Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
8 results about "Neodymium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. Neodymium belongs to the lanthanide series and is a rare-earth element. It is a hard, slightly malleable silvery metal, that quickly tarnishes in air and moisture. When oxidized, neodymium reacts quickly to produce pink, purple/blue and yellow compounds in the +2, +3 and +4 oxidation states. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite. Neodymium is not found naturally in metallic form or unmixed with other lanthanides, and it is usually refined for general use. Although neodymium is classed as a rare-earth element, it is fairly common, no rarer than cobalt, nickel, or copper, and is widely distributed in the Earth's crust. Most of the world's commercial neodymium is mined in China.
Method for enhancing surface of magnesium aluminium alloy by laser remelting
InactiveCN101532134AHigh strengthImprove corrosion resistanceMolten spray coatingSuperimposed coating processOxygenLaser beams
The invention relates to a method for enhancing the surface of magnesium aluminium alloy by laser remelting, aiming at enhancement processing of the surfaces of magnesium aluminium alloy plates and magnesium aluminium alloy rods by the methods of flame spraying of alloyed powder and laser remelting. The method is characterized by cleansing the surface of the magnesium aluminium alloy, carrying out oxy-acetylene flame spraying on the alloyed powder, namely aluminium nickel alloy powder, nickel-chromium-boron-silicon-iron master alloy powder and neodymium powder, carrying out remelting and curing on the surface of the magnesium aluminium alloy on a laser processor, carrying out omnibearing radiation by laser beams according to trace curves set by computer programs so that a nickel base alloy layer is melted and cured on the surface of the magnesium aluminium alloy to form the alloy layer, therefore, the hardness of the surface of magnesium aluminium alloy is greatly improved by 8-10 times as high as that before processing, the wearing resistance and corrosion resistance of the surface of magnesium aluminium alloy are greatly improved respectively by 56% and 56.4%. The method has short process flow, easy realization, safety, stability and reliability and firm solid melting layer, is not easy to fall off and can enhance the surfaces of the magnesium aluminium alloys with various profiles.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
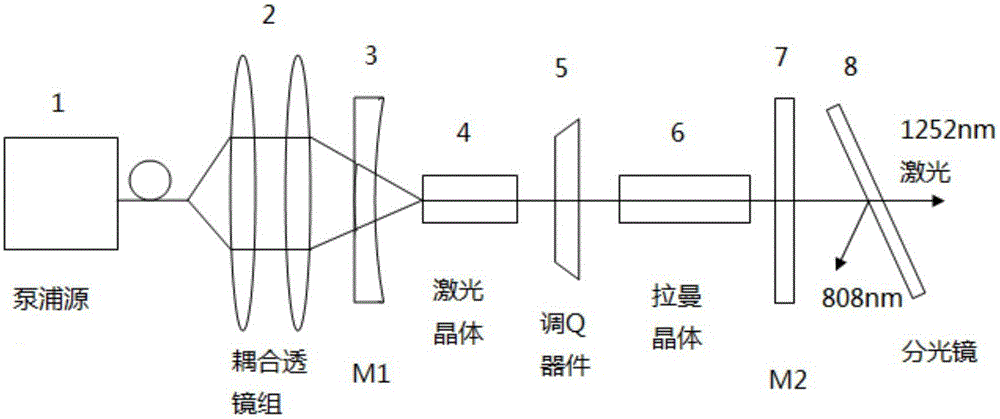
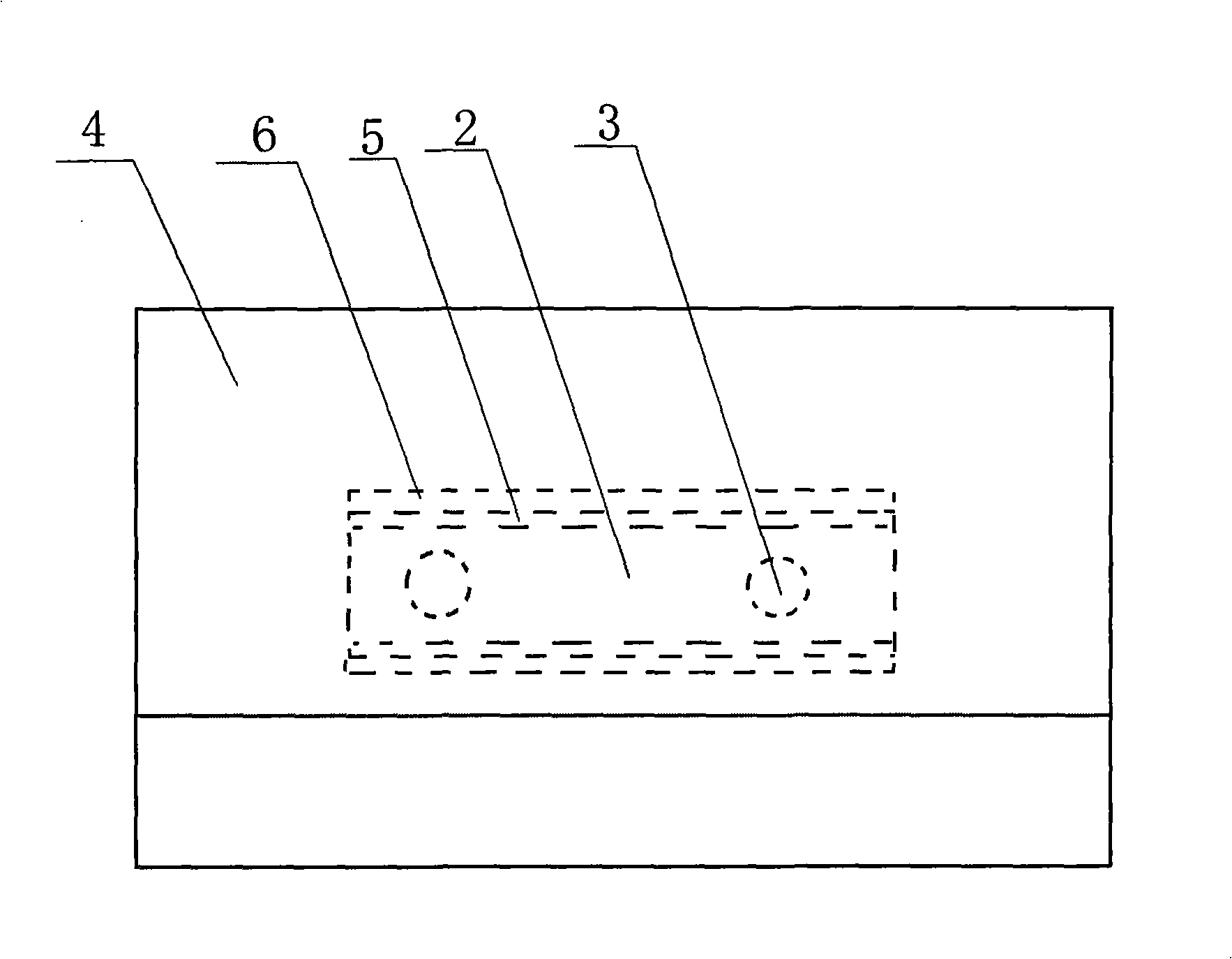
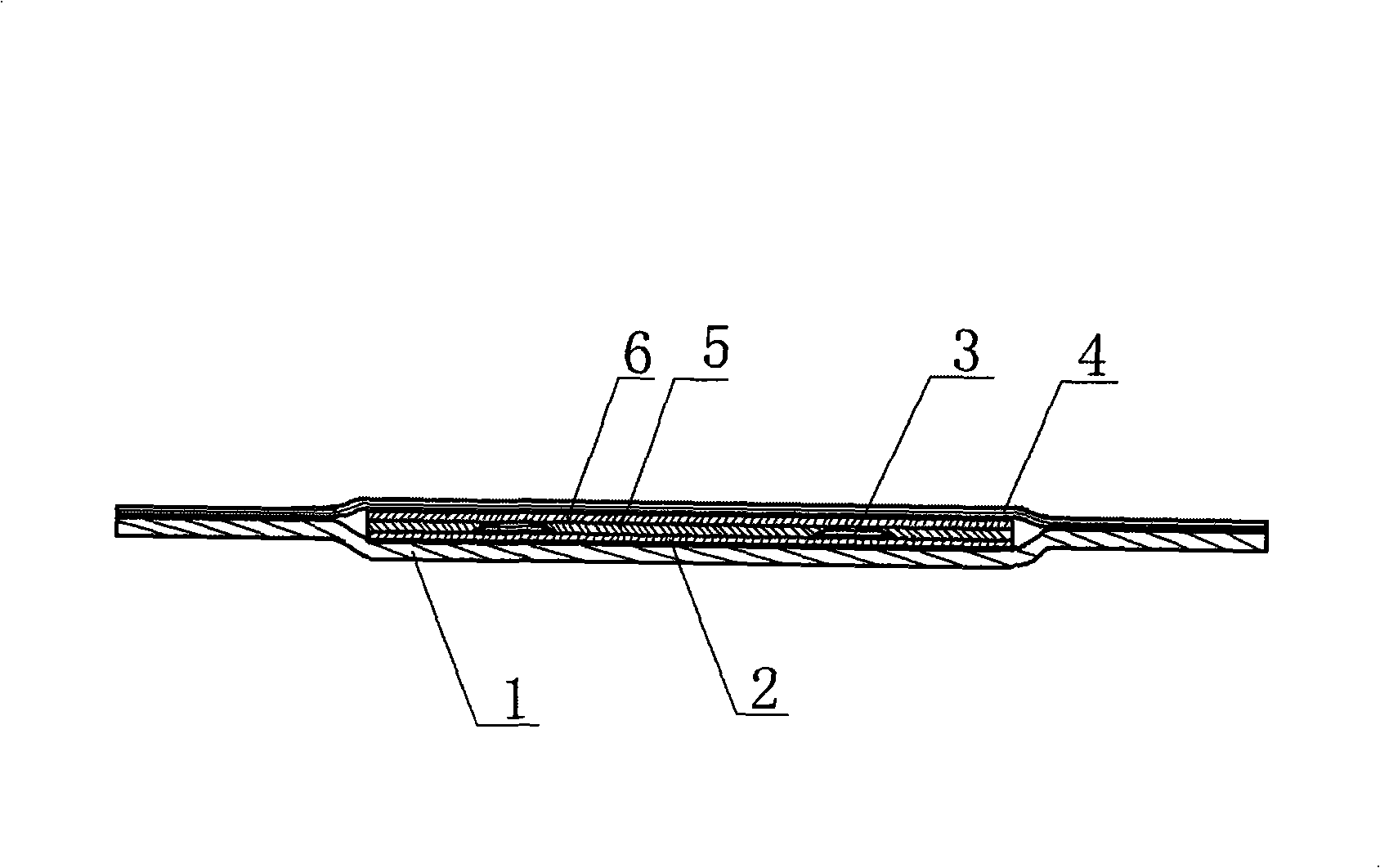
1.2 micron wavelength all-solid-state raman laser
InactiveCN105140775ACompact structureEasy to useLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialDielectricRaman amplifiers
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
High-strength high-conductivity rare earth copper-magnesium alloy contact wire and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106555073AMeet performance requirementsHigh elongationSingle bars/rods/wires/strips conductorsConductive materialRare-earth elementCerium
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel neodymium-doped near-infrared fluorescent material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104130775AGood physical and chemical stabilityGood dispersionLuminescent compositionsPhysical chemistryLight excitation
The invention discloses a novel neodymium-doped near-infrared fluorescent material and a preparation method thereof. The material is mainly characterized in that the composition is X1SiO2-2Al2O3-3Na2O-4Nd2O3 (X1=20-30%, X2=5-10%, X3=2-5%, and X4=1-10%); and the preparation method of the material comprises: (1) uniformly mixing zeolite and neodymium nitrate, heating to 500-600 DEG C, and keeping warm for 2-5 h, so as to obtain a neodymium-doped zeolite precursor; (2) performing hot-pressing forming on the neodymium-doped zeolite precursor, controlling the pressure intensity to be 10 MPa-3 GPa and the heating temperature to be 700 DEG C-1200 DEG C, and keeping the high temperature for 1 hour or more; and (3) naturally cooling in the furnace. The rare-earth fluorescent material with stable physical and chemical properties, which is obtained by using the method, is characterized in that fluorescence is generated at 1064 nm when 582 nm yellow light is employed for exciting the glass, the transmission scope is 300-400 mu s, and the material is widely applicable to fields such as substance analysis, infrared detection, optical communication and the like.
Owner:CHONGQING LEADING NEW MATERIAL CO LTD
Cut application used after operation
InactiveCN101310776APromote growthPromote healingAdhesive dressingsAbsorbent padsWound healingSurface layer
Owner:徐茂山
Preparation method of self-cleaning fibers
ActiveCN109382089ARetain high temperature resistanceRemain flexibleWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsFiberSodium bicarbonate
The invention provides a preparation method of self-cleaning fibers, and belongs to the field of water purification materials. The preparation method of the self-cleaning fibers comprises the following process steps: mixing deionized water, sodium metavanadate and ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium, regulating pH of a solution with hydrochloric acid, and then adding a mixed solution of deionized water, bismuth nitrate pentahydrate, neodymium nitrate and sodium bicarbonate to prepare an active precursor solution; carrying out hydrothermal reaction on the active precursor solution and aluminium silicate fibers, and drying and calcining to obtain the self-cleaning fibers. The self-cleaning fibers consist of aluminium silicate fibers of which the surfaces are coated with bismuth neodymium vanadate, resist high temperature, are flexible, are high in strength, can float in water, and can degrade organic pollutants in water under the condition of illumination.
Owner:JIAXING RUYUN CONSTR TECH CO LTD
Textile fiber product containing rare earth elements
InactiveCN107190503AStrong magneticTo achieve the effect of health carePhysical treatmentNatural fibresRare-earth elementTextile fiber
Owner:屈维勇
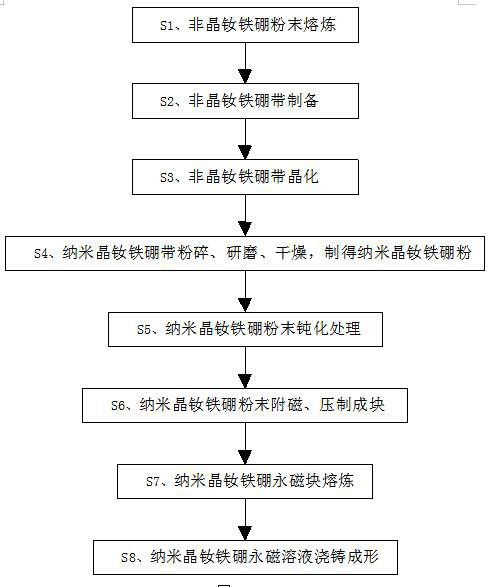
Preparation method of nanocrystalline neodymium-iron-boron permanent magnet block
ActiveCN112002511ALow costImprove consistencyMagnetic materialsInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureNeodymium iron boronMagnetic field
Owner:GANZHOU FORTUNE ELECTRONICS
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap