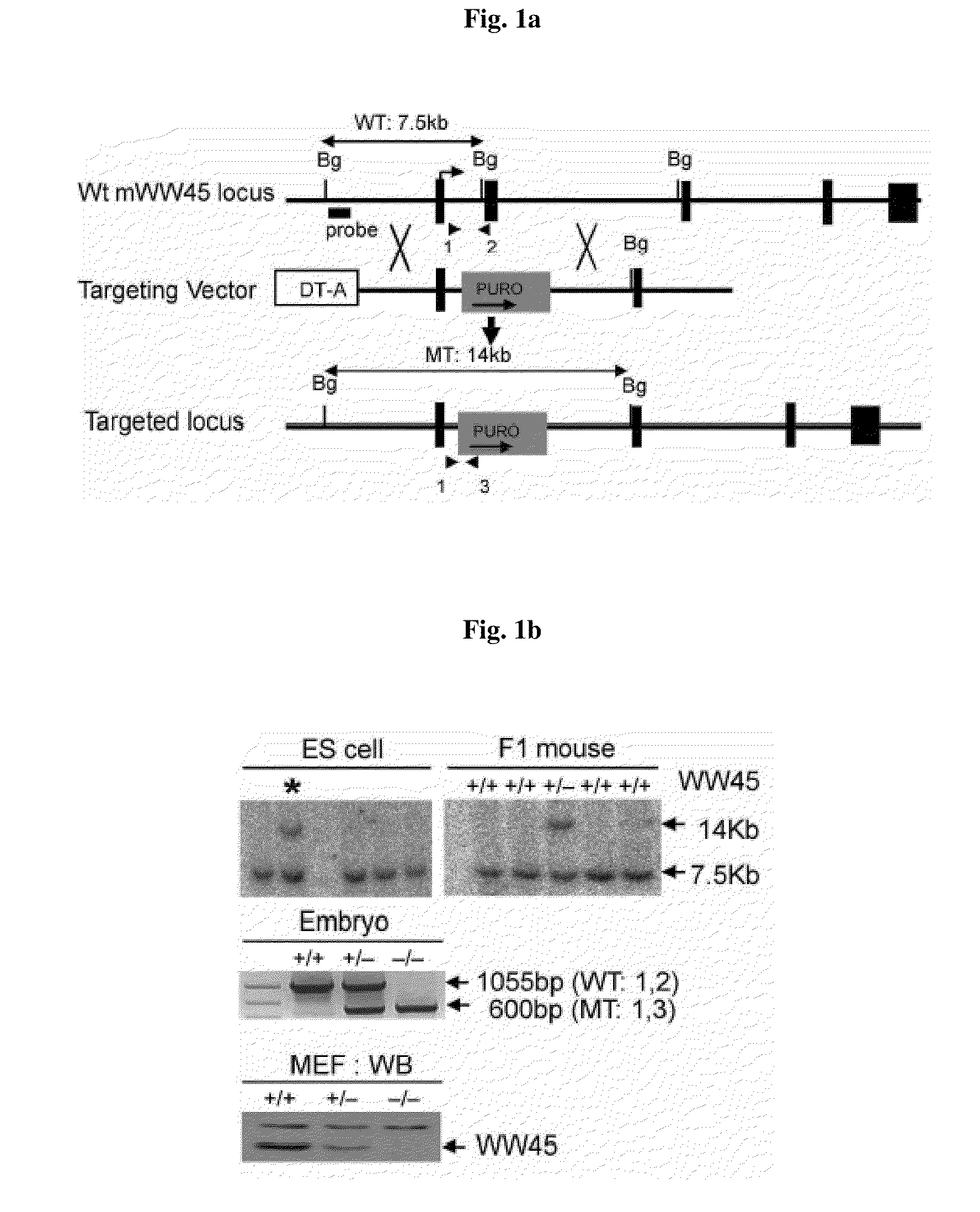
Methods of regulating differentiation in mammals
Mechanisms regulating cell proliferation stop and differentiation initiation during the development stage of mammalian embryo, and the proteins involved therein, are presented. Differentiation regulators, methods of regulating differentiation, transgenic organisms with loss of expression of the differentiation regulator, and methods of preparing the transgenic organisms, are provided.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Biomarker for Detecting High-Altitude Adaptation and High-Altitude Pulmonary Edema
InactiveUS20140030709A1Reduce riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementProlyl HydroxylasesBiomarker (petroleum)
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
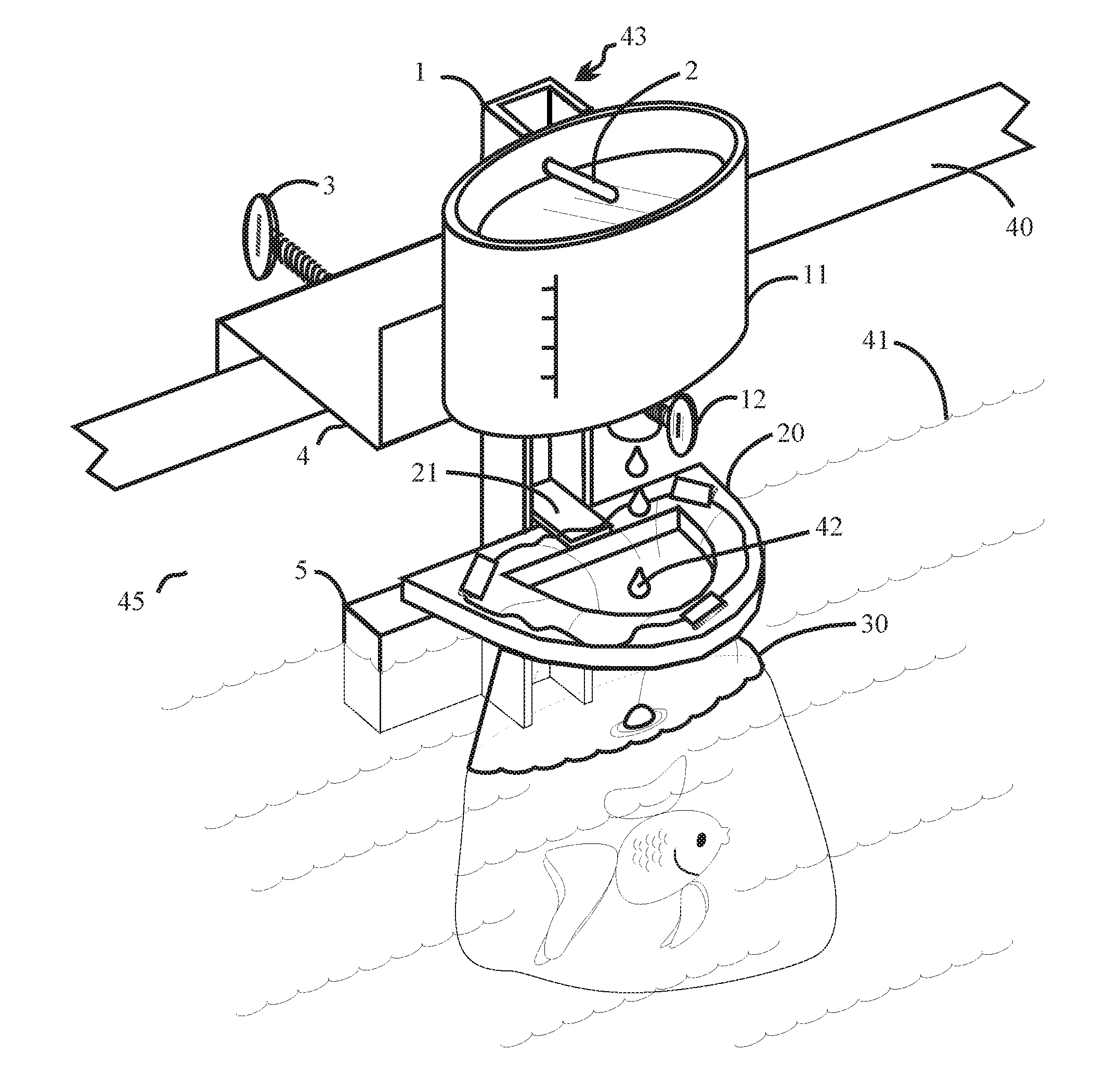
Method and apparatus for acclimating aquatic organisms to a new environment
Owner:LUONG LE QUAN +1
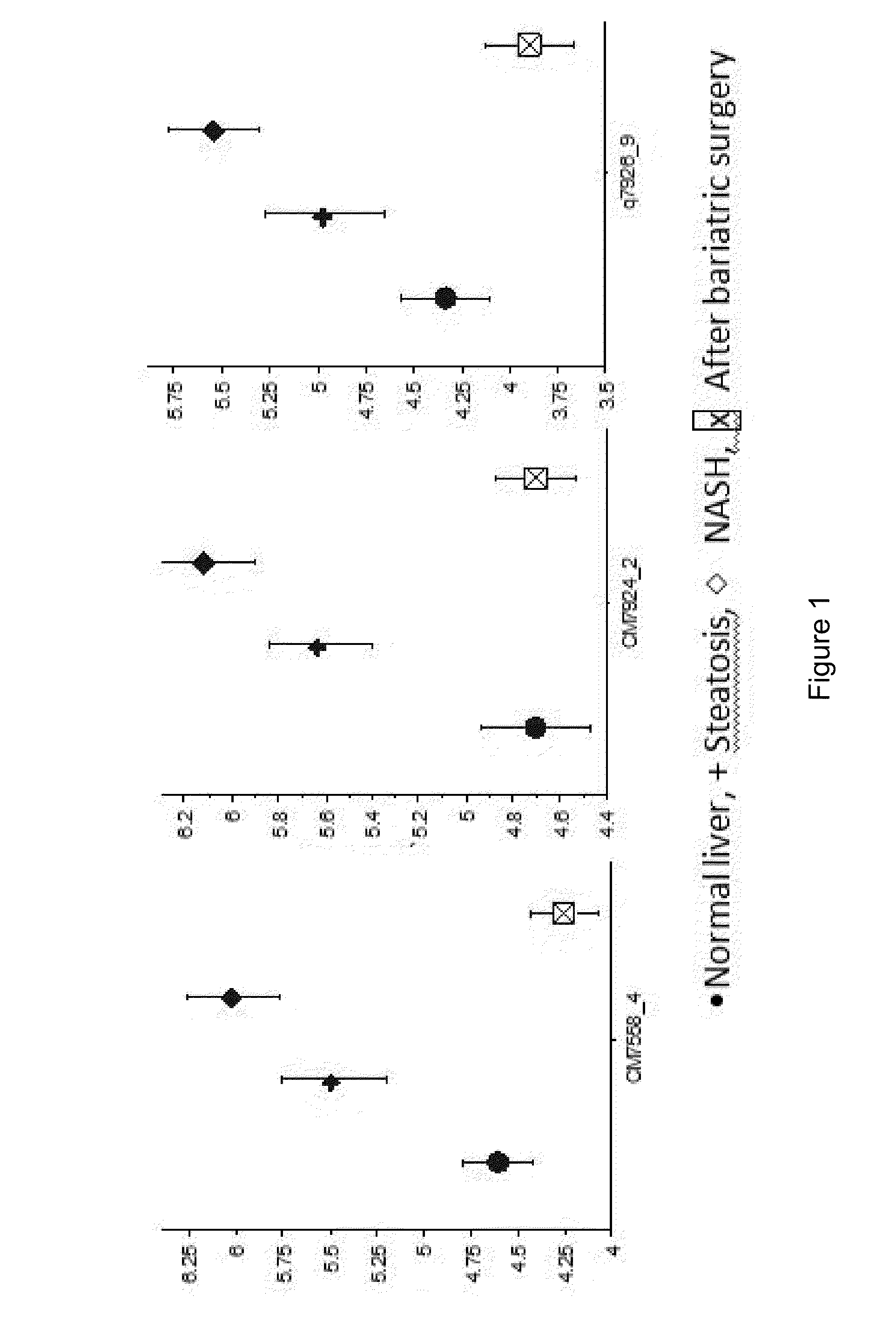
Methods and kits for determining the occurrence of a liver disease in a subject
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Method for estimating in-vitro detoxification effect of mycotoxin detoxification agent by using liquid chromatography
InactiveCN105301134AApplicable adsorption rate evaluationThe evaluation results are close toComponent separationMycotoxinSorbent
Owner:江苏奥迈生物科技有限公司
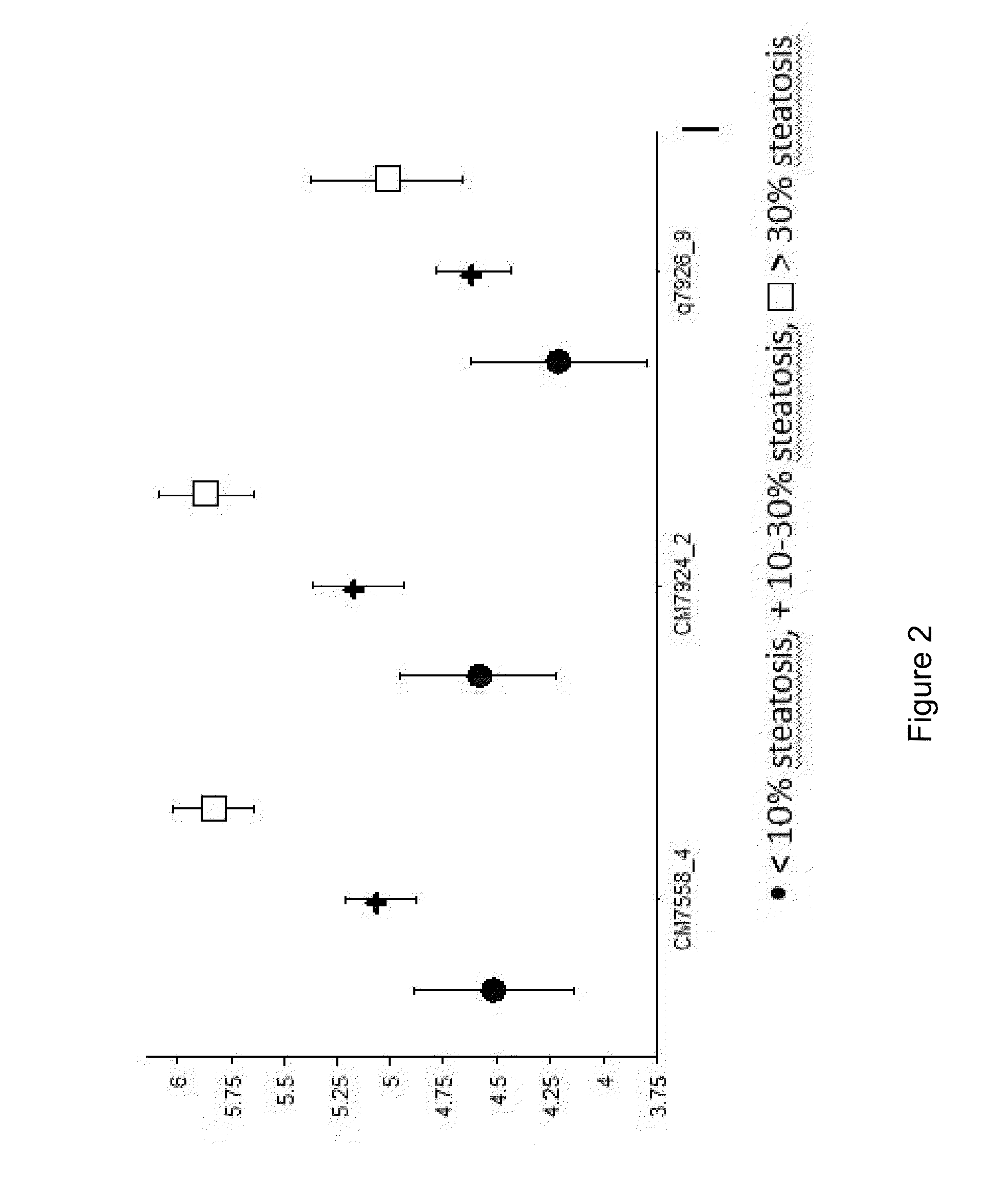
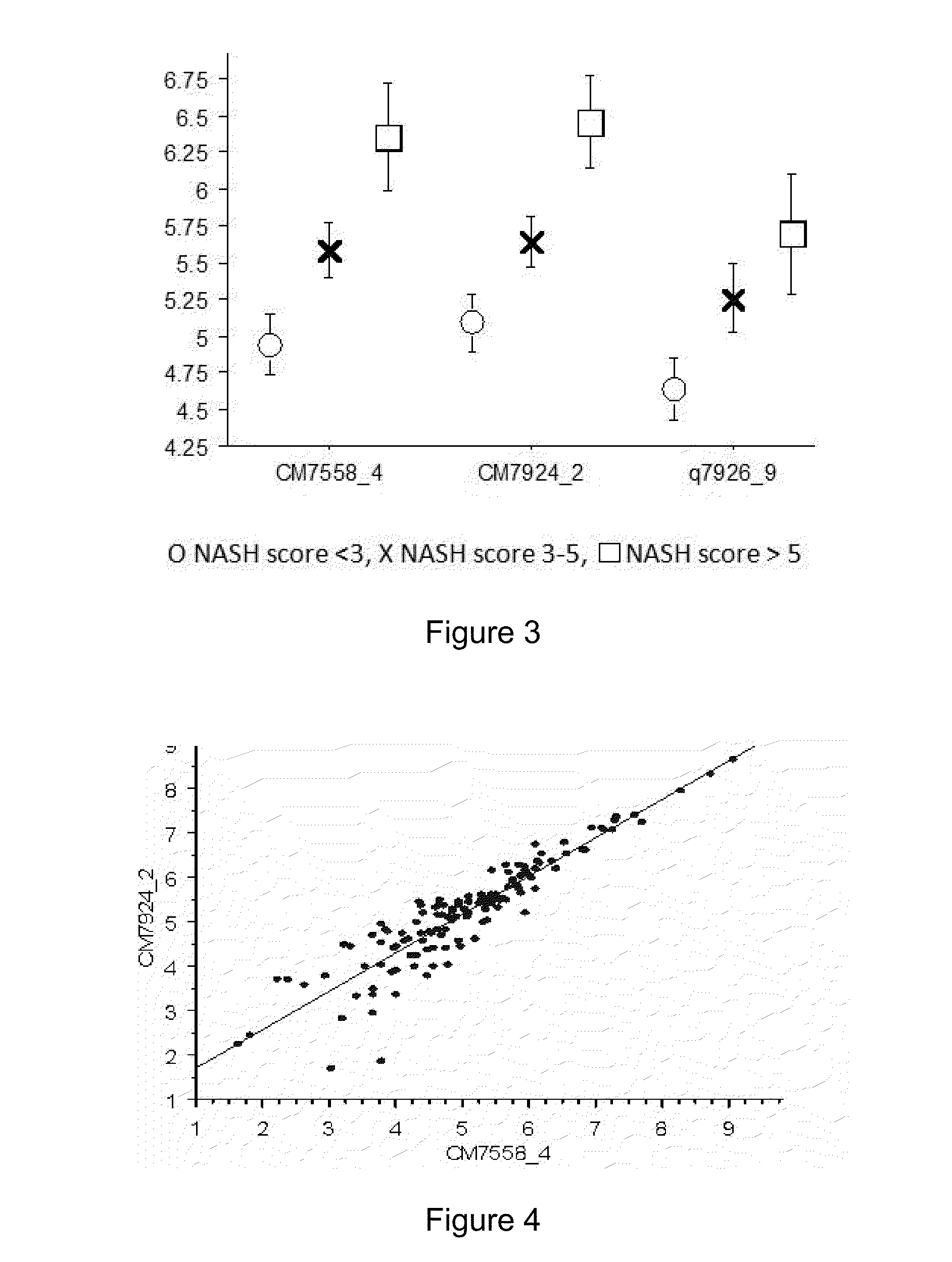
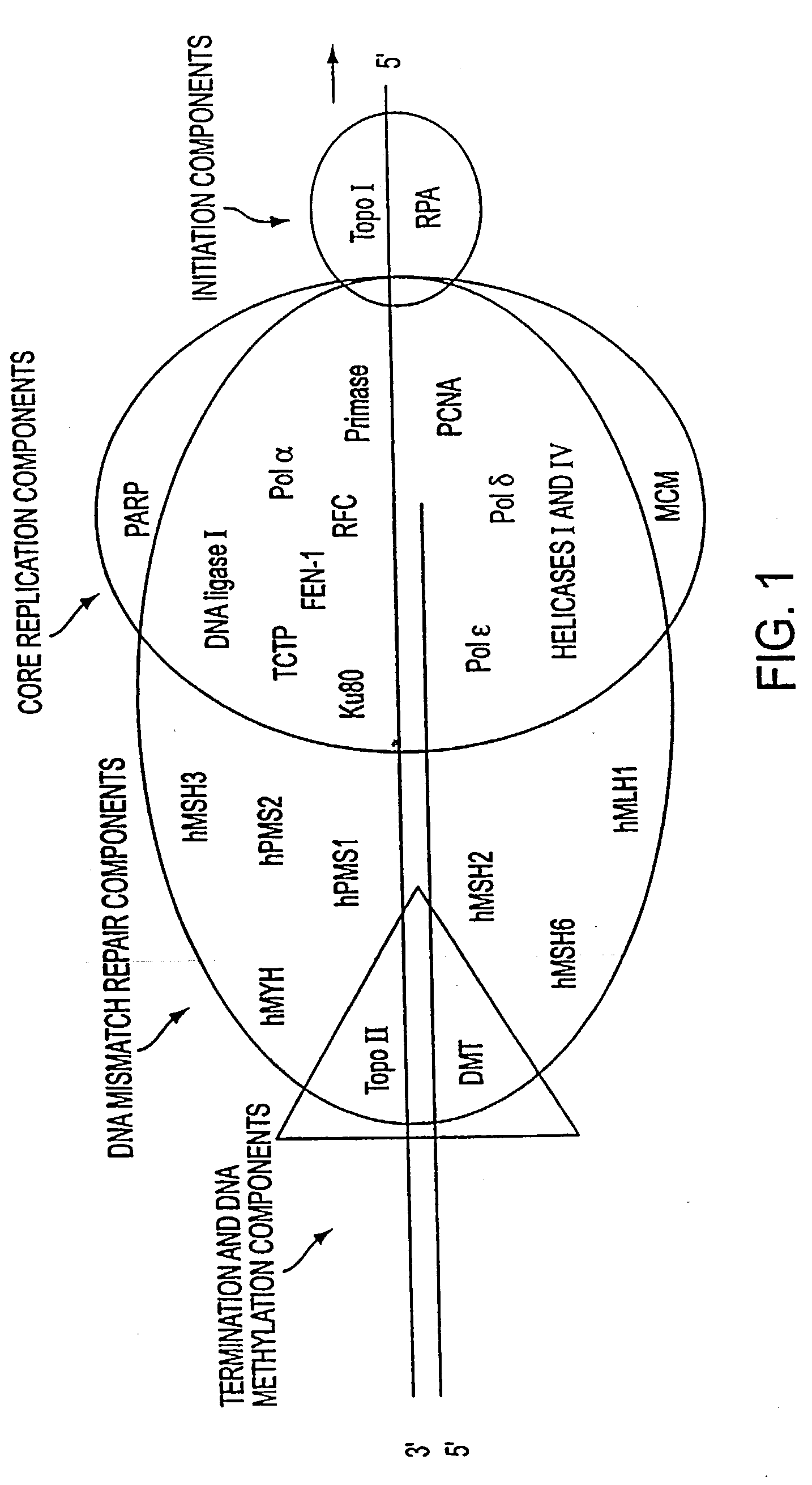
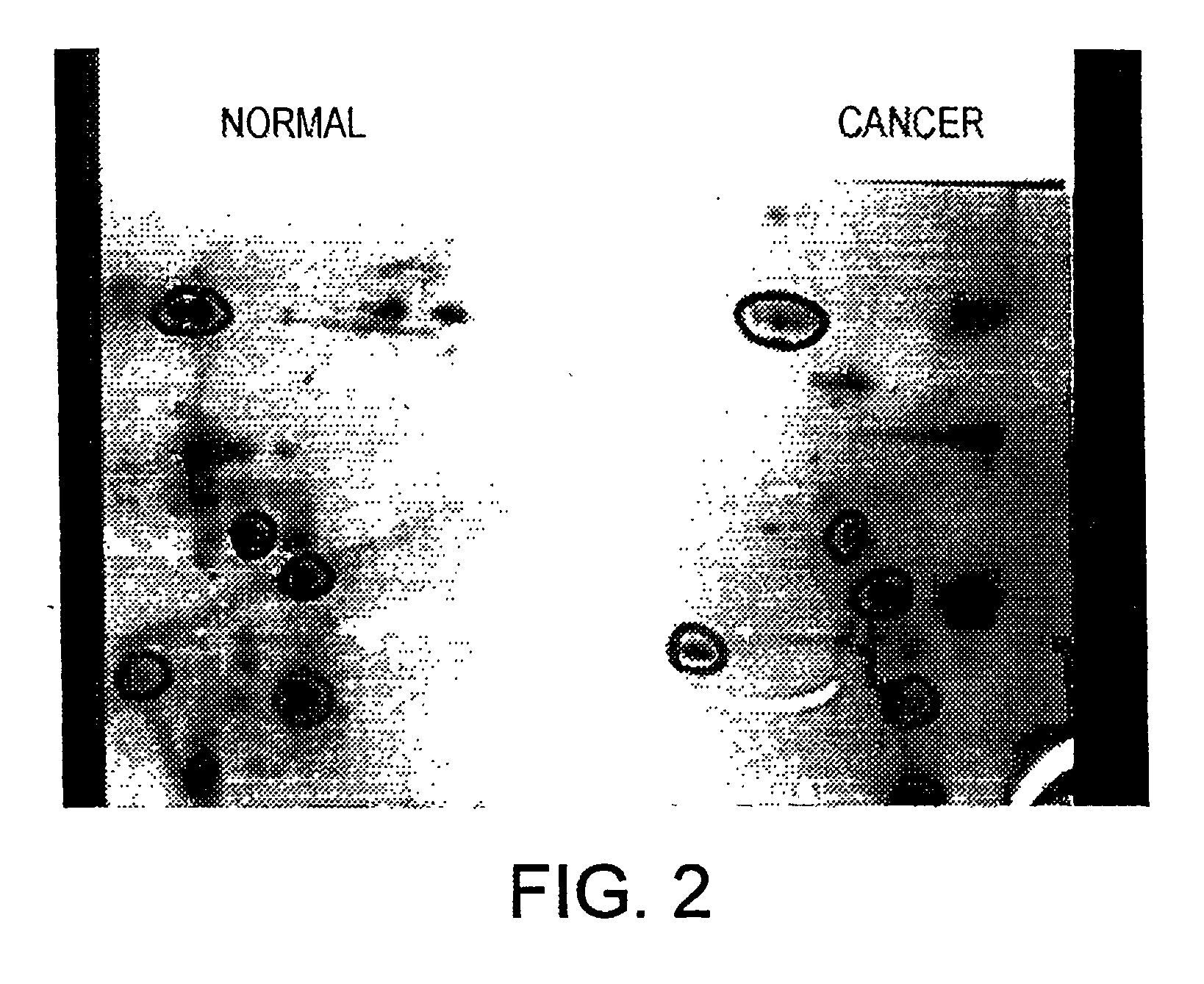
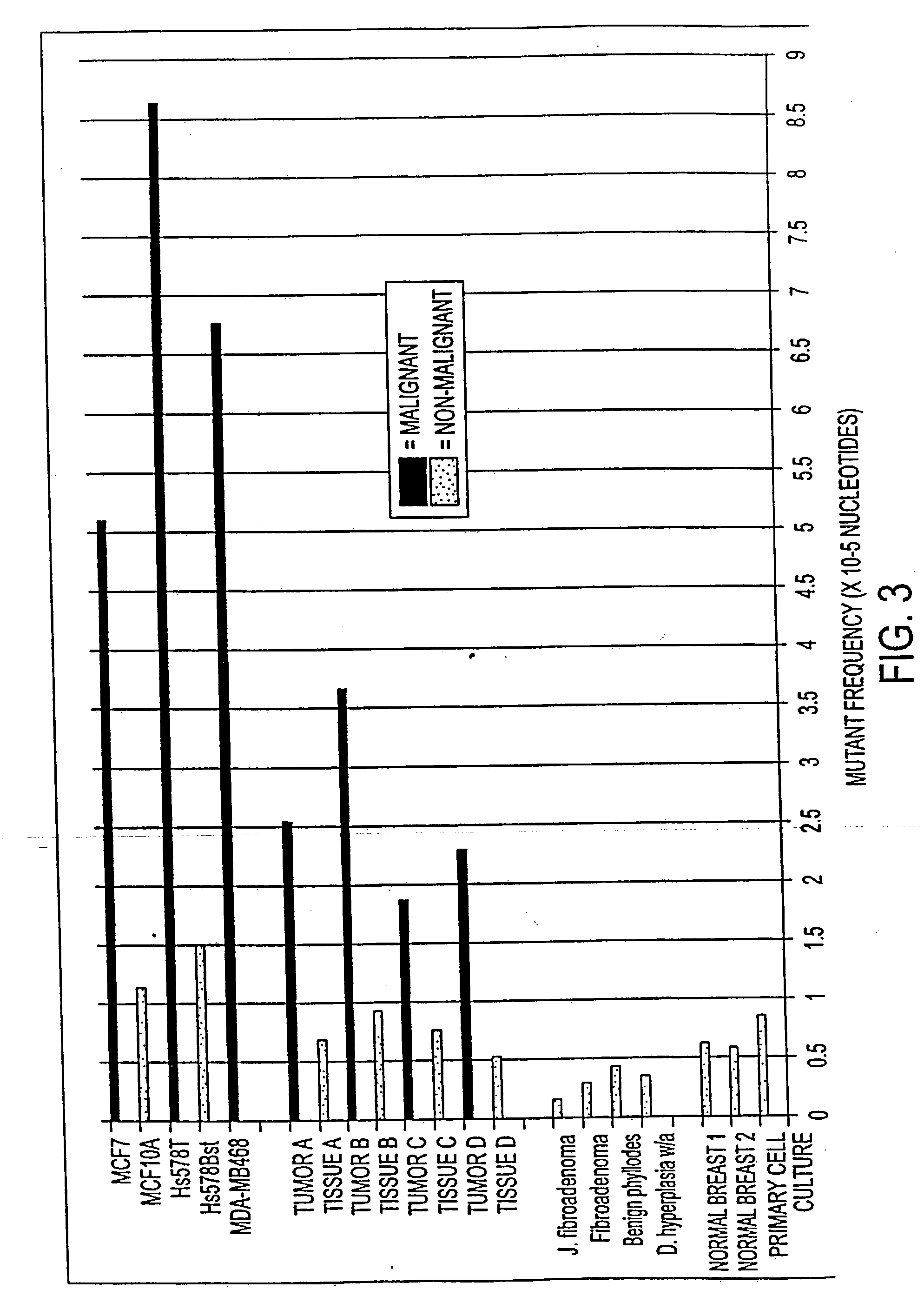
Altered DNA synthesome components as biomarkers for malignancy
InactiveUS20060073477A1Guaranteed functionChange activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMalignant phenotypeNeoplasm
Owner:SCHNAPER LAUREN
Recombinant adenovirus rAd-ORF2-TCE and application thereof
InactiveCN103805573AEnhance humoral immunityEnhance cellular immunityGenetic material ingredientsMicroorganism based processesPorcine circovirusOrganism
The invention relates to a recombinant adenovirus rAd-ORF2-TCE. The recombinant adenovirus rAd-ORF2-TCE is obtained through fusing and connecting an immunogenic protein gene ORF2 of PCV2 (Porcine Circovirus Type 2) and three T lymphocyte epitope (TCE) series genes, and then, recombining to an adenovirus vector. The invention further relates to application of the recombinant adenovirus rAd-ORF2-TCE in porcine viral immunization vaccines. According to the recombinant adenovirus rAd-ORF2-TCE disclosed by the invention, an organism can be effectively stimulated to generate a high-level specific antibody and generate T lymphocyte proliferation, and both the concentration of IFN-gamma in blood serum and the concentration of IL-2 in the blood serum are increased remarkably; compared with ORF2 of separate PCV2, the recombinant adenovirus rAd-ORF2-TCE has the advantage that both humoral immunity level and cellular immunity level of an animal body are increased remarkably.
Owner:GUANGDONG WENS DAHUANONG BIOTECH +1
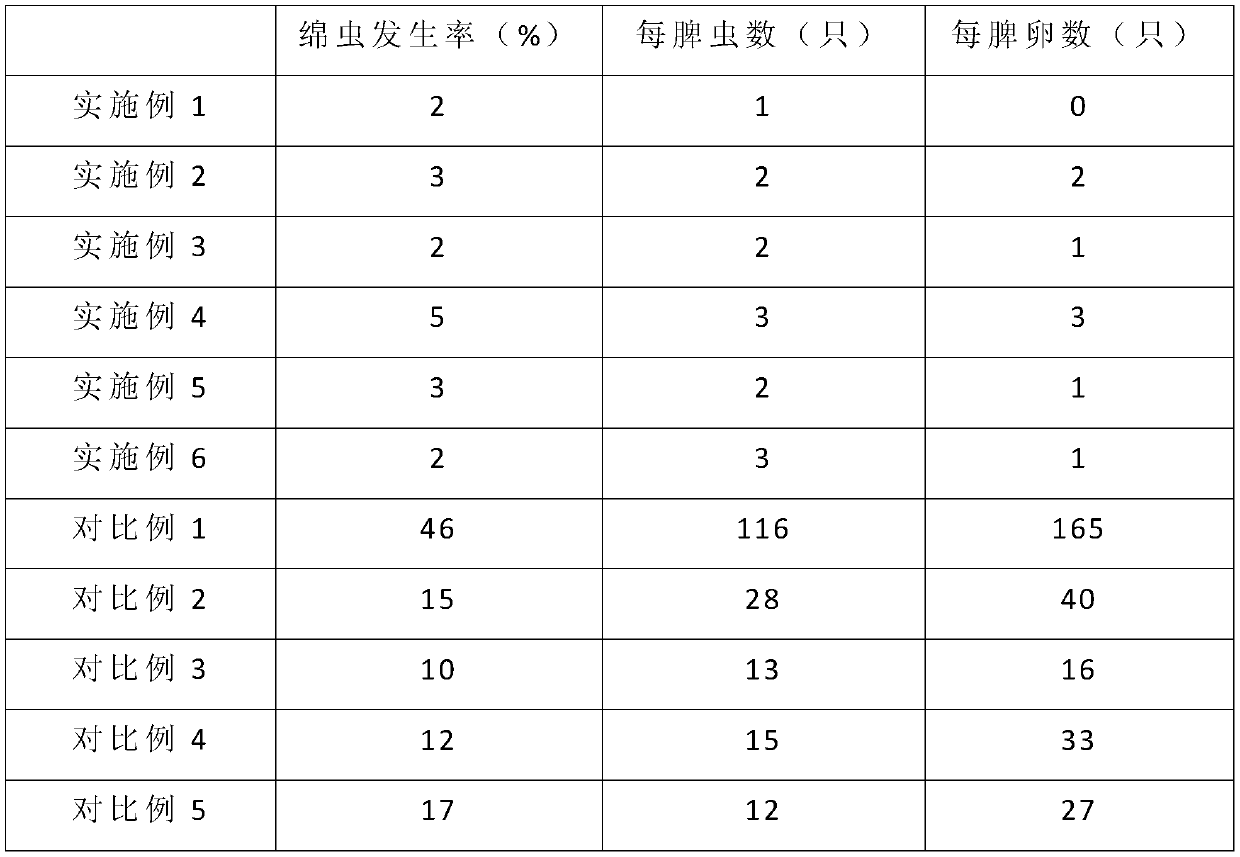
Comprehensive control method for wax-moth larvae in bee hives
InactiveCN110612943AVarious mechanisms of actionLower resistanceBiocideAnimal repellantsWaxBatch extraction
Owner:湖南花可食生物科技有限公司
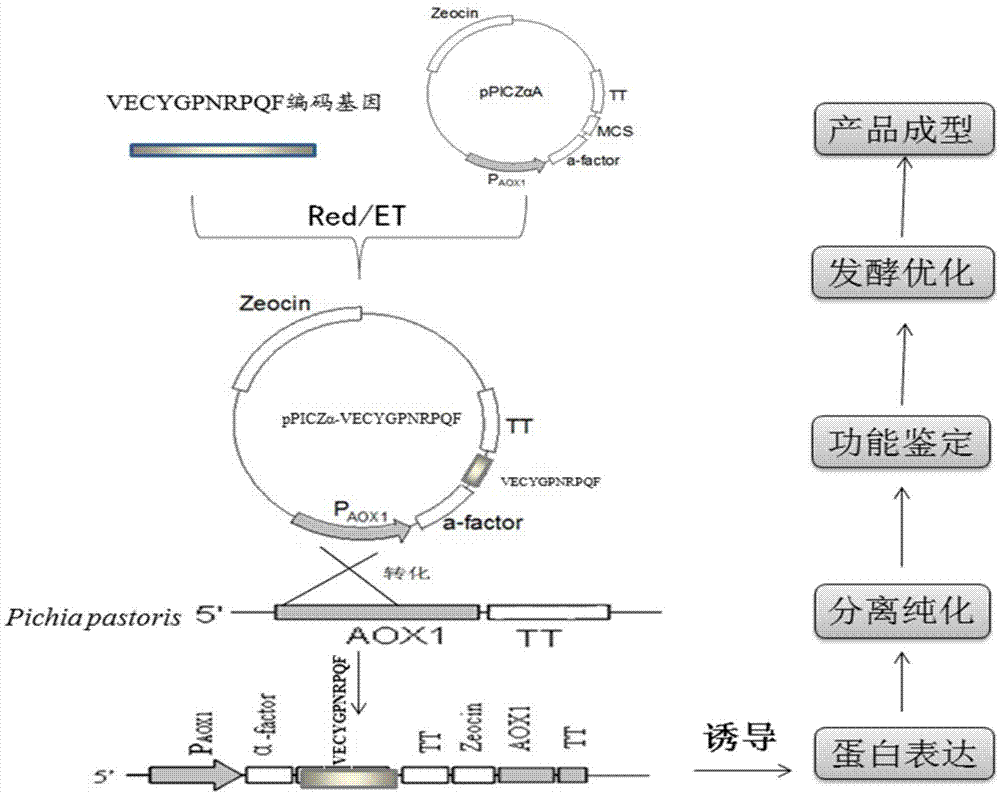
Antioxidant polypeptide expression pichia pastoris engineering bacteria and application
InactiveCN104498377ANo residueRelieve oxidative stressFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisOrganism
Owner:INST OF SUBTROPICAL AGRI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solution for evaluating glucose metabolism based on sialology method and evaluation method thereof
InactiveCN105954270AExtended shelf lifeSolve the inconvenience caused by testing blood sugarMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorAntioxidantHorse radish peroxidase
Owner:樊福好
Sequence Specific and Organism Specific Antimicrobials and Related Materials and Methods
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
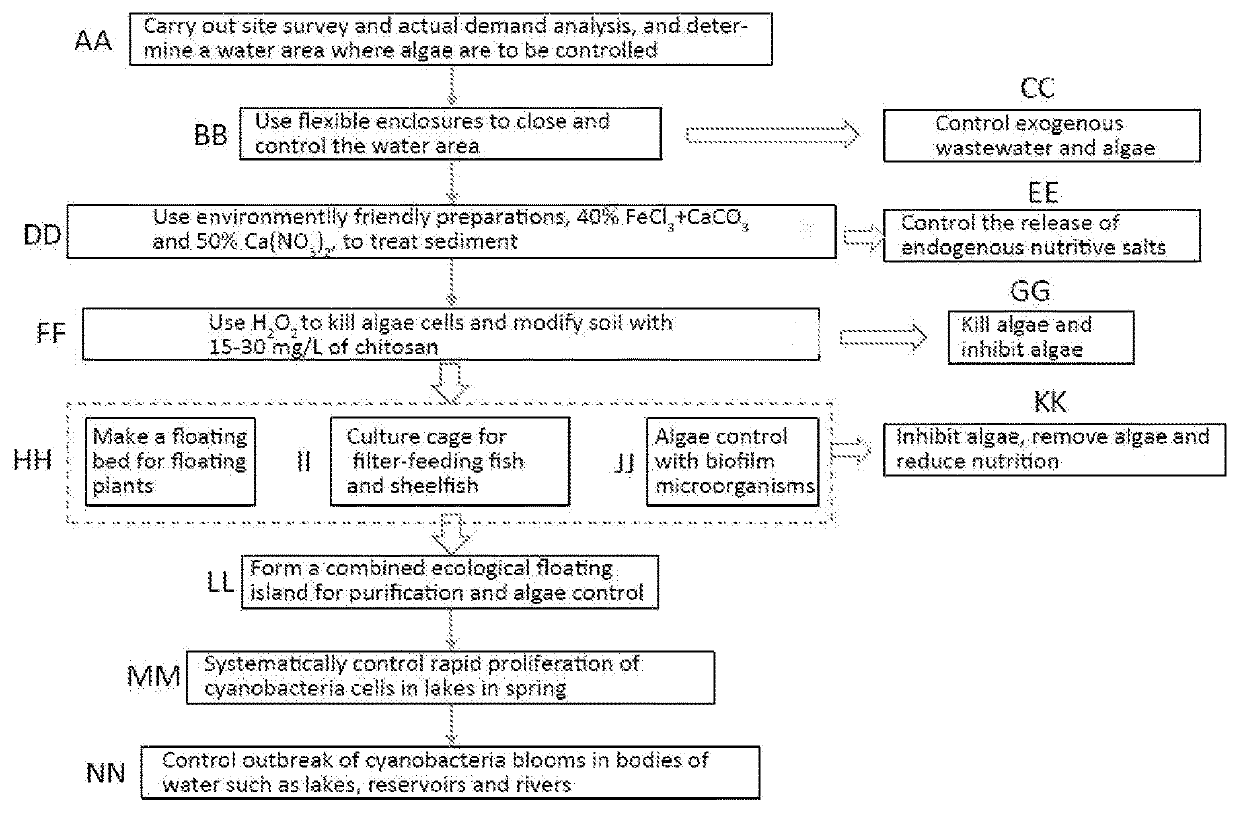
Method for systematically controlling rapid proliferation of cyanobacteria cells in lakes in spring
ActiveUS20210114906A1Efficiently and quickly and persistently controlTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesEnergy based wastewater treatmentMicroorganismMicrobiology
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Abalone mushroom cultivation technology
InactiveCN106171531AMushroom roundEasy to shapeCalcareous fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersThree levelAgricultural science
Owner:湖南湘蕈生物科技有限公司
Method for facilitating in-vitro maturation of human immature oocytes by utilizing 3D printing technology
Owner:GUANGXI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
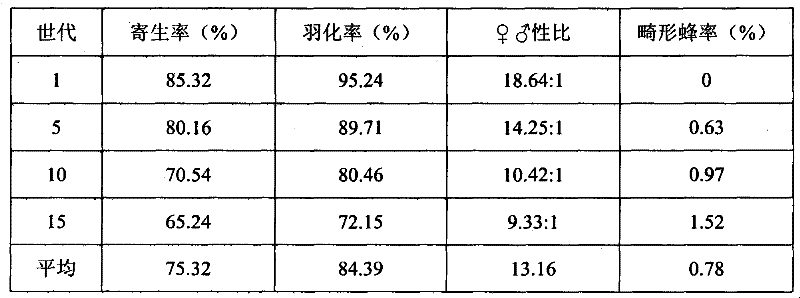
Method for propagating trichogramma pintoi voegele indoors by grapholitha molesta busck egg
InactiveCN102106319BMany types of beesThe quality of bees is obviousAnimal husbandryOrganismSturmiopsis inferens
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for labeling specific cells within living cells or tissues
InactiveUS20080124802A1Easy to exploreOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsFluorescenceImage tracing
The present invention discloses a method for labeling specific cells within living cells or tissues. The method comprises preparing the vectors with genes of photoactivable fluorescent proteins, followed by injecting the vectors containing genes of photoactivable fluorescent proteins together with genes of other fluorescent proteins into living cells or tissues, resulting in biological tissues with traceable systemic expression and irradiating the predetermined areas in living cells or tissues with an activating light source, thereby enhancing the intensity and duration of the emitted fluorescent after other excitations, thus revealing the targets intended for observation out of the background, so that a target-oriented image tracing is achieved.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Cultivation method for observing Plasmodium infestation of Brassicaceae plants
InactiveCN103931476BHigh transparencyImprove permeabilityCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsOrganismOperation safety
Owner:云南省农业科学院园艺作物研究所
Method for detecting infectious pathogens and portable detector
InactiveCN101886118AEasy to carryStrong specificityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiagnosis earlyUltraviolet lights
Owner:HAI KANG LIFE
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap