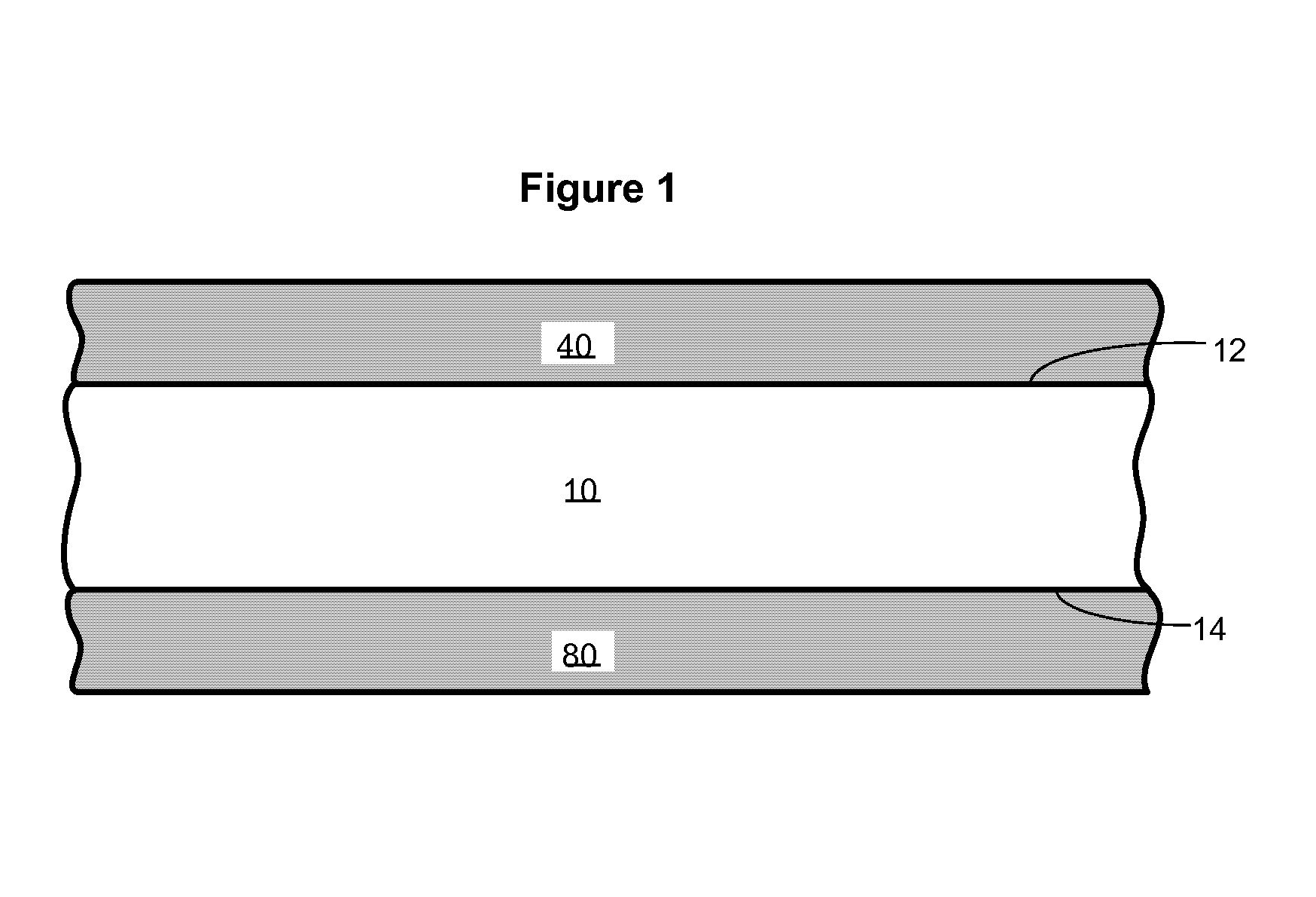
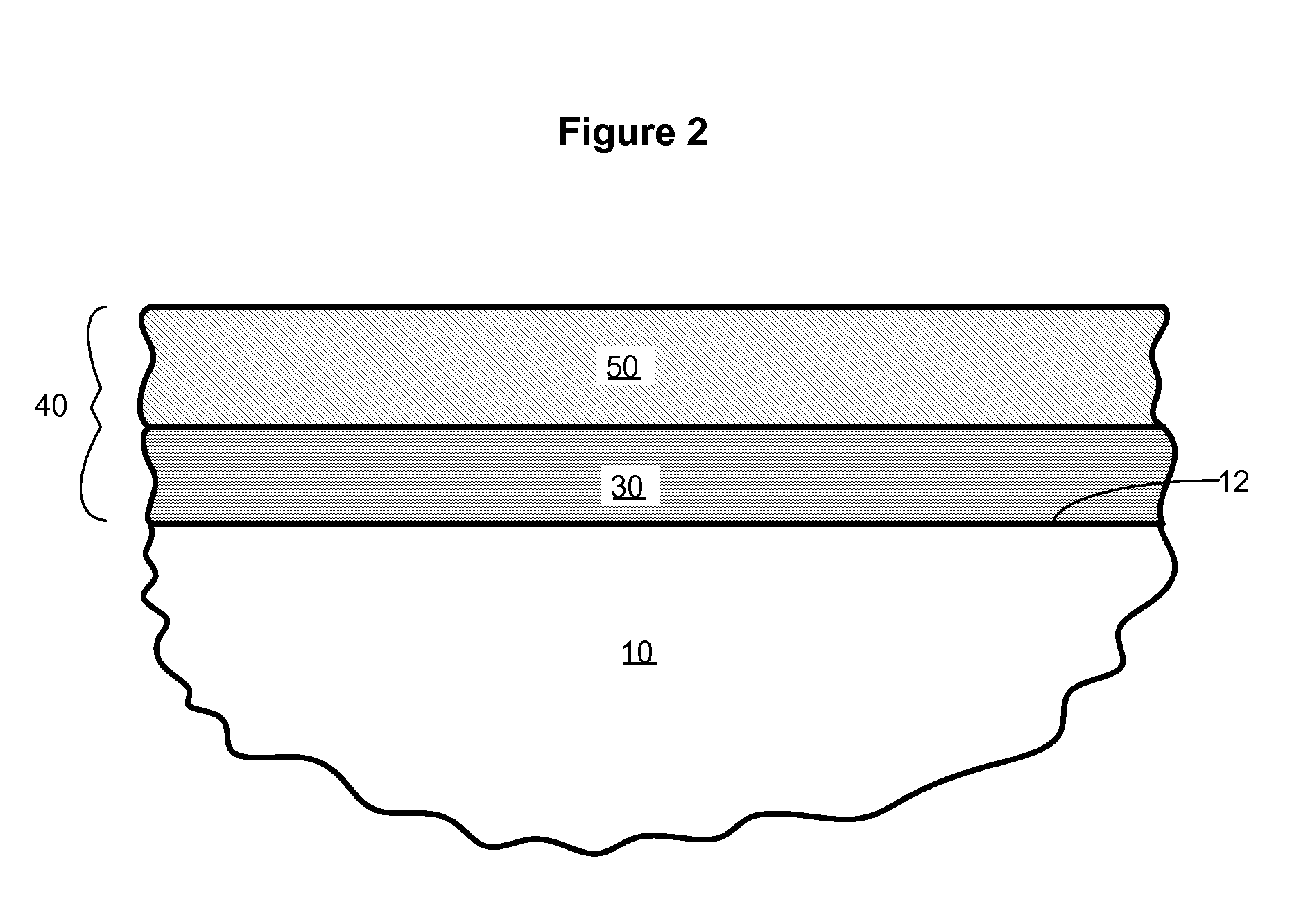
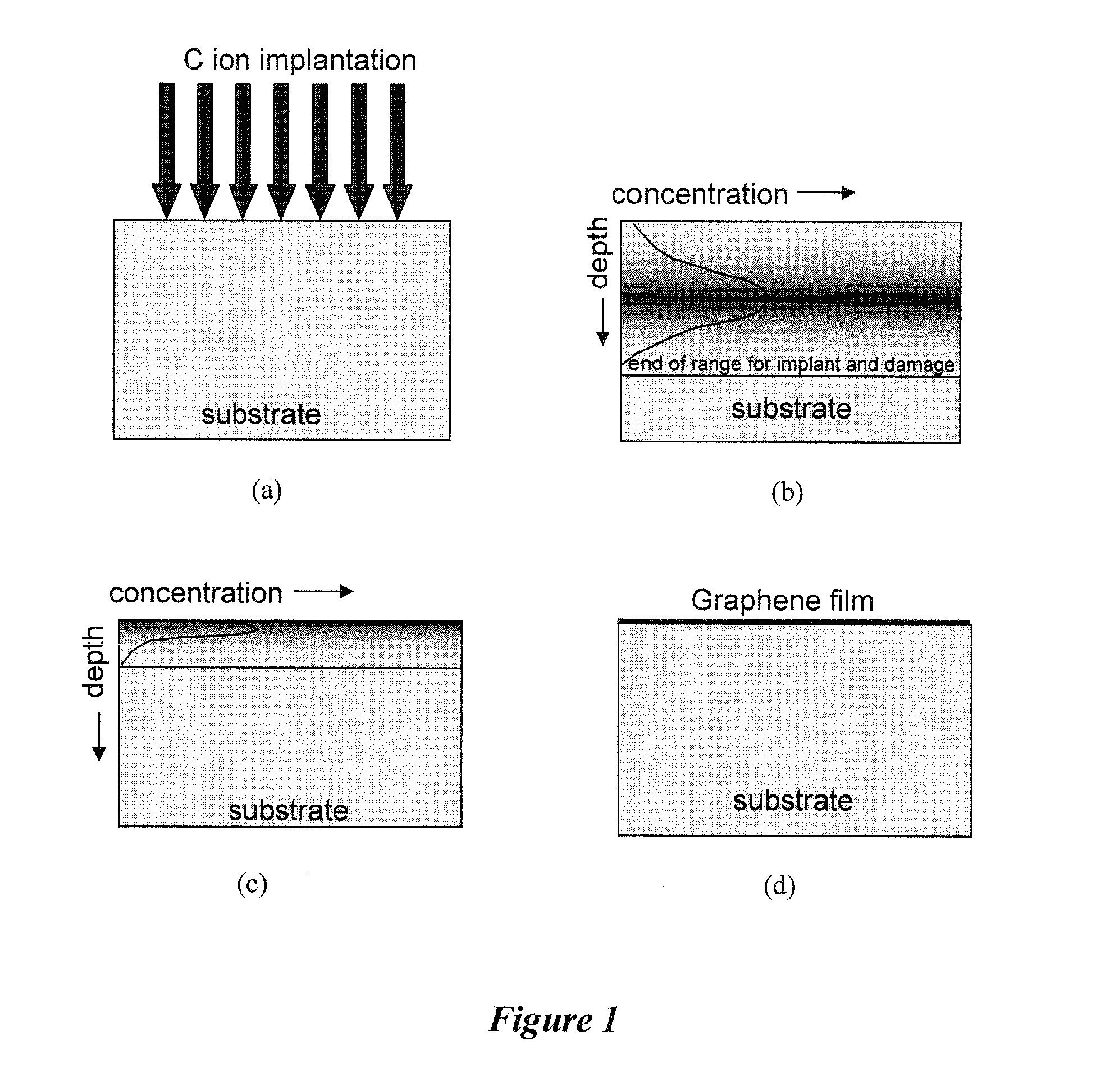
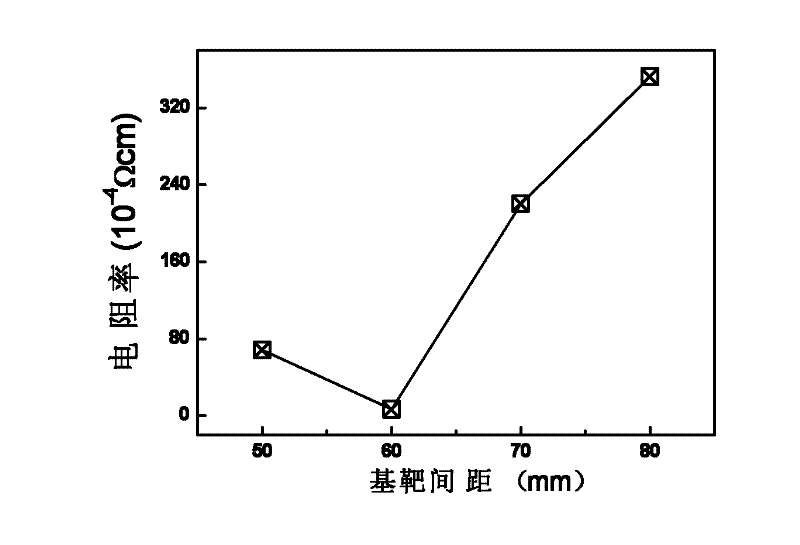
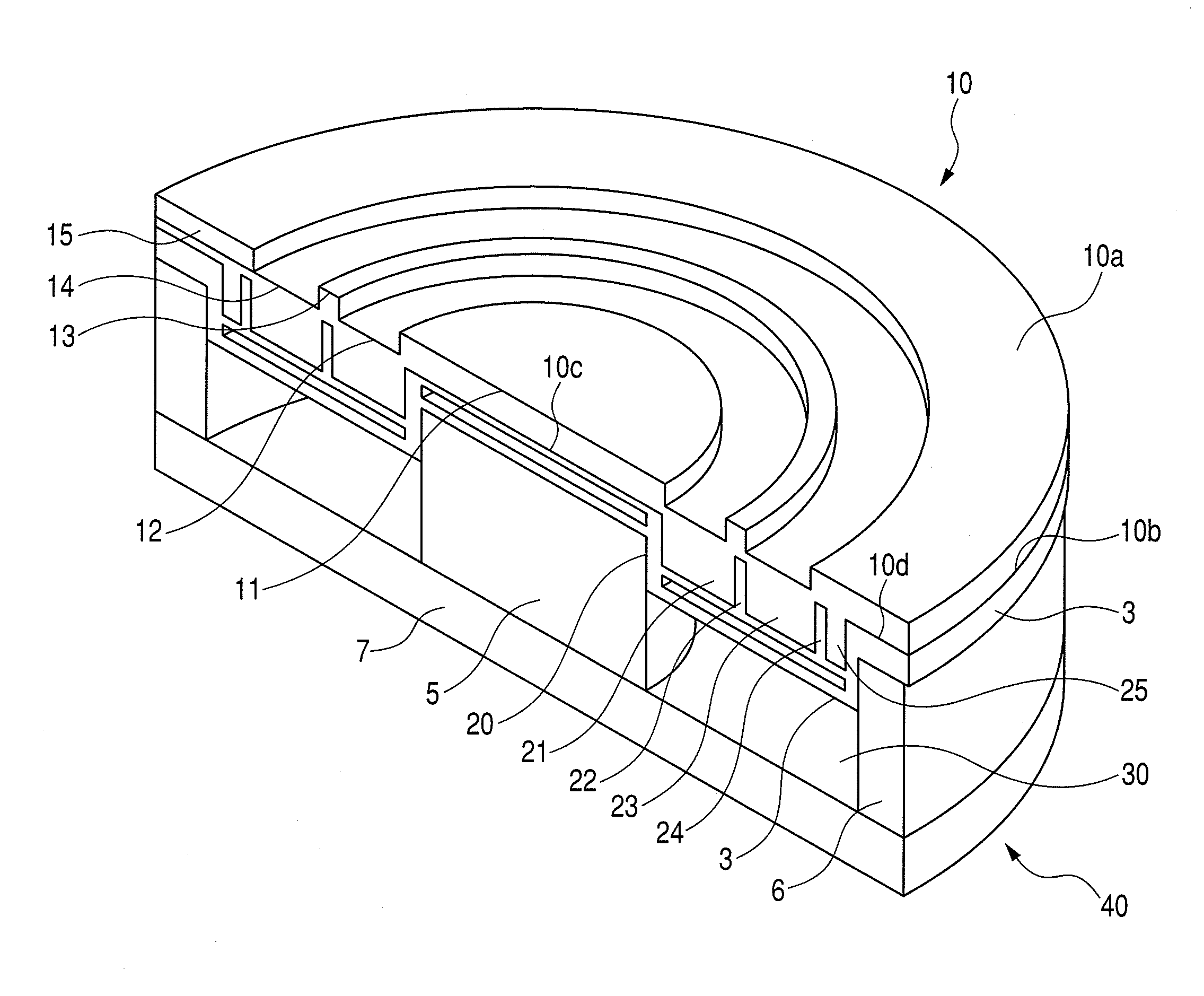
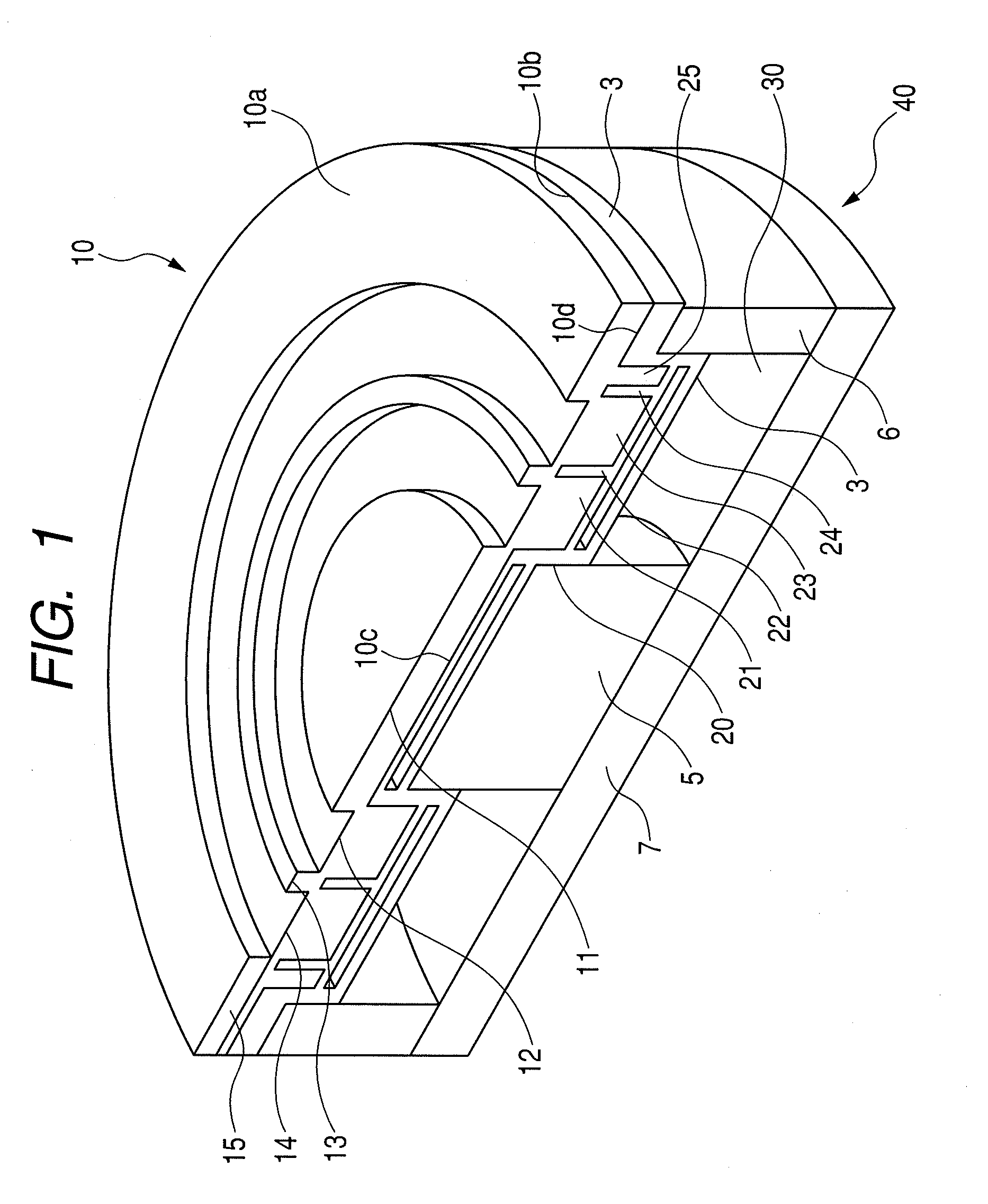
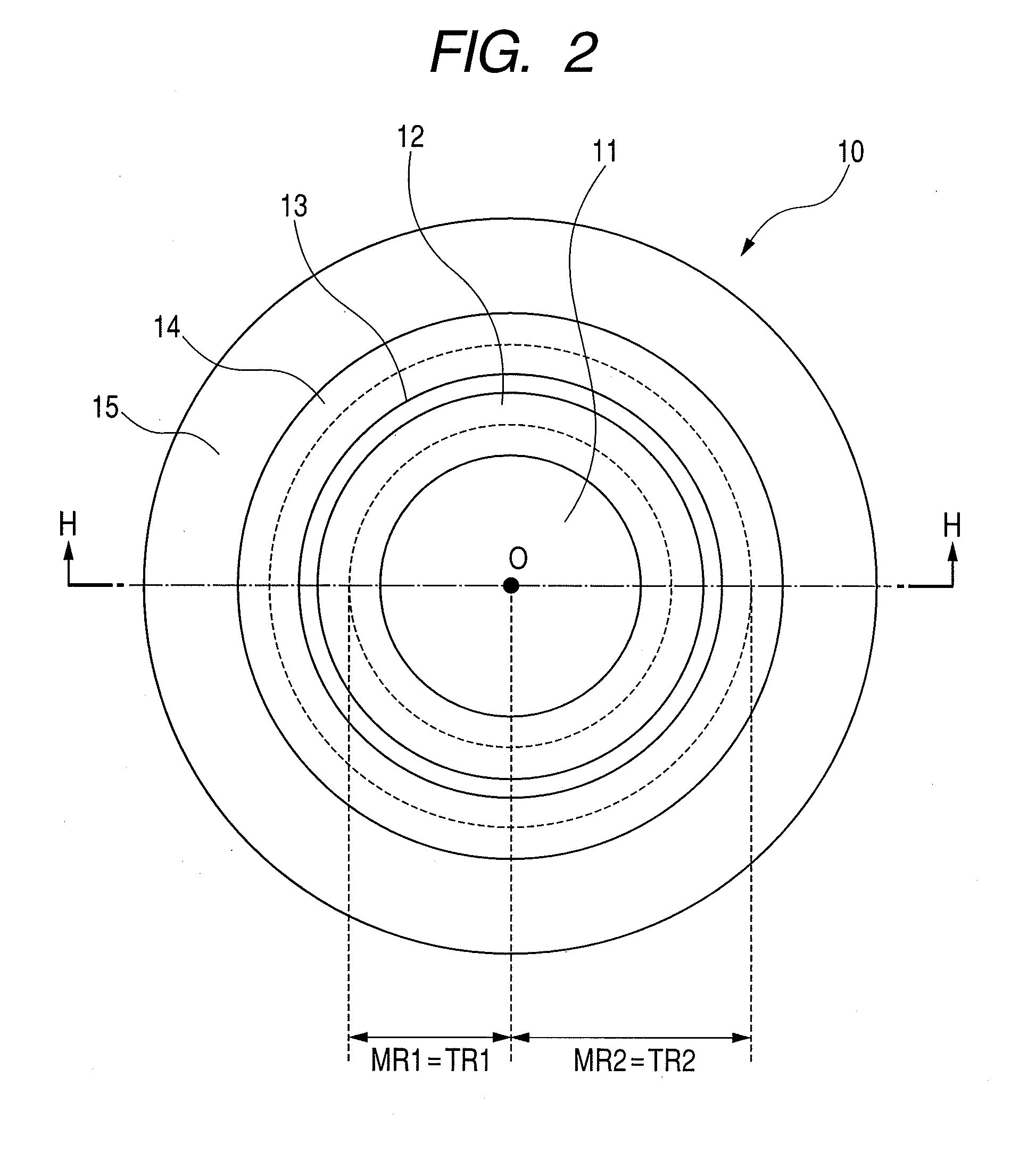
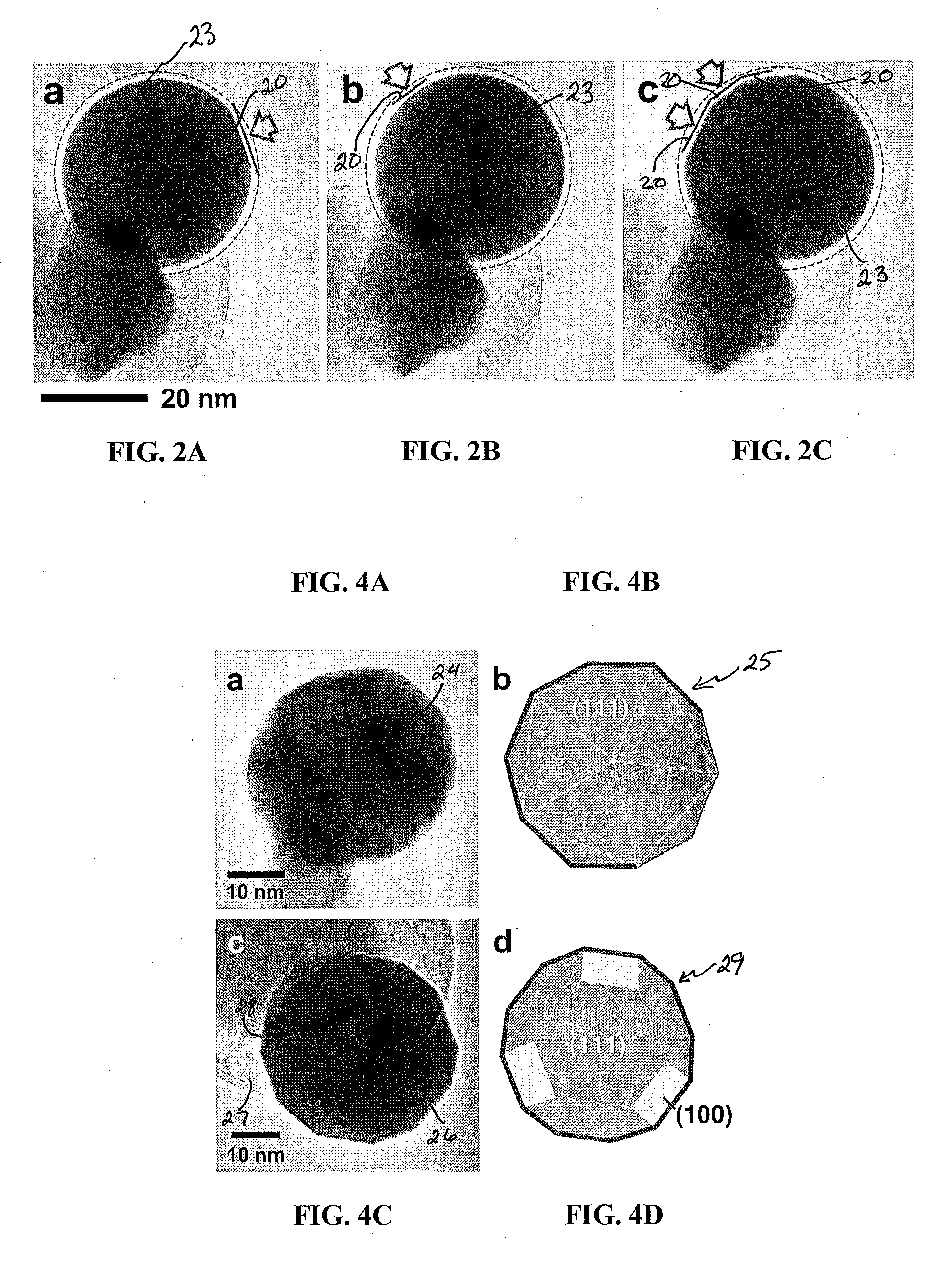
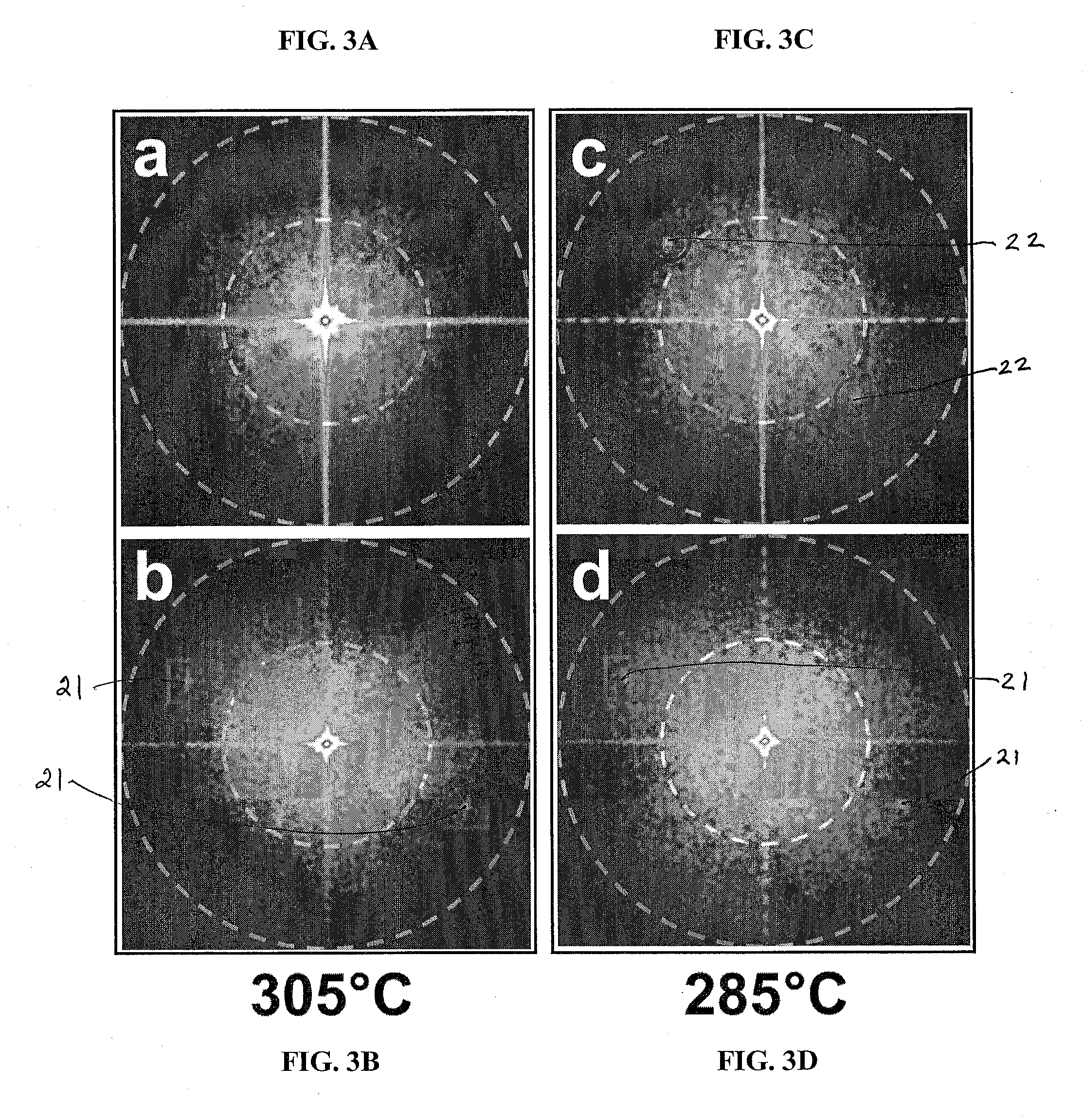
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
74results about "Ion implantation coating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
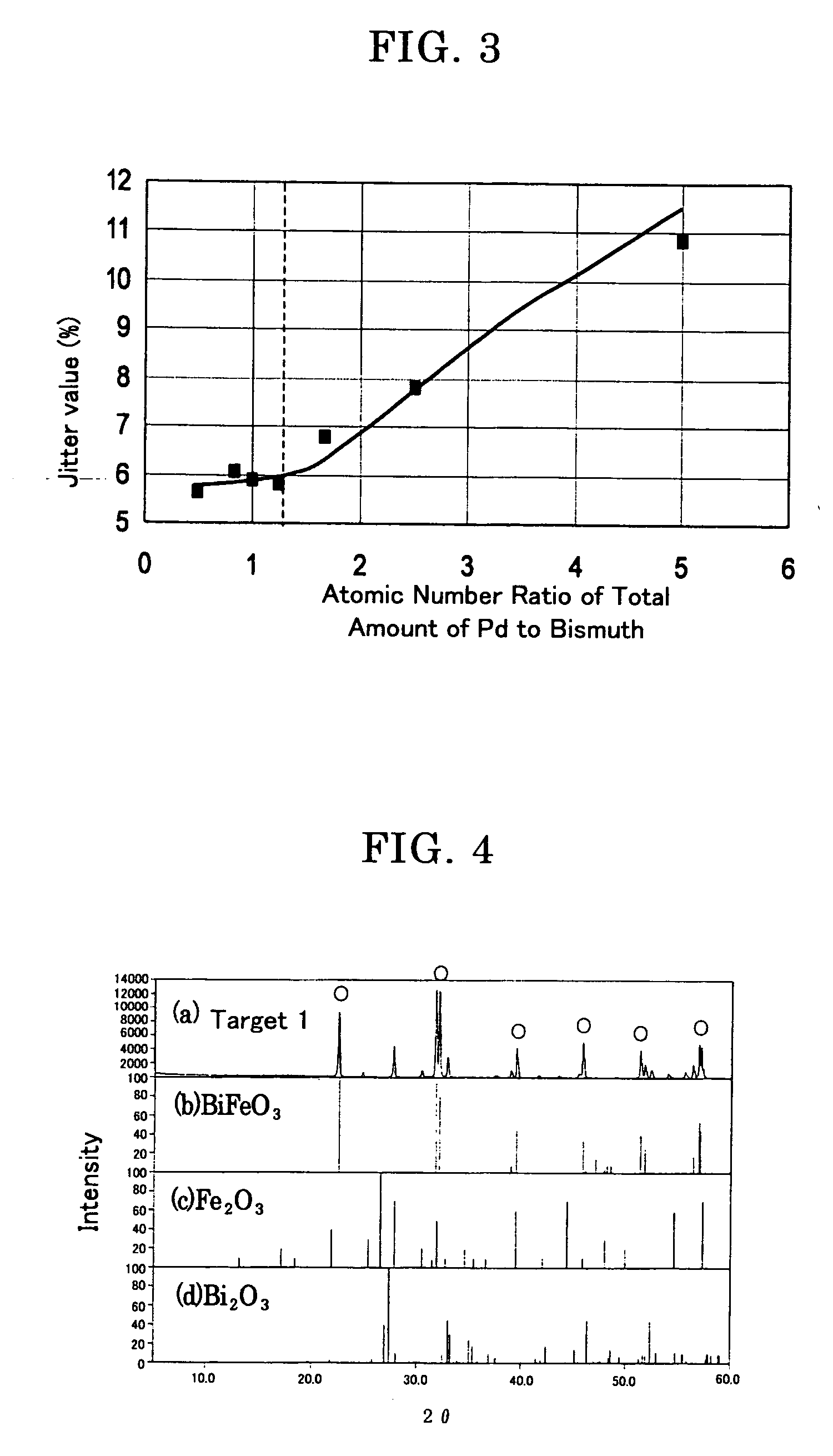
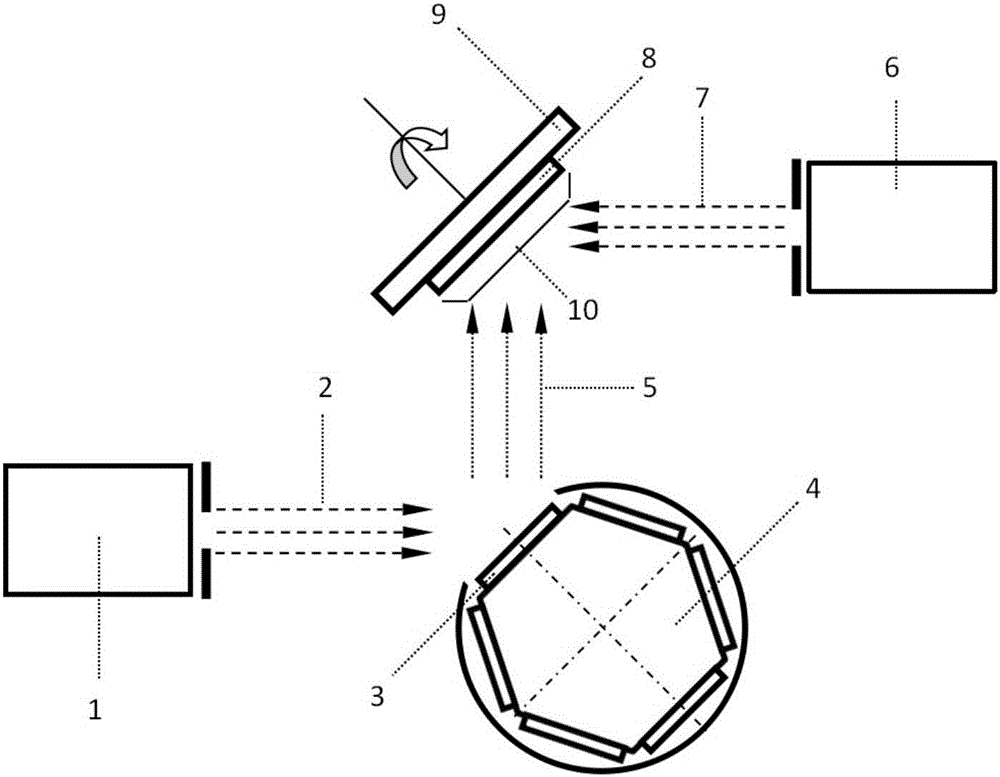
Reactor and method of processing a semiconductor substrate
InactiveUSRE37546E1Accurately determineEliminate needThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryGas syringeEngineering
Owner:KOKUSAI SEMICON EQUIP CORP
Opposed functional coatings having comparable single surface reflectances
ActiveUS20070248756A1Low-emissivity coatingLiquid surface applicatorsDoors/windowsLow emissivityMetallurgy
Owner:CARDINAL CG
Graphene processing for device and sensor applications
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Copper or copper alloy target/copper alloy backing plate assembly
Owner:JX NIPPON MINING& METALS CORP
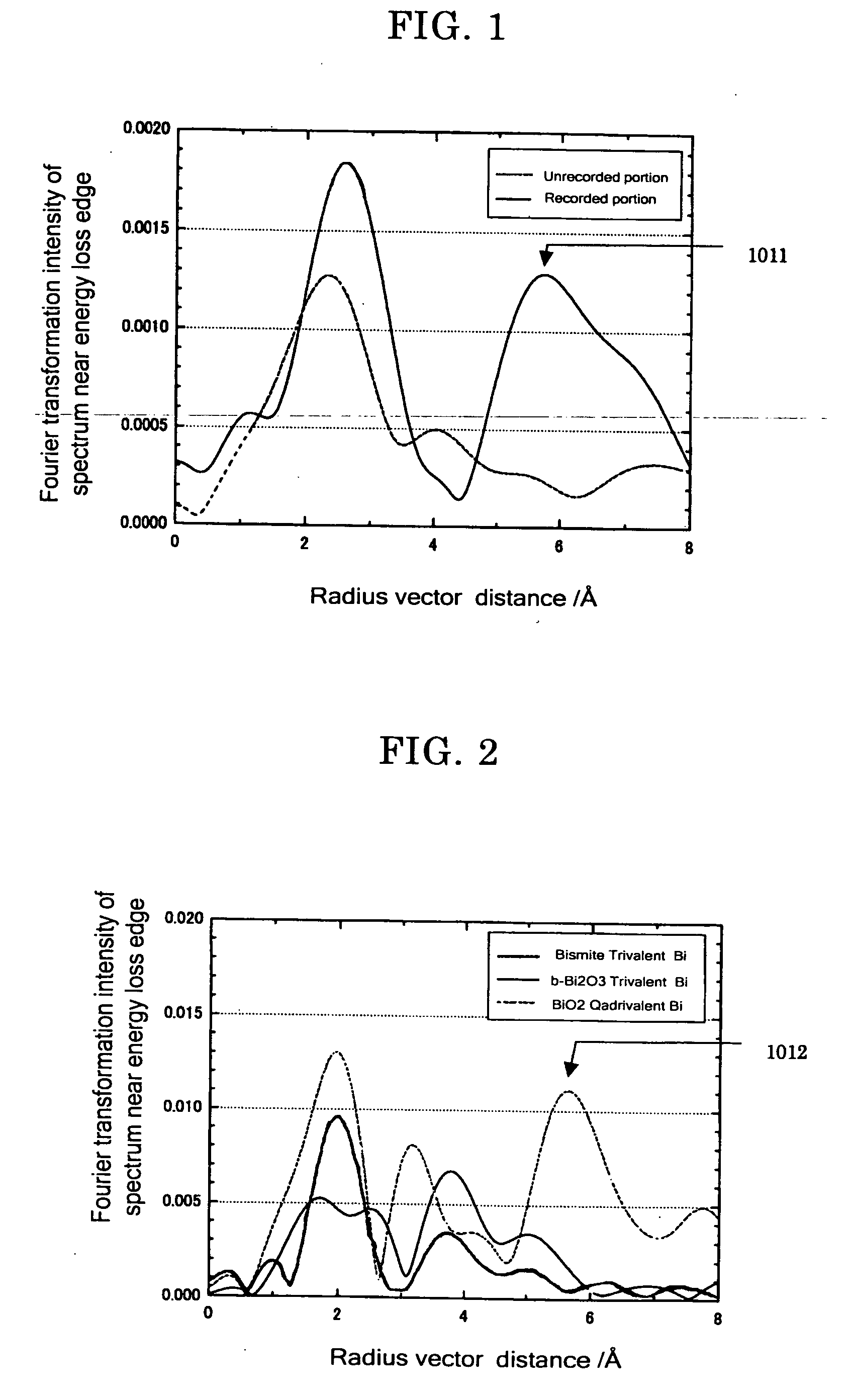
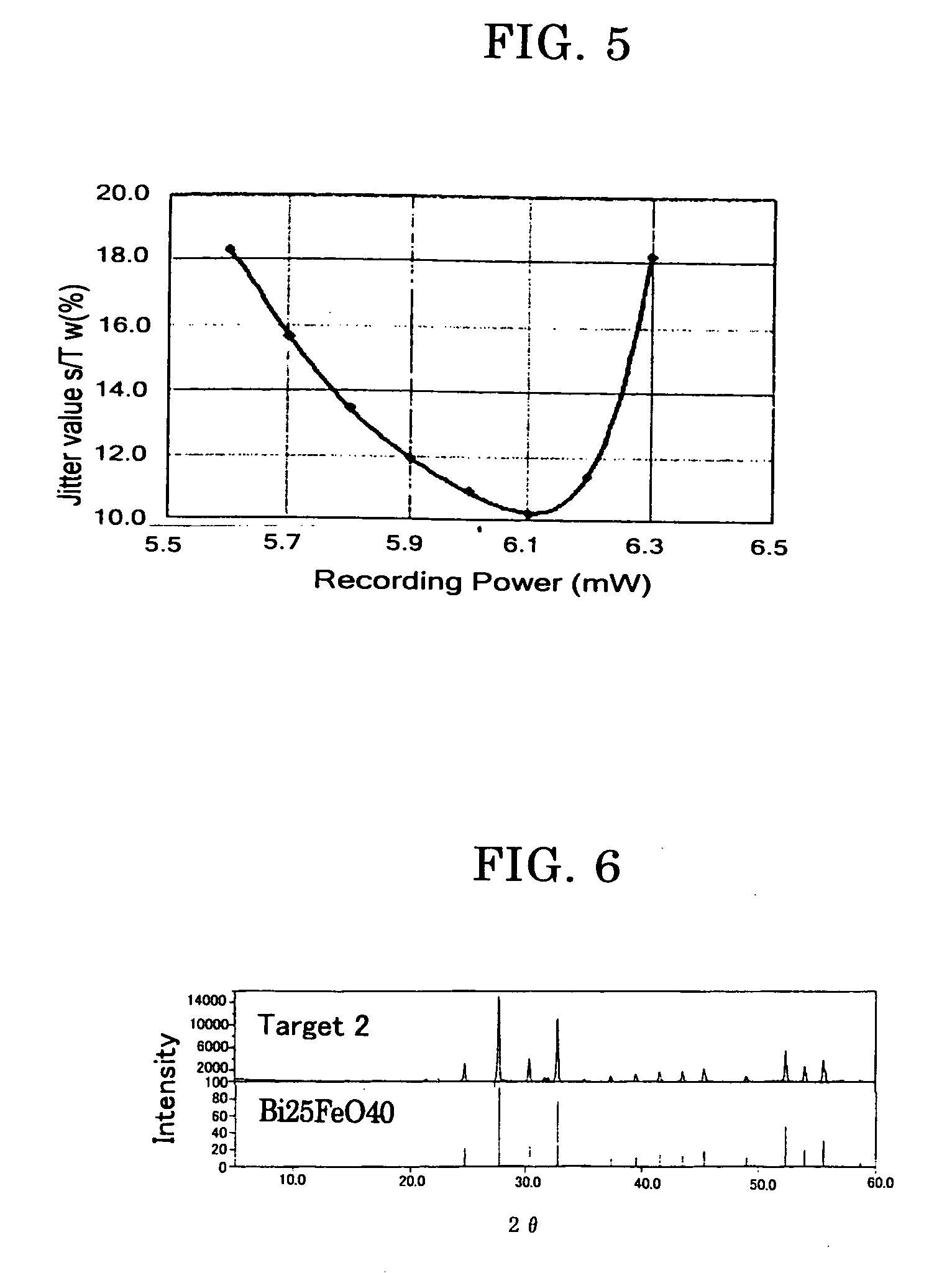
Write-onece-read-many optical recording medium, sputtering target and the production method thereof
InactiveUS20060222810A1High density recordingLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingHigh densityOxygen
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for preparing diamond-like composite coating on surface of piston ring
InactiveCN101665940AImprove wear resistanceImprove the lubrication effectVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingLow temperature plasmaMagnetic filtration
The invention relates to a method for preparing a diamond-like composite coating with high hardness and good abrasion proof and self lubricating properties on the surface of a piston ring. In the method, a nitriding layer with high bonding strength, high hardness and good abrasion resistance is formed on the surface of the piston ring by the low-temperature plasma nitriding treatment, a non-hydrogen diamond-like surface layer with solid lubricating property is deposited by the combination of magnetic filtration cathode arc and magnetic control sputtering, and finally the nitriding / diamond-likecomposite coating, which is dense and smooth and possesses excellent abrasion proof and self-lubricating properties, is obtained on the surface of the piston ring. Compared with the durionising piston ring or CrN plating piston ring, the coating of the piston ring of the invention has higher comprehensive performance.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Au-Sn alloy sputtering target material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105132873ALow germanium contentVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIngotHeating furnace
The invention relates to an Au-Sn alloy sputtering target material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1, Au and Sn are taken as raw materials, vacuum induction melting and vacuum casting are used for casting so as to obtain an eutectic or hypo eutectic Au-Sn alloy ingot, wherein the content of Ge in the alloy ingot accounts for 2 to 12.5 wt percent, and the content of Au serves as the balance; 2, a heating furnace is used for carrying out homogenization heat treatment on the alloy ingot obtained in the step 1; the temperature of the homogenization heat treatment is 270 to 340 DEG C, and the time is 50 to 65 minutes; 3, plastic working equipment is used for carrying out hot plastic processing to the ingot in the thickness direction; 4, the blank is placed inside the heating furnace for temper heat treatment after each 1 to 2 times of processing, the temperature is 270 to 340 DEG C, and the time is 10 to 30 minutes; and 5, the step 3 and the step 4 are repeated until the required target blank dimension is obtained. The Au-Sn alloy sputtering target material obtained through the method is even in components, and has a microscopic structure mainly composed of an Au solid solution and bulks of Ge distributed in a diffused manner.
Owner:GRIKIN ADVANCED MATERIALS
High-hardness and high-elasticity-modulus multi-component nitride coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106835037AIngredient ControlHigh hardnessVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringAlcohol
The present invention is a multi-component nitride coating with high hardness and high elastic modulus. Its chemical formula is AlCrTiZrNbN, and the atomic ratios of Al, Cr, Ti, Zr, Nb and N are respectively 8-12%: 8-12 %: 8~12%: 8~12%: 8~12%: 48~52%, the thickness of the coating is 2~5μm. The present invention also provides a method for preparing the above-mentioned nitride coating. Firstly, the surface of the substrate is subjected to mirror polishing, then ultrasonically cleaned with acetone and alcohol, and after vacuum ion cleaning, the AlCrTiZrNbN layer is deposited by radio frequency reactive sputtering, wherein AlCrTiZrNbN is mostly The component nitride coating is composed of AlCrTiZrNb alloy target with equiatomic molar ratio in (Ar+N 2 ) atmosphere prepared. The coating of the invention has high hardness and high modulus of elasticity, and can be used as a novel protective coating for various service occasions such as cutting tools and molds.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Thickness gradient protective overcoat layers by filtered cathodic arc deposition
InactiveUS20050249983A1Simple methodApparatus is enlargedCellsProtective coatings for layersCathodic arc depositionMaterials science
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method of Fabricating Thin Film by Microplasma Processing and Apparatus for Same
InactiveUS20120021132A1Reduce necessityLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingIonRaw material
Provided is a method of fabricating, with satisfactory adhesion, a thin film of a metal or a metallic-compound, such as a metal oxide or nitride, on a substrate made of a high-melting-point material such as silicon or ceramics by using a metal or metallic-compound target as the primary raw material so as to eliminate the necessity of using harmful gases such as organometallic gas, and by using an atmospheric-pressure plasma generated under atmospheric pressure as a reaction field and also as a heat source. Additionally provided is an apparatus for fabricating the thin film. The thin-film fabrication method by microplasma processing includes the steps of disposing a raw material for thin-film fabrication in one or more tubes (A) having a uniform inner diameter throughout, introducing an inert gas and applying a high-frequency voltage to the narrow tubes (A) to generate high-frequency plasma in the narrow tubes (A), heating / evaporating the raw material while maintaining the flow rate of the plasma gas in the narrow tubes (A) and maintaining the plasma gas temperature high, ejecting the evaporated material from the narrow tubes (A) to spray it onto the substrate, heating the substrate with the plasma, and depositing the sprayed material on the substrate under atmospheric pressure.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Target material and thin membrane manufactured with the target material
InactiveCN101245443AReduce manufacturing costReduce complexityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElemental compositionPowder mixture
The invention mainly provides a target, the elemental composition of which is IBx-IIIAy-VIAz, wherein, IB is selected from at least one of the group as follows: Cu and Ag; IIIA is selected form at least one of the group as follows: In and Ga; VIA is selected from as least one of the group as follows: S, Se and Te; x, y and z are respectively atomic percents of contents of IB, IIIA and VIA while the x is more than or equal to 0 and less than 1, so is the y, the z is more than 0 and less than 1 and the sum of the x, the y and the z is equal to 1; the production method of the target comprises: pre-alloy is formed: the pre-alloy is synthesized by one element of the target and more than one other element in the elemental composition of the target; powder production: the pre-alloy is produced to be powder; powder mix: the powder is directly mixed or mixed with powder of other elements or pre-alloy powder; sintering: the powder mixture forms the target after sintering. The invention also provides a thin-film used in solar battery, which is made by sputtering the target.
Owner:SOLAR APPLIED MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Gallium-doped zinc oxide transparent conducting film, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102534498AHigh resistivityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTransparent conducting filmOmega
Owner:OCEANS KING LIGHTING SCI&TECH CO LTD +1
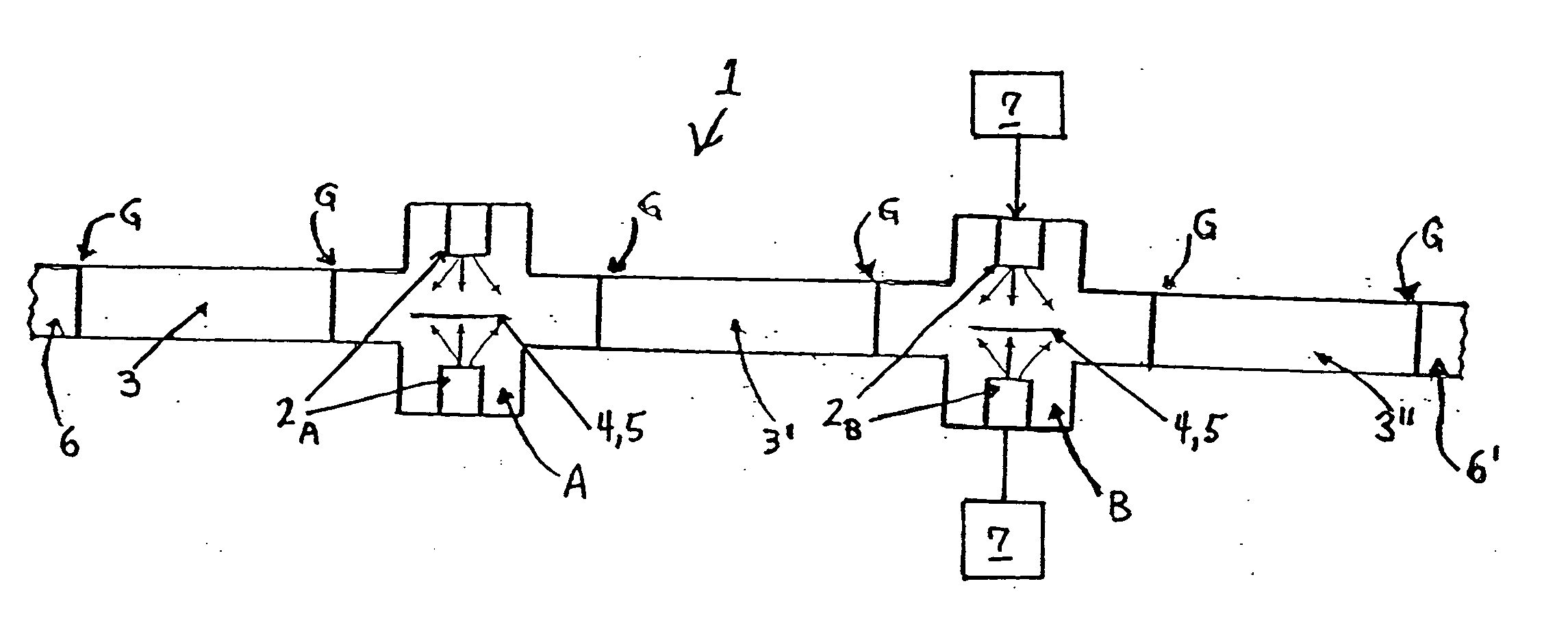
Magnetron sputtering cathode, magnetron sputtering apparatus, and method of manufacturing magnetic device
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Adhesion-prevention Plate Used For Vacuum Film-forming Device And Applications Thereof
InactiveCN104032259AExcellent anti-peeling effectAnodisationVacuum evaporation coatingConvex structureEvaporation
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
High-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer for Cu interconnect integrated circuit and preparation method of high-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer for Cu interconnect integrated circuit
ActiveCN108336062AHigh bulk densityShortened diffusion channelSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh entropy alloysHeat stability
The invention relates to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits, in particular to a high-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer for a Cu interconnect integrated circuit and a preparation method of the high-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer for the Cu interconnect integrated circuit. The high-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer for the Cu interconnect integrated circuit sequentially comprises a Si substrate layer, a high-entropy alloy intermediate coating and a Cu film from bottom to top, wherein the high-entropy alloy intermediate coating sequentially comprises a third coating, a second coating and a first coating from bottom to top; the first coating is an AlCrTaTiZrMo high-entropy alloy coating; the second coating is a pure Ti coating; and the third coating is an AlCrTaTiZrMoNx high-entropy alloy coating. According to the high-entropy alloy diffusion barrier layer for the Cu interconnect integrated circuit, improvement of the atomic bulk density is facilitated,generation of defects, such as vacancies is reduced, a diffusion channel for atoms is reduced, and the diffusion barrier performance and the heat stability of the high-entropy alloy coatings are improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
Plating method for anti-reflection film with high transmittance and low reflectivity
ActiveCN102732830AFully oxidizedOrganizational stabilityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingThermal insulationEngineering
Owner:ANHUI JINGZHUO OPTICAL DISPLAY TECH CO LTD
Pt Ni Al bonding layer doped with binary trace active elements and capable of being completely oxidation resisting at 1200 DEG C and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103966615AImproved high temperature oxidation resistanceImprove high temperature oxidation resistanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingElectron beam physical vapor depositionGas phase
The present invention discloses a Pt Ni Al bonding layer doped with binary trace active elements and capable of being completely oxidation resisting at 1200 DEG C and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of novel thermal barrier coatings and the preparation technologies. According to the invention, firstly, a Pt layer with the thickness of 5-10 microns is prepared on a nickel base monocrystal high temperature alloy matrix through the plating or the electron beam physical vapor deposition method, and then a NiAlHfZr coating with the thickness of 20-60 microns is deposited on the Pt layer through the electron beam physical vapor deposition method. The Pt layer reduces the interfacial holes and effectively improves the adhesion of an oxidation film; binary doping of Hf, Zr enables the NiAl coating surface to be smoother and denser and enables the oxidation film generated during the oxidation process on the coating surface to be straighter, especially with little oxidation increase, and greatly improves the oxidation resistance of the coating. The Pt Ni Al bonding layer is completely oxidation resisting at 1200 DEG C. The service life of the coating is prolonged to certain degree through doping of binary elements namely Hf and Zr and Pt modification.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Systems and methods for enhancing mobility of atomic or molecular species on a substrate at reduced bulk temperature using acoustic waves, and structures formed using same
ActiveUS20140199550A1Improve mobilityReduce the temperatureRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingChemical physicsAcoustic wave
Under one aspect of the present invention, a method for enhancing mobility of an atomic or molecular species on a substrate may include exposing a first region of a substrate to an atomic or molecular species that forms a molecular bond with the substrate in the first region; directing a laser pulse to a second region of the substrate so as to generate an acoustic wave in the second region, the acoustic wave having spatial and temporal characteristics selected to alter the molecular bond; and transmitting the acoustic wave from the second region to the first region, the acoustic wave altering the molecular bond between the substrate and the atomic or molecular species to enhance mobility of the atomic or molecular species on the substrate in the first region.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Manufacturing method of pure copper plates, and pure copper plate
ActiveCN102652182AFine uniform grainsEasy to processVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIngotCopper
Owner:MITSUBISHI SHINDOH CO LTD +1
Apparatus for Dispensing Material
InactiveUS20090257921A1Simple materialIncrease pressureNanotechVacuum evaporation coatingPipetteSize determination
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Method for preparing micro-system radiating device
InactiveCN101794753ASmall sizeLarge specific surface areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCrystal structureThermal contact
Owner:NANTONG DAQING ENERGY SAVING TECH +1
Gallium nitride semiconductor film, gallium nitride-based light emitting dioxide and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN106282917AUniform thicknessHigh precisionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingChemical reactionNitrogen
Owner:北京埃德万斯离子束技术研究所股份有限公司
Nano multi-layer composite solid lubricating film layer with long service life under space irradiation and preparation thereof
ActiveCN112760607AAchieve self-lubricationReduce coefficient of frictionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSputteringAlloy substrate
The invention discloses a nano multi-layer composite solid lubricating film layer with a long service life under space irradiation and preparation thereof. The nano multi-layer composite solid lubricating film layer composed of a Ti binding layer, a TiN bearing layer and an AgTiNi / MoS2Ti nano multi-layer lubricating functional layer is deposited on a titanium alloy substrate, an aluminum alloy substrate, a stainless steel substrate, a bearing steel substrate and the like by adopting a closed magnetic field unbalanced magnetron sputtering technology. The nano multi-layer composite film layer can reliably serve for a long time in strong space irradiation environments such as low-orbit high atomic oxygen density, medium-high-orbit high electron proton density and high ultraviolet irradiation dose, and is high in bearing capacity and low in friction coefficient, thus, the service life of a moving part of a spacecraft exposed in the space irradiation environments can be greatly prolonged, and the reliability of the moving part is improved. In addition, the preparation method has the characteristics that the process is environment-friendly and flexible, the film thickness is uniform, the compactness is good, the preparation process of the film layer is controlled in a programmed manner, the modulation period of the film layer is easy to regulate and control, and batch treatment can be realized, industrial production is easy to realize, and the good application prospect is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI AEROSPACE EQUIP MFG GENERAL FACTORY
Plastics products and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101396890AImprove wear resistanceFeel goodVacuum evaporation coatingSynthetic resin layered productsCopper coatingCeramic coating
The invention relates to a plastic product, comprising plastic substrate. The plastic product is characterized in that the product also comprises a copper coating, a nickel coating, a chrome coating and a ceramic coating from the surface of the plastic substrate to the outside in sequence; the ceramic coating is one or more layer of titanium nitride, titanium carbide and titanium carbonitride. The plastic product made by the invention has excellent wearing resistance, the film formed on the surface of the plastic product has excellent adhesiveness, and the plastic product that is obtained finally also has ceramic texture and good handfeel.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Structural design and use method of net tensioning equipment
PendingCN111112884AHigh precisionEliminate displacementVacuum evaporation coatingWelding/cutting auxillary devicesControl cellStructural engineering
Owner:SUZHOU JINGLAI OPTO CO LTD
Sputtering apparatus and film forming method
InactiveUS20100155227A1Reduce columnar growthImprove film qualityCellsElectric discharge tubesSputteringEngineering
Owner:CANON ANELVA CORP
Manufacturing method of rare earth metal PrNd rotary target
InactiveCN108251802AImprove magnetic propertiesReduce manufacturing costVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingRare-earth elementGraphite
Owner:BAOTOU RES INST OF RARE EARTHS +1
ZnO-Ni photic driving micropipe motor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109504953AControl the direction of motionEfficient use ofVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingUltraviolet lightsEngineering
The invention relates to a ZnO-Ni photic driving micropipe motor and a preparation method thereof. The micropipe motor comprises a photocatalytic material tubular ZnO and a metal layer Ni. The micropipe motor uses hydrogen peroxide as a fuel and ultraviolet light as an excitation light source. A regulation mode of motion speed of the micropipe motor comprises fuel concentration, regulation light intensity or the content of metal Ni. The micropipe motor can effectively absorb excited electrons by utilizing the metallic properties of the Ni to reduce the charge recombination rate of ZnO, so thatthe photocatalytic performance of the ultraviolet light is effectively improved, and then the motor achieves a high-speed bubble movement in hydrogen peroxide solution; on the other hand, the magnetic properties of Ni can be used to achieve the effective motion direction control of the motor. In addition, the preparation process is simple, and the ZnO-Ni tubular photic driving micropipe motor with low cost, long service life, fast movement and controllable direction is prepared.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIV
High-temperature-resisting multilayer solar selective absorbing coating and preparing method thereof
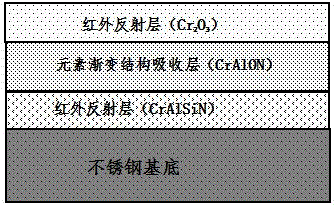
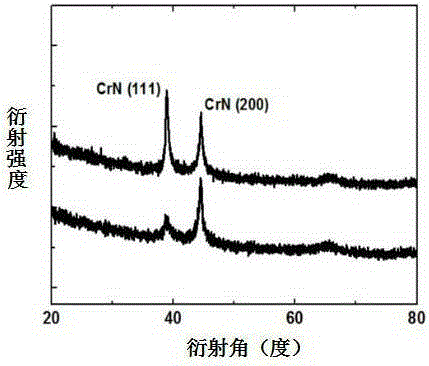
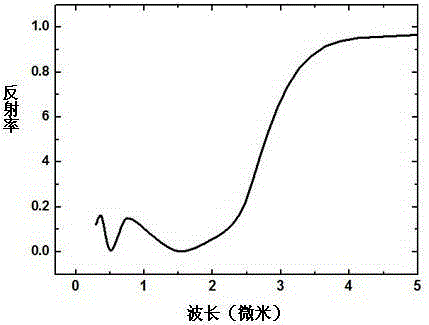
ActiveCN105274474AHigh temperature absorptionExcellent high temperature spectral selective absorption performanceSolar heat devicesVacuum evaporation coatingIr reflectionAbsorptance
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
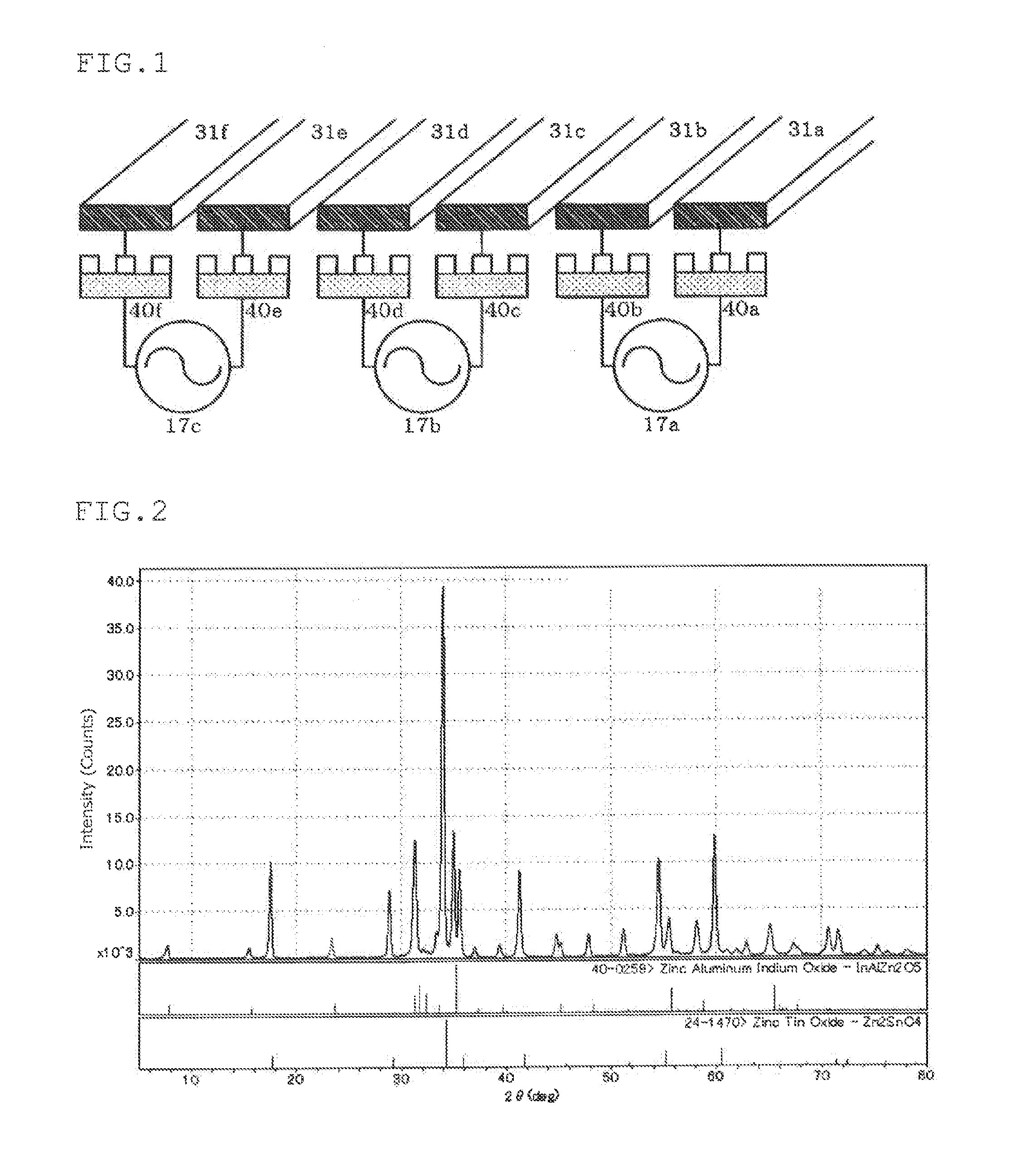
Sputtering target, oxide semiconductor thin film, and method for producing oxide semiconductor thin film
InactiveUS20150311071A1Increase productionSuppress abnormal dischargeTransistorCellsIndiumThin membrane
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap