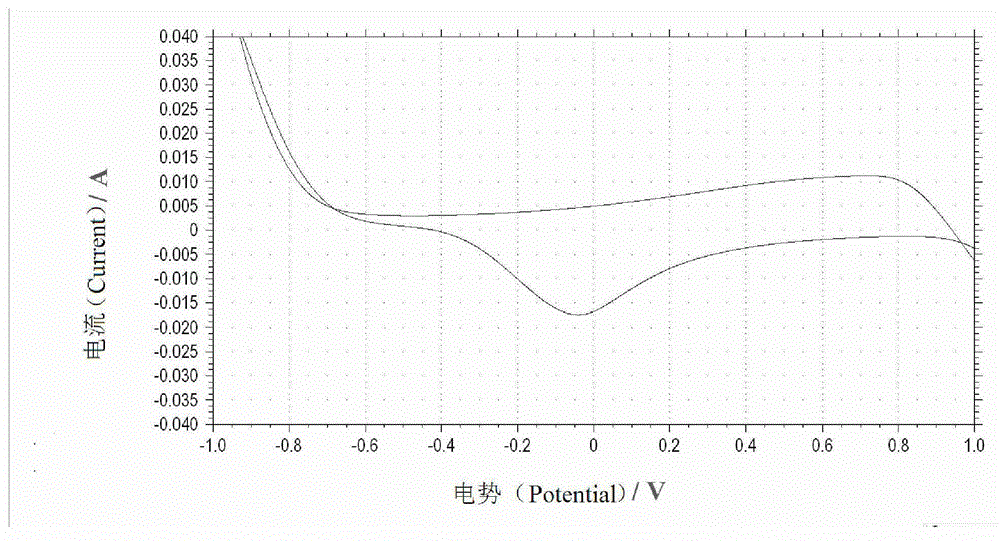
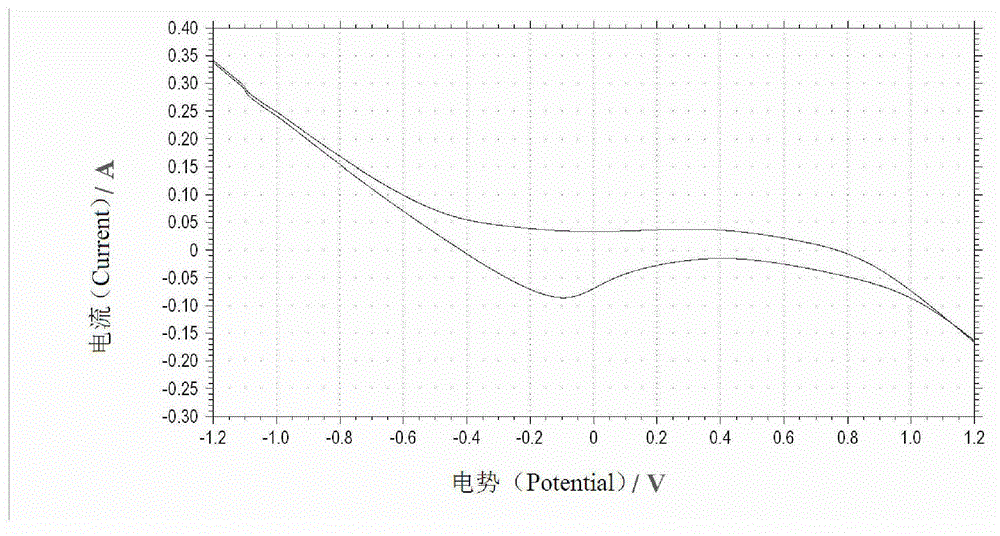
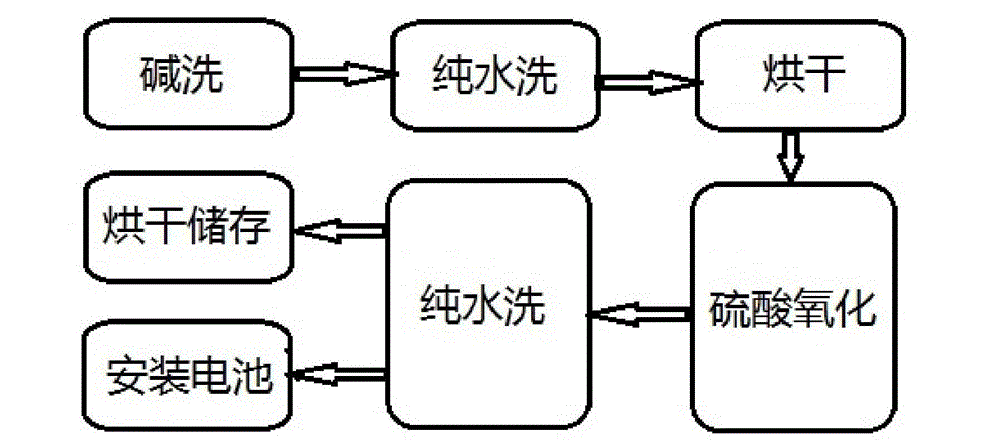
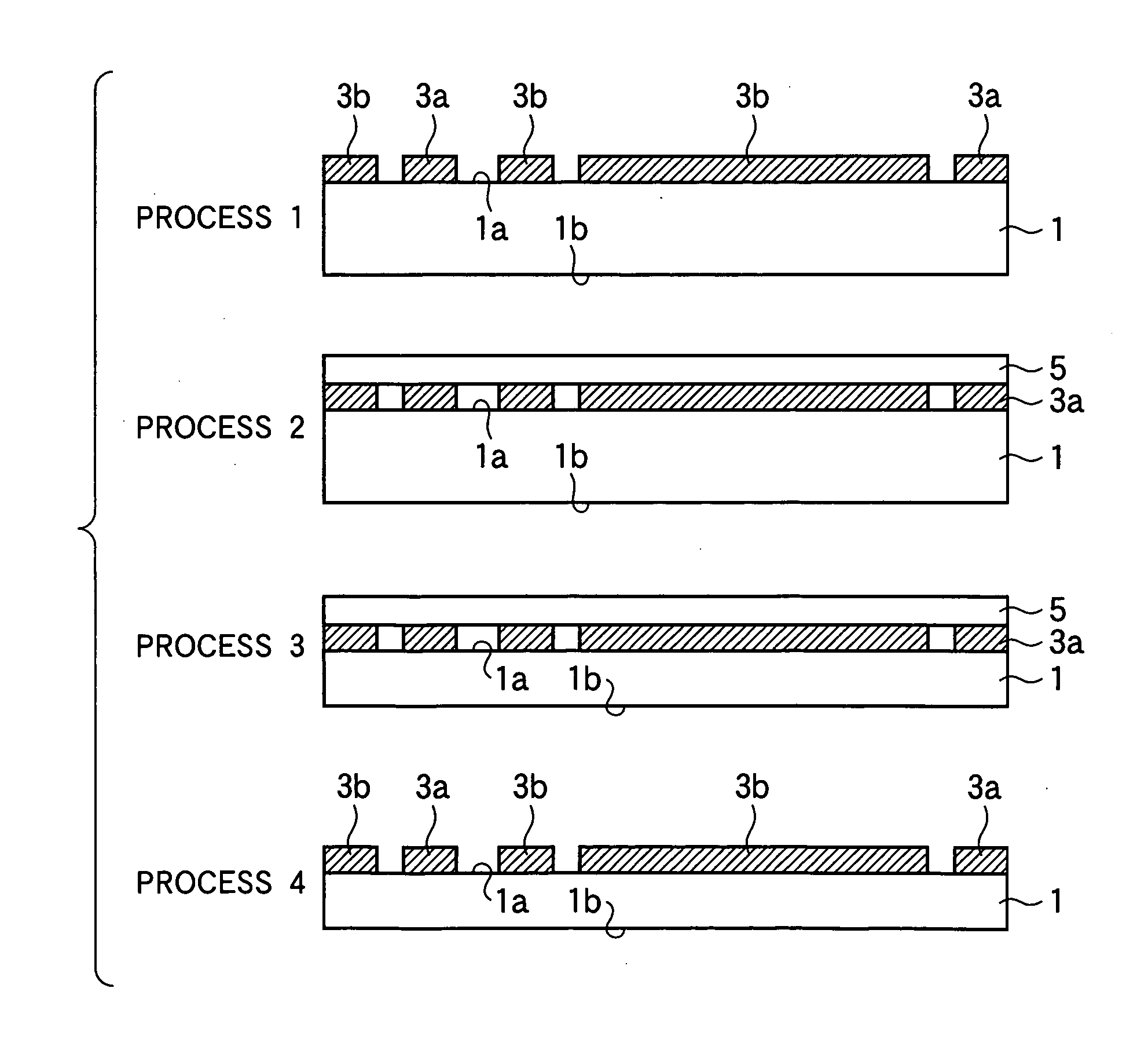
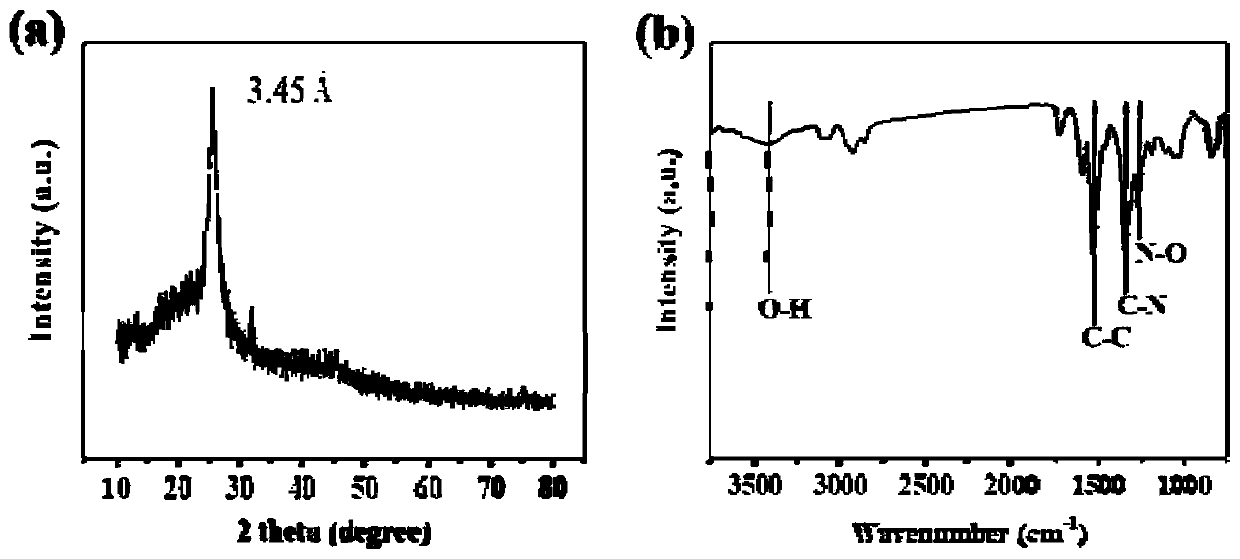
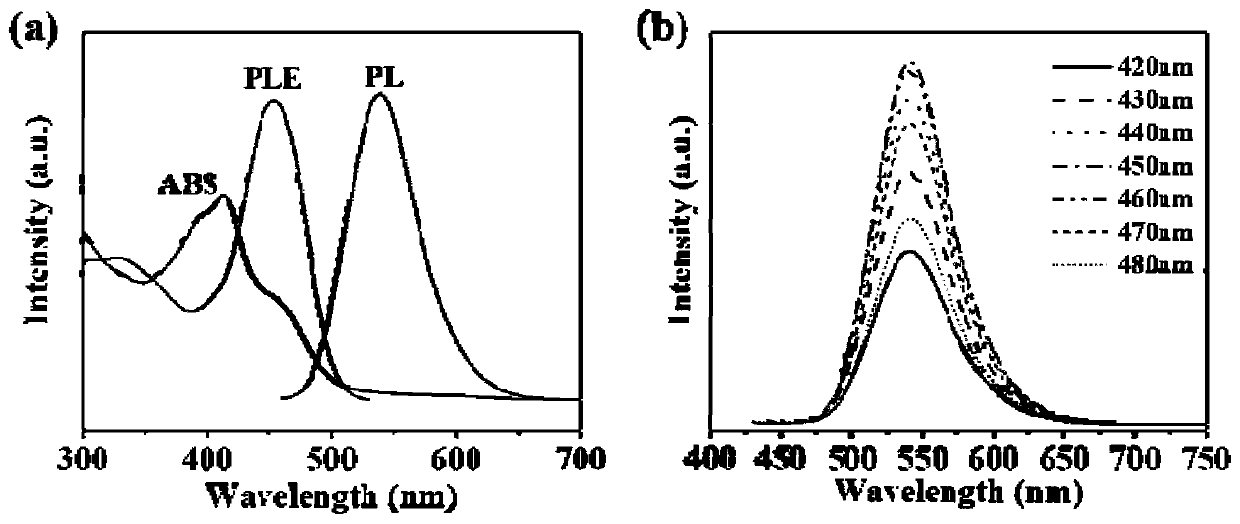
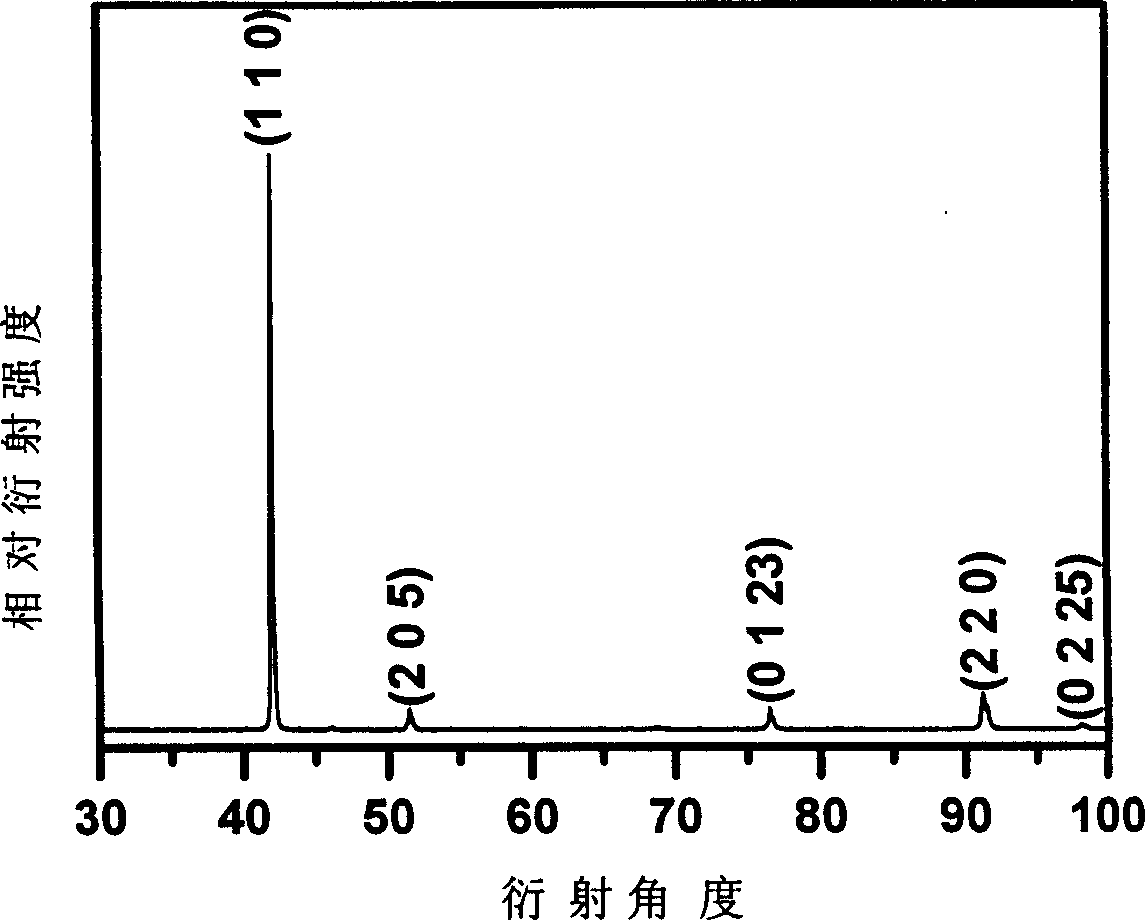
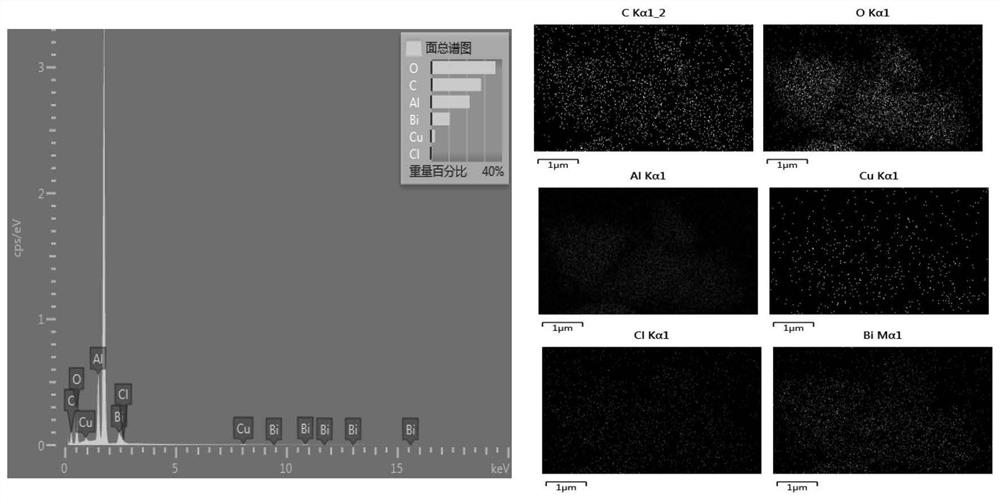
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
37 results about "Nitric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nitric acid (HNO₃), also known as aqua fortis (Latin for "strong water") and spirit of niter, is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The pure compound is colorless, but older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen and water. Most commercially available nitric acid has a concentration of 68% in water. When the solution contains more than 86% HNO₃, it is referred to as fuming nitric acid. Depending on the amount of nitrogen dioxide present, fuming nitric acid is further characterized as white fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 95%, or red fuming nitric acid at concentrations above 86%.
Prepn of nano-cobaltosic oxide powder
InactiveCN1344682ASuitable for large-scale industrial productionEasy to operateCobalt oxides/hydroxidesCobalt carbonatesCobalt(II,III) oxideCobalt salt
The present invention relates to chemical industry technology. The preparation of nanometer cobaltosic oxide powder includes purifying material, cobalt salt deposition, solid-liquid separation and solid calcination. Cobalt sheet is dissolved in nitric acid while being heated and high purity water is added to regulate solution density and pH value so as to obtain cobalt nitrate solution of 1.5-1.65 g / cu cm density and pH 4-5; ammonium bicarbonate suspension in 14-30 wt% is prepared with ammonium bicarbonate and water; cobalt nitrate solution is added into the suspension slowly to result in weight ratio of carbonate radical to cobalt ion being 2.4-2.6; and the wet cobalt carbonate material is heated to 300-450 deg.c for 3-6 hr to obtain black Co3O4 powder.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Preparation method of zirconium oxide-silicon oxide composite aerogel
ActiveCN103214034ALow densityLow thermal conductivitySilicon compoundsZirconium oxidesAlcoholSilicon oxide
The invention relates to a preparation method of zirconium oxide-silicon oxide composite aerogel. The method comprises the following steps of: dissolving siloxane in alcohol and uniformly stirring the solution to obtain alcohol solution of the siloxane; titrating concentrated nitric acid with 65-68% of mass concentration, titrating deionized water after stirring uniformly and continuously stirring; titrating the concentrated nitric acid to the pre-hydrolyzed siloxane solution, titrating zirconium alkoxide after mixing uniformly, adding the deionized water after stirring uniformly and stirring continuously to obtain clear and transparent gel; transferring the gel to a mould, and still standing and aging the gel to obtain the zirconium oxide-silicon oxide composite wet gel; soaking the wet gel by using aging solution; and finally soaking the gel by using absolute ethyl alcohol or isopropanol solvent. The blocky zirconium oxide-silicon oxide composite aerogel featured with low density and low thermal conductivity prepared by the invention basically keeps the former microcosmic undefined structure after thermal treatment at 1000 DEG C, and has specific area up to 353m<2> / g and good high-temperature stability.
Owner:LINXIAO (TIANJIN CHINA) TECH CO LTD
Magnesium alloy surface zinc-calcium series phosphating solution and conversion treatment process thereof
InactiveCN101671824AImprove corrosion resistanceStrong adhesionMetallic material coating processesMg alloysPhosphate
The invention discloses magnesium alloy surface zinc-calcium series phosphating solution and a conversion treatment process thereof; the magnesium alloy surface phosphating solution is aqueous solution formed by the following constituents, namely, every liter solution contains: 10-30g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 4-6g of zinc nitrate, 2-4g of sodium nitrite, s0.5-2g of sodium fluoride, and 0.-2g of calcium nitrate; the process for carrying out surface conversion treatment to the phosphating solution comprises the following process flows: alkaline washing and degreasing->rinsing->acidity activation->rinsing->surface activation->rinsing->phosphating->rinsing->drying; the working temperature is 40-70 DEG C, and the time is 5-60 minutes. The conversion treatment process can obtain phosphateconversion coating on the surface of the magnesium alloy, wherein the conversion coating has good protectiveness, is fine and uniform and stable, and has strong adhesive force, and can improve the corrosion-resisting property of magnesium alloy parts; the conversion treatment process is stable and easy to control, and has low cost.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
Treatment method of carbon felt for vanadium batteries
ActiveCN103066287AImprove hydrophilicityImprove the activation effectCell electrodesActivated carbonCarbon felt
Owner:承德新新钒钛储能科技有限公司 +1
Amino functional graphene quantum dot and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN105174403ACo-precipitationThe production method is simple and convenientWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationActivated carbonIndustrial waste water
The invention discloses an amino functional graphene quantum dot and the preparation and application thereof, and belongs to the field of material preparation. According to the amino functional graphene quantum dot and the preparation and application thereof, activated carbon serves as the raw material, after the activated carbon is oxidized through nitric acid, filtration is conducted to remove the nitric acid, oxidized activated carbon is washed through water to be close to neutral, and the graphene quantum dot is obtained. The surface of the obtained graphene quantum dot is provided with a large number of oxygen-containing functional groups such as carboxyl and hydroxy, and therefore the graphene quantum dot can be stably dispersed into water under the neutral condition. Complexing of the carboxyl and the hydroxy on the surface of the graphene quantum dot and most heavy metal ions can be achieved, agglomeration can be caused, and coprecipitation of the graphene quantum dot and the heavy metal ions is achieved finally. Therefore, the graphene quantum dot can be used for purification of industrial waste water containing the heavy metal ions. The production method of the graphene quantum dot is simple, convenient, rapid, low in cost and high in yield; the obtained graphene quantum dot has a good effect on removing the heavy metal ions, and the graphene quantum dot which is subjected to desorption and regeneration treatments can be recycled.
Owner:QUANZHOU FUDA TECH CONSULTING CO LTD
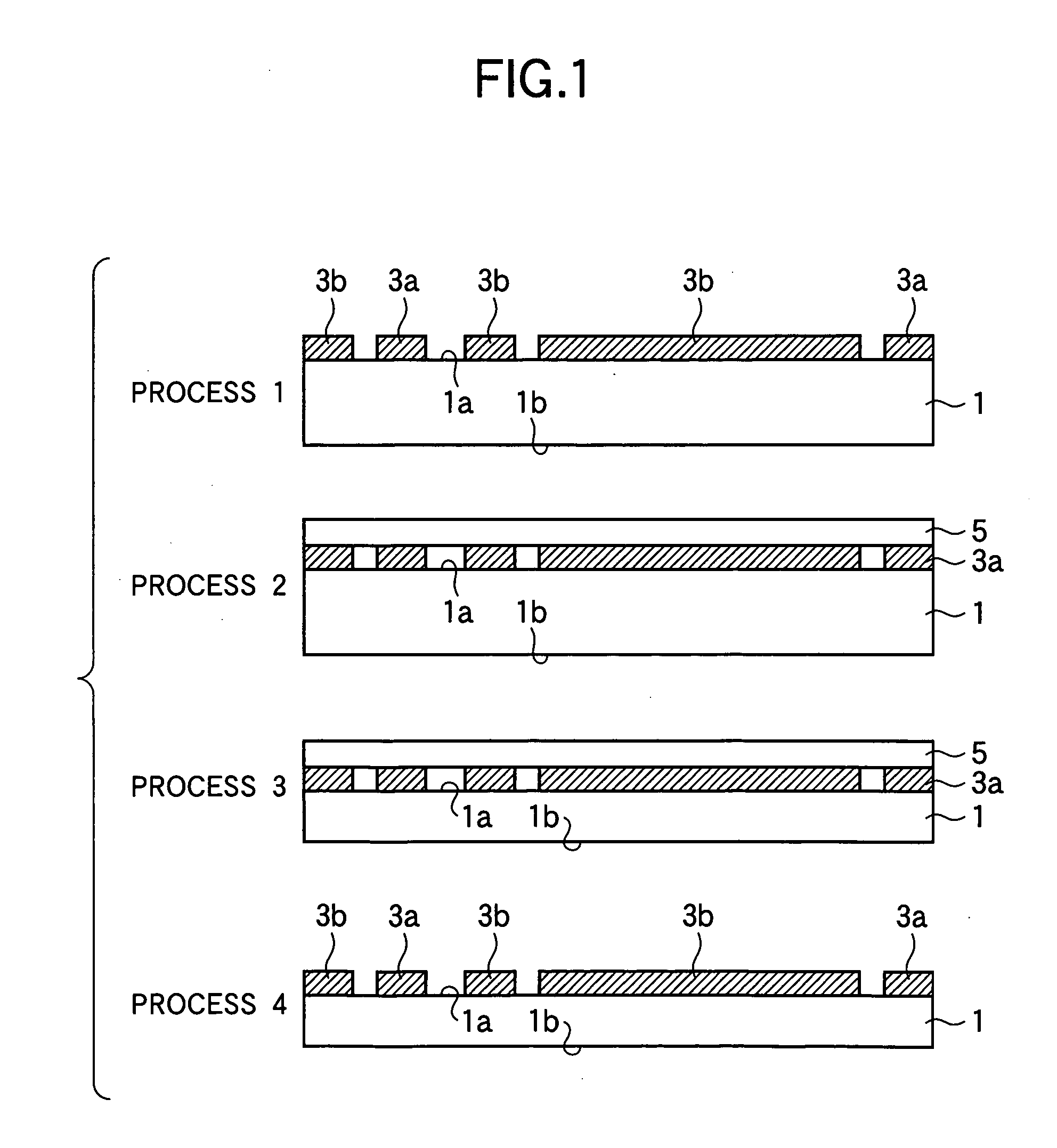
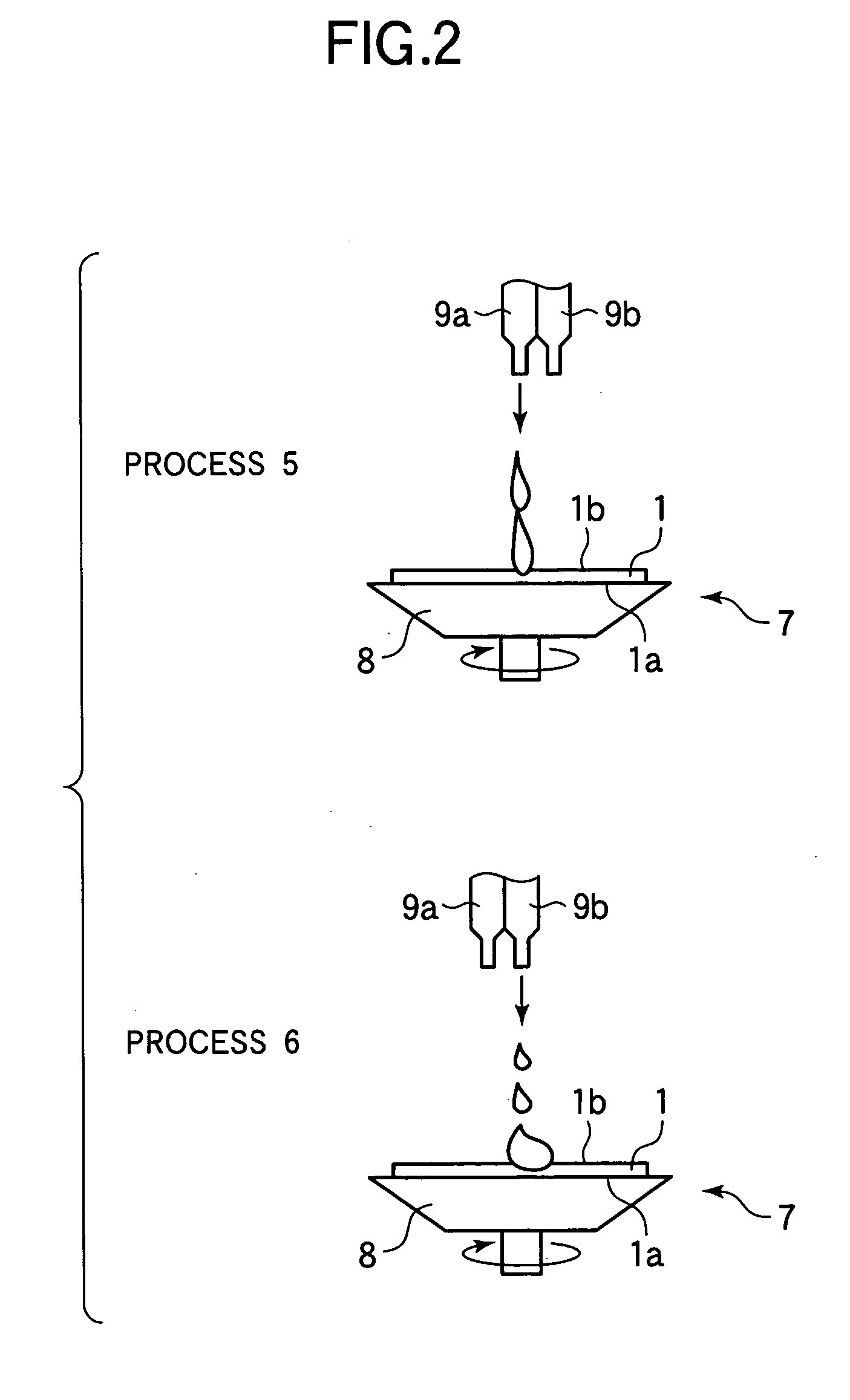
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor wafer
InactiveUS20070093065A1Clean back surfaceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidEtching
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method for separating and recovering phosphoric acid from acetic acid-nitric acid-phosphoric acid series mixed acid waste liquor
ActiveCN102167415AEfficient recyclingGood choiceWater/sewage treatment by extractionPhosphoric acidAcetic acidAcetic acid ear
The invention relates to a method for separating and recovering phosphoric acid from acetic acid-nitric acid-phosphoric acid series mixed acid waste liquor. The method disclosed by the invention is characterized by comprising the following steps of: an acetic acid-nitric acid extracting step: mixing waste liquor containing acetic acid, nitric acid and phosphoric acid with an extracting agent solution of aliphatic series straight-chain saturated hydrocarbon which contains phosphoric trialkyl ester and 6-13 carbon atoms and selectively dissolving and extracting acetic acid and nitric acid from the extracting agent solution; a phosphoric acid recovering step: recovering the phosphoric acid from extracting waste liquor obtained in the extraction step; and an acetic acid-nitric acid stripping step: enabling the extracting agent solution containing the acetic acid and the nitric acid, obtained in the acetic acid-nitric acid extracting step, to be in contact with stripping water so that the acetic acid and the nitric acid are dissolved and transferred to the stripping water. The extracting agent solution is recycled by feeding the oil-phase extracting agent solution obtained in the acetic acid-nitric acid stripping step to the acetic acid-nitric acid extracting step. By means of the invention, the favorable separability of oil phase and aqueous phase in the stripping step can be maintained for a long time, and the phosphoric acid can be selectively and favorably separated and recovered from the acetic acid-nitric acid-phosphoric acid series mixed acid waste liquor for a long time with high efficiency.
Owner:SANWA YUKA INDS
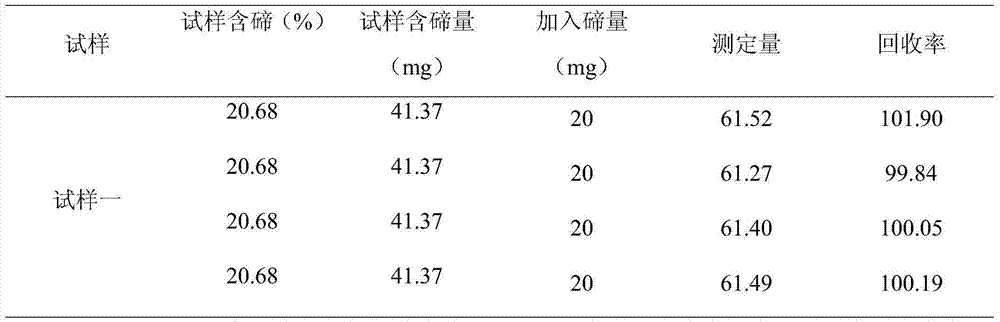
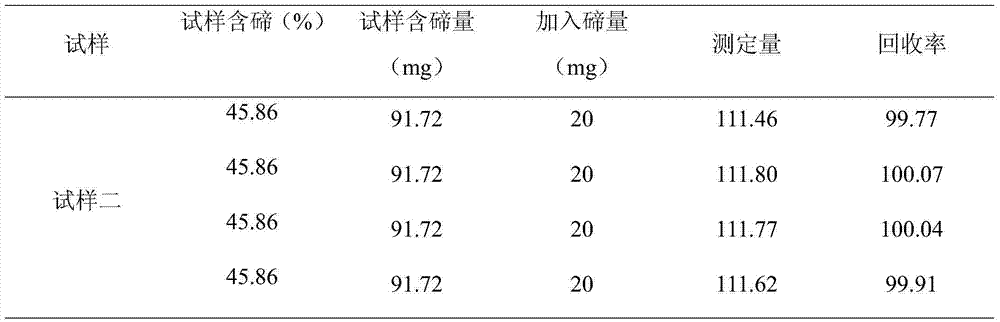
Analyzing method for quickly and precisely measuring tellurium in tellurium smelting process
ActiveCN104237225AFast and accurate determinationImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorValidation methodsTe element
Owner:YUNNAN CHIHONG ZINC & GERMANIUM
Method for preparing organic carbon fertilizer from agricultural wastes as raw materials
The invention discloses a method for preparing organic carbon fertilizer from agricultural wastes as raw materials. The method comprises, 1, raw material pretreatment: crushing agricultural wastes, adding water into the agricultural wastes and carrying out blending, 2, acid addition and digestion reaction, and 3, centrifugal separation or settling separation and supernatant collection. The agricultural wastes comprise straws. The straws comprise corn stalks, wheat straws, paddy rice straws, sugar cane stalks, cotton stalks or the rest part of crops treated by seed collection. The acid comprises more or more of sulfuric acid, nitric acid, perchloric acid, hypochlorous acid and hydrogen peroxide. The digestion reaction temperature is in a range of 80-180 DEG C and digestion reaction time is in a range of 1-30min. A mass ratio of the agricultural wastes to the acid is 100: (1-9). The method has simple and fast processes and small energy consumption. The obtained organic carbon fertilizer comprises micromolecule organic carbon and can be absorbed easily by crops.
Owner:SHENZHEN BATIAN ECOTYPIC ENG
Iron and steel product surface treating agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105256321AReduce productionReduce wasteMetallic material coating processesIndustrial waste waterO-Phosphoric Acid
The invention provides an iron and steel product surface treating agent and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the technical field of metal surface treating agents. The surface treating agent comprises, by weight, 12%-17% of phosphoric acid with the concentration of 85%, 3%-8% of composite phosphate, 7%-12% of nitric acid with the concentration of 65%, 5%-10% of corrosion inhibitor(s), 1%-3% of aqueous surface active agent(s), 3%-6% of zinc chrome, 4%-7% of polyol ester, and the balance water. The iron and steel product surface treating agent can be used for carrying out derusting, deoiling and phosphating on iron and steel products at the same time, and the generation amount of industrial waste water in the production process can be greatly reduced; the iron and steel product surface treating agent can be stored for a long time without lowering of the effectiveness, and uniform and compact phosphating films still can be formed on the surfaces of the iron and steel products even if the iron and steel product surface treating agent is stored for a long time; in addition, when the iron and steel product surface treating agent is used for carrying out comprehensive surface treating on the iron and steel products, the replacement frequency of bath solutions is low, the utilization rate of acid liquor is high, and the production cost of enterprises is low.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV +1
Synthesis method of 2-(2-chloroethoxy) acetic acid
InactiveCN101844978AZero costSimple and fast operationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic compound preparationAcetic acidOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a synthesis method of 2-(2-chloroethoxy) acetic acid, which belongs to the technical field of the preparation and the application of fine chemical engineering products. The invention particularly belongs to the synthesis method of 2-(2-chloroethoxy) acetic acid. The invention uses 2-chloroethoxy ethanol as starting materials, uses water as solvents, and uses nitric acid for direct oxidization to obtain products. The reaction process is shown as the accompanying drawing. The invention adopts water as the solvents, and uses the nitric acid as oxidizing agents for efficiently oxidizing the 2-chloroethoxy ethanol into corresponding acids. The method has the advantages of simple operation, low price of raw materials, easy acquisition of raw materials, simple requirement on equipment, simple after treatment and the like. In addition, the use of the organic solvent has nearly zero cost, and the invention conforms to the environmental protection industrial production requirements, so the invention has wide application prospects.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Preparation method of catalytic electrode for ammonia production through electrochemical reduction of nitrate or nitrite
ActiveCN112981451ASimple preparation processPreparation amplificationElectrodesAmmonia productionPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a catalytic electrode for ammonia production through electrochemical reduction of nitrate or nitrite, which comprises the following steps: soaking metal in hydrochloric acid, soaking the metal in a hydroboron solution, and washing and drying to obtain the catalytic electrode. The catalytic electrode provided by the invention is simple in preparation process and low in cost, and shows excellent ammonia preparation rate and electrocatalytic selectivity in ammonia preparation through electrocatalytic reduction of nitrate or nitrite.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of graphene quantum dots
ActiveCN110540192AHigh fluorescence yieldImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneFluorescenceFiltration
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Multicore palladium cluster compound for catalytically hydrolyzing carbon disulfide and carbonyl sulfide
ActiveCN106046058AAchieve recyclingImprove conversion efficiencyOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarbonyl sulfidePhenanthroline
The invention provides a multicore palladium cluster compound for catalytically hydrolyzing carbon disulfide and carbonyl sulfide. The multicore palladium cluster compound is an azacyclo- di-core palladium (II) cluster compound and has the general formula of ([(N^N)2Pd2(NO3)2](NO3)2), wherein (N^N) represents a ligand and is one selected from pyridine, dipyridine, alkylpyridine, pyrroline and phenanthroline. The invention further provides a preparation method for the multicore palladium cluster compound and an application of the multicore palladium cluster compound. The multicore organic-metal cluster compound provided by the invention serves as a catalyst for removing sulfur from the carbon disulfide and the carbonyl sulfide through hydrolysis and is used for catalytically hydrolyzing the carbon disulfide and the carbonyl sulfide in a low-temperature (room-temperature) aqueous solution in a high-efficiency manner so as to produce a carbon dioxide and sulfidion (S<2->) bridged intermediate product of a tri-core palladium cluster compound, and finally, the recycling of the catalyst is achieved through an oxidation-reduction reaction between concentrated nitric acid and the tri-core palladium cluster compound.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method for measuring cobalt content of microorganism culture system by acidizing treatment method
InactiveCN103575677AAvoid the disadvantages of large interferenceSimple and fast operationPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsVolumetric flaskImpurity
The invention discloses a method for measuring the cobalt content of a microorganism culture system by an acidizing treatment method. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of putting 0.5-3.5 mL of a sample to be measured into a container with an opening, adding 65-68 mass percent of concentrated nitric acid according to a volume ratio of 1:1, and oscillating and mixing the sample and the concentrated nitric acid to be uniform, wherein the sample to be measured is a solution to be measured containing cobalt ions in the microorganism culture system; heating the mixed solution until the mixed solution is boiling, oscillating to remove acid, evaporating the mixed solution until the mixed solution is nearly dried, adding pure water for smelting, losslessly transferring the mixture into a volumetric flask with the volume of 10 mL, and finally adding water into the volumetric flask to fix the volume to a scale line; measuring the cobalt content of the aqueous solution in the volumetric flask by adopting a spectrophotometric method or / and an atomic absorption spectrometry. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the sample to be measured is subjected to acidizing treatment, so that the shortcoming that components of a microorganism culture medium seriously affect cobalt measurement is overcome; meanwhile, other impurities cannot be introduced; therefore, the method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, quickness, accuracy and sensitivity in operation and the like and can be successfully applied to the measurement of the cobalt content of the microorganism culture system.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Copper plating device
Owner:CHENGDU TIANMU ELECTRONICS EQUIP
Preparation method of chromium-doped cobalt phosphide nanorod array growing on carbon cloth in situ
PendingCN112657521AHigh yieldEasy to operatePhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesChromium dopingFree energies
The invention aims to provide a preparation method of a chromium-doped cobalt phosphide nanorod array growing on carbon cloth in situ, which comprises the following specific steps of oxidizing the carbon cloth in nitric acid to enhance the hydrophilicity of the carbon cloth, and growing a layer of precursor CrxCo1-x(OH)F / CC on the carbon cloth in situ by a hydrothermal method, finally, converting the precursor growing on the carbon cloth into chromium-doped cobalt phosphide CrxCo1-x(OH)F / CC through a high-temperature gas-phase phosphating method. The preparation process is simple to operate, easy to control and low in cost and can be used for large-scale production, the chromium-doped cobalt phosphide nanorod array which grows on the carbon cloth in situ and is prepared by adopting the method is uniform in distribution and close in arrangement, the rod-like particle size reaches the nanoscale and is uniform in particle size, and the CoP crystal form is reserved while the free energy of hydrogen adsorption is reduced by chromium doping; the hydrogen evolution reaction can be efficiently, continuously and stably catalyzed.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Preparation method of corrosive self-embrittled type radioactive decontaminant used on surface of iron-based material
ActiveCN110277182ALess secondary wasteImprove acid resistanceRadioactive decontaminationSilicon dioxideRadioactive Pollutants
The invention belongs to the technical field of radioactive decontamination and discloses a preparation method of a corrosive self-embrittled type radioactive decontaminant used on the surface of an iron-based material. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking silica as an inorganic component, modifying the silica by using a silane coupling agent KH550; by taking a ternary random copolymer of methyl methacrylate, methacrylic acid and trifluoroethyl methacrylate as an organic component, carrying out organic / inorganic compounding preparation so as to obtain a compounded self-embrittled type decontaminant; further compounding the decontaminant with corrosive components such as nitric acid, so as to obtain the corrosive self-embrittled type radioactive decontaminant for carbon steel and stainless steel. The decontaminant prepared by using the method aims at strong-stationarity radioactive contaminants on the surface of the iron-based material, an iron-based metallic surface layer is damaged through the corrosive component, and the contaminants are adsorbed and wrapped by the decontaminant and are dried and embrittled to form brittle sheets which are peeled off by self, so that removal of radioactive contaminants on the iron-based metallic surface is achieved.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of etching method of diffusion layer of crystalline silicon solar cell
InactiveCN102290491ASimple processLow equipment requirementsAfter-treatment detailsFinal product manufactureEtchingPhosphoric acid
Owner:WUXI SAIJING SOLAR
Sb2Te3 monocrystalline nanometer line ordered array and its preparation method
InactiveCN1769539ASolve easy hydrolysisAddress effectivenessPolycrystalline material growthElectrolytic organic material coatingNanowireAuxiliary electrode
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
PbS nano-sheet preparation method
InactiveCN104609464APromote growthLow toxicityMaterial nanotechnologyLead sulfidesLead nitrateDecomposition
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method and application of vanadium-doped gallium antimonate visible light photocatalyst
ActiveCN103920487AAvoid obstructionEnter fullyMaterial nanotechnologyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationVanadium dopingAmmonium metavanadate
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Extraction and separation method of trace uranium element in liquid sample
ActiveCN107860816ARaise the ratioGood removal effectPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAmmonium carbonateTrioctylphosphine oxide
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军防化学院
Determination method for contents of elemental silicon, manganese, phosphorus, nickel and chromium in weathering-resistant steel
InactiveCN105352944AMeet the quantitative analysis testReduce pollutionAnalysis by thermal excitationManganeseStock solution
Owner:WUKUN STEEL
Fenton-like catalytic material with electron-deficient Cu center, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN111974423ALarge specific surface areaHigh catalytic activityWater contaminantsCatalyst activation/preparationCopper chloridePhysical chemistry
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Non-crystallization concrete accelerator
A non-crystalline concrete quick-setting agent, the main component is clinker made by mixing bauxite, soda ash and quicklime, and adding 55‑60 parts of acrylic acid copolymer, 5‑15 parts of nitric acid, and 15 parts of silicon powder 20 parts, polyethyleneimine 5-10 parts, malonic acid 1-5 parts. Described acrylic acid copolymer is preferably 57 parts. Compared with the prior art, the present invention has the beneficial effects that: the present invention makes the quick-setting agent have a good effect by adding acrylic acid copolymer, nitric acid, silicon powder and polyethyleneimine.
Owner:SHENYANG CHUANGDA TECH TRADE MARKET
Preparation method of nitrogen-doped three-dimensional interconnected hollow carbon foam electrode material
InactiveCN109994731AImprove performanceSimple preparation processMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesFiltrationSodium-ion battery
The invention discloses a preparation method of a nitrogen-doped three-dimensional interconnected hollow carbon foam electrode material, which specifically includes the following steps: (1) mixing Znpowder and sucrose by ball milling at a mass ratio of 3:1, sealing the mixture in a high-pressure reactor, raising the temperature to 550 DEG C at a rate of 5 DEG C / min and keeping the temperature for10h, and naturally cooling the reactor to room temperature; and (2) chemically etching an obtained precursor with nitric acid aqueous solution, and after complete reaction, washing the precursor withdistilled water to neutral, and carrying out pumping filtration and drying to obtain a nitrogen-doped three-dimensional interconnected hollow carbon foam electrode material. The preparation process is simple and controllable, has low cost and high repetition rate, and is especially suitable for industrial production. The prepared nitrogen-doped three-dimensional interconnected hollow carbon foamelectrode material has excellent cycle performance and rate performance as a negative electrode material for lithium-ion batteries, and has good application prospects in the battery field.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
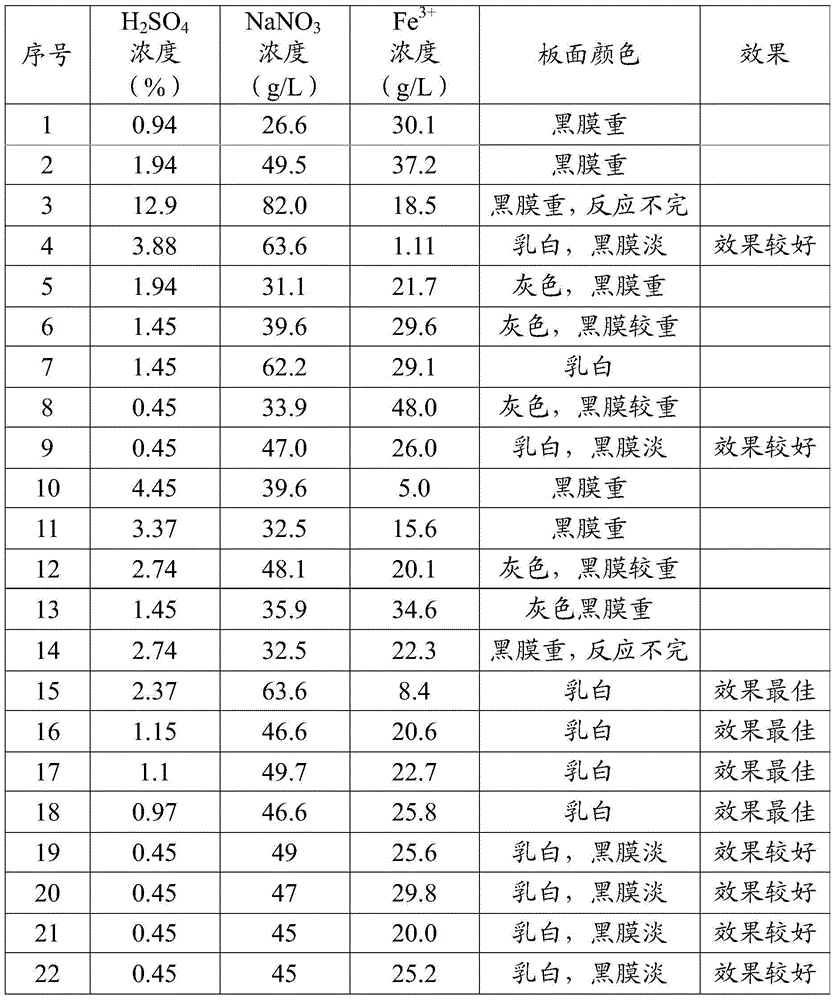
Stainless steel passivating method and used mixed solution
Owner:PANGANG GROUP JIANGYOU CHANGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL
Preparation of 2,4-binitro bromobenzene
InactiveCN101412676BReduce pollutionEasy to separate and purifyNitro compound preparationReaction temperaturePhotochemistry
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Flame retardant ultraviolet resistant material
InactiveCN104311883AFlame retardantImproves UV resistanceSilicic acidEthylic acid
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap